
FIELD REPORT ON FIVE YEARS OF eLEARNING
Observations and Inspirations
Heiko Sturzrehm, Claire Fautsch and Peter Kropf
Institut d’informatique, Universit´e de Neuchˆatel, Neuchˆatel, Switzerland
Keywords:
eLearning, Course evaluation, Case study.
Abstract:
Due to the limitations of staff, especially at small universities, eLearning is a perfect addition to traditional
courses. Nonetheless, the development and maintenance of online courses is not trivial. The usage of these
courses can also be quite challenging for students, who are generally familiar with traditional lectures.
In this paper, we are contributing our experience in creating and maintaining online courses. We will also
describe different types of blended and pure online courses used in our department. Some of the observations
made during this evaluation do not only apply for online courses, but are also true for traditional courses.
Finally several interesting features to improve eLearning are presented.
1 INTRODUCTION
The advances in computer and network technologies
over the last decade resulted in a continuously grow-
ing availability of Internet services and networked ap-
plications. Following this development, many univer-
sities started to offer online courses.
The advancement of eLearning is not only rec-
ognized by universities, but also the industry discov-
ered the advantages of eLearning. particularly to pro-
vide continuing education to their employees. Com-
pared to a traditional course or workshop, an eLearn-
ing course does not require all participants to attend
the course at the same time. Rather, it offers partic-
ipants the opportunity to define individual schedules
that allow them to optimize their use of time. Fur-
thermore, the employer can easily oversee the profes-
sional development of his/her employees. IBM, for
example offers online training not only for its em-
ployees, but also to those of other companies (IBM
Training, 2009).
Most eLearning courses consist of text, graphics
and remote hands-on exercises. They can be used as
a complement or as a replacement for traditional lec-
tures. When eLearning content is supporting regular
courses it is referred to as blended learning.
In this paper we present an overview of current
learning methods used at the Computer Science De-
partment of the University of Neuchˆatel (Switzer-
land), as well as observations made from their usage.
The presented learning methods are in use since about
5 years. The contribution of this paper is an evalua-
tion of online and blended courses from the perspec-
tive of the tutors and developers. First, we will ex-
plain some contextual particularities of the universi-
ties in Switzerland, followed by a discussion of re-
lated work. Section 2 describes the context and back-
ground of our eLearning activities, which are then re-
viewed in the following section. Our proposals to im-
prove eLearning are presented in Section 4. Finally
we conclude our work in Section 5.
1.1 Swiss Context
In the year 2000 the Swiss Virtual Campus project
(SVC) (Swiss Virtual Campus, 2009) was launched.
Its main goal was the development of internet-based
courses at the Swiss institutions of higher education.
Nine years later, 82 courses were available covering
a wide range of disciplines, from computer science to
law or history. One requirement for the development
of these courses was that at least three different insti-
tutions had to participate in their creation.
The SVC closely collaborates with the SWITCH
foundation (SWITCH, 2009), which provides Swiss
wide IT-solutions at institutions of higher education.
One of its services is SWITCHaai, a single sign-on
solution for eLearning and web applications available
to all participating universities in Switzerland. The
SWITCHaai service (see Fig. 1) is improving inter-
operability, privacy, security and trust. Through this
large scale user management system, students can at-
317
Sturzrehm H., Fautsch C. and Kropf P. (2010).
