
AGENT-BASED SYSTEMS DESIGN FOR VIRTUAL
ORGANISATIONS FORMATION
Tiemei Irene Zhang
School of Management and Information Systems, Faculty of Business and Law, Victoria University
Footscray Park Campus, Australia
Keywords: Agent-based systems, Methodology of analysis and design, Virtual organisation.
Abstract: These days, organisations must adapt to business and technical changes which are vital in a competitive and
ever-changing business environment. To meet the dynamically changing requirements, virtual organisation
is widely recognised as an effective solution. Multiple agent technology has been actively discussed and
recognised as the merit of flexibility and adaptability. Thus, this technology can be applied to virtual
organisations. To prevent from being impeded by using incongruous approaches to designing agent-based
systems, systematic approach is essential to incorporate a variety of organisation business units that are
required to meet current and future needs. This paper aims to present a systematic approach including
process of analysis and design to designing virtual organisations. It also demonstrates a case study for
application of this approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
These days, organisations must adapt to business
and technical changes which are vital in a
competitive and ever-changing business
environment. However business processes in
organisations are so complicated that traditional
organisations cannot efficiently cope with this
challenge. Furthermore, the organisations that are
geographically dispersed face more difficulties. To
meet the dynamically changing requirements (Patel
et al, 2005), strategic alliance of business processes
is necessary to be put into practice (Schneider,
2009). Virtual organisation is widely recognised as
an effective solution to be able to address this issue.
As a virtual organisation is the goal-driven dynamic
assembly of organizational tasks (Shan et al, 2006)
and is created for specific business need, it can
simplify business processes.
To establish virtual organisations, IT
infrastructure is fundamental and critical to provide
feasible and supportive solutions. Efficiency and
effectiveness of the infrastructure determines the
success of a virtual organisation in goal sharing,
collaborations, ownerships and functionalities.
Multiple agent technology has been actively
discussed and it is recognised as the merit of
flexibility and adaptability (Kollingbaum et al,
2006), (Udupi & Singh, 2006). Its application to
virtual organisations is a wise decision. To prevent
from being impeded by using incongruous
approaches to designing agent based systems,
systematic approach to designing virtual
organization is essential to incorporate a variety of
organisation business units that are required to meet
current and future needs. Although some of
researchers have applied multiple agent systems to
virtual organisation formation (Leong et al, 2006),
how to systematically design a virtual organization
is neither explicit nor well-developed.
This paper aims to present an agent-based
systematic approach to designing virtual
organisations. Following introduction and
background sections, §3 depicts how a virtual
organisation is logically structured. §4 describes an
engineering process to analyse and design agents for
a virtual organization. A case study is then
presented to demonstrate application of this research
in §5. Finally, §6 concludes the paper and discusses
further research.
54
Irene Zhang T. (2010).
AGENT-BASED SYSTEMS DESIGN FOR VIRTUAL ORGANISATIONS FORMATION.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence - Agents, pages 54-61
DOI: 10.5220/0002728900540061
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 BACKGROUND
2.1 Virtual Organisation
A virtual organization is described as: “a temporary
network of independent companies – suppliers,
customers, even erstwhile rivals – linked by
information technology to share skills, costs and
access to one another’s markets. It will have neither
central office nor an organization chart.” (Byrne,
1993) The term “virtual organization” is also used
to cover a wide range of geographically dispersed
organizations. These may be linked by common
goals with each requiring a new style of
management and reassessment of the role of
management. The Internet and related technologies
are used as a means of communication and
collaboration (Collins, 2002).
In reality, the components that make up a virtual
organization – individual employees, teams,
departments, units or firms – are geographically
distributed, functionally or culturally diverse,
electronically linked and connected via lateral
relationships. These attributes enable the
organization to dynamically modify business
processes to meet market demands, to coordinate via
formal and informal contracts, to define the
boundaries of the firm differently over time or for
different customers or constituencies, and to re-
arrange relationships among components as needed.
(Pedersen & Nagengast, 2008)
2.2 Multiple Agent Systems in Virtual
Organisation
Researchers have actively discussed and addressed
issues of applying software agents to virtual
organisations. After investigating 14 AOSEs
(Agent-Oriented Software Engineering)
methodologies, Leong et al (Leong et al, 2006)
claimed that these methodologies do not have strong
contributions in terms of virtual organisation (VO)
formation and management. VO formation and
management still remain as open research problems.
