
OVERVIEW OF INTERACTIVE GENETIC PROGRAMMING
APPROACHES FOR CONVERSATIONAL AGENTS
Diana Pérez-Marín
1
and Ismael Pascual-Nieto
2
1
Department of Language and Computer Systems I, Rey Juan Carlos University, Madrid, Spain
2
Department of Computing, Universidad Autónoma de Madrid, Spain
Keywords: Interactive Genetic Programming, Conversational Agent, Evolutionary Algorithm, Dialogue System,
Natural Language Generation.
Abstract: Many of the existing conversational agents provide predefined answers. Therefore, the generated dialogue is
quite similar for different users. Interactive genetic algorithms ask humans to provide fitness, rather than
using a programmed function to compute it. This permits a better adjustment to the preferences and needs of
each user. In this paper, a review of how interactive genetic algorithms can be used to provide more flexible
and adaptable dialogues is presented.
1 MOTIVATION
Evolutionary Algorithms (EAs) are general
optimization techniques inspired on the principles of
natural evolution, and able to perform a guided
search with a random component (Holland, 1975;
Goldberg, 1989).
EAs apply stochastic genetic operators to a pool
of potential solutions or individuals. Two typical
operators are crossover that applies a recombination
on two solutions, and mutation that randomly
modifies the contents of an individual to promote
diversity. A fitness function provides a value to
every individual indicating its suitability to the
problem.
EAs start with a population of possible solutions,
which is evaluated based on its fitness. According
to the genetic operators used, some individuals are
selected to renew the population towards new
generations until a certain termination condition or
the required fitness is reached.
EAs have been successfully used to many
different applications (Michalewicz, 1994). In
particular, the application of EAs to Natural
Language Processing tasks is quite natural (Araujo,
2004). For instance, EAs have been used for
grammar induction, text generation, summarization,
document clustering, and machine translation.
It can be highlighted the positive impact of the
use of EAs for automatic text generation. Natural
Language Generation (NLG) investigates how
computer programs can produce high-quality natural
language texts from internal representations of
information (McKeown, 1986).
NLG is usually based on grammars or templates.
Especially the templates are the most popular
technique. It is because grammar-based systems are
more complex and require a great amount of effort
and time. However, template-based systems achieve
poorer results (Oh & Rudnicky, 2002).
All the same, both grammars and templates
require that the developer correctly designs them to
prevent the creation of wrong sentences; and, in
some domains, in which there are many possible
sentence structures, those approaches can result
impractical (Ratnaparkhi, 2002).
EAs can provide solutions to some of those
problems. For instance, EAs can generate: text
structures for discourse planning (Karamanis &
Manurung, 2002); referring expressions (Hervás &
Gervás, 2005); and, dialogues (Kim et al. 2004; Lim
& Cho, 2005).
Our focus is on the application of EAs to
automatically generate text for conversational
agents, that is, computer programs which can have
an animated face and/or body, understand natural
language and respond in natural language to a user
request (Macskassy & Stevenson, 1996).
ELIZA was the first conversational agent, based
on a simple pattern matching technique
(Weizenbaum, 1966). Since then, more and more
359
Perez-Marín D. and Pascual-Nieto I. (2010).
OVERVIEW OF INTERACTIVE GENETIC PROGRAMMING APPROACHES FOR CONVERSATIONAL AGENTS.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence, pages 359-366
DOI: 10.5220/0002769403590366
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Figure 1: Architecture proposed by Kim et al. for a Korean conversational agent (GP means Genetic Programming).
conversational agents have appeared based on
different techniques (Lester et al. 2004).
However, many of them just provide predefined
answers. Therefore, the generated dialogue is quite
similar for all the users, irrespectively of their
preferences and needs.
Genetic Programming (GP) is an extension of
genetic algorithms in which each individual in the
population is a computer program (Koza, 1994).
Interactive Genetic Programming (IGP) is a type
of GP in which the user is asked the fitness (Takagi,
2001).
