
TEACHERS’ COMPUTER SUPPORTED CONSTRUCTIONS
WITHIN A EUROPEAN VIRTUAL COMMUNITY
COLLABORATIVE SPACE FOR SCIENCES EDUCATION
An Experience Achieved in a Multinational European Project
Maria Kordaki
Department of Computer Engineering and Informatics, Patras University, 26500, Rion Patras, Greece
Mihai Bizoi, Gabriel Gorghiu
Automatic Control, Informatics and Electrical Engineering Department,Valahia University, 130082, Targoviste, Romania
Keywords: Teacher Training, Computer Supported Education, Virtual Experiments, Blended Learning.
Abstract: This paper presents some essential considerations referred to the constructions performed by European
teachers in terms of virtual experiments and lesson plans within the framework of a Virtual community
collaborative Space for Sciences education. This framework was set up in the context of the Socrates
Comenius 2.1 European project: “VccSSe - Virtual Community Collaborating Space for Science Education”.
In this project, teachers from five European countries (Romania, Poland, Finland, Spain and Greece)
participated in blended learning courses aiming their training for the use of Information and Communication
Technologies in real teaching and learning practices. Within this framework, on-line training materials and
virtual experiments were created and developed. After the end of the designed courses, teachers were asked
to form their own virtual experiments and lesson plans and then to implement their products in the
classrooms. The analysis of the data shows that teachers who participated in the VccSSe Project encouraged
by the aforementioned blended course, expressed a favourable feedback related to the implementation of
their own virtual experiments in the teaching activities.
1 INTRODUCTION
Appropriately designed educational software can
catalytically affect the changes in the whole learning
context in terms of learning content, learning
activities and the roles of both teachers and learners
(Solloway, 1993; Noss and Hoyles, 1992; Jonassen,
Carr & Yueh, 1998). In particular, computers
provide wide opportunities for the construction of
various, different, linked and dynamic representation
systems such as: texts, images, equations, variables,
tables, graphs, animations, simulations of a variety
of situations, programming languages and
computational objects (Kaput, 1994). The use of
Multiple Representation Systems (MRS) is
acknowledged as crucial in encouraging the
expression of learners‟ different kind of knowledge
regarding the subject to be learned (Dyfour-Janvier,
Bednarz & Belanger, 1987; Janvier, 1987). In
addition, multiple and linked RS provide learners
with opportunities to study how variation in one
system can affect the other. In this way, each learner
can make connections between different aspects of a
learning concept and develop broad views about it
(Lesh, Mehr & Post, 1987; Janvier, 1987).
Appropriately designed computer learning
environments can also provide various tools
(embodying diverse learning concepts) which could
be used alone and in combination for the
construction of multiple solution strategies to the
tasks at hand (Kordaki and Balomenou, 2006). For
the construction of such multiple solution strategies
different learning concepts could be integrated. In
addition, appropriately designed computer learning
environments can provide opportunities for the
learners to actively construct their knowledge as
well as to develop their problem solving skills
(Dubinsky and Tall, 1991; Jonassen, Carr & Yueh,
349
Kordaki M., Gorghiu G. and Bizoi M. (2010).
TEACHERS’ COMPUTER SUPPORTED CONSTRUCTIONS WITHIN A EUROPEAN VIRTUAL COMMUNITY COLLABORATIVE SPACE FOR
SCIENCES EDUCATION - An Experience Achieved in a Multinational European Project.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 349-356
Copyright
c
SciTePress

1998). In addition, richly endowed computer
environments can embody powerful scientific ideas
which students can explore and reflect on as well as
conceptualize, and construct for themselves,
scientific concepts that has already been formulated
by others.
Most importantly, in the context of Information
and Communication Technologies (ICT), modern
social and constructivist perspectives of teaching
and learning can be realized (Papert, 1980;
Balacheff and Kaput, 1996; Noss and Hoyles, 1996;
Jonassen, Carr & Yueh, 1998). From these
perspectives, the need for training primary and
secondary level education teachers in the use of ICT
in education is of vital importance not only for their
integration into the modern social and educational
context created, but also for the integration of ICT
into education (European Commission, 1997). The
necessity of training teachers in ICT concerns the
acquisition of basic technical and pedagogical skills
related to the use of ICT so that they will be capable
of integrating it into the teaching and learning of the
subject-matter they teach (Davis and Tearle, 1998).
