
TACTILE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION IN THE ROBOT-RAT
PSIKHARPAX
Steve N’Guyen, Patrick Pirim
Institut des Syst
`
emes Intelligents et de Robotique, Universit
´
e Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France
Brain Vision Systems, Paris, France
Jean-Arcady Meyer
Institut des Syst
`
emes Intelligents et de Robotique, Universit
´
e Pierre et Marie Curie, Paris 6, France
Keywords:
Tactile perception, Whiskers, Texture discrimination, Kinetic signature, Resonance, Robot.
Abstract:
We endowed a whiskered robot with a simple algorithm allowing to discriminate textures. Its efficiency and
robustness have been demonstrated using both a fixed head and a mobile platform. Comparatively to previous
similar approaches, this system affords greater behavioral capacities and proves to be able to complement or
supply vision in simple navigation tasks. The corresponding results suggest that the length and number of
the whiskers involved play a role in texture discrimination. They also suggest that two hypotheses that are
currently considered as mutually exclusive to explain texture recognition in rats - i.e., the “kinetic signature
hypothesis” and the “resonance hypothesis” - may be, in fact, complementary.
1 INTRODUCTION
Touch is a very important sensory modality for many
species of insects and mammals. For example, the
whiskers of a rat are often compared to human fin-
gertips in terms of their tactile - or haptic - ability.
In particular, they make it possible to finely discrimi-
nate textures (Carvell and Simons, 1990; Guic-Robles
et al., 1989) or objects (Brecht et al., 1997) and
even to precisely determine an aperture width (Krupa
et al., 2001). Biologists have studied rat whiskers for
decades and know quite precisely the pathway from
an individual vibrissa to the somatosensory cortex.
One remarkable property of this haptic system is that
whiskers project somatotopically to this part of the
cortex, into a structure named “barrel cortex”. A “bar-
rel” is a discrete neural structure that receives an input
principally from a given whisker, with little influence
from neighboring whiskers (Petersen and Diamond,
2000). This relatively simple system, as compared to
vision for example, facilitates the study of the neural
coding scheme, as well as its use for perception and
higher-level cognition.
Being simple, efficient and robust, whiskers
should become popular in robotics (Hartmann,
2001) although few robots have been equipped
with such devices in the past. The corresponding
implementations were calling on various sensors
ranging from the simplest binary switch to a very
accurate bi-dimensional torque sensor. Brooks
(1989), for example, used a simple sensor made of a
metal shaft fixed on a push button, providing a very
robust security sensor for a walking robot. Another
implementation called upon probe whiskers made of
a stem glued to a potentiometer with return springs
and was used to evaluate the contour of an object
(Russell, 1985). Even wind sensitive sensors have
been designed (Chapman et al., 2000) allowing a
robot to navigate through a labyrinth. Basically, this
sensor was made of small springs surrounded by
electric contacts and was able to detect the direction
of the wind.
Recently, several artificial whisker systems
have been used in robotics to discriminate textures.
Whisker hairs of real rats, glued to capacitive sensors
(electret microphone), served (Fend et al., 2003;
Lungarella et al., 2002) to produce very precise
haptic sensors, with an uni-dimensional measurement
of dynamic signals. Using an active whisker array
of such sensors mounted on a mobile robot, Fend
et al. (2003) successfully discriminated a set of 11
74
N’Guyen S., Pirim P. and Meyer J. (2010).
TACTILE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION IN THE ROBOT-RAT PSIKHARPAX.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 74-81
DOI: 10.5220/0002730200740081
Copyright
c
SciTePress

textures. Kim and M
¨
oller (2004) tried both piezo
and hall-effect sensors which, mounted in orthogonal
pairs, provided a bi-dimensional measure of vibrissa
deflection. Like capacitive sensors, piezo sensors
cannot deliver static signals, but this can be achieved
using an extra integrator circuit. With a data process-
ing based on spectrum density, these authors were
able to discriminate a set of 7 sandpapers. Likewise,
Seth et al. (2004) performed texture discrimination
using arrays of Flex sensors, which provided an
unidimensional measure of curvature. Here, temporal
differences between pairs of vibrissæ were fed into
a barreloid system with spiking neurons. Finally,
Fox et al. (2009) used two active whiskers with
strain gage-based sensors mounted on a mobile
robot. They explored different bioinspired methods
of feature extraction and the implication of uncon-
strained whisker-texture contact on classification
performance.
The work described herein contributes to the
Psikharpax project (Meyer et al., 2005) which aims at
designing a biomimetic artificial rat. Besides visual,
auditory and vestibular sensors, the corresponding
robotic platform is equipped with an original whisker
system described elsewhere (N’Guyen et al., 2009).
This system is intended to be used for texture discrim-
ination and object recognition and, more generally, as
an auxiliary or a substitute to vision. Its performance
in texture discrimination is the subject of the present
article.
