
UNIFYING SEMANTIC ANNOTATION AND QUERYING IN
BIOMEDICAL IMAGE REPOSITORIES
One Solution for Two Problems of Medical Knowledge Engineering
Daniel Sonntag
German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence, Saarbrcken, Germany
Manuel M¨oller
German Research Center for Artificial Intelligence, Kaiserslautern, Germany
Keywords:
Medical Imaging Systems, Semantic Data Model, User/Machine Dialogue, Semantic Search and Retrieval.
Abstract:
In the medical domain, semantic image retrieval should provide the basis for the help in decision support and
computer aided diagnosis. But knowledge engineers cannot easily acquire the necessary medical knowledge
about the image contents. Based on their semantics, we present a set of techniques for annotating images and
querying image data sets. The unification of semantic annotation (using a GUI) and querying (using natural
dialogue) in biomedical image repositories is based on a unified view of the knowledge acquisition process.
We use a central RDF repository to capture both medical domain knowledge as well as image annotations and
understand medical knowledge engineering as an interactive process between the knowledge engineer and the
clinician. Our system also supports the interactive process between the dialogue engineer and the clinician.
1 INTRODUCTION
Image analysis in the biomedical context plays an im-
portant role in diagnosing and treating diseases; so
does semantic querying of medial image content. The
objective is to enable a seamless integration of medi-
cal images and different user applications by provid-
ing direct access to image semantics. Semantic image
retrieval should provide the basis for the help in clin-
ical decision support and computer aided diagnosis.
For example, during the course of lymphoma di-
agnosis and continual treatment, image data is pro-
duced several times using different modalities. As a
result, the image data consist of many medical images
in different formats, which additionally need to be as-
sociated with the corresponding patient data.
With traditional applications, users may browse or
explore visualized patient data, but little to no help is
given when it comes to the interpretation of what is
being displayed. This is due to the fact that the se-
mantics of the data are not explicitly stated, the se-
mantics therefore remain inaccessible to the system
and in turn also to the medical expert user. This
can be overcome by incorporating external medical
knowledge from ontologies which provide the mean-
ing (i.e., the formal semantics) of the data at hand.
To overcome the limitations of current medical im-
age systems, the authors use the Semantic Web stan-
dards OWL and RDF as a common representational
basis for both medical domain knowledge and anno-
tations in the same formalism. On the application
layer, the system leverages the structural information
in the ontologies to allow a multilingual and multi-
modal search, and to perform query expansion in or-
der to retrieve images which are annotated with se-
mantically similar concepts.
1
In this text, the authors describe the challenges
in Medical Knowledge Engineering (section 2) and
present a set of techniques for analyzing and query-
ing image data sets based on image semantics (sec-
tion 3). We use a natural, dialogue-based interaction
in a multimodal query interface (section 4) accessing
a semantic image repository embedded into an anno-
tation and querying framework (section 5). Section 6
provides related work and a conclusion.
1
This research has been supported in part by the re-
search program THESEUS in the MEDICO project which
is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Economics
and Technology under the grant number 01MQ07016. The
responsibility for this publication lies with the authors.
89
Sonntag D. and Möller M. (2009).
UNIFYING SEMANTIC ANNOTATION AND QUERYING IN BIOMEDICAL IMAGE REPOSITORIES - One Solution for Two Problems of Medical
Knowledge Engineering.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing, pages 89-94
DOI: 10.5220/0002273400890094
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 CHALLENGES
Various challenges exist in medical knowledge engi-
neering, all of which arise from the requirements of
the clinical reporting process. The clinical reporting
process focuses on the general question
What is the disease? (or, as in the lymphoma
case, Which lymphoma?). To answer these questions,
semantic annotations on medical image contents are
required. These are typically anatomical parts such
as organs, vessels, lymph nodes, etc. Image pars-
ing and pattern recognition algorithms can extract the
low-level image feature information. The low-level
information is used to produce higher-level semantic
annotations to support tasks such as differential diag-
nosis.