Blended learning is an approach suitable for
teacher training as it aligns learning undertaken in
face-to-face sessions with learning opportunities
created online (Littlejohn & Pegler, 2006). The aim
of blended learning is basically to join the best
points of classroom or face-to-face learning with the
best points of online learning as well as to
compensate the pitfalls and weakenesses of the one
type of learning with the benefits of the other type
and vice versa. On the one hand the opportunities
presented by online learning in terms of flexible
opportunities to learn anytime and anywhere as well
as to communicate and collaborate virtually
throughout the world (Harasim, Hiltz, Teles &
Turoff, 1995; Pallof & Pratt, 2004; Roberts, 2005;
Van Eijl & Pilot, 2003) are essential for teacher
training because teachers are adults with many
constrains in terms of time and space. On the other
hand, several constraints of online collaboration
such as: not appropriate perceptions about e-
learning, negative attitudes, luck of on-line
collaborative skills, not appropriate knowledge
about the basic technological skills needed for
participation in online learning and a sense of
difference between online learning and reality (Nel
& Wilkinson 2006) can be eliminated through face
to face sessions.
Based on the above, a blended teacher training
framework was formed in the context of a European
project: “VccSSe - Virtual Community
Collaborating Space for Science Education”,
(project number no. 128989-CP-1-2006-RO-
COMENIUS-C21). This 3 years project, started in
October 2006 and carried out by 9 partner
institutions from 5 different European countries
(Romania, Poland, Spain, Finland and Greece) has
as main purpose to adapt, develop, test, implement
and disseminate training modules, teaching
methodologies and pedagogical strategies based on
the use of ICT in terms of virtual instruments and
tools in teaching and learning of positive Sciences :
Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry. To this end, one
of the main targets of this project was to encourage
teachers to develop their own Learning Objects (LO)
consisting of specific constructions based on the use
of appropriate educational software - henceforth
called “Virtual Experiments” (VEs) - and
appropriate lesson plans, and then implement these
LO in their classrooms. Those learning objects are
uploaded in a virtual space frame named “Products
Matrix”, which is included in the VccSSe web-site,
being accessible via Internet, using the following
link: http://www.vccsse.ssai.valahia.ro/main/matrix.
In the following section of this paper the
previously mentioned framework for teacher training
is analytically described. Then, a presentation of the
“Products Matrix” including the teachers‟ learning
objects is demonstrated. Finally, a series of results
are discussed and conclusions are drawn.
2 TEACHER TRAINING IN THE
CONTEXT OF VCCSSE
The project team have implemented an e-learning
platform (Moodle) to support the course activities
and developed the e-Space, a repository of virtual
instruments to be used as examples in the frame of
the course. The course "Virtual Instrumentation in
Science Education" introduces the specific virtual
instruments concepts, pedagogical methods and also
particular and didactical elements for some very
used educational platforms: Cabri Geometry,
LabVIEW, Crocodile Clips and GeoGebra.
Teachers were supported to create their own
learning objects in diverse ways such as providing
training materials and realizing specific meetings
and various types of communications. In fact, the
teacher training process, in the context of the
VccSSe project, can be described in terms of: (a)
aims of the blended teacher training course; (b)
training materials used; (c) training procedure
followed; (d) educational software used.
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
350

2.1 Aims of the Blended Teacher
Training Course
The blended teacher training course within the
context of VccSSe was designed with the aim to
contribute to the acquisition of the following
competences by the teachers:
(a) Familiarization with the use of specific
educational software (Cabri Geometry Plus,
LabVIEW, Crocodile Clips and GeoGebra - the last
one, in the second training phase of the project), in
the teaching and learning of positive Sciences. (b)
Acquisition of educational design abilities in terms
of design of both interactive constructions using the
mentioned educational software and appropriate
lesson plans referred to the implementation of the
constructions in teaching and learning in real
classrooms. (c) Construction of at least one learning
object by each teacher participated in the VccSSe
project. (d) Familiarization with the use of Moodle
platform.
2.2 Training Materials
One of the most important outcomes of the project
was to create and develop specific training materials
to provide teachers with basics about the use of ICT
in education using virtual instruments and tools.
These training materials were dedicated to in-service
teachers from all educational levels in the partners‟
countries.