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Insofar as the impact of the specific implementa-
tion of a rat’s whisker system on its functionalities
is currently unknown, we tried to design an artifi-
cial whisker system mimicking as much as possi-
ble the natural organization. Accordingly, our sys-
Figure 1: Comparison of whisker pads in a real rat and in
our robot.
tem (N’Guyen et al., 2009) is based on a simple,
elastomer-based, artificial skin with two arrays of 33
vibrissæ and an arc/row organization (cf. Fig 1) and a
Table 1: Vibrissæ arcs, with mean measured lengths in mm
(in one adult rattus norvegicus specimen). Compared to
those of a real rat, the robot’s whiskers are approximately
6 times longer.
Arc vibrissæ rat robot
1 α, β, γ, δ,E1 41.8 250
2 A1, B1, C1, D1, E2 37.2 200
3 A2, B2, C2, D2, E3 27.6 150
4 A3, B3, C3, D3, E4 20.6 120
5 A4, B4, C4, D4, E5 12.6 100
6 C5, D5, E6 8.33 90
7 C6, D6, E7 70
8 D7, E8 55
whisker-length gradient (cf. Table 1) quite similar to
those encountered in the rat.
The deflection of each vibrissa is sampled in
both its anteroposterior and dorsoventral axes, pro-
viding two 8-bit measurements at 1157Hz. How-
ever, orientation information being not necessary for
texture discrimination, the two measures are normed
(
√
x2 + y2).
3 TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION
3.1 Feature Extraction
Neither the details of how a rat’s brain actually
encodes texture features, nor the exact nature of
these features, are yet known. Arabzadeh et al.
(2004) experienced different feature codings on both
artificial and natural (in vivo) whiskers. Starting from
the principle that a pure sinusoidal signal can be fully
described by its amplitude A and its frequency f ,
they stimulated a rat’s whiskers with various signals
varying in amplitude and frequency. Then, recording
the induced neural activity in the barrel cortex,
they deduced that the neural activity most probably
encodes a quantity homogeneous to the product A f .
The generalized expression of this quantity to any
natural signal is known as the “equivalent noise level
(ENL)” (for more details see: (Arabzadeh et al.,
2005)), which is usually used to measure sound
power. This quantity can also be related to the more
common ”spectral centro
¨
ıd” (Fox et al., 2009).
To compute the latter, instead of using a Fast Fourier
Transform algorithm - of which no natural equivalent
is known - we simply called upon a time domain
“on-the-fly” estimate of the quantity Xω. The corre-
sponding algorithm (cf. Fig 2) can be compared to
those used in auditory feature extraction, like ZCPA
that is used for speech recognition (Ghitza, 1994;
Kim et al., 1999; Sreenivas and Niederjohn, 1992). It
TACTILE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION IN THE ROBOT-RAT PSIKHARPAX
75
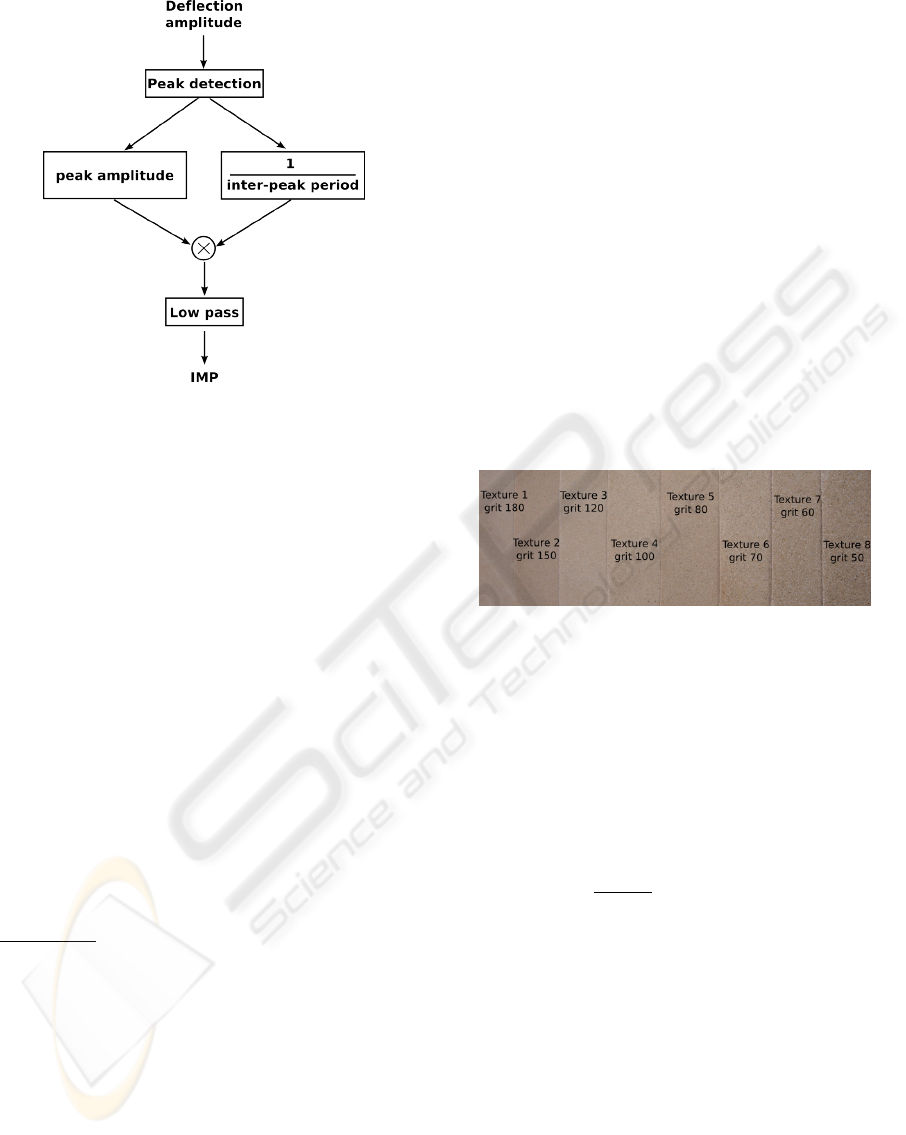
Figure 2: Feature extraction algorithm. ”Peaks” are de-
tected through the monitoring of the signal’s derivative and
frequencies are estimated through the inverses of the time
intervals between successive peaks. Then, the peak ampli-
tude is multiplied by the peak frequency, averaged within a
time window.
