
APPLICATION OF LEAN SIX SIGMA METHODOLOGY TO
OPTIMIZATION PROCESSES OF DATA MANAGEMENT IN AN
EDUCATIONAL CONTEXT
Susana Falcão, Francisco Nunes and Alberto Carneiro
Universidade Autónoma de Lisboa, Rua de Santa Marta, 56, Lisboa, Portugal
Keywords: Lean Six Sigma, Information Systems, Education.
Abstract: This paper aims to contribute with some thoughts about database and information management in
Portuguese educational context, at the level of schools and supervisors schools, as well as about
transmission of information among them. We also emphasize the importance of definition and development
of standardized technology platforms in order to build and develop structures that ensure the interoperability
of information exchange and management among the various entities of an information system. In this paper
we suggest a methodology (Lean / Six Sigma) that combines the reduction of complexity of the process with
the improvement of reliability and efficiency.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper aims to contribute with some thoughts
about database and information management in
Portuguese educational context, at the level of
schools and supervisors schools, as well as about
transmission of information among them.
Presently, information technologies are
considered as an essential part of the modern
educational system. In educational institutions,
professionals of Information and Communication
Technologies (ICT) face many difficulties in
computer networks management because, generally
speaking, their use very limited resources (Pereira,
1998).
There are several issues that must be preserved
and treated with some care, including how to keep
systems running efficiently, how to guarantee
network security in accordance with security
policies, the implementation of easier processes and
how to ensure database functionality, which usually
is a difficult goal to achieve.
Is also emphasize the importance of definition
and development of standardized technology
platforms in order to build and develop structures
that ensure the interoperability of information
exchange and management among the various
entities of an information system.
The marching trend of the new economic order
has generated a new capsule of SIX SIGMA as a
unified approach to process excellence. The tests
reveal that it has transformed some of the most
successful companies in the world like Motorola,
GE etc. It is activated as an approach to aiming at
the target by changing the culture of a company,
involving everyone in the company, not just the
Black Belts and Green Belts (Guarraia, 2009).
2 PROJECT
Thus, the development of the project focused on
identifying ways and mechanisms to increase
efficiency and / or efficacy in database and
educational information management in order to:
• Increase the speed of treatment processes and
educational information management;
• Standardize the model of the information
report between schools and education
authorities;
• Reduce errors, avoid duplication of records
and minimize the area of data warehouse;
• Seek ways to integrate different platforms
and / or information systems;
309
Falcão S., Nunes F. and Carneiro A. (2009).
APPLICATION OF LEAN SIX SIGMA METHODOLOGY TO OPTIMIZATION PROCESSES OF DATA MANAGEMENT IN AN EDUCATIONAL CONTEXT.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing, pages 309-312
DOI: 10.5220/0002306603090312
Copyright
c
SciTePress

• Matching the skills that are required to
improve the process of managing data and
information in school (Harry & Schroeder,
1999).
3 METHODOLOGY
Taking into account the objectives of this project, it
was designed a methodology that combines the
reduction of complexity of the process with the
improvement of reliability and efficiency. Lean Six
Sigma is a methodology that combines tools for
efficient processes with the improvement of the
quality of services and is being applied successfully
in all manufacturing sectors and, more recently, in
services industries, because it combines the focus of
Lean - flow and speed - with the focus of Six Sigma
- variability and quality (George, 2002).
This project cover the importance of definition and
development of standardized technology platforms
in order to build and develop structures that ensure
the interoperability of information exchange and
management among the various educational entities
information systems.
For those that use the Six Sigma system there are
two major methodologies. They include DMADV -
used to create new processes or designs - and
DMAIC – used for existing business processes -
both inspired by Bill Smith and subsequent by
Edwards Deming who are considered the pioneers of
modern quality control.
DMAIC is useful in improving an existing business
process to reduce and eliminate defects and it is
normally defined as a set of practices that improve
efficiency. The DMAIC methodology includes five
steps including; Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve
and Control. Here is some information regarding
each step (Chau, 2009):
Define - The definition of the project/ assignment,
using process map, application area, desired
improvement, likely benefits etc. The importance
lies of having the chance of a high successful
delivery of better quality and saving costs in totality.
Here in the academic strata, the failures include the
definition of the problem in as an identity. The
others may include projects like real life problems
pertaining to “Distractions in the Class Room” for
example.
Measure - This involves the analyses of the process
to determine its present state and the future, as
obtained. The data collection is a well suited frame
for this.
Analyze - This involves the data analysis for
identification of parts of process which affect the
quality of the problem.
Improve - This adds to the process to find a
permanent solution to the problem. This may
involve better forecasting, better scheduling, better
procedures or better equipment, specifying, teaching
techniques, work environment for the teachers and
school campus quality life.
Control - Involves the process of closing the
problem by putting in the right procedures and
management statistics.
DMAIC
4 APPLICATION
The application of this methodology was designed in
two phases. In the first phase the characterization of
reference and definition of the metric are made and
the second phase consider the optimization of data
management and information entities (Pyzdek,
2003).
