
AN INTEGRATED PHYSIOLOGICAL MODEL OF THE LUNG
MECHANICS AND GAS EXCHANGE USING ELECTRICAL
IMPEDANCE TOMOGRAPHY IN THE ANALYSIS OF
VENTILATION STRATEGIES IN ARDS PATIENTS
M. Denaï, M. Mahfouf, A. Wang, D. A. Linkens
Dept of Automatic Control, University of Sheffield, Mappin Street, Sheffield, U.K.
G. H. Mills
Dept of Critical Care, Anaesthesia and Operating Services, Northern General Hospital, Sheffield, U.K.
Keywords: Electrical Impedance Tomography, EIT, Medical imaging, Lung mechanics, Alveolus model, Pressure-
volume curve, Blood gas model, Mechanical ventilation, Dead-space, Shunt.
Abstract: Thoracic Electrical Impedance Tomography (EIT) is a non-invasive technique which attempts to reconstruct
a cross-sectional image of the internal spatial distribution of conductivity from electrical measurements
made by injecting small alternating currents via an electrode array placed on the surface of the thorax.
Because air is highly resistive to electric currents whereas fluids and blood are good conductors, it is
possible to detect changes in lungs air content with EIT enabling the assessment of ventilation distribution.
This paper presents a physiological model which integrates a previously developed gas exchange model
with a model of the lung mechanics. This model is combined with a two-dimensional (2D) finite element
mesh of the thorax to simulate EIT image reconstruction in patients with acute Respiratory Distress
Syndrome (ARDS) under mechanical ventilation. The model was able to track lung ventilation distribution
under various simulated ARDS conditions and ventilator settings.
1 INTRODUCTION
Mechanical ventilation is an essential component in
supportive therapy of patients with Acute
Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS): a
potentially severe form of respiratory failure.
Although, mechanical ventilation can be a lifesaving
intervention for many patients in the Intensive Care
Unit (ICU), it has been associated with potential
complications causing secondary lung damage
known as Ventilator-Induced Lung Injury (VILI)
(Tremblay and Slutsky, 2006). Selecting appropriate
ventilator settings can reduce the risk of VILI.
However, known bedside measures to guide the
clinician when adjusting mechanical ventilation to
provide adequate gas exchange whilst minimising
any adverse effects to the patient’s lungs are limited.
Current methods available for assessing the lung
function in mechanically ventilated patients include
arterial blood gas analysis and graphic waveforms
displayed on the ventilators (flow, pressure, volume
over time as well as airway pressure-volume
curves). However, these can give only an indication
of the overall lung function and fail to provide full
information on the regional lung behaviour.
Currently, chest Computed Tomography (via a CT
scanner) is the most reliable technique for the
clinical assessment of regional lung recruitment and
ventilation distribution in patients with ARDS.
However, CT exposes the patient to radiations and is
not a routine bedside technique.
The aim of Electrical Impedance Tomography
(EIT) is to produce a cross-sectional image of the
internal distribution of conductivity, or alternatively
resistivity of the lungs from electrical measurements
made by injecting small alternating current patterns
via surface electrodes and recording the resulting
boundary voltages. EIT offers a very promising tool
for monitoring the pulmonary function. However,
208
Denaï M., Mahfouf M., Wang A., A. Linkens D. and H. Mills G. (2010).
AN INTEGRATED PHYSIOLOGICAL MODEL OF THE LUNG MECHANICS AND GAS EXCHANGE USING ELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE TOMOGRA-
PHY IN THE ANALYSIS OF VENTILATION STRATEGIES IN ARDS PATIENTS.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 208-213
DOI: 10.5220/0002709502080213
Copyright
c
SciTePress
the technique suffers from some limitations that may
prevent its adoption for routine medical diagnosis.
The first clinical images obtained with EIT were
produced by the Sheffield group (Brown et al.,
1985), who developed a system that used the
electrical impedance of various tissues within the
human body to produce tomographic image maps of
the resistivity distribution. The Sheffield Research
Group produced the first images of the pulmonary
function using a simple back-projection algorithm to
reconstruct cross-section images of the thorax
(Brown et al., 1985). Many current ongoing research
studies are being directed at demonstrating the
ability of EIT to image regional lung ventilation in a
clinical setting (Victorino et al., 2004; Putensen et
al., 2007). Comprehensive literature reviews in this
field can be found in (Frerichs et al., 2000) and
(Panoutsos et al., 2007). Recently a software
package (EIDORS) implementing different methods
for the solution of the forward and inverse problems
in EIT using finite elements modelling techniques
has been made available for public use (Adler and
Lionheart, 2006).
