
ASSESSMENT OF NOISE IMPACT IN SAMPLE
ENTROPY FOR THE NON-INVASIVE ORGANIZATION
ESTIMATION OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
Ra´ul Alcaraz
Innovation in Bioengineering Research Group, University of Castilla-La Mancha, Cuenca, Spain
Jos´e Joaqu´ın Rieta
Biomedical Synergy, Electronic Engineering Dept., Universidad Polit´ecnica de Valencia, Spain
Keywords:
Atrial Fibrillation, Electrocardiogram, Organization Estimation, Sample Entropy, Noise Effect.
Abstract:
In recent studies, Sample Entropy (SampEn) has demonstrated that can be a very promising non-linear index
to assess atrial fibrillation (AF) organization from surface ECG recordings. However, non-linear regularity
metrics are notably sensitive to noise. Thereby, in the present work, the effect that noise provokes in AF or-
ganization estimation based on SampEn is analyzed. Given that AF organization was estimated by computing
SampEn over the atrial activity (AA) signal, to evaluate the noise impact on AA regularity, 25 synthetic signals
with different organization degrees were generated following a published model. Noise coming from real ECG
recordings with different energy levels was added to the synthesized AA signals to obtain different signal to
noise ratios (SNR). Results showed that SampEn, i.e., the AA irregularity, increased with noise, thus hiding
the differences between organized and disorganized recordings. Precisely, in the presence of noise, SampEn
values were increased, in average, by factors of 1.64, 4.46, 9.46 and 14.23 for SNRs of 24, 15, 9 and 3 dB,
respectively. As a conclusion, a successful AF organization evaluation via SampEn requires a proper noise
reduction in the AA signal.
1 INTRODUCTION
Non-linear analysis metrics are valuable in the as-
sessment of physiological time series, because ”hid-
den information” related to underlying mechanisms
can be sometimes obtained (Pincus and Goldberger,
1994; Richman and Moorman, 2000). To date, a
high amount of non-linear complexity measures ex-
ists, such as dimensions, Lyapunov exponents and
entropies. However, their computation is frequently
confronted with the problem of insufficient number
of data points (Chen et al., 2009). Additionally, most
dimension and entropy definitions present application
limitations associated to real world time series, since
all recorded data are, to a certain degree, contami-
nated by noise. In this respect, a 2% noise is seri-
ous enough to prevent accurate estimation (Yu et al.,
2000).
Recently, a method based on sample entropy
(SampEn) has been proposed to estimate organization
of atrial fibrillation (AF) (Alcaraz and Rieta, 2009),
which is the most common cardiac arrhythmia in clin-
ical practice and whose onset and termination mech-
anisms are still unknown (Fuster et al., 2006). The
study of AF organization is a key aspect in the ar-
rhythmia’s knowledge, because it provides informa-
tion on the number of active reentries (Sih et al., 1999;
Everett et al., 2001), which maintain and can perpet-
uate AF. Thereby, in the present work, the noise ef-
fect on this method, which could be useful to predict
spontaneous AF termination or the result of aggres-
sive therapies, such as electrical cardioversion or ab-
lation, is exhaustively analyzed.
2 MATERIALS
Given that AF organization has to be estimated by
computing SampEn over the atrial activity (AA) sig-
nal (Alcaraz and Rieta, 2009) and because AA with
393
Alcaraz R. and Joaquín Rieta J. (2010).
ASSESSMENT OF NOISE IMPACT IN SAMPLE ENTROPY FOR THE NON-INVASIVE ORGANIZATION ESTIMATION OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 393-396
DOI: 10.5220/0002692103930396
Copyright
c
SciTePress

no noise or ventricular residues cannot be obtained
from real ECG recordings, 25 one minute synthetic
AA signals were generated. Thus, the noise effect on
AA organization estimation could be evaluated. The
synthetic AA signals were obtained making use of the
model proposed by Stridh et al (Stridh and S¨ornmo,
2001). In this model, a sinusoid and M − 1 harmon-
ics are used to generate a sawtooth-like shape of AF.
