
SLA MANAGEMENT FOR THE INTERNET OF SERVICES
Matthias Winkler
SAP Research CEC Dresden, SAP AG, Chemnitzer Str. 48, 01187 Dresden, Germany
Thomas Springer
TU Dresden, Faculty of Computer Science, Computer Networks Group, Nthnitzer Str. 46, 01187 Dresden, Germany
Keywords:
SLA Management, Internet of Services.
Abstract:
Business services are a valuable asset to be traded via internet service marketplaces. While they are offered
via the internet their execution often involves manual steps. Provisioning of services is regulated by service
level agreements (SLA). To support the management of SLAs a suitable infrastructure is needed.
In this paper we present the SLA management approach and infrastructure developed and implemented within
the TEXO project. It is based on our SLA lifecycle, which supports the creation, (re)negotiation, and moni-
toring of SLAs. We had two requirements which make the approach suitable for trading business services. It
should enable the specification of key business services aspects instead of being limited to quality of service
(QoS) aspects. Furthermore, the SLA management infrastructure should enable SLA handling for service
providers and consumers without imposing too many infrastructure requirements on them. Our work is illus-
trated based on a logistics service example.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the Internet of services (IoS) services are seen as
tradable goods which are offered and sold via inter-
net service marketplaces. Within the TEXO project
(Pressebuero, 2008) the foundations for making busi-
ness services tradable on service marketplaces are es-
tablished. A methodology and toolset for service en-
gineering as well as a platform for service offering
and provisioning are being developed. Business ser-
vices are any kind of business activity offered by a
service provider to create value for a consumer.
The execution and consumption of services is reg-
ulated by service level agreements (SLA) which de-
scribe the service functionality, its quality of service
(QoS) attributes, pricing, and legal information. At
runtime the service level objectives (SLO), the single
measurable elements of a SLA, are monitored. Moni-
toring of negotiated SLAs is important to ensure effi-
cient provisioning of the service and to build up trust
between the stakeholders, i.e. the providers of atomic
services, the providers of composite services, and the
service consumers. The support for SLA management
is a key issue. SLA management consists of different
tasks, such as SLA creation, negotiation and monitor-
ing, which are part of the SLA lifecycle. Our SLA
management infrastructure was developed with a fo-
cus on trading business services on internet service
marketplaces. This lead to two important require-
ments. First of all it was important to ensure suffi-
cient expressiveness of SLAs to cover the most im-
portant attributes of business services which are rel-
evant for the trading of services. This is realized by
applying the Universal Service Description Language
(USDL) (Cardoso et al., 2009) for describing business
services to enrich SLAs. The second requirement
was to provide good support for SLA management
of service providers and consumers. A common in-
frastructure for SLA management was needed which
enables SLA negotiation as a base for collaboration
between service providers and consumers without im-
posing too many requirements on them. Individual
solutions would easily lead to integration problems
and thus hinder business interaction. In order to avoid
that, the SLA negotiation and monitoring functional-
ity are supported via the marketplace. Furthermore,
SLA handling was simplified by integrating SLA tem-
plate creation with the service engineering approach.
In this paper we present the SLA lifecycle which
is the base for our infrastructure (section 2). Based on
that we present the different SLA management com-
ponents of our approach, describe their integration
384
Winkler M. and Springer T. (2009).
SLA MANAGEMENT FOR THE INTERNET OF SERVICES.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 384-391
DOI: 10.5220/0002287203840391
Copyright
c
SciTePress

SLA
Template
Development
SLA (Re-)
Negotiation
Preparation
Execution
&
Monitoring
Termination
&
Decommission
Figure 1: The SLA lifecycle of the TEXO project.
into the service engineering and provisioning infras-
tructure (section 3) and illustrate our work using an
example from the logistics domain (section 4). Fi-
nally, we discuss our work in the light of related ap-
proaches (section 5) and conclude with a summary
and outlook (section 6).
2 A SLA LIFECYCLE FOR THE
INTERNET OF SERVICES
The management of service level agreements in the
TEXO project follows the lifecycle shown in Fig. 1.
It organizes important SLA management tasks into
a process consisting of five different phases. It pro-
vides a structured view on SLA management and the
relationship of the different SLA management tasks
among each other. The lifecycle is based on the work
presented in (Bianco et al., 2008) and adopted to fit
our needs. A first change was the integration of sup-
port for SLA renegotiation. For that reason the SLA
Negotiation phase was extended to allow for SLA
renegotiation in the case that the SLA needs to be
adopted.
