
ON THE DESIGN OF A HEALTHCARE INFORMATION
SYSTEMS CONCENTRATION
Shafaq Naheed Khan
University of Dubai, U.A.E.
Keywords: Healthcare Information Systems, Program concentration, Curriculum, IS education.
Abstract: Information Systems as a field of academic study has witnessed tremendous growth both in scope and depth
since its beginning in 1960s. With rapid growth of Information Technology in the field of healthcare, there
is a need growing worldwide for IT personnel specializing in healthcare area as well. Market surveys
involving the stakeholders at the regional level indicate the need for a bachelor’s degree in computing and
information systems with concentration in healthcare. This paper proposes a curriculum for such a study as
an addition to the existing accredited portfolio of BSc. in Computer Information Systems (CIS) program
being offered at the university level. Efforts have been made that the proposed HCIS curriculum conforms
both to the standards laid out by the accrediting agency and the University mission. The focus of this report
is to inform others of local efforts needed on their campuses and to share findings that may be of use to
researchers in similar situations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Health information technology has the potential to
transform health care delivery, bringing information
where it is needed and refocusing health care around
the consumer (Tommy and David, 2004). Rapid
growth of information technology and its widespread
adoption for the healthcare delivery are the
indicators of the growing demand for the IT
personnel in healthcare organizations. As observed
by Richard (2003), healthcare workers with IT
knowledge are in great demand. The knowledge and
skill shortfalls with healthcare managers in this
discipline, however, undermine their strategic and
tactical planning responsibilities. Healthcare
information management systems practitioners all
over the world are keenly aware of this shortage with
IT personnel. According to Wilkins, Cheryl and
Marilyn (2002), IS jobs are becoming diversified
and that generic IS curriculum will not meet all the
needs for all IS jobs. According to them, the
curricula can be developed for separate and
distinctive concentrations targeting the diverse job
market requirements. It is the responsibility of
educators to offer programs to meet the future
healthcare information systems (HCIS)
professionals’ demand. It thus becomes imperative
to re-evaluate the situation and design the programs
as should meet such market demand.
The College of Information Technology (CIT)
offers a BSc. in CIS. This program is accredited by
Computing Accreditation Committee (CAC) of
ABET. Courses in the existing program curriculum
meet the ABET standards. CIT has a proposal to
offer the same program with six concentrations
including the one with concentration in HCIS. The
instant paper is the result of efforts at developing a
concentration in HCIS.
With a view to assess the feasibility for the
proposed HCIS concentration at the undergraduate
level, the following questions have been
consideration as the touchstone.
A. Is there is any requirement for this
concentration at the regional and the national
level?
B. Is this concentration should serve the purpose
of the beneficiary institutions?
C. Is this course would invite sufficient numbers
of prospective students to take up the course?
D. Is the institution ready with the faculty and
other support services needed for
implementation of the concentration?
275
Khan S. (2010).
ON THE DESIGN OF A HEALTHCARE INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONCENTRATION.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Health Informatics, pages 275-281
DOI: 10.5220/0002739102750281
Copyright
c
SciTePress
Last two questions are beyond the scope of this
research work and hence not dealt with. As for the
first two questions, measures were taken to study the
market needs and the results are detailed out below.
2 MARKET FEASIBILITY
According to a recent Gulf News (2008) report,
UAE’s healthcare sector is showing robust growth
and is poised to attract foreign direct investment in
sufficient measure in the near future. There are
around 36 hospitals in UAE. The Chamber has
established Dubai Healthcare City (DHCC), an
ongoing project worth $3 billion, as well as the $400
million Dubai Biotechnology and Research Park
(DuBiotech). DHCC has the distinction to be the
world’s first healthcare free zone. It is one of the
numerous specialized 'City-within-a-City' in Dubai
targeting phenomenal growth in healthcare and
pharmaceutical industries. The project comprises of
a collection of medical teaching institutions, private
hospitals and clinics, pharmaceutical research
centers, their offices, spas and rehabilitation centers.
Overall, there are 17 hospitals planned for DHCC.
These are currently partially functional and expected
to be fully operational by 2010. The initiative for
establishing DHCC and DuBiotech aligned with
global positive healthcare prospects will increase
investment in the sector indicating high employment
potential for the work force specialized in this sector.
