
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION
METHODOLOGY
Towards a Practical Approach
Daniel Braghirolli Serrano and Renata Mendes de Araujo
NP2Tec – Research and Practice Group in Information Technology
Federal University of the Rio de Janeiro State - UNIRIO, Av. Pasteur 458, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Methodology, Model, Systematic, Strategy, Holistic, Implementation.
Abstract: Different perspectives from different areas contribute to the consolidation of the knowledge management
research area. However, due to its underdeveloped aspect, the KM model and systematics for KM
implementation found in the literature are still being discussed and there is still a gap between theoretical
frameworks and technological implementation. The lack of a systematic for KM implementation may be
due to the use of reductionist disciplines which do not take into consideration that KM complexity requires
an integrative and holistic approach. The objective of this research work is to propose a methodology for
KM implementation, comprising a KM holistic model and a systematic for knowledge management
implementation to help an organization define its technological requirements.
1 INTRODUCTION
Currently, the greatest organizational advantage is
not its technological apparatus or the amount of
information it possesses, but rather the capacity to
correctly use the information it bears and to generate
new knowledge (innovation).
Knowledge Management (KM), the discipline
the aim of which is to provide the concepts and
means to enable this new knowledge society
dynamics, has been receiving increasing interest
within organizations and academia. Different
perspectives from different areas contribute to the
consolidation of this new body of knowledge.
(Maier and Remus, 2003).
However, due to its underdeveloped aspect, the
proposed KM model and systematics for KM
implementation found in the literature are still being
discussed (McAdam and McCreedy, 1999) and there
still exists a gap between theoretical frameworks and
technological implementations, leaving the
organization with a high risk when implementing a
KM strategy (Maier and Remus, 2003).
The lack of a systematics for knowledge
management implementation, and its associated
problems, may be a consequence of the use of
reductionist disciplines which do not take into
consideration that the KM complexity requires an
integrative and holistic approach (Kalkan, 2008).
Focusing on just one aspect of knowledge creation
and sharing process hinders the potential of
knowledge management (Nonaka et al, 2008).
The aim of this work is to propose a
methodology for KM implementation. This
methodology should comprise a KM holistic model,
derived from the knowledge management
multidisciplinary aspect, and a systematics for KM
implementation itself, which translates the KM
model into a set of methodological steps to help the
organization define its technological requirements.
This paper details a literature review on KM
approaches, which provided grounds for a
preliminary discussion of the holistic model.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
A literature review of previous KM research was
done in order to support the proposed KM holistic
methodology. This review was based on concepts of
systematic literature review approach (Kitchenham,
2004), which follows well-defined methodological
steps to guide the execution of search in indexed
academic reference digital databases.
The selected papers were analyzed regarding the
following aspects: Paradigm (philosophical and
305
Braghirolli Serrano D. and Mendes de Araujo R. (2009).
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION METHODOLOGY - Towards a Practical Approach.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing, pages 305-308
Copyright
c
SciTePress

theoretical framework of the perceived reality used
by the approach), Perspective (chosen approach to
handle the perceived reality), Focus (the problem
being addressed), Knowledge concept (definition of
knowledge within the research context) and Basic
Elements (KM elements/dimensions considered in
the definition of the proposed solution).
The proposed models and techniques in the
literature were based on concepts from one of the
two paradigms: 1) cartesian: the approaches based
on the Cartesian paradigm consider as main goal the
fragmentation of knowledge into objects or
knowledge items possible to be stored in databases
and, as such, valid knowledge is what is stored in the
organizational memory (Xie et al, 2006) (Wang et
al, 2002) (Andersson et al, 2005) (Heravizadeh and
Edmond, 2008) (Luo et al, 2008); 2) holistic
approaches which have the perception that the
process of knowing is more important than what was
learned, meaning that the exploitation of the
organizational potential in developing new
capabilities for acquiring knowledge is more
important than the knowledge acquired (Merali,
2000) (Lin, 2007) (Bhatt, 2001) (Forzi and Peters,
2005) (Wyssusek et al, 2001) (Sunassee and Sewry,
2003) (Papavassiliou and Mentzas, 2003)
(Vanhoenacker et al, 1999) (Li et al, 2004) (Bettoni
and Schneider, 2003) (Swain and Ekionea, 2008)
(Greiner et al, 2007) (Maier and Remus, 2003).
