
ARCHETYPE-BASED SEMANTIC INTEROPERABILITY IN
HEALTHCARE
Alberto Marques, Ant
´
onio Correia, L
´
ucia Cerqueira
Centro Hospitar do T
ˆ
amega e Sousa, Penafiel, Portugal
Jos
´
e Machado, Jos
´
e Neves
Universidade do Minho, Departamento de Inform
´
atica, Campus de Gualtar, Braga, Portugal
Keywords:
Electronic health record, Semantic interoperability, Quality-of-Information.
Abstract:
Advances in new Methodologies for Problem Solving and Information Technology enable a fundamental
redesign of health care processes based on the use and integration of data and/or knowledge at all levels, in a
healthcare environment. Indeed, new communication technologies may support a transition from institution
centric to patient-centric based applications, i.e., the health care system is faced with a series of challenges,
namely those concerning quality-of-information and the cost-effectiveness of such processes. The distribution
of cost-effective health care allowing the patient to take active part in the caring process, provision of evidence-
based care on all levels in the system and effective use and reuse of information are key issues for the health
care organization. The information and communication technology infrastructure should therefore reflect the
view of the health care system as a seamless system where information can flow across organizational and
professional borders. Therefore, in this work it will be address key principles that must be at the center of
patient-centered technologies for disease management and prevention, namely those referred to above.
1 INTRODUCTION
The areas referred to above share the basic problem
of semantic interoperability, which simply means that
semantics is preserved in communication between
health care providers using different information sys-
tems, a circumstance which should be natural but has
proven to be very hard to achieve. Consequently,
demands of information handling within the health
care sector range from clinically valuable, patient-
specific information to a variety of aggregation lev-
els for follow-up and statistical and/or quantifiable
reporting. A number of protocols are for this pur-
pose put into use in domains such as diagnosis, health
dilemmas, interventions, and modus operandi. The
context is to assure quality of service at different lev-
els of abstraction, and to agree to process aggregation
according to different appearances or perspectives of
utilization.
However, almost all existing Electronic Health
Record (EHR) systems are built with an explicit do-
main model, a common approach in current EHR soft-
ware development practice. This means that the med-
ical domain knowledge present in these system results
in higher cost when new requirements in clinical prac-
tices occur. If a research program requires a large
amount of data to be collected from different clini-
cal sites using dissimilar EHR systems, this make it
much more difficult to add a specific feature so the
collected data will be comparable. Indeed, the lack of
integration between the different EHR systems is not
only an obstacle for a more effective clinical practice
and research, but it is also a fact that may lead to a
suboptimal care for the individual patient, including
potential safety problems and an unnecessary waste
of resources. Therefore, the new systems should be
able to record data both from clinical routine docu-
mentation and experimental studies. The users should
not be forced to duplicate the data that already might
exist in others different information systems in use at
the organization.
On the other hand, the users should be able to
link the defined data item to an external terminology,
which later can be utilized for possible data aggre-
gation and classification purposes. More importantly,
such definitions should be shared and reused by other
305
Marques A., Correia A., Cerqueira L., Machado J. and Neves J. (2010).
ARCHETYPE-BASED SEMANTIC INTEROPERABILITY IN HEALTHCARE.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence - Agents, pages 305-308
DOI: 10.5220/0002722303050308
Copyright
c
SciTePress

users than the original author for data recording, so
that the semantics and the quality of service of the
data collected from different information systems can
be maintained.
2 AGENT ORIENTED
PROGRAMMING
Although there is no universally accepted definition
of agent, in this work such an entity is to be under-
stood as a computing artefact, being used in hard-
ware or software devices, that exhibit the properties
of autonomy, reactivity, pro-activity and social be-
haviour. To develop such systems, a standard specifi-
cation method is required, and it is believed that one
of the keyfactors for its wide acceptance is simplicity.
Indeed, the use of intelligent agents to simulate hu-
man decision making in the medical arena offers the
potential to set an appropriate software development
and analysis practice and design methodology that do
not distinguish between agent and human, until im-
plementation.
Agents in a health care facility configure applica-
tions or utilities that collect information about the as-
sets in the organization (Alves et al., 2005). Once that
information has been collected it can be posted di-
rectly to other entities (e.g. a physician), or a server,
saved in a file or emailed to someone to be handled
at a later date, or sent using HL7 (Health Level 7)
1
or web services in a Service Oriented Architecture
(SOA). Indeed, HL7 plays an essential role in extend-
ing the interoperability for the development of health
information exchange, in the standardization of XML
medical document structures and in the specification
of robust vocabulary definitions for use in clinical
messages and documents (e.g., SNOMED CT),
2
en-
abling functional specifications for the EHR
3
.
