
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF BIOMOLECULAR DATA USING
UNICORE WORKFLOWS
Marcelina Borcz
1,2
, Rafał Kluszczy
´
nski
1
and Piotr Bała
1,2
1
Faculty of Mathematics and Computer Science, Nicolaus Copernicus University
Chopina 12/18, 87-100 Toru
´
n, Poland
2
Interdisciplinary Centre for Mathematical and Computational Modelling, University of Warsaw
Pawi
´
nskiego 5a, 02-106 Warsaw, Poland
Keywords:
UNICORE, Workflow, R environment, GridBean.
Abstract:
Nowadays the role of e-Science is important, especially in the area of life sciences. Experiments and their
analysis are carried out in collaboration of many scientific groups from institutes located all over the world.
Moreover, they work with immense amount of data which usually needs to be processed statistically. There-
fore, the need for computing power is increasing. It usually can not be supplied by a standard laboratory. That
is why e-Science makes use of grid technology. UNICORE (Uniform Interface to Computing Resources) is a
middleware enabling access to the Grid resources in a seamless and secure way.
In this paper we present UNICORE gridbean for statistical R environment which enables to process statistically
data on the Grid. Being used as a part of more complex workflow task it can analyze results given by another
applications and calculate needed statistics. By presenting example workflow constructed in UNICORE Rich
Client application, authors show power of the Chemomentum workbench built on UNICORE Grid system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Growing need for computing power in many areas
of scientific research has entailed interest in the grid
technology. It has been successfully used in many
projects within areas such as 3D graphics, quan-
tum chemistry, molecular modeling or bioinformatics.
Particularly, computing power plays an important role
in biology research. Increasing number of known se-
quences, huge molecules systems and metabolic path-
ways demand a lot of computational time for process-
ing. The grid middleware which offers an uniform
access to the resources can be a very attractive solu-
tion. It enables the use of geographically distributed
resources through the Internet. Running several tasks
on the different computing systems can save time sig-
nificantly. Grid environments like UNICORE (Uni-
form Interface to Computing Resources) provide ac-
cess to the resources and applications in a seamless
and secure way.
Applications such as BLAST (Basic Local Align-
ment Search Tool), Clustal and NAMD (Not Another
Molecular Dynamics) are widely used by the molecu-
lar biology scientists. Authors successfully supported
them on the UNICORE Grid (Borcz et al., 2007;
Kluszczy
´
nski and Bała, 2008; Kluszczy
´
nski and Bała,
2009). However, there has been noticed the need for
the statistical tools to analyze data. We have decided
to develop a gridbean which integrates the statistical
environment R with the grid. The purpose of this pa-
per is to present plugin for the UNICORE Rich Client.
Next, authors point out UNICORE ability to construct
scientific workflows to create complex simulations to
process and analyze biomolecular data.
2 MOLECULAR LIFE SCIENCES
The aim of Life sciences is to study living organisms
to help explaining how they are related to each other
and to the environment. Biology plays here key role
along with the computer and information sciences.
Bioinformatics is one of the disciplines which has be-
come very popular nowadays. There exist many con-
fusions about the definition of “bioinformatics”. Ac-
cording to the Bioinformatics Definition Committee
of Biomedical Information Science and Technology
217
Borcz M., Kluszczy
´
nski R. and Bała P. (2010).
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF BIOMOLECULAR DATA USING UNICORE WORKFLOWS.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Bioinformatics, pages 217-220
DOI: 10.5220/0002742102170220
Copyright
c
SciTePress
Initiative Consortium (Huerta et al., 2000) bioinfor-
matics is related to the databases and focuses on com-
putational tools to store, archive, analyze and visual-
ize biology data. It is strongly related to the compu-
tational biology, which studies biological systems by
developing methods for mathematical modeling and
techniques for simulations.
Biologists and programs they use have to han-
dle huge amount of data. As an example can
serve NAMD, an application for molecular dynamics,
which simulates the behavior of a molecular system
of many thousands of atoms. BLAST is used to find
regions of similarity between the DNA sequences. It
searches through huge sequence databases and com-
pares very long strands. Clustal allows for enacting
pairwise alignment and can create a phylogenetic tree
and use it to align multiple sequences. Typical ex-
periments consist of many steps and sequence align-
ment is usually one of them. Therefore programs
widely used by biologists require computing power
that can not be provided by a standard computer facil-
ities available at research lab or department.
