
HIERARCHICAL COORDINATION
Towards Scheme based on Problem Splitting
Said Brahimi
Science Computer Department, University of Guelma, BP 401, Guelma 24000, Algeria
Ramdane Maamri, Zaidi Sahnoun
LIRE Laboratory, University of Mentouri, BP 325 Constantine25017, Algeria
Keywords: Multi-agent planning, Tasks organization, Planning-execution interleaving, Hierarchical coordination.
Abstract: Using multi-agent planning in real and complex environments requires using a flexible coordination
scheme. The aim of this paper is to give a principle of coordination scheme for systems that work in these
environments. This scheme is viewed as a hierarchical structure of coordination cells (CC). Each cell is
controlled by meta-level agent, and is occupied to coordinating a sub-set of plans. The structure of
coordination scheme, that is dynamically formed, can be purely centralized, purely distributed, or
hierarchical according to interdependency degree of plans. The idea, behind of, is based on problem
splitting techniques. This technique that is embodied in the coordination process, allows to reorganizing
structure of CC. there are two mains operation on CC: split and merge. Each CC will be split if the problem
of coordination can be divided. The CCs should be merged according failure of a cell to find a solution.
1 INTRODUCTION
The work presented in this paper is articulate in
multi-agent planning context, where the main
problem is how to coordinating planning agents. A
number of works have been proposed in the past.
They may be categorized in three classes (Durfee
1999): Centralized planning for distributed plans,
Distributed planning for centralized plans, and
Distributed planning for distributed plans. In these
classes of multi-agent planning, two mains
approaches may be distinguished for treating the
coordination problem: centralized and distributed
coordination. In centralized approach there is one
coordination agent that is able to remove a conflict
between plans of all agents. This approach has
advantage that is adequate for loosely independent
plans. But it is not convivial for tightly plans,
especially for inherent distributed application. In a
distributed coordination, the activity of conflict
removing is distributed between several autonomous
agents. If this approach is appropriate for
coordination loosely plans, he is not for tightly
one’s.
Using multi-agent planning in complex and
dynamic environments (like robotic, services web
composition, etc.) requires implementation of
powerful and adaptive systems. These systems must
be able to adapting to the execution context. In this
paper we propose a coordination scheme for
merging plans of several agents. In our approach, the
aspect of centralized or distributed coordination is
dynamically determined, depending on the degree of
interdependency between plans. For implement this
idea we benefit from the nature of abstract reasoning
on hierarchical plans. We propose a technique
allowing dividing the coordination problem into set
of independent sub-problems. This technique is used
for elaborating a new coordination scheme. This
scheme is composed of set of coordination-cells
organized in a hierarchical and dynamic structure.
The remaining of this paper is organized as
follows. In the second section we outline briefly the
background of our work. In next section we present
the idea of the independent sub-problems specifying
and identifying algorithm. In section four, we
describe the new coordination scheme. The fifth
section presents some works related to our model.
327
Brahimi S., Maamri R. and Sahnoun Z. (2010).
HIERARCHICAL COORDINATION - Towards Scheme based on Problem Splitting .
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence - Agents, pages 327-331
DOI: 10.5220/0002728403270331
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Overview of Approach
The multi-agent system considered here is composed
of two types of agents: Domain-Dependant Agent
(DD-agent) and Meta-Level Agents (ML-agent).
The first one concerns the agents that carry out
domain tasks. Each DD-agent Ai is
planning/execution agent. It has hierarchical plan
HP
i
for accomplishing an abstract task T
i
. However,
the second type concerns the coordination agents.
The ML-agents collect {HP
i
}
i=1..N
of all DD-agents
{A
i
}
i=1..N
in order to maintain a global consistency
between them. The result of this phase is conflict-
free set of local plans, {HP’
i
}
i=1..N
. After
coordination phase each DD-agent Ai can start the
execution of his HP’i. In this paper we deal with a
coordination step. The coordination process is
started by one ML-agent as centralized multi-agent
planning. If coordination problem may be divided
into independent sub-problems, then the first ML-
agent may generate one agent for each sub-problem.
