
KNOWLEDGE-BASED REFINEMENT OF BUSINESS
MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS
Saulius Gudas and Audrius Lopata
Kaunas University of Technology, Information Systems Department, Studentu St. 50, Kaunas, Lithuania
Vilnius University, Kaunas Faculty of Humanities, Muitines St. 8, Kaunas, Lithuania
Keywords: Empirical business process modelling, Knowledge-based business process modelling, Management
(control) view, Enterprise management function, Information feedback, Elementary Management Cycle
(EMC), Verification, Validation, Refinement of management function.
Abstract: The paper deals with knowledge-based business process (BP) modeling. The enterprise management is
considered from the control point of view – a formal structure of any enterprise management function is
formally predefined as Elementary Management Cycle (EMC). The acquired from business domain
empirical BP model is interactively enhanced and transformed to business management function model
using predefined knowledge. Transformations are handled by knowledge structure – meta-model of
enterprise management function. Two types of logical gaps are identified by transformations of BP models.
Modified types of WFM are declared and deployed for refinement of business management functions.
1 INTRODUCTION
The business process modeling relies heavily on the
analyst and user; therefore it is not clear whether the
acquired information about problem domain is
adequate (Kapocius K., Butleris R., 2005). Many
mistakes in the area of business process (BP)
modelling and user requirements acquisition can be
avoided when applying knowledge-based enterprise
(business process) modelling (Lopata, A., Gudas S.,
2009), focusing on the verification and validation of
acquired BP models.
There is a great number of Enterprise modelling
methodologies (such as CIMOSA, GERAM
(GERAM, 1999), IDEF suite, GRAI, MDA (Stephen
J., Kendall S., Uhl A., Weise D., 2004), , standards
and methods (ISO 14258, ISO 15704, PSL, ISO TR
10314, CEN EN 12204 (ENV12204, 1996), CEN
40003 (ENV40003, 1990), UEML (Vernadat F.,
2001), DoDAF (DoDAF, 1996), which define the
Enterprise modelling components.
An expert (user as well as analyst) plays the
major role in domain knowledge elicitation and
verification process, and few formalized methods of
information acquisition control are taken into
consideration.
There are two paradigms for Enterprise modelling
(same as for BP modelling):
¾ The empirical Enterprise modelling: it is based
on the problem domain analysis, when
empirically acquired information is captured,
and later BP model is represented using some
structured notations (DFD, WFM, IDEF, BPMN
or some others); in other words this is a
traditional BP modelling.
¾ The knowledge-based Enterprise modelling: it
is based on the predefined knowledge about
essential features of some problem domain (i.e.
in this case about Enterprise as a system), and
handling of robust problem domain analysis
using this domain-specific knowledge for
verification and validation of the empirically
acquired information. In this case we are
discussing the methodological problems in the
area of Enterprise modelling for BP re-
engineering as well as for information systems
development. The problem domain is Enterprise
activities, so, essential feature of Enterprise
activities is knowledge about information
structure of the Enterprise management
(control) activity. Verified and validated BP
management model also is represented using
some structured notations (DFD, WFM, IDEF,
BPMN or some others).
435
Gudas S. and Lopata A. (2009).
KNOWLEDGE-BASED REFINEMENT OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development, pages 435-442
DOI: 10.5220/0002301704350442
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The difference of these two paradigms could be
highlighted in brief as follows: the empirical BP
modelling is focused on the Enterprise business
process modelling. The major concepts from this
modelling perspective are as follows: business
process (activity, action or function), flow (material
or information flow), organizational units (role,
department, organization). There are no predefined
constraints, except syntactical requirements of
selected graphical notation.
Meanwhile knowledge-based BP modelling (from
control point of view (Gudas, S., 1991), (Gupta,
M.M., Sinha, N.K., 1996) is focused on the essential
feature of Enterprise as a system - on the modelling
of components of the Enterprise management
(control) process: enterprise process (concerning
only material flows and transformation), enterprise
management function (concerning only information
transformations in the enterprise process
management (control) loop), enterprise goals and
objectives as well as organizational units (role,
department, organization) (Gudas S., Skersys T.,
Lopata A., 2004 and 2005).