provides a quantity homogeneous to the ENL which
we call the “Instantaneous Mean Power” or IMP
feature.
This approach relies on the strong hypothesis that
the peaks thus characterized provide enough informa-
tion to describe a texture. Such hypothesis is rein-
forced by the fact that, when Licklider and Pollack
(1948) assessed the effects of various signal distor-
tions in human speech recognition, they found that
“infinite clipping” - a treatment that only kept a sig-
nal’s periodicity - did not prevent speech recognition
in humans.
Be that as it may, the corresponding algorithm
is very simple and computationally very cheap as
it necessitates only one division per peak detection
(
Peak amplitude
Peak period
) plus one addition (to compute the
peak’s period) at each time step. As for peak detec-
tion proper, it only entails one subtraction (x
t
−x
t−1
)
and a comparison.
There are however possible limitations to the pro-
posed algorithm. In particular, input data are drasti-
cally reduced by this procedure according to which
a pure sinus input of frequency F and a triangle in-
put of fondamental frequency F will lead to the same
feature value although they obviously don’t have the
same spectrum. Likewise, turns out that amplitude
modulations cannot be detected by a single vibrissa.
Our hypothesis is that such limitations are alleviated
by the fact that the natural filtering of vibrissæ, due to
their intrinsic mechanical characteristics, decomposes
complex signals along the pad in a manner similar to
how the cochlea decomposes auditory signals.
3.2 Fixed Head Experiment
3.2.1 Experimental Appartus
At first, we tested this haptic system according to a
relatively constrained fixed head experiment that con-
sisted in sweeping a whisker pad over a set of eight
sandpapers whose grits varied from P180 to P50 (cf.
Fig 3). Sandpaper provide a complex random texture
appropriate for this task and has been used on vari-
ous experiment with real rats. Using this material, we
performed qualitative experiments with humans that
clearly indicated that the task of discriminating such
textures by tactile contact only is a very difficult one,
an observation also made by Hipp and coll. (2005) .
Figure 3: The texture set used for discrimination.
A vibrissa pad was fixed on the robot’s head which
could move in pan-tilt directions. The pan axis was at
a fixed distance from the texture sample (cf. Fig 4)
that was presented with a small amount of variabil-
ity in position (∼ ±1cm) between each trial, with an
appropriate angle to provide contact with a maximum
number of whiskers.
For each texture, 400 experiments were made, 300
for learning and 100 for testing. The raw data (x and
y deflections, 8 bits resolution sampled at 1157Hz)
were normed (
√
x2 + y2). For each vibrissa, this mea-
sure was fed into the feature extraction algorithm that
output the IMP as one float value. Finally we summed
these IMP values for each vibrissa during the sweep.
Having thus obtained an input vector of 33 floats for
each trial, we fed it into a simple multi layer percep-
tron (MLP) with 33 input neurons, 33 hidden layer
neurons and 8 output neurons, to perform supervised
learning. We used the FANN library (Nissen, 2003)
with the iRPROP training algorithm (Igel and H
¨
uskel,
2000). The final classification was done by a winner-
take-all (WTA) on the 8 output neurons.