In the next’s sections we explain how identifying
and decomposing de coordination problem. We
firstly starting by explain the principle of how
merging a set of hierarchical plan in centralized
manner.
2.2 Main Concepts
In our work we use (with some simplification) the
technique of abstract reasoning, for planning and
coordination, proposed by clement in (Clement
2002).
2.2.1 Local Plan Structure
Local plan HP
i
of DD-agent A
i
is hierarchical plan
(Like the CHiPs model of Clement) that has AND-
OR-tree-like structure. Each node is plan represented
by tuple P = (pre, in, post, type, subplans, order).
pre, in, post are (like Strip model of action)
conditions that must be respectively satisfied before,
in, and after plan execution. type ∈{primitive, and-
plan, or-plan} indicates if a plan P is and-plan (may
be decomposed to sub-plans in subplans), or-plan
(may be instantiated by one plan in subplans), or
primitive. A primitive plan is atomic executable one.
orders is a set of temporal order constraint between
sub-plans (of and-plan only). The pre, in, post
conditions are called summary information because
they summarize the conditions required for abstract
plan execution without refining them. This
information is propagated from primitive plans. The
algorithm of how extracting this information is
explained in (Clement, 1999).
2.2.2 Interaction between Local Plans
Concurrent execution of abstract plans may lead to a
conflicting situation. Formally, there is a conflict
between plans p
i
and p
j
if the following condition is
true: ∃ c, c∈(in(p
i
)∪post(p
i
)) ∧ ¬c∈(in(p
j
)∪pre(p
j
))
such that i,j∈{1,2} and i≠j. Conflict may be
removed by decomposing of and-plan, instantiating
or-plan (by choosing one Subplan of or-plan and
blocking the others), and by plans scheduling. The
conflict may or may not be removed according to i)
nature of the conditions that is mast or may hold, and
ii) order constraints between plans and the fact that it
exist some other plans that mask or may mask the
interference between plans. Three properties can be
used for identifying these interaction situations
(Clement 1999): 1) CanAnyWay or CAW (Ps, Or):
the plans Ps ={P
i
}
i=1..u
under Order Or={ p
i
طq
i
}
i=1..v
are threat-free; the set of plan Ps can be executed in
“safe” manner. 2) MightSomeWay or MSW(Ps, Or):
the conflict between plans in Ps can be solved. 3)
¬MightSomeWay(Ps, Or): the plans Ps have
irresolvable conflicts.
2.2.3 Centralized Coordination Process
Coordination process consists of merging the local-
plans {HP
i
}
i=1..N
in conflict-free Global Plan (GP).
In the centralized coordination process, there is only
one ML-agent that coordinates the plans of all DD-
agents. The GP, is defined by tuple (Ps , Or, Bck)
such that: Ps is set of abstract (or ground) plans, Or
is set of order constraints between plans, and
Bck={(p, {p
i
}
i
)/ p
i
∈ Subplans(p) and p
i
is not
selected} is set of blocked plans. Initially,
coordination process start with GP gp=({pi/pi is
abstract plan in HP
i
}
i=1..N
, {},{}). The result is a
conflict-free gp=(Ps, Or, Bck), or CAW(Ps, Or) is
true.
The Coordination process is viewed as global-
plan refinement. The plans in hierarchical-plans are
progressively merged. The eventual conflicts
between plans are progressively removed until
conflict-free GP is obtained. The backtracking is
possible if current global plan has irresolvable
conflicts, or ¬MSW(GP). For a more thorough
description see (Clement 1999).
The next section illustrates how this technique
will be extended, for passing from the centralized
coordination to partially centralized one.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
328

3 INDEPENDENTS
SUB-PROBLEMS
IDENTIFYING
The reasoning on abstracts plans (using summary
information) allows to characterize the central aspect
of how identify and handle the threat relationships
between abstract plans. We use this principle to
provide a technique that help to identify the fact that
some subset of abstracts plans can (or cannot) be
independently refined. This aspect may lead to
localize the influence of some abstract plans.
