
ReHap: AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM FOR THE HAPLOTYPE
ASSEMBLY PROBLEM FROM SHOTGUN SEQUENCING DATA
Filippo Geraci and Marco Pellegrini
IIT-CNR, Via Moruzzi 1, Pisa, Italy
Keywords:
Haplotype assembly problem, Single individual haplotype reconstruction, Shotgun sequencing.
Abstract:
Single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) is the most common form of DNA variation. The set of SNPs present
in a chromosome (called the haplotype) is of interest in a wide area of applications in molecular biology and
biomedicine. Personalized haplotyping of (portions of/all) the chromosomes of individuals is one of the most
promising basic ingredients leading to effective personalized medicine (including diagnosis, and eventually
therapy). Personalized haplotyping is getting now technically and economically feasible via steady progress
in shotguns sequencing technologies (see e.g. the 1000 genomes project - A deep catalogue of human genetic
variations). One key algorithmic problem in this process is to solve the haplotype assembly problem, (also
known as the single individual haplotyping problem), which is the problem of reconstructing the two haplo-
type strings (paternal and maternal) using the large collection of short fragments produced by the PCR-based
shotgun technology. Although many algorithms for this problem have been proposed in the literature there has
been little progress on the task of comparing them on a common basis and on providing support for selecting
the best algorithm for the type of fragments generated by a specific experiment. In this paper we present Re-
Hap, an easy-to-use AJAX based web tool that provides a complete experimental environment for comparing
five different assembly algorithms under a variety of parameters setting, taking as input user generated data
and/or providing several fragment-generation simulation tools. This is the first published report of a compari-
son among five different haplotype assembly algorithms on a common data and algorithmic framework. This
system can be used by researchers freely at the url: http://bioalgo.iit.cnr.it/rehap/.
1 INTRODUCTION
Shotgun sequencing technology (Pop, 2004) has been
key to the determination of whole genomes of sev-
eral higher species, most notably homo sapiens (Is-
trail et al., 2004). More recently the attention has
shifted from what is common among members of
a species (the genome), to what is different among
members of the same species, thus to the individual
variations in the chromosomic content. This shift is
driven by two forces. One is the importance of pro-
filing individual genetic features for the purposed of
individual genomic medicine (Crawford and Nicker-
son, 2005). The second force is the steady decrease
in the cost of sequencing equipment that will soon
render cost-effective the effort of producing complete
genomic profiles of individuals versus collecting data
on predefined genetic markers, for which other tech-
nologies (such as those based on micro-arrays) may
be more suitable. The first publication of a com-
plete individual diploid human genome sequence has
been announced (Levy et al., 2007) in 2007, and two
individual diploid human sequences were published
in 2008 (Wang and et al., 2008; Wheeler and et al.,
2008). An ambitious project to determine the genetic
profile of about 1200 individuals all over the world
has been launched in 2008 (see. “1000 Genomes
Project - A Deep Catalog of Human Genetic Varia-
tion” http://www.1000genomes.org). As for the cost-
effectiveness of the sequencing technology, the cur-
rent aim of the research community is to attain within
a few yearsa cost of 1000 USD per individual genome
sequenced (Mardis, 2006). The cost of state-of-the-
art technology is decreasing (von Bubnoff, 2008), so
to make the 1000 USD target a realistic one.
The role of individual genomic variations and their
impact in the emergence of diseases is also at the
core of the so called Common disease common
variation hypothesis (CDCV) (Iles, 2008), (Schork
et al., 2009). The compilation of complete individ-
ual genomes including rare (or private) variants might
help in predicting traits and diseases in that particular
19
Geraci F. and Pellegrini M. (2010).
ReHap: AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM FOR THE HAPLOTYPE ASSEMBLY PROBLEM FROM SHOTGUN SEQUENCING DATA.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Bioinformatics, pages 19-25
DOI: 10.5220/0002713400190025
Copyright
c
SciTePress

person. Thus it is important to produce accurate in-
dividual haplotype maps in a timely manner and with
reduced costs.
