
USER GOAL-ORIENTED REQUIREMENTS ELICITATION TO
IMPROVE ACCEPTANCE AND USE
A Case Study on Document Management
Gianmario Motta, Giovanni Pignatelli
Information and Systems Department, University of Pavia, Via Ferrata 1, Pavia, Italy
Paolo Roveri
Business Integration Partners, Piazza San Babila 5, Milano, Italy
paolo.roveri@mail-bip.com
Keywords: Document Management System, Systems Analysis, User involvement.
Abstract: We present a case study that exemplifies an extension of AWARE, a goal oriented requirement elicitation
technique, for a collaborative document management system. The case concerns a multinational fast
growing Management Consulting company. The system serves both marketing activities and actual work of
the variegated consultant community. The system is loaded at “Zero-cost” by the consultants who, through
an editorial model, share the knowledge coming from the document base. The key points of the extension
are a stakeholder orientation that allows to create as many document management environments as the
professional communities, the use of a goal oriented approach that has actually encouraged active
participation of future users, the ever present care in maximizing the value received by each professional
community and minimizing the effort required to use the system. The research is still in progress but the
first phase of the project has been successful, and the consulting company not only is implementing the
system but decided to adopt the methodology for themselves and their customers.
1 INTRODUCTION: USER
ACCEPTANCE AND
SATISFACTION AS DRIVERS
OF IT SUCCESS
Information Systems Science is composed by
interconnected tiles, that could be grouped in three
main areas, namely Business, IT and Social-
Organizational (Spohrer & Riecken, 2006). When
designing an IT solution, analysts and managers
should consider that the mere implementation of IT
can achieve the expected results only if
appropriately supported by changes or innovations
in other perspectives: indeed, the fear to be replaced
by IT systems (Markus, 2004) may generate a
resistance against a new technology may drive to
unanticipated consequences (Benjamin & Eriksson,
2001).
“IT is an effective implementation vehicle of
innovation, but only when coupled with the
approach, enablers, and other implementation
factors” (Davenport, 1993) “IT plays a fundamental
role in business reengineering, but one that is easily
miscast. State-of-art information technology is part
of any reengineering effort as, an essential enabler
[…], since it permits companies to reengineer
business processes. But to paraphrase what often is
said about government and money, merely throwing
computer on an existing business problem does not
cause it to be reengineered” (Hammer & Champy,
1993). The relationships between success of IT
projects, user acceptance and satisfaction are a focus
of different research streams.
A common research assumption is that user
acceptance leads to the actual use of a system. A
first research issue is measuring acceptance, by
scales and indicators to frame user behaviors when
approaching or accepting new IT
solutions/innovation (Gibson, 2004; Rogers, 1995).
The perceived characteristics of innovation can be
described by several classes of variables e.g. ease of
use and relative advantage (Davis, 1989),
compatibility, image, result demonstrably, visibility,
153
Motta G., Pignatelli G. and Roveri P. (2009).
USER GOAL-ORIENTED REQUIREMENTS ELICITATION TO IMPROVE ACCEPTANCE AND USE - A Case Study on Document Management.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing, pages 153-160
DOI: 10.5220/0002293901530160
Copyright
c
SciTePress

and trialability (Moore & Benbasat, 1991). These
variables have been used to define different
acceptance models, that define cause-effect chains
and allow to predict acceptance behaviors. The
major acceptance models are Technology
Acceptance Model - TAM (Davis, 1993), Theory of
Planned Behavior - TPB and Decomposed TPB
(Ajzen, 1985, 1991). The most effective in
predicting the usage is TAM (Davis, 1993). TAM is
extended with new indicators and scales (Schepers
& Wetzels, 2007; Venkatesh & Davis, 2000) and
context variables (or moderation effects) of three
main categories: Organizational, Technology and
Individual factors (Sun & Zhang, 2006).
Another research assumption assumes User
Information Satisfaction (UIS) as a proxy measure
for system success (Ives, Olson, & Baroudi, 1983).
Of course user satisfaction is one of the success
drivers not the only one, as it emerges from several
research studies (Delone & McLean, 2003). User
satisfaction could be decomposed in Information
and System satisfaction (McKinney & Yoon, 2002).
Central in the satisfaction field is the concept of
disconfirmation (Kettinger & Lee, 1994).