3 AIDA
In order to fulfil this goal it was designed and de-
veloped an Agency for the Integration, Difusion, and
Arquive (AIDA), which allows to interoperate with
different information systems at the organization or
area levels. The agency conceptually consists of 9
1
http://www.hl7.org
2
http://www.ihtsdo.org/
3
AIDA-EHR is a portuguese EHR developed at Centro
Hospitalar do Porto and based in Problem Oriented Medical
Record methodology (Weed, 1969).
Figure 1: The AIDA Architecture.
(nine) agent based subsystems: AIDA-RIS - Radio-
logical Information System; AIDA-MEIS - Medical
Exams Information System; AIDA-LIS - Laborato-
ries Information System; AIDA-ISM - Information
System for Monitoring (e.g., vital signals monitor-
ing); AIDA-PRM - Patient Relationship Management
(including communication using SMS); AIDA-OWM
- Organizartion and Work Management (Including
agenda, scheduling, planning and resource man-
agement; AIDA-EHR- Electronic Health Records;
AIDA-HL7 - Interoperation of systems; and AIDA-
SOA - Service Oriented Architecture; where the or-
ganization data (e.g. patient data) is stored and man-
aged (Figure 1). These nine subsystems are commu-
nicating using web services, in terms of HL7 or XML
based messages. The definition of attributes and tem-
plates can be shared among different healthcare units
having separate information systems. AIDA supports
Web based services (AIDA-SOA) to facilitate the di-
rect access to the information and communication fa-
cilities set by the humans, i.e. AIDA construction fol-
lows the acceptance of simplicity, the conference of
the achievement of common goals and the address-
ing of responsibilities. Indeed, the main goal is to
integrate, diffuse and archive large sets of informa-
tion from heterogeneous sources (departments, ser-
vices, units, computers, medical equipments). Un-
der these pressuppositions, a Healthcare Information
System (HIS) will be addressed in terms of (Figure
1). This system is also now a reality in some major
portuguese hospitals, being developed and configured
from generated forms of the EHR and sharing infor-
mation through AIDA.
This system is also now a reality in some major
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
306

portuguese hospitals, being developed and configured
from generated forms of the EHR and sharing infor-
mation through AIDA ((Rigor et al., 2008)). Another
interesting application of ubiquitous intelligent sys-
tems is described in ((Costa et al., 2007)). EHR and
AIDA are the starting point for the creation of Ambi-
ent Assisted Living practices on an ubiquitous com-
putational environment for improving the quality-of-
life of the elderly, being the core system for AIDA-CI
Clinical Inteliigence and Decison Support and AIDA-
IA - Ambient Intelligence.
4 THE COMPUTATIONAL
MODEL
With respect to the computational model, and in or-
der to fulfil all the pre-requisites associated to Agent
Oriented Programming (AOP) stated above, it were
considered extended logic programs with two kinds
of negation, classical negation, ¬, and default nega-
tion, not. Intuitively, not p is true whenever there is
no reason to believe p, whereas ¬p requires a proof of
the negated literal. An extended logic program (pro-
gram, for short) is a finite collection of rules and in-
tegrity constraints, standing for all their ground in-
stances, and is given in the form:
p ← p
1
∧ . . . ∧ p
n
∧ notq
1
∧ . . . ∧notq
m
; and
?p
1
∧ . . . ∧ p
n
∧ notq
1
∧ . . . ∧notq
m
, (n, m ≥ 0)
where ? is a domain atom denoting falsity, the p
i
,
q
j
, and p are classical ground literals, i.e. either posi-
tive atoms or atoms preceded by the classical negation
sign ¬ (Neves et al., 2007). Every program is associ-
ated with a set of abducibles. Abducibles can be seen
as hypotheses that provide possible solutions or ex-
planations of given queries, being given here in the
form of exceptions to the extensions of the predicates
that make the program (Neves, 1984).
These extended logic programs or theories stand
for the agents (or programs) that populate the universe
of discourse. On the other hand, logic programming
enables an evolving agent to predict in advance its
possible future states and to make a preference. This
computational paradigm is particularly advantageous
since it can be used in program synthesis, employ-
ing the methodologies for problem solving that ben-
efit from abducibles, in order to make and preserve
abductive hypotheses (Kakas et al., 1998)(Kowalski,
2006).