A key component of the reconstruction pipeline
is the so called ”haplotype assembly” problem
((Halld´orsson et al., 2004), (Zhao et al., 2007),
(Bonizzoni et al., 2003)). During the fragment gen-
eration phase, depending on the precise technology
used (Morozova and Marra, 2008), a large set of frag-
ments of length in the range of 200/900 bases are read
which cover with multiple overlays the (portion of)
chromosome being analyzed. By the use of refer-
ence maps it is relatively easy to locate the position
and orientation of such fragments in the chromosome,
but not to determine the association of the fragments
to the two homologous copies (paternal and mater-
nal) of a chromosome. The haplotype assembly prob-
lem is the problem of determining the association of
each fragment to one of the two homologous chromo-
somes and to determine the haplotype (i.e. the value
of the bases in the SNP positions of the two homol-
ogous chromosomes). In absence of errors or gaps,
with sufficient coverage, this problem is easily solved,
however more realistic models of the problem take
into account several types and sources of error/noise
in the data, and in this setting the problem is much
more challenging (intractable in some cases). Sev-
eral algorithms and heuristics have been proposed in
the literature to solve the haplotype assembly prob-
lem (see e.g. (Rizzi et al., 2002; Li et al., 2003; Pan-
conesi and Sozio, 2004; Zhao et al., 2005; Lindsay
et al., 2005; Wang et al., 2007; Cilibrasi et al., 2007;
Genovese et al., 2008; Chen et al., 2008; Bansal and
Bafna, 2008)).
A common feature of all these researches is that,
due to lack of a common benchmark and of publicly
available implementations in a unified framework, ex-
perimental comparisons among different methods are
based on a narrow choice of data, parameters and al-
gorithms. Thus, in the view of large scale haplotyp-
ing projects, when the need comes to test the avail-
able algorithms onto the set of data and parameters
of a specific experiment and/or technology, the ques-
tion as to the best algorithm to employ is currently
not explored to the its full extent. To remedy this situ-
ation, and to provide a service to the bioinformatics
community, we have developed the web-based tool
(ReHap) that provides an easy to use environment for
testing several algorithms, on a variety of data sets,
and with a variety of parameter settings. We envision
three modalities of use for our tool.
(I) In modality (I) the user supplies as input the two
testing haplotype strings and sets a series of pa-
rameters relative to the simulation of the fragment
generation. The system simulates the fragmen-
tation process, applies any number of algorithms
(among the 5 methods currently supported) and is
able to measure the reconstruction rate and the re-
construction time of those methods.
(II) In modality (II) the user provides to the system
a matrix of fragments and the system returns the
reconstructed haplotypes. Note that in this case
the reconstruction error cannot be computed by
ReHap. However the quality of the reconstruction
can be assessed by the user that has generated the
fragments.
(III) In modality (III) the user has no data yet but an
hypothesis to be tested on the basic parameters of
the experiment/techology to be employed. In this
case ReHap will use data from Hapmap ((Consor-
tium, 2005)) as haplotype test data. The recon-
struction rate and the reconstruction time is then
measured.
Modality III is interesting since in this modality Re-
Hap can give guidance in an early critical stage of ex-
perimental design. In particular the length of the hap-
lotypes chunks to be reconstructed, the (minimum,
average) coverage of each SNP by fragments, and the
error rate that can be handled in the final reconstruc-
tion phase are critical parameters to be assessed in
early stage of design. Modality I and II can be use-
ful by researchers wishing to develop new assembly
algorithms (even exploiting additional private infor-
mation) since ReHap can provide a common testing
framework and a reference benchmark for the assess-
ment of performance.
ReHap is complementary to other tools such as
Haploview (Barrett et al., 2005), where the emphasis
is on visualization and computation of statistics for
haplotype data from population studies (mainly geno-
type data).
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 de-
scribes the web interface and the practical use of the
tool. Section 3 gives a brief self-contained description
of the five reconstruction algorithms currently sup-
ported. Section 4 gives an example of the results that
can be obtained with this tool.