A second adaptation was the integration of a
loop from the preparation phase to the SLA (Re-
)Negotiation phase to enable the adaptation of a
SLA. For example, this enables a composite service
provider to react to problems during the execution of
a composition. If problems occur with one service
the SLAs with other services can still be adapted if
needed. This is only possible for limited SLA aspects,
but it is nevertheless an important aspect of SLA man-
agement for business services. An example use case
is the information of a transport provider that goods,
which he will pickup for further transport, are only
available at a later point in time, because the truck
of the preceding service provider broke down. The
renegotiation of a contract enables early adaptation
to problems. SLA renegotiation is only successful if
both involved parties agree.
Finally, the assessment phase presented in (Bianco
et al., 2008), which enables the long-term evaluation
of SLA fulfilment as well as strategic considerations
was removed from the SLA lifecycle but was instead
integrated into the TEXO service lifecycle.
The following phases are part of our SLA lifecycle:
1. SLA Template Development: The SLA template
forms the base for SLA negotiation. It is cre-
ated as part of the service engineering process and
made available for SLA negotiation during the de-
ployment of a service.
2. SLA (Re-)Negotiation: This phase supports the
initial negotiation of a SLA based on a SLA tem-
plate as well as the adaptation of an existing SLA.
During this phase different QoS parameters as
well as pricing and legal information are nego-
tiated between the service provider and the con-
sumer.
3. Preparation: During the preparation phase the in-
formation regarding the newly negotiated SLA
or the update through renegotiation is propagated
to relevant components (e.g. monitoring compo-
nents). They will then retrieve the new SLA and
prepare the service execution and monitoring.
4. Execution and Monitoring: The execution of a
service is triggered once a consumer with a valid
SLA requests the service. The monitoring of the
service execution and the validation of the SLA
and its contained service level objectives occurs at
the same time. Once information regarding SLO
violations is available, further actions can be initi-
ated. An example is the adaptation of the service
(e.g. by renegotiating the SLAs for services of the
underlying process).
5. Termination and Decommissioning: SLAs are
valid for a predefined period of time (e.g. single
service call, one month). Once this period is over
the SLA cannot be used as base for service execu-
tion any more. If the provider of a service decides
to discontinue the service offering under the cur-
rent terms, the SLA template for the service is re-
moved, and no new contracts are negotiated based
on it.
3 THE SLA MANAGEMENT
INFRASTRUCTURE
The management of SLAs is handled by different
components which are distributed over the service in-
frastructure for engineering, executing, and trading
SLA MANAGEMENT FOR THE INTERNET OF SERVICES
385
services. We will first outline the overall service in-
frastructure. Following that we describe the different
SLA management components and their functionality
in more detail.
3.1 Integrating SLA Management into
Service Engineering and Execution
Within the TEXO project the infrastructure for engi-
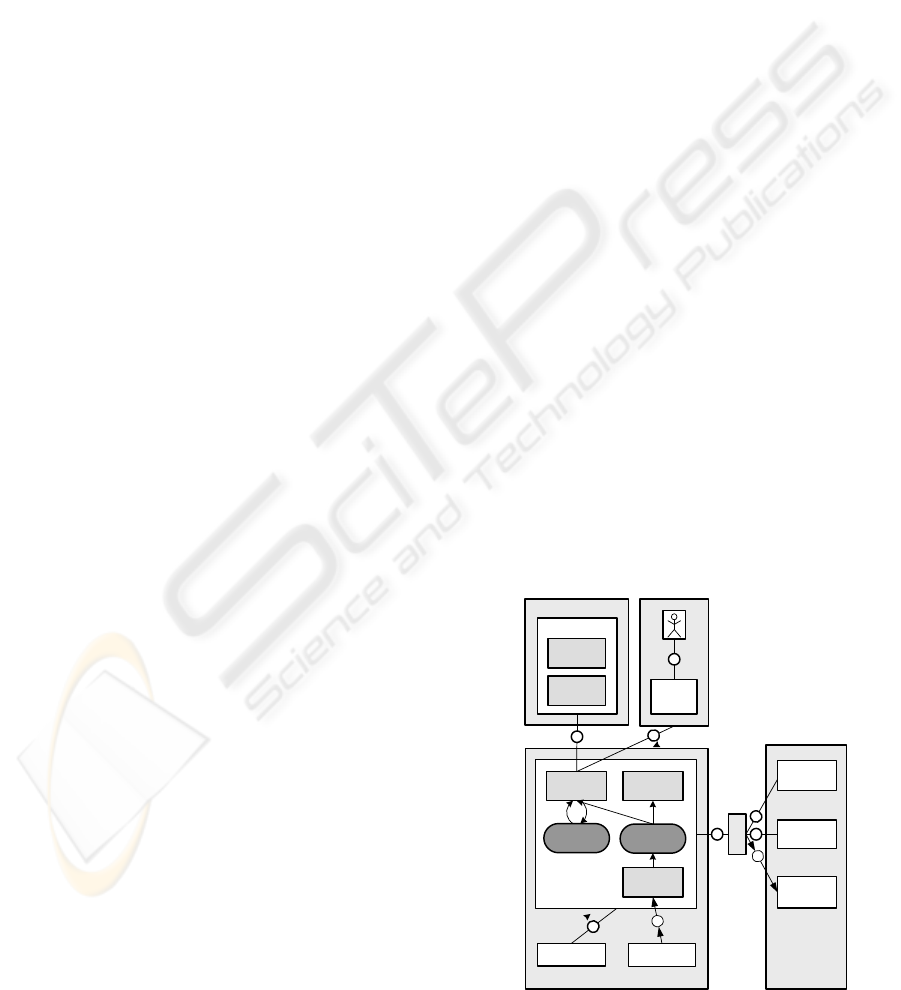
neering, trading, and executing services (see Fig. 2) is