Identifying the subset of interfered plans (those
concerned by conflict removing) can allows to
dividing coordination problem into set of sub
problems, which can be solved by several agents in
parallel manner.
For identify the subset of interfered plans we
define Executable-Any-Way property, note
EAW
Ctxt
(p
1
, p
2
), that indicate (if it is false) that there
is conflict between two plans, p
1
, p
2
. The Cxt=(Ps,
Or) is a context representing the global plan
containing the p1 and p2. The EAW is derived by the
projection of CAW on two plans p
1
, p
2
as follow:
EAW
(Ps, Or)
(p
1
, p
2
) = CAW({p
1
, p
2
}, rel) (1)
where rel is inferred from (Ps, Or).
The problem of global-plan refining may be
divided to several independent sub-problems. Each
sub-problem concerns one partial-global-plans
refinement. Formally independent sub-problem of
GP (Ps, Or, Bck) is defined by SubInd (Ps,Or,Bck) =
∪
i
{(Ps
i
, Or
i
, Bck
i
)}. Such that:
a) Ps
i
⊂ Ps, ∪
i
Ps
i
= Ps
and ∩
i
Ps
i
= ∅
b) ∀ i, j and i ≠ j : ∀ p
l
∈ Ps
i
, ∀p
m
∈ Ps
j
,
EAW
(HPs,Or)
(p
l
, p
m
)
c) ∀ i, ∀ p
li
, p
mi
∈ Ps
i
,
c.1) ¬ EAW
(Ps,Or)
(p
li
, p
mi
) ; or
c.2) ∃ p
ki
∈ Ps
i
such that ¬ EAW
(Ps,Or)
(p
li
, p
ki
)
and ¬EAW
(Ps,Or)
(p
ki
, p
mi
)
d) Or
i
and Bck
i
are obtained by projection Or
and Bck on Ps
i
The property b characterizes Intra-dependency of
plans in one sub-problem. Whereas, the property c
characterizes Inter-Independency of plans belonging
to different sub problems. Based on these property,
we propose the procedure (Split) to compute
independent-sub-problems. The procedure get GP
(Ps, Or, Bck) of current state of refinement problem,
and provide set of subset plans, {Ps
i
}
i=1..ind
,
concerning independent sub-problems (partial-
global-plans).
Procedure Split(Ps,Or)
begin
Cand ← Ps
Ind ← 0
for each p∈ Ps do
Cand←Cand–{p}
if ¬ IsColored(P) then
Ind ← Ind + 1
Ps
Ind
← {p}
Color (p)
Closing(p,Ps
Ind
,Cand,Ps,Or)
end-if
end-for
return ({Ps
i
}
i=1..ind
)
end.
Procedure Closing(p,Ps
Ind
,Cand,Ps,Or)
begin
For p’∈ Cand do
if ¬EAW<Ps,Or>(p’,p) then
Ps
Ind
← Ps
Ind
∪{p’}
Color(p’)
Closing(p’,Ps
Ind
,Cand,Ps,Or)
end-if
end-for
end.
4 TOWARDS
PARTIALLY-CENTRALIZED
PLANS MERGING SCHEME
The identification procedure of independents-sub-
problems can be embodying in the centralized
coordination process as intermediate stage. In each
(or in some) refinement’s iteration, the global-plan is
analyzed and examined to be divide. The
independent sub-problems refinement may be
assigned to new ML-agents and so on. The result is
partially centralized scheme of coordination. For
monitoring the coordination scheme we introduce
some concepts like Mediator and Coordination-Cell.
