
A HYBRID APPROACH TOWARDS INFORMATION EXPANSION
BASED ON SHALLOW AND DEEP METADATA
Tudor Groza and Siegfried Handschuh
Digital Enterprise Research Institute, National University of Ireland, Galway, Ireland
Keywords:
Semantic Metadata, Information Expansion, Information Visualization, Knowledge Capturing.
Abstract:
The exponential growth of the World Wide Web in the last decade, brought an explosion in the information
space, with important consequences also in the area of scientific research. Lately, finding relevant work in a
particular field and exploring links between relevant publications, became a cumbersome task. In this paper we
propose a hybrid approach to automatic extraction of semantic metadata from scientific publications that can
help to alleviate, at least partially, the above mentioned problem. We integrated the extraction mechanisms
in an application targeted to early stage researchers. The application harmoniously combines the metadata
extraction with information expansion and visualization for the seamless exploration of the space surrounding
scientific publications.
1 INTRODUCTION
The World Wide Web has been an essential medium
for the dissemination of scientific work in many
fields. The significant rate at which scientific research
outcomes are growing has inevitably led to substan-
tial increases in the amount of scientific work pub-
lished within journals, conferences, workshops. As an
example, in the biomedical domain, the well-known
MedLine
1
now hosts over 18 million articles, hav-
ing a growth rate of 0.5 million articles / year, which
represents around 1300 articles / day (Tsujii, 2009).
This makes the process of finding relevant work in a
particular field a cumbersome task, especially for an
early stage researcher.
In addition, the lack of uniformity and integration
of access to information can also be considered an as-
sociated issue with the information overload. Each
event has its own online publishing means, and there
exist no centralized hub linking the information, not
even for communities sharing similar interests. These
issues have motivated a variety of efforts. The Se-
mantic Web Dog Food initiative (M
¨
oller et al., 2007)
is a pioneering attempt in which a RDF-based repos-
itory was set up to host metadata about International
and European Semantic Web conferences (and other
Semantic Web events). This data is then served as
1
http://medline.cos.com/
linked open data to the community. While the initia-
tive is getting more and more attention and partici-
pation from organizers of scientific events, it requires
a considerable amount of manual effort to derive the
metadata about the publications (shallow and deep,
such as title, authors, references, claims, positions or
arguments). Without any immediate reward or feed-
back, there is little incentive for authors to generate
the metadata themselves. It is our belief that the adop-
tion of semantic technologies to enable linked open
data in the scientific publication domain can be much
greater if an automatic metadata extraction solution
would exist.
In this paper, we report on a hybrid approach to-
ward automatic extraction of both shallow and deep
metadata from scientific publications, which has been
developed and evaluated. Our proposal combines
document engineering with empirical and linguistic
processing. The result of the extraction is an ontolog-
ical representation of the publication, capturing the
linear and rhetorical structure of the discourse (prove-
nance and semantics), in addition to the usual Dublin-
Core metadata terms. The metadata can then be ex-
ported and used in repositories like the Semantic Web
Dog Food Server, or embedded into the publication
and used for a tighter integration of personal infor-
mation within the Social Semantic Desktop frame-
work (Bernardi et al., 2008). We wrapped all these
109
Groza T. and Handschuh S. (2009).
A HYBRID APPROACH TOWARDS INFORMATION EXPANSION BASED ON SHALLOW AND DEEP METADATA.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development, pages 109-116
DOI: 10.5220/0002271001090116
Copyright
c
SciTePress
features into a highly modularized application
2
that
uses the extracted metadata for achieving information
expansion and visualization. In addition, it emulates
an information hub created on demand, that provides
early stage researchers with an integrated view on
multiple publication repositories.
The rest of the paper is structured as follows: we
start by enumerating the application’s requirements
in Sect. 2, then we detail our approach in Sect. 3.
Sect. 4 discusses the evaluation we carried out and be-
fore concluding in Sect. 6, we present similar research
approaches in Sect. 5.
2 REQUIREMENTS
In order to support researchers with their needs of
finding relevant scientific publications, we performed
a study, that resulted in a list of requirements. The
study featured a series of online surveys, with the
broader scope of analyzing metadata usefulness and
general reading habits. For the current paper, only
parts of them are relevant
3
. In terms of results,
we had 75 researchers answering the call, all acting
within the Semantic Web community. The list of ex-
tracted generic requirements is summarized as fol-
lows:
Automatic Metadata Extraction. Although the vast
majority of researchers agree with the importance
and usefulness of metadata, almost none of them
would spend the time to create it manually. There-
fore, it is important to require as little effort as
possible from authors / readers, and find viable
ways to generate or extract the metadata automat-
ically. In addition, we also target the extraction of
the entire metadata space including abstract and
references, as well as, deep metadata like claims,
positions or arguments. As an example, 90.8% of
the survey subjects consider the abstract impor-
tant or crucial to read, and 85.4% consider deep
metadata (e.g. claims) to improve the understand-
ing of a paper, and that is also why 82.8% usually
manually mark such deep metadata while reading.