For this purpose, we envision a flexible and
generic image understanding software for which im-
age semantics, which are expressed using concepts
from existing medical domain ontologies, play a ma-
jor role for access and retrieval. Unfortunately, al-
though automatic detection of image semantics seems
to be technically feasible (e.g., see (Kumar et al.,
2008)), it is too error-prone (at least on the desired
annotation level where multiple layers of tissue have
to be annotated at different image resolutions). Ac-
cordingly, one of the major challenges is the so-called
knowledge acquisition bottleneck. We cannot easily
acquire the necessary medical knowledge about the
image contents which makes the image retrieval stage
difficult (also cf. (Sonntag et al., 2009)). Further-
more, the representational basis of the image annota-
tions must match the querying architecture. Thus, we
address the knowledge acquisition bottleneckproblem
by concerning ourselves with the problems how to (1)
provide a semantic image annotation tool; (2) provide
a multimodal interface for semantic image querying;
and (3) connect the annotation and querying task into
a common framework.
3 IMAGE ANNOTATION TOOL
The image annotation tool consists of a component
that implements a method to annotate images and up-
load/maintain a remote RDF repository of the im-
ages and image semantics. For annotations, we
reuse existing reference ontologies and terminologies.
For anatomical annotations we use the Foundational
Model of Anatomy (FMA) ontology (Mejino et al.,
2008). To express features of the visual manifesta-
tion of a particular anatomical entity or disease of
the current image, we use fragments of RadLex (Lan-
glotz, 2006). Diseases are formalized using the Inter-
Figure 1: Graphical User Interface of the Annotation Tool.
national Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). Figure
1 shows the graphical user interface of the annota-
tion tool. Images can be segmented into regions of
interest (ROI). Each of these regions can be anno-
tated independently with anatomical concepts (e.g.,
“lymph node”), with information about the visual
manifestation of the anatomical concept (e.g., “en-
larged”), and with a disease category using ICD-10
classes (e.g., “Nodular lymphoma” or “lymphoblas-
tic”). However, any combination of anatomical, vi-
sual, and disease annotations is allowed and multiple
annotations of the same region are possible. In order
to ease the task of finding appropriate annotations, we
use auto-completing combo-boxes. While typing in a
search term, concept names with matching prefixes
are shown in a drop down box and can be selected.
The annotation application leverages information
from headers of images in the medical exchange for-
mat DICOM (Mildenberger et al., 2002) to collect
demographic data about the patient and imaging ac-
quisition parameters. These data are used to provide
the visualization in the top left corner of figure 1. It
shows which body part the current image belongs to
in order to ease the navigation in the image of the
human body. The extracted metadata can further be
used to construct a history of examinations for a pa-
tient. This automatically acquired history is stored
together with the manually added semantic annota-
tions (representing the expert’s diagnoses) in RDF
format in a central Triple Store (see section 5.2). Ex-
isting annotations of an image can also be used to
query online resources on the web such as PubMed
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
90
(http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed) and Clinical-
Trials (http://clinicaltrials.gov) for similar cases.
4 MULTIMODAL INTERFACE
The multimodal query interface implements a
situation-aware dialogue shell for semantic access to
image media, their annotations, and additional tex-
tual material. It enhances user experience and us-
ability by providing multimodal interaction scenarios,
i.e., speech-based interaction with touchscreen instal-
lations for the health professional.
4.1 Medical Dialogue
Which recommendations can support building up and
querying new medical knowledge repositories? A
knowledge engineering methodology (Wennerberg
et al., 2008) helped us to formalize these require-
ments. The medical dialogue illustrates how this
relates to the doctor’s practical interest in using a
semantic search engine or dialogue interface.
For example, consider a radiologist at his daily
work: The diagnostic analysis of medical images
typically concentrates around three questions: i) what
is the anatomy? ii) what is the name of the body
part? iii) is it normal or is it abnormal? To satisfy the
radiologist’s information requirement, this scattered
knowledge has to be gathered and integrated from
disparate dynamic information sources. According
to the Query Pattern Derivation step, a set of hy-
pothetical user queries is derived while using the
domain ontologies and domain corpora (subsequently
evaluated by the clinicians). After identifying the
relevant subparts of the domain ontologies, the query
patterns can be combined into a multimodal dialogue.
Multimodal Example Dialogue
1 U: “Show me the CTs, last examination, patient XY.”
2 S: Shows corresponding patient CT studies as DICOM picture series and
MR videos.
3 U: “Show me the internal organs: lungs, liver, then spleen and colon.”
4 S: Shows corresponding patient image data according to referral record.
5 U: “This lymph node here (+ pointing gesture) isenlarged; solymphoblas-
tic. Are there any comparative cases in the hospital?”