Essentially, satisfaction is measured by the gap
between ex-post perceptions of the system and ex-
ante standard expectations.
User satisfaction appears to be related to the
involvement in system design: involvement leads to
a deeper understanding of the system and, therefore,
it potentially narrows disconfirmation. Based on a
comprehensive survey McKeen (McKeen,
Guimaraes, & Wetherbe, 1994) finds that
“Participation”, “Communication with the
developers” and “Influence on the design” positively
affect the satisfaction of end users.
Finally, user satisfaction could be related to the
user acceptance of the IT innovations (Wixom &
Todd, 2005).
User oriented analysis techniques are a mean to
enhance user acceptance and to some extent user
satisfaction, by common sense an ideal technique of
this kind should be easy to understand by users as
precise for the subsequent phases of the system
development. Furthermore it should produce an
effective vision of the whole system and for the
various user classes.
2 THE ISSUE OF USER
PARTICIPATION AND USER
ORIENTED REQUIREMENTS
ELICITATION
We can easily assume that Requirements Elicitation
(RE) is the key design phase to get users involved
and participative. According with the Rational
Unified Process “A requirement describes a
condition or capability to which a system must
conform; either derived directly from user needs, or
stated in a contract, standard, specification, or other
formally imposed document” (Jacobson, Booch, &
Rumbaugh, 1999). In a broader perspective "a
requirement is just an information unit – a piece of
information about the system under construction –
that is important to keep" (Stevens, Brook, Jackson,
& Arnold, 1998). This definition embraces also
constraints, assumptions, plan items, term
definitions, etc.
The term "elicitation" is usually preferred to
“capture”, to avoid the suggestion that requirements
are out there to be collected simply by asking the
right questions (Jirotka & Goguen, 1994). RE can be
defined as the process in which information about
“what to get” is obtained from key users. The term
“elicitation” implies that the analyst is not directly
asking users about their respective information
requirement but extracts them from their key
variables. A very classic example is CSF (Rockart,
1979) where the analyst asks managers their own
Critical Success Factors (CSF), identifies CSF
metrics and, finally, identifies information sources
and information reports. Actually the analyst does
not ask what information manager needs since they
probably do not know and/or have no time to
perform such analysis. In short CSF offers a well
known and classical paradigm of information RE.
A second critical point in RE is the variety of
users. Actually users can be regarded as stakeholders
of both the business processes the system serves and
the process itself. “A stakeholder in an organization
is (by definition) any group or individual who can
affect or is affected by the achievement of the
organization's objectives." (Freeman & McVea,
1984). A similar definition is given by Eric
Rhenman (Rhenman, 1968) and, by Poulondi
(Pouloudi & Whitley, 1997) in the IS domain and in
the software engineering by (Conger, 1993).
In systems common sense easily identifies
different user/stakeholder classes/roles:
daily users who only operate on the system
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
154

power/key users who are expert of the
business logic underlining the systems and to
some extent of the software itself
process owners namely managers who are
partially or totally in charge of the process the
system supports
occasional users as it happens with web-
oriented applications.
In order to understand the needs of stakeholders,
an analyst should explicit their vision and diverse
viewpoints (Longo & Motta, 2006; Motta &
Pignatelli, 2008). Traditionally RE is accomplished
by conceptual modeling techniques which propose
an abstract view (Goguen & Linde, 1993), that
concentrates on what the system should do. Whereas
traditional conceptual modelling allows to
understand the semantic of information, it often fails
in enabling acceptance by users. Research shows
that many large projects fail because of an
inadequate understanding of the requirements
(Boehm, 1981). This inadequacy is often related to
social, political and cultural factors (Schein, 2004),
as stated by Davenport “IT is an effective
implementation vehicle of innovation, but only when
coupled with the approach, enablers, and other
implementation factors” (Davenport, 1993). The
effort needed to fix these systems has been found to
be very high.
In order to get participative and effective RE a
possible way is to focus on the gaols of stakeholder
classes and elicit the implied information
requirements. The concept of goal is prominent in
recent approaches to RE. Specifically, Goal Oriented
Requirements Engineering (GORE) approaches
emerge in this research area.