being developed by the partners of the TEXO project.
The ISE workbench is comprised of a collection of
service engineering tools that enable the creation and
description of services at design time. The Tradable
Service Runtime (TSR) supports the execution and
monitoring of services. Finally, the Service Man-
agement Platform (SMP) provides the service mar-
ketplace infrastructure for offering and finding ser-
vices, negotiating contracts, and supporting billing.
The components for SLA creation, negotiation, and
monitoring are integrated into the different parts of
the infrastructure.
3.1.1 ISE Workbench
The ISE workbench implements a model-based ser-
vice engineering methodology developed as part of
the TEXO project (Cardoso et al., 2008). It supports
the modelling of services and service compositions as
well as the description of services based on USDL.
The USDL language enables the description of busi-
ness aspects (e.g. pricing and legal issues), opera-
tional aspects (the service functionality), and techni-
cal aspects (e.g. protocols used for service invoca-
tion and security aspects) of services (Cardoso et al.,
2009). The service description provides a base for
searching and finding services. It also serves as a
building block for formalizing SLAs between service
providers and consumers. The SLA Template Gener-
ation component is responsible for the generation of
a SLA template based on a service description. This
happens as part of the service engineering process.
Service compositions are created from services
which are offered via the service marketplace or
which are available in a local service repository of
the composite service creator. If services from the
marketplace are integrated into a composition, ser-
vice level agreements need to be negotiated between
the composite service creator and the providers of the
single services. In order to support this, a wizard for
SLA negotiation was implemented and integrated into
the workbench.
3.1.2 Tradable Service Runtime
The TSR provides the basic functionality that en-
ables service execution, monitoring and process adap-
tation. Each service provider uses the functionality
of a TSR to support service execution. In a typical
scenario there are multiple distributed TSRs for the
different service providers which are interacting with
the central service marketplace. The communication
between the marketplace and the different TSRs is re-
alized via a message-oriented middleware which sup-
ports the exchange of information regarding deployed
services, newly negotiated SLAs, and monitoring in-
formation. The communication between the different
components of the TSR (e.g. to exchange monitoring
information) is also realized via a message-oriented
middleware. In order to support the monitoring of ne-
gotiated SLAs the SLO Monitoring component was
integrated into the TSR.
3.1.3 Service Management Platform
The central SMP represents the service marketplace,
which provides functionality for offering and search-
ing services, SLA negotiation and monitoring as well
as billing and pricing functionality. Thus, it provides
important functionality which supports the work of
the different service providers and consumers and en-
ables the trading of services. One important compo-
nent of the SMP is the SLA Manager, which is the
central component of the SLA management infras-
tructure. It provides SLA (re-)negotiation and mon-
itoring support for the marketplace and is integrated
with all other SLA management components.