With a view to further substantiate the
requirement need; a market feasibility study at the
level of all the stakeholders was organized. There
were two surveys undertaken inside and outside the
University as follows:-
First survey
was conducted within CIT to study
the need for the six concentrations, including the
proposed concentration in HCIS. This survey was
done with existing senior and graduating students at
the college, university faculty, university alumni,
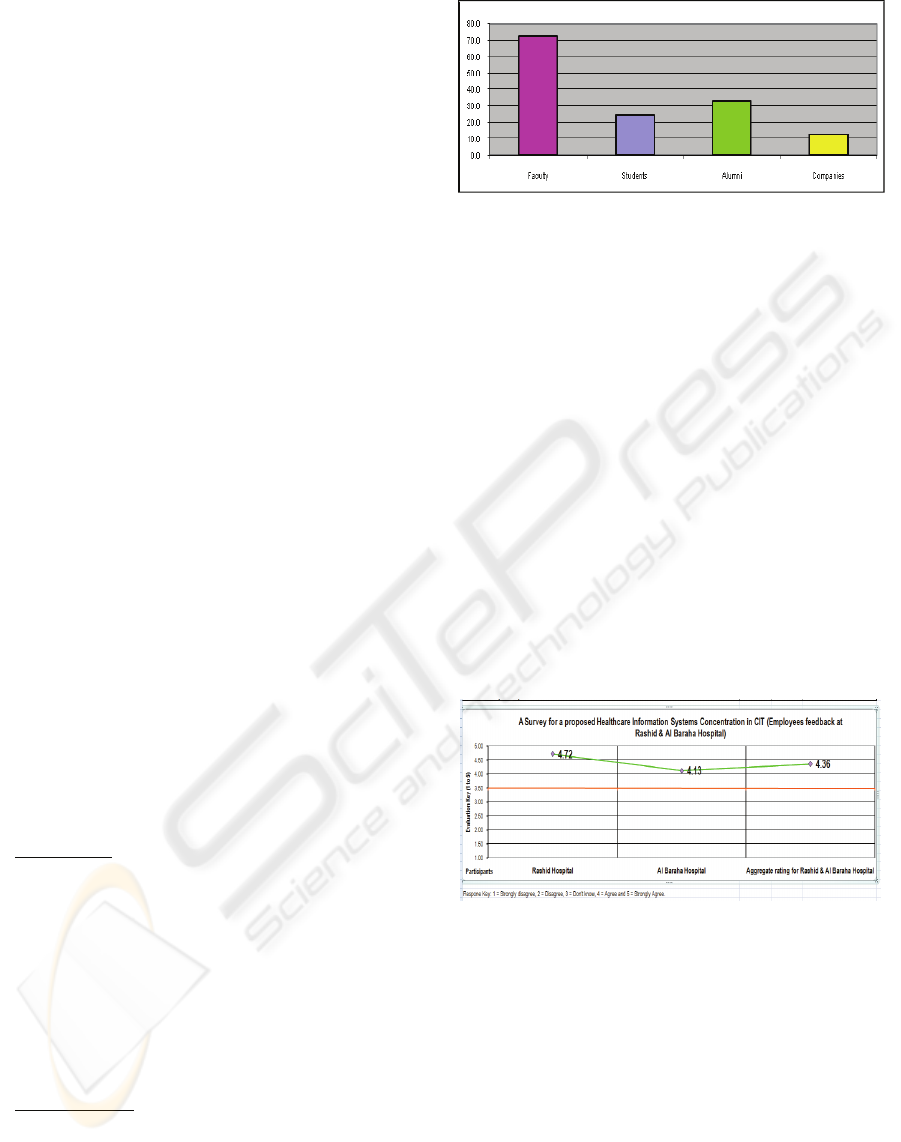
and employers. The survey showed 72.7% demand
from the faculty, 24.1% demand from the students
currently on roll; 33.3 % from the alumni and 12.5%
demand from the employers. Figure 1 here is a
graphic presentation of the demand for HCIS
concentration.
Second survey
was conducted to study the need
for the HCIS concentration specifically. Survey data
was collected from two premier hospitals located in
Dubai.
The survey questionnaire consisted of five parts
Figure 1: Chart Showing the Demand for New
Concentrations in HCIS.
and responses were ranked on 1-5 scale.
Response key 1 represented “Strongly disagree”
performance, key 2 represented “Disagree”, key 3
denoted “Don’t know” key 4 represented “Agree”
and the key 5 stood for “Strongly Agree”.
