
A
MULTI-POPULATION GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR
TREE-SHAPED NETWORK DESIGN PROBLEMS
Dalila B. M. M. Fontes and Jos
´
e Fernando Gonc¸alves
Faculdade de Economia and LIAAD-INESC Porto L.A., Universidade do Porto
Rua Dr. Roberto Frias, 4200-464 Porto, Portugal
Keywords:
Multi-population genetic algorithms, Random keys, Network design.
Abstract:
In this work we propose a multi-population genetic algorithm for tree-shaped network design problems using
random keys. Recent literature on finding optimal spanning trees suggests the use of genetic algorithms.
Furthermore, random keys encoding has been proved efficient at dealing with problems where the relative
order of tasks is important. Here we propose to use random keys for encoding trees. The topology of these trees
is restricted, since no path from the root vertex to any other vertex may have more than a pre-defined number
of arcs. In addition, the problems under consideration also exhibit the characteristic of flows. Therefore, we
want to find a minimum cost tree satisfying all demand vertices and the pre-defined number of arcs. The
contributions of this paper are twofold: on one hand we address a new problem, which is an extension of
the well known NP-hard hop-constrained MST problem since we also consider determining arc flows such
that vertices requirements are met at minimum cost and the cost functions considered include a fixed cost
component and a nonlinear flow routing component; on the other hand, we propose a new genetic algorithm
to efficiently find solutions to this problem.
1 INTRODUCTION
There are many applications where it is necessary to
find an optimal spanning tree. In the minimum span-
ning tree (MST) one wishes to find a least-cost tree
spanning all vertices in a network. The MST prob-
lem arises in many applications in, e.g., communi-
cation networks. Many polynomial-time algorithms
have been proposed for this problem by, for exam-
ple, Dijkstra, Kurskal, Prim (Cormen et al., 2001).
Although the basic MST problem can be solved in
polynomial-time, the addition of one or more con-
straints often transforms it into problems, such as the
MST with a pre-defined number of arcs in any path
from the root vertex, which have been shown to be
NP-hard, see e.g., (Dahl et al., 2006)). For these prob-
lems, a heuristic must be used, at least on larger prob-
lem instances. Genetic algorithms (GAs) are exam-
ples of search heuristics that have been successfully
applied to such problems.
The MST with a pre-defined number of arcs has
numerous practical applications and is frequently en-
countered in network design problems, for example in
computer networks we can find the multicast-routing
problem (see, e.g., (Deering et al., 1994)), where a
number of clients and a server are connected by a
common communication network. The server wishes
to transmit identical information to all clients, and
does so by transmitting the data to the vertices it di-
rectly connects to, and these latter vertices forward
incoming data to their respective children in the tree.
The limit on the number of arcs in each path is usu-
ally used to guarantee a certain quality of service
with respect to availability and reliability constraints
(LeBlanc and Reddoch, 1990; Woolston and Albin,
1988), as well as lower delays (Gouveia and Requejo,
2001), since they limit the number of arcs in each path
from the central service provider. (Woolston and Al-
bin, 1988) have shown that, by including this type of
constraints it is possible to generate network designs
with a much better quality of service and with only a
marginal increase in the total cost.
Recently, Genetic Algorithms (GA) and other
Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs) have been success-
fully applied to solve constrained spanning tree prob-
lems of the real life instances; and have also been
used extensively in a wide variety of communica-
tion network design problems (Gen et al., 2001; Gen
et al., 2005). For example, some authors have pro-
posed GAs for the capacitated MST problem (Ahuja
177
B. M. M. Fontes D. and Fernando Gonçalves J. (2009).
A MULTI-POPULATION GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR TREE-SHAPED NETWORK DESIGN PROBLEMS.