Knowledge–based Enterprise modelling (BP
modelling) includes verification and validation of
empirically acquired BP model against predefined
knowledge about inside structure of the Enterprise
management (control) activity formally defined as
Elementary Management Cycle (EMC) (Gudas S.,
Skersys T., Lopata A., 2004 and 2005).
Therefore, the user and the analyst are two
sources of information about business domain in
traditional IS engineering. Most of user requirements
acquisition techniques are based on empirical
information provided by the user (business domain
expert). Problems occur when empirically acquired
problem domain information (BP model) has to be
verified and validated.
The Enterprise Knowledge Repository of CASE
system is considered to be the third source of
domain knowledge for empirical information about
BP acquired from user. The core component of
Knowledge Repository is Enterprise Meta-Model
which is based on the definition of enterprise
management cycle EMC (Gudas S., Skersys T.,
Lopata A., 2004 and 2005), as well as on the EM
standards (ENV 12204) and languages (PSL, UEML
core) (Vernadat F., 2001).
The presented BP modelling process is developed
from management (control) point of view (Gudas,
S., 1991), (Gudas, S., Lopata A., Skersys, T., 2005).
The workflow modelling (WFM) notation is selected
for representation of BP models. Naturally, some
other BPM notations could be employed instead of
selected WFM notation, for instance, the BPMN,
IDEF0 or IDEF3 as well as DFD or Activity
diagram (UML).
2 THE PRINCIPLES OF
KNOWLEDGE-BASED
ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT
MODELING
The peculiarity of this approach is as follows - BP
modelling is focused on the modelling of enterprise
management (control) aspects. An enterprise
management (control) modelling is considered as
modelling of enterprise information feedback
between two concepts, namely, enterprise
management function and enterprise process.
The information feedback between enterprise
management functions {F} and enterprise processes
{P} could be illustrated, for instance by analysis of
Value Chain Model (Porter, M.E., 1985). The
traditional support activities of Value Chain Model
(financial policy, accounting, human resource
management, technology development,
procurement, etc.) are referred in this approach as
enterprise management functions.
So, an enterprise management function (Fj) is
identified as a type of support activities and
enterprise process (Pi) is identified as a type of
primary activities (see Figure 1).
In this approach structured Value Chain Model is
considered as a framework of enterprise
management activity which refines as a set of pairs
(interactions) {(Fj ; Pi)} of enterprise management
functions {Fj} and enterprise processes {Pi}:
Formally an enterprise management activity is
