
ENHANCING ORGANIZATIONAL SELF AWARENESS
The As-is Enterprise Model Dynamic Updating Process
Nuno Castela and José Tribolet
CODE- INESC/INOV Rua Alves Redol, n.9, 1000-029 Lisbon, Portugal
Keywords: Enterprise Engineering, Enterprise Modelling, Knowledge Acquisition, Knowledge Sharing.
Abstract: The aim of the work described in this paper is to set up the as-is enterprise model continuous updating
process and to develop a supporting tool. The as-is enterprise model continuous updating process uses the
annotations as a mechanism to put the business actors “talking” with the representation of their activities,
either in action and interaction contexts, extracting knowledge and turning it explicit in the as-is enterprise
model . The business actors can act as active updaters of the as-is model through the comparison between
the modelled activities and the ongoing real executed activities. In this way, the enterprise model, which
represents several aspects and perspectives of organizations, can help building and maintaining
organizational self-awareness by adding knowledge to several organizational levels (individual, group,
process/functions). The process and the supporting tool are running in a governmental organization and the
results revealed that they could have an important role, not only in gathering the information needed to
update the model, but also allowing the opening communications channels to share and acquire additional
organizational knowledge.
1 INTRODUCTION
The enterprise model can help building
organizational self-awareness, adding knowledge to
several organizational levels. In order to achieve this
goal, the model must be an updated, trustworthy and
reliable representation of the business processes and
activities, allowing capturing, representing and
distributing the organizational knowledge. However,
the typical usage of the model, as support to some
organizational activities restricted in time, and the
recognized difficulty in maintaining it updated and
aligned with the reality, have prevented the
enterprise model to become a solid foundation to
support the organizational daily activities acting as
an organizational knowledge repository.
The work presented in this paper aims to establish a
process to automate and streamline the management
and updating of the business model in order to align
it with reality, using the annotation mechanism.
In the next section some of the contributions to this
work, in the areas of Organizational Engineering,
Organizational Knowledge and Annotations, are
described. Then, in section 3, the as-is enterprise
model dynamic updating process (called PROASIS)
is presented. The supporting tool to support the
process (called MAPA) is presented in the section 4
of the document. In the end, some results from the
use of the process and tool in a governmental
Portuguese organization are presented, as well as the
conclusions and future work.
2 RELATED WORK
The enterprise engineering bring together concepts,
methods and technologies which allows to
understand, model, develop and analyse all the
changing business aspects through the focus on the
relationships and dependencies among strategy,
processes and the supporting information systems
(Tribolet, 2005a).
Starting with the following definition of
organization (Tribolet 2005b), (Magalhães 2007):
"An organization is the result of the actions of their
human and non-human actors arranged in socio-
technical systems that are self-held through the
actions and interactions of its components, which
have, as a differentiator factor from the remaining
human creation, the fact that human agents are
involved in their formation", the organizational self
awareness concept appears naturally as the result of
315
Castela N. and Tribolet J. (2009).
ENHANCING ORGANIZATIONAL SELF AWARENESS - The As-is Enterprise Model Dynamic Updating Process.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development, pages 315-320
DOI: 10.5220/0002330503150320
Copyright
c
SciTePress

the complex intersection of various consciences -
individual, group, function and process - that guide
the current action in organizations, depending on the
contexts invoked.
The enterprise model allows communicating,
documenting and understanding the organizations
activity (Caetano 2004a). It has a key role in the
representation of knowledge and organizational self
awareness, and can act as a subject of conversation
to incorporate more knowledge in an iterative and
incremental way. This role can be accomplished due
to their intrinsic characteristics in representing
organizational actions and interactions aggregated in
processes which, in turn, are orchestrated sequences
of activities. The processes and activities are the
elements that contain all the information about how,
when and who does the work flow (Magalhães
2007). The primitive, the syntax and semantics of
the business model should allow simple and
immediate verification from each of the
organizational actors from the reality of their
continuing action, once the basis of representation
must be developed in concrete activities, because
this is the only truly verifiable and comprehensive
basis which organizational stakeholders can use
(Tribolet, 2005b).
The enterprise model have to accommodate different
points of view, the individual, the organizational,
and the views of various groups of actors grouped in
organizational contexts, but at the same time the
consistency of the whole model has be guaranteed,
allowing to represent the organizational self
awareness (Magalhães, 2008).
