
MODEL-MAPPING BASED VOICE CONVERSION SYSTEM
A Novel Approach to Improve Voice Similarity and Naturalness using Model-based
Speech Synthesis Techniques
Baojie Li, Dalei Wu and Hui Jiang
Department of Computer Science and Engineering, York University, 4700 Keele Street, Toronto, Ontario M3J 1P3, Canada
Keywords:
Voice conversion, HMM-based speech synthesis, GMM, Model mapping.
Abstract:
In this paper we present a novel voice conversion application in which no any knowledge of source speakers is
available, but only sufficient utterances from a target speaker and a number of other speakers are in hand. Our
approach consists in two separate stages. At the training stage, we estimate a speaker dependent (SD) Gaussian
mixture model (GMM) for the target speaker and additionally, we also estimate a speaker independent (SI)
GMM by using the data from a number of speakers other than the source speaker. A mapping correlation
between the SD and the SI model is maintained during the training process in terms of each phone label. At
the conversion stage, we use the SI GMM to recognize each input frame and find the closest Gaussian mixture
for it. Next, according to a mapping list, the counterpart Gaussian of the SD GMM is obtained and then
used to generate a parameter vector for each frame vector. Finally all the generated vectors are concatenated
to synthesize speech of the target speaker. By using the proposed model-mapping approach, we can not
only avoid the over-fitting problem by keeping the number of mixtures of the SI GMM to a fixed value, but
also simultaneously improve voice quality in terms of similarity and naturalness by increasing the number of
mixtures of the SD GMM. Experiments showed the effectiveness of this method.
1 INTRODUCTION
Voice conversion (VC) is a technique that con-
verts voice of a source speaker to that of a tar-
get speaker. Generally speaking, text-dependent and
text-independent voice conversion represent two main
streams of research directions. In text-dependent
voice conversion, target voice can be produced with
high-quality of correctness and acceptable smooth-
ness based on the provided transcription for input
speech waveform, e.g. (Yoshimura, 2002). By con-
trast, text-independent systems have no knowledge
about the transcription of input waveform, therefore
more mismatches between source and target speakers
are present and the quality of the generated speech
then degrades. For this reason, text-independent voice
conversion attracts a wider range of studies. The tech-
niques presented in this paper are also focused on
text-independent voice conversion.
In the field of text-independent voice conversion,
usually some forms of transforms are estimated from
training data of both source and target speakers, such
as K-means clustering in VTLN-based voice conver-
sion (Suedermann et al., 2003), codebook based map-
ping (Arslan et al., 1999) and GMM based cluster-
ing (Ye et al., 2006). In some applications, how-
ever, no knowledge about source speakers is appli-
cable beforehand. Therefore it is impossible to esti-
mate the transforms between source and target speak-
ers using the conventional techniques. In our previ-
ous work, we built a GMM-based VC system using
hidden Markov model (HMM) based speech synthe-
sis to address such particular requirements. At the
training stage, a SD GMM is trained for the target
speaker using his/her pre-recorded training data. In
the conversion stage, for each utterance from a source
speaker, the best matched Gaussian mixture is cho-
sen from the GMM. Next, the mean vectors of the se-
lected mixtures are concatenated, smoothed and then
sent as inputs to the sound synthesizer, which is pro-
vided by HTS engine (Tokuda et al, 2000; Yoshimura
et al., 2002). By experiments, we found that this ap-
proach was quite capable of conducting voice conver-
sion with acceptable quality. However, we also found
recognizable discontinuity and flatness in the synthe-
sized voices. Through investigation, we found that the
442
Li B., Wu D. and Jiang H. (2010).