Metadata Persistence. Having the metadata ex-
tracted, we need to allow the author / reader to
make it persistent, thus providing the opportunity
for its reuse. Both persistence options are easily
achievable, i.e. (i) exporting the metadata, for di-
rect usage in web repositories, or (ii) embedding
2
The application can be downloaded from
http://sclippy.semanticauthoring.org/
3
The complete surveys including the results can be
found at http://smile.deri.ie/surveys
the metadata into the original publication.
Metadata Usage. Obviously, extracting and storing
the metadata would not be sufficient. We also
need to use it. Considering our target users and
their reading habits, we opted for using it to
achieve information expansion and visualization.
For example, 88.8% of the survey subjects would
look for other publications of the same author or
her co-authors.
3 IMPLEMENTATION
The analysis and refinement of the requirements list
resulted into a workflow that supports the design of
our application. In the following section we describe
this workflow together with its composing parts.
3.1 Workflow
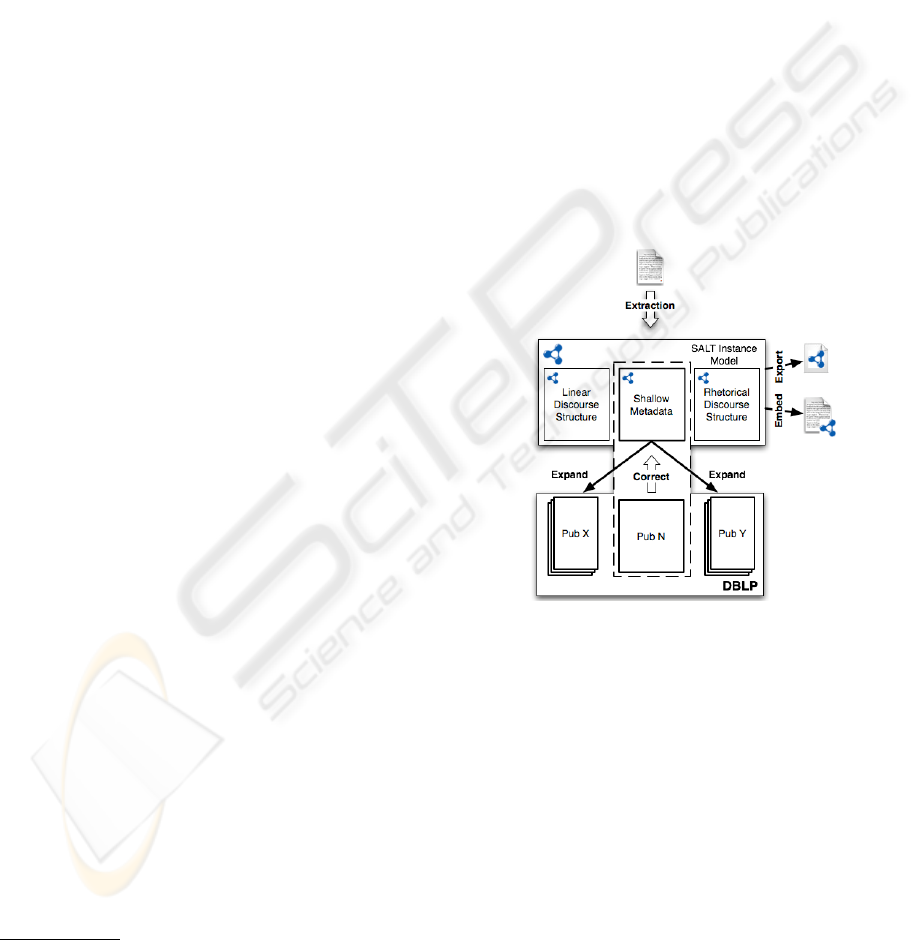
Figure 1: Application workflow.
The workflow, depicted in Fig. 1, can be split into
three main parts, according to the three dimensions
given by the requirements. The first part deals with
the automatic extraction of metadata. Here, we cur-
rently focus only on publications published as PDF
documents. The extraction module takes as input a
publication and creates a SALT (Semantically An-
notated L
A
T
E
X) instance model. SALT (Groza et al.,
2007) represents a semantic authoring framework tar-
geting the enrichment of scientific publications with
semantic metadata. It introduces a layered model that
covers the linear structure of the discourse (the Doc-
ument Ontology), the rhetorical structure of the dis-
course (the Rhetorical Ontology) and additional an-
notations, e.g. the shallow metadata (the Annotation
Ontology).