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
76
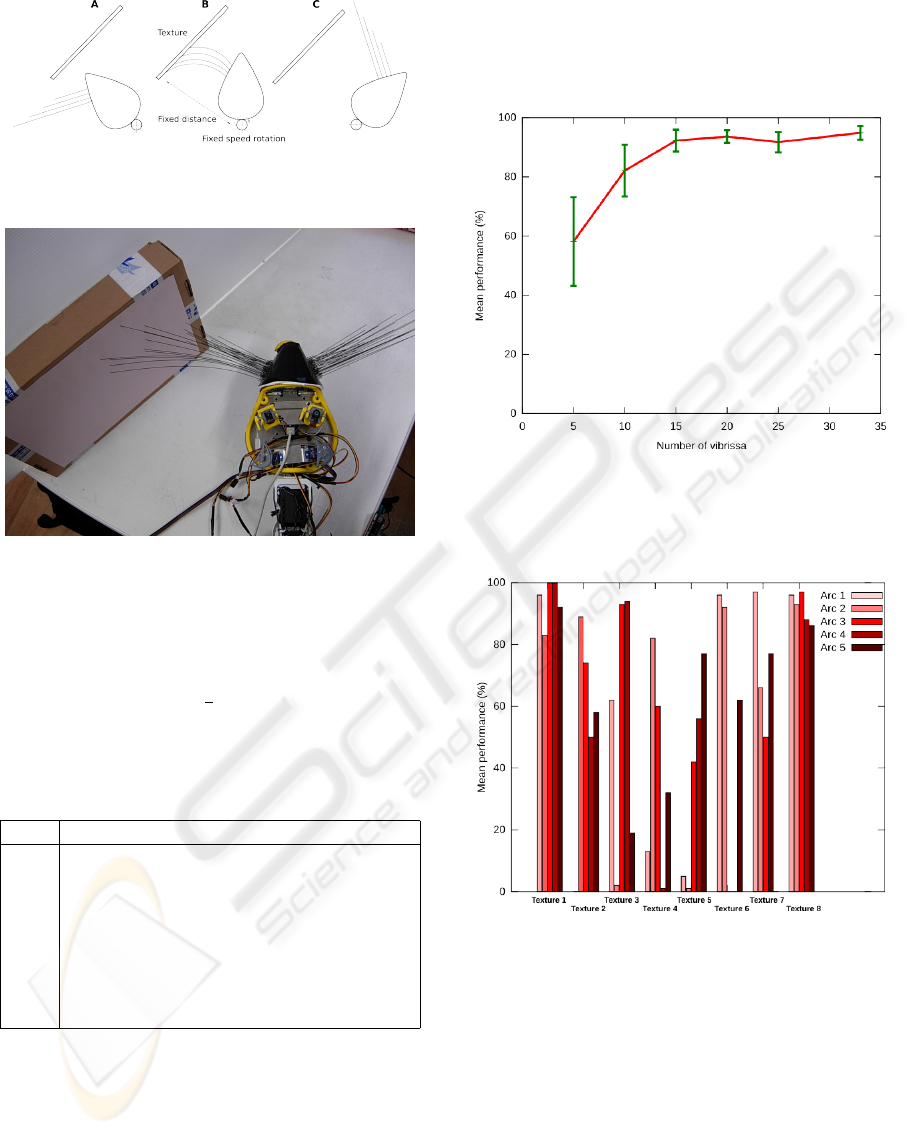
Figure 4: Schematic of the experimental protocol. A: start
position, B: mid position, C: end position.
Figure 5: Top view of the experimental protocol.
3.2.2 Results
Table 2 gives the confusion matrices obtained on 100
test data. The mean performance is clearly above 90%
(here the chance level is
1
8
= 12.5%), which greatly
improves the human aptitude at solving the same task.
Table 2: Confusion matrix obtained for the 8 textures using
IMP.
IMP 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
1 100 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
2 0 99 1 0 0 0 0 0
3 0 2 95 0 3 0 0 0
4 0 0 0 96 4 0 0 0
5 0 0 1 0 99 0 0 0
6 0 0 0 0 1 93 6 0
7 2 0 6 0 3 9 80 0
8 2 0 0 0 0 1 0 97
Using the data thus acquired, we tested the influ-
ence of the number of vibrissæ on the classification
performance. Starting with data obtained with one
arc (Arc 1, 5 vibrissæ cf. Table 1), then with two
arcs (Arc 1 + Arc 2, 10 vibrissæ) etc, up to the whole
whisker pad, we assessed at each stage the quality
of the discrimination. Results are summarized on
Figure 6. The percentage of successful discrimina-
tions is quickly rising with the number of vibrissae
involved and reaches values comprised between 90
and 95% when three or more arcs (15 vibrissæ) are
concerned. This result confirms previously obtained
ones in (Fend et al., 2003; Hipp et al., 2006).
Figure 6: Mean performance (% of successful discrimina-
tions) obtained with IMP, over the number of vibrissæ in-
volved.
Figure 7: Mean performance obtained with IMP for the 5
longer arcs across the 8 textures.
When analyzing the performances obtained with a
single arc (cf. Fig 7), one observes a great variability.
Indeed, it seems that each arc separately performs bet-
ter on a subset of the textures. For example, arc 2 is
very bad at recognizing texture 5, but quite good with
texture 6. This suggests that iso-length arcs comple-
ment each other and probably explains the increase in
performance with the number of arcs involved.