The purpose of this study is to present a
comprehensive physiological model of patients
under mechanical ventilation. The model combines a
blood gas model (SOPAVent) (Wang et al., 2006)
and a model of the lung mechanics with a 2D finite
element model of the thorax to simulate EIT current
injection and image reconstruction. The
physiological model is intended to provide the
foundation for the validation of a new EIT-based
clinical decision support system for optimising
mechanical ventilator settings in ARDS patients.
The rest of the paper is organised as follows.
Section 2 focuses on the description of the
physiological model and its principal components.
The approach used to combine SOPAVent model
with the lung mechanics and EIT is presented.
Section 3 presents a simulation study with
constructed scenarios of ARDS lungs.
2 OVERVIEW OF THE
PHYSIOLOGICAL MODEL
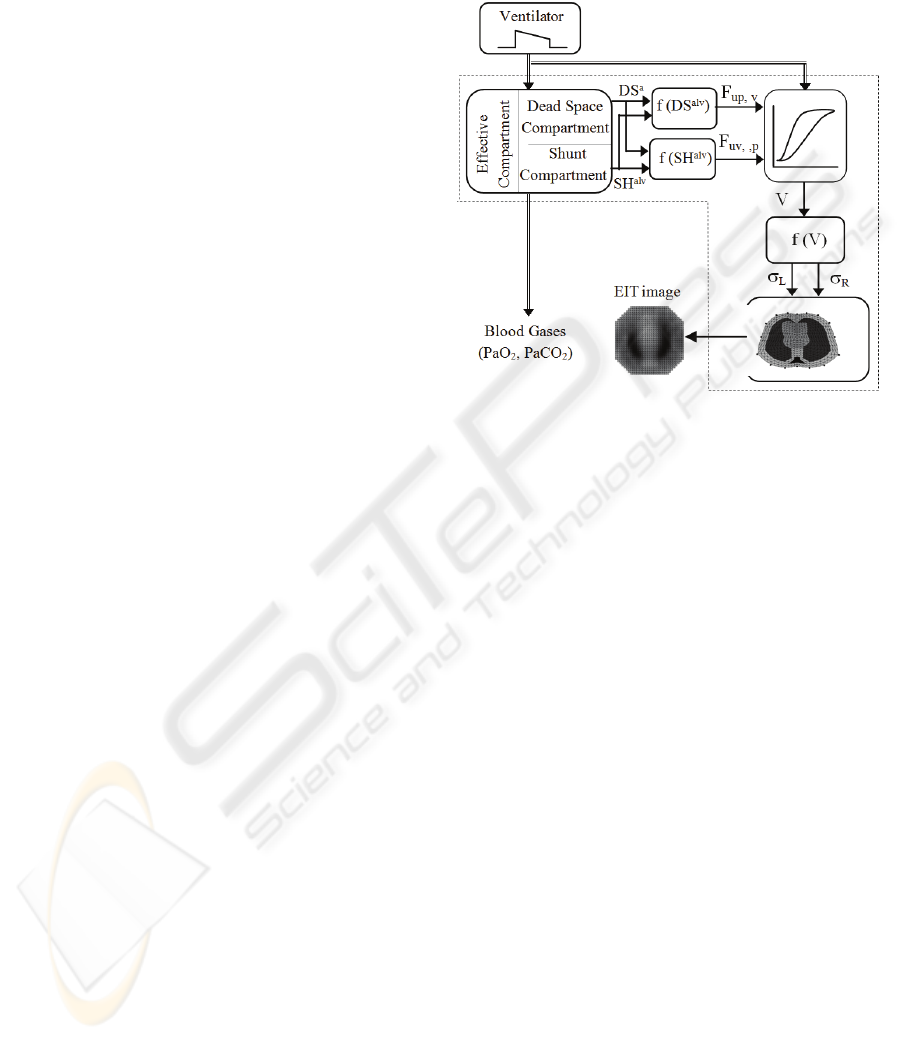
The structure of the simulation model is depicted in
Fig. 1. The model inputs are the ventilator
parameters: the Fraction of Inspired Oxygen (FiO
2
),
the Tidal Volume (V
T
), the Peak End-Expiratory
Pressure (PEEP), the Peak Inspiratory Pressure
(PIP), the Respiratory Rate (RR), the inspiration to
expiration time ratio (I:E). The outputs are the
predicted blood gases: the arterial partial pressure of
oxygen (PaO
2
), the arterial partial pressure of carbon
dioxide (PaCO
2
) and EIT image of the lung
resistivity distribution.