The training materials consisted of: (i) Seminars:
In particular 3 seminars were prepared to present the
specific virtual instrumentation concepts; (ii) Labs:
Specifically, 3 labs were designed in order to
familiarize the teachers with the educational
software particularity and basic steps for VIs
creation; (iii) Familiarization materials - in
pedagogical and technical terms - with the
previously mentioned Educational software selected
for use. The aim of these materials was to
familiarize teachers with the main pedagogical
dimensions of the software as well the basic
technical skills needed for using this software
effectively; (iv) ready made specific VEs which are
dedicated to be used as examples to illustrate the
potential pedagogical features of the aforementioned
pieces of software. In fact, a number of 55 ready
made VEs were presented by the partnership, those
ones being accessible at the following link:
http://www.vccsse.ssai.valahia.ro/main/e-space; (v)
lesson-plan templates to assist teachers to organize
their teaching intervention using the appropriate
VEs.
Assessment tools were also constructed for the
evaluation of these training materials by the
participants in the blended courses performed in
each partners‟ country. All the presented training
materials produced for teacher training and the
assessment tools were initially designed in English
(http://www.vccsse.ssai.valahia.ro/main/outcomes)
and then, these were translated in all partners‟
national languages: Romanian, Spanish, Polish,
Finnish and Greek. It was considered that all the
training materials described above will constituted a
solid basis for the teachers to acquire the knowledge
needed for the creation of their own VEs.
2.3 The Training Procedure
The duration of the training sessions covered an
amount of approximately 42 hours, including the
evaluation through the projects‟ web-page. It is
worth noting that, the face-to-face teaching sessions
provided teachers with opportunities to clarify some
complicated issues related to the construction of VEs
using the selected educational software, to exchange
ideas about didactical issues using ICT, to be
motivated to construct their own VEs and implement
them in their classrooms, and most importantly to
overcome their fears and doubts about the
introduction of an innovation in real educational
practices. In fact, these face-to-face sections became
very serious to the teachers‟ progress in creating and
implementing virtual experiments in their
classrooms. Various type of communications also
helped teachers to make progress in their work such
as telephone calls to their tutors, e-mails to their
tutors and their colleagues as well as asynchronous
communications via forum and synchronous
communications via chat. Some teachers also
motivated to construct their own VEs by their
intention to try new ideas in their classrooms as well
as to improve their knowledge and be well situated
in the 21th century. After they have finished the
training course, teachers have implemented the new
learned methodologies in the classroom and this
activity involving children was evaluated.
The course was implemented in two editions and
started at different moments, depending on each
partner. This offered the opportunity to improve
some elements of the course, based on the partial
evaluation made at the end of the first edition.
TEACHERS' COMPUTER SUPPORTED CONSTRUCTIONS WITHIN A EUROPEAN VIRTUAL COMMUNITY
COLLABORATIVE SPACE FOR SCIENCES EDUCATION - An Experience Achieved in a Multinational European
Project
351

2.4 Educational Software Used
2.4.1 Cabri Geometry II and Geogebra
Dynamic Geometry Systems, and specifically the
well known educational software Cabri Geometry II
(Laborde, 1990), and Geogebra (http://www.
geogebra.org/) offer a context where constructivist
mathematical learning settings can be supported. In
fact, the aforementioned software is highly capable
of facilitating the design of learning activities that
encourage learners to take an investigative and
exploratory perspective, to express their knowledge
and make self-corrections, as well as formulate and
verify conjectures (Straesser, 2001; Kordaki &
Balomenou, 2006). In addition, authentic,
meaningful, real-life learning activities can be
integrated within the context of this software. In
particular, Cabri and Geogebra provide students with
potential opportunities in terms of: (a) A rich set of
tools to perform diverse geometrical constructions
according to various concepts in Euclidean
Geometry; (b) Tools to construct a variety of
representations, both numerical and visual, such as
geometrical figures, tables, equations, graphs and
calculations. These representations are of different
cognitive transparency; consequently, students can
select the most appropriate to express their
knowledge; (c) Linking representations, by
exploiting the interconnection of the different
representation modes provided; (d) Dynamic, direct
manipulation of geometrical constructions, by using
the “drag mode” operation, enhancing their
knowledge about the issue at hand by dynamically
exploring the invariance of their constructions; (e)
The possibility of collecting large amounts of
numerical data. These data can be used by the
students to form and verify conjectures regarding the
geometrical concepts in focus; (f) Interactivity and
multiple types of feedback providing learners with
opportunities to form and verify conjectures as well
to be self-corrected; (g) Presenting information to
the students in various forms; (h) Capturing the
history of student actions to provide teachers and
researchers with a valuable amount of data for
further studies; (i) Extension. Certain operations
could be added as buttons on the interface of the said
software following the formation of specific macros.