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
110

In the second part of the workflow, the extracted
instance model can be exported to a separate file,
or embedded into the original publication (by means
of the same extraction module). The third and last
part uses the shallow metadata modeled by the SALT
instances to perform information expansion. This
is achieved based on different existing publication
repositories. The current implementation realizes the
expansion based on DBLP
4
. This represents only the
first step, as the design of the application allows dy-
namic integration of different other expansion mod-
ules, thus transforming it into an information hub.
In addition, the expanded information can be used to
correct or improve the extracted metadata.
3.2 Extraction of Shallow Metadata and
the Linear Discourse Structure
The extraction of shallow metadata and linear dis-
course structure currently works only on PDF publi-
cations. We have developed a set of algorithms that
follow a low-level document engineering approach,
by combining mining and analysis of the publication
content based on its formatting style and font infor-
mation. Each algorithm in the set deals with one as-
pect of shallow metadata. Thus, there is an authors
extraction algorithm, one for extracting the abstract,
one for the references and last one for the linear dis-
course structure.
Detailing the actual algorithms is out of the scope
of the current paper. Nevertheless we will give an ex-
ample of how the authors extraction works. There are
four main processing steps:
1. We merge the consecutive text chunks on the first
page that have the same font information and are
on the same line (i.e. the Y coordinate is the
same);
2. We select the text chunks between the title and the
abstract and consider them author candidates
3. We linearize the author candidates based on the
variations of the Y axis
4. We split the author candidates based on the varia-
tions of the X axis
To have a better picture of how the algorithm
works, Fig. 2 depicts an example applied on a pub-
lication that has the authors structured on several
columns. The figure shows the way in which the au-
thors’ columns containing the names and affiliations
are linearized, based on the variation of the Y coor-
dinate. The arrows in the figure show the exact lin-
4
http://informatik.uni-trier.de/ ley/db/
Figure 2: Authors extraction algorithm example.
earization order. The variations on the X axis can be
represented in a similar manner.
3.3 Extraction of the Rhetorical
Discourse Structure
For the extraction of deep metadata we followed
a completely different approach. We started from
adopting, as foundational background, the Rhetorical
Structure of Text Theory (RST)
5
. RST was first intro-
duced in (Mann and Thompson, 1987), with the goal
of providing a descriptive theory for the organization
and coherence of natural text. The theory comprises a
series of elements, from which we mention the most
important ones, i.e. (i) Text spans, and (ii) Schemas.
Text spans represent uninterrupted linear intervals of
text that can have the roles of Nucleus or Satellite.
A Nucleus represents the core (main part / idea) of
a sentence or phrase, while the Satellite represents
a text span that complements the Nucleus with addi-
tional information. One the other hand, schemas de-
fine the structural constituency arrangements of text.
They mainly provide a set of conventions that are ei-
ther independent or inclusive of particular rhetorical
relations that connect different text spans. The theory
proposes a set of 23 rhetorical relations, having an al-
most flat structure (e.g. Circumstance, Elaboration,
Antithesis, etc). In SALT, and as well as in our ex-
traction mechanism, we adopted only a subset of 11
relations
6
.
The actual extraction process comprised two
phases: (i) the empirical analysis of a publication col-
lection and development of a knowledge acquisition
module, and (ii) an experiment for determining the
initial probabilities for text spans to represent knowl-
edge items (i.e. claims, positions, arguments), based
on the participation in a rhetorical relation of a certain
type and its block placement in the publication (i.e.
abstract, introduction, conclusion or related work).
5
RST is also the foundation of SALT
6
See http://salt.semanticauthoring.org/ for more details
on the SALT model.
A HYBRID APPROACH TOWARDS INFORMATION EXPANSION BASED ON SHALLOW AND DEEP
METADATA
111

In order to automatically identify text spans and
the rhetorical relations that hold among them, we re-
lied on the discourse function of cue phrases, i.e.
words such as however, although and but. An ex-
ploratory study of such cue phrases provided us with
an empirical grounding for the development of an ex-
traction algorithm. Having as inspiration the work
performed by Marcu (Marcu, 1997) we analyzed a
collection of around 130 publications from the Com-
puter Science field and identified 75 cue phrases that
signal the rhetorical relations mentioned above. For
each cue phrase we extracted a number of text frag-
ments, in order to identify two types of information:
(i) discourse related information (i.e. the rhetorical
relations that were marked by the cue phrases and the
roles of the related text spans), and (ii) algorithmic
information (i.e. position in the sentence, its position
according to the neighboring text spans and the sur-
rounding punctuation). This information constitutes
the empirical foundation of our algorithm that identi-
fies the elementary unit boundaries and discourse us-
ages of the cue phrases. The actual implementation
was embedded into a GATE
7
plugin.
