
DETECTION OF SUBMITTERS SUSPECTED OF
PRETENDING TO BE SOMEONE ELSE TO
MANIPULATE COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMMUNITY SITE
Naoki Ishikawa, Ryo Nishimura, Yasuhiko Watanabe, Yoshihiro Okada
Ryukoku University, Dep. of Media Informatics, Seta, Otsu, Shiga, Japan
Masaki Murata
NICT, Seika-cho, Soraku-gun, Kyoto, Japan
Keywords:
Spoofing, Manipulation of communication, Credibility, Community site.
Abstract:
Community sites offer greater learning opportunities to users than search engines. One of the essential fac-
tors provides learning opportunities to users in community sites is anonymous submission. This is because
anonymity gives users chances to submit messages (questions, problems, answers, opinions, etc.) without
regard to shame and reputation. However, some users abuse the anonymity and disrupt communications in
a community site. For example, some users pretend to be other users by using multiple user accounts and
attempt to manipulate communications in the community site. Manipulated communications discourage mes-
sage submitters, keep users from retrieving good communication records, and decrease the credibility of the
communication site. To solve this problem, we conducted an experimental study to detect submitters sus-
pected of pretending to be someone else to manipulate communications in a community site by using machine
learning techniques. In this study, we used messages in the data of Yahoo! chiebukuro for data training and
examination.
1 INTRODUCTION
In these days, many people use community sites, such
as Q&A sites and social network services, where
users share their information and knowledge. Com-
munity sites offer greater learning opportunities to
users than search engines in the following points:
1. Users can submit ambiguous questions because
other users give some supports to them. Further-
more, users can submit questions in natural and
expressive sentences, not keywords.
Figure 1 is a question submitted to a widely-used
Japanese Q&A site, oshiete! goo, by a student in
the author’s class of media processing. He aimed
to obtain a sample program and do his assignment
of the class. On the other hand, the author ex-
pected students in the class to give the following
keywords to search engines and find informative
web pages and sample programs:
• keywords used in the problem statement of his
assignment. (e.g. ppm, flip, horizontally, 90
degree clockwise)
• keywords which were not used in it. (e.g.
fopen, sscanf)
fopen and sscanf were commands of C program-
ming language. The students could not write C
programs for the assignment without using these
commands. However, it is difficult to think of
these keywords, especially, for students who did
not have detailed knowledge of media processing
and C programming language. By the way, the
student received a sample program with detailed
explanation three hours later after submitting the
question of Figure 1.
2. Communications in community sites are interac-
tive. Users have chances to not only submit ques-
tions but give answers and, especially, join discus-
sions.
As a result, community sites are promising media for
education.
166
Ishikawa N., Nishimura R., Watanabe Y., Okada Y. and Murata M. (2010).
DETECTION OF SUBMITTERS SUSPECTED OF PRETENDING TO BE SOMEONE ELSE TO MANIPULATE COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMMUNITY
SITE.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 166-171
DOI: 10.5220/0002772301660171
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Figure 1: A question submitted to a Japanese Q&A site, oshiete! goo, by a student in the author’s class.
One of the essential factors which provides learn-
ing opportunities to users in community sites is
anonymous submission. In most community sites,
user registration is required for those who want to join
the community sites. However, registered users gen-
erally need not reveal their real names to submit mes-
sages (questions, problems, answers, opinions, etc.).
It is important to submit messages anonymously to
a community site. This is because anonymity gives
users chances to submit messages without regard to
shame and reputation. However, some users abuse the
anonymity and disrupt communications in a commu-
nity site. For example, some users pretend to be other
users by using multiple user accounts and attempt to
manipulate communications in the community site.
