METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIAS
mut
0
/mut
-
and cblC Defects in Portuguese Population
Célia Nogueira, Marta Marques and Laura Vilarinho
Medical Genetics Center/ National Institute of Health, Praça Pedro Nunes,88, Porto, Portugal
Keywords: Methylmalonic acidurias, mut
0
, mut
-
, MUT gene, MMACHC gene.
Abstract: The methylmalonic acidurias (MMAs) are metabolic disorders resulting from deficient methylmalonyl-CoA
mutase (MCM) activity, a vitamin B12-dependent enzyme that uses adenosylcobalamin (Ado-Cbl) as a
cofactor. Several mutant genetic classes that cause MMA are known based on biochemical, enzymatic and
genetic complementation analysis. The mut
0
/mut
-
defects result from deficiency of MCM, while the cblA,
cblB and the variant 2 form of cblD complementation groups are linked to processes unique to Ado-Cbl
synthesis. The cblC, cblD and cblF complementation groups are associated with defective methyl-
cobalamin synthesis as well. Mutations in the genes associated with most of these defects have been
described. In this study we investigate at molecular level four patients with mut
0
/mut
-
MMA phenotype and
19 Portuguese patients with cblC defect. We found four different mutations already described in the
literature, in each MUT and MMACHC genes, respectively. Our data showed an evident difference in the
prevalence of these two diseases, compared with other countries worldwide.
1 INTRODUCTION
Methylmalonic Methylmalonic acidurias (MMAs)
encompass a group of genetically heterogeneous
autosomal recessive disorders of methylmalonate
and cobalamin metabolism caused by a defect in the
conversion of methylmalonyl-CoA to succinyl-CoA.
The different forms of MMAs share the biochemical
marker of increased methylmalonic acid in body
fluids. Methylmalonyl-CoA mutase (MCM)
apoenzyme deficiency is a rare metabolic disease
that may result in distinct biochemical phenotypes of
MMA, namely mut
0
and mut
-
. Patients with the mut
0
MMA phenotype exhibit the most severe, often life
threatening manifestation. Treatment regimens
include a protein-restricted diet, carnitine
supplementation and oral antibiotic therapy. The
MCM gene (MUT) is located in a single copy on
chromosome 6 (6p21.1) and consists of 13 exons
spanning over 35 kb (Jansen et al., 1989). The open
reading frame consists of 2.7kb, encoding 750 amino
acids, the first 32 residues of which form the
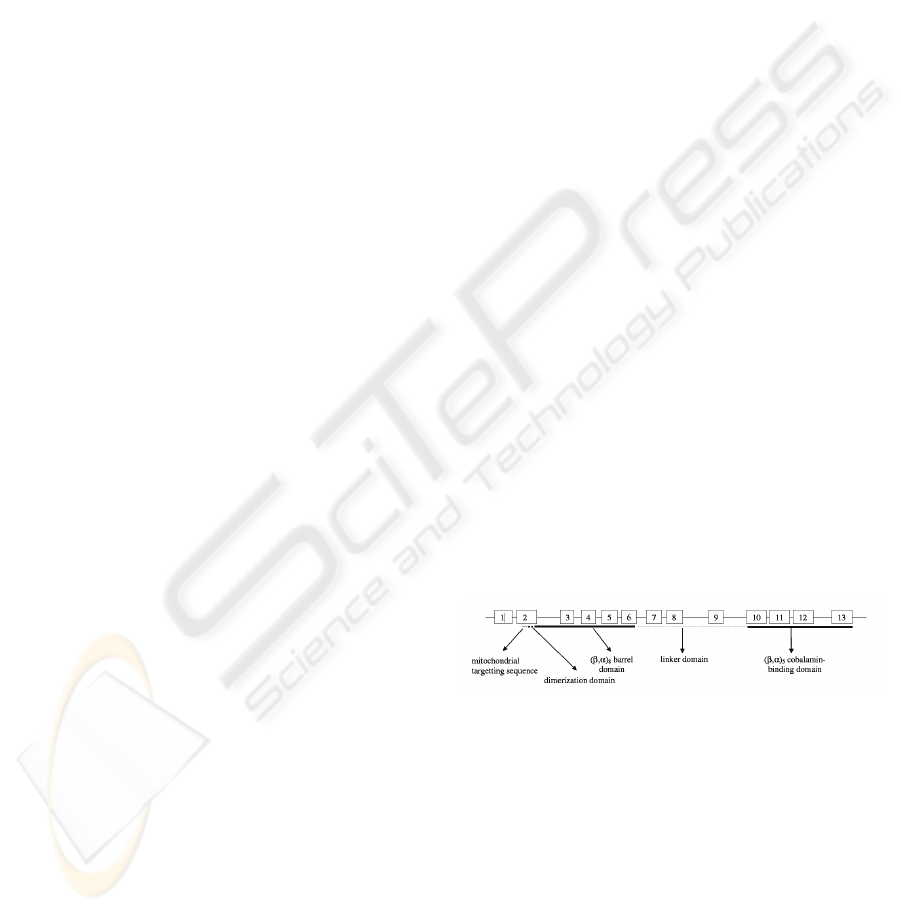
mitochondrial targeting sequence. It comprises
different functional domains (Figure 1), the N-
terminal domain (residues 1-32) followed by an
extended segment (residues 32-87) involved in the
dimerization of the two MCM monomers, the N-
terminal (β/α)
8 barrel (residues 87-416) containing
the CoA binding domain and the C-terminal
cobalamin-binding β/α
5 domain (residues 578-750).