6 S: “The search obtained this list of patients with similar lesions.”
7 U: “Ah okay.”
Our system switches to the comparative records to help the radiologist in the
differential diagnosis of the suspicious case, before the next organ (liver) is
examined.
8 U: “Find similar liver lesions with the characteristics: hyper-intense
and/or coarse texture ...”
9 S: Our system again displays the search results ranked by the similarity
and matching of the medical ontology terms that constrain the semantic
search.
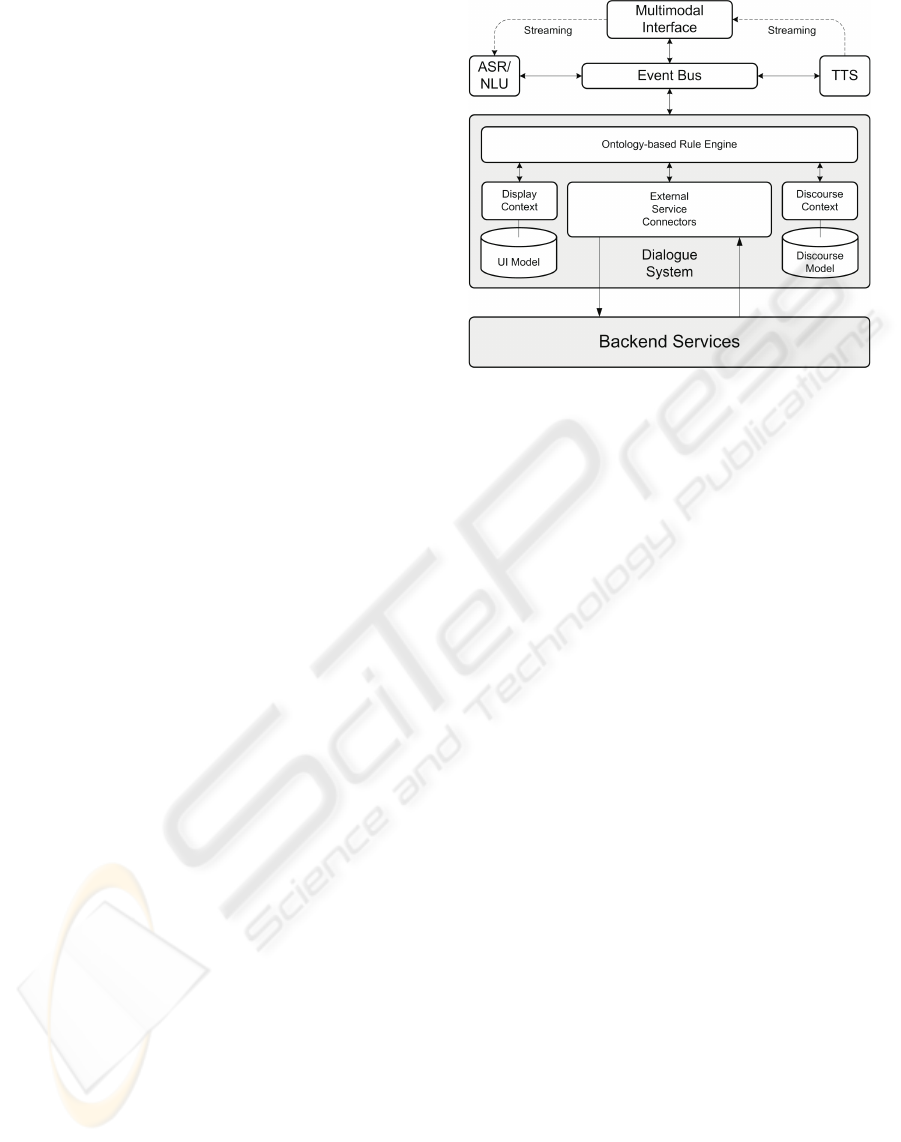
Figure 2: Architecture of the Dialogue System, where ex-
ternal components, such as automatic speech recognition
(ASR), natural language understanding (NLU), and text-to-
speech Synthesis (TTS), are integrated.
4.2 Technical Architecture
In order to accommodate the limited processing capa-
bilities of (mobile) user interface platforms, we use a
distributed dialogue system architecture, where every
major component can be run on a different platform,
increasing the scalability of the overall system (figure
2). Thereby, the dialogue system also acts as mid-
dleware between the clients and the backend services
that hide complexity from the user by presenting ag-
gregated data. There are three major parts: the mul-
timodal interface, the dialogue system, and the event
bus.