4.1 Mediator and Coordination-cell
In the centralized coordination there is one ML-
agent and all DD-agents. The all form one
(Centralized) Coordination-Cell (CC), with one
Coordinator (figure 2, left scheme). If a coordinator
A can divide refinement problem of GP gp to m
independent-sub-problems {pgp
i
}
i=1..m
, it affect each
pgp
i
to new ML-agent A
i
. In this case, the first cell
has been split to n+1 new cells. One cell, controlled
by A , and containing the member {A
i
}
i=1..m
. each one
of the other cells is controlled by A
i
and containing,
HIERARCHICAL COORDINATION - Towards Scheme based on Problem Splitting
329
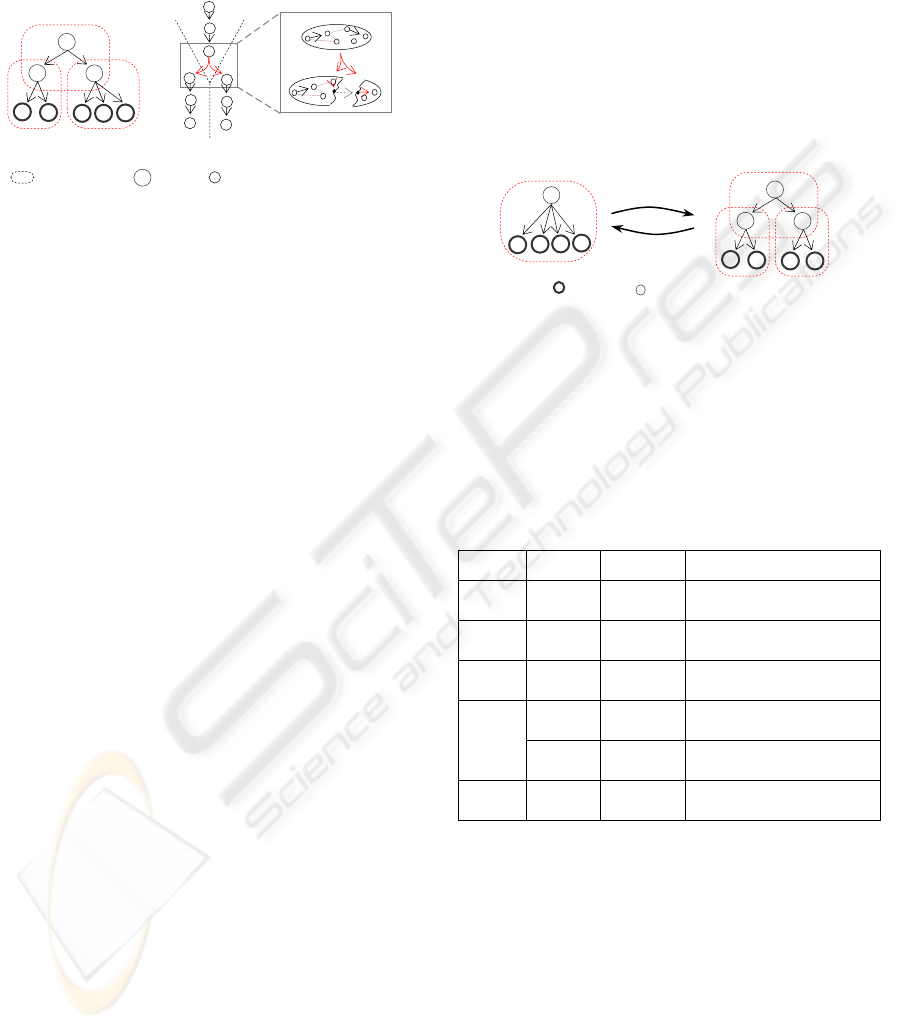
as member, DD-agents that has some plan in partial-
global-plans PGP
i
refined by A
i
. The agent A
become a simple monitor, and each agent A
i
become
Coordinator.
Figure 1: CC (i) and refining space of each ML-agent (ii).
Formally, CC is defined by tuple (M
A
, Ams). M
A
is called Mediator (Coordinator or Monitor) of the
cell, and Ams is a set of Member. The Members of
CC controlled by a Coordinator are DD-agents.