The second phase of the extraction process con-
sisted of an experiment. The annotation of epistemic
items (i.e. claims, positions, arguments) in a docu-
ment is a highly subjective task. Different people have
diverse mental representations of a given document,
depending on their domain or the depth of knowl-
edge of the document in question. Therefore, prob-
ably the most reliable annotator of a scientific publi-
cation would be its author. In order to capture the way
in which people find (and maybe interpret) epistemic
items, we ran an experiment. The goal of the experi-
ment was to allow us to compute initial values for the
probabilities of text spans to be epistemic items.
The setup of the experiment included ten re-
searchers (authors of scientific publications), two col-
lections and two tasks. The tasks represented at their
basis the same task, just that each time performed on
a different collection. The first collection comprised a
set of ten publications chosen by us, while the second
collection had 20 publications, provided by the anno-
tators. Each annotator provided us two of her own
publications. For each publication, we extracted a list
of text spans (based on the presence of rhetorical re-
lations) and presented this list to the annotators. On
an average each list had around 110 items. The an-
notators’ task was to mark in the given lists, the text
spans that they considered to be epistemic items. Al-
though the complexity of the task was high enough
by its nature, we chose not to do experiment in a
controlled environment. Having collected the marked
7
http://gate.ac.uk/
lists from the annotators, we decoded the rhetorical
relations hidden behind each knowledge item in the
list and computed the proportional specific raw inter-
annotator agreement per publication. The result was
a list of proportions of specific (positive, negative and
overall) raw inter-annotator agreements. Each rhetor-
ical relation was then assigned the corresponding av-
erage of the positive agreement values, based on the
originating knowledge items.
The actual extraction implemented in the system
considers a fixed probability threshold for the rhetor-
ical relations and based on the input text, it provides
the list of items having the rhetorical relations proba-
bilities above the threshold.
3.4 Information Expansion
The previous two steps represent together the hy-
brid mechanism for extracting an ontological instance
model from scientific publications. The model can
then be exported or embedded into the original publi-
cation, thus lifting the semantics captured in the docu-
ment, into a machine-processable format. In addition,
we used parts of the model to perform information
expansion. The design of the application allows one
to integrate multiple expansion modules, each con-
nected to a particular publication repository. Cur-
rently, we have implemented such a module based on
DBLP. On demand, the extracted shallow metadata
(i.e. the title and authors) is used to search the repos-
itory for the corresponding publication. Considering
that the extraction works on a best effort basis, the
final metadata might contain errors both in title and
in the authors’ list. The user has the means for cor-
recting it manually, or if the publication is expanded
correctly, she can do it automatically.
The first element used for searching the repository
is the title of the publication. In order to ’correct’
(or mask) the possibly existing errors in the title, we
use string similarity measures to find out the proper
publication. An empirical analysis led us to using a