The non-stationary behavior is created by introducing
a time-varying amplitude and cycle length of the saw-
tooth signal. In every lead of N samples in length, the
AA is modelled by:
y(n) = −
M
∑
i=1
a
i
(n)sin(iθ(n)), n = 1, . . . , N (1)
where the term a
i
(n) with the sawtooth amplitude, a,
the modulation peak amplitude, ∆a, and amplitude
modulation frequency, f
a
, is given by:
a
i
(n) =
2
iπ
a+ ∆asin2π
f
a
F
s
n
(2)
The fundamental frequency of the fibrillation wave-
form is assumed to vary around f
0
with a maximum
frequency deviation of ∆f and modulation frequency
given by f
f
. The phase, θ(n), is then given by:
θ(n) = 2π
f
0
F
s
n+
∆f
f
f
sin2π
f
f
F
s
n (3)
After several tests, the selected parameters were
∆f = 3 Hz, f
f
= 4 Hz, ∆a = 10µV, f
a
= 9 Hz and
F
s
= 1024 Hz in order to synthesize a signal as close
as possible to the real AA. In this respect, Figs. 1(a)
and (b) show a real AA signal obtained by applying
the averaged QRST cancellation technique and a syn-
thetic AA signal generated with the indicated param-
eters, respectively. Because of the typical AA fun-
damental frequency range is 3-9Hz (Bollmann et al.,
2006; Stridh et al., 2001), a fundamental frequency f
0
equal to 6 Hz was selected. In order to obtain differ-
ent regularities, the number of harmonics M and their
amplitude a were varied, such that, a higher num-
ber of harmonics with lower amplitude will gener-
ate a more irregular AA. In this way, M and a were
randomly selected between 5 and 15 and between
6 and 18 µV, respectively. Hence, the most irreg-
ular AA signal presented 15 harmonics with 6 µV
of amplitude. The set of AA signals with different
regularities were used to evaluate if the noise effect
was regularity-dependent. Finally, available noise
in Physionet (Goldberger et al., 2000) coming from
real ECG recordings with different energy levels was
added to the synthesized AA signals. Concretely,
this noise was the recorded signal when the patient
front-end is disconnected from the skin electrodes. In
Figure 1: Comparison example between real and synthe-
sized AA signals depending on added noise.(a) Real AA
signal obtained from the ECG through averaged QRST can-
cellation technique. (b) Synthetic AA signal without noise.
(c) Synthetic AA signal with added noise and SNR of 15
dB. (d) Synthetic AA signal with added noise and SNR of 9
dB.
Figs. 1(c) and (d), a synthetic AA signal that has been
added to the described noise with two differentenergy
levels is shown.
3 METHODS
The 25 synthetic signals were used in order to evalu-
ate the noise impact on AA regularity. The same noise
signal was superimposed to all synthetic AA signals,
which were generated with different degrees of regu-
larity. Firstly, SampEn values of the AA signals with-
out noise were computed. Next, the noise recording
was weighed by different gain factors and added to
the synthetic signals in order to obtain different signal
to noise ratios (SNR). Finally, SampEn values of the
synthetic AA signals contaminated with noise were
calculated. This methodology allowed us to evaluate
the evolution of AA regularity estimation in the pres-
ence of noise.
The SNR of an ECG recording is normally lower
than 30 dB (Laguna and Sornmo, 2000). In addi-
tion, because of the real AA signal is obtained from
ECG recordings using ventricular activity cancella-
tion techniques, the SNR of an AA signal must be
lower than the SNR of an ECG signal. In fact, the
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
394
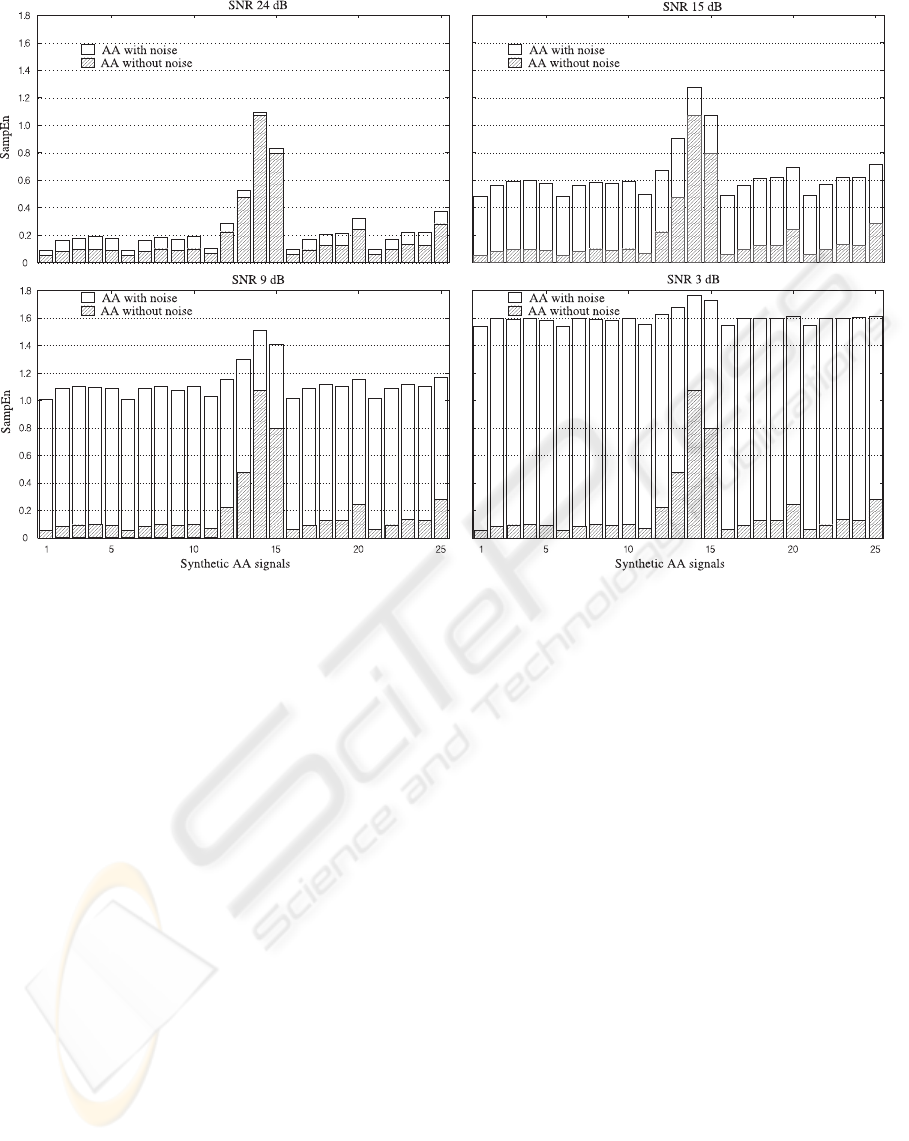
Figure 2: Each plot shows SampEn values of 25 synthetic noise-free AA signals stacked with their corresponding result when