2 FUNCTIONALITIES
ReHap allows the user to generate a SNP matrix
starting from a pair of haplotypes provided by the
HapMap project (Consortium, 2005) (or submits
his/her own data) according to some user-defined pa-
rameters. Haplotypes in (Consortium, 2005) came
from four different populations. For each population,
BIOINFORMATICS 2010 - International Conference on Bioinformatics
20

a number ranging from 44 to 60 of different individu-
als, equally divided in males and females, are avail-
able (in total 209 unrelated individuals). For each
individual the two haplotypes of chromosomes 1-22
are available. For females also the haplotypes of X
chromosome are available. The SNP matrix is gener-
ated according to a model similar to that proposed in
(Myers, 1999), which is considered a good approxi-
mation of the actual physical process of shotgun se-
quencing technology. The generator allows users to
select a specific chromosome, individual and popula-
tion. Once selected the desired haplotype, it is possi-
ble to control many other parameters. Among them:
the haplotype length, the average coverage of each
haplotype, the error probability, a range specifying
the length of each fragment, a range specifying the
expected hamming distance of the two haplotypes,
and the gaps rate. By default ReHap’s parameters are
set with technologically reasonable values. ReHap al-
lows also the user to upload his/her own SNP matrix.
The generated SNP matrix (with and without er-
rors) can be downloaded or inspected inside ReHap.
Errors are highlighted using color codes and the cor-
rect value showed just clicking on an error basis. Be-
sides the SNP matrix, ReHap also computes as a refer-
ence baseline the output of an “omniscient algorithm”
(called the baseline) that can access the true subdivi-
sion of the fragments but still decides the imputation
of SNPs based on majority.
ReHap allows the user to test and evaluate the ef-
fectiveness of four recent reconstruction algorithms:
SpeedHap (Genovese et al., 2008) (a robust algorithm
for individual haplotype reconstruction developed by
the authors), Fast Hare (Panconesi and Sozio, 2004)
(a well known algorithm in the bio-informatics com-
munity), MLF (Zhao et al., 2005), and a two-distances
clustering algorithm for the MEC model (Wang et al.,
2007). All methods have been re-implemented by the
authors. SpeedHap has a flag to enable the use a en-
tropic filter to break ties in the reconstruction of the
haplotypes. MLF accepts as a parameter the number
of trials to run before selecting the “best” haplotypes.
Besides running time, for each selected algorithm Re-
Hap displays the returned haplotype and highlights
the reconstruction errors. Moreover a synthetic nu-
merical evaluation of the performance of each al-
gorithm is computed by the standard reconstruction
rate. All these outputs are available when the data is
generated by ReHap. When the SNP matrix is upload
from the user, only the reconstructed haplotypes are
returned. ReHap provides a contextual help for each
feature of the interface, and a general help page.
3 ALGORITHMS SUPPORTED
ReHap implements five recently proposed algorithms
for the haplotype assembly problem: Speedhap (Gen-
ovese et al., 2008), FastHare (Panconesi and Sozio,
2004), MLF (Zhao et al., 2005), 2D (Wang et al.,
2007) and SHR (Chen et al., 2008). These five al-
gorithm have been selected because (i) they represent
different approaches to the assembly problem and (ii)
they are described in the literature with sufficient de-
tail so that accurate re-implementation is possible.
A common feature of the above cited algorithms
is the use of a notion of distance similar to the stan-
dard Hamming distance to compare two fragments.
When considering a certain position of the compared
strings, if both character in that position are not gaps
they contribute to the distance as in the case of stan-
dard Hamming distance, otherwise they do not con-
tribute. In the following, for sake of completeness,
we provide synthetic description of the implemented
algorithms.
SpeedHap (Genovese et al., 2008) follows a multi-
phase greedy approach: it has four phases and makes
choices that are optimal in a local sense. In each
phase SpeedHap performs three tasks: 1) detect likely
positions of errors 2) allocate fragments to the two
partially built haplotype strings, and 3) build partial
haplotype strings deciding via majority on ambigu-
ous SNPs calls. The difference among the four phases
is twofold: on one hand the algorithm uses knowl-
edge built up in the previous phases, and on the other
hand in passing from one phase to the next it relaxes
the conditions for the decisions to be taken regarding
tasks 1), 2) and 3). The aim is to be always very con-
servatives in the choices made so to introduce as little
error as possible in the early phases. MoreoverSpeed-
Hap (Genovese et al., 2008) solves ties in the allele
determination using an entropy-based biased filter so
to give priority to choices that reduce the entropy of
the final solution.
