
A Design for Real-time Neural Modeling on the GPU
Incorporating Dendritic Computation
Tyler W. Garaas
1
, Frank Marino
1
, Halil Duzcu
2
and Marc Pomplun
1
1
University of Massachusetts Boston
100 Morrissey Boulevard, Boston, MA 02125-3393, U.S.A.
2
Middle East Technical University, İnönü Bulvarı, 06531, Ankara, Turkey
Abstract. Recent advances in neuroscience have underscored the role of single
neurons in information processing. Much of this work has focused on the role
of neurons' dendrites to perform complex local computations that form the basis
for the global computation of the neuron. Generally, artificial neural networks
that are capable of real-time simulation do not take into account the principles
underlying single-neuron processing. In this paper we propose a design for a
neural model executed on the graphics processing unit (GPU) that is capable of
simulating large neural networks that utilize dendritic computation inspired by
biological neurons. We subsequently test our design using a neural model of
the retinal neurons that contribute to the activation of starburst amacrine cells,
which, as in biological retinas, use dendritic computational abilities to produce
a neural signal that is directionally selective to stimuli moving centrifugally.
1 Introduction
As with most research topics, neural modeling has broadened into a spectrum of
methodologies that sometimes use the terms artificial neural networks, computational
neuroscience, and brain models to illustrate methodological differences. The authors
of [1] have chosen the terms realistic brain models and simplified brain models to
illustrate two sides of the research spectrum. Realistic brain models refer to models
that go to painstaking lengths to model the individual components of neurons and
their assemblies. In these models, the goal is often directed toward gaining greater
insight into actual brain function [2]. Indeed, this is a very active avenue of research
in both the neuroscience and computational neuroscience fields.
Unlike their counterpart, simplified brain models, often implemented as artificial
neural networks (ANNs), are usually directed toward computing meaningful
information. Their simplified nature is both a distinct advantage and disadvantage
over realistic brain models, as it is the conceptual and computational intractability that
has hindered the use of realistic brain models as functional entities. Despite the large
range of successful applications of ANNs, future networks that attempt to solve
complex problems such as robust object recognition [3] or modeling complex
behaviors [4] will likely require more realistic organization principles.
If neural networks are to be realized in a more biologically realistic manner, the
two aforementioned hindrances will need to be overcome. The first, conceptual
intractability, is being slowly broken apart by a large number of neuroscientists such
Garaas T., Marino F., Duzcu H. and Pomplun M. (2009).
A Design for Real-time Neural Modeling on the GPU Incorporating Dendritic Computation.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Artificial Neural Networks and Intelligent Information Processing, pages 69-78
DOI: 10.5220/0002265100690078
Copyright
c
SciTePress

as those previously referenced. Their progress has led to many new ideas and models
regarding the functioning of individual neurons. A major insight that has emerged
from these studies involves the role of the single neuron in the computational abilities
of neural networks –both biological and artificial [2, 5]. In particular, the structural
organization of the neuron’s dendrite (the part of the neuron that receives signals from
other neurons) has become an important concept in both the theory of biological
neuron functioning [2, 5-7] and computational studies [8]. Models that do not take
into account the physical structure of the neuron are in effect using point neurons.
Point neurons are named as such to illustrate the lack of dendrites where afferent
neurons instead synapse directly onto the soma (cell body).
One biological phenomenon that has been attributed to interactions between
neurons synapsing at proximal locations on a dendrite is the directionally selective
activation of starburst amacrine cells [9]. Euler et al. [9] demonstrated that the signal,
which responds vigorously for stimuli moving centrifugally –i.e., away from the
soma–, is the result of local computations that take place on the dendrites of the cell.
Following this result, Tukker et al. [10] created a realistic computational model that
showed the directionally selective signal found at the distal tips of the dendrites could
be accounted for by an interaction between a temporally delayed global signal and
local synaptic input.
The second hindrance, computational intractability, is a result of the large number
of calculations needed to model a realistic neuron. One approach that is being used to
overcome computational insufficiencies in highly parallel applications, such as neural
modeling, is to use the graphics processing unit (GPU) [11], which is the primary
computational unit integrated into present-day computer graphics cards.