FIELD REPORT ON FIVE YEARS OF eLEARNING - Observations and Inspirations.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 317-324
DOI: 10.5220/0002779003170324
Copyright
c
SciTePress
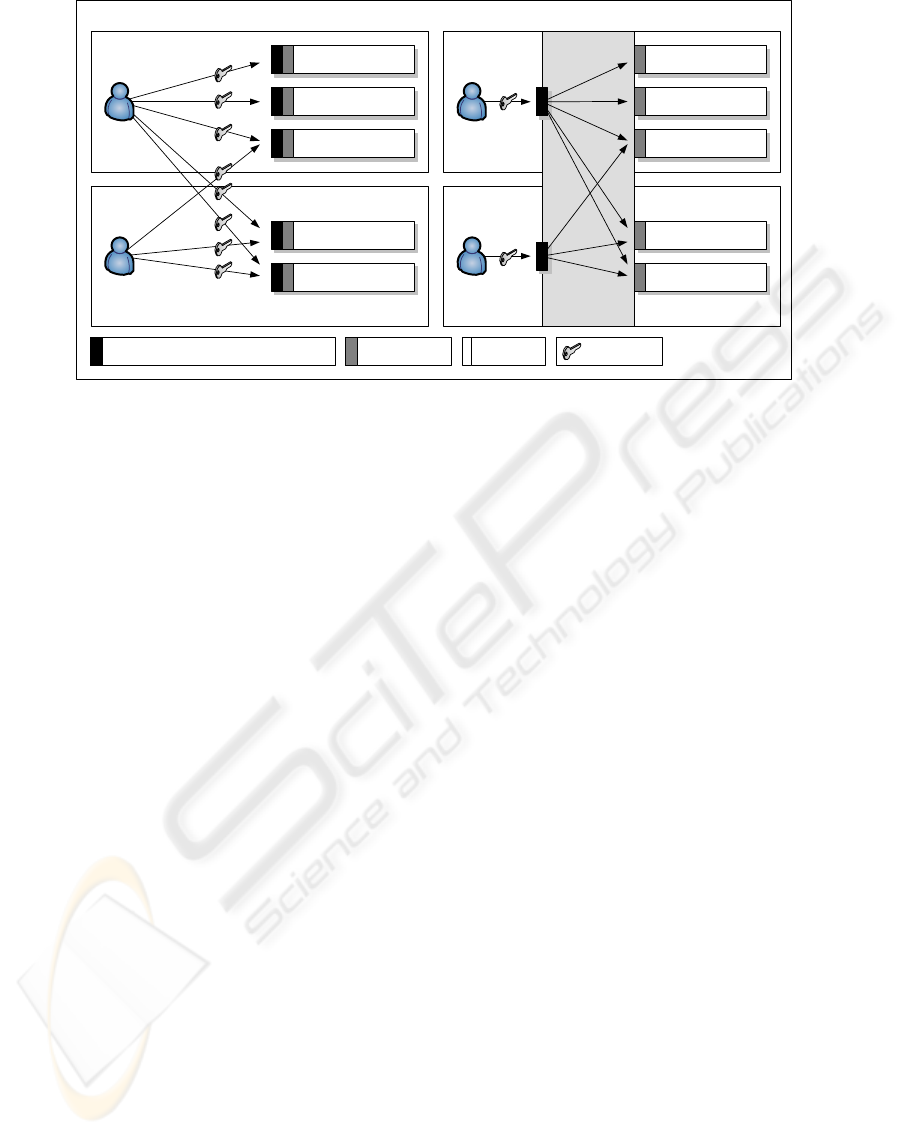
Authorization Resource Credentials
University A
University B
Stud. Admin
Web Mail
E-Learning
Research DB
E-Learning
without SWITCHaai
University A
University B
SWITCHaai
Stud. Admin
Web Mail
E-Learning
Research DB
E-Learning
with SWITCHaai
User Administration / Authentication
Figure 1: Features of SWITCHaai.
tend all SVC courses independently from the location
of their home university.
Most Swiss universities are quite small compared
to the ones in other European countries. As a result,
the collaboration between them is well established.
One of these collaborations is the BeNeFri network
of universities (BeNeFri Network, 2009). All stu-
dents enrolled at the Universities of Bern, Neuchˆatel
and Fribourg can attend courses and acquire credits
at the other facilities. Furthermore, the schedules are
adapted to their needs taking into account that the
travel time between the facilities is at most one hour
by train.
One particularity of BeNeFri concerns the differ-
ent teaching languages. In Bern, the main language
is German, in Neuchˆatel it’s French, and in Fribourg
both languages are used in classes. However, with
the introduction of BeNeFri, more and more classes
are taught in English at all three universities. With
the help of joint online courses, the time the students
need to travel can be reduced and a larger variety of
courses can be offered to the students.
1.2 Related Work
eLearning has been regularly used at universities for
more than a decade. Consequently many of them
are evaluating those courses now. For instance,
Jung et al. (Jung et al., 2008) are focusing their analy-
sis on the acceptance of eLearning by the users. They
identified a relation between the student’s perceived
usefulness of an eLearning system and the student’s
attitude towards it. Therefore, it is very important to
explain the system to the students and to guide them
appropriately, in order to improve the student’s atti-
tude toward the course.