MODEL-MAPPING BASED VOICE CONVERSION SYSTEM - A Novel Approach to Improve Voice Similarity and Naturalness using Model-based
Speech Synthesis Techniques.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 442-446
DOI: 10.5220/0002747104420446
Copyright
c
SciTePress
discontinuity is attributed to frame mismatches. And
the flatness was caused by the use of average of train-
ing samples. To cope with these two problems, we
proposed in this article to renovate our VC system by
introducing additional SI models and model-mapping
technique. We confirmed by experiments that the new
method was quite effective in increasing the quality of
the generated speech.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: we
begin with an introduction to our previous GMM-
based VC system in Section 2. To deal with the dis-
continuity and flatness problems, a model-mapping
strategy is introduced in Section 3, where its effec-
tiveness is evaluated by experiments. We draw the
conclusions in Section 4.
2 GMM-BASED VOICE
CONVERSION SYSTEM
2.1 HMM-based Speech Synthesis
Technique
Our voice conversion system is based on HMM-
based speech synthesis (HTS) techniques (Tokuda
et al., 2000; Yoshimura et al., 2002). The HMM-
based speech synthesis system assumes that suffi-
cient training data and their corresponding transcrip-
tions are available. The system models phonetic and
prosodic parameters simultaneously. At the train-
ing stage, Mel-cepstrum coefficients (MFCC), fun-
damental frequency (F0) and duration are modeled
by multiple-stream HMMs. At the synthesis stage,
a given string of words is firstly decomposed into
a string of phonemes. The system then searches in
the HMM pools the corresponding model for each
phoneme. The mean vector of each model is taken
as a frame to represent that phoneme. Later, all these
frames are then concatenated according to their time
order and passed to a smoother, which improves the
quality of the synthesized speech by smoothing over
the whole sequence of frames using dynamic param-
eters (e.g., delta and delta delta) of MFCCs and F0.
The smoothed frame sequence is then input to the
synthesizer, known as MLSA filter(Tokuda, 2000), to
produce speech waves.
For a text-to-speech task, HTS has been demon-
strated in generating high quality voices especially
in terms of continuity and naturalness. However in
our current task, neither the transcriptions for the in-