Figure 1: Schematic overview of the simulation model.
2.1 Blood Gas Model (SOPAVent)
The blood gas model SOPAVent (Wang et al., 2006)
describes the relationship between the ventilator
settings (FiO
2
, PEEP, PIP, RR, Tinsp) and blood gas
(PaO
2
, PaCO
2
). In the model, the lung is divided into
three compartments: The effective compartment
(ventilated and perfused), the alveolar dead-space
(DS
alv
) compartment (ventilated but unperfused) and
the alveolar shunt (SH
alv
) compartment (perfused but
unventilated). The model is assumed to have an
anatomical dead-space and no extra-pulmonary
shunt. On inspiration, CO
2
gas retained in the
anatomical dead-space from previous expiration is
assumed to re-enter all ventilated alveoli in
proportion to their ventilation.
Following Workman et al. (1965), the volume of
mixed expired gas from the alveolar
component
A
exp
V , is the contribution of the effective
compartment
E
exp
V , and the alveolar dead-space
compartment
alv
DS
exp
V
.
alv
DS
exp
E
exp
A
exp
VVV +=
(1)
The ratio of the volume expired from the alveolar
dead-space compartment to the volume expired from
all ventilated alveoli can obtained as:
AN INTEGRATED PHYSIOLOGICAL MODEL OF THE LUNG MECHANICS AND GAS EXCHANGE USING
ELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE TOMOGRAPHY IN THE ANALYSIS OF VENTILATION STRATEGIES IN ARDS
PATIENTS
209

222
22
alv
COexpCO
A
expCO
E
exp
CO
A
expCO
E
exp
A
exp
DS
exp
)P()P()P(
)P()P(
V
V
+−
−
=
(2)
Where
2
CO
A
exp
)P( is the partial pressure of CO
2
in
the alveolar component of expired gas and
2
COexp
)P(
is the partial pressure of CO
2
in the mixed
expired gas.
Similarly, the contribution to the arterial blood
flow from all perfused alveoli, both ventilated and
unventilated is made up of the arterial blood flow
from the effective compartment plus the arterial
blood flow from the alveolar shunt compartment.
alv
SH
a
E
a
A
a
QQQ
+=
(3)
The perfusion of the alveolar shunt compartment as
a fraction of the total pulmonary perfusion is
obtained from the shunt equation:
22
22
alv
OvO
E
a
OaO
E
a
A
a
SH
a
)S()S(
)S()S(
Q
Q
−
−
=
(4)
Where
2
O
E
a
)S(
is the oxygen saturation contribution
to mixed arterial blood from the effective
compartment,
2
Oa
)S(
is the oxygen saturation from
the mixed arterial blood and
2
Ov
)S(
is the oxygen
saturation of the mixed venous blood.
With the assumption that all ventilated alveoli have
equal ventilation and all perfused alveoli have equal
perfusion; Workman et al. (1965) defined the
fraction of total number of alveoli that are
unperfused but ventilated as follows:
alvalv
alvalvalv
SHDS
SHDSDS
v,up
gf1
gff
F
⋅−
⋅−
=
(5)
And the fraction of total number of alveoli that are
unventilated but perfused as:
alvalv
alvalvalv
SHDS
SHDSSH
p,uv
gf1
gfg
F
⋅−
⋅−
=
(6)
Where
A
DS
DS
V
V
f
alv
alv
exp
exp
=
and
A
a
SH
a
DS
Q
Q
g
alv
alv
=
.
Equations (5) and (6) define the link between the gas
exchange and lung mechanics models.