Fash Hare (Panconesi and Sozio, 2004) is the oldest
simple and practical heuristic algorithm for the hap-
lotype reconstruction problem. It is widely used as a
benchmark for comparisons. In a nutshell, Fast Hare
works as follows: as first step the fragments of the
SNP matrix are sorted so that a fragment precedes
another fragment if the position of the first non-gap
character of the former is lower or equal to the first
non-gap position of the latter. The main loop of Fast
Hare consists in processing the fragments in the SNP
matrix one at time according to their ordering and di-
viding them in two sets. The first set is initialized
with the first fragment while the second set is left
empty. At each iteration, from each set Fast Hare de-
ReHap: AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM FOR THE HAPLOTYPE ASSEMBLY PROBLEM FROM SHOTGUN
SEQUENCING DATA
21
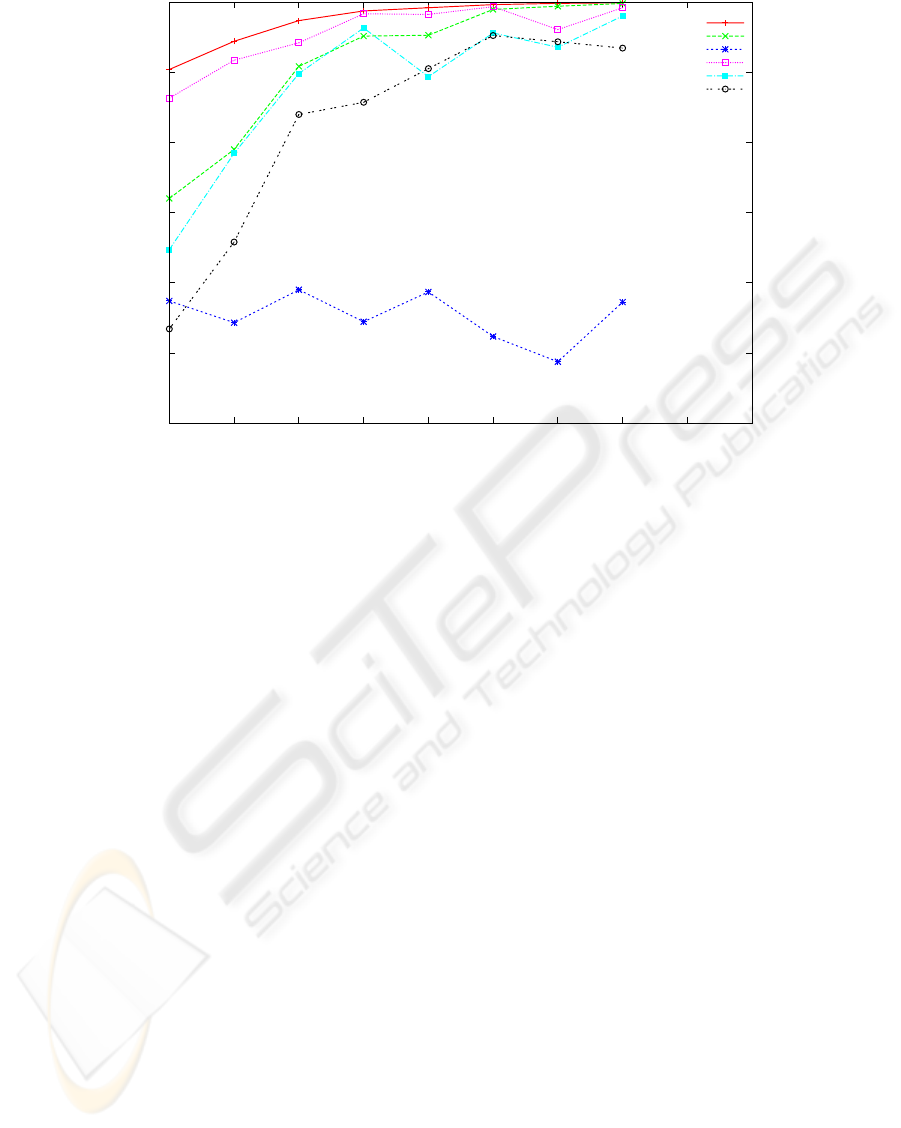
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
average reconstruction rate
Coverage
Baseline
Fast Hare
SHR
SpeedHap
2D
MLF
Figure 1: Reconstruction rate of 5 reconstruction algorithms and the baseline algorithm for covering in the range [3,..,10].
