
COORDINATION OF PLANNING AND SCHEDULING
TECHNIQUES FOR A DISTRIBUTED, MULTI-LEVEL,
MULTI-AGENT SYSTEM
John S. Kinnebrew, Daniel L. C. Mack, Gautam Biswas and Douglas C. Schmidt
Department of Electrical Engineering and Computer Science, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN 37203, U.S.A.
Keywords:
Planning and scheduling, Agent cooperation and coordination.
Abstract:
Planning and scheduling for agents operating in heterogeneous, multi-agent environments is governed by the
nature of the environment and the interactions between agents. Significant efficiency and capability gains can
be attained by employing planning and scheduling mechanisms that are tailored to particular agent roles. This
paper presents such a framework for a global sensor web that operates as a two-level hierarchy, where the
mission level coordinates complex tasks globally and the resource level coordinates the operation of subtasks
on individual sensor networks. We describe important challenges in coordinating among agents employing
two different planning and scheduling methods and develop a coordination solution for this framework. Ex-
perimental results validate the benefits of employing guided, context-sensitive coordination of planning and
scheduling in such sensor web systems.
1 INTRODUCTION
In large-scale, distributed, multi-agent systems
(MAS) that span multiple domains of agent operation,
choosing a single planning and scheduling mecha-
nism for all agents may be inefficient and impractical.
For example, NASA’s Earth Science Vision calls for
the development of a global sensor web that provides
coordinated access to sensor network resources for re-
search and resolution of Earth science issues (Hilde-
brand et al., 2004). This global sensor web must se-
lect and coordinate an appropriate subset of hetero-
geneous, distributed sensors and computational re-
sources for user tasks that often require collaboration
among multiple constituent sensor networks. Com-
plex task execution with resource constraints and time
deadlines presents planning, scheduling, and coordi-
nation issues at multiple levels of the sensor web.
Our Multi-agent Architecture for Coordinated Re-
sponsive Observations (MACRO) platform provides
a powerful computational infrastructure for deploy-
ing, configuring,and operating large sensor webs with
many constituent sensor networks (Suri et al., 2007).
MACRO is structured as a two-level agent hierar-
chy: (1) the mission level, where global coordina-
tion across sensor networks is achieved and planning
and scheduling is handled at an appropriate level of
abstraction to avoid computational intractability, and
(2) the resource level, where operations within a lo-
cal sensor network are coordinated and controlled us-
ing planning and scheduling methods that operate in
dynamic, uncertain and resource constrained environ-
ments. Therefore agents at these different levels of
the system operate in different contexts imply differ-
ent planning and scheduling requirements.
MACRO achieves efficient and effective au-
tonomous planning by employing hierarchical task
network planning with distributed scheduling at the
mission level and decision theoretic planning with re-
source constraint propagation scheduling at the re-
source level. Developing such an agent architec-
ture, however, also presents challenges in coordinat-
ing among the agents . In particular,employing differ-
ent planning and scheduling mechanisms at the mis-
sion and resource levels requires an appropriate trans-
lation of the task, plan, and schedule representations
between levels. It also requires a coordination mech-
anism for deciding when to exchange information be-
tween levels during plan execution.
The remainder of the paper is organized as fol-
lows: Section 2 outlines the key capabilities pro-
vided by the MACRO agent framework; Section 3
summarizes the planning and scheduling coordination
challenges and the solutions we developed for this
184
S. Kinnebrew J., L. C. Mack D., Biswas G. and C. Schmidt D. (2010).
COORDINATION OF PLANNING AND SCHEDULING TECHNIQUES FOR A DISTRIBUTED, MULTI-LEVEL, MULTI-AGENT SYSTEM.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence - Agents, pages 184-191
DOI: 10.5220/0002721001840191
Copyright
c
SciTePress

paper; Section 4 evaluates experimental results that
show the reduction in communication and computa-
tion achieved by using MACRO’s guided, context-
sensitive coordination mechanism for planning and
scheduling; Section 5 compares our work with related
research; and Section 6 presents concluding remarks.
2 OVERVIEW OF MACRO
To provide global coordination of the sensor web, the
MACRO mission level is comprised of broker agents,
user agents, and mission agents. Broker agents act as
the intelligent system infrastructure, providingmatch-
maker services, aggregating relevantdomain informa-
tion, tracking system performance, and mediating al-
location negotiations (Kinnebrew, 2009). User agents
generate the high-level tasks and are typically inter-
faces to mission scientists and wrappers for legacy
systems (e.g. weather modeling applications) that can
request execution of sensor web tasks. Each mission
agent represents an independent sensor network and
achieves its allocated tasks with the resources avail-
able in its sensor network.
As the representative of an entire sensor network,
a mission agent straddles the boundary between the
mission and resource levels. At the resource level,
mission agents divide tasks among the exec agents,
each of which controls a set of computational/sensor
resources within a sensor network and is supported by
additional domain-specific agents. An exec agent also
employs services for planning, scheduling, allocation,
and resource management of the hardware under its
control. These services are shared with any support-
ing agents under its direction, providing a centralized
control and environmental awareness for its set of re-
sources.
2.1 MACRO Mission Level
At the mission level of a sensor web MAS, user
tasks and scheduled plans spanning multiple sensor
networks have a high degree of complexity. Hi-
erarchical analysis helps deal with this complexity,
both for problem/task representation by domain ex-
perts and for coordinated planning and scheduling
among multiple agents. MACRO combines the OGC
SensorML (Botts et al., 2007) representation of sen-
sors and data processing with the Task Analysis, En-
vironment Modeling, and Simulation TÆMS hierar-
chically decomposable task representation (Horling
et al., 1999) for multi-agent planning and schedul-
ing. This combination provides standardized descrip-
tions of task/subtask requirements and effects across
sensor networks. The TÆMS representation also al-
lows the specification of discrete probability distribu-
tions for task/subtask characteristics including poten-
tial outcome quality and duration (Lesser et al., 2004).