Goals are prescriptive statements of intent whose
satisfaction requires the cooperation of actors (or
active components) in the software and its
environment. According to Pohl (Pohl & Haumer,
1997) a “goals represent the objectives an actor
wants to achieve when requesting a certain service"
and it is "is used to describe an objective to be
achieved in the macrosystem, e.g. business goal,
personal goal etc.” Rolland links the concept of goal
to the concept of stakeholder's hope “A goal is
defined as something that some stakeholder hopes to
achieve in the future” (Rolland, Souveyet, &
Achour, 1998). Other definitions come from Van
Lamsweerde (Van Lamsweerde, 2001) and
Dardenne (Dardenne, Lamsweerde, & Fickas, 1993).
Goals have different level of granularity from
high-level, strategic objectives to fine-grained,
technical prescriptions that can be assigned as
responsibilities of single actors.
Goal-Oriented Requirements Engineering
(GORE) uses goals for eliciting, elaborating,
structuring, specifying, analyzing, negotiating,
documenting, and modifying requirements (Van
Lamsweerde, 2001). GORE focuses on early
requirements, when problems are identified, and
alternative solutions are explored and evaluated.
During goal-oriented analysis, the analyst begins
with initial stakeholder goals such as “Fulfil every
customer request” and refines them until goals are
reduced to alternative collections of functional
requirements. Major models that use GORE include:
Knowledge Acquisition in autOmated
Specification – KAOS approach (Dardenne et
al., 1993) that consists of a formal framework
based on temporal logic and AI refinement
techniques.
Non-Functional Requirements (NFR)
approach is based on the notion of soft-goals.
A soft-goal is satisfied rather than achieved
(Mylopoulos, Chung, & Nixon, 1992).
i* (Yu, 1997) develops NFR but it is more
focused on the current organizational
situation. In particular, it relates organizational
stakeholders, goals and candidate software
architectures.
3 GOAL-ORIENTED
REQUIREMENTS LICITATION
(GORE) METHODOLOGY TO
IMPROVE USER
PARTICIPATION
We here describe a methodology developed from
Analysis of Web Application REequirements -
AWARE (Bolchini & Paolini, 2004), that supports
the early interactions between users and analysts.
AWARE is very simple, directly links goals to
requirements and provides robust and straight
definition of requirements categories (Access,
Presentation, Operation, Navigation, etc...).
AWARE, that rapidly defines requirements, has
been already successfully used to elicit requirements
for Ubiquitous Web Applications (Perrone &
Paolini, 2003).
The targets of this extension are information
intensive applications (document management,
knowledge base systems, information repositories,
etc...). Actually their requirements profile is very
similar to the paradigmatic web applications. Indeed
in such applications the primary needs of users are to
access/navigate and/or load documents. By contrast,
USER GOAL-ORIENTED REQUIREMENTS ELICITATION TO IMPROVE ACCEPTANCE AND USE - A Case Study
on Document Management
155

in typical transaction oriented systems, users need to
fill electronic forms that are stored in databases and
retrieve/process collections of tables. In information
intensive applications the range of stakeholder / user
is extended and includes all the user classes
mentioned in the previous section.
The major novelty of the extension is the pro-
active role of analyst that drives a specific analysis
life cycle and the preliminary identification of
system users/stakeholders.
The analysis scenario is not totally usual. First
the analysis team groups with a key user who is
specifically experienced in the domain. In this phase
the group profiles the stakeholder classes of the
systems with a broad definition of their roles and of
the value they should receive from the system.
Based on that profile, the group puts down a draft of
the AWARE goal/navigation schema, candidate
requirements and mock-ups.
As a second phase analysts interview a specific
sample of stakeholder with the objective of
validating/reducing disconfirmation between the
system picture proposed and the actual needs of
users. Users are not asked “What information do you
need?” but “Are these the goals you are pursuing?”,
“Is this the interface you are comfortable with?”, “Is
this the navigation you want?”, “Is the cost of using
the system consistent with the benefits you are
getting?”
The third phase normalizes collected
requirements and the defines their priority levels.
A final phase transforms requirements in Use
Case diagrams as a first step in design of the system.
4 GORE IN CONSULTING
GROUPS: A CASE STUDY
4.1 The Management Consulting
Group
Our project refers to a management consulting
group. Founded in 2003, Business Integration
Partners (BIP) grew so successfully that is now the
largest Italian management consulting with over 400
consultants and some 250 projects.