In addition, they also pointed out that application of
these technologies is lack of software engineering
techniques.
Shan et al (Shan et al, 2006) proposed an agent-
mediated service framework in which an ad hoc
approach is used to design their agents. To improve
the adaptive ability of the agent design methods in
uncertain environment, Zhang (Zhang, 2009)
proposed a modelling method based on role theory
and Agent UML. Pournaras et al (Pournaras et al,
2009) developed an approach to making use of
virtual organisation consisting of agents for
distributed management of resource utilisation.
In summary, it is widely recognised that virtual
organisations are characterised by flexibility and
adaptability. Software agent and multiple agent
systems are actively investigated and determined to
be an efficient way for virtual organisation
formation and management. Although some
methodologies have been developed for agent-based
systems’ analysis and design, due to their
limitations, systematic methodologies and software
engineering techniques for virtual organisation
formation are still open for investigation.
3 VIRTUAL ORGANISATION
ARCHITECTURE
The layered architecture pattern (Buschmann et al,
1996) has been widely accepted as a standard in
network design and software engineering. This
architecture reduces the coupling and complexity of
dependencies that may occur in individual problems.
The architecture can be used to structure
applications that can be decomposed into groups of
subtasks. Each group of subtasks must also be at a
particular level of abstraction.
To apply this architectural pattern to an agent-
based system, the following forces need to be
considered:
An agent system is complex and spans several
levels of abstraction;
There are dependencies between neighbouring
levels, with two-way information flow;
The software architecture must encompass all
aspects of agency;
The architecture must be able to address simple
and sophisticated agent behaviour.
The following several reasons discuss why
agents in a virtual organisation should be
decomposed into layers:
The agents of higher levels, or with more
sophisticated behaviour, depend on lower
level capabilities
Layers only depend on their neighbours, and
there is two way information flow between
neighbouring layers for communication.
The agents of lower levels focus on specific
tasks and services.
The layers can be identified from modelling of
the agents’ real world
AGENT-BASED SYSTEMS DESIGN FOR VIRTUAL ORGANISATIONS FORMATION
55
Each layer provides a level of abstraction and
certain services to the layer above it, while hiding
the implementation of its services from the higher
layers. Also, each layer passes both data and control
information to its corresponding neighbours. This is
similar to communication within an organisation in
the real world. This communication is classified
into categories described as below (Ivancevich et al
1997):
Downward-communication: communication
flows downward from higher levels of the
hierarchy to lower levels. This type of
communication serves some organizational
functions, such as job instruction, job
rationale, and procedures.
Upward-communication: communication flows
from a lower level in an organisation to a
higher level. This type of communication
provides organizational functions, such as
feedback of a problem, and information
required for decision making.
Horizontal-communication: communicators are
in the same level. This is necessary for the
coordination and integration of diverse
organizational functions to get social need
satisfaction.
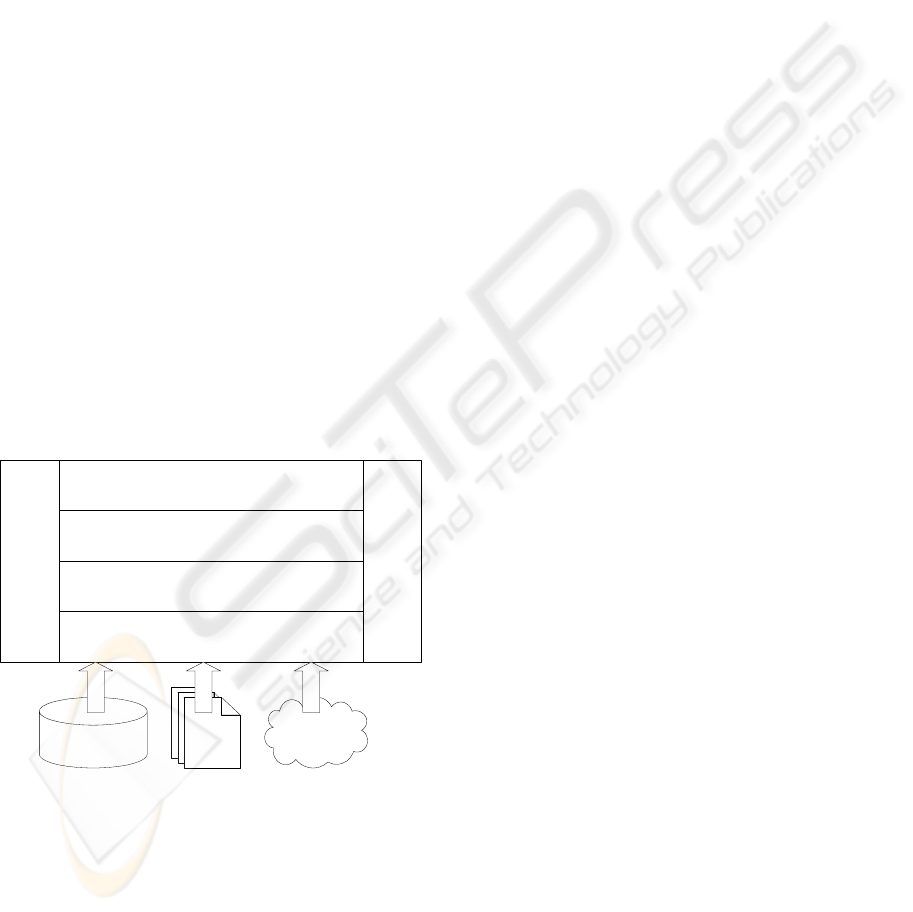
Therefore, a layered architecture is proposed for
agent-based virtual organisation as shown in Figure
1.