The relative quality of these results demonstrates
that the IMP is a suitable feature for texture recog-
nition. However, as Fox et al. (2009) pointed out,
TACTILE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION IN THE ROBOT-RAT PSIKHARPAX
77

the kind of fixed head task used so far is very differ-
ent from that of a robot moving in an environment,
where the distances and angles with which whiskers
touch any texture are constantly varying. Therefore,
to assess the robustness of the IMP, we also performed
such a complementary experiment.
3.3 Mobile Robot Experimentation
3.3.1 Experimental Appartus
In this experiment, a set of complex textures (cf. Fig
8) made of plexiglass were fixed on the sides of two
small corridors (1m long). A different texture was
Figure 8: The four textures used in the mobile robot exper-
iment. These textures were made of relief decorated plexi-
glass.
assigned to each side of each corridor. The robot’s
task was to follow the walls in its environment, to en-
ter a corridor if encountered, to recognize the textures
on its sides, and to learn to turn left or right at the
end of the corridor, depending on the left/right com-
bination of the textures thus recognized. A main dif-
ference with the previous experiment was the “touch
strategy”. We previously swept whiskers on a tex-
ture by rotating the head, trying to maximize the num-
ber of whiskers in contact with the texture. Here, the
whole robot was moving, the head didn’t rotate and
only a subset (∼ 10 vibrissæ, the two longer arcs) of
whiskers were actually touching the textures, from a
varying distance.
To allow the robot to navigate in its environment
using only its whiskers as sensory input, we devel-
oped a simple obstacle avoidance strategy. A distance
information was first computed by taking into account
the iso-length arcs. One minus the mean arc deflec-
tion was weighted by the mean within-arc vibrissa
size. Thus, the more vibrissæ were bent, the smaller
was the output distance. Repeating this computation
for each arc, we obtained a value that decreased with
the contact distance,
D =
1
N
∑
(1 −V
i
) ×L
i
(1)
V
i
being the mean deflection of the i
th
arc and L
i
the
mean length of the i
th
arc. One can notice that the
smaller whiskers - the most frontal ones - contribute
Figure 9: Robot environment showing the 2 corridors and
direction convention used (Top). Robot inside a corridor,
with dimensions and command vector (Bottom).
less to this measure than the longer ones. This may
seem counter intuitive as, when an object touches
the small whiskers, it is probably closer than if it
only touches the longer ones. But generally in the
described task, when an object touches the smaller
whiskers, it also touches the longer ones and the
above weighting prevents an over-reaction. Moreover
this method has shown a better stability in corridors,
where a small variation of vibrissa deflection should
provoke a small orientation reaction in order to make
the corresponding trajectory as straight as possible.
This centering strategy was an important component
of the robot’s behavior since the corridors were 35cm
wide, while the robot’s width was 25cm (including
wheels) and the maximum whisker range was 50cm,
leaving a small error margin for steady forward move-
ment and whisker crack avoidance (cf. Fig 9). We
controlled the robot through a speed vector V applied
at the axis of the neck whose orientation component
V
y
was given by:
V
y
= (D
le f t
−D
right
) ×G (2)
with the gain G = 0.01. V
x
, the translation speed,
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
78
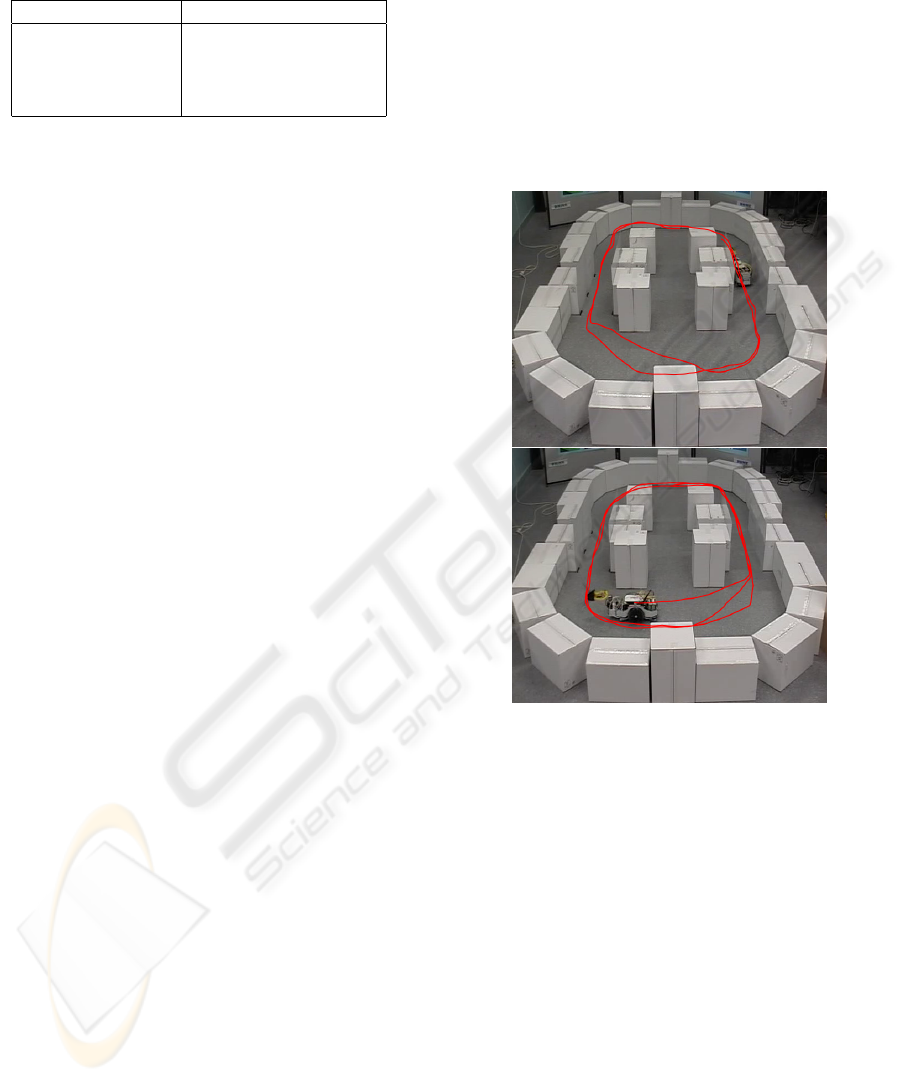
Table 3: Confusion matrix obtained for 20 runs for each
corridor, in each direction.