In this paper, we present a neural network design that has been crafted for
execution on the GPU. The design achieves real-time computational abilities while
preserving potentially crucial features of realistic brain models such as dendritic
computing. To demonstrate the neural network design, we implement a sample
network that simulates the subset of the retinal circuitry responsible for generating the
directionally selective signal in the starburst amacrine cells.
2 GPU Processing
In recent years, the computational abilities of certain systems have seen enhanced
growth due to the expansion of parallel systems such as cluster computing and
distributed computing. Another highly parallel paradigm that has recently been
exploited by computationally hungry scientists is the GPU, which is currently being
used for image processing, computer vision, signal processing, video encoding, and
ray tracing, among others [11]; applications such as these have been given the
acronym GPGPU for general-purpose computation using graphics hardware.
2.1 Brief Overview of GPU Architecture
The massive computational power underlying the GPU comes from its parallel
architecture, which is implemented using a computational unit known as a stream
70

processor. Essentially, a stream processor is a highly restricted form of a processor
core; whereas processor cores are able to perform a wide variety of complex tasks,
stream processors use a specialized instruction set to perform the tasks that are
repeatedly executed during computer graphics rendering. By performing only a
handful of tasks, the GPU can pack hundreds of stream processors into a single GPU,
as opposed to the eight processor cores available in modern CPUs at the time of
writing.
Given the restricted nature of stream processors, applications that wish to exploit
the computational advantages of the GPU must adhere to a narrow flow of execution.
This flow is divided into four primary steps: vertex operations, primitive assembly,
rasterization, and fragment operations. All programs executed on the GPU must
perform all four steps; however, in many GPGPU applications, the first three steps are
executed at a bare minimum to support the bulk of the computation, which takes place
at the final stage. Those interested in the details of the first three stages are
encouraged to visit a community website dedicated to GPGPU programming [12].
The fragment operations that support the bulk of GPGPU computations are
performed by a simple program designed to execute on the GPU known as a fragment
shader. Fragment shaders perform a series of operations that manipulate one pixel of
data per execution. However, since there are hundreds of stream processors, many
millions of pixels of data can be processed in a very short period of time.
Data used by GPGPU applications must also conform to computer graphics
constructs which use images known as textures to store data. In traditional computer
graphics applications, a texture stores visual attributes not suited for –or too
computationally expensive for– representation by geometry, such as the clothes of a
character or the asphalt of a highway.
2.2 Neural Networks on the GPU
Many ANNs involve a highly parallel design that is well suited for implementation on
the GPU. Consequently, a number of researchers have taken advantage of this to
achieve notable gains in execution time [13-15]. For instance, Bernhard and Keriven
[13] were able to achieve a 5 to 20 fold increase in performance over a CPU
implementation while simulating spiking neural networks for image segmentation.
Gobron et al. [14] use the GPU to model the retina using cellular automata, and
Woodbeck et al. [15] use the GPU to implement a model of the processing that takes
place in the primary visual cortex. However, in each of these instances of neural
network processing, simple point-neurons were used to perform the pertinent
computations, which will likely be insufficient to for complex tasks such as robust
object recognition.