A linker region consisting of 160 amino acids
connects the eight-stranded β/α barrel to the C-
terminal β/α domain (Fuchshuber et al., 2000).
More than 80 mutations, including small and large
scale rearrangements, truncating and missense
mutations, have been described.
Figure 1: Functional domains of MUT gene (adapted from
Acquaviva et al., 2005).
MMA with homocystinuria is an inborn error of
intracellular cobalamin metabolism resulting from
impaired conversion of dietary vitamin B12 or
cobalamin to its two metabolically active forms,
methylcobalamin (MeCbl) and adenosylcobalamin
(AdoCbl). MeCbl and AdoCbl are essential
coenzymes to methionine synthase and MCM,
respectively. The defect of these two cofactors
causes the accumulation of methylmalonic acid and
homocysteine in body fluids and a decrease of
methionine. Three genetic defects of intracellular
261
Nogueira C., Marques M. and Vilarinho L. (2010).
METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIAS - mut0/mut- and cblC Defects in Portuguese Population.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Bioinformatics, pages 261-263
DOI: 10.5220/0002759802610263
Copyright
c
SciTePress

cobalamin metabolism, cblC (MIM 277400), cblD
(MIM 277410), and cblF (MIM 277380) cause
combined MMA and homocystinuria. cblC defect is
the most frequent form and patients present with a
heterogeneous clinical picture (Rosenblatt et al,
1997). Based on the age at onset, two distinct
clinical forms have been recognized (early-onset and
late onset form). Recently the identification of the
gene responsible for cblC, MMACHC (MIM#
609831) was reported (Lerner-Ellis et al., 2006).
The gene is located in chromosome region 1p34.1
and has five exons. In the literature, forty-two
different mutations in 204 cblC individuals were
reported, including three common mutations:
c.271dupA, c.394C>T, and c.331C>T. The
c.271dupA and c.331C>T mutations were associated
with early-onset disease while the c.394C>T
mutation was associated primarily with late-onset
disease.
In the present study 19 Portuguese patients with
cblC defect and four patients with mut
0
/mut
-
MMA
phenotype were investigated. We found four
different mutations in MMACHC gene and another
four in MUT gene. We discuss the prevalence of
these diseases in our country/worldwide and the
impact that mutation identification has on routine
diagnostic procedures.
2 MATERIAL AND METHODS
2.1 Patients
In this cohort, the patients were selected after
sharing and matching our databases. The diagnosis
of mut
0
/mut
-
MMA
and cblC defect was based on the
identification of urinary and circulating metabolites
and, whenever possible, confirmed with fibroblast
studies. We studied at a molecular level four
Portuguese patients with the mut
0
MMA phenotype
and 19 with cblC defect diagnosed in our center, six
of them (2/4 and 5/19, respectively) detected by
extended newborn screening. The informed consent
was obtained in all studied patients.
2.2 Methods
The whole coding sequence, the flanking exon–
intron sequences of the MUT and MMACHC genes
were PCR amplified from genomic DNA as
described (Aquaviva, 2005; Lerner-Ellis, 2006).