combination of the Monge-Elkan and Soundex algo-
rithms, with fixed thresholds. The first one analyzes
fine-grained sub-string details, while the second looks
at coarse-grained phonetic aspects. The publications
that pass the imposed thresholds are then checked
based on the existing authors. The best match is then
provided to the user as a candidate for correcting the
existing metadata (see the left part of Fig. 3 the title
highlighted in blue). The same approach is also fol-
lowed for each author of the publication.
The outcome of the expansion process features
two elements: (i) a list of similar publications to the
one given as input, each with its authors, and (ii) for
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
112
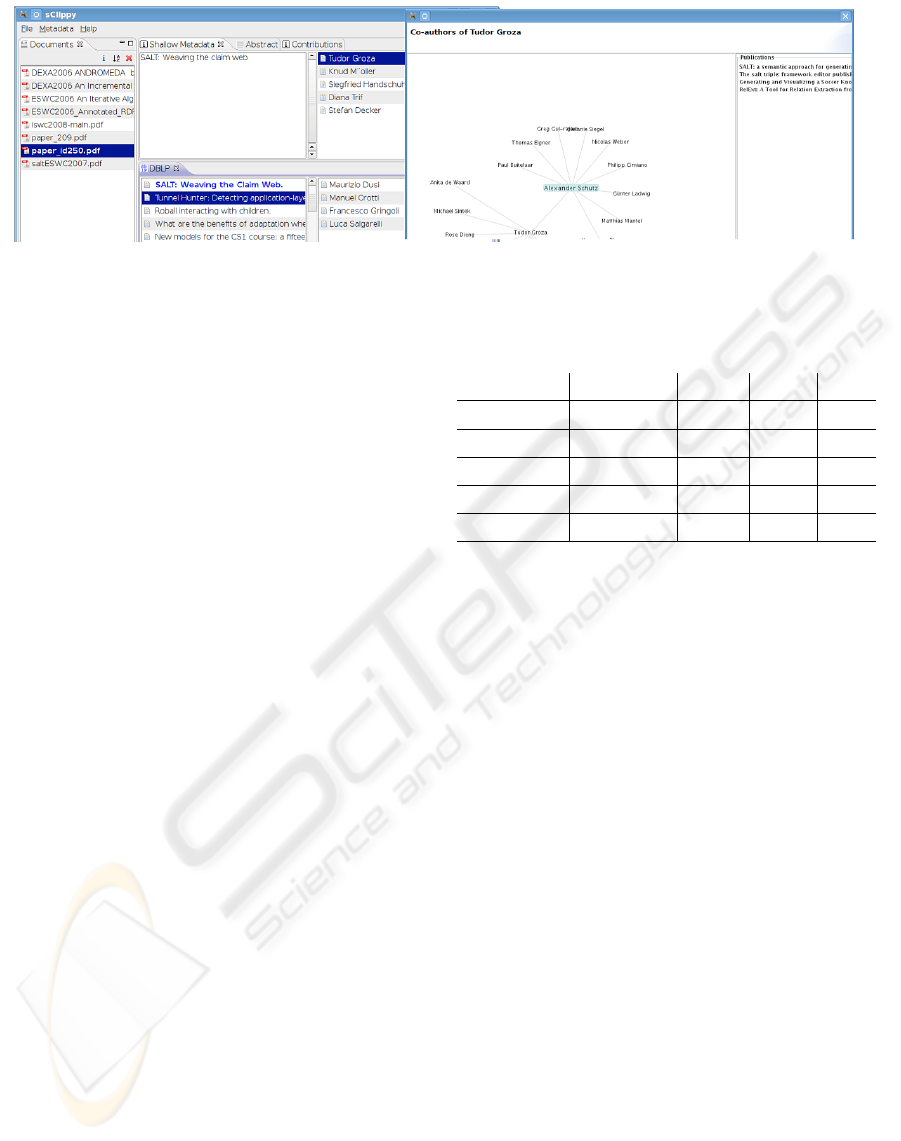
Figure 3: Example of information expansion within our application.
each author of the given publication found, her com-
plete list of publications existing in the respective
repository. This provides the user with the chance
of analyzing both publications that might have sim-
ilar approaches and inspect all the publications of a
particular author.
Based on the same repository, we have also im-
plemented the option of visualizing the graph of co-
authors starting from a particular author, together with
their associated publications. The right side of Fig. 3
shows an example of such an exploration.
4 EVALUATION
We evaluated each of the modules described in the
previous section, and performed a usability study of
the overall application.
Shallow Metadata Extraction. The shallow meta-
data extraction was evaluated by testing the algo-
rithms on a corpus comprising around 1200 publi-
cations, formatted with the ACM or Springer LNCS
styles. The documents forming the corpus were con-
sistent and uniform in terms of encoding and metadata
content, individually for each type of formatting. As
extraction from PDF documents depends on a hand-
ful of factors (e.g. encoding, encryption, etc), the
evaluation results presented here, considers only the
documents for which the actual extraction was valid
(i.e. the PDF parser was able to read the document).
Also, the results present the algorithms working on
a best effort basis (no additional information is pro-
vided about the publications). Nevertheless, our next
step will be to provide the means for optimizing the
algorithms for particular styles and formats.
Table 1 lists the evaluation results. Overall, the
title and abstract extraction algorithms performed the
best, with an accuracy of 95% and respectively 96%.
We observed that most of the cases in which the algo-
Table 1: Performance measures of the shallow metadata ex-
traction.
Accuracy Prec. Rec. F
Title 0.95 0.96 0.98 0.96
Authors 0.90 0.92 0.96 0.93
Abstract 0.96 0.99 0.96 0.97
Sections 0.92 0.97 0.93 0.94
References 0.91 0.96 0.93 0.94
rithms failed to produce a result were documents that
the PDF parser managed to read but failed to actually
parse. If we would eliminate this set of documents,
the accuracy would probably increase with an addi-
tional 2%. The 90% accuracy of the authors extrac-
tion algorithm is mostly due to the lack of adherence
to the formatting style, or presence of special symbols
close to the authors’ names. The sections extraction
algorithm performed extremely well, with an 92% ac-
curacy, which represents that in these cases, it man-
aged to extract the complete tree of sections from the
paper. On the other hand, the references extraction al-
gorithm did not perform as well as we expected, and
had an accuracy of only 91%.