In Proceedings of the International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence, pages 177-182
DOI: 10.5220/0002281101770182
Copyright
c
SciTePress
and Orlin, 2001; Lacerda and Medeiros, 2006), while
others propose GAs for the degree-constrained MST
(Han et al., 2005; Zeng and Wang, 2003) for a hy-
brid GA (with local search). Other researchers have
investigated different encoding methods, see for ex-
ample (Raidl and Julstrom, 2003; Thompson et al.,
2007). GAs have also been proposed to other type
of trees-shaped problems, for instance in (Fontes and
Gonc¸alves, 2007) the authors address problems in-
cluding flows and with general nonlinear cost func-
tions. However, as far as the authors are aware of,
there has not yet been proposed any methods for find-
ing solutions to the MST a with maximum number
of arcs on each path and flow characteristics. Here,
a hybrid genetic algorithm to solve such problem is
proposed. It should be noticed that in this problem
we also have flow decisions to be made. Further-
more, the costs to be minimized include a general
nonlinearly flow dependent cost component and fixed
cost component. Nonlinear cost functions arise nat-
urally in this type of problems as a consequence of
taking into account economic considerations. Set up
costs or fixed-charge costs arise, for example, due to
the consideration of a new customer or a new route.
Economies of scale often exist, and thus an output
increase leads to a decrease in the marginal costs.
On the other hand, further output increase may lead
to an increase in marginal costs, e.g. by implying
the need of extra resources. Therefore, discontinu-
ities are observed. These may also arise due to price-
discounting.
2 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
We consider a problem which is an extension of the
MST with a Limit on the number of Arcs on each
path from the root vertex (MST-LA). For the MST-
LA we wish to find a minimum cost tree spanning all
vertices in a given network such that any path from
the root vertex to any other vertex has no more than a
pre-specified number of arcs. In the problem consid-
ered here, flows are also considered since all vertices,
except for the root vertex, have a nonnegative flow re-
quirement. Therefore, in addition to finding the arcs
that are part of the MST-LA, we must also find the
flows that are to be routed along these arcs.
Let G = (W, A) denote a directed network with a
set W of n + 1 vertices (the source vertex and n de-
mand vertices) and a set A of m directed arcs. Vertices
1 to n have associated a nonnegative integer demand
r
i
, which must be satisfied. The total cost to be mini-
mized is given by the summation of all costs incurred
by both using an arc (a setup cost) and routing flow
through it (a flow cost). The cost of sending r units
of flow through an arc, say (x, z) is given by any func-
tion g
xz
(r) satisfying g
xz
(0) = 0. The flow that can be
routed through each arc (x, z) may have upper u
xz
and
lower l
xz
limits. Let H be the pre-defined maximum
number of arcs in any path connecting the source ver-
tex to any other vertex. Several formulations have
been provided by Gouveia and his co-authors, see
(Gouveia and Requejo, 2001; Gouveia et al., 2008)
and the references therein.
3 METHODOLOGY
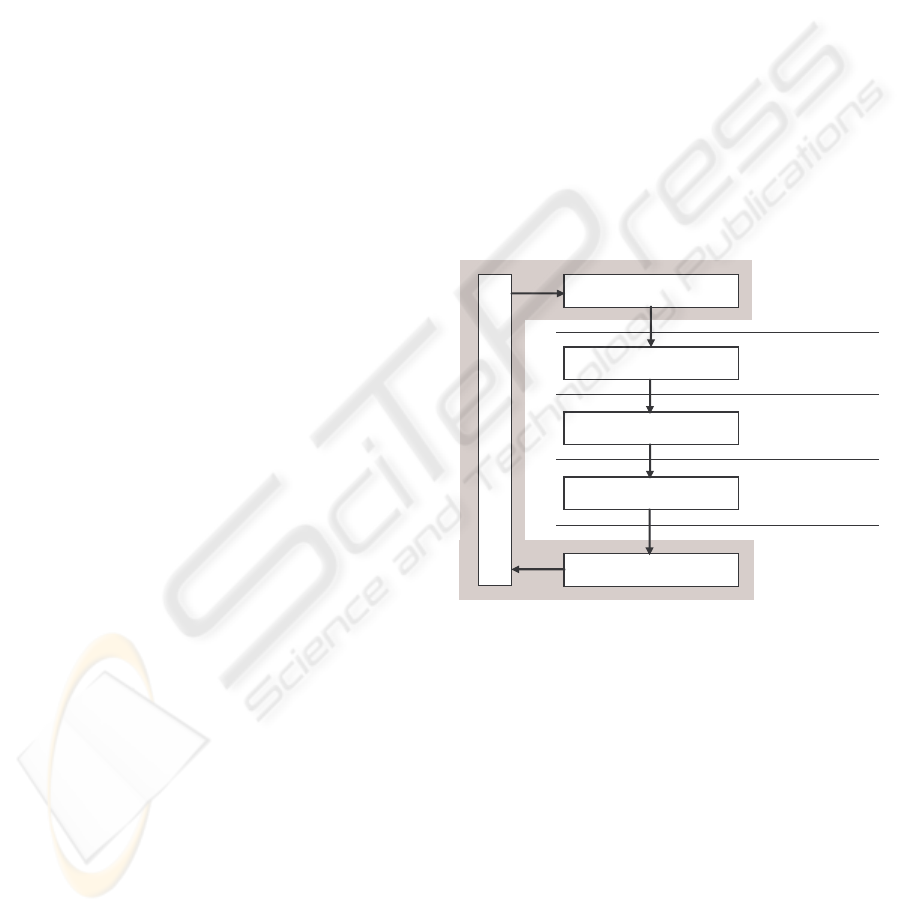
Our approach comprises a GA to evolve the popula-
tion of solutions, a tree constructor to generate trees
satisfying the vertex demands, a penalty cost function
to change the trees so that the maximum number of
arcs in any path H may be satisfied, and a local search
procedure to refine the feasible trees, see Figure 1.