BIP (www.businessintegrationpartners.it)
operates in the area of strategy/organization
structure & business processes with a focus on IT
governance. Customers are very large corporations
in Telecommunications and Utilities. BIP is also in
Spain, Portugal and Argentina and, through
international alliances, in France and the Far East
A management consulting project is quite
different from a typical system integration project
since it does not include software development
activities. Management projects include program
management of very large IS projects, audit,
business process reengineering, planning,
certifications and activities related to IT governance
standard such as ITIL and COBIT.
Figure 1: Project Lifecycle in consulting groups.
The management project life cycle includes the
following phases that radically differ from the
software life cycle:
Proposal: consultants respond to a request
made by the management of a customer
company. Proposal generally includes a
presentation, a quotation, a negotiation
activity and the finalization of the actual
proposal. Key documents in this phase
include:
o References in similar projects and
companies
o Project plan and organization
o Technical proposal
o Project costs
o Resumes of consultants
Planning: after the proposal is accepted
consulting staffs the project and defines in
details deliverables and milestones.
Execution and delivery: consultants write
documents and/or attend meeting with clients.
Generally this phase generates a collection of
progress and / or intermediate reports and it
ends with the final report.
Stakeholders in BIP reflect very closely professional
levels, that very similar to other major consultancies:
Business Analyst: it is the entry in
consultancy. They actually write documents
Consultant/ Senior Consultant: with a more
extended experience he deals with harder
issues and/or coaches Business Analysts.
Manager/ Senior Manager: he manages
project teams. Senior managers actually put
together proposal and plans.
Partner: it is the highest professional level, he
manages large customers grouped by industry
and/or a specific domain (e.g. Governance).
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
156

4.2 The Issue: Enterprise Content
Management (ECM) in a
Management Consulting Group
ECM in a Management Consulting company serves
a dynamic community that spins around
complementary axes, that are the professional
profiles and the projects. This twofold dimension
multiplies ownerships of documents. For instance,
Senior Managers are interested both in general
templates and in documents of individual projects.
This double ownership is typical to the wide range
of project oriented industries as high technology,
aerospace, research and alike. While database is
typical to project oriented industries, the document
is the typical artifact of professional organizations,
such as lawyers, notaries, physicians and of course
consultants.
BIP top management were persuaded that
knowledge is a primary corporate asset. Actually it
shortens the time of delivery by providing pre-
configured documents and appropriate references, it
makes education of junior people much easier by
providing best practices and document templates.
Finally, it allows cross fertilization between teams
and transforms individual knowledge into a
corporate asset.
However, from an internal survey, the existing
ECM was only a partial success. A cumbersome
interface troubled access of users and the effort of
loading documents trough an highly controlled ad-
hoc procedure could not be afforded, in a context
where non billable time is considered a waste.
Figure 2: Different perspective on the Document
Repository.
Finally, interviews to senior managers pointed
out that the document management system should be
profiled on each professional profile. Senior
managers when working on a new proposal are
interested in finding out similar proposals while
business analysts look for templates and document
examples to produce new consulting reports.
Based on this experience, the principles of the
future ECM system were stated as follows:
Zero-cost Tagging and Smart Loading:
loading a project document should be a
costless extension of a routine action such as
sending an email and/or save a document;
tagging should be smart and automatically
associate information from project data and
document meta-data. Also ubiquity is a must:
consultants should access via browser all
functions, since they spends most time outside
the office
Highest Value to Stakeholders: the systems
should provide each professional profile with
useful and necessary contents (e.g. best
practices). This implies an enterprise
repository where each consultant can find his
own documents, applicable templates,
appropriate selection of documents of the
projects he is working on and public
documents that are shared by the professional
profile community
Document and Project Segregation: the
hierarchy of privileges coincides with the
hierarchy of projects. The team leader
validates / authorizes documents of his team,
the senior manager makes the same across
teams; this is a key for a consulting company
who should keep consulting teams segregates
for the sake of customer's privacy. Actually
the system tracks downloads and forces
planned confidentiality constraints.
