
EVALUATING JASON FOR DISTRIBUTED CROWD SIMULATIONS
Victor Fern´andez, Francisco Grimaldo, Miguel Lozano and Juan M. Ordu˜na
Departament d’Inform`atica, Universitat de Val`encia, Avda. Vicent Andr´es Estell´es s/n, 46100, Burjassot, Spain
Keywords:
Multi-agent architectures, Crowd simulation.
Abstract:
Large-scale crowd simulations require distributed computer architectures and efficient parallel techniques to
achieve the rendering of visually plausible images while simulating the behaviour of crowds of autonomous
agents. The Java-based multiagent platforms, devoted to provide the agents with the required lifecycle, rep-
resent a key middleware in crowd systems. However, since they are oriented to maximize portability and to
reduce the development cost, they may reduce performance and scalability, two important requirements in
large-scale crowd simulation systems. This paper studies the performance and scalability provided by Jason,
a well known Java-based BDI-MAS platform, as a plausible framework to be used for large-scale crowd sim-
ulations. The performance evaluation results show that some improvements should be performed in order to
make Jason a suitable middleware for large-scale crowd simulations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Crowd simulation can be considered as a special case
of Virtual Environments where the avatars are intel-
ligent agents instead of user-driven entities. Each
of these agent-based entities can have its own goals,
knowledge and behavior. In recent years, crowd sim-
ulation has become an essential tool for many vir-
tual environment applications in education, mobility,
safety and security in public spaces or entertainment
(Pelechano et al., 2008). However, simulating the re-
alistic behavior of large crowds of autonomous agents
is still a challenge for several computer research com-
munities (Reynolds, 2006; Lozano et al., 2007).
Scalability is a key feature in crowd simulation
and the simulation of high number of autonomous
pedestrian-agents represents an active research area at
the intersection of computer graphics, artificial intel-
ligence and distribute computing.Any scalable model
can be divided into three levels. Firstly, graphic en-
gines must render complex crowded scenes as fast as
posible. Here, the challenge is to display realistic big
size crowded scenes at interactive frame rates. How-
ever, most of the current (graphics oriented) crowd
systems use specific MAS with centralised architec-
tures, so they can hardly simulate a few thousands of
agents and it is also very diffucult to scale these sys-
tems up. Secondly, the MAS platform represents a
middleware between the distributed computer archi-
tecture and the graphical engine. The MAS platform
mainly addresses two important issues, the agents be-
havior modeling and their parallel lifecycle execution.
Some researchers have been testing the performance
of existing agent platforms (Mulet et al., 2006), show-
ing a lack of performance and scalability in many of
them. The main challenge that crowd simulation of-
fers to the MAS platforms is the ability of handling
a massive and concurrent action processing at inter-
active rates (i.e. 250ms/action). Thirdly, large scale
crowd simulation requires distributed computer archi-
tectures (eg. P2P, networked-server,...) to execute the
MAS designed and to be able to increase the number
of agents when required. Hence, scalability is a key
issue that mainly depends on the distributed computer
architecture and the degree of parallelism achieved by
the software architecture.
Bearing these levels in mind, this work evaluates
Jason, a well-known MAS platform, as a plausible
MAS for simulating large-scale interactive crowded
scenes. Although there are several works dealing
with the evaluation of Java-based Multiagent Plat-
forms (Cortese et al., 2002), to our knowledge there is
no such study for the Jason framework. Therefore, the
results presented in this paper will be of great value to
those researches considering Jason as a suitable plat-
form to develop not only crowd simulations but also
other large-scale multiagent applications. The perfor-
mance evaluation carried out has been focused on the
agent action response time and the percentage of CPU
utilization consumed by the MAS when simulating a
locomotion benchmark. The evaluation results show
that some improvements should be performed in order
206
Fernández V., Grimaldo F., Lozano M. and M. Orduña J. (2010).
EVALUATING JASON FOR DISTRIBUTED CROWD SIMULATIONS.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence - Agents, pages 206-211
DOI: 10.5220/0002729802060211
Copyright
c
SciTePress

to make Jason a suitable middleware for large-scale
crowd simulations.
2 RELATED WORK
Crowd simulations must focus on rendering visu-
ally plausible images of the environment, requiring
a high computational cost. Furthermore, from a MAS
level point of view, complex agents must provide au-
tonomous complex behaviors, greatly increasing the
computational cost as well. Hence, this situation re-
quires the use of distributed architectures capable of
managing the corresponding workload.