Tradable
Service
Runtime
Service Management Platform
Service
Monitoring
R
SLA Manager
SLA
Negotiation
SLA
Repository
SLO
Monitoring
Template
Repository
Deployment
M
O
M
Web
Browser
Design Time
ISE
Billing
R
SLA
Deployment
SLA
Monitoring
Service
Modelling
Template
Generation
Adaptation
Coordinator
R
Figure 2: SLA Manager in context.
ACT4SOC-EHST 2009 - 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
386

3.2 The SLA Template Generation
Component
Service level agreements generally contain informa-
tion such as a description of the service to be pro-
vided, the price of the service, and a number of guar-
antees. Much of this information is also available
within the service description. Based on this obser-
vation we decided to apply the service description as
a basic building block for the formalization of service
level agreements.
The negotiation of SLAs, which we implemented
based on the WS-Agreement specification (Andrieux
et al., 2007), requires an SLA template as its starting
point. The template contains the relevant information
about a service which is needed for the negotiation
process. In our work the SLA template is generated
from the service description. The approach consists
of two parts. On the one hand we utilize service de-
scription elements to formalize parts of the SLA tem-
plate. USDL elements describing service provider in-
formation, functionality, legal terms, and pricing in-
formation are included into the SLA template. On the
other hand we map information regarding measurable
attributes to the description of SLOs. This integration
of the service description and the SLA template devel-
opment process helps to automatize parts of the SLA
lifecycle. The final agreement document contains lan-
guage constructs which are specific to the agreement
notation (i.e. WS-Agreement) as well as the service
description language (i.e. USDL). The generation of
SLA templates was implemented as a plug-in into
our Eclipse based ISE workbench. The plug-in con-
tains a model-to-text transformation which was im-
plemented using openArchitectureWare (openArchi-
tectureWare.org, ). It takes a USDL service descrip-
tion as input and generates a WS-Agreement SLA
template. The generated SLA template is then de-
ployed together with the newly created service. The
approach is similar to the work presented in (Reichert,
2008). But while their approach is focused on techni-
cal services and their QoS parameters we put addi-
tional focus on the business aspects of SLAs by de-
scribing pricing models and legal aspects which are
important for the trading of services.
3.3 The SLA Manager
The SLA Manager component supports the handling
of service level agreements at the service market-
place. This includes the deployment of new SLA
templates from the ISE workbench, the negotiation of
SLAs between service consumers and providers, the
monitoring of negotiated contracts during service pro-
visioning, and the renegotiation of contracts by ser-
vice consumers and providers during the lifetime of
a SLA. This functionality is offered via web service
interfaces.
3.3.1 SLA Manager Architecture and Context
In Fig. 2 the main components of the SLA Man-
ager are presented. The SLA Deployment component
supports the deployment of new SLA templates dur-
ing the service deployment process as well as their
removal when a service should not be offered any
more. The templates are received from the Deploy-
ment component, which manages the process of de-
ploying a new service and registering it at the mar-
ketplace. The received SLA template is stored in the
Template Repository where it is available for negoti-
ation. The SLA Negotiation component supports the
negotiation process which is triggered via a web inter-
face by an end user or from within the ISE workbench
by a service engineer. Following the successful nego-
tiation or renegotiation of a SLA, an event is sent to
the message-oriented middleware informing the mon-
itoring components about it. The SLA Monitoring
component receives events about detected SLO vio-
lations from the service runtime. This information is
stored and made available for the billing component.
Furthermore, the SLA Manager makes contract infor-
mation (e.g. consumer information) available to the
billing component.
3.3.2 SLA Template Deployment
The SLA Manager provides interfaces for the deploy-
ment, update and removal of SLA templates. The de-
ployment of SLA templates occurs as part of the ser-
vice deployment process. SLA templates, which form
the base for SLA negotiation, are created as part of the
service engineering process. When a SLA template is
deployed, it is stored in a template repository from
where it is available for the SLA negotiation.
During the lifetime of a service the SLA template
of the service can be updated. This enables to adapt
to consumer requirements, e.g. when a service cannot
be sold due to its current price model. It also enables
the provider to change the contracting terms for the
service when the capabilities for service provisioning
change. The removal of templates is necessary when
a service will not be offered any more.
3.3.3 SLA Negotiation
The SLA Manager supports the negotiation of service
level agreements based on the WS-Agreement spec-
ification. It acts on behalf of the service provider.