In the modern definition of organizational
knowledge, organizations and the organizational
knowledge it self are deeply related, since the theory
of knowledge creation is supported by the individual
interpersonal and group relationships and depends
on facilitation contexts (Magalhães, 2005).
The organizational learning area sees organizations
as cognitive entities, capable of reflecting on their
own actions, conducting experiments to study the
effects of alternative actions, consequently
modifying their actions (Boudreau, 1996).
Nonaka and Takeuchi (1995) define organizational
knowledge as "the ability of a company, as a whole,
to create knowledge, disseminate it through the
organization and incorporating it into products,
services and systems". The conversion of knowledge
(transition from tacit an individual knowledge into
explicit knowledge) allow it use and sharing by all,
serving to create new knowledge (Nonaka, 1995).
The organizational knowledge can reify (making it
explicit) through the enterprise models with the
contribution of the individual knowledge of all who
work in organizations, highlighting the need to
promote the use and usability of organizational
models. To achieve this it is necessary to know the
interaction dynamics between the different
organizational actors. The "context" concept is a key
element helping in filtering relevant information
among all business actors trough the management of
the interactions (Zacarias, 2004).
In general, the annotations are an addition of
information on a particular section of a document or
other entity providing information. Annotations have
specific uses in several distinct areas like biology,
law science, linguistics, programming languages,
modelling languages, to name a few.
The use of the annotation concept in this work is
based on its use to capture the reasons for the
changes that are normally made in software projects
caused by the implicit knowledge of development
teams (Becker-Kornstaedt 2002). The annotations
should capture the activities, resources (entities) and
the context involved (flows). The continuous
improvement of processes requires that the
experience is captured to be continuously
incorporated into business processes and continually
portrayed in the as-is model. The systematic capture
and storage in the context where the experience was
captured has three major benefits (Becker-
Kornstaedt 2002): the experience gained can become
explicit, the experience may be incorporated in the
description of the process and the analysis of the
experience can be reused in other processes for
process improving.
3 PROASIS
The idea explored by defining the as-is enterprise
model dynamic updating process (PROASIS) is
based on the analysis of misalignments between the
distributed model and reality.
3.1 Key Ideas for Updating the
Enterprise Model
The updating process is executed by the people
(organizational actors or agents) who perform the
activities that compose the organizational processes,
using the annotation mechanism.
The annotations allow making proposals for
correcting the model (corrective maintenance),
capture changes in action or interaction contexts
(adaptive maintenance), making free comments that
could anticipate problems (preventive maintenance)
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
316

Figure 1: Actors and contexts participating in the as-is model dynamic updating process.
and promoting process continuous improvement
(perfective maintenance).
At the individual execution level, the actors have a
view, the APV (Activity Personal View) that relates
to their work with the entities that they normally
handle (which may be informational, material, IS
/IT).
In the context of the PROASIS, the annotations can
be of three kinds:
– Individual annotation when it is done by an
organizational actor in the strict context of a
personal activity execution;
– Group annotation when it is done by an
organizational actor in the interaction context
with other organizational actors. In this case the
annotation is proposed by one of the actors
involved in the interaction and have to be revised
by all other participants of the group;
– Organizational Annotation, sub-divided in:
– Process annotation, when done by the owner
of the process. It may be spontaneous or may
be based on one or more annotations made
by the performers of activities that compose
the process;
– Functional annotation, when made by an
organizational unit responsible, where a
process or part of a process is executed. May
be spontaneous or be based on one or more
annotations made by the agents included in
their organizational unit;
The various contexts where annotation can be
applied are summarized in figure 1, where the types
of actors (roles) who can participate (executer, group
of executers (context interaction), process owner and
organizational unit responsible) are identified.
The as-is model dynamic updating process should:
– Define the mechanisms to gather annotations
– Define the workflows needed to capture,
analyse, revise and validate the information
contained in annotations
– Ensure the integrity relationship between all
elements of the architectural model presented in
figure 1 to ensure the model consistency and
integrity.
3.2 Gathering Annotations
In practice an annotation is considered an individual
annotation, if it is done in personal or individual
execution context, that is, if it is made on the activity
or on the informational entities and/or on supporting
information systems that are only used in personal
ENHANCING ORGANIZATIONAL SELF AWARENESS - The As-is Enterprise Model Dynamic Updating Process
317

space of individual execution (Castela, 2008). The
simplest case is illustrated in figure 2, where an
actor makes an annotation of an activity.