In this paper, a review of how IGP can be used
to provide more flexible and adaptable dialogues for
conversational agents is presented.
The paper is organised as follows: in Section 2
the use of grammar structures is described; in
Section 3 the use of Sentence Plan Trees (SPTs) is
described; in Section 4 both approaches are
compared and some possible improvements are
proposed; and finally, Section 5 ends with the main
conclusions and lines of future work.
2 APPROACH 1: USE OF
GRAMMARS IN BNF
This approach was taken by Kim et al. (2004) with
the goal of improving the response adaptability in
conversational agents by responding with sentences
constructed through an evolutionary process.
The system is designed to be used in specific
domains using Interactive Genetic Programming
(IGP). A Korean grammar in Backus Naur Form
(BNF) notation is used as the structure to encode the
sentence patterns, which evolve until a suitable
answer is generated.
The fitness for the evolutionary process can be
defined as ‘whether the answer sentence generated is
natural’. In fact, the users are asked to score each
displayed answer with a value between -2 (worst) to
2 (better). The sentence structure of the answers
scored with 2 points is considered as the most
natural for that user, and therefore these answers are
saved to be used again.
As can be seen in Figure 1, three steps are
needed to generate the answers from the user
queries: preprocessing of the user input, sentence
pattern classification and answer selection.
The preprocessing of the user query involves
several processes such as morpheme analysis,
spacing words and keyword extraction. Only words
relevant to the domain (with a high frequency) are
marked as keywords. Other words are ignored.
The correct identification of at least one keyword
in the script answers database is necessary to
continue with the second step. Otherwise, if no
keywords have been found, the conversational agent
replies with a sentence such as ‘I don’t understand’
or ‘Input another query’.
The sentence pattern classification module
receives as input the keywords extracted in the
previous step, and uses an automaton to recognize
the pattern of the user query.
If the pattern has not been used before, then an
initial grammar structure is generated, and a first
answer is constructed by matching the keywords to
that grammar structure.
Otherwise, if the pattern has been used before,
then several grammar structures are available and
thus, a possible answer for each of them.
The answer selection step chooses the most
adequate answer to show the user according to the
fitness score provided by the user. In particular, if
there is an answer with 2 points, this answer is
shown. Otherwise, if there it not an answer with 2
points, new sentence structures are generated and
shown to the user until one of them is scored as
natural enough.
Figure 2 shows an example of application of this
approach for a conversational agent specialized in
shopping. The original grammar as indicated by Kim
et al. (2004) is:
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
360

Figure 2: Example of conversational agent based on the first approach (source: Kim et al. 2004).
S -> VP | e
VP -> V | NP + c | Z + VP | NP + j + VP
| V + e + VP
NP -> N | N + j + NP | Z + NP | VP + e + NP
| N + NP
(S: a sentence; VP: a verb phrase; NP: a noun
phrase; V: a verb; N: a noun; Z: an adverb; e: ending
word; c: a copula; j: an auxiliary word)
The user query is ‘Where is the location of the
shop?’ that once analyzed by the preprocessing
module is transformed into the list of keywords:
where, location, shop.
These keywords are used by the sentence pattern
classification module to identify that it is a
LocationQuestion. Given that it was not the first
time that this query has been made to the
conversational agent, several grammar structures
were associated to the LocationQuestion pattern in
the script answers database.
Finally, the answer selection chooses ‘It is
located on the 1
st
floor Hyundai department store in
Shinchon’. The reason for that choice is that the first
answer provided to a user was ‘Shinchon Hyundai
Department’ (i.e. sentence pattern N+N+N that is the
default), and it receives a -2 score.
For the matching of the patterns, please notice
that the original sentences were written in Korean
language and thus, there may be differences with the
sentences translated into English language.
Therefore, the sentence pattern N+N+N was
used as starting population to generate new sentence
structures for the LocationQuestion pattern.