Manipulated communications discourage other sub-
mitters, keep users from retrieving good communica-
tion records, and decrease the credibility of the com-
munity site. As a result, it is important to detect sub-
mitters suspected of pretending to be other users to
manipulate communications in a community site. In
this case, identity tracing based on user accounts is
not effective because these suspicious submitters of-
ten attempt to hide their true identity to avoid de-
tection. A possible solution is authorship identifi-
cation based on analyzing stylistic features of mes-
sages. In recent years, a large number of studies
have been made on authorship identification (Craig
99) (de Vel 01) (Koppel 02) (Corney 02) (Argamon
03) (Zheng 06), however, few researchers addressed
the identification issues of authors who submit mes-
sages in a community site. To solve this problem,
in this study, we propose a method of detecting sub-
mitters suspected of pretending to be someone else to
manipulate communications in a community site. In
this method, in order to detect submitters suspected of
pretending to be someone else, we used an submitter
identifier which was developed by learning stylistic
features of user’s messages and determine by whom a
series of input messages are submitted. We used mes-
sages in the data of Yahoo! chiebukuro
1
, a widely-
used Japanese Q&A site, for observation, data train-
ing and examination.
2 COMMUNICATIONS
MANIPULATED BY MULTIPLE
ACCOUNT USERS
In this study, we used messages in the data of Yahoo!
chiebukuro for observation, data training, and exam-
ination. The data of Yahoo! chiebukuro was pub-
lished by Yahoo! JAPAN via National Institute of In-
formatics in 2007
2
. This data consists of about 3.11
million questions and 13.47 million answers which
were posted on Yahoo! chiebukuro from April/2004
to October/2005. In this section, we observed mes-
sages submitted to the following categories in Yahoo!
chiebukuro.
• PC,
• healthcare, and
• social issues.
1
http://chiebukuro.yahoo.co.jp
2
http://research.nii.ac.jp/tdc/chiebukuro.html
DETECTION OF SUBMITTERS SUSPECTED OF PRETENDING TO BE SOMEONE ELSE TO MANIPULATE
COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMMUNITY SITE
167

Table 1: The numbers of submitters and their submitted messages to PC, healthcare, and social issues category in Yahoo!
chiebukuro (from April/2004 to October/2005)
PC healthcare social issues
submitters messages submitters messages submitters messages
question 43493 171848 29954 84364 13259 78777
answer 27420 474687 38223 289578 25766 403306
Table 2: The numbers of submitters and their messages, who submitted more than 200 messages to PC, healthcare, or social
issues category in Yahoo! chiebukuro (from April/2004 to October/2005)
PC healthcare social issues
submitters messages submitters messages submitters messages
question 17 5970 5 1581 39 14088
answer 395 260183 134 57406 312 180503
Table 1 shows the numbers of submitters and
their submitted messages to these categories from
April/2004 to October/2005. Also, Table 2 shows the
numbers of submitters who submitted more than 200
messages. We think that multiple account users who
intend to manipulate communications in community
sites are frequent message submitters.
In Yahoo! chiebukuro, users need not reveal their
real names to submit their messages. However, their
messages are traceable because their user accounts
are attached to them. Because of this traceability, we
can collect any users messages and some of them in-
clude clues of identifying individuals. As a result,
to avoid identifying individuals, it is reasonable and
proper that users change their user accounts or use
multiple user accounts. However, the following types
of message submissions using multiple user accounts
are neither reasonable nor proper.
TYPE I a question and its answer are submitted by
one and the same user.
We think that the user intended to manipulate
the message evaluation. For example, in Yahoo!
chiebukuro, each questioner is requested to deter-
mine which answer is best and give a best answer
label to it. These message evaluations encourage
message submitters to submit new messages and
increase the credibility of the community site. We
think, in order to get best answer labels and seem
a good answerer, the user has repeated this type of
submissions.
TYPE II two or more answers are submitted to the
same question by one and the same user.
We think that the user intended to dominate or dis-
rupt communicationsin the community site. To be
more precise, the user intended to
• control communications by advocating or justi-
fying his/her opinions, or
• disrupt communications by submitting two or
more inappropriate messages.