The survey received feedback from 39
employees from the Rashid Hospital and 60
employees from Al Baraha Hospital. The
respondents were the doctors, head of departments,
nurses, radiographers, pharmacists, hospital
administration staff, executive assistants & etc.
There were 66 female and 30 male respondents
(three participants did not specify their gender). On
the nationality count, 65% respondents were UAE
nationals followed by 35% people from other
nationalities.
The feedback and summary of the ratings from
the employers are shown in Figure 2 hereunder.
Figure 2: Summary of Employer’s Ratings.
2.1 Analysis
• The overall growth pattern in UAE and
initiatives at establishing DHCC and DuBiotech
highly indicate the need for services of HCIS
professionals here.
• First survey results point to the fact that the
• faculty needs such a concentration most and
the least was felt by the organizations, mostly not the
healthcare organizations. However, the second
survey carried out among the healthcare
organizations resulted in an encouraging average of
HEALTHINF 2010 - International Conference on Health Informatics
276

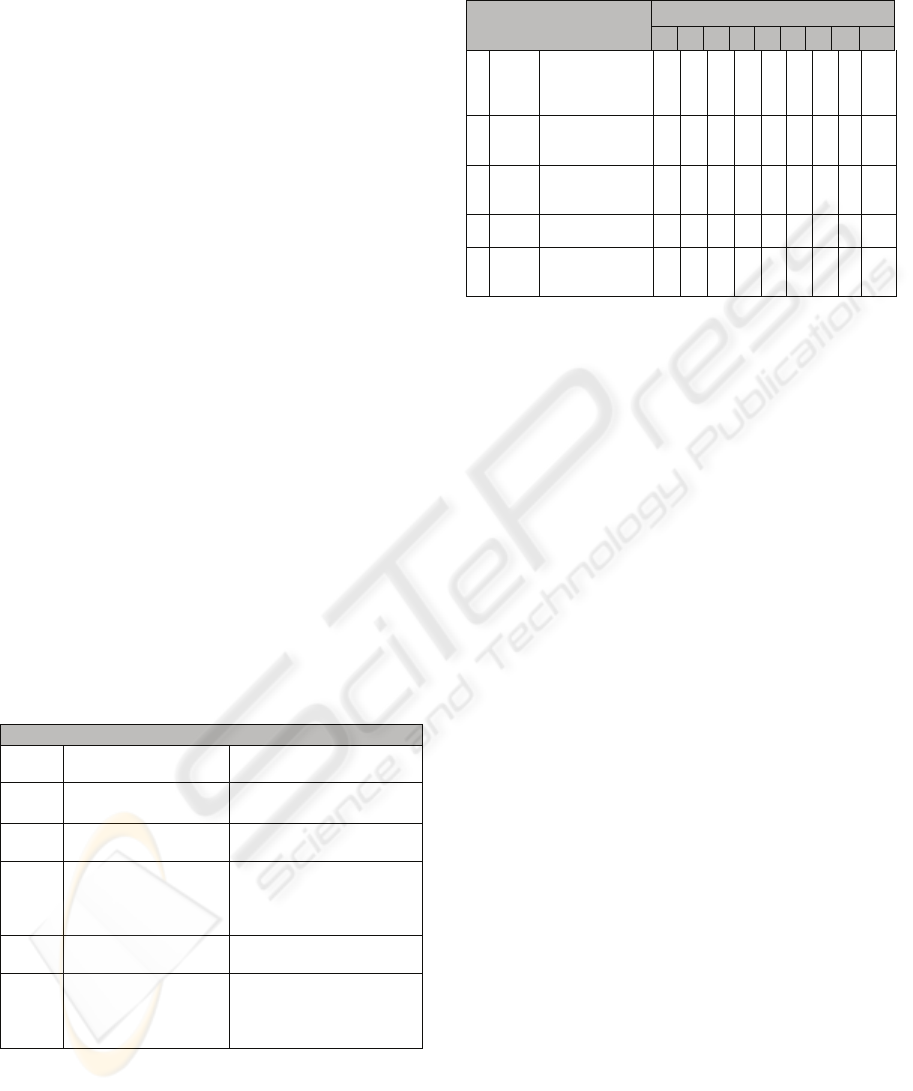
Table 1: Mapping of HCIS concentration objectives to HCIS outcomes.
4.72 on a scale of 1-5 from the Rashid hospital, 4.13
on this scale from the Al-Baraha hospital that gives
an aggregate rating of 4.36 from the two hospitals.
