
XHITS
Multiple Roles in a Hyperlinked Structure
Francisco Benjamim Filho, Raul Pierre Renteria and Ruy Luiz Milidi
´
u
Departament of Informatic, Pontif
´
ıcia Universidade Cat
´
olica do Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords:
Search engines, Keyword-based ranking, Link- based ranking.
Abstract:
The WWW is a huge and rich environment. Web pages can be viewed as a large community of elements that
are connected through links due to several issues. The HITS approach introduces two basic concepts, hubs and
authorities, that reveal some hidden semantic information from the links. In this paper, we present XHITS, a
generalization of HITS, that models multiple classes problems and a machine learning algorithm to calibrate
it. We split classification influence into two sources. The first one is due to link propagation, whereas the
second one is due to classification reinforcement. We derive a simple linear iterative equation to compute the
classification values. We also provide an influence equation that shows how the two influence sources can be
combined. Two special cases are explored: symmetric reinforcement and positive reinforcement. We show
that for these two special cases the iterative scheme converges. Some illustrative examples and empirical test
are also provided. They indicate that XHITS is a powerful and efficient modeling approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
The link structure of the WWW provides valuable in-
formation that can be used to improve information
retrieval quality (Borodin et al., 2001),(Chakrabarti
et al., 2001),(Lempel and Moran, 2001),(Ding et al.,
2002a). There are lot of different proposals for
searching and ranking information on the WWW,
(Mendelzon and Rafiei, 2000), (Cohn and Chang,
2000), (Giles et al., 2000), (yu Kao et al., 2003),
(Fowler and Karadayi, 2002), (Ding et al., 2002b),
(Agosti and Pretto, 2005), (Mizzaro and Robertson,
2007),(Lempel and Moran, 2001). Others just to im-
prove the quality of existing ones, as incorporating
user behavior data can significantly improve ordering
of top results in real web search setting, (Agichtein
et al., 2006).
In a seminal paper (Kleinberg, 1999), Jon Klein-
berg introduced the notion of two fundamental cate-
gories of web pages: authorities and hubs.
Good hubs are the ones that point to good author-
ities, whereas good authorities are the ones that are
pointed by good hubs.
This mutually reinforcing relationship can be eas-
ily formulated through a system of equations. The
HITS algorithm finds a solution to this system.
Here, we generalize Kleinberg’s approach by in-
troducing new page categories. The new system of
equations can still be solved by the power method as
in HITS.
Hence, our XHITS method allows to incorpo-
rate concepts that capture different roles of pages in
the Web domain,such as: hubs, authorities, sponsors,
novelty, portals, mirrors, etc, (Filho, 2005). It is up to
the modeler to define the corresponding semantic of
these categories through the equations that translate
their mutual reinforcement.
This modeling framework provides a clean
method to extract multiple concepts in a hyperlinked
structure such as the Web. Actually, these con-
cepts are extremely related with the human judg-
ments about importance of the information on the
web. Now, we have the engineering knowledge as a
formal method to incorporate several different roles
played by individuals in a hyperlinked environment.
To illustrate this approach, we present a simple ex-
tension to the hubs and authorities categories. This
extension takes into account that good authorities
sometimes also point to novelty in a subject.
Hence, whenever some strong authorities point to
a given document, then this document must receive
our attention, even if it is not pointed by any strong
hub. Chances are that this is relevant new material
that has not been widespread to the hubs. In this il-
lustration, we also consider that good authorities can
play the role of novelty finders. On the other hand, we
189
Benjamim Filho F., Pierre Renteria R. and Luiz Milidiú R. (2009).
XHITS - Multiple Roles in a Hyperlinked Structure.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval, pages 189-195
DOI: 10.5220/0002305601890195
Copyright
c
SciTePress

also introduce a naive notion of portals: good portals
are pages that point to good hubs.
In section 2, we describe our modeling approach
and the corresponding algorithm.
In section 3,we show a simple illustration with
novelties and portals. In section 4, we introduce a ma-
chine learning procedure to calibrate the model. Next,
in section 5,we examine the empirical behaviour of
the proposed approach. Finally, in section 6, we draw
our conclusions and final comments on our findings.
2 XHITS
Here, we first restate the HITS Algorithm in block
matrix form. Next, we highligth some key properties
that are explored on the proposed extension XHITS.