High throughput experiments and large simula-
tions produce output which has to be statistically pro-
cessed. It can be done using various programs like R,
SPSS or Statistica. Authors focus on the first of them.
R is a free software environment and a high level
programming language for statistical calculations and
data analysis. It enables scientists like mathemati-
cians, physicians and biologists to make calculations
and to visualize the data. Besides basic commands
and functions there are available more than 1700 tech-
nical packages providing more advanced tools.
3 SCIENTIFIC WORKFLOW
SYSTEMS
Workflows play central role in the computationally
intensive science (e-Science). They can be used as
analysis pipelines in many disciplines such as biol-
ogy, chemistry, geosciences or physics. In the 2004
the definition of a workflow in the grid systems has
been postulated by the Global Grid Forum (Fox and
Gannon, 2006). In the Grid context workflow is au-
tomation of the processes which involves the orches-
tration of a set of grid services or agents that must be
combined together to solve a problem or to define a
new service. The advantages of the scientific work-
flows are numerous (Yu and Buyya, 2005). Below we
present most important ones:
• an ability to build dynamic applications which use
distributed resources,
Figure 1: UNICORE Rich Client application with loaded
gridbean for R Environment.
• dynamic utilization of resources in order to in-
crease throughput and reduce execution costs,
• promotion of a collaborations between scientific
groups involved in a different parts of the experi-
ment.
Workflow systems are being developed as a part of
grid middlewares and as a standalone applications.
The UNICORE middleware has an ability to build
and run workflows on the grid. The UNICORE work-
flows allow the use of loops and if-else statements to
create sophisticated tasks run on the remote systems.
4 UNICORE GRID MIDDLEWARE
Standards used in grid middlewares have been chang-
ing over the time and new application areas have been
discovered. UNICORE project has been established
in 1997 in order to enable an easy and secure ac-
cess to supercomputers in Germany (Streit, 2009).
During the last decade it has become international
and has been successfully used in many scientific
projects. Its popularity is still growing and today
UNICORE is widely utilized in Europe along with
other widely known grid environments like gLite,
Globus and ARC.
Version 6 of the UNICORE middleware is be-
ing developed based on the web-service technology
and adopts grid services standards. UNICORE pro-
vides a flexible and user-friendly client framework.
UNICORE Rich Client (URC) targets a wide range