Dalsgaard is focusing more on the self-organized
learning aspect (Dalsgaard, 2006). He concludes that
Web 2.0 tools like wikis or blogs can be used to sup-
port independent lifelong learning. When using these
tools in a self-governed and problem-based learning
approach they could improve the learning impact.
Unfortunately eLeaning courses at universities can
not be as open-endedas proposedby him, because de-
gree programs are always aiming a certain goal, e.g.,
graduating or passing a course exam.
Concerning hands-on laboratories many imple-
mentations are available by now, e.g., VISIR (Vir-
tual InstrumentSystems In Reality) fromthe Blekinge
Institute of Technology (Sweden) (Gustavsson et al.,
2008) or our NeOS (Neuchtel Online System)
(Sturzrehm et al., 2008). Unfortunately, most of them
can only be used in a certain area of expertise. VISIR
is a hands-on tool, which allows students to perform
electrical engineering experiments from home. Some
of these experiments would normally include quite
expensive lab equipment, which can be simulated to
prevent damages, or be remotely shared between uni-
versities to reduce costs. On the other hand our NeOS
is constrained to programming tasks and could hardly
be used in other domains.
2 APPLICATION
We will start our case study with a description of
the eLearning architecture used at the University
of Neuchˆatel, followed by brief descriptions of our
eLearning and blended learning courses.
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
318

2.1 Technologies in Use
For the traditional lectures at the University of
Neuchˆatel the open source eLearning platform Claro-
line (Claroline, 2009) is used
1
. Unfortunately, often
only a few of the available features of the system are
utilized, e.g., the system is used as a storage for pre-
sentation slides or as submission portal for exercises.
Other available features included such as chat, forum
or wiki are rarely used.
Another platform, called WebCT
1
from Black-
board (WebCT, 2009), is used for the BeNeFri on-
line courses, which are part of the SVC. Again the
mainly used feature is the content storage, but in con-
trast to traditional lectures the content is presented in
the form of HTML documents. The evaluation of the
students’ acquiredknowledge is done using this portal
with multiple choice questions and hands-on experi-
ments.
Since some of our experiments can only handle
one user at a time, we need to schedule their access.
For those hands-on tasks, we are using a custom built
reservation system (Wulff et al., 2008) allowing the
students to reserve a time slot for conducting their ex-
periments.
In order to protect the lab machines, we are us-
ing the architecture (Braun et al., 2006) shown in Fig-
ure 2. The lab machine is protected from the inter-
net with a firewall which can only be passed through
a ssh connection. When the students want to access
the lab machine, they have to connect to the Apache
Tomcat web server (Apache Tomcat, 2009), which is
using the Shibboleth (Shibboleth, 2009) plug-in. This
plug-in serves as connectorto the SWITCHaai andthe
reservation system. After successful authentication
the student can access the lab machine via a single-
use ssh channel. Normally the access is granted for
one hour. Afterwards the ssh account is disabled.
The technologies used for the exercises are di-
verse. In one task, the students have to configure
routers and switches using a Java applet serving as
network simulator. In an other task the students have
to implementa driver for an USB radio device in the C
language. To realize this assignment, they have con-
sole access to the lab machine to which the device is
connected.
In order to generalize the implementation environ-
ment for assignments, we developed a configurable
hands-on application called NeOS (Sturzrehm et al.,
1
The decision to use the mentioned software is not part
of this publication, nor is this an evaluation of those plat-
forms. The presentation and discussions related to specific
eLearning platforms shall then be considered without loss
of generality.
Apache Tomcat Web Server
with Shibboleth plug-in
Lab Machine
SWITCHaai
User PC
Reservation System
Figure 2: Architecture for our hands-on tasks.
2008). It is using the same architecture as described
above and consists of a Java applet located on the
Shibboleth web server and a Java application on the
lab machine. Both parts allow users to locally pro-
gram in an editor-like user interface and then test the
program on a well secured remote machine. Dur-
ing this test run the implementation is automatically
evaluated and a feedback is returned to the student.