The other parameters are fixed: error rate 0.15 and haplotype length 250 bases. Each point is the average of 20 experiments
with randomly chosen haplotype strings of Hapmap.
rives the consensus haplotypes. A fragment is com-
pared to the consensus haplotypes and assigned to the
set with lower distance.
The MLF algorithm (Zhao et al., 2005) is based on the
well-known one-pass k-means clustering algorithm
due to McQueen (McQueen, 1967). The procedure
initialization consists in randomly splitting the SNP
matrix in two partitions and, for each one, compute
its consensus string. Then, in the main loop fragments
are partitioned again in two sets according to the fol-
lowing procedure. Each fragment is compared with
the two consensus strings and assigned to the set as-
sociated to the closest haplotype. Once all fragments
are processed two new consensus strings can be com-
puted and returned. Since this procedure performance
strongly depends from the initial random partition, it
is repeated a certain (large) number of times and as fi-
nal result is returned the pair of consensus haplotypes
that minimize the MEC (Minimum Error Correction)
score.
The 2D algorithm (Wang et al., 2007) main contri-
bution is the introduction of a notion of distance that
overcome the structural drawbacks of Hamming dis-
tance which assign distance 0 to both: two equal
strings and two strings which cover two disjoint set of
SNPs. The distance introduced in 2D not only gives
a penalty to different characters in a certain position,
but also gives a bonus to equal (not gaps) characters
in a certain position. The procedure goal is to par-
tition the rows of the SNP matrix in two partitions
and works as follows: using the Hamming distance
compute the two furthest fragments and initialize each
partition with one of them. Each fragment is com-
pared using the Hamming distance with the consen-
sus strings derived from each partition. In case of tie
the second distance function is used to break the tie
and select the partition to which assign the fragment.
The corresponding consensus haplotype is updated.
The SHR algorithm (Chen et al., 2008) uses a prob-
abilistic framework to approach the SIH problem.
Fragments in the SNP matrix are divided in two par-
titions according with the following procedure. At
the beginning two fragments f
1
and f
2
randomly ex-
tracted from the SNP matrix are used to initialize two
empty sets, Then, each fragment is compared to f
1
and f
2
and inserted in the set corresponding to the
lower distance. Once all fragments are assigned to a