To coordinate and schedule TÆMS tasks across
sensor networks, MACRO mission agents employ the
Generalized Partial Global Planning (GPGP) (Lesser
et al., 2004) coordination mechanism, which works
in conjunction with a planning and scheduling mech-
anism that can generate an appropriate task decompo-
sition and schedule from a TÆMS task tree. For this
purpose, MACRO mission agents employ Design-
To-Criteria (DTC) (Wagner and Lesser, 2001) plan-
ning/scheduling, which has successfully been used in
conjunction with GPGP coordination (Lesser et al.,
2004). DTC scheduling is a soft real-time, heuristic
approach to solving the combinatorial problem of op-
timally decomposing and scheduling a TÆMS task.
DTC is particularly suited to the MACRO mission-
level because it can optimize plans and schedules
based on user-provided criteria, such as minimizing
execution time or maximizing expected quality.
2.2 MACRO Resource Level
Exec agents use the Spreading Activation Partial
Order Planner (SA-POP) (Kinnebrew et al., 2007),
which generates high utility, scheduled, partial or-
der plans that respect local resource constraints. SA-
POP allows the exec agents to use their limited com-
putational resources to maximize expected utility for
achieving local goals in the dynamic, uncertain en-
vironments at the resource level. Moreover, SA-
POP provides incremental re-planning/re-scheduling
that can quickly revise scheduled plans during ex-
ecution and prevent more expensive re-planning/re-
scheduling at the mission level. In conjunction with
SA-POP, exec agents also employ the Resource Allo-
cation and Control Engine (RACE) (Shankaran et al.,
2007) for resource allocation and management to
meet scheduled deadlines and required quality of ser-
vice (QoS) parameters for deployed applications and
hardware-based actions.
First-principles planning (Blum and Furst, 1997)
and scheduling with SA-POP requires a set of goal
conditions that correspond to the desired outcome.
These goal conditions are specified as desired en-
vironmental and system conditions with associated
utility values and time deadlines. Given these goal
conditions, SA-POP uses current/expected conditions
to generate a scheduled plan of high expected util-
ity (Kinnebrew et al., 2007).
COORDINATION OF PLANNING AND SCHEDULING TECHNIQUES FOR A DISTRIBUTED, MULTI-LEVEL,
MULTI-AGENT SYSTEM
185
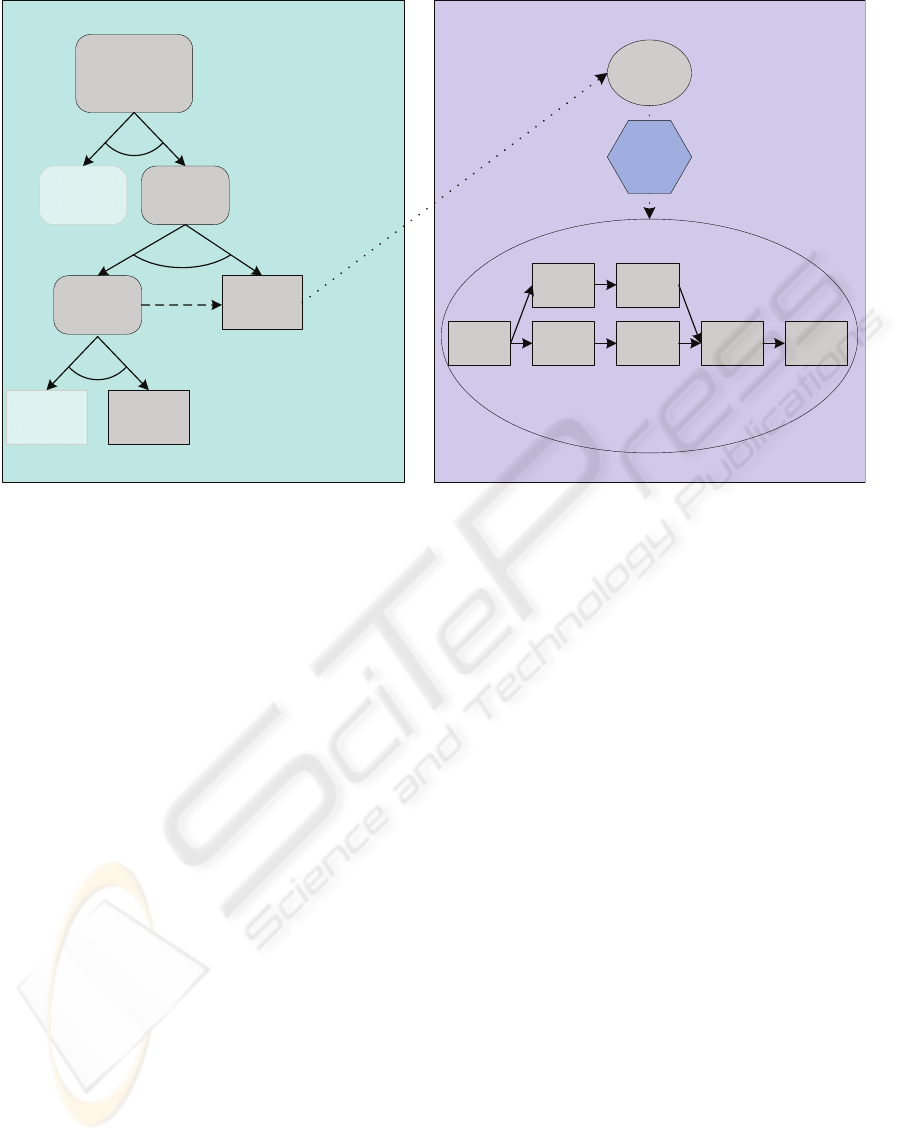
Exec AgentMission Agent
Task T1
Subtask
T1.1
Subtask
T1.2
q_exactly_one()
Subtask
T1.2.1
q_sum_all()
enables
q_exactly_one()
Method
M2
Method
M1
Method
M3
Quality: (70% 10) (30% 0)
Duration: (80% 43s) (20% 28s)
Quality: (75% 4) (25% 0)
Duration: (100% 30s)
Goal
M3
Action
A1
Action
A2
Action
A4
Action
A6
Action
A7
Action
A5
Action
A3
Plan M3
Utility: 100
Start Time: 0s
Deadline: 75s
SA-POP
Figure 1: Planning/Scheduling Representations in MACRO.