2.2 Lung Mechanics Model
The lung mechanics model used in this study has
been adapted from Hickling (2001). The lung is
modelled as multiple units or alveoli which are
distributed into compartments characterized by
different superimposed pressure (gravitational
pressure due to lung weight). In the supine position
the superimposed pressure increases from the ventral
compartment (independent region) to the dorsal
compartment (dependant region). The lung units are
described by their compliance curve which gives a
nonlinear relationship between the applied pressure
and the lung unit volume. The following equation is
used to model this relationship (Salazar and
Knowles, 1964):
))h/2(LogPexp(1(VV
0
−
−
=
(7)
Where
V is the lung volume, V
0
is the maximum
volume at high pressure,
P is the pressure and h is
the half-inflation pressure. In the model, the lung
unit can assume only two possible states: recruited
(or open) and de-recruited (or closed). These two
states are governed only by the Threshold Opening
Pressure (TOP) which the critical pressure above
which the lung unit pops open and Threshold
Closing Pressure (TCP) below which the unit
collapses.
The model uses normally distributed TOP and
TCP pressures (Crotti et al. (2001)). The Mean (
μ )
indicates the pressure at which the maximum of
recruitment (TOP) and derecruitment (TCP) of the
lung units occur, whereas the Standard Deviation
(SD) describes the spread of the lung units’
population with respect to the TOP and TCP (Yuta
et al., 2004). Therefore,
μ and SD may be adjusted
to reflect the heterogeneous characteristic of alveoli
under different abnormal lung conditions such as
ARDS (Table 3) (Markhorst et al., 2004).
The model parameters used throughout are listed in
Table 1 (Hickling , 2001).
Table 1: Lung mechanics model baseline parameters.
Parameters Value
No. of alveoli per compartment
N
calv
9000
Number of compartments N
c
30
Gravitational pressure P
g
cmH
2
O) 0 to
14.5
Lung volume V (litres) 6
V
0
(litres) 3.8
h 5
2.3 EIT Model
A typical EIT system uses a set of 16 electrodes
attached to the surface of the thorax to inject a small
alternating current and record the resulting voltages
to reconstruct a cross-sectional image of the internal
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
210
distribution of the conductivity or resistivity. The
most popular data collection strategy is the so-called
adjacent or four-electrode where current is applied to
an adjacent pair of electrodes and the resulting
voltages between the remaining 13 pairs of
electrodes are measured. The type of reconstruction
algorithm ranges from a simple linearised single-
step method to a computationally intensive iterative
techniques. The EIT problem is often approximated
by Laplace’s equation and Newman type boundary
conditions given by (8) as long as the frequency is in
the range of 0-10 kHz in which biological tissue
exhibits distinct conductivity values (Brown et al.,
1985). However, solutions to the full Maxwell’s
equations have also been investigated (Soni et al.
2006).
0)uσ( =∇⋅∇
⎪
⎩
⎪
⎨
⎧
=
∂
∂
elsewhere 0
electrodes under theJ
n
u
σ
G
G
(8)
Where
σ
is the conductivity, u is the potential,
J
K
is
the density of the injected current and
n
G
is the
normal vector to the surface. A systematic approach
for solving the reconstruction problem is to solve the
forward problem which consists of finding a unique
effect (voltages) resulting from a given cause
(currents) via a mathematical or physical model
(conductivity distribution). The process of
recovering the conductivity distribution within the
body from the applied currents and measured
boundary potentials is known as the
inverse problem
in EIT. There exist two approaches for solving the
image reconstruction problem in EIT.
Static
reconstruction produces an image of the absolute
conductivity distribution of the medium based on
one set of measurements.
Dynamic or difference
imaging attempts to recover the change in resistivity
based on measurements made at two different time
periods. In this paper, difference imaging was used
and the finite element (FE) method was employed
for the numerical solution of equation (8). The FE
model used to simulate the subject’s cross-section of
the thorax (adapted from Adler and Lionheart, 2006)
was divided into four regions of different
conductivities which were fixed to their basal values
except those of the left and right lung that were
updated based on the instantaneous lung volume
generated from the lung mechanics model.
The relationship between changes in the basal
conductivity of the lungs and the inspired fraction of
air is described by a parametric model. The data
used to derive this model were obtained from EIT
and spirometry measurements recorded from a
human subject during a respiratory cycle (Smulders
and van Oosterom, 1992). The left (
σ
L
) and right
(
σ
R
) lung relative conductivities estimated from a
thorax model for different inspiration levels are
listed in Table 2. The inspiration fraction
F is
defined as: F = (V
insp
– V
min
)/(V
max
– V
min
), where
V
insp
represents the tidal volume, V
min
and V
max
are
respectively the minimum and maximum volumes
assumed during tidal breathing.