2.4.2 LabVIEW
LabView (http://www.ni.com/labview/) is an
intuitive graphical programming language with
built-in functionality for simulation, data acquisition,
instrument control, measurement analysis, and data
presentation. This software is suitable for creating a
wide range of applications in different areas of
industries but also in education for Science subjects
teaching. The graphical nature of LabVIEW allows
users to focus on the theory being taught and not on
the tool manipulation and on the programming
nuances. The time to develop complex applications
is shorter than using a general programming
language. Due to the fact that LabVIEW is
specifically designed for engineers and scientists,
and it is used in a wide range of areas, the students‟
transition from school to industry is smoother
(Suduc, et al., 2009).
2.4.3 Crocodile Clips
The Crocodile Clips (http://www.crocodile-
clips.com/) simulation packages are developed
specifically for education and allow students and
teachers to recreate experiments, model
mathematical theories or simulate real life quickly
and easy. Crocodile simulators let students
experiment in a safe, accurate environment, and
come with a wealth of ready-made simulations and
models. Crocodile Clips includes four packages:
Crocodile Physics, Crocodile Chemistry, Crocodile
ICT and Crocodile Mathematics. In the frame of the
VccSSe project, the first two packages were
selected.
The main Crocodile Clips advantages are related
to the user-friendly interface and curricula focus
features for the primary and secondary school. In
order to easily learn how to use these tools, the
Crocodile Clips developers provide many useful free
training videos (Suduc et al., 2009).
3 RESULTS
A number of 363 in-service teachers involved in
lower and upper level of secondary education as
well as in primary education were trained through
the previously mentioned blended learning approach
about how to create, use and implement ICT based
lessons in their real teaching practices. These in-
service teachers - functioned on their background
and goals - were required to choose one of the
software environments for understanding its main
functions and creating at least one LO (that has to
include also at least one VE for students with a
significant level of interaction, for specific Sciences
disciplines: Mathematics, Physics, Chemistry). Their
lesson plans - designed under the previously
mentioned specific Template – proposed explana-
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
352

tions on the concepts to be learned. In the following
section, the components of the “Products matrix”
including those teachers‟ LOs, is presented. This
presentation reveals with the following essential
parts: (a) structure; (b) number of VE‟s; (c) partner
institutions involved; (d) searching; and (e) tools
included.
Table 1: First layer of the Product‟s matrix.
VccSSe Institutions
1st
Edition
Products
2nd
Edition
Products
Valahia University of Targoviste
13
11
Teacher Training and Educational
Innovation Centre Valladolid II
5
14
Teachers Training Centre of Gijon
17
54
Teachers Training Centre of Zaragoza 1
9
6
Warsaw University of Technology
9
4
Regional In-service Teacher Training
Centre "Wom" in Bielsko-Biala
3
20
University of Joensuu
-
13
Babes-Bolyai University Cluj Napoca
19
2
University of Patras
11
8
(a) Structure. The general structure of the
Product‟s matrix for all the partner institutions has a
three layer-structure. The first layer (see Table 1) of
the aforementioned structure is organized in a Table
demonstrating all partner institutions (see column 1)
and the number of VEs constructed by the teachers
in the 1st and 2nd edition of the course (2nd and 3rd
columns correspondingly) by each institution. For
example, in the 2nd row one can see that teachers
participated in the courses organized by Valahia
University of Targoviste produced 13 VEs during
the 1st edition of the course and 11 VEs during its
2nd edition. The second layer (see Table 2) of the
structure of the Product‟s matrix is dedicated for
each partner institution and has the structure
demonstrated by the 1st row of Table 2. To clarify
this structure, a specific example (see Table 3) of the
part of Product‟s matrix dedicated for the 1st Edition
of the course realized by the University of Patras is
demonstrated in Table 2.
To clarify the content of this Table, let‟s present
the content of its 1st row: Here one can see that, a
VE and the appropriate Lesson Plan was constructed
(see 7th column) to teach about „perpendicular line
in the mid of a segment‟ (see 1st column) that is
dedicated for „Lower Secondary school” (see 2nd
column), especially for the learning of Geometry
(see 3rd column). The name of the creator of this
VE and Lesson Plan is “Evagelos Stamos” (see 4th
column) in the school of ”Kato Achaia” (see 5th
column), while the keywords describing the basic
concepts are ”perpendicular line and the mid of a
segment” (see 6th column).
(b) Number of VEs included - First Edition: 86 VEs
were produced in total. Second Edition: 132 VEs
were produced in total. Data indicating relevant
number of products for each discipline/per partner
institution and in total is presented in Table 3. Here,
it is worth noting that, teachers designed a variety of
types of VEs supporting various learning activities.