In a second generation, the sentence pattern
N+N+j+N+j+V+c produces the answer ‘The shop is
on the 1
st
floor Hyundai Department Store’, which
receives a -1 score.
In a third generation, the answer provided in this
example is reached. In particular, the sentence
pattern N+j+N+N+N+N+c produces the answer ‘It
is located on the 1
st
floor Hyundai Department Store
in Shinchon’ which receives a 2 score.
3 APPROACH 2: USE OF
SENTENCE PLAN TREES
This approach was taken by Lim & Cho (2005) with
the same goal than Kim et al. (2004): improving the
response adaptability in conversational agents by
responding with sentences constructed through an
evolutionary process.
The fitness is also evaluated according to how
natural the user thinks that the queries are. However,
in this case the users are asked to score each
displayed answer with a value between 0 (worst) to
10 (better).
Nevertheless, the main change with the previous
approach is the use of Sentence Plan Trees (SPTs),
instead of grammars, to represent the genetic
programming.
SPTs are binary trees used to encode complex
sentences. In each SPT, each leaf node contains one
Simple Sentence (SS), and parent nodes represent
Joint Operators (JO) for combining child nodes.
Figure 3 shows an example of SPT.
OVERVIEW OF INTERACTIVE GENETIC PROGRAMMING APPROACHES FOR CONVERSATIONAL AGENTS
361
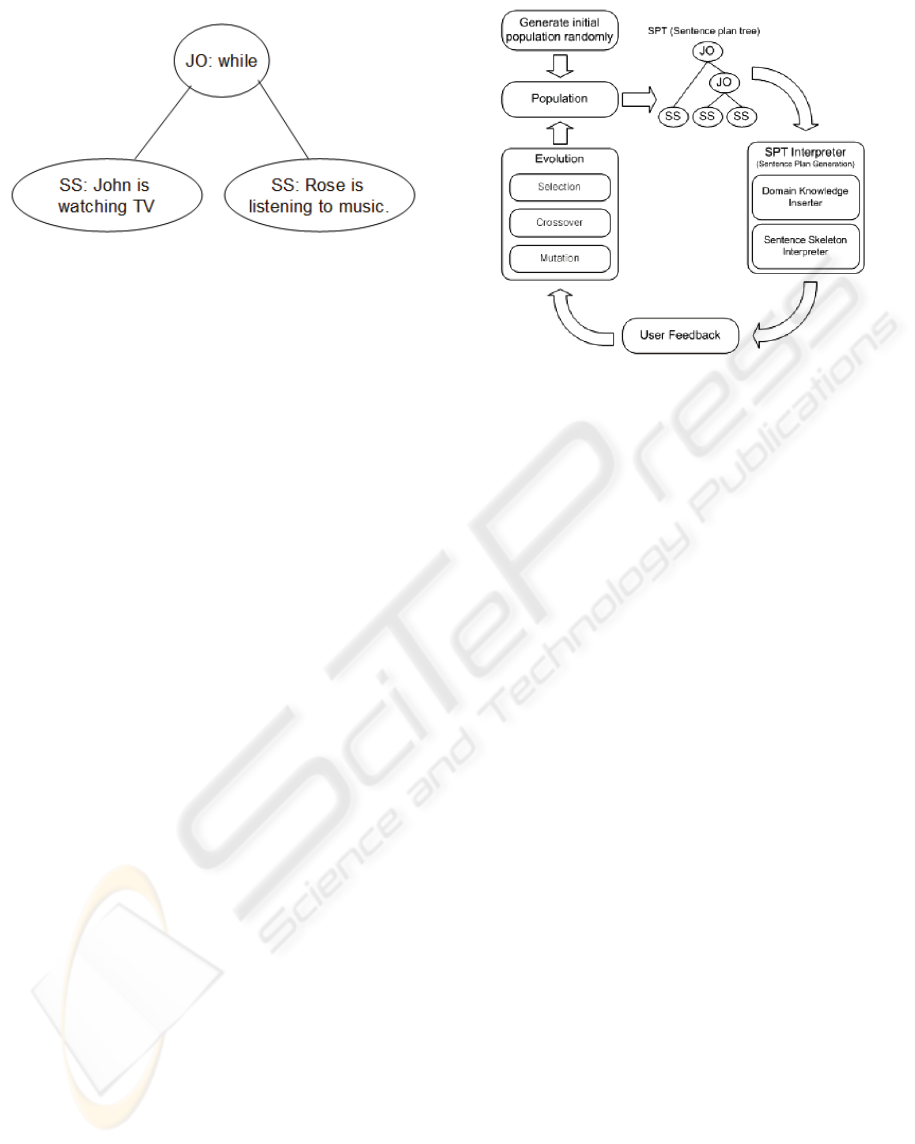
Figure 3: Simple SPT for the sentence ‘John is watching
TV while Rose is listening to music’.