3 MACRO COORDINATION
As described in Section 2.1, mission agents must ef-
ficiently generate and coordinate plans and schedules
provided by the TÆMS task decomposition trees and
criteria-directed scheduling. As shown in Figure 1,
the leaves of a TÆMS task tree are methods, which
in standard TÆMS usage can be directly executed by
the agent. In MACRO, however, mission agents must
communicate these methods to their exec agents for
resource-level planning/scheduling and actual execu-
tion.
At the resource level, the decision-theoretic,
first-principles planning and constraint-propagation
scheduling is efficiently performed by SA-POP for
achievement of goals in the dynamic sensor network
environment shown in Figure 1. Effectively employ-
ing both representations and forms of planning and
scheduling presents multiple challenges for coordina-
tion between MACRO mission and exec agents.
3.1 Translation: Top-Down
Problem. For an exec agent to implement a TÆMS
method, the mission agent must translate it into the
goal format used by SA-POP. SA-POP goals include
one or more goal conditions with associated utility
values and time deadlines. To plan for a goal accu-
rately, SA-POP requires knowledge of expected sys-
tem and environmental conditions at the time the plan
will be executed. Although current conditions and
other exec agent plans provide most of this informa-
tion, other expected conditions may be the result of
methods assigned to other exec agents in the mission
agent’s current plan (i.e., other methods that enable
the method in question by satisfying some of its pre-
conditions).
Solution → Cross-references in Task/Goal Mod-
eling. Domain experts (e.g., scientists and engi-
neers who design and deploy the sensor network)
use MACRO’s domain-specific modeling language
(based on GME (Karsai et al., 2003)) to specify
the TÆMS task tree for a mission agent. In this
model, TÆMS methods are associated with neces-
sary resource-levelpreconditionsand goal conditions,
which in turn are represented in the action network
model employed by the exec agent and SA-POP.
Moreover, the domain expert can automatically derive
method distributions for duration and outcome in this
model by providing potential initial condition settings
(with an associated probability) to SA-POP, which
produces scheduled plans and summarizes their prob-
ability of success, expected duration, and resource us-
age.
Instead of directly executing a method, the mis-
sion agent uses the encoded translation informa-
tion from the model to provide a goal to the exec
agent. This top-down translation is shown by the mis-
sion agent to exec agent information transfer in Fig-
ure 2. The mission agent awards overall task utility to
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
186
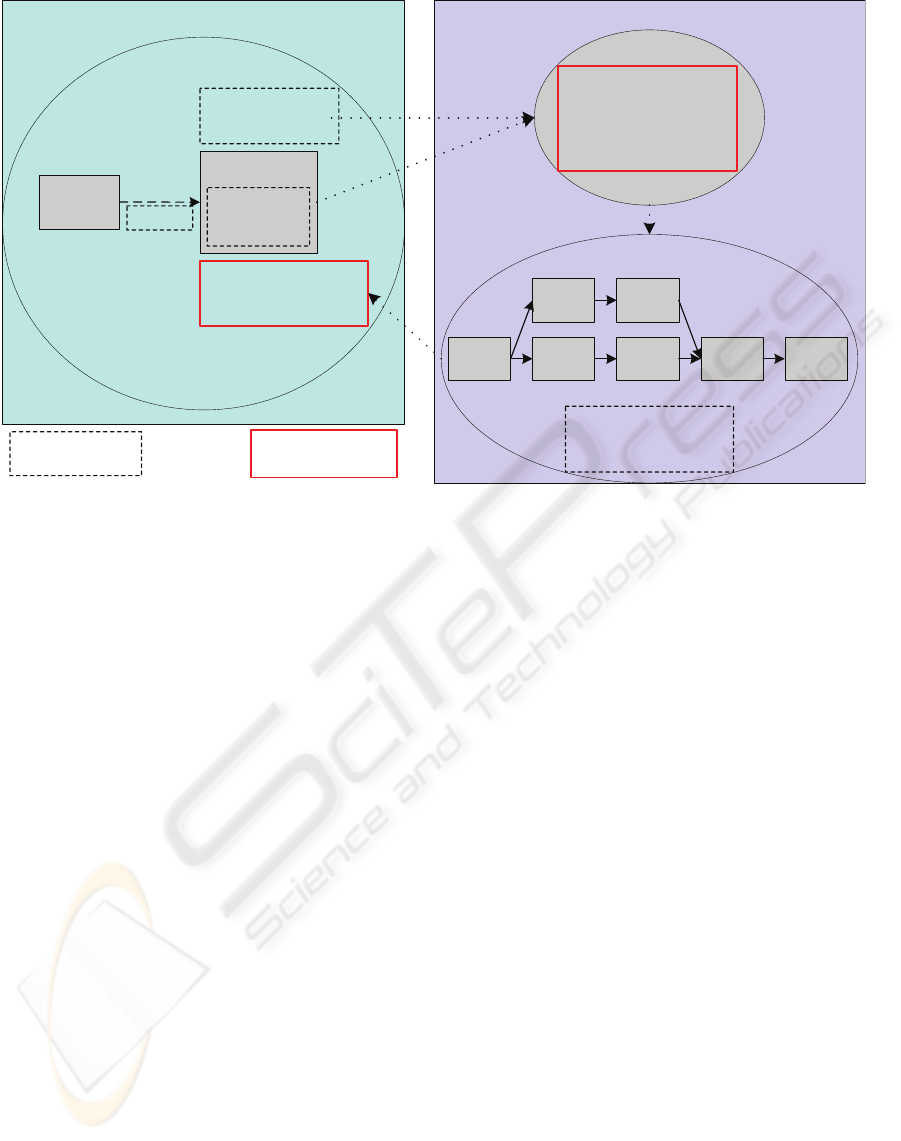
Exec AgentMission Agent
e
n
a
b
l
e
s
Method
M2
Method M3
Quality: (90% 10) (10% 0)
Duration: (100% 43s)
Avg Resource: R1=50%
Max Resource: R1=100%
Goal M3
Action
A1
Action
A2
Action
A4
Action
A6
Action
A7
Action
A5
Action
A3
Plan M3
Utility: 100
Start Window: [30s, 30s]
Deadline: 75s
Goal Condition: C7=True
Goal Condition: C8=True
Initial Condition: C1=True
Probability Success: 90%
Duration: 43s
Avg Resource: R1=50%
Max Resource: R1=100%
Plan T1
Goal: C7=True
Goal: C8=True
Initial: C1=True
C1=True
Externally Provided/
Updated Information
Internally Encoded/
Derived Information
Utility: 100
Start Time: 30s
Deadline: 75s
Figure 2: Planning/Scheduling Translation in MACRO.
methods based on the quality aggregation functions
(QAFs) and expected quality in the TÆMS task tree.
In the chosen decomposition of the TÆMS task
tree, parents with a QAF that requires execution of
all child subtasks/methods pass the full parent utility
to each child, while QAFs that allow any subset of
children pass a percentage of parent utility based on