put waveforms nor the knowledge about the source
speaker is available. Many conventional transform-
based VC approaches are inapplicable in such a sit-
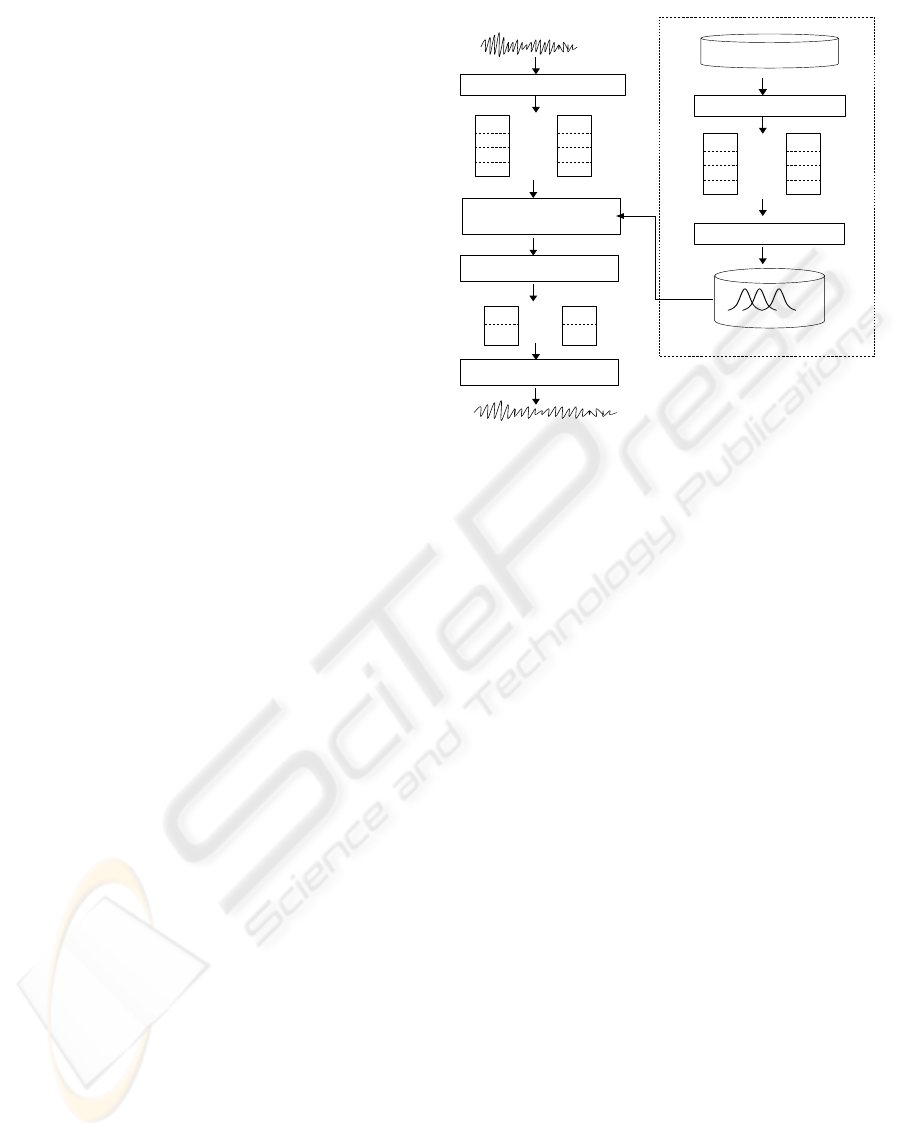
Speech database
Gaussian mixtures
Training stage
Model selection
MLSA Filter
Generated waveforms
Conversion stage
Source speaker Target speaker
Parameter extraction
…..
Model estimation
Parameter extraction
Dynamic feature smoother
2
0
∆
∆
F
MCP
2
0
∆
∆
F
MCP
…..
2
0
∆
∆
F
MCP
2
0
∆
∆
F
MCP
…..
0F
MCP
0F
MCP
Figure 1: GMM-based voice conversion system.
uation. Hence we were motivated to combine speech
recognition and synthesis techniques to conduct voice
conversion.
2.2 Overview of Our VC System
The diagram of our previously proposed VC system
is shown in Figure 1. Our VC system consists of two
stages. At the first stage, parameter vectors are ex-
tracted from training data of the target speaker. Then
Gaussian mixture models are estimated. All mixtures
have no phoneme labels but sequential numbers. At
the conversion stage, a mixture is chosen for each in-
put frame from the GMM set according to distance
or probability metrics. Then the mean vectors of the
selected mixtures are concatenated to form an output
sequence of frames. After smoothed by a smoother
using the dynamic features, the sequence of frames is
input to the MLSA filter to generate speech wave.
2.3 Feature Extraction
The feature vectors are extracted from speech wave-
forms using HTK 3.4 (Young et al., 2003) and
SPTK (Imar et al., 2008). Each vector includes 25-
dimentional MFCCs, 1-dimentional pitch information
(F0), along with their dynamic features. The vector is
divided into four streams: MFCCs and their dynam-
ics, F0, delta F0 and delta delta F0. All streams take
uniform weights.
MODEL-MAPPING BASED VOICE CONVERSION SYSTEM - A Novel Approach to Improve Voice Similarity and
Naturalness using Model-based Speech Synthesis Techniques
443

2.4 Model Estimation
GMM for the target speaker is estimated using the
standard EM algorithm. Considering that correla-
tions between F0s and MFCCs introduce inaccuracy
into probability calculations when a diagonal covari-
ance matrix is used in recognition process, only the
MFCCs are used in mixture clustering process. Af-
ter the mixtures are obtained, all the training data are
aligned into the mixtures. The average of F0 over all
frames in a mixture is set as the mean of this mixture.