The first phase, which includes the first three
steps of the DMAIC methodology – Define,
Measure and analyze - makes a diagnostic analysis
which aims to characterize and measure the current
state of the main areas of data management and
information of each entity, namely:
• Exchange of information between the school
(directory board, teachers) and education
agencies that supervise schools;
• Structure of data and existing technologies in
the school;
• Internal processes for data and information
management in the school;
• Processes that support information exchange.
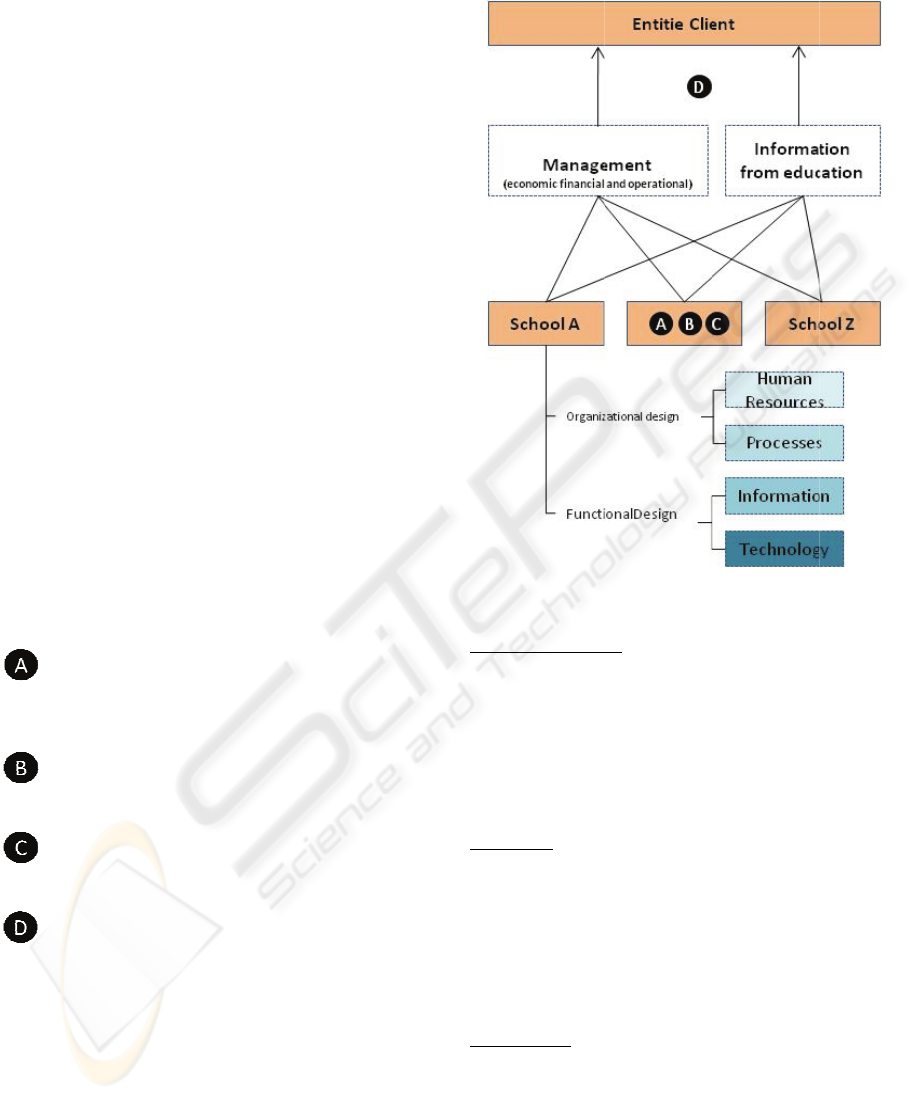
Subsequently, based on the relational schema of
the entities involved, flow maps and the results
obtained in measuring the processes of data
management and exchange of information, solutions
to major problems were identified at the level of
information technology, qualification of human
resources, processes, and information model.
In a second phase, which adds the two final steps
of DMAIC - Implement and Control - the solutions
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
310
p
reviou
s
monitor
i
made.
T
(Chakra
v
• Impro
v
• Devel
o
conve
r
betwe
e
• Imple
m
operat
i
infor
m
author
i
• Establ
i
imple
m
• Mini
m
• Perfor
m
• Conti
n
Propo
s
The pro
definitio
Dimensi
Object
i
I
m
efficien
c
instituti
o
En
s
manage
m
En
s
manage
m
Sta
informa
t
s
ly identifie
d
i
ng of impro
v
T
he solutio
n
v
orty 2009):
v
ement of dat
a
o
pment of
r
gence for t
h
e
n schools an
d
m
en
t
ation of
p
i
onalize a fra
m
m
ation betw
e
i
ty boards;
i
shment of
m
entation of
d
m
izing errors;
m
ance impro
v
n
uous improv
e
s
ed Frame
w
posed frame
n, an In
fo
ons of analys
i
i
ves
m
plement the
c
y in line w
o
ns.