For example, mathematics teachers designed VEs
supporting the following types of learning activities:
(i) Forming/verifying conjectures by focusing on the
alteration of an interactive geometrical construction
using the drag-mode operation; (ii)
Forming/verifying conjectures by focusing on the
numerical data automatically collected during the
alteration of a geometrical construction using the
drag-mode operation; (iii) Verifying a formula by
focusing on the numerical data automatically
collected during the alteration of a geometrical
construction using the drag-mode operation; (iv)
Multiple Representation-based activities; (v)
Constructions simulating real-life problems; (vi)
Black-box activities; (vii) A scenario-based
approach emphasizing the formation of networks of
learning concepts; (viii) Multiple-solution activities.
(c) Partner institutions involved. All partner
institutions were involved and specifically, the
number of VEs per institution is demonstrated in
Figure 1.
24
19
71
15
13
23
13
21
19
Targoviste Valladolid Gijon
Zaragoza Warsaw Bielsko-Biala
Joensuu Cluj Napoca Patras
Figure 1: Number of VEs per institution.
(d) Searching. One can search the content of
Product‟s matrix by realizing step by step the
following procedure: (1) Entering the main page of
VccSSe at http://www.vccsse.ssai.valahia.ro; (2)
Clicking on the link labelled as: “Product‟s matrix”.
In this way the visitor is automatically trans-located
to the 1st layer of the structure of the Product‟s
matrix that is allocated in the URL:
http://www.vccsse.ssai.valahia.ro/main/matrix
TEACHERS' COMPUTER SUPPORTED CONSTRUCTIONS WITHIN A EUROPEAN VIRTUAL COMMUNITY
COLLABORATIVE SPACE FOR SCIENCES EDUCATION - An Experience Achieved in a Multinational European
Project
353
No
Lesson Name
Level
Area /
Category
Teacher
Name
School
Keywords
Final Products
1
Perpendicular Line
in the Mid of a
Segment
Lower
Secondary
School
Maths
Geometry
Evagelos
Stamos
Kato Achaias
Perpendicular line,
mid of a segment
Perpendicular_MId
_point_segment.zi
p
Lesson_Plan.doc
2
Secants of a Circle
Upper
Secondary
School
Maths
Geometry
Dimitris
Kalogeras
1st Lykeum of
Nafpaktos
Circle, Secant, Upper
Secondary schools
Secants of a circle
Lesson Plan
3
The Theorem of
Circle's Secants
Upper
Secondary
School
Maths
Geometry
Dionisia
Kargioti
Private
Academy in
Patras
Circle, Secant's
theorem, Upper
secondary school
The theorem of
circle's secants
Lesson Plan
Table 3: Relevant number of products for each discipline and institution.
VccSSe Institutions
Math
Physics
Chemistry
Technology
Total
Valahia University of Targoviste
16
4
4
0
24
Teacher Training and Educational Innovation Centre Valladolid II
0
6
10
3
19
Teachers Training Centre of Gijon
37
33
0
1
71
Teachers Training Centre of Zaragoza 1
0
15
0
0
15
Warsaw University of Technology
2
8
0
3
13
Regional In-service Teacher Training Centre "Wom" in Bielsko-Biala
21
1
0
1
23
University of Joensuu
10
3
0
0
13
Babes-Bolyai University Cluj Napoca
8
11
2
0
21
University of Patras
19
0
0
0
19
Total Number of Products for Each Discipline
113
81
16
8
218
Here the visitor can explore the matrix demonstrated
in Table 1. The numbers included in the 2nd and 3rd
columns of this Table are dynamic that links
allowing the visitor to access the 2nd layer of the
structure of the Product (3) Clicking on the
numbers included in the 2nd and 3rd columns of the
Table For example, by clicking
on the number 11 which is included in the cell that is
allocated in the crossing point of (row: University of
Patras and column: 1st Edition) the visitor can
automatically trans-located to the URL:
http://www.vccsse.ssai.valahia.ro/main/matrix?org=
9&edition=1. In this place one could acquire an
image of the products performed by the teachers
involved in the 1st Edition of the course realized by
the University of Patras (see Table 3). The content
of the 7th column of this Table is dynamic and
automatically allocate the visitor to the specific VEs
and Lesson Plans constructed by each teacher. (4)
Clicking on the name of each specific VE included
in the 7th column of the Table illustrated in the 2nd
, the
visitor can access the 3rd layer of the structure of
this matrix where specific VEs and their
correspondent lesson plans are allocated.