These kinds of submissions discourage other submit-
ters, keep users from retrieving good communication
records, and decrease the credibility of the commu-
nity site. As a result, it is important to detect users
suspected of pretending to be someone else to manip-
ulate communications in a community site.
TYPE I submissions are sometimes obscurer than
TYPE II submissions because the standards of best
answer selection differ with each questioner. In other
words, it is more possible to disrupt communications
by TYPE II submissions than TYPE I. As a result, in
this study, we intend to investigatea method of detect-
ing users who have repeated TYPE II submissions.
3 DETECTION OF SUBMITTERS
SUSPECTED OF PRETENDING
TO BE SOMEONE ELSE
In order to detect users who repeated TYPE II sub-
missions, we intend to detect users who
• have similar styles of writing, and
• submitted answers to the same questions.
It is easy to detect users who submitted answers to the
same questions by using their submission records. As
a result, in this section, we explain a method of detect-
ing users who have similar styles of writing. Figure
2 shows the outline of our method of detecting users
who have similar styles of writing.
In our method, we used a submitter identifier
which is based on analyzing stylistic features and de-
termines by whom a series of input messages are sub-
mitted. As shown in Figure 2, the submitter identi-
fier consists of N user classifiers developed by learn-
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
168

Figure 2: The outline of our method of detecting users who
have similar styles of writing
s1 the results of morphological analysis on sentences
in the target message
s2 the results of morphological analysis on the sen-
tence and sentence No.
s3 character 3-gram extracted from sentences in the
target message
s4 character 3-gram extracted from the sentence and
its sentence No.
s5 1 ∼ 10 characters at the head of each sentence
s6 1 ∼ 10 characters at the end of each sentence
s7 sequential patterns extracted by PrefixSpan (fre-
quency is 5+, item number is 3+, maximum gap
number is 1, and maximum gap length is 1)
Figure 3: Features used in maximum entropy (ME) method
for learning stylistic features of submitters. PrefixSpan
(http://prefixspan-rel.sourceforge.jp/) is a method of mining
sequential patterns efficiently.
ing users’ stylistic features. Each classifier has a tar-
get user and calculates the probability that a series
of input messages were submitted by the target user.
Then, the identifier determines that a series of input
messages were submitted by the user with the highest
probability. When the user with the highest proba-
bility differs from the user submitted a series of in-
put messages, our method determines that these users
have similar styles of writing. For example, in Fig-
ure 2, a series of input messages submitted by user j
are given to the submitter identifier. Then, the iden-
tifier determines that the series of of input messages
were submitted by user i. In this case, our method de-
termines that user i and j have similar styles of writ-
ing. In this way, the key to detecting users of similar
writing styles is the user classifiers. As a result, we
explain below how to develop these user classifiers.
Suppose that user (rank i) submitted l answers to
a communication site, ranked i-th place in the ranking
of frequent answer submitters, and is the target user
of classifier (rank i). When a series of m answers of
Table 3: The number of target users in PC, healthcare, and
social issues category.
PC healthcare social issues
submitters 395 134 312
messages 260183 57406 180503
user (rank j) are given to classifier (rank i), probabil-
ity score score(i, j) that user i and j were one and the
same user and user i submitted the series of m answers
is calculated as follows:
score(i, j) =
m
∏
k=1
P
ijk
(in case of
m
∏
k=1
P
ijk
>
m
∏
k=1
(1− P
ijk
))
0 (in case of
m
∏
k=1
P
ijk
≤
m
∏
k=1
(1− P
ijk
))
where P
ijk
is the probability that user i submitted mes-
sage k (1 ≤ k ≤ m) in the series of m messages of user
(rank j). P
ijk
is calculated by classifier (rank i), which
was developed by learning stylistic features of user
(rank i). Training data for learning stylistic features
of user (rank i) consists of
• n messages which were selected randomly from l
messages submitted by user (rank i), and
• n messages which are extracted randomly from
messages submitted by other users.