The annotation of an activity (see 1 in figure 2) is by
default a individual annotation (annotation made in
the individual context of the activity execution), but
it can be made to the flow between activities (see 2
in figure 2) that precede or succeed the core activity
shown (X1), but in this case it will only be
considered as individual annotation if the activity
that precedes or succeeds the core activity are also
performed by the same actor. If, for example, X2 is
an activity performed by another actor and if the
actor 1 makes an annotation to the activity flow from
X1 to X2, this will be considered a group annotation
in the interaction context (see interaction context in
figure 1). Similarly, if the annotation is done on an
informational entity considered "private" the actor
(an informational entity produced and consumed
exclusively in the actor personal context of
execution), this will be considered a individual
annotation, but if the informational entity is
produced or consumed by another activity
performed by another actor, the annotation will be
considered a group annotation (for example, the
annotation made to the informational entity IE1,
which is consumed by the activity X3 performed by
another actor (see interaction context in figure 1). In
the context presented in figure 2, the actor 1 can
make an annotation on the information system (see 4
in figure 2). This annotation is considered an
individual annotation if the system in question is
only used in this activity, or may be considered a
group annotation if the information system supports
other activities in the organization. If an annotation
is made on the organizational unit by the responsible
of the unit, it is considered a functional annotation.
If an annotation is made on the business process
level by the owner of the business process, it is
considered a process annotation.
3.3 Workflows for Annotation,
Revision, Approval and Updating
The PROASIS can be automated through the
implementation of a set of workflows defined to
ensure the capture, categorization, contextualization,
validation, approval and incorporation of
annotations in the model, ensuring communication
between the various actors involved.
The process has a set of activities that can have
several typical flows, as many the types of
annotations. Figure 3 shows the example of
workflow initiated by the individual annotation
gathered in the personal action context.
Figure 2: Personal action context.
In this context, the actor sees their activities in
organizational model, and can make an annotation to
the modelling elements in the individual execution
context. To choose the element (modelling) it will be
necessary to categorize the annotation and write a
comment.
After creating the annotation, which is pegged to the
modelling element of the as-is model and to the
actor who made it, there will be a verification to
discover if there are other actors performing the
same activity. If any, they will be notified and
receive the original annotation to be reviewed. The
review should be indexed to the original annotation,
and contains a descriptive text field and a checkbox
to agree or disagree with the original annotation.
Note that all the actors involved at this stage receive
the original annotation, as well all the revisions that
are being made, so (and this include the actor who
produced the original notation) they can make
revisions to add comments to the original
annotation, providing a discussion mechanism
between various stakeholders at this level.
After some time pre-set, the set formed by the
original annotation and the reviews of other actors
that perform the same activities in the organization,
is "sent" to either the organizational unit responsible
and owner of the process (if any), which will have a
pre-defined time to conduct the approval of
individual annotations. These two organizational
actors, after analysing the annotations and the
reviews, must approve or reject the goals of the
annotations, and may re-categorize the annotation
and/or clarify it by inserting additional text.
The consequences of the annotations are
incorporated in the enterprise model, only if there
was a joint approval from the organizational unit
responsible and from the business process owner.
The actors engaged in the approval stage could use
the approval pre-set time to establish a conversation.
If the annotation is not approved by any one of the
actors engaged in the approval stage, the annotation
is considered nor approved.
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
318

Figure 3: Workflow initiated by individual annotation (the personal action context).
The result of the approval will be distributed to all
actors participating in this process (annotation,
review, approval) that will be notified by the
modeller, so the proposed changes are published by
distributing the as-is model updated with the
annotation attached to the modelling elements
involved. If the annotation is rejected, there are no
changes to the model, but the annotation (with the
correspondent reviews and approvals) is distributed
to all stakeholders involved.
Others workflows are considered, differing mainly
by the context where the annotation is made:
– Annotation initiated in the interaction context
(group annotation).
– Annotation made in the organizational context
(process or functional annotation).
Table 1 presents the organizational roles involved in
the process of annotation, review and approval for
each of the modelling elements that can be
annotated:
Table 1: Organizational participating roles.