Lim & Cho defined JOs based on the analysis of
Korean Language. In particular, they proposed 5
operators to be applied differently for each of the 3
possible cases combining two sentences: both of
them statements, one a statement and the other a
question, or both of them questions.
The JOs defined by Lim & Cho for Korean
language are:
SS A = subject (s1) + template (t1) + verb (v1)
SS B = subject (s2) + template (t2) + verb (v2)
JO 1: Combine SS A and SS B by using ‘and’. The
result is ‘s1 t1 v1 and s2 t2 v2’.
JO 2: Combine SS A and SS B which have the same
subject (i.e. s1 = s2).
JO 3: Combine SS A and SS B which have the same
subject and the same verb (i.e. s1 = s2, v1 = v2). The
result is ‘s1 t1 t2 v1’.
JO4: Combine SS A and SS B with the same
communicative act and the same verb (i.e. t1 = t2, v1
= v2). The result is ‘s3 t1 v1’ where s3 is a new
subject which includes s1 and s2 (e.g. ‘they’
includes ‘he’ and ‘she’).
JO5: Combine SS A and SS b with the same subject
and different verbs but with the possibility of
replacing the verbs by another verb v3 which
includes the meaning of v1 and v2 (i.e. s1 = s2, v1
<> v2 but v1 related to v2). The result is ‘s1 t1 t2
v3’ (e.g. ‘travelling’ can replace both to ‘leaving’
and ‘to be going to’).
Figure 4 shows the outline of the procedure to
generate sentences using interactive genetic
programming represented by SPTs.
Figure 4: Procedure to generate sentences using SPTs.
As in the previous approach, the conversation is
started by the user who provides a query. The query
is analyzed by the user input recognizer, using
pattern matching with templates.
Once the conversational agent has found the
most similar template to the user query, it extracts its
relevant information and chooses a SPT group
suitable for generating an answer.
This SPT group has an initial population of
SPTs. A SPT Selector choose one SPT of the group
to pass to the SPT Interpreter, which derives a
complex sentence taking into account domain-
relevant knowledge store in the Domain Knowledge
Inserter.
The generated sentence is shown to the users,
who evaluate the fitness according to how natural
the provided answer is to their query. Then, the
evaluated trees evolve to the next generation.
Figure 5 shows how the crossover operator
transforms a set of SPTs. The upper SPTs are as
before the operator is applied, and the shaded nodes
are the nodes that change. Similarly, Figure 6 shows
how the mutation operator transforms a set of SPTs.
After the evolution of the population, the new set
of SPTs are processed by the SPT Interpreter to
generate a new answer to the user, until the system
finally converges into the preference of the user (i.e.
fitness score = 10).
4 COMPARISON AND POSSIBLE
IMPROVEMENTS
According to Kim et al. (2004), two of the main
problems of the first approach are:
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
362

Figure 5: Crossover operation to SPTs in the Korean conversational agent (source: Lim & Cho, 2005).
Figure 6: Mutation operation to SPTs in the Korean conversational agent (source: Lim & Cho, 2005).