Interface Layer (IL)
Security Layer (AL)
Service Broker Layer (SBL)
Service Layer (SL)
Organizational Layer (OL)
Ontology Layer (ONL)
Services
Organisational
Database
Data
files
Figure 1: Architecture of agent-based virtual organisation.
In this figure, there are six different layers that
make the system more compartmentalised and
modularised. Four of our layers are hierarchical,
and dependencies occur only between adjacent
layers. However both Security and Ontology layers
are utilised by all of the other layers. In the case of
the hierarchical layers, the complexity of the lower
layers is hidden from the higher levels and from the
user. This layered architecture provides a
mechanism allowing adjustment and configuration
of business processes according to organisations’
needs and facilitates integration and reuse. The
proposed agent-based virtual organisation promotes
the advantages, such as flexibility, adaptability,
scalability and security.
An organization requires the ability to accurately
identify the user who is making requests. The
process that verifies and records the user’s identity is
called authentication. This process is designed to
employ an access-control-list that contains a single
entry authorized to grant capabilities for other
layers. In actuality, agents in every layer in an
agent-based virtual organisation have to get security
clearance from the security layer before they can
request services.
Ontology Layer collectively maintains a
knowledge base of the different terminology and
concepts that are employed over the whole
organization. This layer is similar to Security Layer
because ontology can be shared by agents in several
other layers. A given ontology describes and
specifies the terminology or language that would be
used for specifying requests for information. Thus
Ontology Layer is used to adapt or translate a
request to other modules in different layers.
Interface Layer is tied closely to an individual
human’s goals, and it can be used to predict the
user’s intentions and to request services provided by
the remaining modules. The agents in this layer act
on behalf of users to relay specifications and obtain
results
Service Broker Layer predicts or models the
intentions of the overall organization and then
provides services to users via Interface Layer. Both
Interface and Service Broker Layers have their own
objectives, and they may compete with each other to
achieve their goals. Negotiation may occur between
Interface and Service Broker Layers. In order to
provide better services to users, Service Broker
Layer should process the information obtained from
other layers and send results to the user via Interface
Layer.
Service Layer is used to provide services on
behalf of the organization. This layer differs from
Organizational Layer that controls resources. It
represents and provides the high level services of the
organization. These services can be formed by
encoding expertise and by utilizing Organisational
Layer. Service Layer should have policies that
identify if it can provide services to certain
individuals.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
56

Organizational Layer can be used to manage the
organizational resources. One of the important tasks
in this layer is to gather data from various sources
such as data banks, advanced product-planning data,
individual cost estimates, supplier documentation
and engineering test & field data. Data can be
managed by either the legacy applications or new
services provided from cloud computing. It can be
recorded in different ways and must be adjusted to
be consistent and comparable (Fabrycky &
Blanchard, 1991). An individual agent in
Organizational Layer is closely tied to sources of
data.