Graphics oriented proposals tackle crowd simula-
tions as a particle system with different levels of detail
(e.g. impostors) in order to reduce the computational
cost (O’Sullivan et al., 2002). Although these propos-
als can handle crowd dynamics and display populated
interactive scenes (10K pedestrians), they are not able
to produce complex autonomous behaviors for their
actors. On the contrary, a few graphics oriented pro-
posals include socially complex and autonomous be-
haviors (Treuille et al., 2006). However, the main
problem presented by these works is scalability, since
they are generally based on centralised system archi-
tectures. Hence, they can only control hundreds of
autonomous agents at interactive frame rates.
From the distributed computing point of view, dif-
ferent architectures have been applied to crowd sim-
ulation. For instance, a new approach has been pre-
sented for PLAYSTATION3 which supports simula-
tion of simple crowds up to 15000 individuals at 60
frames per second (Reynolds, 2006). This work in-
corporates spatial hashing techniques to improve the
neighboring search and it also distributes the load
among PS3-Cell elements. Parallel simulation based
on classical Reynolds’s boids (Reynolds, 1987), has
been also integrated in a PC-Cluster with MPI com-
munication among the cluster processors (Zhou and
Zhou, 2004). This proposal uses different commu-
nication and partitioning strategies to finally produce
small crowds simulations (512 boids), which are far
from interactive.
In the middle of these two levels, a multiagent sys-
tem must be located in order to: i) efficiently explode
the computational resources involved and ii) to pro-
vide the required data flow to the interactive graphic
application. According to this, the MAS framework
constitutes a key middleware that higly influenciates
the global performance and scalability of the crowd
system. Some researchers have tested the perfor-
mance and scalability of a few existing MAS plat-
forms (Mulet et al., 2006), showing a lack of both
important issues in many of them. Since the main
problem that crowd simulation provides to the MAS
platform is to be able of handling a massive and con-
current action processing (all the crowd actions), a
higly efficient action model will be required. Other-
wise, the MAS platform will not be useful for crowd
simulation purposes.
3 JASON INFRASTRUCTURES
Jason is a Java-based interpreter for an extended ver-
sion of AgentSpeak, a BDI agent-oriented logic pro-
gramming language (Bordini et al., 2007). It offers
an elegant notation based on logic programming to
design agents capable of managing long-term goals
(goal-based behavior), reacting to changes in a dy-
namic environment and handling multiple intentions
concurrently. Beyond the implicit overload that a vir-
tual machine adds to any system, here we are focused
on scalable crowd architectures, which are mainly af-
fected by the possibility of distributing the MAS on
different computers to increase the crowd size with-
out loosing agent performance.
Jason provides three infrastructures to execute a
MAS: Centralised, SACI and JADE. On the one hand,
the Centralised infrastructure places all the compo-
nents of the MAS in the same host. On the other
hand, it is also possible to distribute these components
in several hosts using either SACI or JADE technolo-
gies. Next, we review these three approaches.
3.1 Centralised
The Centralised infrastructure executes both the en-
vironment and the agents of a MAS within a single
computer. Figure 1 depicts the general scheme of this
infrastructure. On the left hand side, the environment
has its own execution thread and it is provided with
a configurable pool of threads (PThE) to attend the
actions requested by the agents. This way, the en-
viroment is able to deal with several agent requests
concurrently. On the right hand side, each agent owns
by default a thread in charge of executing the agent
reasoning cycle. In this manner, all the agents can
run concurrently within the MAS. However, this ap-
proach limits the number of agents that can be exe-
cuted, since the total numberof threads will be limited
by the JVM and finally by the operating system. In or-
der to overcome this limitation, Jason offers the pos-
sibility to optionally add another configurable pool of
threads (PThA), so that the set of agents can share a
smaller number of execution threads but reducing the
EVALUATING JASON FOR DISTRIBUTED CROWD SIMULATIONS
207

Figure 1: Overview of the Centralised infraestructure.
level of concurrency. By default, the PThE holds 4
threads whereas the PThA is disabled.
Agent-agent as well as agent-environment com-
munication is made through event passing in the Cen-
tralised infrastructure. That implies that the message
is not serialized but cloned, and the new object ref-
erence is passed to the receiver. The structure of the
messages in Jason is based on the speech act paradigm
and follows the protocols proposed by the KQML
(Finin et al., 1993) and FIPA (FIPA, 2009) agent com-
munication languages.