Analyzing the perspectives, it is possible to
identify two well-defined groups: 1) human-oriented
(social-cultural): the human-oriented approaches are
related to personalization strategy, in which the
managed knowledge is inside people’s heads and, as
such, the enhancement of communication, training,
knowledge sharing and socialization between
employees become the KM goals (Hansen et al,
1999) (Maier and Remus, 2003) (Jasimuddin, 2008)
(Merali, 2000) (Wyssusek et al, 2001) (Bettoni and
Schneider, 2003); 2) technology-oriented
(technocratic): are related to the codification
strategy, in which knowledge can be separated from
the person and the objectives of KM entail the
documentation of knowledge, development of
databases and knowledge capture (Hansen et al,
1999) (Maier and Remus, 2003) (Jasimuddin, 2008)
(Xie et al, 2006) (Wang et al, 2002) (Andersson et
al, 2005) (Heravizadeh and Edmond, 2008) (Luo et
al, 2008).
However, a third perspective, the process-
oriented, is beginning to emerge on the literature. In
this case, the organization is seen as an interrelated
chain of events in which everything exists in relation
(Nonaka et al, 2008) (Maier and Remus, 2003)
(Bhatt, 2001) (Lin, 2007) (Forzi and Peters, 2005)
(Papavassiliou and Mentzas, 2003) (Vanhoenacker
et al, 1999) (Sunassee and Sewry, 2003) (Li et al,
2004) (Swain and Ekionea, 2008) (Greiner et al,
2007).
About focus, it was possible to define seven
groups of problems discussed: Aligning KM and
Business Strategy (Sunassee and Sewry, 2003)
(Papavassiliou and Mentzas, 2003) (Swain and
Ekionea, 2008) (Greiner et al, 2007) (Maier and
Remus, 2003), Handling Contextual Knowledge
(Andersson et al, 2005) (Heravizadeh and Edmond,
2008), Handling collaboration and knowledge
sharing (Vanhoenacker et al, 1999) (Xie et al, 2006)
(Wang et al, 2002) Handling the learning process
(Merali, 2000) (Wyssusek et al, 2001) (Li et al,
2004), Handling the evolution of KM through time
(Lin, 2007), Integrating KM techniques and factors
(Forzi and Peters, 2005) (Bhatt, 2001) and
Identifying KM constructs (Bettoni and Schneider,
2003) (Nifco, 2005).
Within each analyzed proposals, several concepts
of knowledge are used. However, two major
categories can be observed: 1) discrete quantifiable
objects: closely related to the Cartesian paradigm,
the knowledge concept as quantifiable objects takes
into consideration that knowledge is something
which can be divided into different types/categories
and/or stored in databases, and valid knowledge is
what is stored in the organizational memory. This
concept tends to be used by technological
approaches of KM, in which the storage in best
practice repositories became the central concern
(Papavassiliou and Mentzas, 2003) (Andersson et al,
2005) (Heravizadeh and Edmond, 2008) (Luo et al,
2008) (Li et al, 2004) (Xie et al, 2006) (Wang et al,
2002); 2) continuum of a learning process: opposed
to the mechanistic conceptualization of knowledge is
the perception of the process of knowledge creation
and transformation through socialization and
learning between individuals. In this case, it is not
possible to divide knowledge, and it is inherent, to
the people involved, and it depends on the context of
each one of these (Forzi and Peters, 2005)
(Wyssusek et al, 2001) (Vanhoenacker et al, 1999)
(Bettoni and Schneider, 2003) (Bhatt, 2001) (Merali,
2000) (Maier and Remus, 2003).
All of the analyzed approaches possess a set of
basic elements which together, define the proposed
solution. These elements are the KM dimensions, the
key entities considered in the proposed solutions. It
was possible to identify elements such as: People,
Groups, Projects, Organization, IT, Culture, Process,
Techniques, etc., which relate in different ways,
depending on the perspective and focus used.