the child’s percentage of total expected quality for the
parent. For example, a task with an overall utility of
100 that is decomposed into two subtasks of expected
quality 3 and 7 with a sum QAF would assign util-
ity of 30 and 70, respectively, to its subtasks. Future
work will investigate more advanced methods of re-
ward assignment in the decomposition of TÆMS task
trees.
3.2 Translation: Bottom-Up
Problem. Another important challenge is codifying
the bottom-up translation between SA-POP plans and
TÆMS method parameters. Standard TÆMS meth-
ods include a priori probability distributions for dura-
tion and outcome quality, which are used during ini-
tial criteria-directed scheduling by the mission agent.
After an exec agent plans to achieve a goal, the re-
sultant scheduled plan may imply significantly dif-
ferent probability distributions for the corresponding
method. Similarly, as a plan is being executed by
the exec agent, there may be further changes to the
expected duration or probability of outcomes for the
plan and its corresponding method. To improve the
efficiency of future criteria-directed scheduling and to
trigger appropriate mission-levelre-scheduling, infor-
mation about the exec agent’s plan must be commu-
nicated to the mission agent.
Solution → Summarize Resource-level Plans. In-
stead of providing the complete resource-level plan
to the mission agent (whose format is ill-suited to
its planning and scheduling capabilities), a MACRO
exec agent summarizes its plan by providing relevant
information only, including (1) expected duration, (2)
probability of achieving the goal, and (3) average
and maximum resource usage over expected execu-
tion. The mission agent uses these values to update
method parameters with more accurate information,
based on the resource-level planning and scheduling
for the current and expected environmental/system
conditions. The updated method parameters allow the
mission agent to more effectively perform any further
planning and scheduling for its task(s).
3.3 Context-Sensitive Updates
Problem. In addition to translating between the mis-
sion and exec agent planning/scheduling representa-
tions, MACRO agents must also decide when to up-
date and communicate the translated information. In
particular, during execution of exec agent plans, de-
viations may occur (e.g., differences between actual
and expected duration of actions). Only some vari-
COORDINATION OF PLANNING AND SCHEDULING TECHNIQUES FOR A DISTRIBUTED, MULTI-LEVEL,
MULTI-AGENT SYSTEM
187

ations, however, will impact the rest of the mission-
level plan—or other plans—in a manner that would
be of interest to the mission agent.
Solution → Leverage Mission-level Task Context.
Given the hierarchical relationship between mission
and exec agents, the top-down decision to commu-
nicate (i.e., when the mission agent should com-
municate information to an exec agent) is relatively
straightforward. Specifically, whenever a new task is
decomposed/scheduled or method parameters in the
plan are changed by re-planning/re-scheduling, the
mission agent communicates the new or revised goals
(translated from the methods) to the assigned exec
agents.
For bottom-up updates, however, an exec agent
can use its knowledge of a mission agent’s overall
goals/interests to guide its decision of when to com-
municate. Without mission agent guidance, an exec
agent would be forced to communicate on a peri-
odic basis or whenever the execution deviates from
the scheduled plan, which may happen frequently in
a dynamic sensor network environment. When task-
ing an exec agent with a goal, therefore, the MACRO
mission agents also provide guidance and contextual
information, such as the optimization criteria for the
related task. Knowledge of the optimization criteria
allows the exec agent to configure SA-POP’s planning
and scheduling to prefer plans based on that criteria.