defined as Elementary Management Cycle (EMC)
from the control point of view (see Figure 2)
(Gudas, S., 1991).
The components of enterprise management
function (aligned with the definition of EMC) are
depicted in Figure 3.
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
436

Figure 1: The structured Value Chain Model.
Figure 2: The information structure of any enterprise management function (Fj) is considered as cycle of information flows
and transformations.
Figure 3: The structure of enterprise management function aligned with the definition of EMC.
KNOWLEDGE-BASED REFINEMENT OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS
437
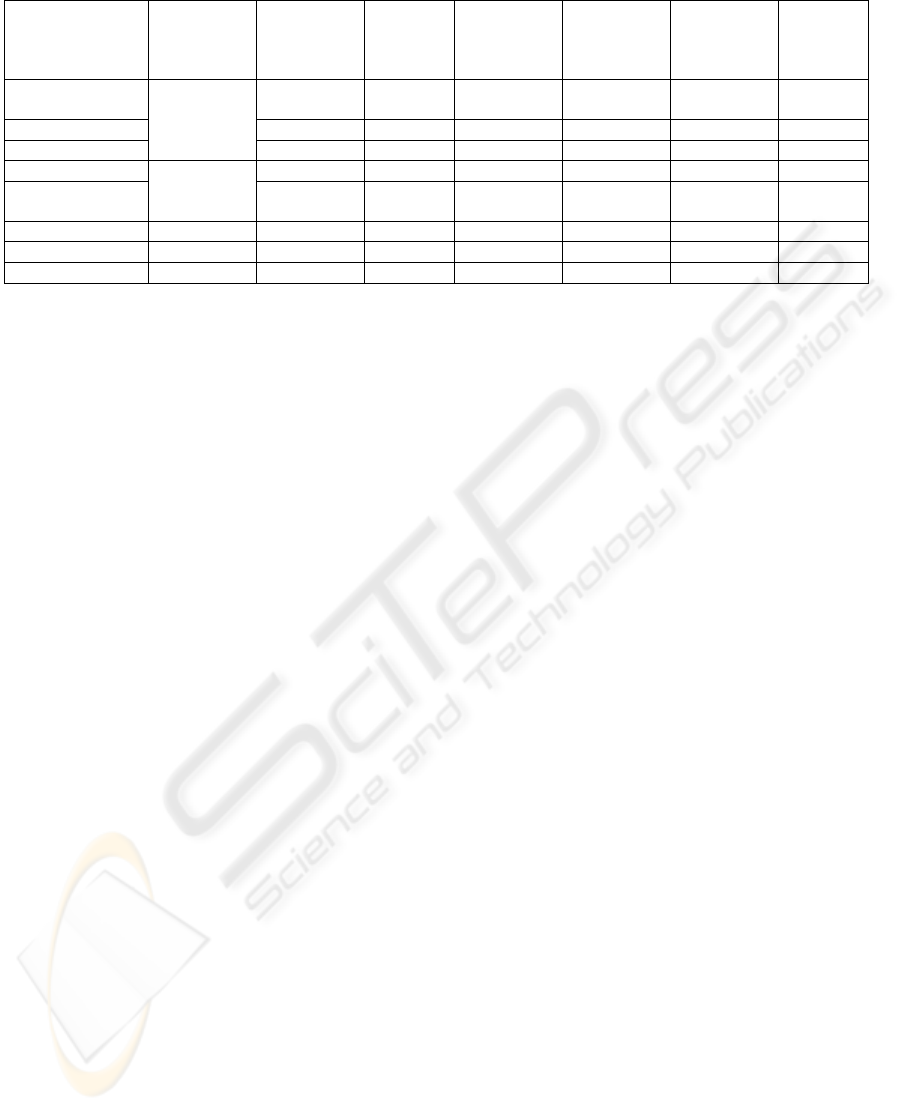
Table 1: Comparison of traditional and modified workflow models.
Workflow
model
Components
Traditional
WFM
VP_WFM
(BPM1)
P_ WFM
(BPM2)
F_ WFM
(BPM3)
P_WFM*
(BPM2*)
F_WFM*
(BPM3*)
FS_WFM
(BPM4)
Business
Process
+ (not
detailed)
+ – – – – –
Activity – – + – + +
Process – + – + – +
Material Flow + (not
detailed)
+ + – + – +
Information
Flow
+ – + – + +
Actor + + + + + + +
Activity type – – – – – – +
Logical Gaps + + + + – – –
An enterprise management Function (Fj) consists
of the predefined sequence of mandatory steps of
information transformation (Interpretation (IN),
Data Processing (DP), Decision Making (DM),
Realization of Decision (RE)); all these steps
compose a closed management cycle (a feedback
loop). A definite types of attributes (Process State
Attributes (A), Clear-out Raw Data (B), Business
Data (C), Management Decisions (D), Controls of
Process (E)) are formed and transmitted during each
management cycle step (Gudas S., Lopata A.,
Skersys T., 2005).
The workflow modelling (WFM) notation is used
for business process modelling. Few new types of
WFM (modified WFM) are defined and deployed
for presentation and transformation of initial
(empirical) Business Process model (BPM1) into
Enterprise Management model (i.e. knowledge-
based BP management model (BPM4)).
3 STEPS OF ENTERPRISE
MANAGEMENT KNOWLEDGE
ELICITATION
This knowledge–based BP modelling approach
includes transformations of few types
(modifications) of the workflow model as follows:
1. BPM1 is empirical BP model, represented
as Workflow Model of Business Processes
(VP_WFM);
2. BPM2 is model of enterprise processes
(material flow), represented as Workflow
Model of Processes (P_WFM);
3. BPM3 is model of enterprise information
activities (information flow), represented as
Workflow Model of Functions (F_WFM);
4. Intermediate results (BPM*):
a. BPM2* is enhanced Workflow Model of
Processes without gaps;
b. BPM3* is enhanced Workflow Model of
Functions without gaps;
5. BPM4 is formally correct enterprise
management function model, refined using
predefined knowledge, and represented as
Workflow Model of Functional
Composition (FS_WFM).