set, the procedure computes the MEC score induced
from f
1
, f
2
and the computed bipartition. Due to its
probabilistic nature, the above procedure is repeated
a certain number of times and as final bipartition it is
selected the one with lower MEC score. At the end
the consensus haplotypes are computed by majority
from the final bipartition. The main contribution of
this algorithm stands in the theoretical framework de-
veloped by its authors.
BIOINFORMATICS 2010 - International Conference on Bioinformatics
22
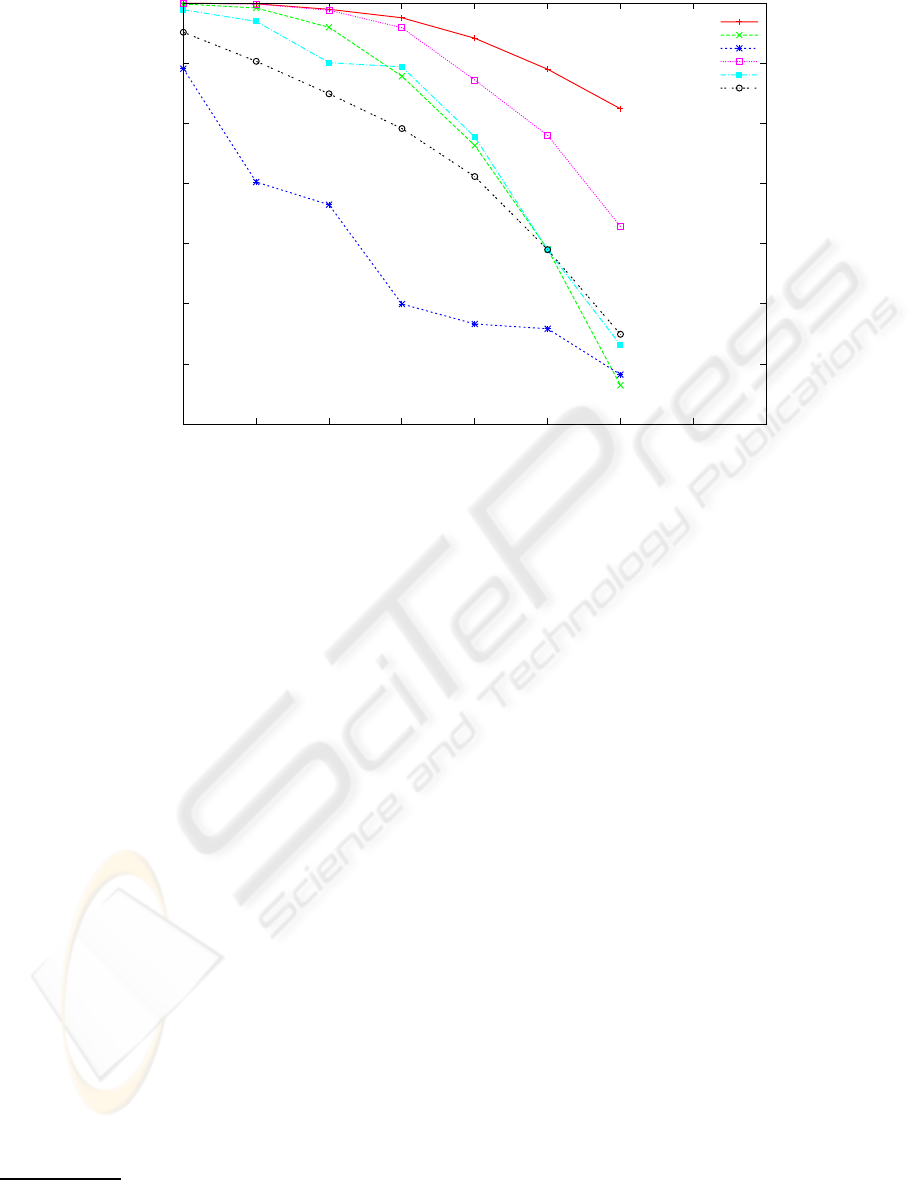
0.65
0.7
0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
0 0.05 0.1 0.15 0.2 0.25 0.3 0.35 0.4
average reconstruction rate
Error rate
Baseline
Fast Hare
SHR
SpeedHap
2D
MLF
Figure 2: Reconstruction rate of 5 reconstruction algorithms and the baseline algorithm for error rates in the range [0.0,..,0.30].
The other parameters are fixed: covering 8 and haplotype length 250 bases. Each point is the average of 20 experiments with
randomly chosen haplotype strings of Hapmap.
4 EXPERIMENTS
In this section we report on experiments in modality
(III), using Hapmap data to explore relative perfor-
mance in a range of possible parameter choices. We
concentrate on three parameters (covering, error rate,
length) and we measure the reconstruction rate
1
of the
reconstructed haplotype returned by five algorithms.
The reconstruction rate is a real number in the range
[0.0, .., 1.0] and has value 1.0 for perfect reconstruc-
tion. We also include the outcome of the baseline al-
gorithm that has access to the true association of the
fragments to the two haplotype strings and decides the
base call by majority vote. This algorithm is clearly
useful only as a reference in simulations, as an ideal
for the proper algorithms that have no access to this
information. To the best of our knowledge this is the
first published report of a comparison among five dif-
ferent haplotype assembly algorithms on a common
data and algorithmic framework.
As fragment coverage increases we expect the perfor-
mance of all the algorithms also to improve. This is
expectation confirmed for all algorithms, except SHR
that seems unaffected. From figure 1 one can observe
that for high coverage (say 10 and more) SpeedHap,
1
The reconstruction rate is the ratio of correctly re-
constructed bases over the length of the reconstructed se-
quences.
Fast Hare, MLF and 2D match the baseline and are
above 95% reconstruction rate, while at low cover-
age (3-7) Speedhap is notably more accurate and very
close to the baseline.