When their program successfully solves the task, an
encrypted file is sent to the student. This file is sub-
mitted to the course portal as final solution. The en-
cryption enables us to identify the student and raises
the efforts needed to betray. For the decryption of this
file, so that the tutor can grade it, our framework is
aiding the tutor with a small application. This tool
is also supporting a cross check system for detecting
plagiarism in the solutions.
2.2 SVC Online Courses
Our department took part in the development of two
online courses created for the SVC. Both courses use
English as teaching language.
The first course covers the topics of telecommu-
nications and computer networks and is called Vir-
tual Internet and Telecommunications Laboratory of
Switzerland (VITELS) (VITELS, 2009). It was a
joint development of the universities of Bern, Fri-
bourg, Geneva and Neuchˆatel as well as the Engineer-
ing School of Fribourg. Ten modules were available
covering the following content: (i) Simulation if IP
Network Configuration, (ii) Client/Server Concepts,
(iii) IP Security, (iv) Sockets and RPC, (v) Remote
Method Invocation, (vi) Application Server, (vii) Se-
curity and Privacy in the Internet, (viii) Firewall Man-
agement, (ix) Protocol Analysis, and (x) Wireless
LAN. After several years of usage, only the first seven
modules are still available, due to technical limita-
tions.
After the creation of the VITELS course, a sec-
FIELD REPORT ON FIVE YEARS OF eLEARNING - Observations and Inspirations
319
ond course was created learning from the experiences
made with VITELS. This course is covering the top-
ics of operating systems and is called Operating Sys-
tem Laboratory (OSLab) (OSLab, 2009). The partic-
ipants for this project were the universities of Bern,
Fribourg and Neuchˆatel as well as the University of
Rostock (Germany). At the moment five modules
out of seven are available, namely (i) Device Driver
and Input/Output, (ii) Process Scheduling, (iii) Mem-
ory Management, (iv) File Systems, and (v) Security.
The modules Distributed File Systems and Inter Pro-
cess Communication are still under development and
should be released soon.
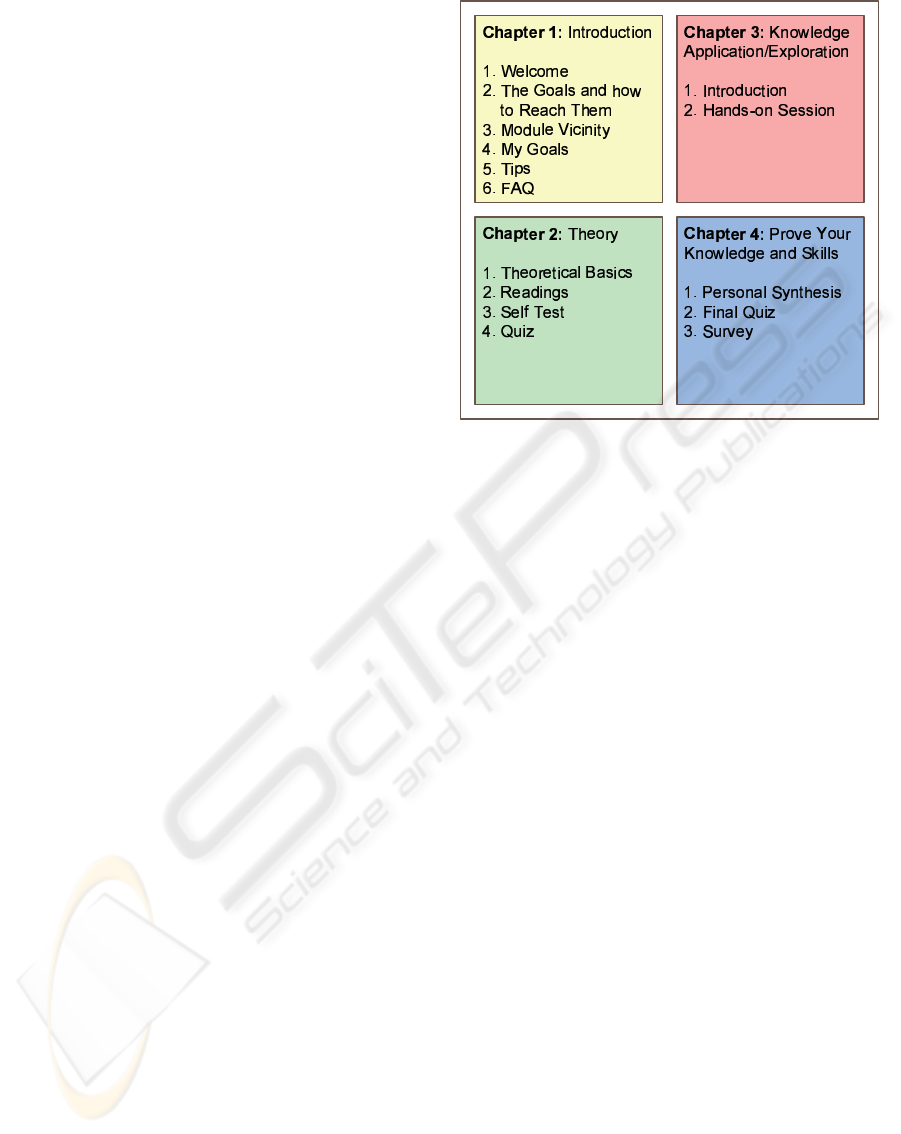
Both courses follow the same general scheme ( 3)
based on Bloom’s new Taxonomy (Passig, 2003), an
updated version of Bloom’s Taxonomy (Bloom et al.,
1964). First, the topic is introduced and requirements
for this module are presented. In the second chap-
ter, the theory of this module is conveyed to the stu-
dents. It consists of replenished lectures and required
or recommended readings, e.g., papers or books. At
the end of this part, the students can perform a self
test to check their knowledge. Afterwards, they have
to prove their knowledge of the theory in complet-
ing a quiz consisting of multiple choice and free re-
sponses. In the third chapter, the students must apply
their knowledge in hands-on sessions. These sessions
are all available online, as described in Section 2.1.
Some exercises require real hardware which is ac-