OVERVIEW OF INTERACTIVE GENETIC PROGRAMMING APPROACHES FOR CONVERSATIONAL AGENTS
363
– The limitations imposed by the definition of the
Korean grammar.
– The difficulty in designing a correct grammar
which covers all possibilities.
Lim & Cho (2005) also claimed that the use of
grammar-based approaches in Interactive Genetic
Programming for conversational agents has the
defect of making wrong sentences if the algorithm
does not have enough time for evolution.
The approach based on the use of Sentence Plan
Trees (SPTs) requires less time and effort for the
developer to design the system. In particular, it is
only necessary to construct several templates.
Another advantage of using SPTs instead of
grammars is that the domain can be more general.
However, the second approach also requires a
certain number of generations to provide a correct
answer, and it is possible that awkward query
generations arise when a tree contains statements
and questions together, which refer to the same kind
of information.
Lim & Cho solved that problem by only
indicating the kind of information involved in each
sentence in the corresponding leaf nodes.
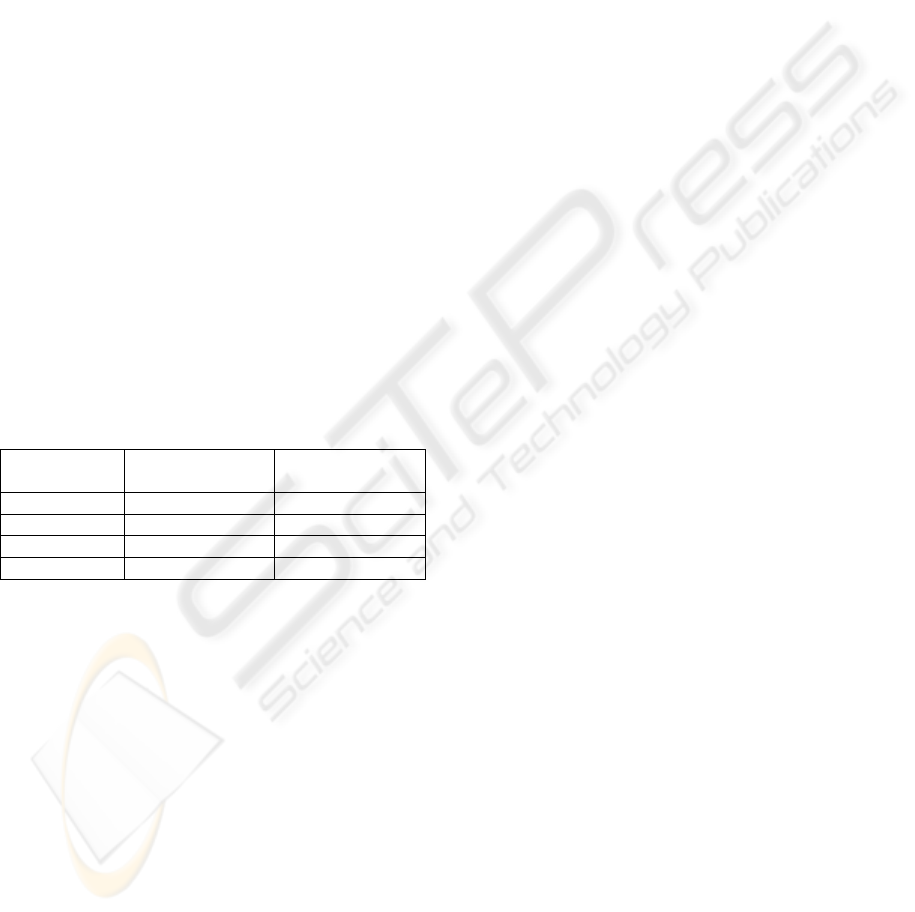
Table 1 shows a summary of the comparison
between using grammars and SPTs for IGP in
conversational agents.
Table 1: Comparison between both approaches.