3 Neural Network Design
3.1 Single Neuron Model
As mentioned previously, researchers now believe the physical organization of
synapses plays a key role in the processing of information by neurons. In the design
71
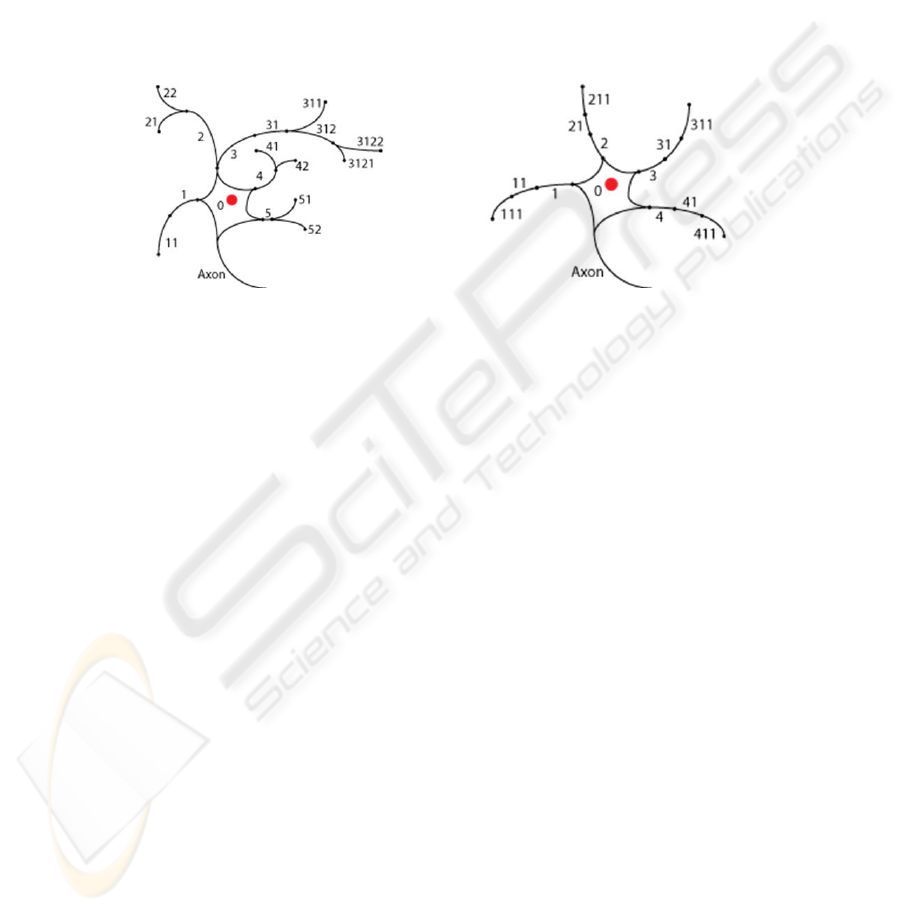
presented here, we take into account the organization of afferent synapses to facilitate
some of the mechanisms that underlie the computational power of biological neurons.
Figure 1 shows two neurons that can be simulated using the present model. The key
thing to notice is the labeling of dendrite segments, which permits local computations
to take place in individual segments. London and Häusser [5, pp. 509] note, “Because
the branch points in the dendritic tree can be seen as summing up the current in
individual branches, ... the whole dendrite can implement complex functions.” The
addition of this type of organization will allow the use of what London and Häusser
refer to as the dendritic toolkit [5]. In the sample network we use this dendritic toolkit
to compute a direction selective signal in the dendrites of a simulated starburst
amacrine cell.
Fig. 1. Illustration of potential neurons in the present model.
3.2 Single Neuron Creation
The single neuron model described in the previous section allows inputs to be
grouped together on a single dendrite segment so that local computations can take
place independently. However, it may not be entirely clear how the dendrite segments
can be generated or how afferent synapses can be connected to each segment.
Consequently, we have included the pseudocode for a recursive function that
generates the dendrite branching patterns from a branch code. For example, the
branch code that is used to generate the left neuron in Figure 1 is given on the first
line of pseudocode, and the branch code to generate the right neuron is
41110111011101110.
Essentially, each digit in the branch code, which can be stored in string form,
represents the number of new segments that are to be generated from the current
location. For example, ‘2’ represents a binary split, ‘1’ represents a single segment,
and ‘0’ represents the end of a segment. When a split is encountered, the subsequent
digit(s) is used to generate the first segment of the split until that branch is terminated
with a ‘0’ at which point the following digit(s) is used to generate the second segment
of the most recent split, and so on until all segments have been terminated.
branchCode = “5210102101012102101021010110”
SetupDendriteSegment(int codeIndex)
if branchCode[codeIndex] equals ‘0’
delete digit from branchCode at codeIndex and
return
72

DendriteSegment d = new DendriteSegment
while SynapsesNeeded() equals true
Add GetNextSynapse() to d
for i = Integer of branchCode[codeIndex] to 0
SetupDendriteSegment(codeIndex+1)
delete digit from branchCode at codeIndex and return
End SetupDendriteSegment
The SetupDendriteSegment function can generate a complex branching
pattern from a string of digits; however, it still must be decided how afferent inputs
will be connected to the individual dendrite segments. Since this is different for each
type of neuron, a general procedure is described which invokes two undefined
functions, SynapsesNeeded and GetNextSynapse which are left to the reader
to implement as needed by their application.