4.3 The Analysis
After many discussions with the management, we
came out with a short document that really founded
the project. The document defined the user scenario
of the ECM system. A summary is illustrated in
Figure 3: the list of stakeholders was extracted from
the organization chart. The needs were defined by
informal interviews with a partner and the head of
quality. Though apparently simplistic this started a
complete user acceptance.
After the laundry list of profiles we decided to
use AWARE method because examples made on the
fly proved to be very understandable to all
USER GOAL-ORIENTED REQUIREMENTS ELICITATION TO IMPROVE ACCEPTANCE AND USE - A Case Study
on Document Management
157
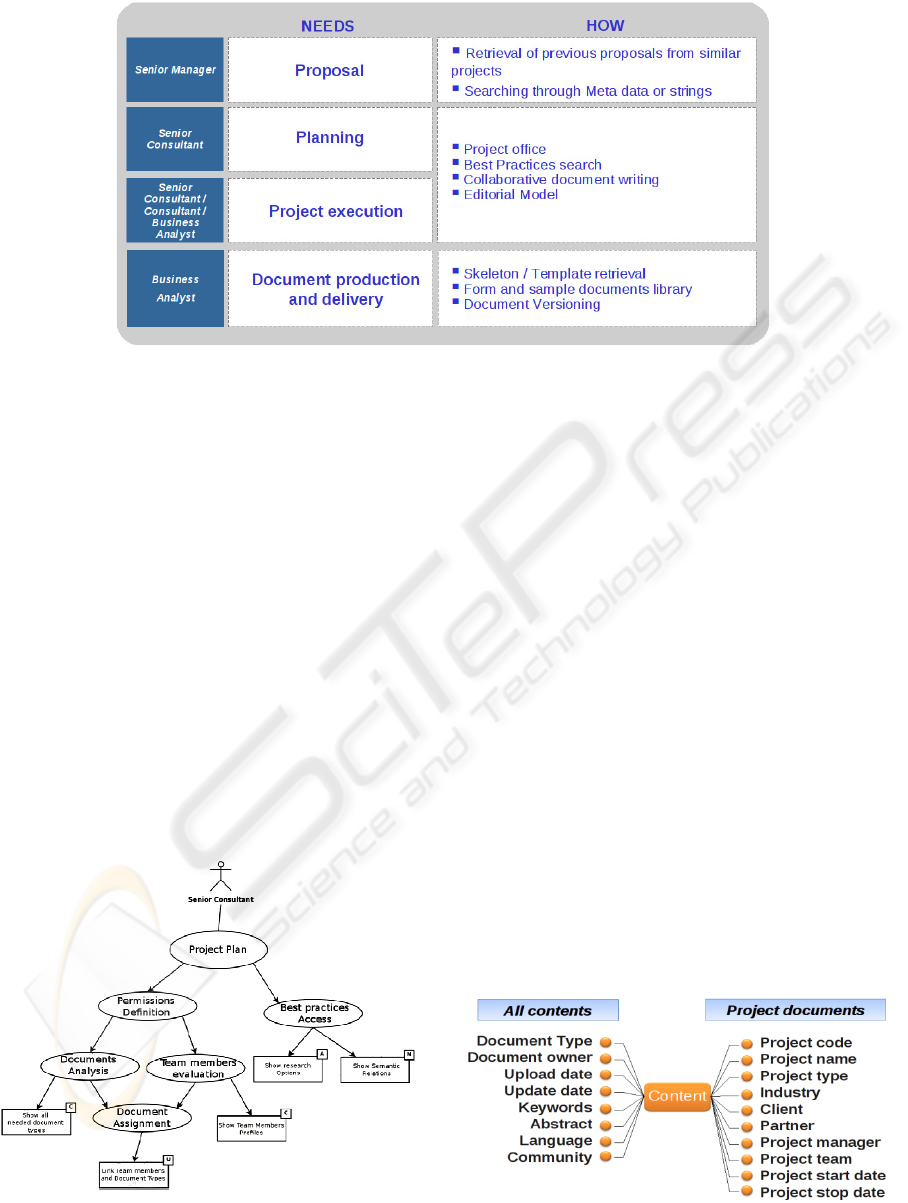
Figure 3: Preliminary list of Stakeholders and relative needs.
consultants, from partners down to analysts. An
example is shown in Figure 4.