However The Members of CC controlled by a
Monitor are ML-agents that are Mediator in other
cells. To each Mediator X, we associate two
functions: Pb(X) and Pbs(X). Pb(X) is the initial
state of problem refining, and Pbs(X) is the state of
problem refining requiring the split. So for each CC
(M
A
, Ams):
SubInd (Pbs(M
A
)) = {Pb(X
i
) / X
i
∈ Ams}
(2)
Coordination-Cells are organized in hierarchical
structure (
Figure 1). One ML-agent may be mediator
in one cell and Member in other’s one (agent B and
C in figure 1.i). Moreover, a mediator may be
superMediator (sM) and/or groundMediator (gM). A
superMediator is the mediator that starts the
coordination process, groundMediator is
Coordinator. So, the same DD-agent may be
required in several CC (agent E in figure 1.i).
4.2 Coordination Scheme Monitoring
Once Coordination-Cell (M
A
, Ams) is split to {(M
A
,
Ams’)}∪{(M
Ai
, Amsi)}
i
, the agent M
A
become
Monitor, and each new Mediator M
Ai
become
groundMediator. In this state, the Monitor waits
notification from Members cell, Ams’, about sub-
problems solutions. However, each new
groundMediator M
Ai
continues the refinement of one
partial-global-plan. As the backtracking is possible
where current (partial) global plan P has irresolvable
conflicts (¬MSW(P), coordinator may fail to find
one solution (conflict-free PGP). In this case the CC
controlled by this coordinator must be destroyed. As
the solutions of sub-problems are all required for the
global solution, some CCs must be merged in order
to be split in other manner. Formally, in
configuration {(M
A
, Ams’)}∪{(M
Ai
,Ams
i
)/ M
Ai
∈
Ams’}
i
, the fail of one cell (M
Ai
, Ams
i
) lead to merge
all cells {(M
Ai
, Ams
i
)}
i
in one cell controlled by M
A
,
or (M
A
, ∪
i
Ams
i
). The configuration of CC is
dynamically updated according to CC-splitting and
CC-merging operations (
Figure 2). It will stabilize if
conflict-free global-plan would be obtained.
Formally the stabilization state is configuration in
which all groundMediator found conflict-free PGP.
Figure 2: splitting and merging of CC.
The mediators communicate together by sending
message five messages (table 1): PGP (partial global
plan), Good (sub-problem is successfully solved),
Bad (sub-problem may not be solved), OK
(confirmation of solution), and Cancel (cancel
problem solving).
Table 1: Message sent between ML-agents.
M
essage Sender Receiver Trigger
PGP
Mediator
of CC
members of
CC
The Problem is split
Good
Member
of CC
Mediator of
CC
The sub-problem is
solved
Bad
Member
of CC
Mediator of
CC
sub-problem has not
solution
OK
sM of CC
members of
CC
Receive Good from All
members of CC
Mediator
of CC
members of
CC
Receive OK from his
Mediator
Cancel Mediator
members of
CC
Receive Bad from some
member of CC
If the solution of all sub-problems has been
finding, they are sent to involved DD agents. If one
of sub-problem is failed to be solved, the other sub-
solution must be cancel (via Cancel message). The
cancel message concern backtracking case. Finally,
OK message should be sent by high level mediator
to confirm the sub-solution of mediator at low level.