cessed remotely, while for others the hardware is sim-
ulated. After mastering the hands-on sessions the stu-
dents can finalize the module with a conclusive test.
For the final evaluation of the course the students have
to pass an oral exam to demonstrate their knowledge
of all completed modules.
2.3 Blended Learning
As mentioned previously, the Claroline platform is
used at our university for blended learning. As an
example we will present the advanced software en-
gineering (ASE) course and exercises held at our de-
partment since several years. The goal of the course
is to familiarize the students with the application of
sophisticated software development tools and devel-
opment cycles. The theory is presented in traditional
lectures with slides. Those are made available online
on the course portal a posteriori. In the exercises the
students have to solve task sheets and submit their re-
sults to the portal. The tasks range from programming
to sketching rapid prototypes. The evaluation of their
tasks is presented to them as well via the Claroline
platform.
Figure 3: Structure of our online course modules.
3 OBSERVATIONS
This section considers the observations we have made
using the two online courses, VITELS and OSLab,
and the blended course ASE. The two online courses
are offered to the students since five (VITELS) re-
spectively three (OSLab) years. The blended learn-
ing approach is already in use since eight years at our
university.
3.1 Students
A first major observation made during five years of
eLearning is that only a motivated and interested stu-
dent is capable to fully benefit from an online course.
An unmotivated student, doing the course only be-
cause he/she has to, is likely to postpone the workload
as long as possible. This will result in average perfor-
mance. In our opinion, it is therefore important to fix
a schedule for each task and to present the content in
an interesting way.
Another fact that occurred to us, is the minimal
knowledge the students retain from online courses.
There is a discrepancy between the knowledge the
students think they acquired and the knowledge they
actually have absorbed. During the final oral exams,
we realized many times that students can remember
headingsof a topic, but unfortunately not the morede-
tailed content. Or they cannot apply or combine their
knowledge. Normally, those students just printed out
the content of the course or read it online. They
missed to take notes, either electronically or on pa-
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
320

per. Furthermore, it seems that they are not able to
differentiate between important information and facts
included in the course and secondary or additional in-
formation.
A further problem is that not all available modules
of the proposed eLearning courses require the same
amount of work from the students, however the same
number of credits is given to each module. As a re-
sult students are preferringthe ones with the least per-
ceived effort, since they can chose which module they
take.