4 AGENT DESIGN PROCESS
To design agents for a virtual organisation, it is
critical to smoothly and efficiently transform
requirements to implementation through analysis
and design. Doing so requires systematic approach
in SDLC (software development life cycle). The
following figure describes an approach for software
agent analysis and design:
Goals
Goal Cases and
Beliefs
Roles
RRC
(Role-Responsibility-
Collaborator)
Develop Goal Cases
GCB
(Goal Cases,
Collaborators, and
Beliefs)
RGC
(Responsibility-Goal-
Collaborator)
AgentsCompose Roles as Agent
Assign Goals to Responsibility
I
d
e
n
t
i
f
y
G
o
a
l
s
I
d
e
n
t
i
f
y
R
o
l
e
s
Figure 2: Systematic approach to designing agents.
In this figure, both Goals and Roles can be
identified from use cases. A goal is an objective or a
desired state that can be achieved or ascertained by
an agent. A goal identifies what is to be done, and it
should change less often than more detailed
processes/activities. This is because a process or
activity identifies how things are to be done. Goals
are important to agent-based systems because agents
are autonomous and proactive. Goals can be
achieved through their autonomous and proactive
behaviour which is defined as a collection of
scenarios (goal cases) about agents’ interactions.
Each scenario describes a sequence of plans to
handle events that the agent initiates. An agent can
start a goal case when the corresponding goal is
triggered. The use of goal cases also helps with
traceability because they are developed according to
goals that are derived from the system requirements.
Roles can be identified from use case and
relevant role models (Kendall, 1999). A role model
contains a set of roles, their corresponding
responsibilities and collaborators. A role can be
described by role model name, role types,
responsibilities, and collaborators, which is
represented as a RRC (Role-Responsibility-
Collaborator)
card described below:
Table 1: RRC card.
Role model name
Role type Responsibility Collaborator
Names of
Roles
List all
responsibilities
List all
collaborators
Examining all role models, roles can be
categorized and composed into many sub-groups
according to the description of the layers in Figure 1.
Each role or composed role can be described as a
RGC (Responsibility, Goal, and Collaborator) card
as shown in Table 2.
Table 2: RGC card.
Role
Responsibilities Goals Collaborators
List responsibilities List goals List collaborators
In this card, role name, its associated
responsibilities and collaborators are documented
and goals are assigned to the appropriate
responsibilities.
An agent plays at least one role and each role
possesses its goals and collaborators. Subsequently
goal cases and beliefs with these goals are
determined. As a result of this, an agent can be
specified as GCB (Goals, Goal Cases, Collaborators,
and Beliefs) card described below:
Table 3: Agent specification template (GCB card).
Agent Name:
Goal Goal Case Collaborator Belief
List all
goals
List all goal
cases
List all
collaborators
List all
beliefs
AGENT-BASED SYSTEMS DESIGN FOR VIRTUAL ORGANISATIONS FORMATION
57

5 CASE STUDY
To demonstrate application of the systematic
approach developed in section 4, a case study has
been developed for designing a virtual organisation,
which is able to gather information for life cycle cost
estimation. The following subsections present the
case, the analysis & design process and
implementation of the agent-based virtual
organisation.
5.1 Overview
This case study aims to establish a virtual
organisation to gather information from various data
sources and then estimate life cycle operation and
supporting (O&S) costs for a product such as a
computer system as shown in Figure 3:
Computer
Computer
System
Computer Case
Power Supply
Electronic Board
Keyboard
Floppy Disk Drive
Floppy Disk Interface
Hard Disk Drive
Hard D isk Interface
Hard D isk Interface
Monitor
Monitor Case
Screen
M onitor Control BoxCD ROM
Printer
Printer Interface
Modem System
M odem Interface
Modem
Modem Cable
CD ROM Interface
Figure 3: A computer system breakdown structure.
In this figure, the computer system is broken
down into subsystems, which are comprised of
assemblies (subsystems) and parts. Each assembly
may in turn be comprised of other assemblies and
parts. Furthermore, these assemblies can recursively
be divided until no more assembly is found. The
agent-based system goes through all parts and
subsystems to accumulate the different costs in
certain cost categories. Moreover, the CASA model
(Manary, 1996) that provides algorithms to assess
life cycle cost is chosen as a life cycle costing model
for this case study.