From figure 2 one observes that increasing the error
rate in the range [0.0,..,0.3] the baseline reference al-
gorithm is also affected. This is to be expected, as the
accumulation of many errors in the same SNP posi-
tion makes it impossible even for the baseline method
to decide correctly by majority. Speedhap although
performing worse than the baseline is not far from it,
and it is much better than the other 4 algorithms at
high error rate, attaining a respectable reconstruction
rate only 0.1 below the baseline, even with 30% of
reading errors. Fast Hare MLF, and 2D perform rea-
sonably well, better than SHR, but all four converge
to the similar reconstruction rate (about 0.70-0.75) for
the higher reading error situation.
From figure 3 one can observe that for the set of pa-
rameters tested the length of the haplotype has little
influence on the relative performance of the 5 algo-
rithms w.r.t. the baseline. Speedhap, Fast hare and
2D have reconstruction rate above 90% for the range
of length considered, while MLF and SHR have re-
construction rate in a lower region (0.75% - 0.85%).
ReHap: AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM FOR THE HAPLOTYPE ASSEMBLY PROBLEM FROM SHOTGUN
SEQUENCING DATA
23

0.75
0.8
0.85
0.9
0.95
1
100 200 300 400 500 600
average reconstruction rate
Haplotype length
Baseline
Fast Hare
SHR
SpeedHap
2D
MLF
Figure 3: Reconstruction rate of 5 reconstruction algorithms and the baseline algorithm for length in the range [50,..,500].
The other parameters are fixed: error rate 0.15 and covering 8. Each point is the average of 20 experiments with randomly
chosen haplotype strings of Hapmap.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The integrated frameworkReHap for testing and com-
paring five different haplotype assembly algorithms
is described. Our hope is that ReHap will help the
bioinformatics community in selecting the most suit-
able algorithm for each specific haplotype assem-
bly task, as large scale individual haplotyping pro-
grammes are getting momentum. This system can
be accessed and used by researchers freely at the
url: http://bioalgo.iit.cnr.it/rehap/ without any login
requirement.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the European Com-
munity’s Seventh Framework Programme FP7/2007-
2013 under grant agreement N 223920 (Virtual Phys-
iological Human Network of Excellence).
REFERENCES
Bansal, V. and Bafna, V. (2008). Hapcut: an efficient and
accurate algorithm for the haplotype assembly prob-
lem. Bioinformatics, 24(16):i153–159.
Barrett, J. C., Fry, B., Maller, J., and Daly, M. J. (2005).
Haploview: analysis and visualization of LD and hap-
lotype maps. Bioinformatics, 21(2):263–265.
Bonizzoni, P., Vedova, G. D., Dondi, R., and Li, J. (2003).
The haplotyping problem: an overview of computa-
tional models and solutions. J. Comput. Sci. Technol.,
18(6):675–688.
Chen, Z., Fu, B., Schweller, R. T., Yang, B., Zhao, Z.,
and Zhu, B. (2008). Linear time probabilistic algo-
rithms for the singular haplotype reconstruction prob-
lem from snp fragments. In Brazma, A., Miyano, S.,
and Akutsu, T., editors, APBC, volume 6, pages 333–
342. Imperial College Press.
Cilibrasi, R., van Iersel, L., Kelk, S., and Tromp, J. (2007).
On the complexity of the single individual SNP hap-
lotyping problem. Algorithmica.
Consortium, T. I. H. (2005). A haplotype map of the human
genome. Nature, 437:1299–1320.
Crawford, D. and Nickerson, D. (2005). Definition and
clinical importance of haplotypes. Annu. Rev. Med.,
56:303–320.
Genovese, L., Geraci, F., and Pellegrini, M. (2008). Speed-
hap: An accurate heuristic for the single individual
snp haplotyping problem with many gaps, high read-
ing error rate and low coverage. IEEE/ACM Transac-
tions on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics,
5(4):492–502.
Halld´orsson, B. V., Bafna, V., Edwards, N., Lippert, R.,
Yooseph, S., and Istrail, S. (2004). A survey of com-
putational methods for determining haplotypes. In
BIOINFORMATICS 2010 - International Conference on Bioinformatics
24

Computational Methods for SNPs and Haplotype In-
ference, volume 2983 of Lecture Notes in Computer
Science, pages 26–47.
Iles, M. M. (2008). What can genome-wide association
studies tell us about the genetics of common disease?
PLoS Genet, 4(2).