Feature Grammar
(approach 1)
SPTs
(approach 2)
Design time High Low
Design effort High Low
Generality Low High
Adaptability High High
Nevertheless, both approaches:
– Wait for the user to start the interaction, so the
possibility of the conversational agent as the
initiator of the dialogue is not contemplated.
– Rely on the subjective feeling of the user when
scoring the generated answers.
It could be easily implemented the possibility of
users starting the interaction with the agent when
using SPTs. The conversational agent could have
several templates for greetings, so that whenever the
conversational agent is run it could choose one of
them to start the dialogue. Similarly, the agent could
also wait a certain amount of time for a user query,
giving always priority to the user.
The issue of up to which point is adequate that
users have to score the generated answers is more
complex in both approaches.
If the fitness is calculated as in traditional
genetic programming it could take several
generations until the conversational agent provides
an answer to the user. Hence, the user may leave the
application whenever the time to produce the answer
is too long.
Another alternative could be that the fitness is
calculated from the satisfaction of the user as
expressed in the own dialogue. This would solve the
problem of having to artificially answer the user for
the fitness, and at the same time the computation of
the fitness would be faster enough to provide an
answer in a reasonable time.
Natural Language Processing tools can be used
to extract the degree of satisfaction of the users from
their answers to the conversational agent. The range
of possible tools varies from the recognition of
positive adjectives to indicate a high degree of
satisfaction to classification algorithms to identify
sentences in which users show a positive or negative
attitude towards the agent.
Up to our knowledge, this alternative approach
has not been implemented yet. Furthermore, there
are not studies in which Genetic Programming is
used for conversational agents in other languages
such as English or Spanish.
Given that the second approach based on SPTs
seems more promising, it could be adapted by
incorporating the JOs for English and Spanish, and
to avoid the step of asking the users the fitness by
using a procedure to automatically extract their
degree of satisfaction from their answers.
The JOs for English would be as follows:
SS A: s1 v1 c1
SS B: s2 v2 c2
where c means complement such as a direct object
JO 1: Combine SS A and SS B by using a union
operator (U). The result is ‘s1 v1 c1 O s2 v2 c2’. For
instance, in English if SS A is ‘John is watching
TV’, SS B is ‘Rose is listening to music’, and U is
‘and’, then the combined sentence is ‘John is
watching TV and Rose is listening to music’.
JO 2: Combine SS A and SS B which have the same
subject (i.e. s1 = s2). The result is ‘s1 v1 c1 U v2
c2’. For instance, if SS A is ‘John is watching TV’,
SS B is ‘John is listening to music’ and U is ‘and’,
the combined sentence is ‘John is watching TV and
listening to music’.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
364

JO 3: Combine SS A and SS B which have the same
subject and the same verb (i.e. s1 = s2, v1 = v2). The
result is ‘s1 v1 c1 U c2’. For instance, if SS A is
‘John is eating apples’, SS B is ‘John is eating
bananas’ and U is ‘and’, the combined sentence is
‘John is eating apples and bananas’.
JO4: Combine SS A and SS B with the same
complement and the same verb (i.e. c1 = c2, v1 =
v2). The result is ‘s3 v1 c1’ where s3 is a new
subject which includes s1 and s2. For instance, if SS
A is ‘John is eating apples’ and SS B is ‘Rose is
eating apples’, the combined sentence is ‘They are
eating apples’. Note here that the verb has to be in
concordance with the new subject.
JO5: Combine SS A and SS B with the same subject
and different verbs but with the possibility of
replacing the verbs by another verb v3 which
includes the meaning of v1 and v2 (i.e. s1 = s2, v1
<> v2 but v1 related to v2). The result is ‘s1 v3 c1’.
For instance, if SS A is ‘John is leaving to Madrid’
and SS B is ‘John is going to Madrid’, the combined
sentence is ‘John is travelling to Madrid’.
New JOs could be generated from a systematic study
of the combination possibilities of s, v, and c of both
sentences. In particular, for English we propose, for
the first time, the following JOs:
JO6: Combine SS A and SS B in which the subject
of A is the same than the complement of B (i.e. s1 =
c2). The result is ‘s1 v1 c1 while s2 v2 pronoun’.