More specifically, assume we have N frames {x
n
} and
K mixtures. Each mixture has a probability distribu-
tion as N (x | µ
k
, Σ
k
) with a weight of w
k
. Then each
frame contributes to this mixture as γ
γ
nk
=
w
k
N (x
n
| µ
k
, Σ
k
)
∑
K
j=1
w
j
N (x
n
| µ
j
, Σ
j
)
(1)
And the total number of samples accumulated in
this mixture is N
k
=
∑
N
n=1
γ
nk
. Note that only the
MFCC part of vector x
n
are used in the above calcula-
tion. Then we get the F0 parameters for this mixture
as
µ
F0
k
=
1
N
k
∑
γ
nk
x
F0
n
(2)
where µ
F0
k
is the F0 part of µ
k
, and x
F0
n
the F0 part of
x
n
respectively.
2.5 Model Selection
In conversion stage, each input frame from a source
speaker is calculated on the GMMs of the target
speaker (excluding the F0 parameters). The mixture
with the highest probability is selected as the output.
l
∗
t
= argmax
k
w
k
N (x | Σ
k
, µ
k
) (3)
where µ
k
and Σ
k
is the mean and covariance for
the k-th Gaussian component, respectively.
2.6 Dynamic Features Smoothing
All the mean vectors of the selected Gaussian com-
ponents are concatenated to form a sequence. The
sequence is smoothed according to its delta and delta
delta information in the same way as in HMM-based
speech synthesis (Tokuda,2000; Yoshimura,2002).
Then a new sequence consisting of only static MFCCs
and static F0 features is obtained. We denote
the static, delta, delta delta features for time t as
(c
t
, ∆c
t
, ∆
2
c
t
). Then, they are defined as
4c
t
=
+L
(1)
+
∑
−L
(1)
−
w
(1)(τ)
c
t+τ
(4)
4
2
c
t
=
+L
(2)
+
∑
−L
(2)
−
w
(2)(τ)
c
t+τ
. (5)
where w
( j)
(τ), j ∈ {1, 2} are weight coefficients
and τ is a length of time. The new static features se-
quence C = [c
1
, c
2
, ··· , c
T
]
>
can be estimated by solv-
ing a system of linear equations as follows:
C = (W
T
U
−1
W)
−1
W
>
U
−1
S
>
, (6)
where
S = [µ
>
l
∗
1
, µ
>
l
∗
2
, ··· , µ
>
l
∗
T
]
>
(7)
U
−1
= diag[Σ
−1
l
∗
1
, Σ
−1
l
∗
2
, ··· , Σ
−1
l
∗
T
] (8)
W = [w
1
, w
2
, ··· , w
T
]
>
(9)
w
t
= [w
(0)
t
, w
(1)
t
, w
(2)
t
] (10)
w
(n)
t
= [0
M×M
, ··· , 0
M×M
, w
(n)
(−L
(n)
−
I
M×M
,
··· , w
(n)
I
M×M
, ··· , w
(n)
(L
(n)
+
)I
M×M
,
0
M×M
, ··· , 0
M×M
]
>
, n = 0, 1, 2.
(11)
where M is the number of the dimensions of static
MFCC features without dynamic features and l
∗
t
de-
notes the index of the best-matched Gaussian compo-
nent, selected as in Eq. (3).
2.7 Experiments
Experiments were conducted on The Continuous
Speech Recognition Wall Street Journal Phase I
(CSR-WSJ0) Corpus (Linguistic Data Consortium).
Speaker 001 (male, 598 utterances) and 002 (female,
600 utterances) were alternatively used as source and
target speaker. 1720 Gaussian mixtures were trained
for each target speaker. subjectively listening to the
converted utterances were conducted. Five listeners
were given ten generated utterances for each target
speaker. They were asked to give to each utterance a
score which is ranged from 1 to 5. The score average
of each listener across the ten sentences is listed in
Table 1.
Table 1: Subjective evaluation scores for GMM VC.