Corridor-direction 1-1 1-2 2-1 2-2
1-1 75 15 10 0
1-2 0 100 0 0
2-1 15 0 85 0
2-2 0 15 0 85
was fixed to 10cm/s. This simple control produced an
obstacle avoidance behavior, with a tendency to wall
following. Additionally, this control produced a rela-
tively stable corridor centering behavior - which was
its principal objective. Finally, using D
le f t
and D
right
values, we could roughly determine the corridor’s
aperture size and trigger the learning/recognition pro-
cedure only when the robot was inside a corridor as
determined by a distance threshold.
We first ran a series of 10 experiments for each
corridor and each direction. We simply positioned
the robot approximately in front of the corridor and
recorded the IMP feature output at each time step
within the corridor. We when fed 7 data runs to a
MLP (2 ×33 neurons in the input layer, 2 ×33 neu-
rons in the hidden layer and 4 neurons in the output
layer), keeping the 3 others runs to test the learning
result. A typical data run length was ∼ 7000.
3.3.2 Results
Once the learning was completed, we ran four series
of 20 additional experiments to evaluate the capacity
of the robot to turn in the right direction at each end
of each corridor. While the robot moved in a given
corridor, in a given direction, we fed the smoothed
(low pass filter) 2 ×33 IMP output to the previously
learned MLP and computed the WTA on the output
layer. By accumulating this winner value through the
whole corridor, we obtained a mean decision vector
which served to take the final decision (once again by
a WTA). The corresponding results are summarized in
Table 3. As expected, the trajectory stability played a
role in performances as dithering in the corridor in-
duced variations in the perceived vibrations. Most of
the errors occurred when the robot’s trajectories were
unstable (lot of dithering).
We finally conducted qualitative experiments in
the whole maze using the above described naviga-
tion rules. The maze was a round corner rectangle
of 2.20m by 4.10m made of cardboard boxes with 2
corridors (cf. Fig 9). We added a simple hand ca-
bled behavior consisting of turning left or right at the
end of a corridor, depending on the recognized tex-
tures. The robot was initially positioned near the wall
on the top of the maze with left or right orientations.
Any other starting position could have been used with
the limitation of avoiding a direct wall facing, as no
“reversal” behavior was implemented. In these condi-
tions, the robot succeeded to autonomously circulate
around the maze, following either direction indicated
by the textures on the corridor’s sides. Several tours
could be completed in a row thus demonstrating the
efficiency of the robot’s haptic system.
Figure 10 shows an example of the kind of trajec-
tories obtained.
Figure 10: Typical trajectory of the robot into the maze.
Top: left oriented start. Bottom: right oriented start.
4 DISCUSSION
If some research efforts have been devoted to tex-
ture discrimination in “fixed head” tasks (Fend et al.,
2003; Lungarella et al., 2002; Kim, 2004; Fox et al.,
2009), very few robots have been able to navigate and
recognize tactile cues in a less constrained environ-
ment using whiskers. One such work was done using
curvature sensors with two different types of surfaces
that one may consider more as a “shapes” than as a
“textures”, as they seem to induce a mere deflection
sequence rather than a complex vibration (Seth et al.,
2004). This robot could be conditioned to associate an
aversive response with a given texture. A related work
concerned a smooth versus rough discrimination task
in an open arena and involved an active microphone-
based whisker sensor with a natural rat’s hair (Fend,
TACTILE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION IN THE ROBOT-RAT PSIKHARPAX
79

2005). Feature extraction called upon spectral analy-
sis and lead to qualitatively good results. However, as
the author concludes, such system could not be used
to perform a more complex task without an improve-
ment of its discriminatory capability and reliability.