(e) Tools included. The tools included in the
Products Matrix are: (i) the Products Matrix
Updater - First Edition (PMU-1st) and (ii) the
Products Matrix Updater - Second Edition (PMU-
2nd). These tools are identical, except the fact that
each one serves as a tool to update the 1st and 2nd
Editions of the course correspondingly. Both tools
are located in the 1st layer of the structure of the
Products Matrix. By clicking on the Products
Matrix Updater- First Edition link, the system
automatically transfer the user in the following
location:
http://www.vccsse.ssai.valahia.ro/main/matrix-up
Here, the system asks the user for username and
password to trans-locate him/her to update the
second layer of the Products Matrix dedicated to a
specific partner institution. Accesses to this layer
have only the local coordinators. For instance,
considering Patras University, after entering the
appropriate username and password, the system
transfer the user in the following page:
http://www.vccsse.ssai.valahia.ro/main/matrix-up
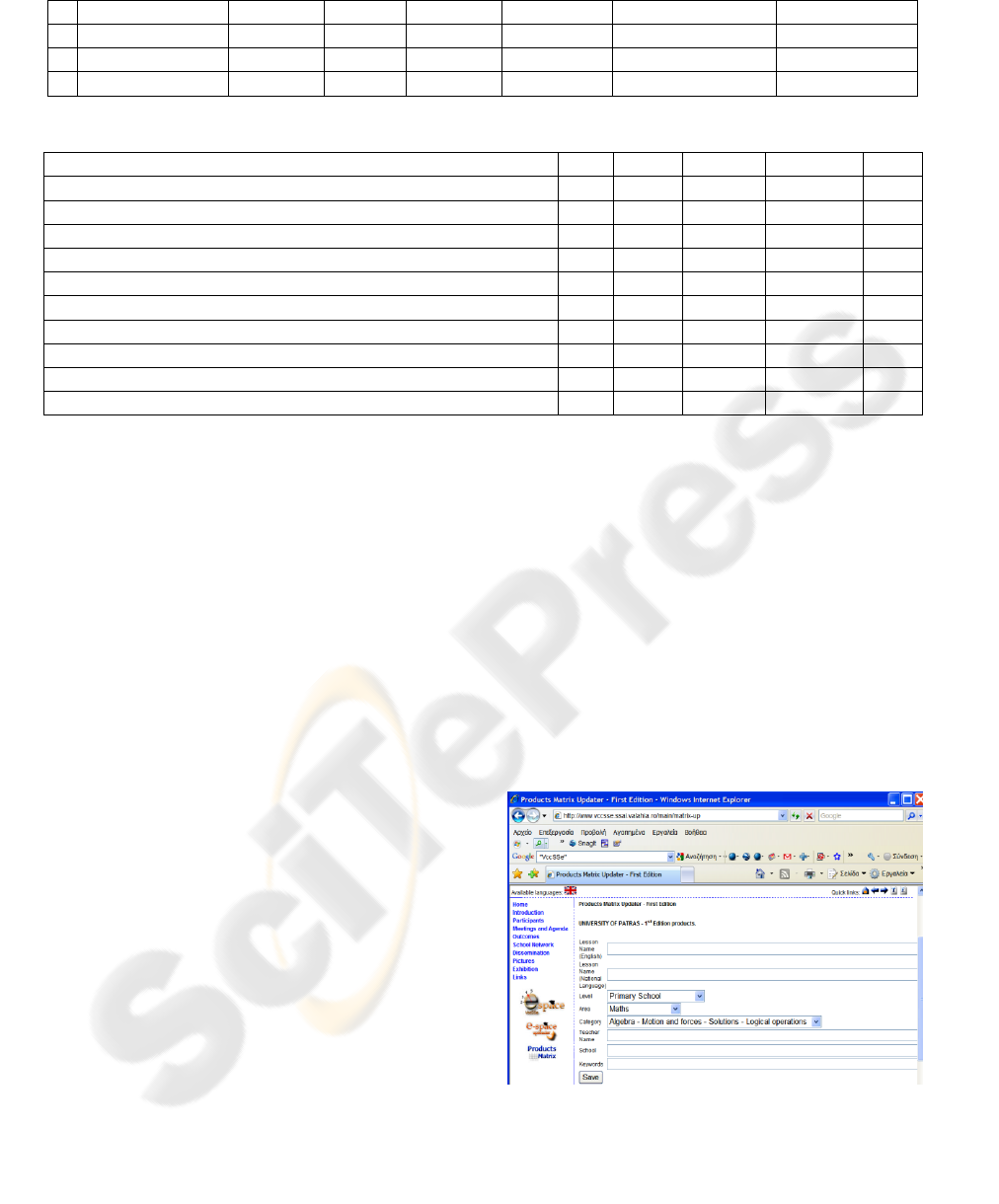
Figure 2: The form dedicated to the adaptation of the
Products Matrix with information regarding teacher VEs
and Lesson Plans.