One final item needs to be handled before the segments are complete, which is the
fact that the local membrane potentials of neighboring segments should be part of the
local computation that takes place on each individual dendrite segment. This can be
solved by simply treating the neighboring segments as synapses and identifying these
with a unique synapse type (described in the following section).
3.3 Data Storage
In the present model, functionally identical neurons are arranged into a single layer
which forms the functional unit of the network. Each layer of simulated neurons in the
network requires three textures to be maintained throughout execution: a neuron
texture, a dendrite texture, and a synapse texture. Individual pixels in the neuron
texture store the activation (i.e., membrane potential; A
N
) for each individual neuron
as well as an index to the first dendrite segment of the neuron (I
D
) stored in the
dendrite texture. Pixels in the dendrite texture store the local membrane potential of
each dendrite segment (A
D
), an index to the first synapse of the segment (I
S
) stored in
the synapse texture, and a weight used to moderate how much local potential is
transferred from the segment (W
D
). Finally, each pixel in the synapse texture stores an
index to the afferent membrane potential that is being transferred by the synapse (I
A
);
for instance, bipolar cells in the sample network receive input from the photoreceptor
neurons, which will be indexed by the synapse texture of the bipolar cell’s synapses.
However, as with biological neurons, synapses in the model can also receive their
input from a dendrite segment of another neuron. The synapse texture also contains a
weight used to modify the synapse strength (W
S
) and the type of the synapse (T)
which determines the texture that is indexed by the synapse. Figure 2 illustrates a
summary of the data model described above.
3.4 Model Execution
As mentioned in the previous section, functionally identical neurons are grouped into
layers. Each layer is executed by two fragment shaders each time a neuron’s
activations are calculated. The first fragment shader computes the local activation
73

function of individual dendrite segments. This shader executes by beginning at the
first indexed synapse in the synapse texture and iterating over subsequent synapses
until a blank synapse is encountered –denoted by a -1 in I
A
. The membrane potential
calculated in this way is then stored in the G component of the dendrite texture. The
second shader computes the global activation function of the neurons in the network.
This shader works in a manner very similar to the first shader by iterating over the
dendrite segments directly connected to the neuron soma, and the activation of the
neuron is stored in the G component of the neuron texture.
Fig. 2. Data model for the neural network design. Each pixel (grey square) is used to store the
various indexes and parameters used to compute the activations of the neurons and dendrites in
the network.
4 Sample Network
The sample network presented hereafter is used to demonstrate how the organization
principles previously described can be implemented to achieve both function and
efficiency. To this end, the following network will be used to model a subset of the
retinal circuitry responsible for the directionally selective signal found in the distal
dendrite branches of the starburst amacrine cells. In particular, we model the
photoreceptors (short-, medium-, & long-wavelength cones; implemented in the
model using individual red, green, and blue color channels), horizontal cells (H1 and
H2), on-center bipolar cells (short-, medium-, & long-wavelength cells), and starburst
amacrine cells. The local membrane potentials of the network demonstrate that the
computation of the centrifugal direction selective signal is very similar to that of
biological neurons [9, 10].
74

4.1 System Overview
Input to the network is achieved using a standard webcam setup that captures video at
30 frames per second (FPS). After each frame is captured, it is transferred to video
memory on the graphics card using the OpenGL API. Fragment shaders, which
encompass nearly all of the network processing and implementation, are implemented
using OpenGL’s high level shading language, GLSL. The neuron, dendrite, and
synapse textures are created prior to execution using an extension of the methods
detailed in previous sections. All computations were executed on a desktop computer
running Windows XP with a 2.6 Ghz AMD 64 bit dual-core processor with 4 GBs or
RAM and a Nvidia GTX 280 graphics card.