4.2.1 Multimodal Interface
The multimodal interface is implemented as a na-
tive application using a special window manager for
pointing gestures on a touchscreen display (figure 3).
The client provides means to connect to the dialogue
system via the event bus, to notify it of occurred
events, to record and playback audio streams, and to
render the received display data obtained from the di-
alogue system. In general, the client application is de-
signed as a lightweight component, and the dialogue
system is responsible for maintaining the interaction
and display context.
4.2.2 Dialogue System
The ontology-based dialogue platform (including
ASR/NLU and text-to-speech (TTS)) provides a run-
time environment for multimodal dialogue applica-
tions supporting advanced dialogue interaction. The
UNIFYING SEMANTIC ANNOTATION AND QUERYING IN BIOMEDICAL IMAGE REPOSITORIES - One Solution
for Two Problems of Medical Knowledge Engineering
91

Show me the internal
organs: lungs, liver, then
spleen and colon.
Figure 3: Multimodal Touchscreen Interface. The clinician
can touch the items and ask questions about them.
central component is a dialogue system which pro-
vides a programming model for connecting external
components (both in the frontend and backend layer).
On the frontend side, it connects with the mobile de-
vice for presentation and interaction purposes. This
includes the representation of displayed graphics and
speech output, natural language understanding, and
the reaction to pointing gestures. On the backend
side, the dialogue system provides interfaces to rel-
evant third-party software, e.g., ASR and TTS. In-
terestingly, the NLU component directly delivers the
concepts to be searched for in ontological form ac-
cording to the domain ontologies. These concepts are
the input to generate the SPARQL queries (following
the guidelines in (Sonntag et al., 2007)).
4.2.3 Event Bus
The main task of the event bus is routing messages
between each connected component which currently
includes a third-party ASR, a third-party TTS mod-
ule, and several client applications (i.e., the touch-
screen client and the dialogue system itself). When
the multimodal client connects to the event bus, it es-
tablishes a new session for the client at the dialogue
system. It informs the client about the connection
parameters of the ASR and TTS. The speech data is
streamed to/from the device in order to ensure fast re-
action times. Since we use push-to-activate for the
microphone (the user activates the microphone manu-
ally), a typical message flow for speech interaction is
as follows:
1. The user pushes the microphone button on the
GUI.
2. The client sends a respective pointing gesture
event via the event bus to the dialogue system.
3. The dialogue system resolves the pointing ges-
ture as open the microphone and informs the
ASR/NLU via the event bus that it should pre-
pare for speech input. (The doctor poses a medical
question.)
4. The ASR/NLU acknowledges this to the dia-
logue system, which in turn notifies the client that
recording and streaming can now begin (on the
client GUI, the microphone button turns green).
5. The user can talk to the client/touchscreen inter-
face. Upon successful recognition of a spoken
phrase, the ASR/NLU sends the recognition result
(as NLU-Info structure) to the dialogue system.
6. The dialogue system informs both the ASR and
the client to stop the recording and close the mi-
crophone (the microphone button turns red again).
7. Finally, the dialogue system processes the re-
sult by sending a SPARQL query to the backend
servers.
5 ANNOTATION AND QUERYING
5.1 Basic Strategy
Maintaining a remote repository, we view medical
knowledge engineering as an interactive process be-
tween the knowledge engineer and the clinician. The
first essential step requires the knowledge engineer
to gather and pre-processes available medical knowl-
edge from various resources such as domain ontolo-
gies and domain corpora, whereupon the domain ex-
pert, i.e., the clinician, evaluates the outcome of the
process and provides feedback and, finally, the im-
age annotations. To provide access to the incremen-
tal knowledge base, a subset of SPARQL can be
used (a popular standard used to access RDF and
OWL data). The semantic RDF store Sesame, also
see http://www.openrdf.org, serves assertions on el-
ements (e.g., images and image annotations, i.e., re-
lationships such as is part of, has disease annotation,
or has anatomy) in the medical datasets provided by
the use case.