SLA MANAGEMENT FOR THE INTERNET OF SERVICES
387

It provides two web service interfaces supporting the
negotiation process. A consumer can request a SLA
template for a service and refine it according to his
needs, thus creating an agreement offer. He needs to
enter information about himself (i.e. consumer infor-
mation), can make adjustments to the provided terms
(e.g. select a concrete value for service reliability),
and select a price model (e.g. pay-per-use, flatrate)
according to the available offer and his needs. Once
all refinements are made the agreement offer is sub-
mitted to the SLA Manager as a request for creating
an agreement. Each agreement offer is evaluated by
the SLA Manager to check if all terms are valid and
acceptable (e.g. the required reliability must be within
the bounds specified in the SLA template). If the offer
is accepted, it is stored as SLA in the SLA Repository
and the consumer is informed. Furthermore, an event
is sent to the message-oriented middleware informing
interested components of the service provider about
the new SLA. They are then able to request the new
agreement and use its information for service execu-
tion and monitoring.
A further functionality provided by the SLA Ne-
gotiation component is the renegotiation of SLAs. It
allows to adapt single SLOs of a SLA if the service
provider and the consumer agree. Renegotiation is
only possible for SLOs which were marked as rene-
gotiable during the SLA negotiation procedure.
3.3.4 SLA Monitoring
Monitoring information regarding the service execu-
tion is collected during runtime. The evaluation of the
single measurements is not realized by the SLA Man-
ager itself but instead by the SLO Monitoring compo-
nent which is a part of each TSR. The handling of all
monitoring events by the SLA Manager would create
a bottleneck. The SLA Manager receives information
regarding detected SLO violations. This information
is stored and evaluated when other components or a
service client request the status of an SLA.
SLA status information is very important for the
process of billing a service consumer for the usage of
a service. The billing component uses the status in-
formation to determine the final price to be charged
to the consumer for using the service. If the negoti-
ated SLOs were violated, the consumer may receive a
discount.
3.4 SLO Monitoring Component
The SLO Monitoring component is responsible for
evaluating monitoring data at a TSR. It requests the
negotiated SLAs from the SLA Manager upon receiv-
ing a notification that a new SLA has been negotiated.
The monitoring information is made available by
monitoring sensors via the message-oriented middle-
ware for better scalability. When the SLA Monitoring
component receives monitoring information, it evalu-
ates it based on information in the negotiated SLA. As
a first step the monitoring data is analysed to find out
under which SLA the service was executed. Based on
the type of measurement data received, it retrieves the
SLO information from the SLA and analyses this in-
formation. If a SLO violation is discovered an event
is sent to the message-oriented middleware in order to
inform other components about the occurrence of the
problem.
4 LOGISTICS EXAMPLE
In this section we want to illustrate how the SLA man-
agement components are applied in an example of a
logistics service for transporting goods within a city.