Parameter GenerationDecoding of Vertex Priorities
Construction of
a Solution Tree
Improvement of the solution
using a Local Search Procedure
Solution Generation
Solution Improvement
Phase
Feedback of Quality of Chromosome
( Cost )
Chromosome
Evolutionary Process of the Genetic Algorithm
Figure 1: The solution approach.
Usually GAs do not perform well in fine tuning
near local optimum solutions, since they tend to get
trapped into a local optimum and also to have most
of its population concentrated on a small part of the
search space located around the local optimum, which
is usually termed premature convergence. This prob-
lem can be obviated by using structured populations
or by hybridization. In the methodology proposed
here both are used. For the former case we use a
multi-population strategy that evolves populations in-
dependently. On each population the dispersion of ge-
netic material is slowed down, giving the algorithm
more time to settle on the most promising part of the
search-space. Interaction between the populations is
provided by interchanging information on good chro-
mosomes. In addition, we use a local search proce-
IJCCI 2009 - International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence
178

dure which tries to improve the current solutions by
means of small perturbations.
3.1 The Genetic Algorithm
GAs often perform well approximating solutions to
all types of problems because they, ideally, do not
make any assumption about the underlying fitness
landscape; this generality is shown by it successes in
diverse fields and problems.
To build such an algorithm many choices have to
be made.
3.1.1 Representation Scheme
The GA described in this paper proposes a random-
key alphabet, which is comprised of real-valued ran-
dom numbers between 0 and 1, for encoding trees.
Random keys have been used successfully for ad-
dressing problems where the relative order of tasks
is important e.g., (Gonc¸alves, 2007; Gonc¸alves and
Almeida, 2002; Gonc¸alves et al., 2005; Gonc¸alves
and Resende, 2004). The evolutionary strategy used
is similar to that of (Bean, 1994), the main difference
occurring in the crossover process which is equal to
the one proposed in (Gonc¸alves and Almeida, 2002).
3.1.2 Encoding and Decoding
A chromosome, which is made of n genes, is repre-
sented as a vector of random numbers, where n is the
number of vertices. These numbers impose an order
to the vertices, which we use as priorities to generate
trees. Since in this encoding scheme the feasibility is-
sue is moved into the objective function, if a random
key vector can be interpreted as a feasible solution
then any crossover vector is also feasible.
The values of the random key vector are used to
obtain the vertex priorities with which the tree is con-
structed. The decoding is accomplished by sorting the
genes is ascending order, see Figure 2.
3.2 Evolutionary Strategy
Given the current population and the fitness value of
each chromosome, i.e. total cost incurred in con-
structing the tree and routing the flow, the population
is divided into two sets: the elite solutions subset and
the remaining solutions. The elite subset is a small
subset containing only the very good solutions.
The population in the next generation is formed
by all solutions in the elite set, a small number of new
randomly generated solutions (mutant), and solutions
obtained by mating solutions of the current population
(offspring), see Figure 3.
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
Chromosome = ( 0.45, 0.67, 0.35, 0.49, 0.07, 0.78, 0.17 )
Increasing order
Vertices
Chromosome = ( 0.07, 0.17, 0.35, 0.45, 0.49, 0.67, 0.78 )
5 7 3 1 4 2 6
Vertices
Vertices in the solution tree
Figure 2: Decoding procedure.