The model of Business Processes BPM1
(VP_WFM) is a traditional (empirical) workflow
model aimed to specify an expert knowledge
(empirical information) about problem domain (i.e.
enterprise processes or functions, material and
informational flows and actors).
The model of enterprise Processes BPM2
(P_WFM) is a part of VP_WFM and includes only
material (manufacturing) processes, material flows
and related actors of the problem domain.
BPM3 or model of enterprise Functions (F_WFM)
includes only information (data) flows and related
actors of the problem domain. BPM2* is model of
enterprise Processes without gaps as well as BPM3
is model of Functions without gaps are intermediate
results in transformations from empirical BP model
(VP_WFM) to knowledge-based BP management
model (FS_WFM).
BPM4 is model of Functional Composition
(FS_WFM) and specifies the internal components of
definite (selected by user or analyst) business
management function in accordance with definition
of EMC (Gudas S., Lopata A., Skersys T., 2005).
The refinement of formally correct enterprise
management function is a sequence of
transformations of BP models listed above.
Comparison of components of traditional workflow
model and modified workflow models is presented in
Table 1 where “+” means that the component is the
part of the following Workflow model and “-“ means
that the component is not the part of such model.
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
438

Figure 4: Knowledge-based refinement of business management function.
The refinement of formally correct enterprise
management function (according to definition of
EMC, i.e. according to composition of EMM) is a
sequence of transformations of BP models BPM1 –
BPM4:
Step1. Analysis of empirical model BPM1,
identification of business processes (BPM2) and
informational activities (BPM3): A1(BPM1) ->
[A2(BPM2); A3(BPM3)] ;
Step2. Interactive identification and elimination of
gaps in the BPM2 and BPM3: [A2(BPM2);
A3(BPM3)] -> [A2(BPM2*); A3(BPM3*)];
Step3. Verification and validation of selected
(definite) enterprise management function (Fj):
[A2(BPM2*); A3(BPM3*)] -> A4(BPM4);
The analysis steps of the BP models (analysis
starts with empirical one BPM1 (VP_WFM) finally
refines formally correct model BPM4 of some
selected (defined by analyst or user) enterprise
management function (FS_WFM)):
a) A1 -> A2: Identifies informational activities
and material processes (presented in empirical BP
model BPM1 (VP_WFM) and separates VP_WFM
into Model of Processes BPM2 (P_WFM) and
Model of Functions BPM3 (F_WFM);
b) A2. Identifies and eliminates logical gaps in
the Model of Processes BPM2 (P_WFM); verified
model BPM2* is developed;
c) A3. Identifies and eliminates logical gaps in
the Model of Functions (F_WFM); verified model
BPM3* is developed;
d) [A2; A3] -> A4. Validation of enhanced
models BPM2* and BPM3* against Knowledge
Base constraints, and composition BPM4
(FS_WFM) of selected (particular) enterprise
management function (Fj). Validation of BPM4 is
performed according to the formal definition of
enterprise management function (predefined as
Elementary Management Cycle (EMC)).
The major steps of problem domain analysis and
knowledge acquisition are presented in Figure 4.
4 IDENTIFICATION AND
ELIMINATION OF BP
MODELLING GAPS
The logical gaps could appear when problem domain
knowledge (i.e. empirical BPM1) is incomplete.
Logical gaps are identified during the analysis of
input and output flows of enterprise activities. For
instance, a logical gap in the BPM2 (P_WFM) or
BPM3 (F_WFM) is identified if some Process or
Activity is not related to input flow or output flow.
It is likely that on separating VP_WFM into
F_WFM and P_WFM logical gaps may be identified
in newly created F_WFM and P_WFM. A logical
KNOWLEDGE-BASED REFINEMENT OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS
439

gap is a semantic discontinuity among the elements
of the workflow model. The logical gaps appear
when problem domain knowledge is acquired
incompletely. On purpose to eliminate gaps of
P_WFM, detecting and eliminating algorithm is
applied. Without reference to elimination method,
P_WFM is complemented by non–existing, but
wrongly or hardly specified knowledge (process,
material flow and actor). Logical gaps of P_WFM
are identified during the analysis of input and output
flows of each material process.