In the fields of the form illustrated in Figure 2
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
354

the appropriate information regarding each teacher
VEs could be recorded. After saving this
information, the user is provided with the
opportunity to upload the correspondent files
namely; the specific VI and Lesson Plan constructed
by the teacher.
4 DISCUSSION
In this section the “Products matrix” is discussed in
terms of appropriateness of its essential parts
referred to in the previous section, namely: (a)
appropriateness of the structure, (b) relevant number
of products for each discipline, (c) relevant number
of products for each partner, (d) usability of the
searching engine, (e) usability of the up-loader.
(a) Appropriateness of the structure. The structure of
Products Matrix is appropriate to save and provide
access to the VEs and Lesson Plans constructed by
the teachers. It is also simple, and easy to use.
Visitors can search the teachers‟ products in each
country and Edition of the course.
(b) Relevant number of products for each discipline.
More than half of teachers‟ VEs and Lesson Plans
related to the learning of Maths (113 VEs and
Lesson Plans; 52%). A considerable number of
teachers‟ VEs and Lesson Plans related to the
learning of Physics (81 VEs and Lesson Plans; 37%)
while some of teachers‟ VEs and Lesson Plans
related to the learning of Chemistry (16 VEs and
Lesson Plans; 7%). Finally, few teachers‟ VEs and
Lesson Plans related to the learning of Technology
(8 VEs and Lesson Plans; 4%).
(c) Relevant number of products for each partner. A
considerable number of products were constructed
by all institutions (218 VEs and Lesson Plans) as
well as by each partner institution; Maximum: 71
VEs and Lesson Plans (33%) and Minimum: 13 VEs
and Lesson Plans (6%).
(d) Usability of the searching engine. It is very
convenient; just three clicks to visit a specific
teacher construct (a VE or a Lesson Plan).
(e) Usability of the up-loader. This tool is very
convenient; just six clicks to upload a VE and a
Lesson Plan constructed by a teacher followed by a
description in terms of: teacher name, school name,
lesson name, education level, key-words and
discipline.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presented the diversity of LOs in terms of
VEs and lesson plans designed by the European
teachers who participated in a Virtual Community
Collaborative Space for Science Education
(VccSSe). At first glance, the results emerging from
this study show that teachers designed a variety of
types of LOs supporting diverse type of learning
activities but most importantly, these teachers used
these LOs in their actual classroom practices. By
performing such learning activities, students had the
chance to experiment, express their individual
knowledge, make interconnections with various
concepts, develop multiple perspectives regarding
the learning concepts in focus and also be motivated
to be actively involved in their learning process.
On the whole, the results of this study suggest
that teachers are able to design pedagogically sound
learning activities using ICT and also use these
activities in their teaching practices. More effort is
needed to ensure support in such communities for
teacher professional development and lifelong
learning as well as for the use of ICT in everyday
classroom practices. To this end, the integration of
ICT in the typical school curricula, the provision of
appropriate technical infrastructure in schools, and
the training of teachers through formal procedures
will constitute a solid background for the
introduction and exploitation of the benefits of ICT-
based teaching and learning in the every day
classroom of 21 century.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was funded through Project 128989-CP-
1-2006-1-RO-COMENIUS-C21 from European
Commission, Education and Training, School
Education: Socrates: Comenius. We thank to all the
partners and teachers for all their cooperation and
work.
REFERENCES
Balacheff, N. & Kaput, J. (1996). Computer-based
learning environments in mathematics. In A. J.
Bishop, K. Klements, C. Keitel, J. Kilpatric and C.
Laborde (Eds), International Handbook on
Mathematics education (pp. 469-501). Dortdrecht:
Kluwer.
Davis, N. & Tearle, P. (1998). A Core Curriculum for
Telematics in Teacher Training. Proceedings of thw
TEACHERS' COMPUTER SUPPORTED CONSTRUCTIONS WITHIN A EUROPEAN VIRTUAL COMMUNITY
COLLABORATIVE SPACE FOR SCIENCES EDUCATION - An Experience Achieved in a Multinational European
Project
355

XV, IFIP World Computer Congress – Teleteaching
‟98 Distance Learning, Training and Education, Vol.1
(pp. 239-248), Vienna & Budapest, 31 August – 4
September, 1998.