5.2 Role Identification and
Composition
To illustrate how to identify roles, consider an agent
(in Service Layer) which is responsible for cost
estimation by cooperating with other agents to
gather information. This agent should play a service
role to provide expertise that the organization
possesses to external customers and internal units.
The main purpose of the service role is to distribute
work to the other roles and then to compute a final
result by using the returns from the others. This
behaviour can be modelled by the Master/Slave role
pattern where the service role plays the role of
Master (Aridor & Lange, 1998; Buschmann et al,
1996). In addition, the service role can receive
requests from other roles; hence it also needs to play
the role of Slave.
This agent also plays roles to collaborate with
other layers, such as Security Layer, Service Broker
Layer and Ontology Layer. With Security Layer, it
plays Client and Subject roles in the Bodyguard role
model; with Service Broker Layer, it plays Subject-
proxy role in the Broker role model; with Ontology
Layer, it plays Client and Target roles in the Adapter
role model. These roles can be composed to form
the agent. As each role associates its responsibilities
identified by relevant role model, it is not difficult to
produce the following RRC card:
Table 4: RRC card of Service Role.
Service Role
Role type Responsibilities Collaborators
M
aster
(Maste
r
/
Slave)
1. To collaborate with
the Slave and send
requests
>
Organizational
Layer
Subject-proxy
(Broker)
2
. Register the service
3. Provide the service
>
Service
Broker Layer
C
lient &
T
arget
(Adapter)
4
. To send message to
Adapter and
collaborate with
the Target
5. To receive the
message sent by
Client
6. To perform a task
and send a reply
<
>Ontology
Layer
C
lient &
Subject
(Bodyguard)
7
. To request the
permission of a
service
8. To accept the
notification of a
service
<
>Security
Layer
Note:
>represents servers of the collaborating agent.
<represents clients of the collaborating agent.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
58

In a similar manner, role models, such as
Observer, Broker, Master/Slave, Manager/Owner
Bodyguard and Adaptor can be applied to Figure 1
to identify potential roles for all layers in a virtual
organisation. These roles can be composed as
agents and instantiated for this case study. All
instantiated agents can be structured as shown in
Figure 4.
Figure 4: Organization of agents.
In this figure, the agents at the lowest level, such
as Project Manager Agent, Support Agent, Inventory
Agent and Resource Agent are called Organizational
Agents. They are specific to their own information
sources. The legacy databases, represented by
cylinders, can be accessed by only Organizational
Agents. In Service Layer, there are two agents,
Planning Agent and Estimation Agent that are
categorised to Service Agents. These agents provide
services based on the information that
Organizational Agents provide. Security Agent in
Security Layer collaborates with User Agent and
Maintenance Agent in our application. User Agent
in Interface Layer acts on behalf of a user to
communicate with Maintenance Agent in Service
Broker Layer. Information Agent in Ontology Layer
is used to access the ontology database that stores
ontological commitments between different
organizations. Both Service Agents and
Organizational Agents interact with it.
To develop a RGC card, examine Estimation
Agent in more details. Estimation Agent aims to
estimate the life cycle cost. Once receiving the
request to estimate O&S cost, it has to achieve goals
such as “Estimate Labour”, “Estimate Equipment”,
“Estimate Material”, “Estimate Management”,
“Estimate Support”, and “Estimate Miscellaneous”,
one by one. To achieve these goals Estimation
Agent has to ask the individual agent in
Organisational Layer for information which the
organisational agent is specific with. Table 5
documents the typical RGC card of this agent.
Table 5: RGC card of Estimation Agent.