Except the first and the last processes of the
workflow model each Process of the P_WFM must
be related to at least one input material flow and one
output material flow, in the same as each Activity of
F_WFM must be related to at least one input
information flow and one output information flow.
On purpose to eliminate logical gaps of P_WFM, the
prototype of informational system, eliminating
P_WFM gaps was created by MS “VISIO 2000”
CASE tool and MS “ACCESS 2000” data base
management system.
The principles of elimination logical gaps in
the BPM3 (F_WFM) are analogical to that of BPM2
(P_WFM). The main difference is that all analysis
actions of BPM3 (F_WFM) are performed with
modeling concepts activities and information flows,
but not with processes and material flows of BPM2
(P_WFM).
Table 2 presents the components of
management function model BPM4 (FS_WFM),
which are defined according to activities input and
output flows identified in BPM3 (F_WFM).
According to the types of informational input and
output flows, three types of the BPM4 information
activities (internal steps of management function by
definition – see Figure 2) can be distinguished:
Interpretation, IP and Realization (described in
detail in (Gudas S., Lopata A., Skersys T., 2005).
A set of rules for BPM4 analysis is
developed. For instance, if input and output of
FS_WFM information activity are information flows
“Process Output”, situation “impossible type of
activity” is identified. Information activities of
FS_WFM, according to definition of EMC, cannot
have informational input and output flows of the
same type. Activities, which have information input
and output flows (“Process Output”, “IP Input”, “IP
Output”, “Process Input”) of same type, can exist
neither. If activity input is “Process Output” and
output is “IP Input”, the activity will be identified as
component (part) Interpretation of management
function. Interpretation is set of rules, intended to
transform information flow “Process Output” into
“IP Input”, which is prepared for IP processing.
Interpretation is a necessary component of
management function, because “Process Output”
information flow can mismatch data format,
determined for functional IP element input “IP
Input”.
If activity input is “IP Input” and output is
“IP Output
”, the activity is identified as component
Information Processing (IP) of management
function. Information Processing (IP) is functional
component, which is mainly intended to control
process of information processing and decision
making. If activity input is “IP Output” and output is
“Process Input”, the activity is identified as
component (part) Realization (RE) of management
function. Realization is functional part, performing
process, which is contrary to Interpretation (IN).
Realization transforms “IP Output” data (processed
in IP stage) into “Process Input” format (suitable to
direct process control).
5 META-MODEL OF
ENTERPRISE MANAGEMENT
FUNCTION
The result of validation of functional composition
(Step3 in Figure 4) is model BPM4 of formally
correct Enterprise Management Function (presented
as Work Flow Model of Functional Composition
(FS_WFM). Elements of Workflow Model of
Functions (F_WFM) are specified in the Enterprise
Management Function model (FS_WFM) as
component types, formally defined by structure of
EMC (see Figure 3).
Every Enterprise Management Function
model (FS_WFM) specifies some particular
Enterprise management function (Fj), which controls
one of processes (Pi), specified in model BPM2 of
Enterprise Processes (P_WFM).
According to the internal structure of
Enterprise management function (Fiji) (see Figure
3), there are three allowable types of information
activities: Information activity of interpretation,
Information activity of data processing and decision
making (IP), Information activity of realization.
Each BPM3 (F_WFM) information activity
may correspond to one of the above mentioned
component parts of functions.