of users with varying grid experience. It provides a
graphical view of the grid and can be run on most of
the platforms. URC offers to the users a full set of
functionalities in a graphical representation. The user
may see his previous and currently running jobs and
download the results or specific resources from the
BIOINFORMATICS 2010 - International Conference on Bioinformatics
218
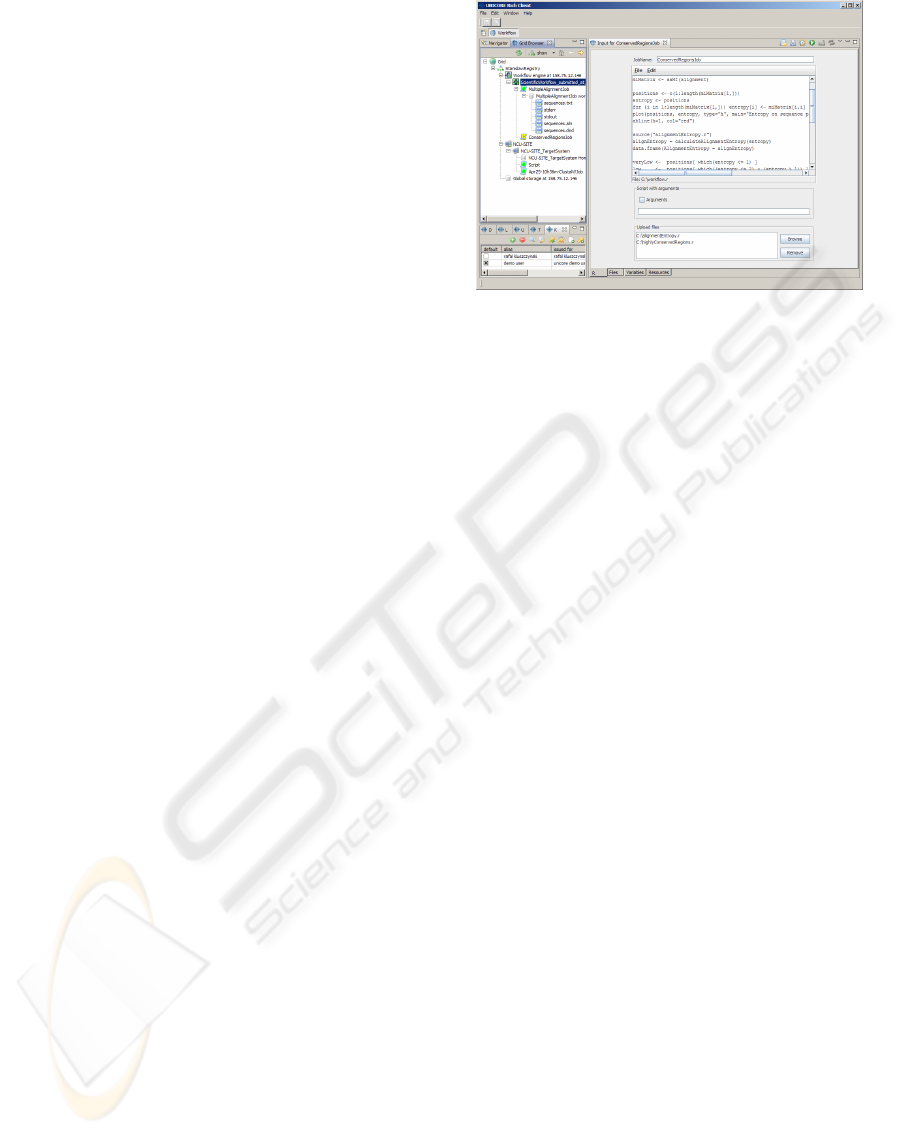
grid (Fig. 1).
Applications are integrated with the UNICORE
infrastructure through gridbeans. Gridbeans separate
the layer of application specific user interface from
the actual implementation of grid middleware. This
idea emerges from the experience of UNICORE 5
(Ratering, 2005) and is considered as one of the high-
est advantages of UNICORE.
5 APPLICATION GRIDBEANS
Gridbeans are plugins which provide a graphical in-
terface to the application. Grid environments sup-
ply clients with special services enabling to down-
load plug-ins by simply selecting them from the list.
Once gridbean is loaded into the client, a user can run
tasks without any specific knowledge about the envi-
ronment or the way of executing the program on the
host. He just has to fill in particular fields and op-
tions in the interface and than press submit button.
Moreover, UNICORE clients have an ability to check
the existence of application on the grid. User can see
available programs on particular target systems and
decide which one to use.
In the last years, authors have developed grid-
beans for bioinformatics tools like BLAST, NAMD
or Clustal (Borcz et al., 2007; Kluszczy
´
nski and Bała,
2008; Kluszczy
´
nski and Bała, 2009). All mentioned
gridbeans provide a graphical interface which makes
possible to run the applications in an easy way. They
contain special fields and components to input data
and to set up options. Moreover, BLAST and Clustal
interfaces are designed in a way similar to the existing
web interfaces, to which biologists are used to.
Recently, we have designed and implemented
RGridBean. It integrates statistical R environment (R
Development Core Team, 2005) with the grid and it
can be used as a part of workflow. The R has been
already integrated with the ACGT grid environment
based on Globus Toolkit 4 (Wegenera et al., 2009),
however it cannot be reused in the UNICORE work-
flows. Grid solutions proposed in (Grose et al., 2006;
Wegenera et al., 2009) demand knowledge about new
R packages from the users. UNICORE Rich Client
allows to run R scripts on the grid without execution
of additional commands. With the help of RGridBean
users just select the script and submit it to the remote
system. The script remains in the same form in which
it was executed locally on the PC.