Current Population
Next Population
Copy Best
Crossover
Randomly Generated
Best
Worst
TOP
BOT
Figure 3: Evolutionary strategy.
By copying the best solutions, we guarantee that
the best solution is monotonically improving. How-
ever, it may lead to excessive convergence to a lo-
cal optimum. To overcome this problem we use two
strategies. On one hand, we use mutation as described
below, and on the other hand we use several popula-
tions, which are evolved separately.
3.2.1 Selection and Crossover
Two individuals are randomly chosen to act as par-
ents. One of them is chosen amongst the elite so-
lution set, while the other is chosen from the re-
minder. Genes are chosen by using a biased uniform
crossover, that is, for each gene a biased coin is tossed
to decide on which parent the gene is taken from. This
way, the child inherits the genes from the elite parent
with higher probability.
A MULTI-POPULATION GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR TREE-SHAPED NETWORK DESIGN PROBLEMS
179

3.2.2 Mutation
As the mutation operator we use the so-called immi-
gration operator. Immigration acts like a mutation op-
erator, however, instead of performing gene-by-gene
mutation with very small probability, at each genera-
tion some new individuals are introduced into the next
generation. This new individuals are randomly gener-
ated from the same distribution as the original pop-
ulation and thus, no genetic material of the current
population is brought in.
3.3 Tree Constructor
We use the vertex priorities, given by the decoding
procedure, to determine the order by which vertices
are considered by the tree constructor. The algorithm
repeatedly performs the following three steps in turn,
until either a tree or an infeasibility has been obtained.
1. Find the highest priority vertex not yet supplied;
2. Search for the set of vertices that can act as a par-
ent, for the vertex found in 1.
3. Chose as the parent, the highest priority vertex not
creating a cycle, if one exists.
As said before, the arc limit H is handled implic-
itly and not considered within the constructor proce-
dure. When computing the solution fitness, we also
consider a penalty function, which is dependent on
the constraints violation degree, that is we penalize
vertices having more than H arcs in the path from the
source vertex, as follows.
∑
f or all vertices
Max{0, patharcs
i
− H} × M, (1)
where M is a very large number.
3.4 The Local Search
The local search improves on a given solution by
comparing it with adjacent extreme solutions. As no
transshipment vertices exist, adjacent extreme solu-
tions are obtained by replacing an arc currently in the
solution by an arc not in the solution such that the new
solution is still an extreme flow, i.e., a tree.
The order by which candidate arcs are considered
is determined by the priorities associated with the out-
coming vertex of each candidate arc.
3.5 The Multi Population Strategy
As mentioned before several populations are evolved,
each being randomly generated. The populations are
left to evolve independently and after a predetermined
number of generations they interact by exchanging
the best solutions. When evaluating possible inter-
change strategies we have noticed that exchanging too
much information, i.e. too many chromosomes leads
to the disruption of the evolutionary process. Also, if
the populations exchange information very frequently
they do not have enough time to produce good results
since their evolutionary process is disrupted before
good solutions can be achieved. Therefore, we chose
a strategy that after a pre-determined number of gen-
erations (determined empirically) inserts only the best
two chromosomes in all populations.
4 COMPUTATIONAL
EXPERIMENTS
The efficiency and effectiveness of the multi popula-
tion GA was tested on network flow problems involv-
ing nonlinear cost functions made of two components:
a set-up cost and a routing cost. The problems data
can be downloaded from the OR-Library and a de-
tailed description is provided in (Fontes et al., 2003).
Three different cost function types are considered:
types G1 and G2 are variations of the fixed-charge
cost function where discontinuities other than at the
origin are introduced; and type G3, where arc costs
are initially concave and then convex, having a dis-
continuity at the break point.
g
i j
(r) =
0, if r = 0,
−a
i j
r
2
+ b
i j
r + c
i j
if r ≤
¯
R,
a
i j
r
2
+ b
i j
r + c
i j
+ k otherwise,
where a
i j
= 0 for G1 and G2, k = b
i j
for G1, k = −b
i j
for G2, and k = 0 for G3.
In tables 1 to 3 we summarize the results obtained
for uncapacitated problems involving cost functions
of types G1, G2, and G3, respectively, with the dis-
continuity point occurring at 50% of the root vertex
outflow. Four different arc limit values have been con-
sidered H = 3, 5, 7, 10. For each size, cost function
type and H value we have solve 30 problem instances.