In order to accomplish such goal, i.e., to model
the universe of discourse in a changing environment,
the breeding and executable computer programs (or
agents) will be ordered in terms of the quality of ser-
vice that stems out of them, when subject to a pro-
Figure 2: A blended of the agents that make the Universe of
Discourse.
cess of conceptual blending (Turner and Fauconnier,
1995). In blending, the structure or extension of two
or more predicates is projected to a separate blended
space, which inherits a partial structure from the in-
puts, and has an emergent structure of its own. Mean-
ing is not compositional in the usual sense, and blend-
ing operates to produce understandings of composite
functions or predicates, the conceptual domain, i.e.,
a conceptual domain has a basic structure of enti-
ties and relations at a high level of generality (e.g.,
the conceptual domain for journey has roles for trav-
eler, path, origin, destination). In our work we will
follow the normal view of conceptual metaphor, i.e.,
metaphor will carry structure from one conceptual do-
main (the source) to another (the target) directly (Fig-
ure 2). In Figure 2 INPUT denote the agents (or pro-
grams) that are object of optimization and correlative
evolution.
We construct a dynamic virtual world of complex
and interacting population of agents, entities that are
built as evolutionary logic programs or theories that
compete against one another in a rigorous selection
regime, in order to produce the optimal model to a
particular problem(i.e., the OUTPUT, Figure 2). In
other words, the agents or logical theories evolve in
order to model the universe of discourse, in which fit-
ness is judged by one criterion alone, the quality of
service (Analide et al., 2008).
It is now possible to measure or quantify the qual-
ity of service, which is given in terms of the logic
program or theory, defined at meta-level, according to
the logic program (or agent) given below:
{¬qos(Agent, Q
service
) ←
not qos(Agent, Q
service
)∧
not exception
qos
(Agent, Q
service
),
exception
pa
(ag
pa
, 0.5),
exception
pa
(ag
pa
, 0.33),
?(((pa(ag
pa
, X)∨
ARCHETYPE-BASED SEMANTIC INTEROPERABILITY IN HEALTHCARE
307
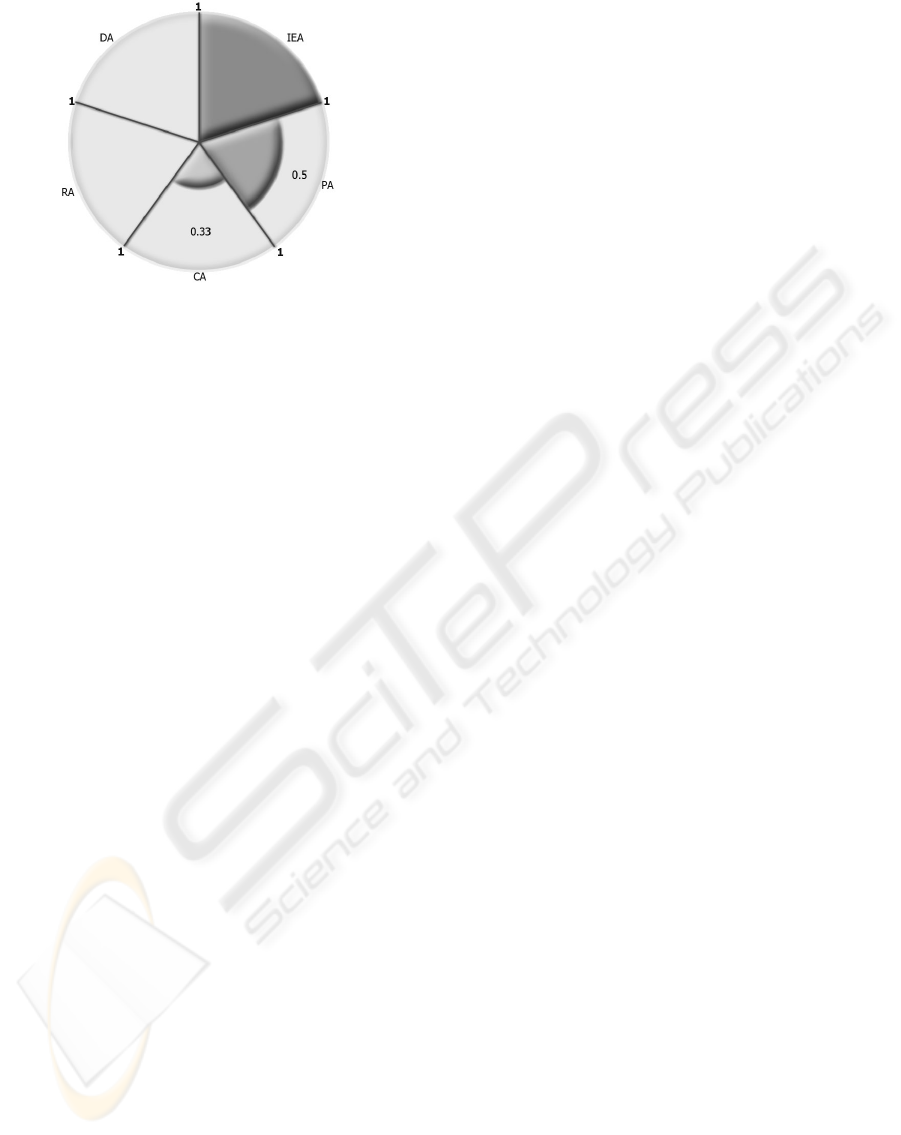
Figure 3: Quality of service reported by the qos agent for
the Healthcare Information System.