We introduce the notion of influence matrix, a lin-
ear structure that combines both the mutual classifi-
cations reinforcement and the link propagation mech-
anism. Two special cases naturally follow from this
structure: symmetric reinforcement and positive rein-
forcement. Under some mild assumptions, we show
convergence proofs for an extended iterative equation.
As usual, we represent web pages as the nodes in a
directed graph. The links are represented by the edges
of this graph. The corresponding adjacency matrix
is denoted by A. The extraction of these graphs is
made in the same way of Jon Kleinberg did in his ap-
proach,(Kleinberg, 1999).
2.1 HITS
In the HITS model, each page i has a corresponding
authority weight a
i
and also a hub weight h
i
. These
weights are subject to mutual reinforcement through
the link structure.
Formally, we have
a ∝ A
T
h
h ∝ Aa
This system of two sets of linear constraints can
be condensed in block matrix form, given the unique
equation
a
h
∝
0 A
T
A 0
.
a
h
(1)
Equation 1 provides immediate ways to iteratively
compute both a and h. Nevertheless, it is necessary to
guarantee that the values converge.
In order to examine the convergence issues in-
volved in iteration 1, we define the influence matrix
M by
M =
0 A
T
A 0
(2)
It is easy to see that M is a symmetric ma-
trix. Therefore, iteration 1 is just an instance of the
well known Power Method for eigenvalues extraction.
Hence, the iteration converges.
Another interesting representation of M is given
by
M =
0 1
0 0
⊗ A
T
+
0 0
1 0
⊗ A (3)
In 3, we use the direct product ⊗ to reveal the in-
fluence structure,(Searle, 1982).
2.2 The Algorithm
To enhance the basic Hubs and Authorities Model, we
introduce new categories. Now, instead of just two
concepts, we have k categories.
Hence, each page i receives its corresponding uth
class weight c
iu
, where u = 1, ...,k. These weights are
reinforced through the links. We have both forward
and backward influences, and these are not necessar-
ily symmetrical.
Whenever page i points to page j, each weight c
jv
contributes to the score of c
iu
with a linear amount of
F
uv
.c
jv
. Similarly, when j points to i, each weight c
jv
contributes to the score of c
iu
with a linear amount
of B
uv
.c
jv
. Therefore, we have a k × k matrix F of
forward category influences, and a k × k matrix B of
backward category influences.
Formaly, for each weight c
iu
we have
c
iu
∝
∑
j→i
k
∑
v=1
B
uv
.c
jv
+
∑
i→ j
k
∑
v=1
F
uv
.c
jv
By stating these equations in matrix form we get
C ∝ A
T
CB
T
+ ACF
T
(4)
Equation 4 provides an efficient iterative compu-
tation to find C, provided convergence is guaranteed.
2.3 Influence Structure
Equation 4 can be restated by transforming matrix C
into a vector, that is, by
vec(C) ∝ vec(A
T
CB
T
+ ACF
T
)
Using well known properties of the vec operator
(Searle, 1982), we get
vec(C) ∝ [(B ⊗ A
T
) + (F ⊗ A)].vec(C)
The matrix M defined by
M = (B ⊗ A
T
) + (F ⊗ A) (5)
KDIR 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
190

is called the influence matrix.
The influence matrix reveals the combination of
the two sources of mutual influence: link propagation
and category reinforcement. Therefore, it is very con-
venient when one investigates theoretical aspects of
the model.
Next, we highligth two important special cases
where we have convergence for iteration 4.
2.4 Symmetric Reinforcement
In the case of symmetrical mutual reinforcement, we
have that
B
vu
= F
uv
for all u and v. Hence, we have that B = F
T
.
Now, equation 5 simplifies to
M = (F ⊗ A)
T
+ (F ⊗ A) (6)
It is easy to see that M is a symmetric matrix.
The Power Method provides a straightforward al-
gorithm to find both the largest eigenvalue and a cor-
responding eigenvector for M. Therefore, iteration 4
converges and generalizes Kleinberg’s original pro-
posal.
Finally, we state a Proposition that characterizes
symmetric reinforcement.
Proposition. Let us assume that A 6= A
T
. Then,
the influence matrix M is symmetric iff B = F
T
.