Also, the audio-visual absorption of knowledge
during a traditional lecture is missing, which in our
opinion improves the long term memorization. Even
though the students may not actively listen, they still
learn subconsciously (implicit learning (Cleeremans,
1997)). In addition, the tutor might spontaneously
point out important features, which is not possible
for a self-learning course. Later, when students are
preparing the exam, the probability of losing this
memory is quite high. The students concentrate them-
selves on the passing of the exam and thus forget that
the long term memorization and especially applica-
tion of knowledge are actually the main goals of their
studies.
In some of the VITELS hands-on exercises the
students had to program on a distant lab machine via
the console. With the improvement of the Internet
technologies we wanted to support them with a bet-
ter programming environment. We therefore intro-
duced the NeOS framework in the hands-on exercises
of the OSLab. It provided them with an editor-like
Java applet in which they could implement their tasks.
Nonetheless, most students just programmed in their
favorite integrated development environment (IDE),
like Eclipse (Eclipse IDE, 2009) or NetBeans (Net-
beans IDE, 2009), and copied their solutions to our
tool. According to the students’ statements, their
main reason to use an external IDE rather than the
proposed one, was the lack of automatic correction
and error detection offered by the IDE, i.e., missing
features.
In our online courses the students have to plan
their advancement on their own ensuring a maximum
of flexibility. As a result, quizzes and tests are done at
different times, but still they have always the same
questions. So there is a high probability that they
just exchange the questions and answers among each
other.
3.2 Tutors
In this section we briefly outline the experiences of
tutors with online and blended courses and the chal-
lenges they face. We refer to tutor as the person which
the students approachif they need any assistance. The
responsibilities of the tutor are generally limited to
maintain the course portal and guide the students. It
is thus important to offer the tutors an introduction to
the handling and usage of the respective platforms.
For eLearning courses, evaluating quizzes is also
part of the tutor’s task. Commonly used eLearning
platforms provide evaluation tools, e.g., showing the
student’s solutions as well as the expected solution.
For multiple choice tests, a pre-evaluation can be pro-
vided. This approach considerably simplify the task
of the tutor. However, the exercises and the solutions
are generally provided by the developers, knowledge-
able of the topic, at the same time the course is cre-
ated. It can thus happen that the solutions are very
short or incomplete, especially if the developers as-
sume that the tutors are also knowledgeable of the
topic, which is not necessary the case.
Another problem that might occur with predefined
solutions, is that they are out of date. For instance, in
the server-client module of VITELS, one task of the
students is to collect HTML communications with a
certain web server. Over the years, the used technol-
ogy on this server changed, resulting in a discrepancy
to the original solution. Therefore there should exist
a defined cycle for regular updating these courses.
For blended courses, the tutor is generally assist-
ing the course instructor. The tutor prepares and holds
exercise sessions and gives assistance to the students.
The tutor also manages the online platform for the
given course, e.g., making the slides of the courses
available, handling the submitted exercises, or mak-
ing announcements.
A problem observed using blended learning con-
cerned the evaluation of tasks. It happens that stu-
dents submit their solutions by email or by paper
rather than using the online portal. Introducing the
evaluation results in the platform can then be quite
complicated, since one can only evaluate content di-
rectly submitted to the portal. In fact, the tutor nor-
mally has to use an alternative method to store the re-
sults of the students, e.g., on paper or in spread sheets.
These other result collections are most of the time
not available online. Consequently, the students need
also to store their results externally. A solution to this
problem is to inform the students of the procedures
to be used, and grade only assignments correctly sub-
mitted.
3.3 Developers
Besides students and tutors, developers play an im-
portant role in eLearning courses. Online courses are
FIELD REPORT ON FIVE YEARS OF eLEARNING - Observations and Inspirations
321

often developed in the boundaries of a project last-
ing only a few years, but the course will be used over
a longer time period. Staff members (e.g., PhD stu-
dents) are enrolled to design the courses, however,
due to the academic environment, the staff changes
rapidly. Consequently, it is possible that different per-
sons are in charge of initial planing, final stage, main-
tenance and tutoring. Even though each step is doc-
umented, details on technical issues, interpretation of
exercises, or content might be lost, making especially
maintenance and tutoring difficult.
In most cases the content for an online course is
already available from a traditional lecture. Still, the
adaption is not trivial, since the slides of a lecture are
not presenting the whole course. Often the profes-
sors are adding additional content like examples or
explaining certain points in detail.