SNR is 24, 15, 9, and 3 dB. The presence of noise produces a disorganization increase in the AA signals and reduces the
differences between initially organized and disorganized signals. Therefore, noise reduction is essential to assess successfully
AF organization with SampEn.
SNRs of the AA signals obtained from 50 real ECGs
analyzed in a previous work were within the 16.4–2.7
dB range (Nilsson et al., 2006). In the study, the SNR
is defined as the ratio between the mean of the funda-
mental and first harmonic power magnitudes and the
power magnitude of the background noise. Whereby,
AA signals with SNR of 24, 15, 9 and 3 dB were gen-
erated.
4 RESULTS
Fig. 2 shows the evaluation results of noise effect on
AA organization estimation via SampEn. As can be
seen, SampEn values for the 25 noise-free synthetic
AA signals are shown and increased with their corre-
sponding SampEn values for 24, 15, 9 and 3 dB SNR,
respectively. It can be observed that SampEn, i.e., the
AA irregularity, increases with noise, thus hiding the
differences between organized and disorganized ac-
tivities. Precisely, in the presence of noise, SampEn
values were increased, in average, by factors of 1.64,
4.46, 9.46 and 14.23 for SNRs of 24, 15, 9 and 3 dB,
respectively. In addition, the difference between the
two signals without noise that presented the highest
and lowest SampEn values was reduced by factors of
1.07, 1.29, 2.05 and 4.67 for the signals with SNRs of
24, 15, 9, and 3 dB, respectively.
We also tested the same experiment by adding
Gaussian noise instead of ECG noise to the synthe-
sized AA signals and results were very similar, hence,
they have been omitted. However, bearing this simi-
lar behavior in mind, any other kind of random and
non-deterministic contaminating signal should pro-
voke similar results of SampEn.
5 DISCUSSION AND
CONCLUSIONS
Results showed that the noise presence masks the dif-
ferences, evaluated with SampEn, between organized
and disorganized activities. Thereby, it could be con-
sidered that when AA is contaminated by noise or any
other undesired signal, the organization difference be-
tween AF episodes are considerably reduced. This
fact is crucial, for example, in the successful pre-
diction of paroxysmal AF termination. Considering
ASSESSMENT OF NOISE IMPACT IN SAMPLE ENTROPY FOR THE NON-INVASIVE ORGANIZATION
ESTIMATION OF ATRIAL FIBRILLATION
395

that the AA obtained from the ECG often presents
QRS residua and noise (Petrutiu et al., 2006), the ob-
tained results with synthetic AA signals can be used
to justify the poor discrimination outcome reported
by other groups when direct AA organization analy-
sis was applied (Nilsson et al., 2006).
Moreover, the results are also coherent with the
highly improved paroxysmal AF termination predic-
tion reached by applying SampEn to the fundamental
waveform associated to the AA (Alcaraz and Rieta,
2009), its wavelength being the inverse of the domi-
nant atrial frequency (DAF) (Holm et al., 1998). As
this signal is obtained by applying a selective filter-
ing to the AA centered on the DAF, most part of the
undesired contaminating signals are avoided. As a
consequence, to obtain a successful AF organization
assessment through SampEn, noise and nuisance in-
terferences in the AA signal should be considerably
reduced prior to the computation of the non-linear in-
dex.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the projects TEC2007-
64884 from the Spanish Ministry of Science and
Innovation, PII2C09-0224-5983 and PII1C09-0036-
3237 from Junta de Comunidades de Castilla La Man-
cha and PAID-05-08 from Universidad Polit´ecnica de
Valencia.