In this study, we used the maximum entropy (ME)
method for data training. Figure 3 shows feature
s1 ∼ s7 used in machine learning on experimental
data. s1 and s2 were obtained by using the results of
the morphological analysis on experimental data. s3
and s4 were obtained by extracting character 3-gram
from experimental data. This is because Odaka et al.
reported that character 3-gram is good for Japanese
processing (Odaka 03). s5 and s6 were introduced
because, we thought, clue expressions to the author
identification are often found at the head and end of
sentences. s7 was obtained by using PrefixSpan
3
.
PrefixSpan is a method of mining sequential patterns
efficiently and often used in document classification.
By using PrefixSpan, Tsuboi et al. identified mail
senders (Tsuboi 02) and Matsumoto et al. classified
reviews into positive and negative ones (Matsumoto
04).
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
To evaluate our method, we conducted the following
experiments:
3
http://prefixspan-rel.sourceforge.jp/
DETECTION OF SUBMITTERS SUSPECTED OF PRETENDING TO BE SOMEONE ELSE TO MANIPULATE
COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMMUNITY SITE
169
experiment 1 The accuracy measurement of the user
classifiers.
experiment 2 The accuracy measurement of the sub-
mitter identifier.
experiment 3 The detection of users who have simi-
lar styles of writing and submitted answers to the
same questions.
In this experiment, the target users were all sub-
mitters who submitted over 200 answer messages to
PC, healthcare, or social issues category in Yahoo!
chiebukuro. Table 3 shows the numbers of target sub-
mitters and their messages in each category.
75
80
85
90
95
100
1 2 3 4 5
percent accuracy
number of input messages (answers)
training data (100 ans.)
PC
healthcare
social issues
(a) training data (100 answers)
75
80
85
90
95
100
1 2 3 4 5
percent accuracy
number of input messages (answers)
training data (200 ans.)
PC
healthcare
social issues
(b) training data (200 answers)
75
80
85
90
95
100
1 2 3 4 5
percent accuracy
number of input messages (answers)
training data (300 ans.)
PC
healthcare
social issues
(c) training data (300 answers)
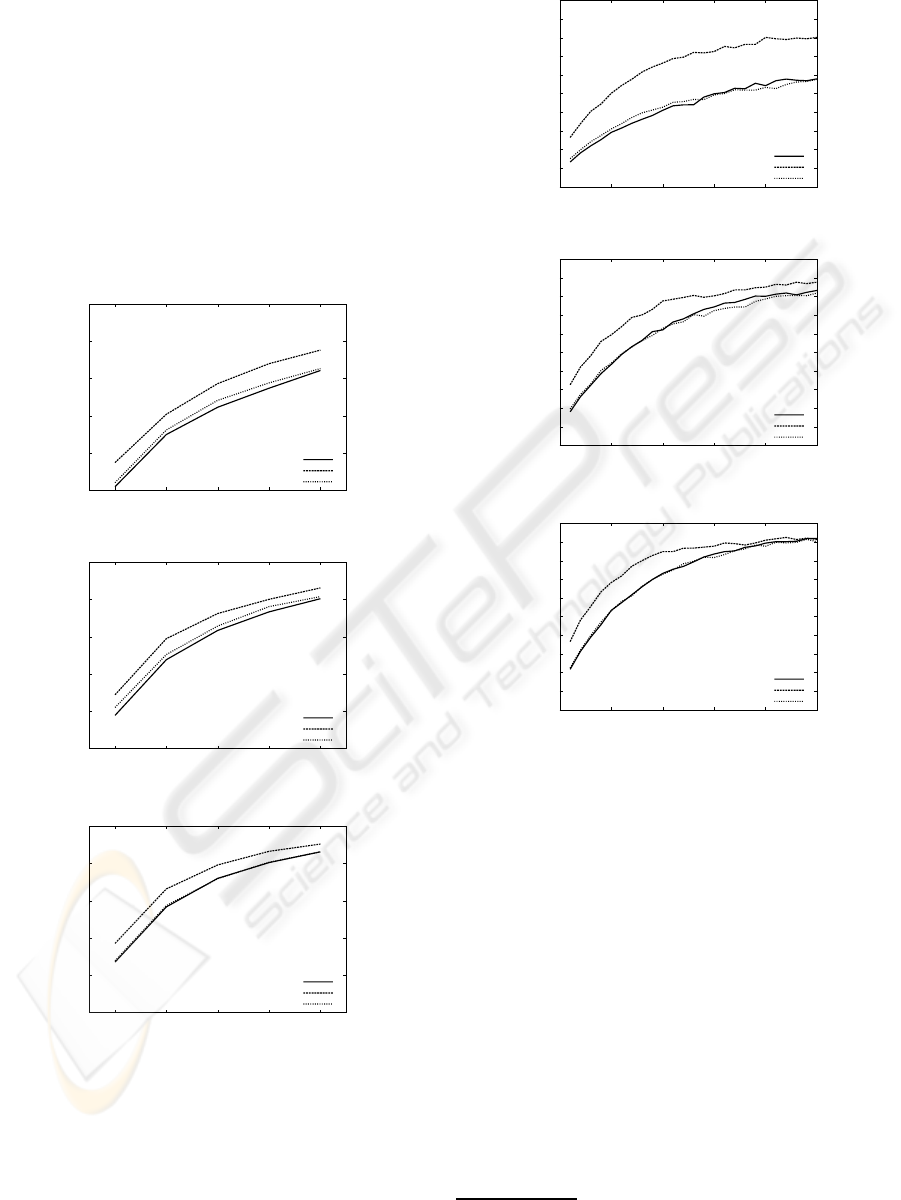
Figure 4: The accuracy of the classifiers which determine