3.2 SACI
The Simple Agent Communication Infrastructure
(SACI) is an API of Java with a set of tools for the de-
velopment of societies of distributed agents (Sichman
and H¨ubner, 2009). SACI offers a programming com-
munication API oriented to two important features:
i) composing, sending, and receiving messages; and
ii) getting the agents designers rid of the underlay-
ing computer architecture. As shown in figure 2, the
agents in SACI group in societies and they are pro-
vided with a mailbox to interact among them. Every
society has a Facilitator agent who makes the location
of the agents transparent in the network. This way,
agents can exchange messages between their queues
of incomming and outgoing messages. Then, the pro-
grammer can specify in which host to run each agent
through the configuration file of the multiagent sys-
tem (i.e. the mas2j file).
With regard to the agent-agent and agent-
environment communication, the SACI infrastructure
uses Java Remote Method Invocation (Java RMI).
RMI uses object serialization to marshal and unmar-
shal the messages being exchanged. Besides, as mes-
sages in SACI are formatted in KQML, every Jason
message will have to be recoded by the sender in or-
der to be delivered.
Figure 2: Overview of the SACI infraestructure (Sichman
and H¨ubner, 2009).
Figure 3: Overview of the JADE infraestructure (TILAB,
2009).
3.3 JADE
The latest infrastructure available in Jason is the well-
known Java Agent DEvelopment Framework (JADE)
(TILAB, 2009). JADE simplifies the implementa-
tion of multiagent systems through a middleware that
complies with the FIPA specifications (FIPA, 2009).
Thus, the agent platform can be distributed across ma-
chines as shown in figure 3. The agent execution en-
vironments in JADE are called Containers and the ac-
tive set of Containers that form the MAS is known as
the Platform. Each Platform has a Main Container
with two special agents: i) the Agent Management
System (AMS), that provides the naming service and
represents the authority in the platform; and ii) the Di-
rectory Facilitator (DF), that provides a Yellow Pages
service. Currently, the specification of the JADE set-
tings to run Jason projects over JADE is not fully sup-
ported by the mas2j configuration file. Thus, the pro-
grammer is left in charge of manually creating the one
or more Platforms and of distributing the environment
and the agents among the Containers by means of the
command-line JADE commands.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
208

Communication in JADE follows an asyn-
chronous message exchange approach where every
agent has a mailbox within which the container intro-
duces the messages sent by other agents. The mes-
sages have the format specified by the FIPA ACL
language. Then, message passing is done through
RMI when the agents share the same platform but are
placed in different containers.
4 TEST DESCRIPTION
The goal of this work is to evaluate Jason as a
plausible MAS framework for simulating interactive
crowded scenes. We should notice that normal com-
munication procedures of software agents are far from
the crowd ones. Crowd agents do not communicate
among them often, but they need to act very fre-
quently in a shared environment. Motion actions are
the most frequent actions within a crowd and they
must be executed carefully in order to ensure the
world consistency.
Therefore, we have defined a locomotion testbed
where a set of wanderer agents request movement ac-
tions to a grid-like single environment, which in turn
replies with the result of the execution. Wanderer
agents are written in AgenSpeak and they cyclically
execute the following steps: (i) take start time, (ii)
request a random movement to the enviroment, and
(iii) take finish time. On the other hand, the environ-
ment executes each movement action in a synchro-
nized manner to ensure the world consistency. This
testbed is repeated for the three infrastructures being
studied: Centralised, SACI and JADE. For the dis-
tributed versions we used two hosts, one devoted to
run the environment and the other to execute all the
wanderer agents. In the JADE case, a single platform
has been created and the environment has been placed
in the main container.
The performance evaluation carried out in section
5 measures the environment response time and the
percentage of CPU utilization consumed while run-
ning the locomotion benchmark. We define this Re-
sponse Time (RT) as the time elapsed between an
agent asking for an action and receiving the reply
from the environment. Although each agent performs
500 movements or cycles, we only consider the 100
mesurements in the middle to obtain the average re-
sponse time (RT). This interval reflects the system
behavior at full load whereas the first and the last 200
cycles measurements are distorted due to the agent
creation/destruction as demonstrated in figure 4.
In order to evaluate the scalability of Jason, we
have increased the number of wanderer agents (N
ags
).
Figure 4: Response Time evolution.