4.2 Network Organization
The wiring of photoreceptors, horizontal cells, and on-center bipolar cells is modeled
directly from the biological wiring described in [9, 10, 16, 17]. Figure 3 (left)
illustrates the connections that exist between a single starburst amacrine cell and the
cells that contribute to its activation; essentially, the neurons shown for the classic
receptive field for a single starburst amacrine cell. Dendritic branching of horizontal
and bipolar cells incorporates only single dendrite branch segments –e.g., a branch
code of 410101010. Bipolar cells compute a contrast modulated activation through
an antagonistic center-surround organization of its afferent synapses from cones
(center) and horizontal cells (surround). For the sake of brevity, the equations used to
compute neural activations are not presented. However, the neural activations follow
very closely those of their biological counterparts as described by Dowling [17], and
are similar in effect to those of [18].
Starburst amacrine cell dendrites follow the basic design present in Figure 1. This
dendrite branching pattern, though highly simplified, still preserves the necessary
geometric relationship that allows the computation of the centrifugal-selective signals
as described by Tukker et al. [10]. As dendrite segments of the starburst amacrine cell
move progressively farther from the soma, inputs to these segments are selectively
received from bipolar cells that are more distant from the starburst cell.
75

Fig. 3. Connections and data flow in the sample network. (left) A 3-dimensional rendering of
the actual connections that contribute to the activation of a single starburst amacrine cell in the
sample network. Illustrated neurons represent the classic receptive field of the starburst neuron.
(right) Source image and the activations of each layer in the network. Lighter portions represent
higher activations whereas the color represents the relative contribution by red, green, and blue
components of the source signal.
76

4.3 Network Results
The sample network consists of nine layers of neurons, more than 225,000 individual
neurons, and more than 2 million synapses. Despite its size, the activations of every
neuron in the network can be computed in 7 ms or, put another way, the network
operates at roughly 142 pulses per second (1 pulse = 1 computation of all neuron
activations). In preliminary versions of the network, the GPU version outperformed
an analogous, multi-threaded CPU version by a factor of approximately 20 when
executed on a 2.4 Ghz quad-core processor.
The activations of the individual layers in the network are illustrated in Figure 3
(right). The activations of all layers, with the exception of the starburst amacrine
layer, are illustrated during a single, similar pulse step. The activations of the starburst
amacrine layer, however, are from a pulse that is many steps into the future relative to
the other layers, which demonstrates the motion of the robot pictured. Although the
starburst amacrine cells are directionally selective, their highly overlapped nature
instead results in activations similar to image subtraction from traditional image
processing techniques. This result in itself could be achieved with a simpler network
[c.f., 18]; however, starburst amacrine cells form a crucial input for the
computationally more complex directionally selective ganglion cells [9]. As such, this
network represents a significant first step in the creation of a larger, more complex
network dedicated to modeling the complex visual processes that contribute to our
own remarkable visual abilities.
5 Discussion
In the present work we have demonstrated a novel neural network design that
combines biologically realistic –and potentially computationally crucial– mechanisms
that can be executed in real-time by taking advantage of the highly parallel
organization of modern GPUs. This design was then demonstrated by modeling the
subset of the retinal neural circuitry that is responsible for computing a directionally-
selective signal in the starburst amacrine cell. As in its biological form, the signal
computed in the cell is the result of the physical organization of the afferent input on a
starburst cell’s dendrites.
The sample network, which consists of more than 225k neurons, can be computed
at a rate that is nearly 5x the frame rate of the incoming signal. As such, this sample
network could already be extended to include much more sophisticate motion
processing by including layers subsequent to starburst cells such as directionally
selective ganglion cells and neurons in extra-striate areas and the middle temporal
area, which are known to be very important to motion processing in primate vision
[19]. Additional cortical mechanisms important for primate vision have been
proposed to directly rely on computations that take place in the dendrites [e.g., 20,
21]. The single neuron model that is introduced here could be used directly to
implement such proposed complex neural mechanisms in a computationally efficient
manner. Future work will be directed toward building more complex visual abilities
of the network, and, when necessary, utilizing the dendritic toolkit that is supported
by the current neural network design to implement such abilities.