Model Elements Annotation Revision Approval
Activities,
flows, IE and IS
Executers (E) E PO and
OUC
Processes Process owner
(PO)
PO and
OUC
PO and
OUC
Organ. Units Org. Unit
chief (OUC)
PO and
OUC
PO and
OUC
4 THE MAPA TOOL
To support PROASIS, a tool was developed and
named MAPA (Monitoring and Annotation of
Processes and Activities) with the following general
requirements:
– Annotations, revisions and validations edition:
– The actors need support to make annotations
in the context where the experience is
gained. Thus, a system allowing the creation,
modification and deletion of annotations by
users must be developed.
– Different levels of granularity:
– Should be possible to annotate any object in
the process model.
– Access rights:
– To protect the annotations authors, different
levels of access rights should be supported to
ensure the privacy.
– Mapping annotations to entities:
– For each annotation is crucial to know to
which object it is attached. A mechanism
relating annotations and objects should be
developed.
– Enterprise model integrity assurance:
– Even if each view only represents the vision
of a part of the organization, it should be
possible to represent the whole organization
through the aggregation of the several parts,
ensuring integrity through the use of a
relational database.
The tool developed aims to capture the changes
proposed by the actors to the organizational model
through the implementation of workflows involving
analysis and annotation of the modelling and
subsequent annotations review and approval. The
main view of the tool (see diagram in figure 4)
provide to the activity executers a view to the APV
diagrams (Personal View Activity) which aggregate
the activity and its context (documents used and
ENHANCING ORGANIZATIONAL SELF AWARENESS - The As-is Enterprise Model Dynamic Updating Process
319
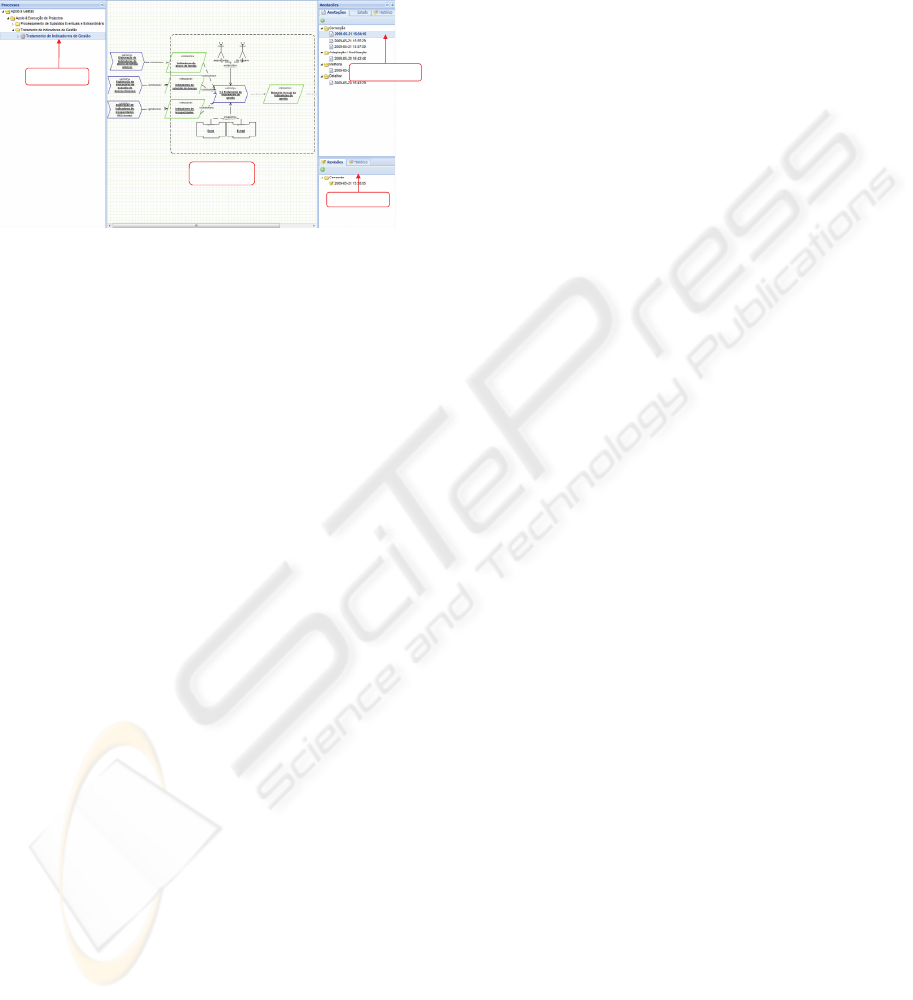
produced, information systems, previous and
subsequent activities, annotations , etc.). This view
will allow the access to services indexed by the
modelling elements (software service and user
manuals, helpdesk, etc.) in the needed context,
promoting the tool usage.