AWARE diagrams proved to be not only very rapid
to draw but also immediately understood by
everybody and easily integrated by screenshot,
navigation schemas and use case descriptions.
Unexpected results were additional goals added by
interviewed people (1-3 for each stakeholder class).
An example is the idea of tagging documents based
on the dynamic navigation of the documents by the
user. Also the system automatically proposes
documents that all the colleagues downloaded when
performing similar searches. This successful and
rich analysis hardly would have been feasible with
traditional structured approaches, that lack of
participation, or informal participative techniques t
hat lack of structured output.
To foster participation we managed that every
interviewed people and every interviewer could
Figure 4: An example of Goal Diagram for the Senior
Manager.
track his own suggestions on a log of proposed
changes and additions regardless they were
incorporated or not. This was a successful idea for
participation and allowed also to prioritize
suggestions. Loading ECM by project emails,
discussed here below, was one of these suggestions.
Finally we have to mention a philosophy that
really drove all the design that we call “Zero-cost”
i.e. the user whoever is should spend only a marginal
effort to load or access the ECM. High effort is a
primary failure cause not only in consulting but in
most information intensive systems. Users by
instinct balance the value received against the effort
spent. In Figure 5 we show the meta data of a
document. Administrative meta data are extracted
from corporate ERP while document meta-data
come from tags of the loading tools, that can be
email, web portal and batch for initial population.
In the actual project, after the RE phase,
benchmarking and prototype activities gave proof of
concept and fit-gap analysis against main proprietary
and open source Document Management Systems.
The system is now being implemented. BIP has also
decided of adopting the extended AWARE
methodology as a reference technique to audit /
evaluate strategic information requirements.
Figure 5: Document Metadata.
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
158

5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
DEVELOPMENTS
With the obvious limit of a case study, we have
illustrated how much effective can be a goal and
stakeholder oriented approach to RE. Of course this
applies to document management domain. A
comprehensive survey would be necessary to set a
contingent theory on the relative effectiveness
degree of RE techniques such as UML related
techniques, traditional structured requirement
collection and analysis, goal oriented techniques
unstructured and creative approaches. Nevertheless
we can underline some points:
participative approaches require participative
analysts who are really familiar with the
domain issues and can imagine the minds of
users even without interviewing them
the participation is only a method but it
implies a value aware design epitomized by
the “Zero-cost” philosophy
simple and straight approaches do not mean
less rigour or less effectiveness but simply a
more efficient and effective analysis
Stakeholder patterns as represented by
AWARE diagrams can be stored in a
knowledge base could in turn foster a even
faster approach.
REFERENCES
Ajzen, I. (1985). From intentions to actions: A theory of
planned behavior. IN: J.
Ajzen, I. (1991). The theory of planned behavior.
Organizational behavior and human decision
processes, 50(2), 179-211.
Benjamin, R., & Eriksson, I. (2001). Dilemmas for
managers: Unintended consequences of information
and communications technologies. Information
technology and the future enterprise: Prentice Hall.
Boehm, B. W. (1981). Software engineering economics.
Englewood Cliffs.
Bolchini, D., & Paolini, P. (2004). Goal-driven
requirements analysis for hypermedia-intensive Web
applications. Requirements Engineering, 9(2), 85-103.
Conger, S. A. (1993). The new software engineering:
Course Technology Press Boston, MA, United States.
Dardenne, A., Lamsweerde, A. V., & Fickas, S. (1993).
Goal-directed requirements acquisition. Science of
computer Programming.
Davenport, T. H. (1993). Process innovation:
reengineering work through information technology:
Harvard Business School Press.
Davis, F. D. (1989). Perceived usefulness, perceived ease
of use, and user acceptance of information technology.
MIS quarterly, 319-340.
Davis, F. D. (1993). User acceptance of information
technology: system characteristics, user perceptions
and behavioral impacts. International journal of man-
machine studies, 38(3), 475-487.
Delone, W. H., & McLean, E. R. (2003). The DeLone and
McLean model of information systems success: a ten-
year update. Journal of Management Information
Systems, 19(4), 9-30.
Freeman, R. E., & McVea, J. (1984). A stakeholder
approach to Strategic management.
Gibson, C. F. (2004). IT-enabled business change: an
approach to understanding and managing risk.