Listener id 1 2 3 4 5 Ave
naturalness 2.9 3.4 2.6 3.8 3.2 3.2
similarity 2.9 3.2 2.3 3.2 2.0 2.7
We found that the quality of generated voices was
acceptable. Most of the literal contents were identifi-
able. However there were also noticeable discontinu-
ity and flatness in the voices.
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
444

3 IMPROVE VOICE SIMILARITY
AND NATURALNESS BY
MODEL MAPPING
By investigating the output frames in the previous ex-
periments, We noticed that the mis-selection of mod-
els resulted in remarkable discontinuity and the use
of mean vectors of Gaussian mixtures made the gen-
erated speech sounds flat. More specifically speak-
ing, each mean vector of a Gaussian mixture used for
speech synthesis was an average over some training
frames. This average effaced the details of the char-
acteristics of the target speaker. we tried to increase
the number of Gaussian mixtures to capture more de-
tails of the target speaker. However, when a certain
number was exceeded, the recognition performance
started to decrease thus degrading the quality of the
synthesized voice. This was due to that when number
of mixtures went up, the trained models perfectly fit-
ted the training data but gave a very poor representa-
tion of the test data thus resulting in a bad recognition
performance. This behaviour is known as over-fitting.
To solve this problem, we introduced an additional
model set for recognition, which was a SI model set
trained from a number of speakers.
In this method, both the SI models and the tar-
get SD models were trained for all phonemes. Each
phoneme model consists of a number of Gaussian
mixtures. Therefore, between the SI and SD model
sets, we could construct a mapping list by the model
labels. The modified VC system is depicted as in Fig-
ure 2. In conversion stage, we firstly searched over
SI GMMs to find out the closest model to the input
frame. Then according to the mapping list, its coun-
terpart model in the target speaker model set was se-
lected as the output model. This scheme enabled us
to capture more detailed characteristics of the target
speaker by increasing the number of mixtures of tar-
get speaker models, without losing high recognition
performance for the input frames by keeping the num-
ber of mixtures of SI models fixed.
3.1 Reduce Mismatch in Recognition
To recognize frames from an unknown speaker, the
SI model set performs much better than the target
speaker model set. When given an input frame x from
source speaker, it is firstly calculated on the SI model
set
p(x) =
K
∑
j=1
w
j
N (x | µ
j
, Σ
j
). (12)
and assigned to a phoneme model which has the
Phoneme “a”
SI models
SD models for
Gaussian mixtures
“a”
“b”
target speaker
Model selection
Conversion stage
Parameter vectors from source speaker
Generated parameter vectors
…..
2
0
∆
∆
F
MCP
2
0
∆
∆
F
MCP
…..
2
0
∆
∆
F
MCP
2
0
∆
∆
F
MCP
Gaussian mixtures
Phoneme “b”
Figure 2: Modified our voice conversion system.
highest probability, e.g., model ah. Then its counter-
part in the target model set can be found according
to the mapping list. Next we will try to find a best
matched mixture among all the mixtures belonging to
the target SD model ah. To alleviate model mismatch,
we shift the input frame according to
y = µ
SD
+
s
Σ
SD
Σ
SI
(x − µ
SI
) (13)
Assume each model in the target model set con-
sists of K mixtures, the nearest mixture to vector y is
selected by calculating the normalized Euclidean dis-
tances
l
∗
= argmax
k
M
∑
m=1
(y
m
− µ
k
m
)
2
Σ
k
m
(14)
where M is the dimensionality of MFCCs, µ
k
m
the
m-th dimension of the mean vector of k-th mixture.
Experiments were conducted using the same cor-
pus as in Section 2.7. 7138 utterances from SI-84
speakers were used to train the SI GMMs. Each tri-
phone model consists of 10 mixtures (after mixture
sharing, the total number of mixtures was 1720, the
same as that in Section 2.7). The same scoring crite-
rion was applied. The results are listed in Table 2.
Table 2: Subjective evaluation scores for modified VC.