The size of the environment has been adapted accord-
ingly so that the density remains around 40%. In
this paper, we show the results between 500 and 3500
agents since the system saturates beyond 3500 agents
due to the JVM limitation in the number of threads.
5 PERFORMANCE EVALUATION
The results shown in this section have been obtained
using a PC cluster of 24 AMD Dual-Core Opteron
processors running at 1.6 GHz with 4 GB of RAM
and connected via Gigabit Ethernet. The cluster runs
the 64-bit version of CentOS 5.1 and the Java imple-
mentation used is Sun JDK 1.6.
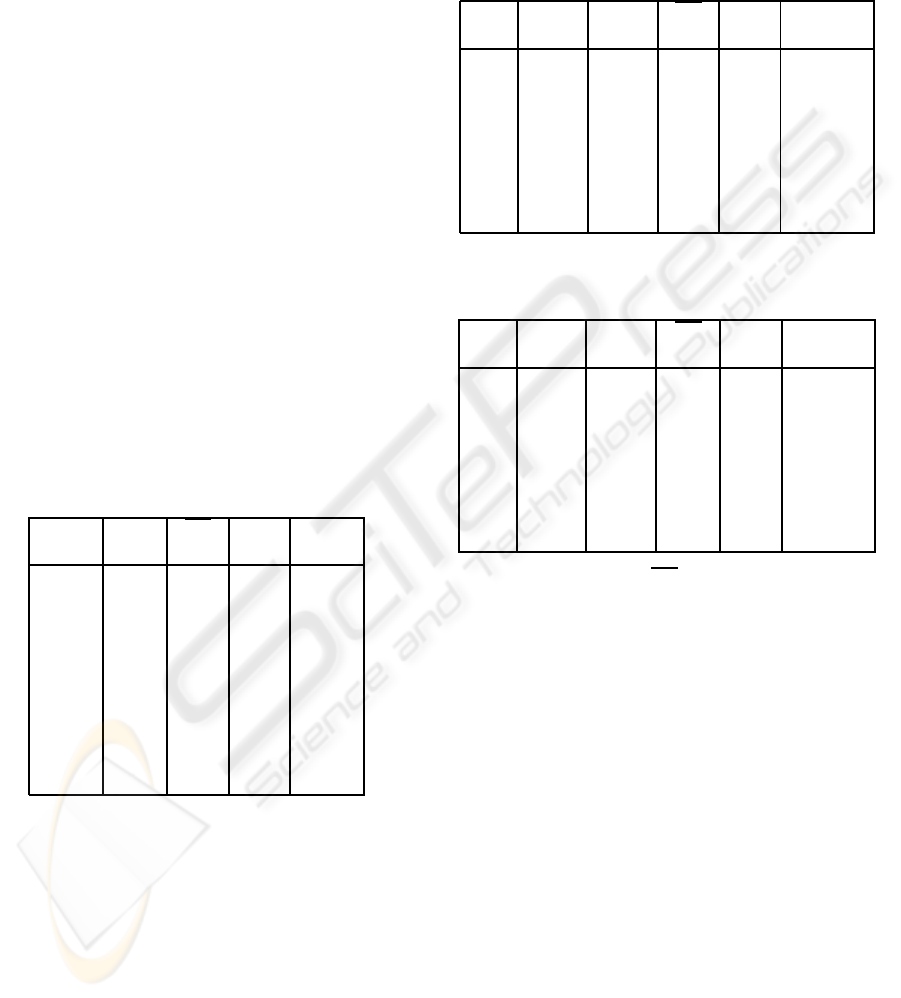
Table 1 shows the performance obtained for the
test defined in section 4 in the Centralised architecture
with PThA disabled and 50 threads in PThE. From
left to right, the columns represent: the number of
simulated agents (N
ags
); the percentage of CPU uti-
lization consumed; the average of the response time
for each agent movement action (RT); its correspond-
ing standard deviation (σ
RT
); and the total Time con-
sumed by the simulation.
Table 1: Performance obtained in a Centralised infrastruc-
ture (PThA=0 and PThE=50).