In addition to optimization criteria, the mission
agent can specify acceptable deviations (in either di-
rection), success probability, expected utility, dura-
tion, and resource usage of an executing plan. This
information provides the exec agent with guidance
on the context for the corresponding method in the
mission agent’s plan, which allows the agent to more
intelligently determine when to update its scheduled
plan and provide the revised summary to the mission
agent. Specifically, during execution of a plan, the
exec agent will only re-plan and re-schedule if the ex-
pected utility falls below, or if the duration surpasses,
specified thresholds. When other thresholds are ex-
ceeded, the exec agent simply communicates updated
summary information to the mission agent.
Figure 3 shows the execution of the resource-level
plan from Section 3.2. To demonstrate the benefit of
the guidance/context provided by the mission agent,
we focus on deviations of action duration from ex-
pected duration in the critical path (i.e., the linked
sequence of actions that requires the longest time to
complete). Although the planning and scheduling in
MACRO does not rely on identification of the critical
path, such a path(s) always exist, and it constrains the
expected completion time of the plan.
Without the context provided by duration thresh-
A1
E[T]: 10s
A[T]: 9s
A4
E[T]: 5s
A[T]: 8s
A2
E[T]: 8s
A[T]: 8s
A6
E[T]: 14s
A[T]: 16s
A7
E[T]: 6s
A[T]:4s
A3
E[T]: 6s
A[T]: 9s
A5
E[T]: 3s
A[T]:3s
39s 46s 54s 70s 74s30s
Finished Early
Finished Late
s
Deadline: 75s
Finished within
Time Window
Figure 3: A Resource-level Plan (Critical Path High-
lighted).
olds, the exec agent would have no knowledgeof what
deviations were important to the mission agent and
would have to communicate updates based on each
deviation. It would recalculate its schedule every time
an action did not complete with exactly its expected
duration. It would also transmit the new expected du-
ration of the plan either with every recalculation or at
least every time an action finished outside of its sched-
uled end window (either before or after that window).
The example execution in Figure 3 shows a typi-
cal case in which the mission agent provides an over-
threshold on duration equal to the difference between
the expected end-time of the plan and the original
deadline. In other words, the mission agent is only in-
terested in changes to the resource-level schedule that
would result in its finishing later than the deadline. In
this example, the exec agent would have to re-plan/re-
schedule only when execution of action A6 goes be-
yond its scheduled end window. Without the appro-
priate context (i.e., the duration threshold), the exec
agent would have also had to unnecessarily recalcu-
late or re-plan/re-schedule three times (after comple-
tion of A1, A4, and A3) and communicate unneces-
sary updates twice (after A1 and A4).
4 COORDINATION RESULTS
This section presents the results of mission and exec
agent coordination through the simulated execution of
randomly-generated resource-level plans with a vari-
ety of duration distributions for actions. These re-
sults validate our claims that MACRO’s use of guided,
context-sensitive coordination in planning/scheduling
can reduce communication and computation, while
still providing relevant information in a timely fash-
ion.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
188
4.1 Experimental Design
Our experiments simulate a scheduled, partial-order
plan generated by SA-POP for an exec agent at the
resource level of MACRO. These plans include a set
of actions with expected start and end time windows,
as well as ordering links. For these experiments, we
only simulate cases in which a valid plan can be gen-
erated.
One experimental parameter is the variability of
actual durations for actions, which requires differ-
ent probability distributions parameterized by a sigma
value. The experiments included both uniform dis-
tributions and Gaussian (Normal) distributions. The
uniform distributions showed the same trends ob-
served in the Gaussian distributions (results are omit-
ted due to the length constraints). The action duration
distributions have a mean of 100 seconds and “low”
and “high” variance scenarios providing a 95% like-
lihood (for the Gaussian) that durations are within 25
seconds or 75 seconds of the mean, respectively.
Another experimental variable is the length of the
critical path. The distributions provide all actions
with an expected duration of 100 seconds. The ex-
pected time for completion of the plan therefore de-
pends solely on the number of actions in the critical
path.
The final experimental variable is the time thresh-
old provided by the mission agent in MACRO
context-sensitivecoordination, which determines how
far actions can surpass their expected end times be-
fore the mission agent must be notified for potential
mission-level re-planning and re-scheduling. To as-
sess computation and communication overhead of the
coordination mechanism, we employed random gen-
eration of plans across a range of parameters rather
than using a few example problems. These experi-
ments do not assess the quality or utility of plans or
potential plan changes during coordination. MACRO
coordination will not result in any degradation of plan
quality in comparison to the baseline coordination,
however, since plan and schedule information that
triggers mission-level re-planning and re-scheduling
is providedby both MACRO coordinationmechanism
and the baseline mechanism at the same time.
Since these experiments employ randomly-
generated plans to cover a range of potential applica-
tions, they do not allow changes to resource-level or
mission-level plans during execution. Whenever an
action execution exceeded its scheduled end window,
the schedule was updated and communicated to the
mission agent, but no changes to the plan or threshold
were made. Without re-planning, the MACRO
coordination overhead is an over-estimate of the real
overhead. After a critical path action’s end window is
exceeded, execution of further actions will continue
to exceed action end windows. Re-planning reduces
this possibility.