For instance, if SS A is ‘John watches TV’ and SS B
is ‘Mary looks at John’, the combined sentence is
‘John watches TV while Mary looks at him’.
JO7: Combine SS A and SS B in which the subject
of B is the same than the complement of A, and the
verbs v1 and v2 are not related (i.e. c1 = s2, v1 <>
v2). The result is ‘s1 v1 c1, which v2 c2’. For
instance, if SS A is ‘Mary looks at the window’ and
SS B is ‘The window needs to be cleaned’, the
combined sentence is ‘Mary looks at the window,
which needs to be cleaned’.
JO8: Combine SS A and SS B with the same
complements and the subjects are related (i.e. c1 =
c2). The result is ‘s1 v1 c1 v2_passive by s2’. For
instance, if SS A is ‘John eats apples’ and SS B is
‘Mary buys apples’, the combined sentence is ‘John
eats apples bought by Mary’.
JO9: Combine SS A and SS B in which the subject
of B is the same than the verb and complement of A
(i.e. v1+c1 = s2). The result is ‘s1 v1 c1. s2 v2 c2’.
For instance, if SS A is ‘John watches TV’ and SS B
is ‘To watch TV is funny’, the combined sentence is
‘John watches TV. To watch TV is funny’.
JO10: Combine SS A and SS B with the same verbs
and different complements but with the possibility of
replacing the complements by another complement
c3 which includes the meaning of c1 and c2 (i.e. v1
= v2, c1 <> c2 but c1 related to c2). The result is ‘s3
v1 c3’. For instance, if SS A is ‘John buys apples’
and SS B is ‘Mary buys bananas’, the combined
sentence is ‘They buy fruit’.
Furthermore, the same JOs are applicable to Spanish
as shown in the following examples:
JO 1: If SS A is ‘Juan está viendo la televisión’, SS
B is ‘María está escuchando música, and U is ‘y’,
then the combined sentence is ‘Juan está viendo la
televisión y María está escuchando música’.
JO 2: If SS A is ‘Juan está viendo la televisión’, SS
B is ‘Juan está escuchando música’ and U is ‘y’, the
combined sentence is ‘Juan está viendo la televisión
y escuchando música’.
JO 3: If SS A is ‘Juan está comiendo manzanas’, SS
B is ‘Juan está comiendo plátanos’ and U is ‘y’, the
combined sentence is ‘Juan está comiendo manzanas
y plátanos’.
JO4: If SS A is ‘Juan está comiendo manzanas’ and
SS B is ‘María está comiendo manzanas’, the
combined sentence is ‘Ellos están comiendo
manzanas’.
JO5: If SS A is ‘Juan saldrá para Madrid’ and SS B
is ‘Juan irá a Madrid’, the combined sentence is
‘Juan viajará a Madrid’.
JO6: If SS A is ‘Juan está viendo la televisión’ and
SS B is ‘María mira a Juan’, the combined sentence
is ‘Juan está viendo la televisión, mientras María le
mira a él’. Note here that the only change is that the
English word ‘which’ has to be replaced with the
Spanish word ‘mientras’.
JO7: If SS A is ‘María mira la ventana’ and SS B is
‘La ventana está sucia’, the combined sentence is
‘Mary mira la ventana que está sucia’. Note here that
OVERVIEW OF INTERACTIVE GENETIC PROGRAMMING APPROACHES FOR CONVERSATIONAL AGENTS
365

the English word ‘which’ is replaced here with the
Spanish word ‘que’.
JO8: If SS A is ‘Juan come manzanas’ and SS B is
‘María compra manzanas’, the combined sentence is
‘Juan come manzanas compradas por María’.
JO9: If SS A is ‘Juan está viendo la televisión’ and
SS B is ‘Ver la televisión es divertido’, the
combined sentence is ‘Juan está viendo la televisión.