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
440
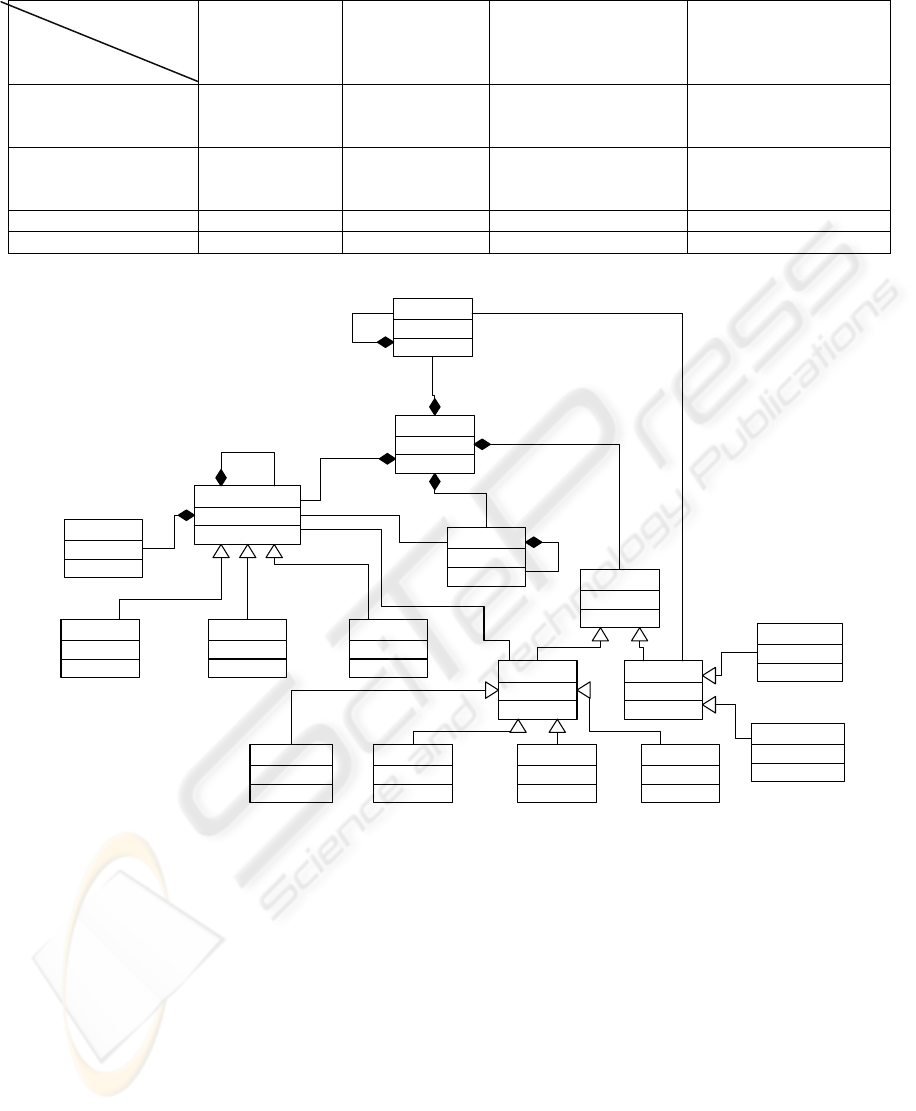
Table 2: Input flows and output flows of components “information activity” of BPM4.
Type of Activity
Output
Type of
Activity Input
Process Output
IP Input
IP Output Process Input
Process Output
Impossible Interpretation
(IN)
Interpretation (IN),
Information Processing
(IP)
Interpretation (IN),
Information Processing
(IP), Realization (RE)
IP Input
Impossible Impossible Information Processing
(IP)
Information
Processing (IP),
Realization (RE)
IP Output
Impossible Impossible Impossible Realization (RE)
Process Input
Impossible Impossible Impossible Impossible
FS_WFM
Process
Flow
Inf. Flow Mat. Flow
Information Activity
Actor
Interpretation
IP Realization
Business Rule
Process_Output IP_Input IP_Output Process_Input
1
*
1
1
1
*
1
1..*
1
*
Mat. Output Flow
Mat. Input Flow
1
1..*
1
1..*
1
*
11..*
1
1..*
1
1..*
Figure 5: Meta-model of enterprise (business) management function (represented as Work Flow Model of Functional
Composition (FS_WFM).
Algorithm determines what part of function
activities belong to and what material process do
they control in F_WFM. Each activity of F_WFM,
specified in FS_WFM, can be analogical component
(Interpretation, IP or Realization) of several
FS_WFM. FS_WFM metamodel is presented in
Figure 5.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The peculiarity of this approach to BP modelling is
the enterprise management (control) modelling view
(Gudas S., Lopata A., Skersys T., 2005). An
enterprise management modelling is considered as
modelling of interaction of two major concepts,
namely, enterprise management function and
enterprise process. The concepts of enterprise
management function and enterprise process is
illustrated by analysis of Value Chain Model.