Deep Metadata Extraction. The deep metadata
extraction was tested based on a preliminary evalu-
ation, and with an emphasis put on the extraction of
the knowledge items. The setup of the evaluation was
similar to the one of the experiment described in the
previous section. We used two corpora (with a total of
30 publications), one with the evaluators’ own papers
and one containing a set of paper we chose. Each
evaluator was asked to mark those text spans in the
text that she considers to be knowledge items, both
in her own paper and the one we assigned. In paral-
lel, we ran our tool on the same set of publications
and compiled the predicted list of candidates. At the
end we computed the usual performance measures,
A HYBRID APPROACH TOWARDS INFORMATION EXPANSION BASED ON SHALLOW AND DEEP
METADATA
113

Table 2: Evaluation results.
Corpus Prec. Recall F-Measure
I (own) 0.5 0.3 0.18
II (provided) 0.43 0.31 0.19
i.e. precision, recall and f-measure. The evaluation
results are summarized in Table 2.
One could interpret of the performance measures
of the extraction results in different ways. On one
side, we see them as satisfactory, because they rep-
resent the effect of merely the first step from a more
complex extraction mechanism we have envisioned.
At the same time, if we compare them, for example,
with the best precision reached by (Teufel and Moens,
2002), or 70.5, we find our 0.5 precision to be encour-
aging. And this is mainly because in our case there
was no training involved, and we considered only two
parameters in the extraction process, i.e. the rhetor-
ical relations and the block placement, while Teufel
employed a very complex na
¨
ıve Bayes classifier with
a pool of 16 parameters, and 20 hours of training for
the empirical experiment. On the other hand, these
results clearly show that we need to consider as well
other parameters, such as, the presence of anaphora, a
proper distinction between the different types of epis-
temic items, or the used verb tense, parameters which
are already part of our future plans.
Secondly, the formula we have used for com-
puting the final probabilities, within this preliminary
evaluation, has a very important influence on the ex-
traction results. Currently, we opted for a simple
formula that gives more weight to the probabilities
emerged from the annotation of own papers. Such an
approach should be used when the automatic extrac-
tion is performed by an author on her own papers, for
example, in real time while authoring them. This is
clearly reflected in the positive difference in precision
between the own corpus and the provided one. On the
other hand, if used for information retrieval purposes,
by readers and not by authors, the computation for-
mula should be changed, so that it gives more weight
to the probabilities emerged from the annotation of
given papers. This practically translate into shaping
the extraction results in a form closer to what a reader
would expect.
Usability Study. The usability study was per-
formed with 16 evaluators and included a series of
tasks to cover all the application’s functionalities. Ex-
ample of tasks included: extraction and manual cor-
rection of metadata from publications, expansion of
information starting from a publication or exploration
of the co-author graph. At the end, the evaluators
had to fill in a questionnaire, comprising 18 ques-
tions, with Likert scale or free form answers, focus-
ing on two aspects: (i) suitability and ease of use,
and (ii) design, layout and conformity to expectan-
cies. The complete results of the questionnaire can be
found at http://smile.deri.ie/sclippy-usabilitystudy.
Overall, the application scored very well in both
categories. For example, the vast majority of the eval-
uators (on average more than 90%) found the tool
both helpful and well suited for the extraction and ex-
ploration of shallow and deep metadata. In the other
category, the same amount evaluators considered the
application easy to learn and to use while having the
design and layout both appealing and suited for the
task. Possible issues we discovered in two cases. The
first one would be the self-descriptiveness of the ap-
plication’s interface, mainly due to the lack of visual
indicators and tooltips. The second case was related
to the suggested list of similar publications. Although
the application always proposed the exact publication
selected for expansion, the rest of the list created some
confusion. We believe that the cause of the confu-
sion is the fact that the similarity measures we have
adopted were not well suited.
This study led us to a series of directions for im-
provement. First of all, the need to make use of a more
complex mechanism for suggesting similar publica-
tions. This will depend to a large extent on the reposi-
tory used for expansion and on the information that it
provides. For example, in the case of the ACM Portal,
we will consider also text of the abstract when com-
puting the candidates list. Secondly, augmenting the
expanded information with additional elements (e.g.
abstract, references, citation contexts), thus providing
a deeper insight into the publications and a richer ex-
perience for the users. Lastly, the integration of the
application within the Social Semantic Desktop plat-
form. This will lead to a centralized data persistence
and deeper integration and linking of the metadata
into the more general context of the personal infor-
mation.
5 RELATED WORK
Our approach combines different directions for
achieving its goals. In the following we will try to
provide a good overview of the related efforts corre-
sponding to each research direction. We will cover
mainly: (i) methods used for automatic extraction
of shallow metadata, (ii) models for structuring dis-
course, and (iii) information visualization for scien-
tific publications.
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
114

There have been several methods used for au-
tomatic extraction of shallow metadata, like regular
expressions, rule-based parsers or machine learning.