REFERENCES
Alcaraz, R. and Rieta, J. J. (2009). Sample entropy of the
main atrial wave predicts spontaneous termination of
paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Med Eng Phys, page
doi: 10.1016/j.medengphy.2009.05.002.
Bollmann, A., Husser, D., Mainardi, L., Lombardi, F., Lan-
gley, P., Murray, A., Rieta, J. J., Millet, J., Olsson,
S. B., Stridh, M., and S¨ornmo, L. (2006). Analysis of
surface electrocardiograms in atrial fibrillation: tech-
niques, research, and clinical applications. Europace,
8(11):911–926.
Chen, W., Zhuang, J., Yu, W., and Wang, Z. (2009). Mea-
suring complexity using FuzzyEn, ApEn, and Sam-
pEn. Med Eng Phys, 31(1):61–68.
Everett, T. H. t., Kok, L. C., Vaughn, R. H., Moorman, J. R.,
and Haines, D. E. (2001). Frequency domain algo-
rithm for quantifying atrial fibrillation organization to
increase defibrillation efficacy. IEEE Trans Biomed
Eng, 48(9):969–978.
Fuster, V., Ryd´en, L. E., Cannom, D. S., Crijns, H. J.,
Curtis, A. B., Ellenbogen, K. A., and et. al. (2006).
ACC/AHA/ESC 2006 guidelines for the management
of patients with atrial fibrillation: a report of the
American College of Cardiology/American Heart As-
sociation task force on practice guidelines and the
european society of cardiology committee for prac-
tice guidelines (writing committee to revise the 2001
guidelines for the management of patients with atrial
fibrillation): developed in collaboration with the eu-
ropean heart rhythm association and the heart rhythm
society. Circulation, 114(7):e257–e354.
Goldberger, A. L., Amaral, L. A., Glass, L., Hausdorff,
J. M., Ivanov, P. C., Mark, R. G., Mietus, J. E., Moody,
G. B., Peng, C. K., and Stanley, H. E. (2000). Phys-
iobank, physiotoolkit, and physionet: components of
a new research resource for complex physiologic sig-
nals. Circulation, 101(23):E215–E220.
Holm, M., Pehrson, S., Ingemansson, M., S¨ornmo, L., Jo-
hansson, R., Sandhall, L., Sunemark, M., Smideberg,
B., Olsson, C., and Olsson, S. B. (1998). Non-invasive
assessment of the atrial cycle length during atrial fib-
rillation in man: introducing, validating and illustrat-
ing a new ECG method. Cardiovasc Res, 38(1):69–81.
Laguna, P. and Sornmo, L. (2000). Sampling rate and the
estimation of ensemble variability for repetitive sig-
nals. Med Biol Eng Comput, 38(5):540–546.
Nilsson, F., Stridh, M., Bollmann, A., and S¨ornmo, L.
(2006). Predicting spontaneous termination of atrial
fibrillation using the surface ECG. Med Eng Phys,
28(8):802–808.
Petrutiu, S., Ng, J., Nijm, G. M., Al-Angari, H., Swiryn,
S., and Sahakian, A. V. (2006). Atrial fibrillation and
waveform characterization. A time domain perspec-
tive in the surface ECG. IEEE Eng Med Biol Mag,
25(6):24–30.
Pincus, S. M. and Goldberger, A. L. (1994). Physiological
time-series analysis: what does regularity quantify?
Am J Physiol, 266(4 Pt 2):H1643–H1656.
Richman, J. S. and Moorman, J. R. (2000). Physiological
time-series analysis using approximate entropy and
sample entropy. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol,
278(6):H2039–H2049.
Sih, H. J., Zipes, D. P., Berbari, E. J., and Olgin,
J. E. (1999). A high-temporal resolution algorithm
for quantifying organization during atrial fibrillation.
IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 46(4):440–450.
Stridh, M. and S¨ornmo, L. (2001). Spatiotemporal QRST
cancellation techniques for analysis of atrial fibrilla-
tion. IEEE Trans Biomed Eng, 48(1):105–111.
Stridh, M., S¨ornmo, L., Meurling, C. J., and Olsson, S. B.
(2001). Characterization of atrial fibrillation using
the surface ECG: time-dependent spectral properties.
IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng, 48(1):19–27.
Yu, Small, Harrison, and Diks (2000). Efficient implemen-
tation of the gaussian kernel algorithm in estimating
invariants and noise level from noisy time series data.
Phys Rev E Stat Phys Plasmas Fluids Relat Interdiscip
Topics, 61(4 Pt A):3750–3756.
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
396