s
ure more ap
p
m
ent in the E
n
s
ure the o
p
m
ent for the S
ndardize th
e
t
ion between
s
d
are imple
m
v
ements aris
i
n
s of this
a
a
structures e
x
methodolo
h
e exchang
e
d
regulating a
u
pr
ocesses tha
t
m
ework for
r
e
en educati
o
p
rocedures
t
d
ata managem
v
emen
t
;
e
ment of the s
y
w
or
k
work inclu
d
fo
rmation
M
i
s.
most exped
i
ith best pra
c
p
ropriate skil
l
n
tity-School.
p
erational
m
chool organi
z
e
format f
o
s
chools and E
n
m
ented, and
i
ng from the
m
a
pproach inc
x
is
t
ing in sch
o
gies for
e
of inform
a
u
thority;
t
should enab
l
r
apid exchan
g
o
n entities
t
hat support
en
t
processes
;
y
ste
m
.
d
es the objec
t
M
odel and
i
tious and gr
e
c
tices from
o
l
s for inform
a
m
odels of
z
ation.
o
r reporting
n
tities-Client
s
the
m
is
lude
o
ols;
fas
t
a
tion
l
e to
g
e of
and
the
;
t
ives
the
e
ater
o
ther
a
tion
data
of
s
.
M
o
Di
m
Hu
m
• I
d
I
n
•
Q
i
n
• I
d
w
Pr
o
• I
d
r
e
pr
•
D
a
s
s
y
Inf
o
• I
d
• C
• I
d
o
del Inform
a
m
ensions of
m
an Resourc
e
d
entification
o
n
formation m
a
Q
ualifications
n
formation of
d
entification
o
w
ith extra-and
o
cesses:
d
entification
o
e
sponsibility
r
ocesses of th
e
D
esign proces
s
s
sets, identif
y
y
stems suppo
r
o
rmation:
d
entify the da
t
haracteristics
operational);
d
entification
information (
a
tion
Analysis
e
s:
o
f roles and re
a
nagement;
and expe
r
the entity;
o
f entities r
e
intra-school;
o
f develop
e
in support
p
e
educational
s
es to develo
p
y
ing those re
s
r
t and inform
a
t
a kind and /
o
of informati
o
of require
m
history).
sponsibilities
r
ience in
e
sponsible fo
e
d activities
a
p
rocesses an
d
system
p
over the lif
e
s
ponsible, in
f
a
tion flow.
o
r informatio
n
o
n (financial
o
m
ents for st
o
in the
IT and
r
contact
a
nd their
d
in the
e
cycle of
f
ormation
n
;
or
o
rage of
APPLICATION OF LEAN SIX SIGMA METHODOLOGY TO OPTIMIZATION PROCESSES OF DATA
MANAGEMENT IN AN EDUCATIONAL CONTEXT
311

Technology:
• Define objectives for the Information Systems
Model in order to support the Asset Management;
• Identification of applications that support
management (architecture application);
• Define workflow information for applications;
• Impact of storage requirements and workflow
information in technology infrastructure.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Summarizing, this methodology allows assessing the
weaknesses that exist within the information systems
in an educational environment, particularly
identifying and quantifying the main problems at the
level of data management and information
organization in school.
On the other hand, it allows overcoming the
more frequent difficulties in implementing this
methodology in the educational context, opening
ways for the creation of proposals to improve results
in this type of projects, ensuring their
implementation in similar contexts.
REFERENCES
Chakravorty, S.. (2009). Six Sigma programs: An
implementation model. International Journal of
Production Economics, 119(1), 1. Retrieved July 16,
2009, from ABI/INFORM Global. (Document ID:
1704883411).
Chau, K., Liu, S., & Ip, W.. (2009). Enhancing enterprise
information integration using Six Sigma. Total Quality
Management & Business Excellence, 20(5), 537.
Retrieved July 16, 2009, from ABI/INFORM Global.
(Document ID: 1743572121).
George, M. (2002), Lean Six Sigma, McGraw-Hill, ISBN:
0-07-141821-0.
Guarraia, P., Carey, G., Corbett, A., & Neuhaus, K..
(2009). Six Sigma - at your service. Business Strategy
Review, 20(2), 56-61. Retrieved July 16, 2009, from
ABI/INFORM Global. (Document ID: 1703249311).
Harry, M., and Schroeder, R. (1999), Six Sigma: The
breakthrough Management Strategy Revolutionizing
the World’s Top Corporations, Random House Audio,
ISBN-10 / ASIN: 0553456695, ISBN-13 / EAN:
9780553456691.
Pereira, J. Luís, (1998), Tecnologia de Bases de Dados,
FCA-Editora de Informática, ISBN: 9789727221431.
Pyzdek, Thomas (2003), The Six Sigma Handbook –
revised and expanded, McGraw-Hill, ISBN: 0-17-
141015-5.
KMIS 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Management and Information Sharing
312