Goguen, J. A., & Linde, C. (1993). Techniques for
requirements elicitation. Requirements Engineering,
93, 152-164.
Hammer, M. C., & Champy, J. (1993). J.(1993)
Reengineering the Corporation: A Manifesto for
Business Revolution: HarperBusiness.
Ives, B., Olson, M. H., & Baroudi, J. J. (1983). The
measurement of user information satisfaction.
Jacobson, I., Booch, G., & Rumbaugh, J. (1999). The
unified software development process. Reading:
Addison-Wesley.
Jirotka, M., & Goguen, J. A. (1994). Requirements
engineering: social and technical issues: Academic
Press Professional, Inc. San Diego, CA, USA.
Kettinger, W. J., & Lee, C. C. (1994). Perceived Service
Quality and User Satisfaction with the Information
Services Function*. Decision Sciences, 25(5-6), 737-
766.
Longo, A., & Motta, G. (2006). Design Processes for
Sustainable Performances: A Model and a Method.
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, 3812, 399.
Markus, M. L. (2004). Technochange management: using
IT to drive organizational change. Journal of
Information Technology, 19(1), 4-20.
McKeen, J. D., Guimaraes, T., & Wetherbe, J. C. (1994).
The relationship between user participation and user
satisfaction: an investigation of four contingency
factors. MIS quarterly, 427-451.
McKinney, V., & Yoon, K. (2002). The measurement of
web-customer satisfaction: An expectation and
disconfirmation approach. Information Systems
Research, 13(3), 296.
Moore, G. C., & Benbasat, I. (1991). Development of an
instrument to measure the perceptions of adopting an
information technology innovation. Information
Systems Research, 2(3), 192-222.
Motta, G., & Pignatelli, G. (2008). Designing business
processes for business performance: a framework.
Mylopoulos, J., Chung, L., & Nixon, B. (1992).
Representing and using nonfunctional requirements:
aprocess-oriented approach. IEEE Transactions on
Software Engineering, 18(6), 483-497.
Perrone, V., & Paolini, P. (2003). An Approach for
Designing Ubiquitous Web Applications: A Case
Study.
Pohl, K., & Haumer, P. (1997). Modelling contextual
information about scenarios.
USER GOAL-ORIENTED REQUIREMENTS ELICITATION TO IMPROVE ACCEPTANCE AND USE - A Case Study
on Document Management
159

Pouloudi, A., & Whitley, E. A. (1997). Stakeholder
identification in inter-organizational systems: gaining
insights for drug use management systems. European
Journal of Information Systems, 6(1), 1-14.
Rhenman, E. (1968). Industrial democracy and industrial
management: Van Gorcum.
Rockart, J. F. (1979). Chief executives define their own
data needs. Harvard Business Review, 57(2), 81.
Rogers, E. M. (1995). Diffusion of innovations: Free
Press.
Rolland, C., Souveyet, C., & Achour, C. B. (1998).
Guiding goal modeling using scenarios. IEEE
Transactions on Software Engineering, 24(12), 1055-
1071.
Schein, E. H. (2004). Organizational culture and
leadership: Jossey-Bass.
Schepers, J., & Wetzels, M. (2007). A meta-analysis of the
technology acceptance model: Investigating subjective
norm and moderation effects. Information &
Management, 44(1), 90-103.
Spohrer, J., & Riecken, D. (2006). Special Issue: Services
Science. Comm. ACM, 30-32.
Stevens, R., Brook, P., Jackson, K., & Arnold, S. (1998).
Systems engineering: coping with complexity:
Prentice-Hall Europe.
Sun, H., & Zhang, P. (2006). The role of moderating
factors in user technology acceptance. International
Journal of Human-Computer Studies, 64(2), 53-78.
Van Lamsweerde, A. (2001). Goal-oriented requirements
engineering: A guided tour.
Venkatesh, V., & Davis, F. D. (2000). A theoretical
extension of the technology acceptance model: four
longitudinal field studies. Management science, 186-
204.
Wixom, B. H., & Todd, P. A. (2005). A theoretical
integration of user satisfaction and technology
acceptance. Information Systems Research, 16(1), 85.
Yu, E. S. K. (1997). Towards modelling and reasoning
support for early-phaserequirements engineering.
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
160