4.2 Experimental Results
Each experimental run included 10,000 trials with the
given parameter settings. In each trial, a series of (n)
actions formed the critical path, and each action had
an expected duration of 100 seconds. Using the cho-
sen distribution, random values are generated that cor-
respond to actual execution times. The number of up-
dates and messages are calculated using those values.
4.2.1 Investigating Critical Path Length
These experiments were performed under the assump-
tion that the mission agent simply requires a method
to be completed by the provided deadline and should
only be notified if the expected execution time will
exceed that deadline. The threshold value is therefore
set to the difference between the deadline and the ex-
pected duration of the plan. This threshold is varied
in the experiments between 0 and 200 seconds in 5
second increments.
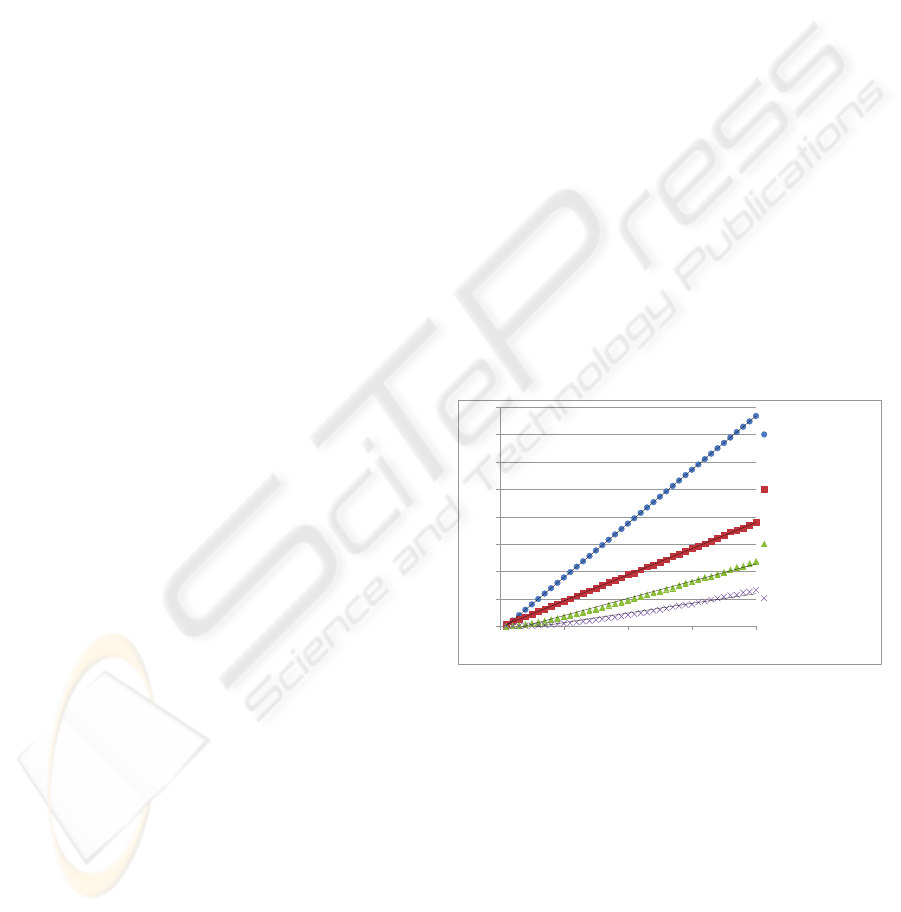
y = 0.9839x - 0.9453
R² = 1
y = 0.4784x - 0.19
R² = 0.9998
y = 0.3142x - 1.2183
R² = 0.9926
y = 0.1769x - 1.1454
R² = 0.9654
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
0 10 20 30 40
Messages/Updates
Length of the Critical Path
Baseline
MACRO Thresh = 5s
MACRO Thresh = 50s
MACRO Thresh = 100s
Figure 4: The effect of critical path length with selected
thresholds with a low variance Gaussian.
Figure 4 shows the information from the mission
agent results in significantly less computation and
communication than the baseline condition for all but
the smallest of critical paths The linear trend suggests
that in the worst case (i.e., a tight threshold/deadline),
MACRO sends about half as many messages as the
baseline machanism. As the threshold increases,
MACRO performs even better, whereas the baseline
performance does not change.