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
306
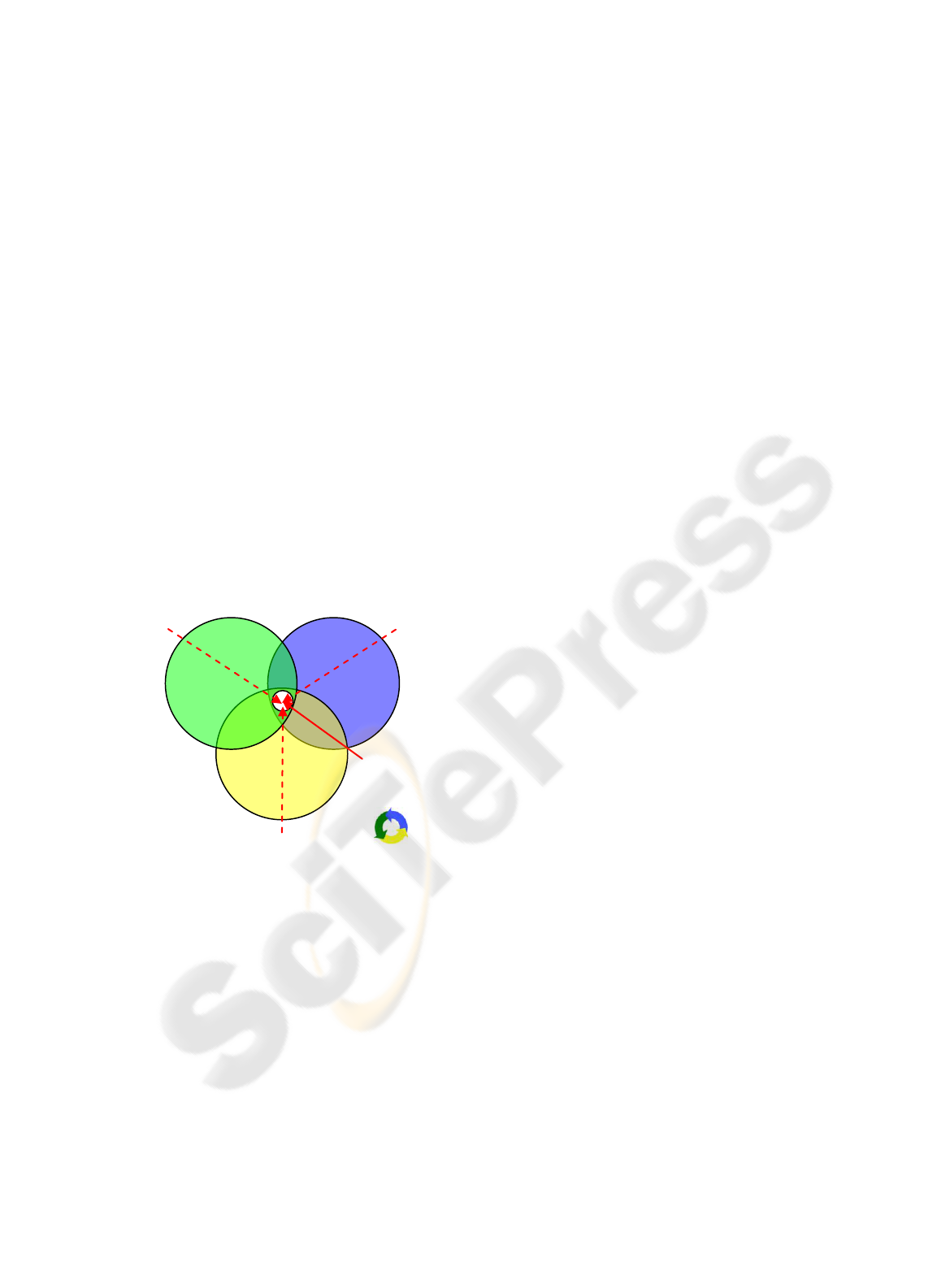
3 HOLISTIC MODEL
This work argues that it is possible to define a KM
implementation methodology following a holistic
paradigm and providing guidelines for obtaining
KM requirements in organizations. From the
literature review, it was possible to identify a trend
toward considering, at some level, People,
Organization and Context as basic elements in the
KM approaches. In the proposed model, Figure 1,
the elements People and Organization are translated
into broader concepts as Individual and Groups; the
element Mission was added to represent the sense of
purpose, and their intersection defines the Context.