The acquired from business domain BP model is
represented as Workflow model. This empirical BP
model is interactively enhanced and transformed
step by step to business management function model
using predefined knowledge. Transformations are
handled by knowledge structure – meta-model of
enterprise management function.
KNOWLEDGE-BASED REFINEMENT OF BUSINESS MANAGEMENT FUNCTIONS
441

The enterprise management activities are
considered from the control point of view. The
predefined knowledge about enterprise management
functions (namely, defined as Elementary
Management Cycle (EMC)) is used for modelling,
verification and validation of enterprise management
(control) interactions. Workflow modelling notation
is used for visualization of BP models. Modified
types of WFM are declared and deployed for
refinement of business management functions.
The selected notation for manifestation of BP
models and refinement of enterprise management
function is Workflow modelling notation,
meanwhile some other notations could be used
instead, for instance, DFD, BPMN as well as
Activity diagram of UML or IDEF3.
Domain knowledge acquisition and analysis
process is described as a sequence of interactive
transformations of empirical BP model to formally
defined BP management function model where a
Knowledge Base is an active source of essential
knowledge about structure and behaviour of
enterprise management components.
REFERENCES
Kapocius K., Butleris R., 2005. Business rules driven
approach for elicitation of IS requirements. In WMSCI
2005 : proceedings of the 9th World Multiconference
on Systemics, Cybernetics and Informatics, July 10-13,
2005, Orlando, Florida, USA. Vol. 4. Orlando:
International Institute of Informatics and Systemics,
2005. p. 276-281 ISBN 980-6560-56-6.
Stephen J., Kendall S., Uhl A., Weise D., 2004. MDA
Distilled: Principles of Model-driven Architecture.
Addison-Wesley Pub. Co. 2004
Vernadat F., 2001. UEML: Towards a Unified Enterprise
modelling language. In Proceedings of International
Conference on Industrial Systems Design, Analysis
and Management (MOSIM’01), Troyes, France, 2001-
04-25/27, http://www.univ-troyes.fr/mosim01
GERAM, 1999. Generalised Enterprise Reference
Architecture and Methodology, Version 1.6.3. IFIP–
IFAC Task Force on Architectures for Enterprise
Integration (1999).
ENV 12204, 1996. Advanced Manufacturing Technology
Systems Architecture - Constructs for Enterprise
Modelling. CEN TC 310/WG1 (1996).
ENV 40003, 1990. Computer Integrated Manufacturing
Systems Architecture - Framework for Enterprise
Modelling, CEN/CENELEC (1990).
DoDAF, 1996. Department of Defence Technical
Architecture Framework for Information
Management. Version 3.0. Defence Information
Systems Agency, Center of Standards (1996).
Gudas, S., 1991. Organisational System as a Hierarchy of
Information Processes. In Applications of Artificial
Intelligence in Engineering VI (AIENG 91).
Computational Mechanics Publications, Southampton
Boston (1991), p. 1037 –1050 ISBN 1-85312-141-X.
Gudas S., Skersys T., Lopata A., 2004. Framework for
Knowledge-based IS Engineering. In Advances in
Information Systems ADVIS‘2004, T. Yakhno, ed.,
Springer-Verlag, Berlin, LNCS 3261, 2004, pp. 512-
522., ISSN 0302-9743
Gudas S., Lopata A., Skersys T., 2005. Approach to
Enterprise Modelling for Information Systems
Engineering. In Informatica, Vol. 16, No. 2, Institute
of Mathematics and Informatics, Vilnius, 2005, pp.
175-192., 2005 ISSN 0868-4952
Porter, M.E., 1985. Competitive Strategy: Creating and
Sustaining Superior Performance. The Free Press,
New York.
Gupta, M.M., Sinha, N.K., 1996. Intelligent Control
Systems: Theory and Applications. The Institute of
Electrical and Electronic Engineers Inc., New York
(1996).
Lopata, A.,Gudas S., 2009. Workflow-based acquisition
and specification of functional requirements.
Proceedings of the 15th International Conference on
Information and Software Technologies (IT2009),
Kaunas University of Technology, 2009, p. 417-426
ISSN 2029-0020
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
442