77

References
1. Sejnowski, T. J., Koch, C. & Churchland, P. S. (1988). Computational neuroscience.
Science, 241, 1299-1306.
2. Koch, C. & Segev, I. (2000). The role of single neurons in information processing. Nature
Neuroscience, 3, 1171-1177.
3. Gray, C. M., König, P., Engel, A. K. & Singer, W. (1989). Oscillatory responses in cat
visual cortex exhibit inter-columnar synchronization which reflects global stimulus
properties. Nature, 338, 334-347.
4. Vaadia, E., Haalman, I., Abeles, M., Bergman, H., Prut, Y., Slovin, H. & Aertsen, A.
(1995). Dynamics of neuronal interactions in monkey cortex in relation to behavioural
events. Nature, 373, 515-518.
5. London, M. & Häusser M. (2005). Dendritic computation. Annual Review of Neuroscience,
28, 503-532.
6. Agmon-Snir, H., Carr, C. E. & Rinzel, J. (1998). The role of dendrites in auditory
coincidence detection. Nature, 393, 268-272.
7. Mainen, Z. F. & Sejnowski, T. J. (1996). Influence of dendritic structure on firing pattern in
model neocortical neurons. Nature, 382, 363-366.
8. Segev, I & Rall, W. (1988). Computational study of an excitable dendritic spine. Journal of
Neurophysiology, 60, 499-523.
9. Euler, T., Detwiler, P. B. & Denk, W. (2002). Directionally selective calcium signals in
dendrites of starburst amacrine cells. Nature, 418, 845-852.
10. Tukker, J. J., Taylor, W. R. & Smith, R. G. (2004). Direction selectivity in a model of the
starburst amacrine cell. Visual Neuroscience, 21, 611-625.
11. Owens, J. D., Luebke, D., Govindaraju, N., Harris, M., Krüger, J., Lefohn, A. E. & Purcell,
T. J. (2007). A survey of general-purpose computation on graphics hardware. Computer
Graphics Forum, 26, 80-113.
12. GPGPU. Retrieved April 01, 2009 from http://www.gpgpu.org
13. Bernhard, F. & Keriven, R. (2006). Spiking Neurons on GPUs. International Conference
on Computation Science. Workshop general purpose computation on graphics hardware
(GPGPU): Methods algorithms and applications, Readings, U.K.
14. Gobron, S., Devillard, F. & Heit, B. (2007). Retina simulation using cellular automata and
GPU programming. Machine Vision and Applications, 18, 331-342.
15. Woodbeck, K., Roth, G. & Chen, H. (2008). Visual cortex on the GPU: Biologically
inspired classifier and feature descriptor for rapid recognition. IEEE Computer Society
Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Anchorage, AK, U.S.A.
16. Dacey, D. M. (2000). Parallel pathways for spectral coding in primate retina. Annual
Review of Neuroscience, 23, 743-775.
17. Dowling, J. E. (1987). The Retina: An Approachable Part of the Brain. Cambridge, MA,
USA. Belknap Press.
18. Garaas, T. W. & Pomplun, M. (2007). Retina-inspired visual processing. Proceedings of
BIONETICS, Workshop on Computing and Communications from Biological Systems:
Theory and Applications (CCBS). Budapest, Hungary.
19. Blake, R., Sekuler, R., & Grossman, E. (2003). Motion processing in human visual cortex.
In J H Kaas and C E Collins (Eds.), The Primate Visual System. Boca Raton: CRC Press.
20. Mel, B. W., Ruderman, D. L., & Archie, K. A. (1998). Translation-invariant orientation
tuning in visual “complex” cells could derive from intradendritic computations. The
Journal of Neuroscience, 18, 4325-4334.
21. Barlow, H. (1996). Intraneuronal information processing, directional selectivity and
memory for spatio-temporal sequences. Network, 7, 251-259.
78