The knowledge creator (the person) possesses
values, beliefs and needs that dictate the
organizational dynamics. The individual is able to
present new insights regarding a given subject to the
context and, create new knowledge. This knowledge
emerges from the person’s past experience, which
dictates who he is and how he relates to the world
(Nonaka et al, 2008).
Figure 1: KM Holistic Model
Those individuals interact with each other in a
non-deterministic manner creating what can be
understood as social networks. The element
“Groups” in the model represents this relationship
among individuals and the awareness they have
regarding the environment they belong to (Nifco,
2005). The intersection between the elements
“Individual” and “Groups” represent the
understanding that the organization/group has a set
of characteristics that only rise from interactions..
Both “Individual” and “Groups” are guided by a
set of objectives and motivations (“Mission”)
dictating context in the organization. It is the
organization’s vision and values which provide
meaning to each action and an outlook of the future
(Nifco, 2005) (Nonaka et al, 2008). The element
“Mission” represents the need for analyzing each
action/decision based on which context it was taken,
meaning the process of questioning “why?” and
understanding a given reality.
These elements in the proposed model should be
analyzed in an integrated and holistic fashion, and
the alignment between them should become the
central objective of the KM approach. Based on
Nonaka’s theory, KM efficacy depends on a
capacitating context (Ba), a shared environment
enabling new relationships, which can be real,
virtual, mental, or all of these (Nonaka et al, 2008).
As such, KM is a never-ending process in which
an individual deeply reflects on his past experiences,
shares his experiences with the group and evolves by
becoming a new self (Nonaka et al, 2008) through
the interactions with the organization, and defining a
new meaning to its actions.
Considering that the Ba comprises the
intersection of groups, individuals and mission, it is
argued that business models (Sharp and McDermott,
2009) can be a viable perspective to be used in order
to help the analysis of the Ba within an organization.
Business models are approaches for understanding
organizations regarding their business objectives,
processes and participants. From business models, it
is possible to observe the different facets of the
holistic model in a way so as to help the
identification of knowledge management
requirements aligned to the business strategy.
4 CONCLUSIONS
KM is usually discussed through abstract
considerations at a conceptual level. In addition,
when implemented, this is done in a non-systematic
manner tending to a technocratic or social
perspective, leading to initiative failure.
A KM holistic model was proposed. However,
the model alone does not provide the guidance
needed, demanding a set of methodological steps in
order to aid the organizations which need to and are
interested in, implementing a KM solution.
As such, three major phases were proposed for
an initial discussion towards the definition of a
systematics for KM implementation: collection of
expectation (the definition of KM objectives inside
the organization, as well as the process of defining
the expectation towards the KM initiative);
establishment of a common context (analysis and
Awareness
– Present –
Meaning
– Future –
Knowledge
– Past –
Groups
(collaboration)
Individual
(individuation)
Mission
(contextualization)
“Capacitating
Context (Ba)”
Reflect
Evolve
Share
KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT IMPLEMENTATION METHODOLOGY - Towards a Practical Approach
307

understanding of the organizational context using
the business process as an integrative/holistic
perspective); Identification of problems
(identification of knowledge gaps between what is
expected and what actually happens)
The process-oriented perspective was chosen,
focusing on the KM requirements elicitation which
enables alignment with the business strategy. As
future work, the need is outlined for detailing the
systematics and the conduction of an exploratory
study in order to observe its preliminary results.
REFERENCES
Andersson B., Bider I., Perjons E., 2005. “Business
Process Support as a Basis for Computerized
Knowledge Management”, LNCS 3782, Springer, pp.
542 - 553.
Bettoni, M.C.; Schneider, S., 2003. “The Essence of
Knowledge Management: A constructivist approach”.
In ICEIS 2003, Fifth Intern. Conf. on Enterprise
Information Systems, Vol. 2, 191-196
Bhatt, G. D., 2001. “Knowledge Management in
organizations: examining the interaction between
technologies, techniques, and people”, Journal of
Knowledge Management, Vol. 5, Issue 1, pp.68-75.
Forzi, T.; Peters, M., 2005. “A methodology and a toolkit
that integrate technological, organizational, and
human factors to design KM within knowledge-
intensive networks”, Journal of Universal Computer
Science, vol. 11, no.4, pp. 495-525.
Greiner, M. E.; Böhmann, T.; Krcmar, H., 2007. “A
strategy for knowledge management”, In Journal of
Knowledge Management, vol. 11, no. 6, pp.3-15.