Within the Interactive Semantic Mediator, we im-
plemented a highest-level API for the purpose of
interactive semantic mediation within the dialogue
shell. For example, we can populate and maintain
an RDF store with only two upper-level Java func-
tions. The HTTP Server consists of a number of
Java servlets that implement a protocol for accessing
Sesame repositories over HTTP. Here, we provide a
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
92

Interactive Semantic Mediator
Application
Layer
Query Model/
Semantic
Search Layer
Dynamic
Knowledge
Base
Layer
IUI, Multimodal Dialogue System
Dialogue Manager, GUI:
Query by images, text, speech
Sesame/SPARQL
Retrieval Engine
Concept Query Dialogue Module
Remote
Information
Source
Remote
Information
Source
Remote
Information
Source
Figure 4: Three Tier Querying Architecture.
wrapper around the Sesame client library to handle
the communication for Remote Use Case Reposito-
ries. Figure 4 outlines the three tier architecture con-
sisting of an application layer (the dialogue system),
a query model/semantic search layer, and a dynamic
knowledge base layer which addresses information
sources in general. The knowledge layer hosts the
access ontologies and the interactive semantic medi-
ator which is responsible for inducing an appropriate
(partial) alignment between two heterogeneous infor-
mation services, e.g., different ontologies.
5.2 Central RDF Repository
The semantic image repository, a triple store setup
at the remote RDF repository site, is based on two
VMWare instances which differentiate between
development and production environment. (Both
systems use the open source triple store Sesame.) We
use this central RDF repository to store and retrieve
information about the medical domain, clinical
practice, patient metadata, and image annotations.
(Also cf. the dynamic knowledge base layer in figure
4.) OWL-Horst reasoning (supporting a subset of
OWL-DL) is performed using Ontotext’s OWLIM on
top of Sesame.
The integration cycle for new ontologies and
updates begins with a check-in to a central subversion
repository. Nightly checks with the open source tool
Eyeball (http://jena.sourceforge.net/Eyeball) ensure
syntactic correctness and detect common modeling
mistakes. New versions of the ontology are first
checked out from the SVN to the development RDF
repository and tested before being propagated to the
production system. From here the ontologies are
accessed by with the Interactive Semantic Mediator.
The central repository offers different interfaces
for data retrieval and manipulation. They provide
access to two different abstraction layers of the
data. A direct access to the RDF statements is
possible while using the query language SPARQL.
This allows us to specify queries of almost arbitrary
complexity. They can span from patient metadata to
image annotations to medical domain knowledge and
are used to translate most of the dialogue questions
presented in section 4.
The system also allows us to perform a semantic
query expansion based on the information in the
medical ontologies. Accordingly, a query for the
anatomical concept lung also retrieves images which
are not annotated with “lung” itself but parts of the
lung. The query expansion technique is implemented
in Java and provided as an API. Below we show a
SPARQL query example, according to our query
model in the semantic search layer in figure 4, which
retrieves all images of patient XY annotated with the
FMA concept “lung”.
SELECT ?personInstance ?patientInstance ?imageRegion ?imageURL WHERE {
?personInstance surname ?var0 .
FILTER (regex(?var0, "XY", "i")) .
?patientInstance referToPerson ?personInstance .
?patientInstance participatesStudies ?studyInstance .
?seriesInstance containedInStudy ?studyInstance .
?seriesInstance containsImage ?mdoImageInstance .
?mdoImageInstance referenceFile ?imageURL .
?imageRegion hasAnnotation ?imageAnnotation1 .
?imageAnnotation1 hasAnatomicalAnnotation ?medicalInstance1 .
?medicalInstance1 rdf:type fma:Lung.
?imageInstance hasComponent ?imageRegion .
?imageInstance hasImageURL ?imageURL .
?mdoImageInstance referenceFile ?imageURL . }
Note that this query spans across patient metadata
(the name, automatically extracted from the image
header) and anatomical annotations (manually added
by the radiologist). For readability, we removed the
name spaces from most of the properties. The query
example is an indirect translation of the clinician’s
dialogue question. The dialogical competence and
the query complexity increases with additional image
annotations. Figure 5 comprises an attempt to illus-
trate this process, in which the clinician’s expertise is
paramount, in a common view.
Medical knowledge engineering is an interactive
process between the knowledge engineer and the clin-
ician; and dialogue engineering is an interactive pro-
cess between the dialogue engineer and the clinician.