Finally, Fox et al. (2009) also obtained good results in
a smooth/rough discrimination task on a mobile robot
equipped with active whiskers using an “onset” fea-
ture. This “onset” feature is roughly the FFT magni-
tude within a short frequency band (2-3kHz) during
the onset period of the whisker-texture contact (the
first 12.8ms of the contact). Moreover, this feature
is invariant to the relative position and orientation of
whiskers and textures. Experimental conditions were
slightly different from ours, as the texture position
was chosen randomly and the robot didn’t move while
touching a texture.
None of these related approaches seems suitable for
performing a more complex task than simply discrim-
inating smooth versus rough textures. In contrast, the
haptic system that has been described herein proved
to be able to use texture discrimination to afford min-
imal navigation capacities in a complex environment.
Such capacities could be used to complement vision
in daylight conditions or to replace it in the dark.
With this haptic system, texture recognition is
possible in both fixed and mobile robot conditions.
This tends to indicate that, despite the underlying
simple algorithm and the various approximations on
which it relies, the IMP feature is robust.
Conversely, we already mentioned that the
whisker orientations in our system is not always well
suited. Indeed, our whiskers are oriented toward the
front (cf. Fig 5), which occasionally prevents all the
whiskers from touching a texture. Within a corridor,
for instance, about 10 whiskers only were touching
the walls. Additionally, our implementation some-
times entails brusque return jumps of some whiskers
when they are stuck on a given surface, rather than
a gentle sweeping, which makes their signals totally
unreliable. Fortunately, this problem only occurs in
corridors and with a minority of whiskers (usually
the more dorsal and ventral ones) and thus the clas-
sifier can see it as mere noise. Obviously, a system in
which the whisker orientation could be dynamically
controlled - such as the one used in (Fox et al., 2009)
- would be more adapted to alleviate this specific in-
convenience and would be closer to the natural active
whiskering system of rats.
Another remark concerns our feature extraction
technique. We chose to design an algorithm that ex-
tracts an estimation of the amplitude-frequency prod-
uct. This choice was based on a recent finding
about how texture signals are encoded in a rat’s brain
(Arabzadeh et al., 2004). Using such a feature, we
were able to perform fine texture discrimination. This
finding is an argument in favor of the so-called “ki-
netic signature” hypothesis which stands that each
vibrissa encodes a specific signature of the touched
surface in term of magnitude and temporal pattern.
Likewise, the fact that our results suggest that the
texture discrimination capacities depend both on the
length and number of the involved whiskers, seems to
back up the “resonance hypothesis” (Moore and An-
dermann, 2005; Neimark et al., 2003) which stands
that the self resonance property of a vibrissa plays
a crucial role in vibration transduction and, in some
way, helps to enhance texture perception. The exact
manner in which this resonance property is exploited
in rats is still unclear, but it seems quite reasonable to
think that a kind of signal filtering is involved. Addi-
tional experiments with the current system might help
clarify this issue.
Be that as it may, already acquired results strongly
suggest that two hypotheses that are currently consid-
ered as mutually exclusive to explain texture recog-
nition in rats - i.e., the “kinetic signature hypothe-
sis” and the “resonance hypothesis” - may be, in fact,
complementary.
5 CONCLUSIONS
We endowed a whiskered robot with a simple algo-
rithm allowing to discriminate textures. Its efficiency
has been demonstrated using both a fixed head and a
mobile robot. Comparatively to previous similar ap-
proaches, this system affords greater behavioral ca-
pacities and may complement or supply vision in sim-
ple navigation tasks. Future work will be devoted
to demonstrating its ability to perform shape recog-
nition. On a fundamental level, it will also be used to
investigate the influence of whiskers resonance prop-
erties on texture transduction.
REFERENCES
Arabzadeh, E., Panzeri, S., and Diamond, M. E. (2004).
Whisker Vibration Information Carried by Rat Barrel
Cortex Neurons. J. Neurosci., 24(26):6011–6020.
Arabzadeh, E., Zorzin, E., and Diamond, M. E. (2005).
Neuronal encoding of texture in the whisker sensory
pathway. PLoS Biol, 3(1):e17.
Brecht, M., Preilowski, B., and Merzenich, M. (1997).
Functional architecture of the mystacial vibrissae. Be-
havioural Brain Research, 84(1-2):81–97.
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
80

Brooks, R. A. (1989). A robot that walks: Emergent be-
haviors from a carefully evolved network. Technical
Report AI MEMO 1091, MIT.
Carvell, G. and Simons, D. (1990). Biometric analyses of
vibrissal tactile discimination in the rat. Journal of
Neuroscience, 10(8):2638–2648.
Chapman, T., Hayes, A., and Tilden, T. (2000). Reactive
maze solving with a biologically-inspired wind sen-
sor. In J. Meyer, A. Berthoz, D. F., Roitblat, H., and
Wilson, S., editors, From Animals to Animats 6. Proc.
of the 6th Int. Conf. on Simulation of Adaptive Be-
havior, pages 81–87. MA: MIT PRESS. A Bradford
Book.