Estimator
Responsibilities Goals Collaborators
T
o collaborate
w
ith the Slave
a
nd send requests
•
Request Labour
Item Cost
•
Request
Equipment Item
Cost
>
Resource Agent
•
Request
Material Item
Cost
>
Inventory
Agent
•
Request
Management
Item Cost
>
Support Agent
•
Request Support
Item Cost
•
Request
Miscellaneous
Item Cost
R
egister
•
Estimate O&S
cost
<Maintenance
Agent
P
rovide the
service
•
Estimate Labour
Cost
• Estimate
Equipment Cost
• Estimate
Material Cost
• Estimate
Management
Cost
• Estimate
Support Cost
• Estimate
Miscellaneous
Cost
>Planning Agent
T
o send message
t
o Adapter and
c
ollaborate with
t
he Target
•
Search
Alternative
>Information
Agent
Security
Agent
Supplier’s
Products
Support
Agent
Resource
Resource
Agent
Inventory
Inventory
Agent
Planning
Agent
Estimation
Agent
Maintenance
Agent
User Agent
Projects
Project
Manager Agent
Specifications
Information
Agent
Ontology
Interface Agent
Broker Agent
Service Agent
Organizational
Agents
Data
Source
Support
Information
AGENT-BASED SYSTEMS DESIGN FOR VIRTUAL ORGANISATIONS FORMATION
59
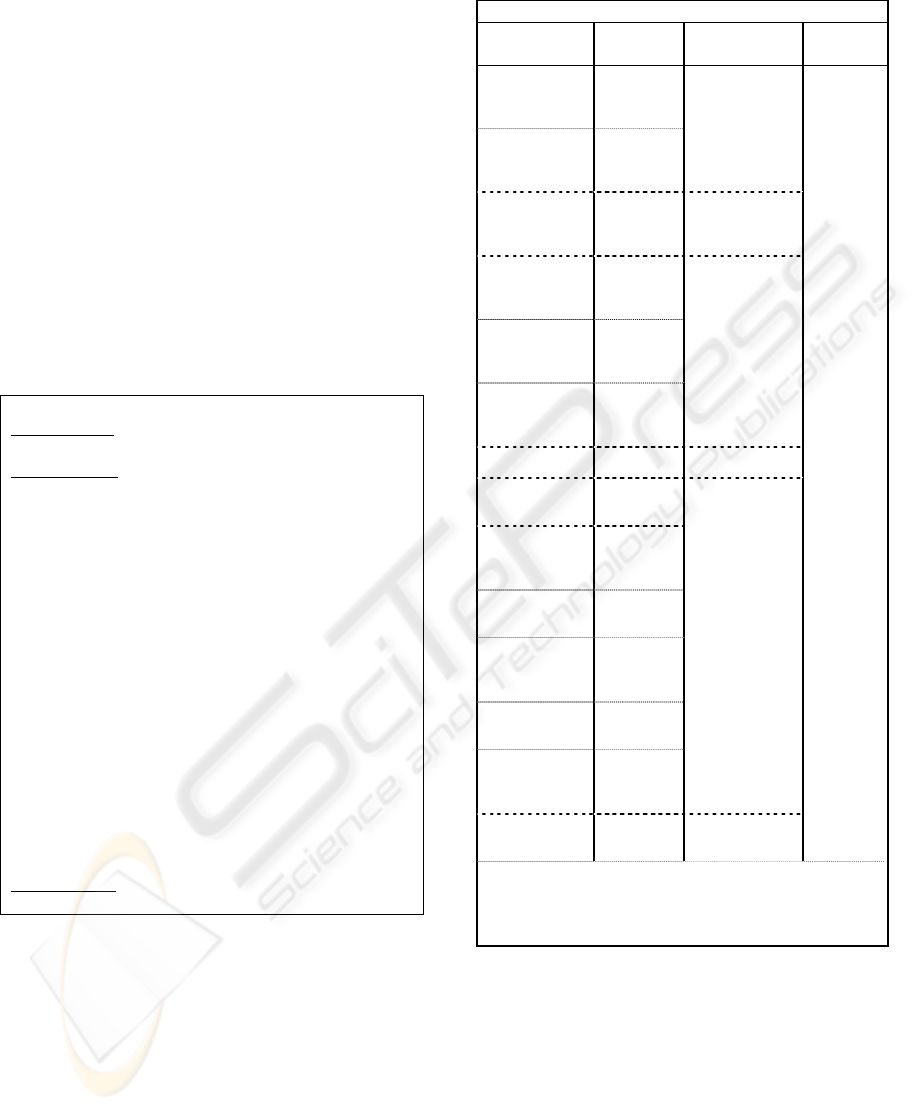
5.3 Goals, Goal Cases and Agent
Specification
Using GCB card to specify an agent requires
providing the agent’s goals and goal cases. To
demonstrate how to develop an agent specification,
consider material cost estimation as an example. To
estimate the total cost of sub-category of material,
the goal “Estimate Material Cost” should be
achieved. This high level goal can be broken down
further to the sub-goals, e.g. “Search Alternatives”
and “Request Material Item Cost” which is used to
calculate the material cost for a part or a subsystem
in the product. To achieve a goal, a goal case needs
to be developed. Table 6 shows a goal case to
achieve the goal “Estimate Material Cost”.