Ver la televisión es divertido’.
JO10: If SS A is ‘Juan compra manzanas’ and SS B
is ‘María compra plátanos’, the combined sentence
is ‘Ellos compran fruta’.
It is our belief that this procedure can also be applied
to other European languages such as French or
Italian.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
Interactive Genetic Programming can be used in
generating dialogues for conversational agents. Two
different approaches have been reviewed. The first
approach based on the use of grammars, and the
second approach based on the use of Sentence Plan
Trees (SPTs).
Both approaches present the advantage of
providing answers adapted to each user thanks to the
evolutionary process, instead of giving predefined
static answers.
The use of SPTs as representation format is
recommended given that the use of grammars is
domain-specific, more complex for the designer of
the conversational agent, and it requires more time
to reach good answers.
Furthermore, as future work it is advisable to
permit users to start the dialogue, to find out the
satisfaction degree of the users by their answers, and
extending the procedure to other languages.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been sponsored by the project
CCG08-UAM/TIC-4425.
REFERENCES
Araujo, L., 2004. Symbiosis of evolutionary techniques
and statistical natural language processing. IEEE
Transactions on Evolutionary Computing 8(1),14–27.
Araujo, L. 2007. How evolutionary algorithms are applied
to statistical natural language processing, Artificial
Intelligence Review 28, 275-303.
Goldberg, D.E., 1989. Genetic algorithms in search,
optimization and machine learning. Addison Wesley.
Hervás, R., Gervás, P., 2005. Applying genetic algorithms
to referring expression generation. In: Tenth
international conference on computer aided systems
theory, EUROCAST.
Holland, J.J., 1975. Adaptation in natural and artificial
systems. University of Michigan Press, Ann Arbor.
Karamanis, N., Manurung, H.M., 2002. Stochastic text
structuring using the principle of continuity. In:
Proceedings of the second international natural
language generation conference, Association for
Computational Linguistics, Harriman, NY, 81-88.
Kim, K., Lim, S., Cho, S., 2004. User Adaptive Answers
Generation for conversational Agent Using Genetic
Programming, in Z.R. Yang et al., ed. Intelligent Data
Engineering and Automated Learning, Lecture Notes
in Computer Science 3177, Springer-Verlag, 813-819.
Koza, J., 1994. Genetic programming, Automatic
discovery of reusable programs, the MIT Press.
Lester, J., Brandy, K., Mott, B., 2004. The Practical
Handbook of Internet Computing, Chapman & Hall,
chapter Conversational Agents, 220-241.
Lim, S., Cho, S., 2005. Language Generation for
Conversational Agent by Evolution of Plan Trees with
Genetic Programming, in V. Torra et al., ed., Modeling
Decisions for Artificial Intelligence, Lecture Notes in
Artificial Intelligence 3558, Springer-Verlag, 305-315.
Macskassy, S., Stevenson, S., 1996. A conversational
agent, Master Essay, Rutgers University, 1996.
McKeown, K., 1986. Language generation: Applications,
issues, and approaches, IEEE Proceedings 74(7),
905-919.
Michalewicz, Z., 1994. Genetic algorithms + data
structures = evolution programs, 2nd ed. Springer,
New York.
Oh, H., Rudnicky, I., 2002. Stochastic natural language
generation for spoken dialog systems, Computer
Speech and Language, 16(3-4), 387-407.
Ratnaparkhi, A., 2002. Trainable approaches to surface
natural language generation and their application to
conversational dialog systems, Computer Speech and
Language, 16(3-4), 435-455.
Takagi, H., 2001. Interactive evolutionary computation:
Fusion of the capabilities of EC optimization and
human evaluation, IEEE Proceedings, 89(9), 1275-
1296.
Weizenbaum, J., 1966. Eliza -a computer program for the
study of natural language communication between
man and machine, Communications of the ACM, 9, 26-
45.
ICAART 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Agents and Artificial Intelligence
366