Listener id 1 2 3 4 5 Ave
naturalness 3.2 4.1 3.4 4.3 3.7 3.7
similarity 3.0 3.1 2.8 3.3 2.5 2.9
The SI model did improve the naturalness of
MODEL-MAPPING BASED VOICE CONVERSION SYSTEM - A Novel Approach to Improve Voice Similarity and
Naturalness using Model-based Speech Synthesis Techniques
445

the generated speech. The speech sounded more
smoothly.
3.2 Improve Similarity by Increasing
Number of Mixtures of SD Models
In the following experiments, we keep the number of
mixtures of the SI models fixed to maintain a good
recognition performance, while increasing the num-
ber of mixtures of the target models to capture the
detailed characteristics of the target speaker. This is
based on the assumption that even a target SD mixture
lacks of training data, it is still capable of represent-
ing the voice of the target speaker since it came from
the real samples of that speaker. Experiments were
conducted by fixing the SI models to 1720 mixtures
while changing the target models with different num-
ber of mixtures. Here we listed the evaluation scores
in Table 3 and Table 4 .
Table 3: Naturalness for different number of mixtures.
Listener Id 1 2 3 4 5 Ave
1720 mix 3.2 4.1 3.4 4.3 3.7 3.7
3440 mix 4.1 4.3 3.6 3.9 4.1 4.0
6880 mix 3.5 4.3 4.0 4.2 3.7 3.9
13760 mix 2.8 3.8 3.4 3.7 3.6 3.5
Table 4: Similarity for different number of mixtures.
Listener Id 1 2 3 4 5 Ave
1720 mix 3.0 3.1 2.8 3.3 2.5 2.9
3440 mix 3.2 3.8 3.2 4.4 3.7 3.6
6880 mix 3.8 3.7 4.2 4.0 3.9 3.9
13760 mix 3.3 4.1 3.1 4.3 3.3 3.6
As shown in the tables, increasing the number of
mixtures not only brought improvement in natural-
ness, but also improved similarity remarkably. As
long as the number of mixtures did not go to extreme,
the quality of generated voice was improved greatly.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have presented a new approach for
voice conversion. By introducing a SI model set into
the GMM VC system, naturalness of the converted
voice was improved due to the improved recogni-
tion performance. Moreover the new system could
use more mixtures in target models for parameter
generation, therefore more detailed features of input
speeches could be captured to improve similarity. In
comparison with the original GMM VC system, both
naturalness and similarity were improved.
REFERENCES
T. Yoshimura, ”Simultaneous Modelling of Phonetic and
Prosodic Parameters and Characteristic conversion for
GMM-based Tex-to-speech Systems” ,Ph.D. disserta-
tion, Nagoya Institute of Technology, 2002.
D. Sundermann and H. Ney, ”VTLN-based Voice Con-
version”, Proc. of Signal Processing and Information
Technology (ISSPIT)”, Dec. 2003, pp. 14-17.
K. Tokuda, T. Yoshimura, T. Masuko, T. Kobayashi and T.
Kitamura, ”Speech parameter generation algorithms
for GMM-based speech synthesis”, Proc. of ICASSP,
pp.1315-1318, June 2000.
L. Arslan and D. Talkin, ”Speaker Transformation Algo-
rithm using Segmental Codebooks (STASC)”, Speech
Commun., pp. 211-226, 1999.
H. Ye and S. Young, ”Quality-enhanced Voice Morphing
Using Maximum Likelihood Transformation”, IEEE
Trans. on Audio, Speech and Language Processing,
Vol.14, No.4, pp.1301-1312, 2006.
S. Young et al., ”HTKBook (V3.4)”, Cambridge University
Engineering Department, 2006.
S. Imai et al., ”Speech Signal Processing Toolkit Ver.3.2”,
http://sp-tk.sourceforge.net, 2008 .
Linguistic Data Consortium, ”The LDC Corpus Catalog”,
http://www.ldc.upenn.edu/Catalog/
BIOSIGNALS 2010 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
446