The results of the surveys strongly recommend the
need for graduates with specialization in healthcare
information systems.
• The fact that no university in UAE is offering
such a specialization reaffirmed the need for offering
such a concentration hereafter.
• International recognition of the program,
academic and professionally qualified faculty,
University association with Dubai Chamber and the
University’s focus on learning and applied IT
research are the factors that will promote the
students to enroll themselves for the HCIS
concentration program.
3 CURRICULUM VS
STANDARDS
Developing and revitalizing the IS curricula is an
evolutionary process because of the exponential
development of technology (Hunt, 2004) and (Tracie
& Rebecca, 2008). Several available curriculum
models provide guidelines for adoption and further
shaping the curriculum for undergraduate programs.
Recent public draft of IS 2009 and its predecessors
IT 2008, OEIS (Organizational End-User
Information Systems) and MTC (Managerial,
Technical & Communication) models are there to
name a few. Accreditor’s guidelines are equally
important for developing and analyzing the
curricula.
Concentration in HCIS comes under the umbrella
of the CIT’s CIS program. Efforts were made to
ensure that the HCIS concentration is in agreement
with the ABET standards. ABET has five statements
about objectives and assessment (Criteria for
Accrediting Computing Programs, 2007). First two
standards related to the objectives are:
Standard I-1. The program must have
documented educational objectives.
Standard I-2. The program’s objectives must
include expected outcomes for graduating students.
The objectives and outcomes of the CIS program
strongly conform to the University mission. An
important design aspect of the HCIS concentration
was the need for a HCIS curriculum that would
relate to the objectives and outcomes of the CIS
program. Objectives and outcomes of the BSc. CIS
with concentration in HCIS are defined below.
3.1 Program Objectives (with
Concentration in HCIS)
The CIS program with concentration in HCIS is
designed to prepare graduates who are able to:
1. Demonstrate knowledge of concepts and
practices of healthcare systems and the
processes required to support health service
delivery.
2. Understand and analyze the important issues
with regard to the social impact of advanced and
emerging computer information technologies
3. Apply a variety of techniques, software tools
and applications to enhance the effectiveness
and efficiency of health care organizations.
4. Formulate questions and critically investigate
and solve business-related computing &
HCIS Concentration Outcomes
HCIS Concentration Objectives
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
1. Apply knowledge of computing, information systems and mathematics.
X X
2. Analyze a healthcare IS- related problem, identify and define the computing and
information systems requirements appropriate to its solution
X X X X
3. Design, implement and evaluate a computer-based system, process, component, or
program to meet desired needs.
X X X X
4. Function effectively in teams to create a project plan to accomplish a common goal.
X X
5. Understand professional, ethical and social responsibilities.
X
X X
6. Communicate effectively with a range of audiences.
X
X X
7. Analyze the impact of computing on individuals, organizations and society, including
ethical, legal, security and global policy issues
X
X X
8. Apply current techniques, skills, and tools to enhance the operational and managerial
aspects of healthcare organizations
X
9. Understand the organizational, administrative, managerial, and regulatory processes that
support the delivery and management of evolving health systems
X X
ON THE DESIGN OF A HEALTHCARE INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONCENTRATION
277

information systems problems
5. Be engaged in ethical issues in information
systems, particularly questions of social
responsibility and professional decision-making
6. Build and lead team of professionals to tackle
challenging Computing & Information Systems
Projects
7. Communicate effectively and professionally
with technical and non-technical professionals.
3.2 Program Outcomes (with
Concentration in HCIS)
Upon graduation, each CIS graduate with
concentration in HCIS will possess the knowledge,
skills, and ability to:
1. Apply knowledge of computing, information
systems and mathematics.
2. Analyze a healthcare IS-related problem,
identify and define the computing and
information systems requirements appropriate to
its solution.
3. Design, implement and evaluate a computer-
based system, process, component, or program
to meet desired needs.
4. Function effectively in teams to create a project
plan to accomplish a common goal.
5. Understand professional, ethical and social
responsibilities.
6. Communicate effectively with a range of
audiences.
7. Analyze the impact of computing on
individuals, organizations and society, including
ethical, legal, security and global policy issues.
8. Apply current techniques, skills, and tools to
enhance the operational and managerial aspects
of healthcare organizations.
9. Understand the organizational, administrative,
managerial, and regulatory processes that
support the delivery and management of
evolving health systems
The mapping between the HCIS concentration
outcomes and the corresponding HCIS concentration
objectives is highlighted in Table 1on next page.