A comparison of the low variance action duration
distribution in Figure 4 to a high variance one in Fig-
ure 5 shows that with the smallest thresholds a ratio
COORDINATION OF PLANNING AND SCHEDULING TECHNIQUES FOR A DISTRIBUTED, MULTI-LEVEL,
MULTI-AGENT SYSTEM
189
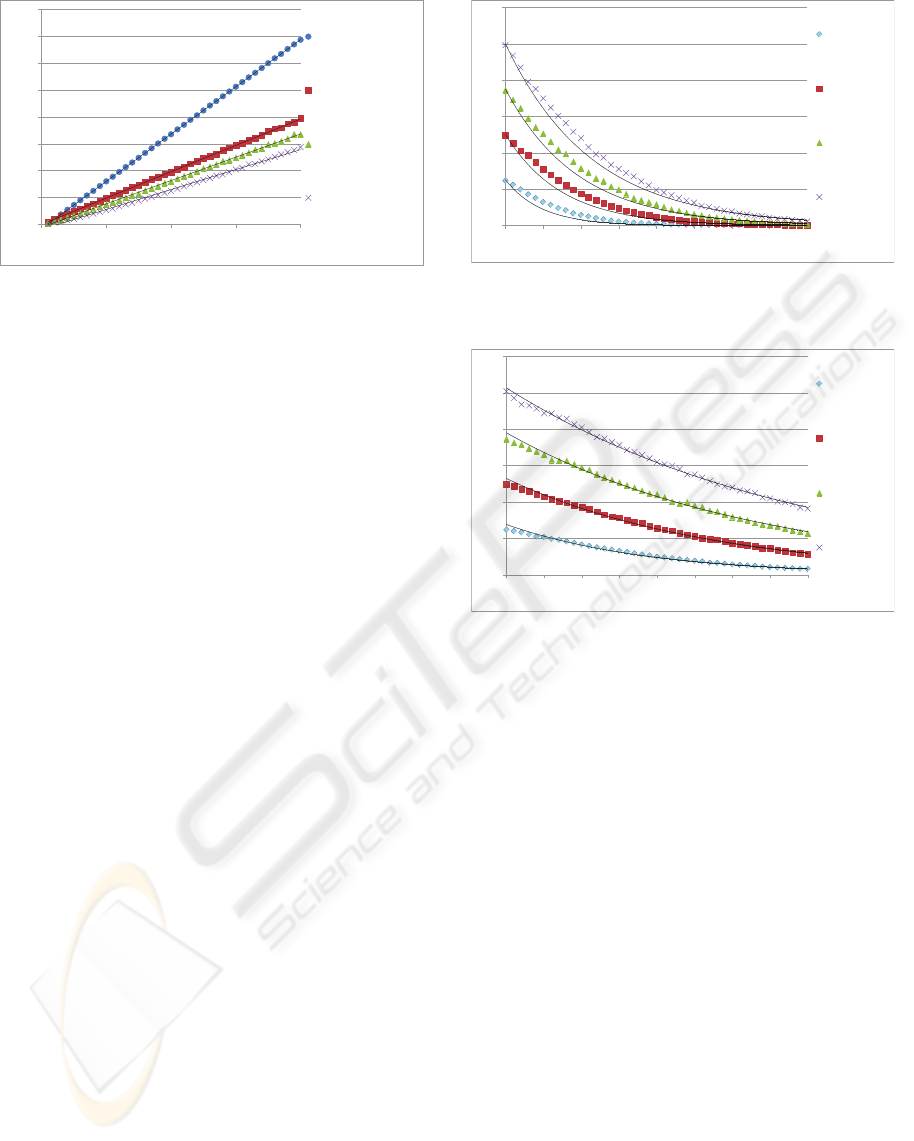
y = 0.8815x - 0.8413
R² = 1
y = 0.4917x - 0.0522
R² = 0.9999
y = 0.4346x - 0.5674
R² = 0.9992
y = 0.3721x - 0.9923
R² = 0.997
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
0 10 20 30 40
Updates/Messages
Length of the Critical Path
Baseline
MACRO Thresh = 5s
MACRO Thresh = 50s
MACRO Thresh = 100s
Figure 5: The effect of critical path length with selected
thresholds with a high variance Gaussian.
of approximately 1 update per 2 actions in the critical
path is required for both distributions. The 1:2 ra-
tio is thus an approximate upper limit on the average
number of updates required in MACRO, even when
re-planning and re-scheduling is not possible.
The baseline mechanism shows a slight, relative
improvement in the high variance case, but MACRO’s
context-sensitive coordination still requires far fewer
updates. However, the number of updates required
in MACRO with different thresholds are much closer
in the high variance case than the low variance case.
This result suggests that when action durations are
less certain, the critical path length is significantly
more important than the threshold, because even large
thresholds can be exceeded by a series of actions that
begins with an unexpectedly long-running action.
4.2.2 Investigating Time Thresholds
Figure 6 and Figure 7 show the trends in communi-
cation and computation with respect to the duration
threshold. The baseline results are not included in
these figures because they do not use of the thresh-
old value, therefore, they would produce a horizontal
line close to the number of actions in the critical path.
These results show that as the threshold increases,
the number of MACRO updates decreases. Figure 6,
shows a steep initial decrease which levels off. Qual-
itatively, this trend occurs since longer thresholds al-
low a series of actions to exceed their expected dura-
tion by a greater amount before requiring an update.
Extreme variation, however, from expected durations
can occur and will still require some updates, even
with relatively large thresholds. These results also
show, that even when uncertainty of action duration
is high, the exec agent can leverage the contextual in-
formation provided by the mission agent to minimize
coordination overhead.
y = 2.5e
-0.042x
R² = 0.9539
y = 5e
-0.027x
R² = 0.9777
y = 7.5e
-0.021x
R² = 0.9831
y = 10e
-0.018x
R² = 0.9865
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200
Updates/Messages
MACRO Threshold
CP = 5 Tasks
CP = 10 Tasks
CP = 15 Tasks
CP = 20 Tasks
Figure 6: The effect of Slack with selected critical paths on
a low variance Gaussian.
y = 2.7609e
-0.011x
R² = 0.9945
y = 5.2883e
-0.007x
R² = 0.9958
y = 7.8007e
-0.006x
R² = 0.9956
y = 10.271e
-0.005x
R² = 0.9972
0
2
4
6
8
10
12
0 25 50 75 100 125 150 175 200
Updates/Messages
MACRO Threshold
CP = 5 Tasks
CP = 10 Tasks
CP = 15 Tasks
CP = 20 Tasks
Figure 7: The effect of Slack with selected critical paths on
a high variance Gaussian.
5 RELATED WORK
MACRO’s approach to planning and scheduling
builds upon and extends a significant body of
related work. At the mission level, MACRO
agents employ Design-To-Criteria (DTC) plan-
ning/scheduling (Wagner and Lesser, 2001) operating
on an augmented TÆMS task tree to efficiently op-
timize for relevant criteria in generating a scheduled
plan to perform assigned subtasks. At the resource
level, exec agents employ SA-POP (Kinnebrew et al.,
2007) for decision-theoretic planning with constraint-
propagation scheduling.