Dubinsky, E. and Tall D. (1991). Advanced Mathematical
Thinking and the Computer. In Tall D. O. (ed.),
Advanced Mathematical Thinking, Kluwer: Holland,
231–248.
Dyfour-Janvier B., Bednarz N. & Belanger M. (1987).
Pedagogical considerations concerning the problem of
representation. In C. Janvier (Eds), Problems of
representation in teaching and learning of
mathematics. London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates,
pp. 109-122.
European Commission (1997). V Framework Programme:
Information Society programme for technologies and
skills acquisition. Proposal for a research agenda.
Draft for large scale consulting, European Commision
DG XIII_C, Brussels, , Weets, G. (Eds)..
Harasim, L., Hiltz, S.R., Teles, L., & Turoff, M. (1995).
Learning Networks: a field guide to Teaching and
Learning Online. Cambridge: MIT Press.
Janvier, C. (1987). Representation and understanding: The
notion of function as an example. In C. Janvier (Eds),
Problems of representation in teaching and learning of
mathematics. London: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates,
pp. 67-72.
Jonassen, D. H., Carr, C. & Yueh, H-P. (1998). Computers
as Mindtools for Engaging Learners in Critical
Thinking. Tech Trends, 43(2), 24-32.
Kaput, J. J. (1994). Τhe Representational Roles of
Technology in Connecting Μathematics with
Authentic Experience. In R. Biehler, R. W. Scholz, R.
Strasser, B., Winkelman (Eds), Didactics of
Mathematics as a Scientific Discipline: The state of
the art (pp. 379- 397). Dordrecht: Kluwer Academic
Publishers.
Kordaki, M. & Balomenou, A. (2006). Challenging
students to view the concept of area in triangles in a
broader context: exploiting the tools of Cabri II.
Ιnternational Jοurnal of Computers for Mathematical
Learning, 11(1): 99-135.
Laborde, J-M. (1990). Cabri-Geometry [Software].
France: Universite de Grenoble.
Lesh, R., Mehr, M. & Post, T. (1987). Rational number
relations and proportions. In C. Janvier (Eds),
Problems of representation in teaching and learning of
mathematics (pp. 41-58). London: Lawrence Erlbaum
Associates.
Littlejohn, A. & Pegler, C. (2006) Preparing for Blended
E-Learning: Understanding Blended and Online
Learning. London: Routledge.
Νoss R. & Hoyles C. (1992). Looking Back and Looking
Forward. In C. Hoyles and R. Noss (eds), Learning
Mathematics and Logo (pp. 431-470). Cambridge, Ma:
MIT Press.
Noss, R. and Hoyles, C. (1996). Windows on
mathematical meanings: Learning Cultures and
Computers. Dordrecht : Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Palloff, M.R., & Pratt, K. (2004). Learning together in
Community: Collaboration Online. In 20th Annual
Conference on Distance Teaching and Learning,
August 4-6, 2004, Madison, Wisconsin, Retrieved on
Sept. 30, 2009, from http://www.uwex.edu/disted/
conference/Resource_library/proceedings/04_1127.pdf
Papert, S. (1980). Mindstorms: Children, Computers, and
Powerful Ideas. NY: Basic Books.
Roberts, T. S. (2005). Computer-supported collaborative
learning in higher education: An introduction. In:
Roberts, T. S. (ed). Computer-supported collaborative
learning in higher education. Idea Group Publishing,
Hershey, pp 1–18.
Solloway, E. (1993). „Reading and Writing in the 21st
Century”. Communications of the ACM, May 1993;
36(5).
Straesser, R. (2001). Cabri-Geometre: does Dynamic
Geometry Software (DGS) change geometry and its
teaching and learning?. Ιnternational Jοurnal of
Computers for Mathematical Learning, 6: 319-333.
Suduc, A.M., Gorghiu, G., Bîzoi, M., Masior, W., Latka,
M. (2009). A Comparative Analysis on Using Several
Virtual Instrumentation Software in Education,
Proceedings of the 1st International Conference on
Computer Supported Education, CSEDU 2009,
Lisbon, Vol. 1, p. 435-438, Portugal, 2009.
Van Eijl, P. & Pilot, A. (2003). Using a virtual learning
environment in collaborative learning: Criteria for
success. Educational Technology, 43(2): 54–56.
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
356