Diagram (APV)
Selected activity
Sel ected annotation
Revision
Figure 4: MAPA screenshot.
5 THE CASE STUDY
The purpose of this case study is to apply the MAPA
tool to the Social Security District Centre of Castelo
Branco (CDSSCB) supporting the as-is enterprise
model updating process (PROASIS) trough the
stakeholders involvement, doing annotations, and
then reviewing and approving them in order to
update the distributed model. The CDSSCB is part
of the Portuguese Institute of Social Security. The
tool is already running in the CDSSCB’s Centre for
Management Support, which is divided in 4 teams:
Training, Planning, Infrastructure Support and
District Inter-speakers.
The figure 4 shows one Activity Personal View in
the case study scope.
6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The tool to support the as-is enterprise model
dynamic updating is currently being used in a
governmental Portuguese organization, where the
actors are now making the annotations and reviews.
The available results indicate that initially the actors
mostly made annotations as corrections to the
distributed model, allowing and promoting an
opening conversation about the operation procedures
by the executers of the activities. The tool is been
used also to propose some improvements to the
work practices by the activities executors.
The introduction of the tool in a real organization
revealed that it could have an important role not only
in gathering the information needed to update the
model, but also in opening a communication
channel, sharing and gathering knowledge about the
activities of the organization.
The tool is being improved to allow the direct
edition of the APV diagrams, and to incorporate the
modeller area to edit, redesign and distribute the as-
is model.
REFERENCES
Becker-Kornstaedt, U. and Roman Reinert (2002), A
Concept to Support Process Model Maintenance
through Systematic Experience Capture, SEKE ’02,
July 15-19, Ischia, Italy.
Boudreau, M-C., Robey, D. (1996), Coping with
contradictions in business process re-engineering,
Information Technology & People, Vol.9 No4.
Caetano A., Silva A., Tribolet J, (2004), Object-Oriented
Business Process Modeling with Roles. 7th ISIM,
Czech Republic, 2004.
Castela, N., Tribolet, J.M. (2008): As-Is Continuous
Representation in Organizational Engineering, 10th
ICEIS (3-1), Barcelona, Spain, 2008.
Magalhães, R. “Fundamentos da Gestão do Conhecimento
Organizacional”, Edições Sílabo, 2005
Magalhães, R, Tribolet, J. (2007): Engenharia
Organizacional: das partes ao todo e do todo às partes
na dialéctica entre pessoas e sistemas. Capítulo no
livro “Ventos de Mudança”, editora Fundo de Cultura,
Brasil.
Magalhães, R., Sousa, P., Tribolet, J., (2008) The Role of
Business Processes and Enterprise Architectures in the
Development of Organizational Self-Awareness,
Polytechnical Studies Review, Vol VI, nº 9.
Nonaka, I. & Takeuchi, H., “The Knowledge-Creating
Company”, Oxford University Press, 1995
Oinas-Kukkonen, H. (2005), Towards evaluating
knowledge management through the 7C Model,
Proceedings of ECITE ’05, Turku, Finland.
Tribolet J., Winter R., Caetano A., (2005a) “Editorial
Message: Special Track on Organizational
Engineering”, ACM-SAC, Santa Fe, New Mexico,
2005.
Tribolet, J. (2005b), in Sistemas de Informação
Organizacionais, Chapter "Organizações, Pessoas,
Processos e Conhecimento: Da Reificação do Ser
Humano como Componente do Conhecimento à
"Consciência de Si" Organizacional", 2005, Edições
Sílabo - Ed. L. Amaral, 2005
Zacarias, M, Pinto, S. and Tribolet, J., ZACARIAS, Redes
de conhecimento em engenharia organizacional: o
imperativo dos contextos de acção, Cadernos BAD,
Lisboa, N.1 (2004), p.6-23.
KEOD 2009 - International Conference on Knowledge Engineering and Ontology Development
320