These healthcare concentration objectives and
outcomes map directly to the CIS program
objectives and outcomes and are thus aligned with
the University mission to prepare high caliber
graduates of lifelong learning and serve the
educational and professional needs of all
stakeholders.
4 CONCENTRATION COURSE
DESIGN PHILOSOPHY
A review of the ABET standards show that students
must have at least 30 semester hours of study in
information systems topics, at least 15 semester
hours of study in an information systems
environment, such as business, at least 9 semester
hours of study in quantitative analysis, and at least
30 semester hours of study in general education. The
information systems area is further broken into core
content and advanced content. According to ABET
Standard IV-9 (Criteria for Accrediting Computing
Programs,2007) all students must take at least 12
credit hours of advanced course work in information
systems that provides breadth and builds on the IS
core to provide depth.
BSc. CIS degree consists of 41 courses, an
internship and an applied research project. Each
course is worth three credits. Students must
complete 129 credit hours to be awarded a BSc.
degree. CIT requires the same 129 credit hours for
the degree of BSc. with concentration in HCIS as
shown in Table 2. However, the curriculum for
BSC-CIS with concentration in HCIS has been
customized to include 15 credit hours for HCIS
concentration requirements comprising of five
courses.
Table 2: Curriculum for BSc. CIS – Concentration HCIS.
SN
o
CATEGORY
REQUIREMENTS
General
Requirement
I
T
Total
1 General Education 27 27
2 Humanities & Social
Sciences
6 6
3 Natural & Applied
Sciences
6 6
4 Business Requirements
for IT professionals
33 33
5 IT Core Requirements 4
2
42
6
HCIS Concentration
Requirements
1
5
15
TOTAL 72 5
7
129
4.1 Design Criteria
According to Srinivasan, Guan and Wright (1999) &
Charles and Terri (2002), a strong partnership
between IS academics and industry is vital for the
curriculum development. There is a growing
demand for clearer, higher, and measurable
educational outcomes as well as increased industry
input into the development of the standards (Grubb
and Lazerson, 2004).
HEALTHINF 2010 - International Conference on Health Informatics
278
Essential characteristic for graduates seeking
employment is not the knowledge alone but also
their proficiency in technical and non-technical skills
(Karoly and Panis, 2004),(Charles and Terri, 2002),
(Judy and D'Amico, 1998), (Smith, Hunt, Berry, and
Hunt, 2005), (Lee, Trauth, and Farwell, 1995),
(Judith, Eric, Gary and Laura,2008), (Karoly and
Panis, 2004), (Gandossy, Tucker and Verna,2006),
(Karoly and Panis, 2004) & (Judy and D’Amico,
1998).
Addressing the local employment needs is not
the only objective for the Bsc. HCIS-Concentration.
Students from IS program should be able to accept
jobs in widely dispersed geographic areas.
Therefore, it is necessary to maintain programs that
are consistent both with regional and national level
employment job market and with the common body
of knowledge of the IS field (IS, 2002).
Relevant and suitable HCIS-Concentration
specific courses and their learning outcomes have
been designed carefully based on following criteria:-
1. The need to equip the students with the HCIS
knowledge and skills.
2. The appropriateness of the support (pre-
requisite) courses provided by the existing CIS
program.
4.2 List of Newly Introduced Courses
HCIS specialization courses introduced in the
curriculum are listed in Table 3 below.
Table 3: HCIS Specialization Requirements.
Specialization Requirements (15 Cr. Hrs)
Course
Code
Course title Course pre-requisite
ITHS
450
Healthcare Informatio
n
Systems Management
ITGN 215: Introduction to
Information Systems
ITHS
451
Healthcare Computer-
based risk
ITGN 315: Object-
Oriented Programming
ITHS
453
Healthcare Process
Improvements
ITGN 220: Software
Project Management
BBUS 200: Quantitative
Methods for Business
ITHS
464
Electronic /Mobile –
Healthcare Systems
ITGN 350: Web Design &
Development
ITIS
465
Database Security and
Audit
ITGN 250: Database
Management Systems
ITGN 345: Information
Systems Security
Each course in the HCIS curriculum is out-
come focused and detailed. All the outcomes are
mapped to the assessment tools and HCIS
concentration outcome. Finally each syllabus shows
(also shown in the Table 4) the course mapping to
the program-level outcomes.