As a first step, the service provider models its service
using the ISE Workbench. The outcome of this, a ser-
vice description based on USDL, is used to generate a
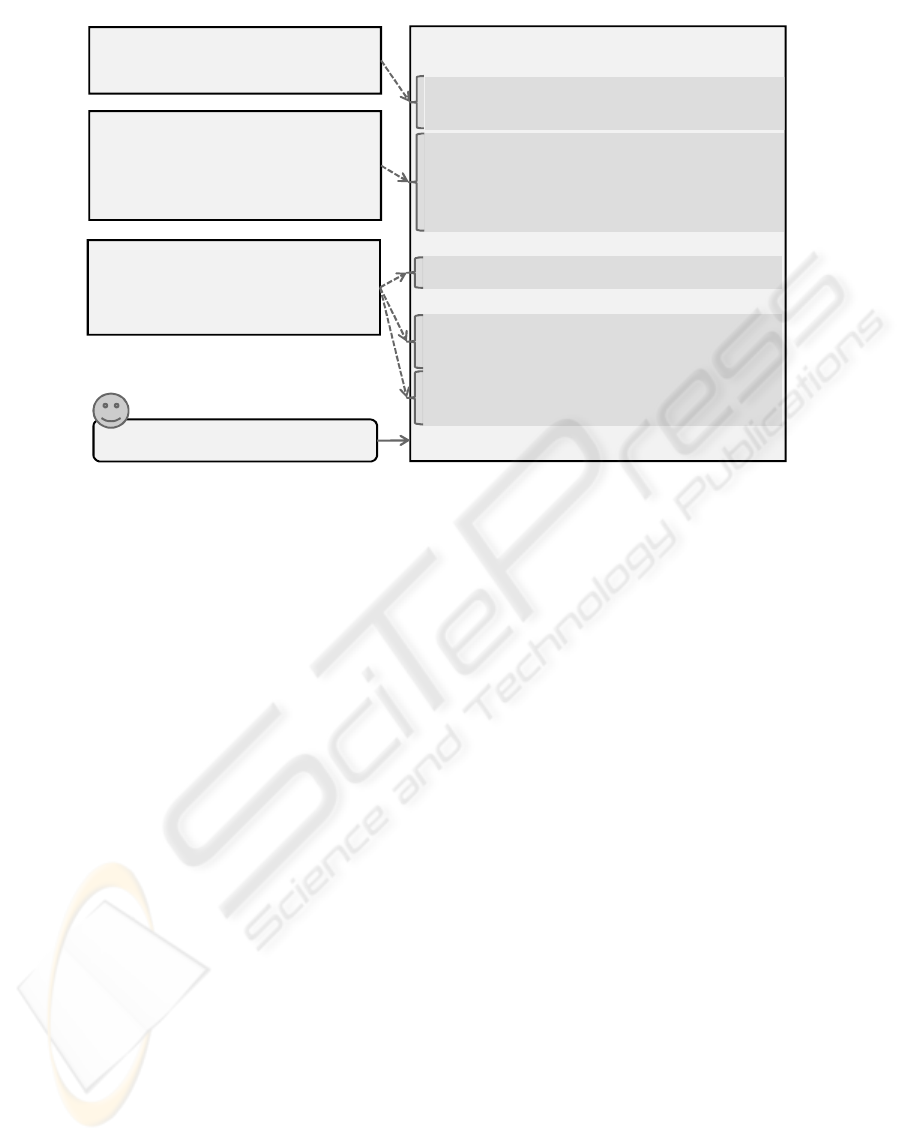
SLA template. Fig. 3 shows three extracts of a USDL
description: the service classification, pricing infor-
mation, and service level information. USDL blocks,
which describe the service and are not measurable ser-
vice level attributes, are integrated into the service de-
scription terms section of the SLA template as USDL
markup. Service level information is used to gener-
ate the service level and guarantee terms sections. For
each service level attribute modelled in the USDL ser-
vice description a variable and a service level objec-
tive are created. The USDL service level description
may be specified as a concrete value (e.g. deliveryAd-
dress=Dresden) to set certain constraints (i.e. goods
can only be delivered to Dresden) or as a place holder
(e.g. deliveryTime) for the negotiation phase. Please
note that the USDL and SLA template code of this
example are simplified.
As a next step the service and the SLA tem-
plate are deployed and made available at the mar-
ketplace. Interested consumers can then negotiate an
SLA based on the SLA template. The consumer re-
quests the SLA template for a service from the SLA
Manager, adjusts the service level objective values,
selects a price model from the list of available ones
(e.g. flatrate or pay-per-use), and returns the docu-
ment in form of an SLA offer to the SLA Manager.
The offer is then evaluated, i.e. it is checked if the
values specified in the offer are in accordance with
the original template. For example, the service level
objective values must be within the range specified in
the SLA template. In our example a user specifies
ACT4SOC-EHST 2009 - 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
388
© SAP 2007 / Page 6
The Universal Service Description Language
<wsag:Template>
<wsag:ServiceDescriptionTerm wsag:Name=“Truck DD”>
<usdl:ServiceName>Truck DD</usdl:ServiceName>
<classifications>
<name> Logistics UN/SPSC </name>
<concept> 81141601 </concept>
</classifications>
<priceModels>
<flatrate>
<priceCurrency> EUR </priceCurrency>
<pricePeriod> 50 </pricePeriod>
<paymentMethod> VISA </paymentMethod>
</flatrate>
</priceModels>
</wsag:ServiceDescriptionTerm>
<wsag:ServiceProperties>
<wsag:Variable wsag:Name="deliveryTime“/>
<wsag:Variable wsag:Name="deliveryAddress“/>
</wsag:ServiceProperties>
<wsag:GuaranteeTerm>
<wsag:ServiceLevelObjective renegotiable=“true”>
<wsag:KPIName> deliveryTime</wsag:KPIName>
<wsag:Target> ... </wsag:Target>
</wsag:ServiceLevelObjective>
<wsag:ServiceLevelObjective renegotiable=“true”>
<wsag:KPIName> deliveryAddress </wsag:KPIName>
<wsag:Target> Dresden </wsag:Target>
</wsag:ServiceLevelObjective>
</wsag:GuaranteeTerm>
</wsag:Template>
<classifications>
<name> Logistics UN/SPSC</name>
<concept> 81141601 </concept>
</classifications>
<priceModels>
<flatrate>
<priceCurrency> EUR </priceCurrency>
<pricePeriod> 50 </pricePeriod>
<paymentMethod> VISA </paymentMethod>
</flatrate>
</priceModels>
USDL
WS-Agreement template
deliveryTime = 2009-04-27T14:30:00
deliveryAddress = Talweg 3, Dresden
SLA Negotiation
<serviceLevel>
<deliveryTime>...</deliveryTime>
<deliveryAddress>
Dresden
</deliveryAddress>
</serviceLevel>
Figure 3: SLA template for logistic service.