Thus, overall we have solved 150 problem instances
for each H value and cost function type.
We report the average computational time, in sec-
onds, required by the Multi Population GA (MPGA)
and also on the average deviation from the optimal
value. These values have been computed using the
optimal solutions obtained by the dynamic program-
ming methodology proposed in (Fontes, 2009).
As it can be seen, from the results reported in ta-
bles 1 to 3, the MPGA finds an optimal solution for
most problems, except when H is very small. Fur-
thermore, for H = 3 there are 19 problems for which
IJCCI 2009 - International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence
180

Table 1: Solution quality (% deviation from optimal) and
time (s) for cost function type G1.
Number of vertices
H 10 12 15 17 19
3 0.00 0.13 0.05 0.082 0.782
5 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.000 0.193
7 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.000 0.011
10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.000 0.000
Time 12.60 22.50 33.40 50.10 63.00
DP time 0.03 0.36 9.91 113.13 1972.33
Table 2: Solution quality (% deviation from optimal) and
time (s) for cost function type G2.
Number of vertices
H 10 12 15 17 19
3 0.14 0.13 0.05 0.08 0.78
5 0.00 0.02 0.00 0.00 0.20
7 0.00 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.01
10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
Time 12.70 20.40 34.20 50.90 64.10
DP time 0.04 0.36 9.67 108.89 1864.30
Table 3: Solution quality (% deviation from optimal) and
time (s) for cost function type G3.
Number of vertices
H 10 12 15 17 19
3 0.00 0.16 0.03 0.16 0.53
5 0.00 0.01 0.00 0.00 0.21
7 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.01
10 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00 0.00
Time 15.10 25.30 44.60 64.50 85.00
DP time 0.04 0.34 9.74 107.89 2053.50
no feasible solution exists and the constraints are ef-
fective for almost all problems. For H = 10 the con-
straints are no longer effective.
In order to better understand the results obtained
and the conclusions drawn we provide some graphical
representations see figures 4 and 5. From the compu-
tational times reported it can be seen that the DP algo-
rithm time requirements grow very rapidly, however,
this trend is not observed in the proposed algorithm,
see Figure 5.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We have presented a hybrid Multi Population GA
(MPGA) that finds nearly optimal, actually optimal
for most problems, Hop-Constrained Trees in Non-
linear Cost Flow Networks. Recall that a DP method
was used to obtain an optimal solution for these
problems. The proposed algorithm combines a local
search algorithm with a MPGA, where several popu-
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Optimality gap (%)
Type G1
n=10
n=12
n=15
n=17
n=19
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Optimality gap (%)
Type G2
n=10
n=12
n=15
n=17
n=19
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Optimality gap (%)
Problem Size (number of vertices)
Type G3
n=10
n=12
n=15
n=17
n=19
Figure 4: The effect of the value of H on solution quality,
for type G1, G2, and G3, respectively.
lations are evolved independently.
The results obtained have been compared with ex-
isting literature and the comparisons have shown the
proposed algorithm to improve upon the efficiency
of existing methods, since the computational time re-
quirements are modest for all problem sizes (always
bellow two minutes). We have solved 150 problem
instances with four different H values and three cost
function types. When the Hop-constraints are not
very tight we were able to find an optimal for almost
all problems. Nevertheless, when they are very tight
we are still able to find very good solutions.
Thus, the Hybrid MPGA proposed here is capable
of efficiently finding heuristic solutions, close to opti-
mal, for the Minimum Nonlinear Cost Spanning Tree
Problem with a limit on the maximum number of arcs
in each path from the root vertex and routing flows,
which is NP-hard.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported by funds granted by
project PTDC/GES/72244/2006.
A MULTI-POPULATION GENETIC ALGORITHM FOR TREE-SHAPED NETWORK DESIGN PROBLEMS
181

0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
Computational Time (s)
Type G1
GA
DP
0
200
400
600
800
1000
1200
1400
1600
1800
2000
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
Computational Time (s)
Type G2
GA
DP
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19
Computational Time (s)
Problem Size (number of vertices)
Type G3
GA
DP
Figure 5: The effect of the value of H on computational
time, for type G1, G2, and G3, respectively.