pa(ag
pa
, Y )∧
¬((pa(ag
pa
, X)∧
pa(ag
pa
, Y ))),
exception
pa
(X, Y ) ← da(ag
pa
, Y ),
da(ag
da
, da),
ca(ag
ca
, 1),
. . .}
qosagent
where the integrity constraint or invariant for ag
pa
stated above denotes an exclusive or, i.e., the qual-
ity of service associated with the ag
pa
is tailored by
the exceptions referred to above for ag
pa
(in this case
the value of 0.5). Therefore, the quality of service
reported by the qosagent for the Healthcare Informa-
tion System is given by the dashed area of the Figure
3, where pa, da, ca, ra and iea are respectively pred-
icates for evaluating the quality of service of proxy
agents, decision agents, computing agents, resource
agents and interaction and explanation agents.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This work presents ongoing research and some de-
velopments on improving semantic interoperabil-
ity of different information systems, using open
archetypes. It was introduced an archetype-based
agency-independent testing framework, the agency
AIDA, that can validate archetype implementations
and help ensure quality of service and interoperabil-
ity of singular information systems. Challenges for
integrating archetype and terminology was discussed
and a candidate open language for expressing termi-
nological value sets was presented. Finally, advanced
archetype-based data sharing using clinically mean-
ingful scenarios was demonstrated. The aim was not
only to view the exchanged data but also utilized the
archetype semantics of the data. The scenarios in-
cluded the use of local decision support rules on re-
ceived data, namely drug interactions and warnings.
REFERENCES
Alves, V., Machado, J., Abelha, A., and Neves, J. (2005).
Agent based decision support systems in medicine. In
WSEAS on Biology and Biomedicine, Issue 2, Volume
2.
Analide, C., Abelha, A., Machado, J., and Neves, J. (2008).
An agent based approach to the selection dilemma in
cbr. In Badica, C., Mangioni, G., Carchiolo, V., and
Burdescu, D. D., editors, IDC, volume 162 of Studies
in Computational Intelligence, pages 35–44. Springer.
Costa, R., Neves, J., Novais, P., Machado, J., Lima, L., and
Alberto, C. (2007). Intelligent mixed reality for the
creation of ambient assisted living. In Neves, J., San-
tos, M., and Machado, J., editors, Progress in Artifi-
cial Intelligence, volume 4874. LNAI, Springer.
Kakas, A., Kowalski, R., and Toni, F. (1998). The role of
abduction in logic programming. In Gabbay, D., Hog-
ger, C., and Robinson, J., editors, Handbook of logic
in Artificial Intelligence and Logic Programming, vol-
ume 5, pages 235–324. Oxford University Press.
Kowalski, R. (2006). The logical way to be artificially intel-
ligent. In Toni, F. and Torroni, P., editors, Proceedings
of CLIMA VI. LNAI, Springer Verlag.
Neves, J. (1984). A logic interpreter to handle time and
negation in logic databases. In Proceedings of ACM
1984 Annual Conference, San Francisco, USA.
Neves, J., Machado, J., Analide, C., Abelha, A., and Brito,
L. (2007). The halt condition in genetic programming.
In Neves, J., Santos, M. F., and Machado, J., editors,
EPIA Workshops, volume 4874 of Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, pages 160–169. Springer.
Rigor, H., Machado, J., Abelha, A., Neves, J., and Alberto,
C. (2008). A web-based system to reduce the nosoco-
mial infection impact in healtcare units. In Cordeiro,
J., Filipe, J., and Hammoudi, S., editors, WEBIST (1),
pages 264–268. INSTICC Press.
Turner, M. and Fauconnier, G. (1995). Conceptual inte-
gration and formal expression. In Johnson, M., edi-
tor, Journal of Metaphor and Symbolic Activity, vol-
ume 10.
Weed, L. (1969). Medical records, medical education, and
patient care. the problem-oriented record as a basic
tool.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
308