the delivery time and address for the goods transport.
Upon successful negotiation the SLA Manager sends
an event which triggers the SLO Monitoring compo-
nent to request the new agreement. After the nego-
tiation both parties still have the chance to renegoti-
ate the delivery time and address since both SLOs are
marked as “renegotiable”.
During the execution of the service the delivery
time and location are monitored, e.g. via RFID events
when the goods arrive at the destination. Our im-
plementation does not make assumptions where the
monitoring data comes from (RFID reader or software
sensor). These events are received and evaluated by
the SLO Monitoring component. To do so, it com-
pares the event data with the negotiated SLA. In the
case that a violation is detected, this information is
forwarded to the SLA Manager where it is available
for the billing process. In addition, the information
about violations is made available for other runtime
components such as the adaptation coordinator which
are responsible for handling violations (e.g. by adapt-
ing the business process or informing responsible per-
sonnel).
5 RELATED WORK
There are a number of projects that have dealt with
the management of SLAs.
Within the Advanced Services Grid (ASG) project
a framework for service monitoring was created. Ser-
vice level agreements regulate technical parameters
on different software stack levels including the op-
erating system, middleware, or the application itself.
Attributes considered for monitoring include techni-
cal aspects such as response time, availability, and
database connectivity (Flehmig et al., 2006).
In (Ameller and Franch, 2008) the SALMon ar-
chitecture for monitoring SLAs is presented. Mon-
itors measure different attributes such as availability
and response time. This information is stored in a data
base and analysed for determining SLA violations. In
the case of a violation the Decision Maker component
is informed. It is responsible for choosing a suitable
strategy for reacting to the SLA violation.
The GRIA SLA Management Service (Boniface
et al., 2007) was developed to provide functional-
ity for SLA negotiation, monitoring, and enforcement
at runtime. It supports the handling of SLAs at the
technical as well as at the business level. Techni-
cal SLOs cover CPU time and disc space which are
needed to provide a service to the consumer. Ser-
vice consumers are rather interested in business level
aspects which describe their actual tasks. Business
level SLOs cover for example the number of rendered
video frames. The GRIA system supports the map-
ping of business level SLOs to technical SLOs which
can then be monitored by the system. It also enables
the service provider to determine thresholds for the
early detection of upcoming SLA violations and man-
agement actions for handling these problems.
Most closely related to our work are the frame-
SLA MANAGEMENT FOR THE INTERNET OF SERVICES
389

works Cremona (Ludwig et al., 2004) and WSAG4J
(Waeldrich, 2008). Both provide functionality for the
negotiation and monitoring of SLAs based on the WS-
Agreement specification. The provided interfaces can
be extended by domain specific implementations.
The focus of the ASG and SalMon approaches
was on the handling of technical services and their
QoS parameters. In contrast, our approach handles
a variety of service attributes such as pricing, pay-
ment information, and legal aspects which is impor-
tant for business services. The GRIA system supports
the specification of business level SLOs. The focus is
on the application domain of the user but not on SLA
aspects which are specific to the trading of services.
While the Cremona framework is not available,
we analysed in how far we can base our implemen-
tation of the SLA Manager component on WSAG4J.
While this would have been possible for the nego-
tiation and monitoring functionality, the integration
with service engineering, i.e. deployment and unde-
ployment of SLA templates would have required the
adaptation of core parts of the WSAG4J functionality.