Proof.: The sufficency condition was the subject
of the discussion above. To prove the condition is
necessary, observe that
M = M
T
implies that
(B ⊗ A
T
) + (F ⊗ A) = (B ⊗ A
T
)
T
+ (F ⊗ A)
T
that is,
(B − F
T
) ⊗ A
T
= (B
T
− F) ⊗ A
From the definition of direct product, it follows
that for all pair of pages r and s and for all pair of
classification degrees i and j we have
(B
i j
− F
ji
).A
rs
= (B
ji
− F
i j
).A
sr
By assumption, we have a particular r and s such
that A
rs
= 1 and A
sr
= 0. Hence, we obtain that,
(B
i j
− F
ji
).1 = (B
ji
− F
i j
).0
Therefore, B
i j
= F
ji
for all pairs of classification
degrees i and j. This completes our proof.
2.5 Positive Reinforcement
Another interesting case of the XHITS multiple roles
model is when we have that all B
uv
and F
uv
are posi-
tive. This is called positive reinforcement.
Under this assumption, it is easy to see that the
influence matrix M is also positive.
In this case, the Perron-Frobenius Theorem asserts
that the largest eingenvalue is positive and there is
also a corresponding eigenvector with positive coor-
dinates. This is enough to guarantee convergence of
iteration 4.
3 NOVELTIES AND PORTALS
To illustrate the XHITS approach, we extend the basic
Hubs and Authorities Model, by introducing two new
concepts: novelties and portals.
Now, each page i receives its corresponding nov-
elty weight n
i
and portal weight p
i
. We extend
the conversation by introducing novelty and portal
weights into our constraints. First, observe that good
authorities are always pointed by good hubs, some-
times pointed by good portals and also point to good
novelties. Hence, we have that
a
i
∝
∑
j→i
h
j
+ w
1
.
∑
j→i
p
j
+ w
2
.
∑
i→ j
n
j
i = 1, . .. ,n
By a similar reasoning, we obtain the equations
for the other three weights. By stating these equations
in matrix form we get
a ∝ A
T
h + w
1
A
T
p + w
2
An
h ∝ Aa + w
3
A
T
p + w
4
An
p ∝ w
1
Aa + w
3
Ah + w
5
An
n ∝ w
2
A
T
a + w
4
A
T
h + w
5
A
T
p
where w
1
, w
2
, w
3
, w
4
and w
5
are additional effect
reduction parameters.
One can combine the four equations above into a
single one, to obtain
a
h
p
n
∝
0 A
T
w
1
A
T
w
2
A
A 0 w
3
A
T
w
4
A
w
1
A w
3
A 0 w
5
A
w
2
A
T
w
4
A
T
w
5
A
T
0
.
a
h
p
n
(7)
It is easy to see that in this illustration we have
B = F
T
and
XHITS - Multiple Roles in a Hyperlinked Structure
191

F =
0 0 0 w
2
1 0 0 w
4
w
1
w
2
0 w
5
0 0 0 0
Equation 7 is a special case of mutual reinforce-
ment XHITS. Therefore, this iteration converges.
Observe that the parameters w
1
, w
2
, w
3
, w
4
and
w
5
can be used to fine tune our method.
4 MACHINE LEARNING FOR
XHITS
4.1 Approach
As seen in early sections, we have a set of queries,
each one having its own graph of pages. In particu-
lar case, the XHITS algorithm gives us a ranking of
these pages through the eigenvector associated to the
biggest eigenvalue of M:
M =
0 A
T
w
1
A
T
w
2
A
A 0 w
3
A
T
w
4
A
w
1
A w
3
A 0 w
5
A
w
2
A
T
w
4
A
T
w
5
A
T
0
(8)
where w
i
are parameters that you can use to fine tune
the method.
Basically, as we change the values of these param-
eters, the value of eigenvector modifies and the rank
as well. Under this assumption, we can define the
XHITS as a function H
j
(~w,G
i
) = O
i j
, where ~w is the
vector with the parameters w
1
,w
2
,. .. ,w
5
, G
i
is the
graph related with the query q
i
, O
i j
is the rank of the
page j and the query i. So we can view H
j
as ranking
function that gives each website a rank according to
their topological organization and mutual reinforce-
ment influence.