Regular expressions and rule-based systems have the
advantage that they do not require any training and
are straightforward to implement. Successful work
has been reported in this direction, with emphasis on
PostScript documents in (Shek and Yang, 2000), or
considering HTML documents and use of natural lan-
guage processing methods in (Yilmazel et al., 2004).
A different trend in the same category is given by ma-
chine learning methods, that are more efficient, but
also more expensive, due to the need of training data.
Hidden Markov models (HMMs) are the most widely
used among these techniques. However, HMMs are
based on the assumption that features of the model
they represent are not independent from each other.
Thus, HMMs have difficulty exploiting regularities
of a semi-structured real system. Maximum entropy
based Markov models (McCallum et al., 2000) and
conditional random fields (Lafferty et al., 2001) have
been introduced to deal with the problem of indepen-
dent features. In the same category, but following a
different approach, is the work performed by Han et
al. (Han et al., 2003), who uses Support Vector Ma-
chines (SVMs) for metadata extraction.
Some remarks worth to be noted here regarding
a comparison between the above mentioned methods
and ours. First of all, the comparison between the vi-
sual/spatial approaches (Shek’s and ours) and the ma-
chine learning ones is not really appropriate. This is
mainly because the latter can easily cope with general
formats, while the former are “static” methods, fo-
cused on a particular format. Nevertheless, the learn-
ing methods impose a high cost due to their need of
accurate training data, while the static methods have
no training associated. Secondly, due to the lack of
a common dataset, a direct comparison of efficiency
measures cannot be realized. The main reason is be-
cause most of the machine learning methods work
on plain text already extracted by some other means,
while the spatial approaches work on the actual doc-
uments. Still, we consider Shek’s approach to be the
closest to ours, although targeting a different docu-
ment format. Based on a purely empirical comparison
we observe a higher accuracy for our title and authors
extraction method (around 5%), as well as a higher
accuracy for the linear structure extraction (around
15%), while also providing additional metadata (i.e.
abstract or references).
In the area of discourse structuring, we can find
a rich sphere of related work. One of the first mod-
els was introduced by (Teufel and Moens, 2002) and
tried to categorize phrases from scientific publica-
tions into seven categories based on their rhetorical
role. Later, the authors developed an automatic ex-
traction approach, following a similar method to ours,
starting from a corpus of manually annotated docu-
ments and a set of probabilities emerged from inter-
annotator agreement studies. Teufel did not make use
of any relations between the extracted items. (Shum
et al., 2006) were the first to describe one of the
most comprehensive models for argumentation in sci-
entific publications, using as links between the epis-
temic items Cognitive Coherence Relations. They de-
veloped a series of tools for the annotation, search
and visualization of scientific publications based on
this model, which represent our main inspiration. The
automatic extraction approach they followed was the
same as the one developed by Teufel, i.e. by com-
piling and using a list of particular cue-phrases. Al-
though their model is richer than the previous, due to
the presence of relations, they do not make use of the
placement of the item in the publication.
With respect to information visualization of sci-
entific publications, a number of methods and tools
have been reported in the literature. The 2004 InfoVis
challenge had motivated the introduction of a number
of visualization tools highlighting different aspects of
a selected set of publications in the Information Vi-
sualization domain. (Faisal et al., 2007) reported on
using the InfoVis 2004 contest dataset to visualize ci-
tation networks via multiple coordinated views. Un-
like our work, these tools were based on the contents
of a single file, containing manually extracted meta-
data. As noted by the challenge chairs, it was a diffi-
cult task to produce the metadata file (Plaisant et al.,
2008) and hence the considerable efforts required,
made it challenging for wide-spread use. In (Neirynck
and Borner, 2007), a small scale research manage-
ment tool was built to help visualizing various rela-
tionships between lab members and their respective
publications. A co-authorship network visualization
was built from data entered by users in which nodes
represent researchers together with their publications
and links show their collaborations. A similar effort
to visual domain knowledge was reported by (Mur-
ray et al., 2006), with data source being bibliographic
files obtained from distinguished researchers in the
“network science” area. While this work was also
concerned with cleansing data from noisy sources, the
metadata in use was not extracted from publications
themselves and no further information available from
external sources such as DBLP was utilized.
A HYBRID APPROACH TOWARDS INFORMATION EXPANSION BASED ON SHALLOW AND DEEP
METADATA
115

6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented an application that integrates a
series of different approaches for achieving informa-
tion expansion and visualization based on extracted
shallow and deep metadata. The extraction process of
the shallow metadata followed a low-level document
engineering approach, combining font mining and
format information. On the other hand, the extraction
of deep metadata (i.e. the rhetorical discourse struc-
ture) was performed based on a combined linguistic
and empirical approach. The metadata was used for
information expansion and visualization based on dif-
ferent publication repositories. The evaluation results
of all of the application’s components encourages us
to continue our efforts in the same direction, by in-
creasing the efficiency of the extraction mechanisms.