Hansen, M. T.; Nohria, N.; Tierney, T., 1999. “What’s
your strategy for managing knowledge?”, Harvard
Business Review, Vol. 77 Issue 2, pp.106-117.
Heravizadeh, M.; Edmond, D., 2008. “Making Workflows
Context-aware: A Way to Support Knowledge-
intensive Tasks”, In APCCM’08, 5th Asia-Pacific
Conference on Conceptual Modeling, v. 79, p.79-88.
Ing, D., 1999. “Studying the Sense & Respond Model for
Designing Adaptive Enterprises and the Influence of
Russell Ackoff’s System of Thinking”, In Russell.
Ackoff Conference, Villanova University, p. 2-10.
Jasimuddin, S. M., 2008. “A holistic view of knowledge
management”, Journal of Knowledge Management,
vol. 12, no.2, pp.57-66.
Kalkan, V. D., 2008. “An overall view of knowledge
management challenges for global business”,
Business Process Management J., v.14, n.3, p390-400.
Kitchenham, B., 2004. “Procedures for Performing
Systematic Reviews”, Joint Technical Report Software
Engineering Group, Keele University, Australia.
Li, M.; Gao, F.; Kameoka, A., 2004. “Enhancing
creativity and imagination in process management:
combinative use of systems methods and knowledge
management tools”, In IEMC’04, 2004 International
Engineering Management Conference, v.2, p.505-509.
Lin, H., 2007. “A stage model of knowledge management:
an empirical investigation of process and
effectiveness”, J. of Info. Science, 33(6), p643-659.
Luo, T.; Xiong, Z.; Fang, Y., 2008. “A framework of
knowledge management for mass customization
internet-based”. In ISISE'08, International
Symposium on Information Science and Engineering,
v.2, p.462-466.
Maier, R.; Remus, U., 2003. “Implementing process-
oriented knowledge management strategies”. Journal
of Knowledge Management, vol. 7, no. 4, pp. 62-74.
McAdam, R.; McCreedy, S., 1999. “A critical review of
knowledge management models”, The Learning
Organization, Vol. 6 Issue 3, pp. 91-100.
Merali, Y., 2000. “Individual and collective congruence in
the knowledge management process”, Journal of
Strategic Information Systems, Vol. 9 Issue 2/3, p213.
Nifco, N., 2005. “A conceptualization of knowledge
management practices through knowledge, awareness
and meaning”. The electronic Journal of Knowledge
Management, vol. 3, no. 1, pp.45-52.
Nonaka, I., Toyama, R., Hirata, T., 2008. “Managing flow:
a process theory of the knowledge-based firm”,
Palgrave Macmillan, New York.
Papavassiliou, G.; Mentzas, G., 2003. “Knowledge
Modeling in Weakly-Structured Business Processes”,
Journal of Knowledge Management, v.7, n. 2, p.18-33.
Sharp, A., McDermott, P., 2009. “Workflow modeling:
tools for process improvement and application
development”, Artech House, Second Edition.
Sunassee, N. N.; Sewry, D. A., 2003. “An Investigation of
Knowledge Management Implementation Strategies”,
In SAICSIT’03, vol. 47, pp.24-36, ACM.
Swain, D. E.; Ekionea, J. B., 2008. “A framework for
developing and aligning a knowledge management
strategy”, Journal of Information & Knowledge
Management, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 113-122.
Vanhoenacker, J., Bryant, A.; Dedene, G., 1999.
“Creating a knowledge management architecture for
business process change”,SIGCPR,pp.231-241, ACM.
Wang, C.; Chen, Y.; Chen, Y., 2002. “A distributed
knowledge model for collaborative engineering
knowledge management in allied concurrent
engineering”, In IEMC '02, 2002 IEEE International
Engineering Management Conference.
Wyssusek, B., Schwartz, M., Kremberg, B., 2001.
“Knowledge management – a sociopragmatic
approach”, In 2nd European Conference on
Knowledge Management, pp. 767–776.
Xie, X.; Zhang, W.; Xu, L., 2006. “A Description Model
to Support Knowledge Management”, In IMSCCS'06,
1st International Multi-Symposiums on Computer and
Computational Sciences.
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
308