N
ags
CPU RT σ
RT
Time
% (ms) (ms) (ms)
500 83 61 129 34528
1000 84 85 264 65510
1500 84 76 249 99815
2000 84 201 464 143170
2500 82 305 669 179427
3000 77 410 652 229985
3500 76 429 746 272099
Firstly, we focus on the response time since it is an
important feature of crowd simulations that directly
affects the degree of interactivity achieved. Gener-
ally, 250 ms/action is considered as a reference ratio
EVALUATING JASON FOR DISTRIBUTED CROWD SIMULATIONS
209
(maximum period) for these domains (Lozano et al.,
2007). Although this value is exceeded after 2K
agents, this constraint is only satisfied for 500 agents
due to the high standard deviation values. For in-
stance, in the 1K agents simulation the 70% of the ac-
tions are served in 85 ± 264 ms. That is, even though
the average value (85 ms) indicates that many actions
are served very fast, there are a few agents that must
wait more than 250 ms for their actions to be exe-
cuted. Besides, the percentage of CPU utilization de-
creases for higher number of agents. This situation
indicates that the scheduling policies used to access
the environment threads in PThE as well as the syn-
chronized action code must be carefully reviewed to
provide a more equilibrated RT distribution.
Table 2 evaluates the influence of the size of
PThE. In this case, we have fixed the number of
agents to a value of 1000. The average response
times decrease when increasing the size of PThE, but
the standard deviation shows huge values with an in-
creasing slope and the percentage of CPU utilization
decreases. These results show that, even though the
agents have more threads to act, the current schedul-
ing policies and the cost of handling the pool of
threads highly increases the standard deviation.
Table 2: Influence of the number of threads in PThE in the
Centralised infrastructure with N
ags
=1000 and PThA=0.
N
PThE
CPU RT σ
RT
Time
% (ms) (ms) (ms)
100 85 119 351 66489
200 83 106 396 66958
300 84 121 547 68124
400 83 106 564 66701
500 83 88 608 67467
600 83 81 522 62341
700 81 76 560 62755
800 81 67 597 65393
900 81 93 672 64489
1000 81 78 601 65094
Although not included in this paper, we have also
demonstrated that using the PThA makes the global
agent cycle run slower due to the new thread com-
petition introduced. Thus, it is only interesting when
you want to run a lot of agents with limited resources.
For comparison purposes, we have executed the
same locomotion benchmark over the two distributed
infrastructures offeredby Jason: SACI and JADE. For
these simulations we used a simple distributed archi-
tecture composed by two hosts, the first one allocating
the agents and the second one handling the environ-
ment. Tables 3 and 4 show the results obtained for
SACI and JADE, respectively. These tables distin-
guish the percentage of CPU utilization required by
both the host in charge of the agents (CPU
a
) and the
host in charge of the environment (CPU
e
).
Table 3: Influence of the number of agents in the SACI in-
frastructure with PThA=0 and PThE=50.
N
ags
CPU
e
CPU
a
RT σ
RT
Time
% % (ms) (ms) (ms)
100 32 36 100 11 162021
200 32 35 198 20 314212
300 32 35 299 31 468057
400 32 35 398 46 621113
500 31 35 503 52 780493
600 31 36 610 70 946934
700 31 36 707 93 1112253
800 31 35 810 111 1277237
Table 4: Influence of the number of agents in the JADE
infrastructure with PThA=0 and PThE=50.
N
ags
CPU
e
CPU
a
RT σ
RT
Time
% % (ms) (ms) (ms)
100 45 39 130 18 267926
200 45 39 258 31 513394
300 45 39 382 36 772402
400 45 39 521 46 1045591
500 44 39 641 61 1286356
600 45 39 783 77 1552234
700 45 39 907 78 1808992
800 44 39 1026 86 2048948
According with the RT column, both SACI and
JADE show a linear response with the number of
agents, although this response is slightly better for
the SACI case. Furthermore, the standard deviation
shown in both tables is considerably lower than the
Centralised outcomes. However, the high values ob-
tained for the RT are far from the interactive response
time desired in crow simulation (i.e. 250 ms).
Additionally, tables 3 and 4 show very low per-
centages of CPU (CPU
a
and CPU
e
) utilization. These
results suggest that the problem here comes from
the communication platform in both infrastructures,
which use RMI instead of method invocation to per-
form the message passing. In this way, when com-
paring the total time consumed with the centralised
approach (table 2), the distributed simulation requires
longer execution times to complete the same work.