Table 2: Left and right lung conductivities (
σ
L
,
σ
R
) for
different inspiration levels (F).
F (%)
σ
L
σ
R
0 0.8 0.8
20 1.0 0.8
40 0.9 0.7
60 0.7 0.6
80 0.5 0.6
100 0.4 0.5
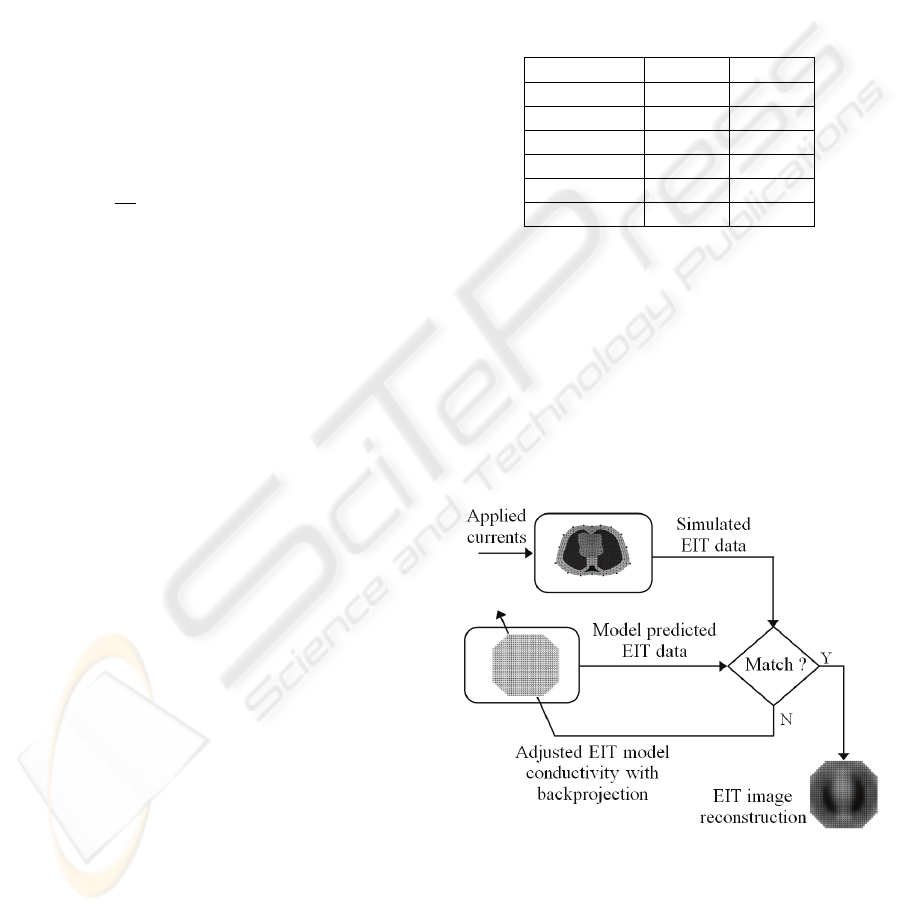
In this simulation study, the back-projection
algorithm (Brown et al., 1985) was used for image
reconstruction. The image reconstruction process is
illustrated in Fig. 2. At each pressure step, the
calculated lung volume is used to set the left and
right lung conductivities on the FE thorax model.
EIT data (assumed to be the real measurements) are
then generated using adjacent drive patterns with an
injected current of 5 mA and matched with the
model predicted data set using the backprojection
matrix until some precision is reached.
Figure 2: Image reconstruction based on the
backprojection.
AN INTEGRATED PHYSIOLOGICAL MODEL OF THE LUNG MECHANICS AND GAS EXCHANGE USING
ELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE TOMOGRAPHY IN THE ANALYSIS OF VENTILATION STRATEGIES IN ARDS
PATIENTS
211

3 SIMULATION STUDIES
In ARDS, the lungs become stiffer and the lung
units tend to open and collapse at higher pressures.
To reproduce these conditions in the model,
μ
and
SD which are related to TOP and TCP pressures
were given the values shown in Table 3 (Markhorst
et al., 2004).
Table 3: Simulated ARDS scenarios.