Another issue can occurin the development of for-
eign language courses, but not exclusively. When cre-
ating the content, typing or grammatical errors can
occur. To minimize those, peer reviews and profes-
sional editing are important and recommended. Ad-
ditionally, a cooperate design should be chosen for the
whole course to improve recognition.
4 PROPOSALS TO IMPROVE
ONLINE COURSES
In the previous sections we presented our experiences
with blended learning and eLearning. In this section,
we discuss several approaches which could improve
all kinds of blended learning and eLearning.
4.1 Motivation
In this first part we want to point out strategies to
increase the morale of the students. Lately casual
games have become quite a big economical success,
e.g., games like Dr. Kawashima’s Brain Age for the
Nintendo DS (a.k.a. Brain Training). This game is
based on the research of Dr. Kawashima (Kawashima,
2005). Those games consist of a collection of mini
games, i.e., games which normally last just a few
minutes. With the success rate and a success graph
the user is motivated to improve and redo the games.
Those games can address many different skills, men-
tal and physical ones. For instance skills like dex-
terity, eye reaction, calculating, foreign languages or
logic can be conveyed.
Our proposal is to apply this concept as well to
eLearning courses, so the students are learning by
playing. In the domain of computer networks for ex-
ample, imagine a game where the student is acting
as a firewall and has to decide if arriving or depart-
ing packets pass or have to be blocked. The time the
student needs to process a certain amount of pack-
ets correctly can be used as indicator for their perfor-
mance. One could also support the student with dif-
ferent tools, which are an abstraction of real used ap-
proaches, e.g., black or white lists. Additionally, the
students could have the possibility to compare their
results with their colleagues or play in an attacker-
defender scenario.
Another idea concernsthe adaptionof the achieve-
ment concept also known from computer games. It is
used to award special behavior or achieved goals. In
terms of online courses it could be used to motivate
the students to solve their task very well. The reward
could for instance be a joker for another exercise or
the oral exam, i.e., the student could ask for a small
clue in a question.
4.2 Memorization
As we mentioned already in Section 3.1 it is impor-
tant that students do more than just reading the theory.
Therefore we present below features to overcome this
gap.
For instance, it could be useful that each time the
students enter the course portal, they have to answer a
question regarding already finished modules, or there
could be a pop-up window in the portal with a known
content randomly chosen. A very experimental ap-
proach could be that only students with good results
from the daily quizzes can unlock the additional or
following content.
In Section 3.2 we outlined the difficulties with
shifted schedules and their influence on quizzes. As
a solution we think a randomized test would be ap-
propriate. When the questions the students are asked
vary, it becomes useless to pass on the questions and
solutions to the fellow students. Of course, the de-
velopers of a course have to create more than twice
more questions and they shoould be replaced over
time. Eventually, each question could also be given a
level of difficulty, in order to present to each student a
variety of questions with different levels of difficulty.
To support students not just with plain text or pic-
tures, maybe an audio book of the content could be
helpful. They could listen to it while reading the con-
tent or doing other activities. The audio stream could
contain additional examples or could explain pictures
in a more detailed way.
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
322

4.3 Simplicity
Last but not least, the usability of online courses
should not be disregarded, since the student should
focus on the content and not on the handling of the
interface.
In the OSLab course (see Section 3.1), most of the
students used the Eclipse IDE. Since this is an open
source platform supportingplug-ins, we think it could
be a good improvement to create an interface to our
secured architecture. It would have the advantage that
the students can program in their usual environment
while still providing the needed security for the access
to the lab machines.
In our opinion, eLearning environments could be
improved by using a topic specific wiki for the con-
tent, which can only be edited by approved tutors.
This could be done nation- or world-wide to gather
the knowledge for a specific lecture topic. With a spe-
cial license, e.g., Creative Commons (Creative Com-
mons, 2009), the content could then be reused in other
eLearning courses, which is not necessarily the case
with books.
It could also be a great advantage to use a stan-
dard content creation language, independent from the
used content management system. For instance wiki-
or Tex-based systems would be a good solution, since
these markup languages are widely used at universi-
ties and are designed for easy content creation and
document layout.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this field study we presented the eLearning envi-
ronment (SVC and the SWITCH) as used in Switzer-
land. Furthermore, we described our two online
courses (OSLab and VITELS) and presented our re-
alization of the blended learning concept.