MACRO Agents communicate the most useful in-
formation at an appropriate abstraction level and at
the right time. The translation from resource-level
plans to mission-level method parameters has some
similarities to research that uses plan summary in-
formation to coordinate between agents employing
HTN planning (e.g., (Clement and Durfee, 1999;
Clement and Durfee, 2000)). MACRO mission and
exec agents, however, employ different representa-
tions for planning and scheduling. Moreover, the re-
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
190

source and scheduling constraints in MACRO require
summary information beyond the pre-, in-, and post-
conditions used in Clement’s task summary info ap-
proach (Clement and Durfee, 1999).
6 CONCLUDING REMARKS
This paper presented key research challenges for
coordinating planning and scheduling at two lev-
els of a hierarchical multi-agent system. We dis-
cussed MACRO’s solutions to coordinating HTN
task decomposition with criteria-directed scheduling
and first-principles decision-theoretic planning with
constraint-propagation scheduling. We also report
the results of experiments that showcased the bene-
fits gained by employing MACRO’s guided, context-
sensitive coordination of planning and scheduling.
Our experimental results quantified the effects of
different distributions from which average duration
information is derived for resource-level actions. The
experiments also showcase the effects of other plan-
ning/scheduling parameters, including the length of a
scheduled plan’s critical path and the restrictiveness
of the deadline. Moreover, our results verify the scal-
ability of MACRO planning/scheduling coordination
when execution time is the primary criteria of inter-
est to the mission agent. Our future work will explore
other forms of utility assignment in TÆMS task tree
decomposition and evaluate the benefits of context-
sensitive coordination with thresholds on plan char-
acteristics other than execution time.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported in part by NASA Advanced
Information Systems Technology (AIST) program
under grants NNA04AA69C and NNX06AG97G.
REFERENCES
Blum, A. and Furst, M. (1997). Fast Planning Through
Planning Graph Analysis. Artificial Intelligence,
90(1):281–300.
Botts, M. et al. (2007). Sensor Model Language (Sen-
sorML). Technical Report OpenGIS Implementa-
tion Specification Document 07-000, Open Geospatial
Consortium.
Clement, B. and Durfee, E. (1999). Theory for Coordi-
nating Concurrent Hierarchical Planning Agents us-
ing Summary Information. Proceedings of the Six-
teenth National Conference on Artificial Intelligence
and Eleventh Innovative Applications of AI Confer-
ence, pages 495–502.
Clement, B. and Durfee, E. (2000). Performance of Co-
ordinating Concurrent Hierarchical Planning Agents
using Summary Information. Proceedings of the
Fourth International Conference on Multi-Agent Sys-
tems, pages 373–374.
Hildebrand, P., Wiscombe, W., Albjerg, M., Booth, J.,
Miller, R., Miller, T., Mlynczak, M., Paules, G., Pe-
terson, D., Raymond, C., et al. (2004). NASA Earth
Science Vision 2030: Working Group Report. Tech-
nical Report NP-2003-2-611-GSFC, NASA.
Horling, B., Lesser, V., Vincent, R., Wagner, T., Raja, A.,
Zhang, S., Decker, K., and Garvey, A. (1999). The
TAEMS White Paper. Technical report, Multi-Agent
Systems Lab, University of Massachusetts.
Karsai, G., Sztipanovits, J., Ledeczi, A., and Bapty, T.
(2003). Model-Integrated Development of Embedded
Software. Proceedings of the IEEE, 91(1):145–164.
Kinnebrew, J. S. (2009). Global Sensor Web Coordination
and Control in a Multi-agent System. In Proceedings
of the AAAI Doctoral Consortium (at IJCAI ’09).
Kinnebrew, J. S., Gupta, A., Shankaran, N., Biswas, G., and
Schmidt, D. C. (2007). Decision-Theoretic Planner
with Dynamic Component Reconfiguration for Dis-
tributed Real-time Applications. In Proceedings of the
8th International Symposium on Autonomous Decen-
tralized Systems (ISADS 2007), Sedona, Arizona.
Lesser, V., Decker, K., Wagner, T., Carver, N., Garvey, A.,
Horling, B., Neiman, D., Podorozhny, R., Prasad, M.,
Raja, A., et al. (2004). Evolution of the GPGP/TÆMS
Domain-Independent Coordination Framework. Au-
tonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems, 9(1):87–
143.
Shankaran, N., Schmidt, D. C., Chen, Y., Koutsoukous, X.,
and Lu, C. (2007). The Design and Performance of
Configurable Component Middleware for End-to-End
Adaptation of Distributed Real-time Embedded Sys-
tems. In Proc. of the 10th IEEE International Sym-
posium on Object/Component/Service-oriented Real-
time Distributed Computing (ISORC 2007), Santorini
Island, Greece.
Suri, D., Howell, A., Schmidt, D. C., Biswas, G., Kin-
nebrew, J., Otte, W., and Shankaran, N. (2007). A
Multi-agent Architecture for Smart Sensing in the
NASA Sensor Web. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE
Aerospace Conference, Big Sky, Montana.
Wagner, T. and Lesser, V. (2001). Design-to-Criteria
Scheduling: Real-Time Agent Control. Lecture Notes
in Computer Science, pages 128–143.
COORDINATION OF PLANNING AND SCHEDULING TECHNIQUES FOR A DISTRIBUTED, MULTI-LEVEL,
MULTI-AGENT SYSTEM
191