Table 6: Example of goal case.
Estimate Material goal case (GC 6.8.1)
Pre-condition:
Start date, end date, maintenance level, and part id.
Flow of events
Basic paths:
1. The goal case starts when Estimation Agent
attempts to achieve the “Estimate Material
Cost” goal.
2. Estimation Agent asks Information Agent to find
keywords for information required in the
organization (GCI.1.0).
3. Estimation Agent requests Planning Agent for
factors used in the algorithms of CASA model.
4. Estimation Agent asks Inventory Agent for those
factors using the “Request Material Item Cost”
goal case (GC6.8.2).
5. Estimation Agent calculates item cost by using
the CASA algorithms.
6. Estimation Agent stores the cost in the agent
database.
Alternatives:
In step 2, 3, 4, if failure to achieve the goal,
Estimation Agent asks the user to enter it.
Post-condition
Estimation Agent stores material item cost data
From this goal case, all material item costs are
determined and they can be accumulated and
determined to be a total material cost stored as the
belief “Material Cost”. Other goal cases for costs of
labour, equipments, management and support in this
research can be processed in a similar manner.
These costs will be feed to the CASA model for the
assessment of total O&S cost and life cycle cost.
As a result of Tables 4, 5 and 6, the following
table documents relationships among all goals, goal
cases, collaborators and beliefs for Estimation
Agent:
Table 7: Estimation Agent specification (GCB).
Estimation Agent specification
Goal Goal
Cases
Collaborators
(Agents)
Beliefs
R
equest
L
abour Item
c
ost
G
C A.4.1*
>
Resource
R
esource
C
ost
M
aterial
C
ost
M
anage-
m
ent Cost
Support
C
ost
M
iscellan
e
ous Cost
T
OS
R
equest
E
quipment
I
tem cost
G
C A.4.2*
R
equest
M
aterial Item
C
ost
G
C 6.8.2*
>
Inventory
R
equest
M
anagement
I
tem Cost
G
C A.4.4*
>
Support
R
equest
Support Item
C
ost
G
C A.4.6*
R
equest
M
iscellaneous
I
tem Cost
G
C A.4.8*
E
stimate TOS
G
C 6.8.3*
<
Maintenance
E
stimate
L
abour cost
G
C A.4.3*
>
Planning
E
stimate
E
quipment
c
ost
G
C A.4.0*
E
stimate
M
aterial cost
G
C 6.8.1
E
stimate
M
anagement
C
ost
G
C A.4.5*
E
stimate
Support Cost
G
C A.4.7*
E
stimate
M
iscellaneous
C
ost
G
C A.4.9*
Search
A
lternative
G
CI.1.0*
>
Information
Note:
*represents goal cases developed in this research but
they are not shown in this paper. They are included
only for completeness.
5.4 Implementation
The JACK agents (Busetta et al, 1999) are used to
implementing the proposed agents in the virtual
organisation for life cycle cost estimation. To
construct JACK agents, four class-level constructs:
Agent, Database, Event, and Plan are used. The
Agent construct declares types of events and plans
used to handle the events. It does not only have
methods and data members just like objects, but also
contains database relations that an agent can use to
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
60

store beliefs, descriptions of events that the agent
can handle, and plans that agent use to handle the
events. Table 8 shows a map between GCB card
and JACK constructs.
Table 8: GCB card to JACK agent.
GCB card Goal Goal
Case
Collaborator Belief
JACK agent
Constructs
Event Plan
Agent Database
The mapping rules above are used to implement
the designed agents in the case study. The similar
implementation has been done by Zhang (Zhang,
2002).