In the following parts we analyzed the attitude of
students, tutors, and developers, resulting in possi-
bly new approaches to improve eLearning as well as
blended learning courses, from the view point of the
staff.
The main observation of this paper is the high rel-
evance of the students’ motivation. Contrary to tra-
ditional courses, online courses do not have regular
schedules, where for instance the students have to
attend once a week lectures and exercises. Further-
more, the content of an eLearning course should be
presented in an attractive and diversified way in order
to keep the studentsfocusedover a longer time period.
In addition, the students should not have the impres-
sion that eLearning courses are a burden or a free ride
compared to traditional courses. Otherwise, eLearn-
ing courses will not be accepted by the students and
thus conventional courses would lead to greater suc-
cess.
REFERENCES
Apache Tomcat (20-Oct-2009). http://tomcat.apache.org/.
BeNeFri Network (20-Oct-2009).
http://www.unifr.ch/benefri/de.
Bloom, B. S., Mesia, B. B., and Krathwohl, D. R. (1964).
Taxonomy of Educational Objectives. David McKay,
New York.
Braun, T., Graf, C., Ultes-Nitsche, U., Baier, A., and
Bernoulli, T. (2006). Case study of the usage of an
authentication and authorization infrastructure (aai) in
an e-learning project. In Proceedings of the ISSA 2006
from Insight to Foresight Conference. ISSA, Pretoria,
South Africa.
Claroline (20-Oct-2009). http://www.claroline.net/.
Cleeremans, A. (1997). Principles for Implicit Learning.
Oxford University Press.
Creative Commons (20-Oct-2009).
http://creativecommons.org/.
Dalsgaard, C. (2006). Social software: E-learning beyond
learning management systems. European Journal of
Open, Distance, and E-Learning, 2006(2).
Eclipse IDE (20-Oct-2009). http://www.eclipse.org/.
Gustavsson, I., Zackrisson, J., Nilsson, K., Garcia-Zubia, J.,
H˚akansson, L., Claesson, I., and Lag¨o, T. (2008). A
flexible instructional electronics laboratory with local
and remote lab workbenches in a grid. In Proceedings
of the 2nd International Workshop on e-learning and
Virtual and Remote Laboratories. Universit¨atsverlag
Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany.
IBM Training (20-Oct-2009).
http://ibm.com/training/us/certify.
Jung, M.-L. L., Loria, K., Mostaghel, R., and Saha, P.
(2008). E-learning: Investigating university student’s
acceptance of technology. European Journal of Open,
Distance, and E-Learning, 2008(2).
Kawashima, R. (2005). Train Your Brain: 60 Days to a
Better Brain. Kumon Publishing North America, Tea-
neck.
Netbeans IDE (20-Oct-2009). http://www.netbeans.org/.
OSLab (20-Oct-2009). http://www.oslab.ch/.
Passig, D. (2003). A taxonomy of future higher thinking
skills. Informatics in education, 2(1):79–92.
Shibboleth (20-Oct-2009). http://shibboleth.internet2.edu/.
Sturzrehm, H., Aubert, F., Kropf, P., and Corfu, R. (2008).
Neos: Neuchˆatel online system. In Proceedings of
the 2nd International Workshop on e-learning and
Virtual and Remote Laboratories. Universit¨atsverlag
Potsdam, Potsdam, Germany.
FIELD REPORT ON FIVE YEARS OF eLEARNING - Observations and Inspirations
323

Swiss Virtual Campus (20-Oct-2009).
http://www.virtualcampus.ch/.
SWITCH (20-Oct-2009). http://switch.ch/.
VITELS (20-Oct-2009). http://www.vitels.ch/.
WebCT (20-Oct-2009). http://www.blackboard.com/.
Wulff, M., Lauer, P., and Braun, T. (2008). Content man-
agement and architectural issues of a remote learning
laboratory. In Proceedings of the 2nd International
Workshop on e-learning and Virtual and Remote Lab-
oratories. Universit¨atsverlag Potsdam, Potsdam, Ger-
many.
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
324