REFERENCES
Ahuja, R. and Orlin, J. (2001). Multi-exchange neighbor-
hood structures for the capacitated minimum spanning
tree problem. Mathematical Programming, 91:71–97.
Bean, J. (1994). Genetics and random keys for sequenc-
ing and optimization. ORSA Journal on Computing,
6:154–160.
Cormen, T. H., Leiserson, C. E., Rivest, R. L., and Stein, C.
(2001). Introduction to algorithms. MIT press Cam-
bridge, MA, 2nd edition.
Dahl, G., Gouveia, L., and Requejo, C. (2006). On for-
mulations and methods for the hop-constrained mini-
mum spanning tree problem. In Pardalos, P. M. and
Resende, M., editors, Handbooks of Telecommunica-
tions, pages 493–515. Springer.
Deering, S. E., D., D. E., and Farinacci (1994). An archi-
tecture for wide-area multicast routing. Proceedings
of SIGCOMM.
Fontes, D. B. M. M. (2009). Optimal hop-constrained trees
for nonlinear cost flow networks. INFOR, to appear.
Fontes, D. B. M. M. and Gonc¸alves, J. F. (2007). Heuristic
solutions for general concave minimum cost network
flow problems. Networks, 50:67–76.
Fontes, D. B. M. M., Hadjiconstantinou, E., and
Christofides, N. (2003). Upper bounds for single
source uncapacitated minimum concave-cost network
flow problems. Networks, 41:221–228.
Gen, M., Cheng, R., and Oren, S. (2001). Network de-
sign techniques using adapted genetic algorithms. Ad-
vances in Engineering Software, 32:731–744.
Gen, M., Kumar, A., and Kim, R. (2005). Recent network
design techniques using evolutionary algorithms. In-
ternational Journal of Production and Economics,
98:251–261.
Gonc¸alves, J. (2007). A hybrid genetic algorithm-
heuristic for a two-dimensional orthogonal packing
problem. European Journal of Operational Research,
183:1212–1229.
Gonc¸alves, J. and Almeida, J. (2002). A hybrid genetic
algorithm for assembly line balancing. Journal of
Heuristics, 8:629–642.
Gonc¸alves, J., Mendes, J., and Resende, M. (2005). A
hybrid genetic algorithm for the job shop scheduling
problem. European Journal of Operational Research,
167:77–95.
Gonc¸alves, J. and Resende, M. (2004). An evolutionary al-
gorithm for manufacturing cell formation. Computers
and Industrial Engineering, 47:247–273.
Gouveia, L., Paias, A., and Sharma, D. (2008). Modeling
and solving the rooted distance-constrained minimum
spanning tree problem. Computers & Operations Re-
search, 35:600–613.
Gouveia, L. and Requejo, C. (2001). A new lagrangean re-
laxation approach for the hop-constrained minimum
spanning tree problem. European Journal of Opera-
tional Research, 132:539–552.
Han, L., Wang, Y., and Guo, F. (MAY 2005). A new genetic
algorithm for the degree-constrained minimum span-
ning tree problem. IEEE International Workshop on
VlSI Design and Video Technology, pages 125–128.
Lacerda, E. and Medeiros, M. (2006). A genetic al-
gorithm for the capacitated minimum spanning tree
problem. IEEE Congress on Evolutionary Computa-
tion, 1-6:725–729.
LeBlanc, L. and Reddoch, R. (1990). Reliable link topol-
ogy/capacity design and routing in backbone telecom-
munication networks. First ORSA telecommunica-
tions SIG conference.
Raidl, G. and Julstrom, B. (2003). Edge sets: An effective
evolutionary coding of spanning trees. IEEE Transac-
tions on Evolutionary Computation, 7:225–239.
Thompson, E., Paulden, T., and Smith, D. (2007). The dan-
delion code: A new coding of spanning trees for ge-
netic algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Evolutionary
Computation, 11:91–100.
Woolston, K. and Albin, S. (1988). Design of centralized
networks with reliability and availability constraints.
Computers & Operations Research, 15:207–217.
Zeng, Y. and Wang, Y. (2003). A new genetic algorithm
with local search method for degree-constrained min-
imum spanning tree problems. Proceedings of IC-
CIMA, pages 218–222.
IJCCI 2009 - International Joint Conference on Computational Intelligence
182