Therefore, we can conclude that the final perfor-
mance is being seriously affected by the communi-
cation costs.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
210

6 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
This paper studies the performance and scalability
provided by Jason as a suitable framework to be used
for large-scale crowd simulations. The results for
the Centralised infrastructure show that the schedul-
ing policy followed in PThE to provide a parallel ac-
tion execution must be reviewed, in order to achieve
a more equilibrated RT distribution. Otherwise, a few
agents in each cycle must wait for a long time to
execute their actions. For the distributed infrastruc-
tures, the results show the effects of the communica-
tion platform on this particular problem. Both SACI
and JADE are based on RMI and result in a similar
scalability degree (considering scalability as a func-
tion that associate the number of agents with the RT
obtained). However, the distributed simulations re-
quire longer execution times and the performance (in
terms of the response time) is seriously affected by the
communication costs. Finally, the CPUs have never
reached saturation due to both the number of agents
waiting to gain access to the environment threads in
PThE and the synchronized action code.
These conclusions allow us to address future work
in the following directions. First, we should study the
scheduling policy of both the pool of threads of the
environment and the synchronized action code. Then,
a new P2P architecture can be proposed to distribute
the problem, where each peer will be a computer ex-
ecuting a centralised version of the system (agents
+ environment) dealing with a smaller piece of the
environment. In this case, spatial criteria should be
used to distribute the agents to the computers, and dy-
namic algorithms will be required to keep the work-
load properly balanced during the simulation.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been jointly supported by the Spanish
MEC and the European Commission FEDER funds,
under grants Consolider-Ingenio 2010 CSD2006-
00046 and TIN2009-14475-C04-04.
REFERENCES
Bordini, R. H., H¨ubner, J. F., and Wooldrige, M. (2007).
Programming Multi-Agent Systems in AgentSpeak us-
ing Jason. Wiley.
Cortese, E., Quarta, F., and Vitaglione, G. (2002). Scal-
ability and performance of JADE message transport
system. In AAMAS Workshop on AgentCities.
Finin, T., Weber, J., Wiederhold, G., Genesereth, M., Fritz-
son, R., McKay, D., McGuire, J., Pelavin, R., Shapiro,
S., and Beck, C. (1993). Specification of the KQML
agent communication language. DARPA Knowledge
Sharing Initiative External Interfaces Working Group.
FIPA (2009). FIPA (Foundation for Intel-
ligent Physical Agents). Available at
http://www.fipa.org/specs/fipa00023/.
Lozano, M., Morillo, P., Ordua, J. M., and Cavero, V.
(2007). On the design of an efficient architercture
for supporting large crowds of autonomous agents. In
Proceedings of IEEE 21th. International Conference
on Advanced Information Networking and Applica-
tions (AINA’07), pages 716–723.
Mulet, L., Such, J. M., and Alberola, J. M. (2006). Per-
formance evaluation of open-source multiagent plat-
forms. In AAMAS ’06: Proceedings of the fifth inter-
national joint conference on Autonomous agents and
multiagent systems, pages 1107–1109, New York, NY,
USA. ACM.
O’Sullivan, C., Cassell, J., Vilhjmsson, H., Dingliana, J.,
Dobbyn, S., McNamee, B., Peters, C., and Giang, T.
(2002). Levels of detail for crowds and groups. Com-
puter Graphics Forum, 21(4):733–742.
Pelechano, N., Allbeck, J. M., and Badler, N. I. (2008). Vir-
tual crowds: Methods, simulation, and control. Syn-
thesis Lectures on Computer Graphics and Animation,
3(1):1–176.
Reynolds, C. (2006). Big fast crowds on ps3. In sandbox
’06: Proceedings of the 2006 ACM SIGGRAPH sym-
posium on Videogames, pages 113–121, New York,
NY, USA. ACM.
Reynolds, C. W. (1987). Flocks, herds and schools: A
distributed behavioral model. In SIGGRAPH ’87:
Proceedings of the 14th annual conference on Com-
puter graphics and interactive techniques, pages 25–
34, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
Sichman, J. and H¨ubner, J. F. (2009). SACI - Simple
Agent Communication Infrastructure. Available at
http://www.lti.pcs.usp.br/saci/.
TILAB (2009). JADE (Java Agent DEvelopment Frame-
work). Available at http://jade.tilab.com/index.html.
Treuille, A., Cooper, S., and Popovic, Z. (2006). Continuum
crowds. In SIGGRAPH ’06: ACM SIGGRAPH 2006
Papers, pages 1160–1168. ACM.
Zhou, B. and Zhou, S. (2004). Parallel simulation of group
behaviors. In WSC ’04: Proceedings of the 36th con-
ference on Winter simulation, pages 364–370. Winter
Simulation Conference.
EVALUATING JASON FOR DISTRIBUTED CROWD SIMULATIONS
211