Istrail, S., Sutton, G. G., Florea, L., Halpern, A. L., Mo-
barry, C. M., Lippert, R., Walenz, B., Shatkay, H.,
Dew, I., Miller, J. R., Flanigan, M. J., Edwards, N. J.,
Bolanos, R., Fasulo, D., Halldorsson, B. V., Hannen-
halli, S., Turner, R., Yooseph, S., Lu, F., Nusskern,
D. R., Shue, B. C., Zheng, X. H., Zhong, F., Delcher,
A. L., Huson, D. H., Kravitz, S. A., Mouchard, L.,
Reinert, K., Remington, K. A., Clark, A. G., Water-
man, M. S., Eichler, E. E., Adams, M. D., Hunkapiller,
M. W., Myers, E. W., and Venter, J. C. (2004). Whole-
genome shotgun assembly and comparison of human
genome assemblies. Proceedings of the National
Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,
101(7):1916–1921.
Levy, S., Sutton, G., Ng, P., Feuk, L., Halpern, A., and et al.
(2007). The diploid genome sequence of an individual
human. PLoS Biology, 5(10).
Li, L., Kim, J. H., and Waterman, M. S. (2003). Haplo-
type reconstruction from SNP alignment. In Proceed-
ings of the seventh annual international conference
on Computational molecular biology, pages 207–216.
ACM Press.
Lindsay, S. J., Bonfield, J. K., and Hurles, M. E. (2005).
Shotgun haplotyping: a novel method for surveying
allelic sequence variation. Nucl. Acids Res., 33(18).
Mardis, E. R. (2006). Anticipating the $1,000 genome.
Genome Biology, 7.
McQueen, J. (1967). Some methods for classification and
analysis of multivariate observations. In Proc. of the
5
th
Berkeley Symposium on Mathematical Statistics
and Probabilily, volume 1, pages 281–297. University
of California Press.
Morozova, O. and Marra, M. A. (2008). Applications of
next-generation sequencing technologies in functional
genomics. Genomics, 92(5):255 – 264.
Myers, G. (1999). A dataset generator for whole genome
shotgun sequencing. In Proceedings of the Seventh
International Conference on Intelligent Systems for
Molecular Biology, pages 202–210. AAAI Press.
Panconesi, A. and Sozio, M. (2004). Fast hare: A fast
heuristic for single individual SNP haplotype recon-
struction. In WABI, pages 266–277.
Pop, M. (2004). Shotgun sequence assembly. Advances in
Computers, 60:193–248.
Rizzi, R., Bafna, V., Istrail, S., and Lancia, G. (2002). Prac-
tical algorithms and fixed-parameter tractability for
the single individual SNP haplotyping problem. In
Proceedings of the Second International Workshop on
Algorithms in Bioinformatics, pages 29–43. Springer-
Verlag.
Schork, N. J., Murray, S. S., Frazer, K. A., and Topol, E. J.
(2009). Common vs. rare allele hypotheses for com-
plex diseases. Current Opinion in Genetics & Devel-
opment, 19(3):212 – 219.
von Bubnoff, A. (2008). Next-generation sequencing: The
race is on. Cell, 132(5):721 – 723.
Wang, J. and et al. (2008). The diploid genome sequence of
an asian individual. Nature, 456:60–65.
Wang, Y., Feng, E., and Wang, R. (2007). A clustering algo-
rithm based on two distance functions for mec model.
Computational Biology and Chemistry, 31(2):148–
150.
Wheeler, D. and et al. (2008). The complete genome of
an individual by massively parallel dna sequencing.
Nature, 452:872–876.
Zhao, Y., Xu, Y., Zhang, Q., and Chen, G. (2007). An
overview of the haplotype problems and algorithms.
Frontiers of Computer Science in China, 1(3):272–
282.
Zhao, Y.-Y., Wu, L.-Y., Zhang, J.-H., Wang, R.-S., and
Zhang, X.-S. (2005). Haplotype assembly from
aligned weighted SNP fragments. Computational Bi-
ology and Chemistry, 29(4):281–287.
ReHap: AN INTEGRATED SYSTEM FOR THE HAPLOTYPE ASSEMBLY PROBLEM FROM SHOTGUN
SEQUENCING DATA
25