But we don’t know what is the best value of ~w =
(w
1
,w
2
,w
3
,. .. ,w
5
). Our approach to learn these pa-
rameters will be machine learning. That means, that
we simply give the information we have to a learn-
ing algorithm and it use this information to forms ~w
correctly. In the next section, we start with explana-
tion about gradient descent method and how it can be
applied on the problem of finding the vector ~w.
4.2 Learning of Parameters with
Gradient Descent
To proceed with the learning process of
W, we have some input and output pairs
(X
11
,Y
11
),. .. ,(X
1q
,Y
1q
),. .. ,(X
pq
,Y
pq
), that we
will use to learn the parameters that makes O
i j
≈ Y
i j
.
When H
j
(~w,G
i
) gets the input ~w and G
i
it com-
putes a value O
i j
, and if O
i j
came from ~w we are
looking for, then O
i j
would already be very close to
Y
i j
.Therefore we need a measure for the error between
O
i j
and Y
i j
. This is done by the cost function C
i
,
which is the deviation value between the output O
i j
of the current value of ~w, and the target output Y
i j
we
want to reach with the learning machine.
The overall cost function, which summarizes all
errors then would be
E
train
=
1
pq
p
∑
i=1
q
∑
j=1
C
i
(Y
i j
,O
i j
) (9)
and replacing O
i j
for H
j
(~w,G
i
) in 9, we have
E
train
=
1
pq
p
∑
i=1
q
∑
j=1
C
i
(Y
i j
,H
j
(~w,G
i
)) (10)
As you can see, ~w is a direct input to
the training function and the set of pairs
(X
11
,Y
11
),. .. ,(X
1q
,Y
1q
),. .. ,(X
pq
,Y
pq
) is defi-
nite, so we can use the gradient descent method to
find a value of ~w that minimizes E
train
.
Method 1. (The gradient descent method) This is an
approximation method, which at each point chooses
the direction of steepest descent to find the minimum
of a multidimensional function f, which is a function
of the variables w
1
,w
2
,. .. ,w
n
. So, this method oper-
ates according to the following rule, when proceeding
from one iterate to the next:
w
m+1
i
= w
m
i
− µ
∂ f (~w)
∂w
i
(11)
Figure 1: Evaluation of the eigenvalue during the neighbor-
hood searching.
In the above:
•
∂ f (~w)
∂w
i
denotes the partial derivative of f with re-