In the example presented in the section 6 the R
plugin processes the results given by other biology ap-
plications. The main panel (Fig. 1), besides a field for
a job name, contains a text area to write commands
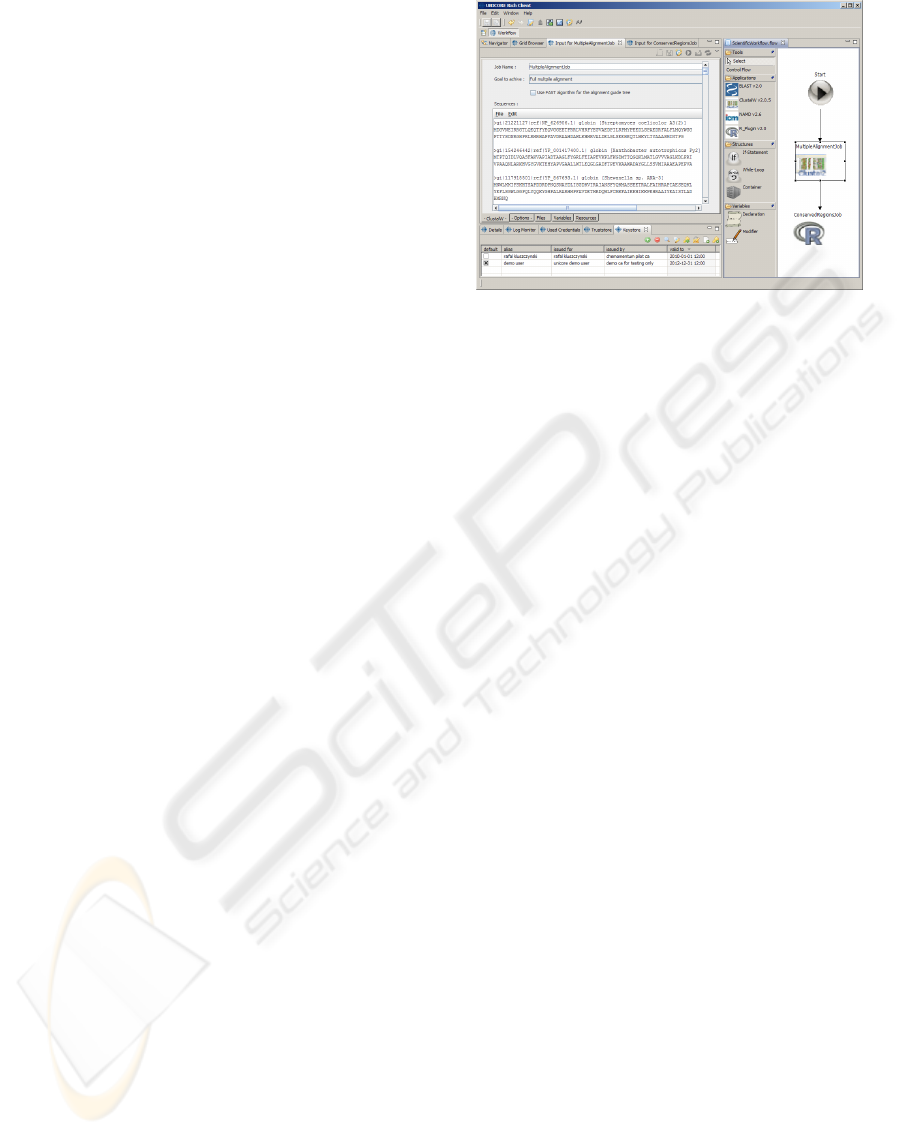
Figure 2: An example of a scientific workflow involving
Clustal and R gridbeans. The workflow is presented in the
dedicated editor of the UNICORE Rich Client.
and open or save scripts. Moreover, there have been
prepared special components, which allow to input
script arguments and attach additional files. After job
is finished, user can see its results shown in two dif-
ferent output panels. In the first one, there are visible
results of calculations presented as text. In the sec-
ond there are displayed generated plots which can be
saved in a PNG format.
6 WORKFLOW EXAMPLE
UNICORE Rich Client has an ability to design work-
flow tasks combining several applications. This func-
tionality is provided by a workflow editor. It en-
ables a graphical construction of tasks together with
programming blocks realizing loops and if-else state-
ments. Workflows consist of tasks or processes.
Workflow elements are related by dependencies cor-
responding to the data flow between them. As blocks
of such workflows there are used gridbeans, which
are downloaded to the client. Of course some tasks
can be independent and not related to other work-
flow components. With every sub-job, user can assign
the site where it should be run or leave decision to
the workflow service. Dedicated editor enables very
user-friendly and intuitive construction of workflows.
URC supports drag-and-drop technique, which makes
it easy to design workflow structure and dependencies
between elements.
In Fig. 2 there is presented an example workflow
which uses Clustal and R gridbeans. Designed ex-
periment at the first stage aligns a family of globin
proteins. Next, the multiple alignment obtained by
Clustal is statistically processed. The results are pre-
sented in the text and graphical form. It is impor-
tant to mention, that once designed workflow can be
STATISTICAL ANALYSIS OF BIOMOLECULAR DATA USING UNICORE WORKFLOWS
219

used in the future. To execute simulations for another
family of proteins the user should just change the se-
quences data in the gridbean for Clustal and resubmit
the workflow.