Table 4: Mapping CIS-HCIS Curriculum to Program
Outcomes.
Specialization
Requirements (15 Cr.
Hrs.)
Program Outcomes (PO)
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
1
ITHS
450
Healthcare
Information
Systems
Management
X
X
2
ITHS
451
Healthcare
Computer-based
Risk
X X
X
X X X
3
ITHS
453
Healthcare
Process
Improvement
X
X X X
4
ITHS
464
E/M-Healthcare
Systems
X
X X X
5
ITIS
456
Database
Security &
Auditing
X
X
X X
4.3 Course Design Considerations
The following section outlines the design criteria
that have been adopted in the selection of the HCIS
concentration-specific courses and their learning
outcomes.
ITHS 450: Healthcare Information Systems
Management
This course will provide students with the ability to
define operational and strategic objectives for health
services management information systems.
Particular emphasis will be placed upon the technical
knowledge area and the proper interpretation and
utilization of processed information for program
management purposes. Students will get hands-on
knowledge of software tools and applications.
Addressing investment decisions will be a part of
this course. By addressing the additional social,
legal, and ethical issues related to IS usage and their
practical implications from a healthcare perspective
(Criteria 1). A student with a basic understanding of
information systems concepts will be able to take-up
this course. Therefore, the course “Introduction to
Information Systems” has been chosen as the pre-
requisite to this course, in accordance to criteria 2.
ITHS 451: Healthcare Computer-based Risk
This course provides an overview of the theory and
applications of risk management practices within
healthcare organizations and aims to develop
students’ ability to manage risk associated with
potential system failures. It explains what needs to
be done to successfully achieve quality and
compliance of computer systems in the
pharmaceutical and healthcare industries. This
course will address criteria 1. In this course, Java
will be used as the implementation language to apply
ON THE DESIGN OF A HEALTHCARE INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONCENTRATION
279

various risk management and validation techniques
within healthcare applications. Hence, the course
“object-oriented programming” has been selected as
the pre-requisite course (criteria 2).
ITHS 453: Healthcare Process Improvements
This course exposes students to the programs,
techniques, and tools for process improvements in
healthcare settings. Students will learn quality and
performance improvement tools and techniques and
apply them to improve various healthcare processes
like patient flow, patient scheduling, inventory
tracking etc. Students will use several software tools.
This course will address the concepts and
applications of IT knowledge area in HCIS (criteria
1). With the push towards decentralizing the IT
decision-making process, it is imperative that
healthcare administrators become adept at managing
IT projects. Students will be gaining this
knowledge/skill through the pre-requisite courses
ITGN 220- Software project management criteria
2.
BBUS 200-Quantitative Methods for Business has
also been selected as the pre-requisite for this course,
as it equips students with the required background in
Linear programming and decision analysis.
ITHS 464: Electronic / Mobile Healthcare
Systems
The purpose of including this course in the
concentration is to make students aware of the recent
trends in electronic and mobile healthcare. It will
also expose students to the application of these
technologies to add value to a health-care
organization. Students will learn the best approaches
used in developing the internet strategies, in dealing
with transition from traditional care to e-healthcare
and the legal pitfalls of these applications. In
addition, as part of the course work, students will
work on a project to develop an on-line health
application (criteria 1). Hence, ITGN 350 - Web
Design & Development has been selected as the pre-
requisite to this course (criteria 2)
ITIS 465: Database Security and Audit
The ability to structure, access, manage and leverage
patient records and associated data is becoming more
and more critical to any healthcare organizations,
large or small, public or private. Central to
supporting this ability, and at the core of every
healthcare information system, is the database.
Security has always been a problem when
implementing medical information systems, where
data represent in many cases a valuable and sensitive
asset. The fundamentals of database technology have
been adequately addressed in ITGN 250 - Database
Management Systems course. Hence, security of the
database is the priority and the focus of this course.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Feasibility of adding a concentration in HCIS to the
existing CIS program was studied. Curriculum was
designed to be in alignment with the University
mission and the accrediting agency standards.
HCIS-Concentration courses were designed to meet
the objectives and the outcomes of the concentration.
While conforming to the mentioned design criteria,
these courses have been designed to address the
market need by preparing IT professionals with the
knowledge and skills necessary to fill entry level
HCIS management, analytical, technical and
administrative roles.
Each specialization course syllabus in the
proposed concentration is a descriptive document
having specific learning objectives and outcomes.