5 RELATED WORKS
Our work extends multi-level centralized
coordination (clement 2002) by adding the
A
B
C
Coordination-Cell
-i-
-ii-
(A,{B,C})
A
B
C
D
E
F G
GP
PGP
1
PGP
2
E
(C,{F,G,E}) (B,{D,E})
x
agent
State of problem refining
A
B
C
D
E
F
G
A
D
E
F
G
CC-Splitting
CC-Merging
DD-agent
ML-agent
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
330

decentralized dimension to coordination process. For
this end we are based on idea similar to the one
proposed in (Lotem & Nau 2000). Furthermore our
work focuses on the use of mediation idea and
partially centralized aspect. This ideas is similar to
those used in other works like (Sims et al, 2006,
Mailler & Lesser 2006, Durfee & Lesser, 1991).The
first are focuses on static organization where
mediator is determined in static way. However, in
our work the mediation is dynamic and related to the
interdependently degree of plans. The second work
(Sims et al, 2006), that use “Optimal Asynchronous
Partial Overlay” (OptAPO) algorithm, while it used
for DCSP problem, he has similar idea of the
dynamic Mediation role designation. In other hand,
the mediation is established by sub-problem
merging. The main difference is that a mediation
role definition and assignment was focused on the
abstraction aspect of the plans. Furthermore the
mediation is depending on the sub-problems
Merging and Splitting technique together. There is
another works (Hayashi 2007, DesJardins &
Wolverton 1999) similar to ours work. It base on the
idea of delegating a part of planning problem of
parent agent to its child agents. The multi-agent
planning scheme is relatively similar to the one in
our work. The main difference is situated in the
splitting method. The work was not taken in
consideration the independent splitting. This point is
important especially in the case of dynamic
planning.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we presented some principles for
implementing a scheme of hierarchical coordination,
based on Coordination-Cell concept (CC). The CCs
in this scheme, that are hierarchical organized, are
progressively structured. The evolution of the
structure is based on two operations: CC-splitting
and CC-merging. The structure is stabilized once the
conflict-free global plan is obtained. The idea behind
is based on incorporation of problem splitting
technique into centralized coordination. The global
plan is dynamically decomposed to set of partial-
global-plan based on localization of interference
between plans. This hybridization, between
centralized and distributed coordination, is
appropriate especially in complex and dynamic
environments. This scheme of coordination can
favor the interleaving of planning and execution,
some part of global plan can be repaired when others
are in execution.
The future work will be focused on formalization
of the theoretical concepts. We will deal also with
how monitoring the hierarchical coordination
process in the case of dynamic planning (where the
planning and execution process are interleaved).
REFERENCES
Clement, B. J. 2002. Abstract Reasoning for Multiagent
Coordination and Planning. P.H.D. Dept. of
Computer Science, university of Michigan.
Clement, B. J., and Durfee, E. H. 1999. Theory for
Coordinating Concurrent Hierarchical Planning
Agents Using Summary Information. Proceedings of
the Sixteenth National Conference on Artificial
intelligence, pp 495-502
Durfee, E. H., and Lesser, V. R. 1991. "Partial Global
Planning: A Coordination Framework for Distributed
Hypothesis Formation." IEEE Transactions on
Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Special Issue on
Distributed Sensor Networks, SMC-21(5):1167-1183.
Durfee, E. H. 1999. Distributed problem solving and
planning. In G.Weiss (ed.), In G. weib, Editor, A
modern approach to the distributed Artificial
Inteligence, chapter 3,
DesJardins, M., and Wolverton, M. 1999. Coordinating
planning Activity and Information Flow in a
Distributed planning system. AI Magazine, Volume
20, Number 4.
Hayashi, H. 2007. Stratified Multi-agent HTN Planning in
Dynamic Environments. KES-AMSTA 2007, LNAI
4496, pp. 189–198.
Lotem, A., and Nau, D. S. 2000. New Advances in
GraphHTN: Identifying Independent Subproblems in
Large HTN Domains. In Proc. Fifth International
Conference on Artificial Intelligence Planning and
Scheduling pp. 206-215. Breckenridge, CO, April 14-
17.
Mailler R., Victor R. Lesser. 2006. Asynchronous Partial
Overlay: A New Algorithm for Solving Distributed
Constraint Satisfaction Problems. Journal of Artificial
Intelligence research 25.
Sims M., Mostafa H., Horling B., Haizheng, V. Lesser.
2006, Daniel Corkill, and John Phelps. Lateral and
Hierarchical Partial Centralization for Distributed
Coordination and Scheduling of Complex Hierarchical
Task Networks. American Association for Artificial
Intelligence.
HIERARCHICAL COORDINATION - Towards Scheme based on Problem Splitting
331