During the protein sequence analysis scientists
usually look for motifs. These are small con-
served regions which have functional and structural
significance. However, regions with a high num-
ber of changes are responsible for the specificity of
molecules. Shannon entropy as the measure of uncer-
tainty in a data set is a good indicator of variability
(Bui et al., 2007). Entropy can be calculated in the
R environment in an easy way using aaMI package
(Wollenberg, 2005).
The article (Bui et al., 2007) provides an example
of such an application. Its authors analyze the are-
navirus protein sequence variability to identify con-
served regions that could be targeted for development
of a universal renaviral vaccine. They looked also for
high variable regions which could be helpful in diag-
nosis. To do this they performed multiple sequence
alignments of chosen proteins using ClustalW pro-
gram and calculated Shannon entropy. Fig. 2 presents
an example of a workflow performing similar tasks.
Of course workflows can be much more compli-
cated. The UNICORE can handle workflows with
thousands of elements and dependencies. With the
help of an editor it is very easy to create even so com-
plex simulations.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper authors presented plugin designed for
statistical R environment. It makes it possible to
analyze and process data from many scientific ap-
plications, not only limited for molecular ones like
BLAST, Clustal or NAMD. Being used as a part of
workflow, it plays crucial role in experiment conclu-
sions. The workflow systems can be very useful for
scientists. With the help of special editors, like the
one in UNICORE middleware, workflow construction
is intuitive and user-friendly. An additional advan-
tage is the reduction of frequency of human errors.
Once designed workflow can by used for different
data. This automates the process of experiment en-
abling the scientists to focus only on results and con-
clusions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by European Commission
under IST grant Chemomentum (No. 033437) and
the European Social Fund with the National Budget
of the Republic of Poland under the Integrated Re-
gional Development Operational Programme, Objec-
tive 2.6 ,,Regional Innovation Strategies and trans-
fer of knowledge“ project of Kujawsko-Pomorskie
Province ,,Scholarships for PhD Students 2008/2009
- ZPORR“.
REFERENCES
Borcz, M., Kluszczy
´
nski, R., and Bała, P. (2007). BLAST
Application on the GPE/UnicoreGS Grid. In et al., L.,
editor, Euro-Par 2006 Workshops: Parallel Process-
ing, volume 4967 of LNCS, pages 245–253. Springer
Berlin / Heidelberg.
Bui, H., Botten, J., Fusseder, N., Pasquetto, V., Mothe,
B., Buchmeier, M., and Sette, A. (2007). Protein
sequence database for pathogenic arenaviruses. Im-
munome Research, 3.
Fox, G. and Gannon, D. (2006). Special issue: Workflow in
grid systems. Concurrency and Computation: Prac-
tice and Experience, 18(10):1009–1019.
Grose, D., Crouchley, R., van Ark, T., Kewley, J., Allan,
R., Braimah, A., and Hayes, M. (2006). sabreR: Grid-
enabling the analysis of multi-process random effect
response data in R. Proc. Second International Con-
ference on e-Social Science.
Huerta, M., Haseltine, F., Liu, Y., Downing, G., and Seto,
B. (2000). NIH working definition of Bioinformatics
and Computational Biology.
Kluszczy
´
nski, R. and Bała, P. (2008). Supporting NAMD
Application on the Grid using GPE. In et al., W., ed-
itor, PPAM 2007, volume 4967 of LNCS, pages 762–
769. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Kluszczy
´
nski, R. and Bała, P. (2009). Supporting Clustal
Application on the UNICORE Grid. Polish Journal of
Environmental Studies, 18(3B):165–169.
R Development Core Team (2005). R: A Language and
Environment for Statistical Computing. R Founda-
tion for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. ISBN:
3-900051-07-0.
Ratering, R. (2005). Grid Programming Environment
(GPE) Concepts. GPE documentation.
Streit, A. (2009). UNICORE: Getting to the heart of Grid
technologies. eStrategies, Projects, 9th edition, pages
8–9.
Wegenera, D., Sengstag, T., Sfakianakis, S., Rpinga, S., and
Assi, A. (2009). GridR: An R-based tool for scientific
data analysis in grid environments. Future Generation
Computer Systems, 25:481–488.
Wollenberg, K. (2005). Mutual information for protein se-
quence alignments. Package ’aaMI’ for R environ-
ment.
Yu, J. and Buyya, R. (2005). A Taxonomy of Scientific
Workflow Systems for Grid Computing. SIGMOD
Record, 34(3):44–49.
BIOINFORMATICS 2010 - International Conference on Bioinformatics
220