spect to w
i
, which is evaluated at ~w;
• µ denotes what is usually referred to as the step
size.
By knowing
∂E
train
∂W
, the gradient descent algorithm
for this problem can be adapted to:
~w
m+1
← ~w
m
− µ
∂E
train
∂~w
(12)
KDIR 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
192
Now, we have to find the partial derivatives of
E
train
with respect to the vector ~w:
∂E
train
∂~w
=
1
pq
p
∑
i=1
q
∑
j=1
∂C
i
∂~w
(Y
i j
,H
j
(~w,G
i
)) (13)
In this way, we can define the deviation function
C
i
as (Y
i j
− O
i j
)
2
and applying it in 13 we have:
∂E
train
∂~w
= −
2
pq
p
∑
i=1
q
∑
j=1
(Y
i j
− H
j
(~w, G
i
))
∂H
j
(~w, G
i
)
∂~w
(14)
But, H
j
(~w,G
i
) gives the eigenvector associated
with the biggest eigenvalue of M associated with G
i
,
so, the partial derivatives of H
j
(~w,G
i
), corresponds
to:
∂H
j
(~w,G
i
)
∂~w
=
∂x
i
∂~w
(15)
where ~x
i
denotes the eigenvector of M. According to
(Kalaba et al., 1981), we can write the partial deriva-
tives of ~x
i
as:
∂x
i
∂~w
=
n
∑
l=1
"
(x
T
l
∂M
∂~w
x
i
)
(λ
i
− λ
l
)
#
x
l
(16)
However, to calculate 16 we have to find all eigen-
vectors and eigenvalues of M, and it is, in computa-
tional terms, expensive. Instead of using 16, we de-
cide to use the partial derivatives of the eigenvalue as-
sociated with ~x
i
, extracted from (Kalaba et al., 1981),
that is:
∂λ
i
∂~w
= (x
T
i
∂M
∂~w
x
i
) (17)
We used this adaptation because there is an in-
herent relation between eigenvalues and eigenvectors,
and it’s a good simplification without loss of general-
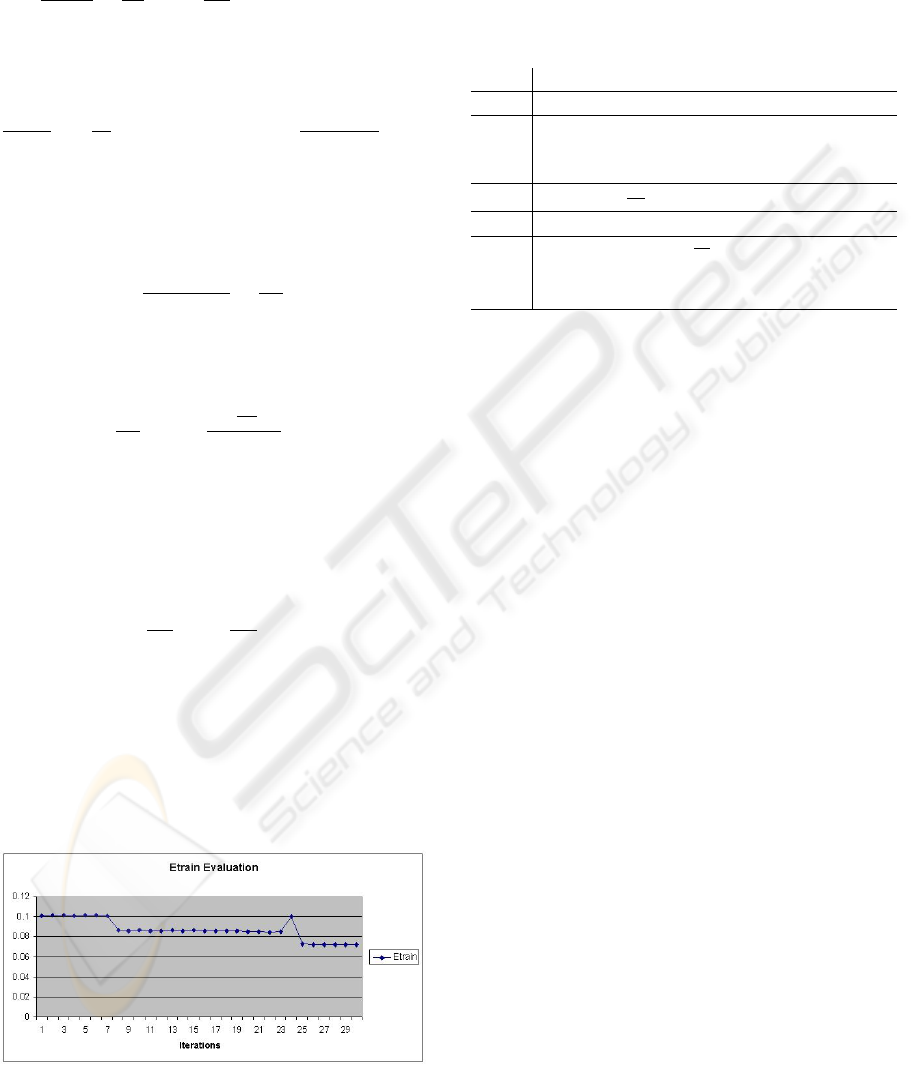
ity. The graphics in figures 1 and 2 shows empirically
this relation. The value of the eigenvalue is getting up
while the value of E
train
is getting down and converges
to a local minimum. Next section shows a description
of the algorithm for the approach discussed here.
Figure 2: Evaluation of the E
train
during the neighborhood
searching.
4.3 Algorithm
We are now able to write the algorithm that teaches
H
j
(~w,G
i
). The algorithm can be resumed as shown in
table 1.
Table 1: Learning Algorithm for H
j
(~w, G
i
) function.
Step Activity
1 Initiates ~w
1
with some values.