Fend, M. (2005). Whisker-based texture discrimination on
a mobile robot. Advances in Artificial Life - Proceed-
ings of the 8th European Conference on Artificial Life
(ECAL), pages 302–312.
Fend, M., Bovet, S., Yokoi, H., and Pfeifer, R. (2003). An
active artificial whisker array for texture discrimina-
tion. In Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International
Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS),
volume II, pages 1044–1049.
Fox, C. W., Mitchinson, B., Pearson, M. J., Pipe, A. G.,
and Prescott, T. J. (2009). Contact type dependency
of texture classification in a whiskered mobile robot.
Autonomous Robots. In press.
Ghitza, O. (1994). Auditory models and human perfor-
mance in tasks related to speech coding and speech
recognition. IEEE Transactions on Speech and Audio
Processing, 2(1):115–132.
Guic-Robles, E., Valdivieso, C., and Guarjardo, G. (1989).
Rats can learn a roughness discrimination using only
their vibrissal system. Behavioural Brain Research,
31(3):285–289.
Hartmann, M. J. (2001). Active sensing capabilities of the
rat whisker system. Autonomous Robots, 11:249–254.
Hipp, J., Arabzadeh, E., Zorzin, E., Conradt, J., Kayser,
C., Diamond, M. E., and Konig, P. (2006). Tex-
ture Signals in Whisker Vibrations. J Neurophysiol,
95(3):1792–1799.
Igel, C. and H
¨
uskel, M. (2000). Improving the rprop learn-
ing algorithm. In Proceedings of the Second Interna-
tional Symposium on Neural Computation, NC2000,
pages 115–121.
Kim, D.-S., Lee, S.-Y., and Kil, R. M. (1999). Auditory
processing of speech signals for robust speech recog-
nition in real-world noisy environments. IEEE Trans-
actions on Speech and Audio Processing, 7(1):55–69.
Kim, D. and Moller, R. (2004). A biomimetic whisker for
texture discrimination and distance estimation. From
Animals to Animats 8, pages 140–149.
Krupa, D. J., Matell, M. S., Brisben, A. J., Oliviera, L. M.,
and Nicolelis, M. A. L. (2001). Behavioural prop-
erties of the trigeminal somatosensory system in rats
performing whisker-dependent tactile discrimination.
J. Neurosci., (21):5752–5763.
Licklider, J. C. R. and Pollack, I. (1948). Effect of differ-
entiation, integration, and infinite peak clipping upon
the intelligibility of speech. Journal of the acoustical
society of america, 20(1):42–52.
Lungarella, M., Hafner, V., Pfeifer, R., and Yokoi, H.
(2002). Artificial whisker sensors in robotics. Intel-
ligent Robots and System, 2002. IEEE/RSJ Interna-
tional Conference on, 3:2931– 2936.
Meyer, J.-A., Guillot, A., Girard, B., Khamassi, M., Pirim,
P., and Berthoz, A. (2005). The psikharpax project:
Towards building an artificial rat. Robotics and Au-
tonomous Systems, 50(4):211–223.
Moore, C. I. and Andermann, M. L. (2005). The Vibrissa
Resonance Hypothesis, chapter 2, pages 21–60. CRC
Press.
Neimark, M. A., Andermann, M. L., Hopfield, J. J., and
Moore, C. I. (2003). Vibrissa resonance as a transduc-
tion mechanism for tactile encoding. The Journal of
Neuroscience.
N’Guyen, S., Pirim, P., and Meyer, J.-A. (2009). Elastomer-
based tactile sensor array for the artificial rat
psikharpax. In ISEF 2009 - XIV International Sym-
posium on Electromagnetic Fields in Mechatronics,
Electrical and Electronic Engineering. In press.
Nissen, S. (2003). Implementation of a Fast Artificial Neu-
ral Network Library (fann). Report, Department of
Computer Science University of Copenhagen (DIKU),
31.
Petersen, R. S. and Diamond, M. E. (2000). Spatial-
Temporal Distribution of Whisker-Evoked Activity in
Rat Somatosensory Cortex and the Coding of Stimu-
lus Location. J. Neurosci., 20(16):6135–6143.
Russell, R. A. (1985). Object recognition using articu-
lated whisker probes. In Proc. 15th Int. Symp. Industr.
Robots., pages 605–612.
Seth, A. K., McKinstry, J. L., Edelman, G. M., and Krich-
mar, J. L. (2004). Spatiotemporal processing of
whisker input supports texture discrimination by a
brain-based device. In Schall, S., Ijspeert, A., Bil-
lard, A., Vijayakumar, S., Hallam, J., and Meyer, J.,
editors, From Animals to Animats 8. Proc. of the 8th
Int. Conf. on Simulation of Adaptive Behavior. MA:
MIT PRESS.
Sreenivas, T. V. and Niederjohn, R. J. (1992). Spectral anal-
ysis for formant frequency estimation in noise. IEEE
Transactions on Signal Processing, 40(2):282–293.
TACTILE TEXTURE DISCRIMINATION IN THE ROBOT-RAT PSIKHARPAX
81