6 RELATED WORK
AND CONCLUSIONS
Large scale efforts exist for the effective or-
ganization and aggregation of medical image
data, for example the Cancer Biomedical Infor-
mation Grid (https://cabig.nci.nih.gov), myGrid
(http://www.mygrid.org.uk), and the THESEUS
UNIFYING SEMANTIC ANNOTATION AND QUERYING IN BIOMEDICAL IMAGE REPOSITORIES - One Solution
for Two Problems of Medical Knowledge Engineering
93

Knowledge
Engineering
Text & Image
Source Data
Command
Dialogue
Dialogue
Specificity
Dialogue
Engineering
Data
Abstraction
Repository
Dialogue Shell
Medical Domain Expert
Remote
Figure 5: Knowledge and Dialogue Engineering in a com-
mon view. More data abstraction (i.e., image annotation
through the medical expert) leads to more dialogue possi-
bilities according to the image semantics.
MEDICO program (http://theseus-programm.de/en-
us), whereby only the latter two explicitly state
working with Semantic Web data structures and
formats. In recent years there has been great interest
in storage, querying, and reasoning on assertion box
(ABox) instances, for which several Semantic Web
frameworks for Java (e.g., JENA and OWLIM) have
been proposed. We chose Sesame because of its
easy online deployment and fast built-in persistence
strategies.
Maintaining a single central repository with
remote access, we presented medical knowledge
engineering as an interactive process between the
knowledge engineer and the clinician. The first es-
sential step requires the knowledge engineer to gather
and pre-processes available medical knowledge
from various resources such as domain ontologies
and domain corpora. The domain expert, i.e., the
clinician, evaluates the outcome of the process and
provides feedback and, finally, the image annotations,
as well as the corresponding dialogue questions. To
satisfy the radiologist’s information need, scattered,
heterogeneous information has to be gathered, se-
mantically integrated and presented to the user in a
coherent way. An enabling force towards this goal
has been provided, principally, by unifying semantic
annotation and querying, as discussed. The common
annotation and dialogue querying framework will
now be tested in a clinical environment (University
Hospitals Erlangen). Furthermore, the question of
how to integrate this information and image knowl-
edge with other types of data, such as patient data, is
paramount.
In intensive discussions with clinicians we an-
alyzed how the use of semantic technologies can
support the clinician’s daily work tasks, apart from
the fact that in daily hospital work, clinicians can
only manually search for similar images—for which
we provided a solution. For clinical staging and
patient management the major concern is which
procedure step has to be performed next in the
treatment process. This is where the textual content
of the patient records and other semi- and unstruc-
tured external medical knowledge comes into play
and has to be semantically integrated. Thus, our
current work focuses on investigating information
extraction techniques to include patient health record
information into the remote RDF repository.
REFERENCES
Kumar, V. S., Narayanan, S., Kurc, T., Kong, J., Gurcan,
M. N., and Saltz, J. H. (2008). Analysis and semantic
querying in large biomedical image datasets. Com-
puter, 41(4):52–59.
Langlotz, C. P. (2006). Radlex: A new method for in-
dexing online educational materials. RadioGraphics,
26:1595–1597.
Mejino, J. L., Rubin, D. L., and Brinkley, J. F. (2008).
FMA-RadLex: An application ontology of radiolog-
ical anatomy derived from the foundational model of
anatomy reference ontology. In Proc. of AMIA Sym-
posium, pages 465–469.
Mildenberger, P., Eichelberg, M., and Martin, E. (2002).
Introduction to the DICOM standard. European Radi-
ology, 12(4):920–927.
Sonntag, D., Engel, R., Herzog, G., Pfalzgraf, A.,
Pfleger, N., Romanelli, M., and Reithinger, N. (2007).
SmartWeb Handheld—Multimodal Interaction with
Ontological Knowledge Bases and Semantic Web Ser-
vices. In Proc. of Artifical Intelligence for Human
Computing, pages 272–295.
Sonntag, D., Wennerberg, P., Buitelaar, P., and Zillner, S.
(2009). Cases on Semantic Interoperability for Infor-
mation Systems Integration, chapter Pillars of Ontol-
ogy Treatment in the Medical Domain. ISR.
Wennerberg, P., Zillner, S., Mller, M., Buitelaar, P., and Sin-
tek, M. (2008). KEMM: A Knowledge Engineering
Methodology in the Medical Domain. In Proc. of the
5th International Conference on Formal Ontology in
Information Systems (FOIS).
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
94