2 Calculate the eigenvectors, x
i
,
and eigenvalues,λ
i
for M(~w)
for the training set
3 Calculate
∂x
i
∂~w
4 Calculate ~w
i
m+1
5 Calculate E
train
=
1
pq
∑
p
i=1
∑
q
j=1
C
i
(Y
i j
,O
i j
)
and if it is small enough stop,
else go back to step 2
5 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
To illustrate the computational issues and also to high-
ligth the modeling power of XHITS, we perform
some exploratory experiments.
5.1 Test Goal
Our major performance measure is ranking quality.
As a first instance, we examine the naive Novelties
and Portals classification model.
Our goal is to show that even this simple model
provides a remarkable improvement over previous
algorithms. It shows a ranking quality similar to
the complex algorithms engineered inside comercial
search engines.
5.2 Test Environment
We adopt a pragmatic scheme to build our benchmark.
First, we fix a set of queries. There are 300 queries
in the set with no overlaps, derived from the most
google’s fifteen searched topic for each week in a pe-
riod of five months. Those queries have been chosen
because if our approach reveals a good performance
with them, it will be close from the real searched top-
ics at least.
As well-known, cross-validation is the statistical
practice of partitioning a sample of data into subsets
such that the analysis is initially performed on a sin-
gle subset, while the other subset(s) are retained for
subsequent use in confirming and validating the ini-
tial analysis. To test the learning algorithm presented
in this work, we randomly split up the benchmark set
XHITS - Multiple Roles in a Hyperlinked Structure
193

Table 2: Precision at 10, HITS and XHITS.
Algorithm Precision at Ten (P@10)
HITS 0.125678
XHITS 0.385678
into two subsets: one is the training set and the other
is the test set. The training set is used for fine-tuning
the parameters w
1
,w
2
,. .. ,w
5
. We validated the learn-
ing process applying the 10-fold cross validation in
the training set. After the training step, the parame-
ters had chosen are used and the XHITS is applied in
the test set.
Next, instead of using humans to provide the refer-
ence rank for each query,we use one artificial expert:
Google. This Search Engine is built around several
algorithms that engineer a lot of specific Web knowl-
edge. For our purpose, we considered the fourth first
pages returned by the expert as the relevant ones.
5.3 Test Results
Different performance metrics are appropriate in dif-
ferent circumstances. For recommendation systems
and information retrieval settings, where results are
displayed to users incrementally with the most rele-
vant first, the metric P@10 is most appropriate. It
represents the precision of the first page of results dis-
played. To evaluate ranking quality we focus on the
top 10 pages ranked by the artificial expert. We con-
sidered these as the relevant pages.
Hence,we check the avarege precision perfor-
mance of the Novelties and Portals model. We just
need to count how many relevant pages were recov-
ered among the top ranked by our model.
In table 2 we summarize the test results. One
can see a 206% improvement of XHITS over HITS
on the average.Comparing the proximity of the ranks
produced by XHITS and Google, the maximum prox-
imity was observed for query daytime emmys and the
minimum for query narnia. The corresponding val-
ues were 1 and 0.1 in P@10. During the period we
selected the queries, Narnia, the movie, was about
to be launched and the official site was returned be-
tween the ten first pages at least. The daytime emmys
topic is related with National Academy television that
was happening in that week. All the ten first pages
matched with Googles first ones. You can see the re-
sult in table 3.
Table 3: The first ten links returned by XHITS engine after
the training.
Position URL
1 http://www.emmyonline.org/
emmy/daytime.html/
2 http://www.emmys.tv/awards/
daytimeawards.php/
3 http://www.emmyonline.org/
4 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
Daytime Emmy Award/
5 http://www.soapcentral.com/
soapcentral/awards/
emmys/index.php/
6 http://www.tvweek.com/news/2008/06/
tyra ellen light winners at da.php/
7 http://www.miamiherald.com/
776/story/576599.html/
8 http://www.msnbc.msn.com/
id/25291338/
9 http://www.infoplease.com/
ipa/A0151371.html/
10 http://television.aol.com/
daytime-emmys/
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Searching the web accurately is becoming increas-
ingly critical as the web grows. In this paper we ex-
plored the utility of extending the HITS model to im-
prove web search ranking. The XHITS model pro-
vides a powerful approach to engineer key Web char-
acteristics into ranking algorithms. But we had to deal
with new parameters that didn’t exist in the Klein-
berg’s approach.