6 CONCLUSIONS/FUTURE
WORK
This paper has presented a systematic approach to
design software agents for virtual organization
formation. In this approach, role pattern and layered
architecture are used to simplify agent analysis and
design processes. Various card templates used to
define agent behaviours are developed to assist agent
design. The case study has been used to verify and
validate the approach. Subsequently, the approach
can be applied to different businesses which involve
data and services from various sources. As a result
of this research, the approach has demonstrated its
advantages of flexibility, adaptability, scalability and
robust. Future work will be focused on extension of
the case study to incorporate services provided by a
cloud computing platform.
REFERENCES
Aridor, Y., and Lange, D.B., 1998. Agent Design Patterns:
Elements of Agent Application Design. Autonomous
Agents (Agents’98), Minneapolis, pp. 108-115.
Busetta, P., Ronnquist, R., Hodgson, A. and Lucas, A,
1999. Light-Weight Intelligent Software Agents in
Simulation. SimTech 99, Melbourne Australia, 1999.
Bryne, J.A. 1993. The Virtual Corporation. In Business
Week, February 8, p.103.
Buschmann, F., R. Meunier, H. Rohnert, P. Sommerlad,
and M. Stal, 1996. Patter-Oriented Software
Architecture: A System of Patterns, Wiley, USA.
Collins, P., 2002. Virtual and networked organizations,
Capstone Publishing, Oxford.
Pournaras, E., Warnier, M. and Brazier, F., 2009. A
Distributed Agent-based Approach to Stabilization of
Global Resource Utilization. In 3
rd
International
Conference on Complex, Intelligent and Software
Intensive Systems, pp.185-192. Fukuoka Institute of
Technology (FIT), Japan, March, 16th – 19th 2009.
Fabrycky, W.J., and B. Blanchard, 1991. Life-Cycle Cost
and Economic Analysis, Prentice-Hall, Inc., New
Jersey, USA.
Gary P. Shneider, 2009. Electronic Commerce, Course
Techonology, Cengage Learning, ISBN-13: 978-1-
4239-0305-5
Ivancevich, J., Olekalns, M. and M. Matteson, 1997.
Organisational Behaviour and Management,
McGraw-Hill Book Company Australia Pty Ltd.,
Richard D. Irwin, Inc.
Kendall, E. A., 1999. Role models, aspect oriented
programming and agent engineering. Technical report,
British Telecom,
Kollingbaum, M., Mehangjiev, N. and Brown, K., 2006.
Engineering Organisation-Oriented Software. In
WISER '06. 2
nd
International Workshop on Workshop
on interdisciplinary Software Engineering Research,
pp23-28. Shanghai, China, May 20 - 20, ACM Press,
New York.
Leong, P., Miao, C. and Lee, B., 2006. Agent Oriented
Software Engineering for Grid Computing. In
CGRIDW’06. Sixth IEEE International symposium on
Cluster Computing and Grid Workshops, pp-2.
Singapore, May 16-19.
Manary, J.M., 1996. DSMC’s CASA Model Still Going
Strong. PM: JANUARY-FEBRUARY 1996, p37-40.
Patel, J. etc, 2005. Agent-based Virtual Organisation for
the Grid. In AAMAS’05. 4th International Joint
Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-agent
Systems, Utrecht, Netherlands, July 25-29.
Pedersen, C. and Nagengast, J., 2008. The virtues of the
virtual organization. Strategic HR Review, 7 (3). pp.
19-25. ISSN 1475-4398
Shan, B., Han, Y., and Sun, W., 2006. An Agent-Mediated
Service Framework Facilitating Virtual Organizations.
In Proceedings of the 10
th
International Conference on
Computer Supported Cooperative Work in Design.
2006, LNCS 4402, pp. 438-446, 2007.
Udupi, Y. B. and Singh, M. P., 2006. Multiagent Policy
Architecture for Virtual Business Organisations. In
SCC’06, 3
rd
IEEE International Conference on
Services Computing, pp. 44-51. Chicago, USA,
September 18 – 22.
Zhang, J., 2009. Research on Modeling Method of Virtual
Enterprise in Uncertain Environments. In ICEE’09,
2nd International Conference on Computer
Engineering and Technology, pp. 541-544. Singapore,
January 22 - 27.
Zhang, T. I, 2002. Agent-based Information Gathering
System for Life Cycle Costing, Ph.D. thesis, RMIT
university, Melbourne, Australia, 2002.
AGENT-BASED SYSTEMS DESIGN FOR VIRTUAL ORGANISATIONS FORMATION
61