Agarose-gel purified amplicons were directly
sequenced using the BigDye Terminator Cycle
Sequencing Version 3.1 (Applied Biosystems, Foster
City, CA), and analyzed on an ABI 3130XL DNA
Analyzer. Multiple linear regression analysis was
used to identify significant predictors of the
genotype in the entire sample, including gender, age
and clinical features. Statistical analyses were
performed using a Chi-square test with Yates
corrections (or, when appropriate, Fisher’s exact
test). Statistical significance was set at p < 0.01.
3 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
In our center we diagnosed four cases of mut
0
/mut
-
MMA (two through newborn screening) and 19
cases of cblC defect (five from newborn screening).
The number of symptomatic cases is in agreement
with the prevalence found by expanded newborn
screening although we know that the mild forms of
cblC cannot be detected by newborn screening using
the C3 (propionylcarnitine) and C3/C2
(acetylcarnitine) and C3/C16 (palmitoilcarnitine)
ratios without the homocysteine determination. In
most populations, mainly in Europe, the mut
0
/mut
-
MMA is more prevalent than the cblC defect. In the
Mediterranean countries a few studies were carried
out and some patients were identified although this
condition is a very rare disease in middle and north
of Europe (Nogueira et al., 2008; Richard et al.,
2009).
We investigated the molecular basis of MMA in 23
unrelated patients by sequencing the entire coding
region and intron-exon boundaries of the MUT and
MMACHC gene using genomic DNA. The mutations
were homozygous in 14 patients, and compound
heterozygous in 8 patients.
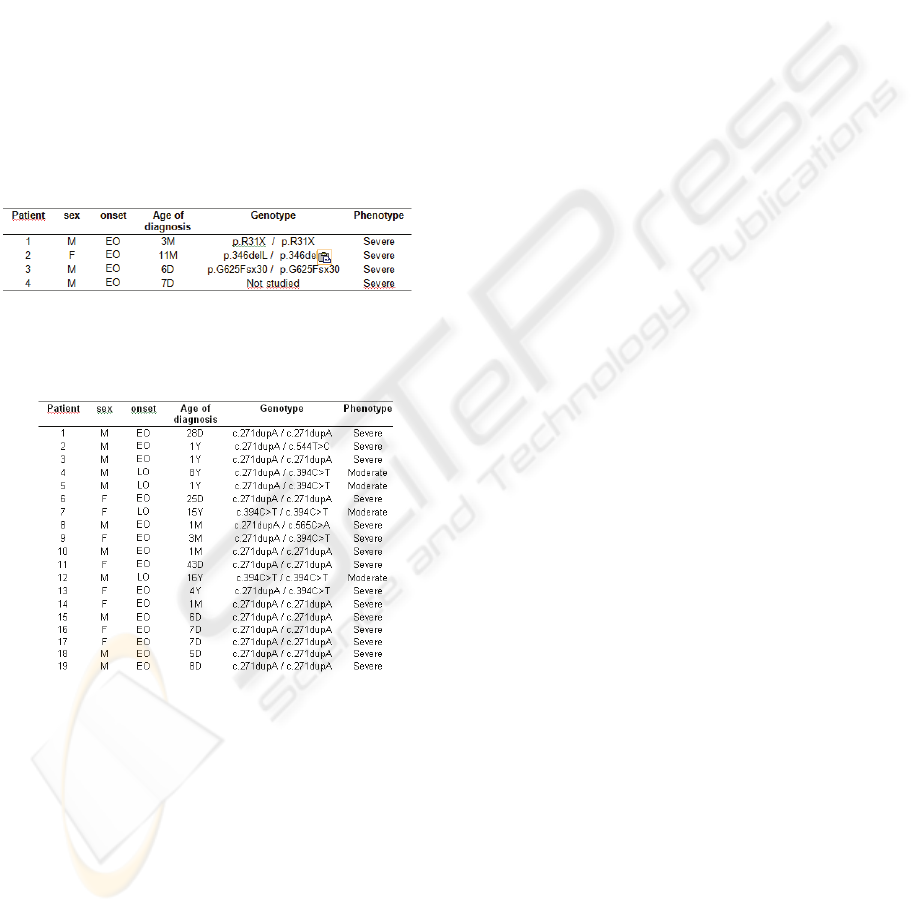
All the MUT mutations have been previously
reported; one of them is a nonsense mutation
(p.R31X) and two are small deletions (p.L346del
and p.G625FsX30) (Table 1).