So, an interesting open problem is how to find the
set of parameters that best fits to a given data set.
This is a learning problem that we are currently work-
ing on and trying to evaluate. Furthermore, by using
machine learning was easy to find parameter values
that give to simple XHITS models the same precision
power of deep Web knowledge specific algorithms.
This approach has its own benefits, as follow:
• Since the parameters learned consist of several
different queries put together it is harder to ma-
nipulate results;
• Given that the advances in the machine learning
field have increased a lot through the last couple
of years, we are able to benefit from them;
• This mechanism could provide a low cost substi-
tute to current intricate ad hoc models.
KDIR 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Information Retrieval
194

For testing the model, we chose Google as our
ranking expert and compared the performance of
HITS and XHITS in relation to it. The gains of
XHITS’ model over HITS’ are substantial as shown
in the experimental result, over 200 % gain of qual-
ity. One promising direction for future work that we
are exploring is to extend this work by changing the
benchmark and apply the XHITS to GOV2 collection
and compare the performance with others ranking al-
gorithms already explored and reported in the litera-
ture.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Part of this work is supported by Brazilian Army
Technology Center - CTEx. We give our thanks to
all people who have contributed to this research and
development.
REFERENCES
Agichtein, E., Brill, E., and Dumais, S. (2006). Improv-
ing web search ranking by incorporating user behav-
ior information. In SIGIR ’06: Proceedings of the
29th annual international ACM SIGIR conference on
Research and development in information retrieval,
pages 19–26, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Agosti, M. and Pretto, L. (2005). A theoretical study of a
generalized version of kleinberg’s hits algorithm. Inf.
Retr., 8(2):219–243.
Borodin, A., Roberts, G. O., Rosenthal, J. S., and Tsaparas,
P. (2001). Finding authorities and hubs from link
structures on the world wide web.
Chakrabarti, S., Joshi, M., and Tawde, V. (2001). Enhanced
topic distillation using text, markup tags, and hyper-
links. pages 208–216.
Cohn, D. and Chang, H. (2000). Learning to probabilisti-
cally identify authoritative documents.
Ding, C., He, X., Husbands, P., Zha, H., and Simon, H. D.
(2002a). Pagerank, HITS and a unified framework for
link analysis. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual In-
ternational ACM SIGIR Conference on Research and
Development in Information Retrieval, Poster session,
pages 353–354.
Ding, C., Zha, H., Simon, H., and He, X. (2002b). Link
analysis: Hubs and authorities on the world wide web.
Filho, F. B. (2005). Xhits: Extending the hits algorithm
for distillation of broad search topic on www. Mas-
ter’s thesis, Pontif
´
ıcia Universidade Cat
´
olica do Rio
de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil.
Fowler, R. H. and Karadayi, T. (2002). Visualizing the web
as hubs and authorities richard H. fowler and tarkan
karadayi.
Giles, C. L., Flake, G. W., and Lawrence, S. (2000). Effi-
cient identification of web communities.
Kalaba, R., Spingarn, K., and Tesfatsion, L. (1981). Vari-
ational equations for the eigenvalues and eigenvectors
of nonsymmetric matrices. Journal of Optimization
Theory and Applications: Vol. 33, No. 1.
Kleinberg, J. M. (1999). Hubs, authorities, and communi-
ties. ACM Computing Surveys (CSUR), 31(4es):5.
Lempel, R. and Moran, S. (2001). SALSA: the stochastic
approach for link-structure analysis. ACM Transac-
tions on Information Systems, 19(2):131–160.
Mendelzon, A. O. and Rafiei, D. (2000). What is this page
known for? computing web page reputations.
Mizzaro, S. and Robertson, S. (2007). Hits hits trec: ex-
ploring ir evaluation results with network analysis. In
SIGIR ’07: Proceedings of the 30th annual interna-
tional ACM SIGIR conference on Research and devel-
opment in information retrieval, pages 479–486, New
York, NY, USA. ACM.
Searle, S. R. (1982). Matrix Algebra Useful for Statistics.
John Wiley & Sons, NY, USA.
yu Kao, H., ming Ho, J., syan Chen, M., and hua Lin, S.
(2003). Entropy-based link analysis for mining web
informative structures.
XHITS - Multiple Roles in a Hyperlinked Structure
195