None of the approaches for handling SLAs known to
us supports the comprehensive business service prop-
erties which are necessary for trading business ser-
vices. This is achieved in our approach by integrat-
ing USDL into SLAs. Our approach is also differ-
ent from other approaches in that it supports much of
the work of service providers and consumers. It of-
fers core SLA management functionality via the ser-
vice marketplace. In addition to that, the integration
of the SLA management with the service engineering
methodology and toolset is achieved by supporting
the creation of SLA templates from service descrip-
tions.
6 SUMMARY
AND CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we presented the SLA lifecycle and man-
agement infrastructure developed within the TEXO
project. We also presented the SLA management
components and described how they are integrated
into the different parts of the service engineering, pro-
visioning, and marketplace infrastructure. By inte-
grating important parts of the SLA management in-
frastructure into the marketplace, the infrastructure
requirements for service providers and consumers,
who want to participate in the marketplace, are min-
imized. If service providers utilize the service engi-
neering and runtime tools all needed functionality is
provided to them. An important requirement for the
trading of services was that SLAs could express rele-
vant attributes from the business domain. To achieve
that we based our implementation on USDL, an ex-
pressive service description language, which was de-
signed to meet the specific requirements for describ-
ing business services.
Further work is necessary to evaluate our ap-
proach in an end-to-end logistics scenario. We plan
to use a supply chain simulator to simulate the execu-
tion of a logistics process. Simulated monitoring data
can be used to evaluate the SLAs.
Furthermore, we are currently extending our work
with regard to the efficient SLA management in ser-
vice compositions where dependencies between dif-
ferent services in a composition need to be considered
when SLAs are renegotiated.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The TEXO project was funded by means of the Ger-
man Federal Ministry of Economy and Technology
under the promotional reference 01MQ07012. The
authors take the responsibility for the contents.
REFERENCES
Ameller, D. and Franch, X. (2008). Service level agree-
ment monitor (salmon). In Proceedings of the Seventh
International Conference on Composition-Based Soft-
ware Systems (ICCBSS 2008), Washington, DC, USA.
IEEE Computer Society.
Andrieux, A., Czajkowski, K., Dan, A., Keahey, K., Lud-
wig, H., Nakata, T., Pruyne, J., Rofrano, J., Tuecke,
S., and Xu, M. (2007). Web services agreement speci-
fication (ws-agreement). Technical report, Open Grid
Forum.
Bianco, P., Lewis, G. A., and Merson, P. (2008). Service
level agreements in service-oriented architecture en-
vironments. Technical Note CMU/SEI-2008-TN-021,
Carnegie Mellon University.
Boniface, M., Philips, S. C., Sanchez-Macian, A., and Sur-
ridge, M. (2007). Dynamic service provisioning using
gria slas. In Proceedings of ICSOC.
Cardoso, J., Voigt, K., and Winkler, M. (2008). Service
engineering for the internet of services. In Filipe, J.
and Cordeiro, J., editors, Enterprise Information Sys-
tems, volume Volume 19 of Lecture Notes in Business
Information Processing, pages 15–27. Springer Berlin
Heidelberg.
Cardoso, J., Winkler, M., and Voigt, K. (2009). A service
description language for the internet of services. In
Proceedings of ISSS 2009.
Flehmig, M., Troeger, P., and Saar, A. (2006). Design and
integration of sla monitoring and negotiation capabil-
ities. Adaptive Services Grid Deliverable D5.II-7.
ACT4SOC-EHST 2009 - 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
390

Ludwig, H., Dan, A., and Kearney, R. (2004). Cremona: an
architecture and library for creation and monitoring of
ws-agreents. In ICSOC ’04: Proceedings of the 2nd
international conference on Service oriented comput-
ing, pages 65–74, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
openArchitectureWare.org. openArchitectureWare. Project
page.
Pressebuero, T. (2008). Texo - Business Webs
im Internet der Dienste. http://theseus-
programm.de/scenarios/de/texo.
Reichert, J. (2008). Serviceabhngige qualittsparameter in
dienstgtevertrgen. Java Spektrum, (6):29–33.
Waeldrich, O. (2008). Wsag4j. WSAG4J project page. last
visited 29.01.2009.
SLA MANAGEMENT FOR THE INTERNET OF SERVICES
391