The four different mutations found in cblC defect
were: two missense (c.544T>C and c.565C>A), one
nonsense (c.394C>T) and a small insertion causing
frameshift (c.271dupA) (Table 2).
Our data compared with other southern-European
populations, such as Italians and Spanish, have
showed a less molecular heterogeneity (Nogueira et
al., 2008.
The recent inclusion of these conditions in the
Portuguese expanded newborn screening program
since 2004, resulted in a substantial improvement in
the ability to identify suspected cases and allows for
a more reliable determination of their incidence,
considering the total number of individuals screened
until now. By MS/MS 420,000 neonates were
BIOINFORMATICS 2010 - International Conference on Bioinformatics
262
screened and two cases of mut
º
/mut
-
(1/210.000) and
five cases of cblC (1/84.000) were identified.
The present study represents the first determination
of the incidence of MMA in Portugal, indicating that
the cblC is more frequent in our country than
worldwide. All the patients identified by newborn
screening revealed homozygosity for c.271dupA
associated with the early phenotype. As long as
more newborns will be screened, a more reliable
comparison between symptomatic versus screened
detected patients will be established.
Another prospect of molecular studies is to facilitate
projections on the clinical type and severity of a
disease. These projections may be essential to guide
a proper monitoring of patients and that is why
phenotype-genotype studies are needed.
Table 1: Genotype and clinical subgroup of patients with
mut
0
/mut
-
MMA.
Table 2: Genotype and clinical subgroup of patients with
combined methylmalonic aciduria and homocystinuria,
cblC type.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In summary, we described the genetic background of
23 Portuguese patients with MMAs (four mut
0
/mut
-
MMA and 19 MMA-cblC type. Moreover, we found
four different mutations already described in the
literature, in each MUT and MMACHC genes,
respectively. Our data showed an evident difference
in the prevalence of these two diseases, compared
with other countries worldwide. This study
corroborate the importance of a molecular testing to
confirm mut
0
/mut
-
MMA and MMA-cblC patients,
detected by extended newborn screening programs,
to offer accurate treatment and future prenatal
diagnosis to couples at high risk of having affected
children. The molecular data also contributes to
molecular epidemiology of these diseases in our
population.
REFERENCES
Acquaviva C., Elion J., 2005. Molecular basis of
methylmalonyl-CoA mutase apoenzyme defect in 40
European patients affected by mut(o) and mut- forms
of methylmalonic acidemia: identification of 29 novel
mutations in the MUT gene. Hum Mutat., 25(2):167-
76.
Fenton W., Rosenblatt D., 2001. Disorders of propionate
and methylmalonate metabolism. In: Scriver CR,
Beaudet AL, Sly WS, Valle D, editors. The metabolic
and molecular basis of inherited disease. New York:
McGraw-Hill. P 2165–2193.
Fuchshuber A, Hildebrandt F., 2000. Mut0 methylmalonic
acidemia: eleven novel mutations of the
methylmalonyl CoA mutase including a deletion-
insertion mutation. Hum Mutat., 16(2):179.
Jansen R., Ledley F., 1989. Cloning of full-length
methylmalonyl-CoA mutase from a cDNA library
using the polymerase chain reaction. Genomics,
4:198–205.
Lerner-Ellis J.P., Rosenblatt D.S., 2006. Identification of
the generesponsible for methylmalonic aciduria and
homocystinuria, cblC type. Nat. Genet., 38 93–100.
Nogueira C., Dionisi-Vici C., 2008. Spectrum of
MMACHC mutations in Italian and Portuguese
patients with combined methylmalonic aciduria and
homocystinuria, cblC type. Mol Genet Metab.
93(4):475-80.
Richard E., Pérez B., 2009. Genetic and cellular studies of
oxidative stress in methylmalonic aciduria (MMA)
cobalamin deficiency type C (cblC) with
homocystinuria (MMACHC). Hum Mutat., 16 [Epub
ahead of print].
Rosenblatt D., Seashore M., 1997. Clinical heterogeneity
and prognosis in combined methylmalonic aciduria
and homocystinuria (cblC). J. Inherit. Metab. Dis., 20
528–538.
METHYLMALONIC ACIDURIAS - mut0/mut- and cblC Defects in Portuguese Population
263