whether a series of messages were submitted by their target
users, under the various number (1 ∼ 5) of input messages
and the various size (100, 200, and 300 messages) of train-
ing data. The target users were all submitters who submit-
ted over 200 answer messages to PC, healthcare, and social
issues category in Yahoo! chiebukuro.
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
5 10 15 20 25
percent accuracy
number of input messages (answers)
training data (100 ans.)
PC
healthcare
social issues
(a) training data (100 answers)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
5 10 15 20 25
percent accuracy
number of input messages (answers)
training data (200 ans.)
PC
healthcare
social issues
(b) training data (200 answers)
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
5 10 15 20 25
percent accuracy
number of input messages (answers)
training data (300 ans.)
PC
healthcare
social issues
(c) training data (300 answers)
Figure 5: The accuracy of the identifier which determines
by whom a series of messages were submitted, under the
various number (1 ∼ 25) of input messages and the vari-
ous size (100, 200, and 300 messages) of training data. The
target users were all submitters who submitted over 200 an-
swer messages to PC, healthcare, and social issues category
in Yahoo! chiebukuro.
We developed experimental data for data training
and examination in the next way. First, in order to de-
velop experimental data of examination, we extracted
50 messages from each user’s messages. Then, from
the other messages of each user, we extracted 50, 100,
and 150 messages and, as mentioned in section 3, de-
veloped three different sizes (100, 200, and 300 mes-
sages) of experimental data for data training. In the
experiments, we used a package for maximum en-
tropy method, maxent
4
, for data training. We also
4
http://www2.nict.go.jp/x/x161/members/mutiyama/
software.html#maxent
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
170

Table 4: The numbers of user pairs who have similar styles
of writing and submitted answers to the same questions.
frequency of submissions
to the same questions
category one or more ten or more
PC 87 12
healthcare 17 0
social issues 109 22
used a Japanese morphological analyzer, Mecab
5
, for
word segmentation of messages.