Future work will focus especially on improving
the extraction of deep metadata by considering word
co-occurrence, anaphora resolution and verb tense
analysis. These improvements will also be reflected
into a new iteration over the initial weights (probabil-
ities) assigned to the epistemic items, resulted from
this paper. At the application level, we will implement
additional expansion modules, thus integrating more
publication repositories. Also, we intend to release
the application’s core source code as open source so
that its adoption can be directly coupled with its fur-
ther development, including contributions from the
researchers that would like to use it.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The work presented in this paper has been funded
by Science Foundation Ireland under Grant No.
SFI/08/CE/I1380 (Lion-2). The authors would like
to thank VinhTuan Thai, Georgeta Bordea and Ioana
Hulpus for their support and help.
REFERENCES
Bernardi, A., Decker, S., van Elst, L., Grimnes, G., Groza,
T., Handschuh, S., Jazayeri, M., Mesnage, C., M
¨
oller,
K., Reif, G., and Sintek, M. (2008). The Social Se-
mantic Desktop: A New Paradigm Towards Deploying
the Semantic Web on the Desktop. IGI Global.
Faisal, S., Cairns, P. A., and Blandford, A. (2007). Building
for Users not for Experts: Designing a Visualization
of the Literature Domain. In Information Visualisation
2007, pages 707–712. IEEE Computer Society.
Groza, T., Handschuh, S., M
¨
oller, K., and Decker, S.
(2007). SALT - Semantically Annotated L
A
T
E
X for
Scientific Publications. In ESWC 2007, Innsbruck,
Austria.
Han, H., Giles, C. L., Manavoglu, E., Zha, H., Zhang, Z.,
and Fox, E. A. (2003). Automatic document metadata
extraction using support vector machines. In Proc.
of the 3rd ACM/IEEE-CS Joint Conf. on Digital li-
braries, pages 37–48.
Lafferty, J., McCallum, A., and Pereira, F. (2001). Con-
ditional random fields: Probabilistic models for seg-
menting and labeling sequence data. In Proc. of the
18th Int. Conf. on Machine Learning, pages 282–289.
Mann, W. C. and Thompson, S. A. (1987). Rhetorical struc-
ture theory: A theory of text organization. Technical
Report RS-87-190, Information Science Institute.
Marcu, D. (1997). The Rhetorical Parsing, Summarization,
and Generation on Natural Language Texts. PhD the-
sis, University of Toronto.
McCallum, A., Freitag, D., and Pereira, F. (2000). Maxi-
mum entropy markov models for information extrac-
tion and segmentation. In Proc. of the 17th Int. Conf.
on Machine Learning, pages 591–598.
M
¨
oller, K., Heath, T., Handschuh, S., and Domingue, J.
(2007). Recipes for Semantic Web Dog Food – The
ESWC and ISWC Metadata Projects. In Proc. of the
6th Int. Semantic Web Conference.
Murray, C., Ke, W., and Borner, K. (2006). Mapping scien-
tific disciplines and author expertise based on personal
bibliography files. In Information Visualisation 2006,
pages 258–263. IEEE Computer Society.
Neirynck, T. and Borner, K. (2007). Representing, ana-
lyzing, and visualizing scholarly data in support of
research management. In Information Visualisation
2007, pages 124–129. IEEE Computer Society.
Plaisant, C., Fekete, J.-D., and Grinstein, G. (2008). Pro-
moting Insight-Based Evaluation of Visualizations:
From Contest to Benchmark Repository. IEEE Trans-
actions on Visualization and Computer Graphics,
14(1):120–134.
Shek, E. C. and Yang, J. (2000). Knowledge-Based Meta-
data Extraction from PostScript Files. In Proc. of the
5th ACM Conf. on Digital Libraries, pages 77–84.
Shum, S. J. B., Uren, V., Li, G., Sereno, B., and Mancini,
C. (2006). Modeling naturalistic argumentation in re-
search literatures: Representation and interaction de-
sign issues. Int. J. of Intelligent Systems, 22(1):17–47.
Teufel, S. and Moens, M. (2002). Summarizing scientific
articles: Experiments with relevance and rhetorical
status. Computational Linguistics, 28.
Tsujii, J. (2009). Refine and pathtext, which combines text
mining with pathways. Keynote at Semantic Enrich-
ment of the Scientific Literature 2009 (SESL 2009).
Yilmazel, O., Finneran, C. M., and Liddy, E. D. (2004).
Metaextract: an nlp system to automatically assign
metadata. In JCDL ’04: Proceedings of the 4th
ACM/IEEE-CS joint conference on Digital libraries,
pages 241–242.
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
116