Estimated values for FRC under the degrees of
ARDS conditions considered are listed in Table 3. It
is worth noting that, the amount of collapsed alveoli
associated with the shunt fraction are taken into
account in the model .
In this initial simulation study, the estimated values
for
F
uv,p
(Table 3), expressed as a percentage of the
a priori known total number of alveoli, are used to
simulate the number of collapsed alveoli in these
ARDS scenarios. A tidal breathing cycle is
simulated by traversing up (inflation) and then down
(deflation) the airway pressure range in small steps
from 0 cmH
2
O to PIP=40 cmH
2
O and then back
from PIP to 0 cmH
2
O respectively.
The simulated ARDS scenarios presented in Table 3
are reproduced on the physiological model where the
shunt fraction is assumed to quantify the fraction of
collapsed alveoli F
uv,p
(Smith et al., 2005). Fig. 3
shows the sequence of reconstructed images during a
breathing cycle (progressing from left to right and
top to bottom) for simulated moderate ARDS
scenario.
Figure 3: Reconstructed images for moderate ARDS
scenario during a breathing cycle.
The patient’s blood gas model SOPAVent has been
validated in a previous study with clinical data
gathered from a group of ICU patients (Wang et al.,
2007). Table 4 gives the ventilator and model
parameters relating to one of the patients.
Table 4: Ventilator settings and SOPAVent predictions.
FiO
2
(%)
PEEP
(cmH
2
O)
RR
(breath/min)
PIP
(cmH
2
O)
65 10 14 28
Estimated parameters Predicted blood gases
Shunt 31.8 PaO
2
(kPa) 10.3
Dead space 26 PaCO
2
(kPa) 5.4
CO (litres) 7.4
VCO
2
( ml/min) 138.9
VO
2
, (ml/min) 173.6
The shunt fraction and relative dead-space in Table
4 have been assumed here to approximate the
alveolar shunt (SH
alv
) and alveolar dead-space
(DS
alv
) respectively and are used to update equations
(5) and (6) in the physiological model. The model is
cycled through a tidal expiration from FRC to a tidal
inspiration and the results are shown in Fig. 4. The
fraction of collapsed alveoli obtained from (6) was
25.72% therefore the lungs were ventilated with
over 200,000 alveoli. Fig. 4b shows the collapsed
lung regions assumed in the model to occur in the
dependant sections of the lungs subjected to the
gravitational pressure.
Figure 4: PV curve and EIT images showing end
expiration (a) and end inspiration (b) reproduced from this
patient’s data.
4 CONCLUSIONS
EIT is an established monitoring technique with the
potential of becoming a valuable bedside tool for the
Degree of
ARDS
TOP
(cmH
2
O)
TCP
(cmH
2
O)
FRC
(litres)
F
uv,p
(%)
normal 4.5 ± 2 2 ± 2 2.4 0
mild 10 ± 2.9 2.5 ± 2.4 2.2 15
moderate 14.5 ± 3.8 4.5 ± 2.9 1.8 25
severe 24.5 ± 4.8 13 ± 3.8 1.5 35
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
212

assessment of the pulmonary function in ICUs. EIT
is also capable of tracking local changes in
pulmonary air contents and thus, can be used to
continuously guide the titration of ventilation in
ARDS patients whilst minimising the risk of VILI.
A physiological model which combines a blood
gas model with a model of lung mechanics has been
developed and used to demonstrate the principles of
EIT image reconstruction on simulated scenarios of
ARDS lungs under mechanical ventilation. The
model leads to a good understanding of respiratory
physiology in ARDS affected lungs. After its
validation against clinical data recorded on real-
patients, the model can therefore be used to evaluate
a new EIT-based decision support system for
effective therapy which is currently being developed
by the Sheffield Research Group.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial
support of the UK Engineering and Physical
Sciences Research Council (EPSRC) under Grant
EP/520807/1.
REFERENCES
Adler, A. and Lionheart, W.R.B., 2006. Uses and abuses
of EIDORS: an extensible software base for EIT,
Physiology Measurement, 27, S25–S42. (Available:
http://eidors3d.sourceforge.net/).
Brown, B.H., Barber, D.C. and Seager, A.D., 1985.
Applied potential tomography: possible clinical
applications, Clin Phys Physiol Mea., 6, 109-121.