These outcomes become the basis for assessment of
students learning. In particular, each course syllabus
includes:
1. Course objectives linked to
measurable learning outcomes.
2. Course learning outcomes that are
measurable and that cover the appropriate spectrum
of Bloom’s cognitive domains with focus on
"higher-order thinking skills" as student’s progress
in their studies.
Besides following the ABET standards,
CIT solicited inputs from the various stakeholders
including the faculty, Academic Advisory Council,
Business Advisory Council, alumni, and currently
enrolled CIT students. Some renowned international
schools offering similar concentrations were also
studied as input reference for the course designs.
This work can be useful to other institutions
offering similar concentrations.
Survey results by Charles and Terri (2002 )
suggest that the geographic location of the survey
sample seems to play a part in the perception of
desirable skills. Hence, an important area of
improvement is to modify the survey questionnaire
to gather information about the knowledge and the
skill areas that the prospective employers are looking
for. That will help in improving the curriculum
based on the market requirements.
The proposed curriculum focuses mainly on
the hospital information systems. Current trends
focusing on the home care technologies, elderly care
HEALTHINF 2010 - International Conference on Health Informatics
280

and telemedicine needs to be addressed adequately.
REFERENCES
Charles R., Woratschek. and Terri L. Lenox. (2002)
Information Systems Entry-Level Job Skills: A Survey
Of Employers, Isecon .
Criteria For Accrediting Computing Programs, 2007.
http://www.abet.org
Gandossy, R.P., Tucker,E., and Verna, N. (2006)
Workforcs Wakeup Call:Your workforce is changing,
are you?
Grubb, W.N and Lazerson, M. (2004) The educational
Gospel: The economic power of schooling. Boston:
Harvard University Press.
Gulf-new (2008) Strong growth in UAE healthcare sector,
posted on 18/12/2008,
http://www.uaeinteract.com/docs/Strong_growth_in_U
AE_healthcare_sector/33371.htm.
Hunt, S. (2004). Forward. In organizational & end user
information systems: Curriculum model for
undergraduate education in information technology.
Morehead, KY: Organizational Systems Research
Association.
IS 2002: Model Curriculum and Guidelines for
Undergraduate Degree Programs in Information
Systems.
http://www.acm.org/education/is2002.pdf
Judith G. Calhoun, Eric T.Vincent, Gary L. Calhoun, and
Laura E. Brandsen. (2008) Why Competencies in
Graduate health management and Policy Education?,
The Journal of Health Administration Education, 17 -
36.
Judy, R.W. and D'Amico,C.D. (1998) Workforce 2020:
Work and workers in the 21st centuary, Eric
Documnet Reproduction Service No. ED409463.
Karoly,L.A. and Panis,C.W.A. (2004) The 21st centuary at
work:Forces shaping the future workforce and
workplace in the United States.
Lee, Denis M. S., Eileen M. Trauth, and Douglas Farwell.
(1995) Critical Skills and Knowledge Requirements of
Professionals: A Joint Academic/Industry
Investigation, MIS Quarterly, Vol. 19, No. 3 313-340.
Richard D.Lang. (2003) Healthcare Information
Management Systems Concentration Curriculum
Choices: Evaluating the CIO Perspective., Journal of
Information Systems Education, Vol. 14(4) 373 - 380.
Smith, L. B., Hunt, C. S., Berry, R. and Hunt. D. (2005)
An Integrated IT curriculum model for advancing
education in information technologies, learning and
performance, Information Technology, Learning &
Performance Journal; Vol. 23 Issue 1, p7-19, 13p.
Srinivasan, S., Guan, J., and Wright, A.L., (1999) A new
CIS curriculum design approach for the 21st centuary,
Journal of Computer Information Systems , 99 -106.
Tommy G. Thompson and David J. (2004) "The Decade of
Health Information Technology:Delivering Consumer-
centric and Information-rich Health Care.".
Tracie M. Dodson, Rebecca J. Giorcelli (2008).
Curriculum Decisions: Assessing and Updating IS
Curriculum. Proceedings of the Fourteenth Americas
Conference on Information Systems, Toronto, ON,
Canada August 14th-17th 2008.
Wilkins, Cheryl L. Noll and Marilyn. (2002) Critical Skills
of IS professioanls: A Model for Curriculum
Development. Journal of Information Technology
Education, 143 -154.
ON THE DESIGN OF A HEALTHCARE INFORMATION SYSTEMS CONCENTRATION
281