In experiment 1, we first developed user classifiers
by applying maximum entropy (ME) method to the
training data. Then, we varied the numbers of input
messages to the classifiers and measured the accuracy
of them. Input messages were extracted from the ex-
perimental data for examination. Figure 4 shows the
accuracy of the classifiers under the various numbers
(1 ∼ 5) of input messages and the various sizes (100,
200, and 300 messages) of training data. As shown in
Figure 4, we obtained more than 95% accuracy when
we set the size of training data and the number of in-
put messages to be 300 (including 150 target user’s
messages) and 4, respectively. Furthermore, we found
character 3-gram (s3) and 1 ∼ 10 characters at the
head and end of sentences (s5 and s6) are effective to
this experiment.
In experiment 2, we measured the accuracy of the
identifier. It consisted of N classifiers, the accuracy
of which are shown in Figure 4. Figure 5 shows the
accuracy of the identifier under the various numbers
(1 ∼ 25) of input messages and the various sizes (100,
200, and 300 messages) of training data. As shown in
Figure 5, we obtained more than 80% accuracy when
we set the size of training data and the number of in-
put messages to be 300 (including 150 target user’s
messages) and 15, respectively.
In experiment 3, because we wanted to use the
identifier with more than 85 % accuracy, we gave
training data consisting of 300 messages (including
150 target user’s messages) and set the number of in-
put messages to be 16. Table 4 shows the numbers
of user pairs who have similar styles of writing and
submitted answers to the same questions. In this ex-
periment, we found two user pairs suspected of pre-
tending to be someone else to manipulate communi-
cations. Those user pairs submitted answers to the
same questions in social issues category 43 and 17
times, respectively. We intend to examine whether
these user pairs are multiple account users, from var-
ious perspectives.
5
http://mecab.sourceforge.net/
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we proposed a method of detecting users
who have similar styles of writing and submitted an-
swers to the same questions in a community site fre-
quently. Our method detected some user pairs sus-
pected of pretending to be someone else and manip-
ulating communications in a community site. We in-
tend to examine this experimental results and refine
our method. Then, we wish to contribute to learners
in community sites.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has been supported partly by the
Grant-in-Aid for Scientific Research (C) under Grant
No.20500106.
REFERENCES
Craig: Authorial attribution and computational stylistics:
if you can tell authors apart, have you learned any-
thing about them?, Literary and Linguistic Comput-
ing, 14(1), (1999).
de Vel, Anderson, Corney, and Mohay: Mining e-mail con-
tent for author identification forensics, ACM SIG-
MOD Record, 30(4), (2001).
Koppel, Argamon, and Shimoni: Automatically Categoriz-
ing Written Text by Gender, Literary Linguistic and
Computing, 17(4), (2002).
Corney, de Vel, Anderson, and Mohay: Gender-Preferential
Text Mining of E-mail Discourse, ACSAC 2002,
(2002).
Argamon, Saric, and Stein: Style mining of electronic mes-
sages for multiple authorship discrimination: first re-
sults, 9th ACM SIGKDD, (2003).
Zheng, Li, Chen, and Huang: A Framework of Author-
ship Identification for Online Messages: Writing Style
Features and Classification Techniques, Journal of the
American Society for Information Science and Tech-
nology, 57(3), (2006).
Odaka, Murata, Gao, Suwa, Shirai, Takahashi, Kuroiwa,
and Ogura: A Proposal on Student Report Scoring
System Using N-gram Text Analysis Method, IEICE
trans., J86-D-I(9), (2003).
Tsuboi and Matsumoto: Authorship Identification for Het-
erogeneous Documents, ISPJ-NL-148, (2002).
Matsumoto, Takamura, and Okumura: Sentiment Classifi-
cation using Word Sequences and Dependency Trees,
FIT2004, (2004).
DETECTION OF SUBMITTERS SUSPECTED OF PRETENDING TO BE SOMEONE ELSE TO MANIPULATE
COMMUNICATIONS IN A COMMUNITY SITE
171