Crotti, S., Mascheroni, D., Caironi, P., Pelosi, P., Ronsoni,
G., Mondino, G.M., Marini, J.J. and Gattinoni, L.,
2001. Recruitment and derecruitment during acute
respiratory distress syndrome, Am J Respir Crit Care
Med, 164, 131-140.
Frerichs, I., 2000. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT)
in applications related to lung and ventilation: A
review of experimental and clinical activities, Physiol
Meas, 21, R1-R21.
Hickling, K.G., 2001. Best compliance during a
decremental, but not incremental, positive end-
expiratory pressure trial is related to open-lung
positive end-expiratory pressure: A mathematical
model of acute respiratory distress syndrome lungs.
Am J of Respir Crit Care Med, 163, 69-77.
Markhorst, D.G., van Genderingen, H.R. and van Vught,
A.J., 2004. Static pressure-volume curve
characteristics are moderate estimators of optimal
airway pressures in a mathematical model of
(primary/pulmonary) acute respiratory distress
syndrome,” Intens Care Med, 30, 2086-2093.
Panoutsos, G., Mahfouf, M., Brown, B.H. and Mills, G.H.,
2007. Electrical impedance tomography (EIT) in
pulmonary measurement: a review of applications and
research,” Proceedings of the 5
th
IASTED
International Conference: biomedical engineering,
Innsbruck, Austria, 221-230.
Putensen, C., Wrigge, H., and Weiler, N., 2007. Electrical
impedance tomography guided ventilation therapy,
Current Opinion in Critical Care, 13(3), 344–350.
Salazar, E. and Knowles, J.H., 1964. Analysis of the
pressure-volume characteristics of the lungs, J of Appl
Physiol, 19, 97-104.
Smith, B.W., Rees, S., Tvorup, J., Christensen, C.G. and
Andreassen, S., 2005. Modelling the influence of the
pulmonary pressure-volume curve on gas exchange,
Proceedings of the 27
th
IEEE Annual Conf on
Engineering in Medicine and Biology, Shangai, China.
Smulders, L.A. and van Oosterom, A., 1992. Application
of electrical impedance tomography to the
determination of lung volume, Clin Phys Physiol
Meas, 13, 167-170.
Soni, N.K., Paulsen, K.D., Dehghani, H. and Hartov, A.,
2006. A 3-D reconstruction algorithm for EIT planner
electrode arrays, IEEE Trans. Medical Imaging, 25(1),
55-61.
Tremblay, L.N. and Slutsky, A.S., 2006. Ventilator-
induced lung injury: from the bench to the bedside,
Intensive Care Med, 32, 24-33.
Victorino, J.A., Borges, J.B., Okamoto, V.N., Matos,
G.F.J, Tucci, M.R., Caramez, M.P.R., Tanaka, H.,
Sipmann, F.S., Santos, D.C.B., Barbas, C.S.V.,
Carvalho, C.R.R. and Amato, M.B.P., 2004.
Imbalances in regional lung ventilation: A validation
study on electrical impedance tomography, Am J
Respir Crit Care Med, 169, 791-800.
Wang A., Mahfouf M. and Mills G.H.., 2006. A
continuously updated hybrid blood gas model for
ventilated patients. The 6
th
IFAC Symposium on
Modelling and Control in Biomedical Systems, Reims,
France.
Wang A., Panoutsos, G., Mahfouf M. and Mills G.H.,
2007. An improved blood gas intelligent model for
mechanically ventilated patients in the intensive care
unit. The 5
th
IASTED International Conference on
Biomedical Engineering, Innsbruck, Austria.
Workman, J.M., Penman, W.B., Bromberger-Barnea, B.,
Perut, S. and Riley, R.L., 1965. Alveolar dead space,
alveolar shunt, and transpulmonary pressure. Journal
of Applied Physiology, 20, 816-824.
Yuta, Y., Chase, J.G., Shaw, G.M. and Hann, C., 2004.
Dynamic models of ARDS lung mechanics for optimal
patient ventilation, Proceedings of the 26
th
Annual
International Conference: of the IEEE EMBS San
Francisco, USA, 861-864.
AN INTEGRATED PHYSIOLOGICAL MODEL OF THE LUNG MECHANICS AND GAS EXCHANGE USING
ELECTRICAL IMPEDANCE TOMOGRAPHY IN THE ANALYSIS OF VENTILATION STRATEGIES IN ARDS
PATIENTS
213
