
THE NEED FOR SPECIAL GAMES
FOR GAMERS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS
Andrea Hofmann, Imke Hoppe and Klaus P. Jantke
Fraunhofer Institute for Digital Media Technology IDMT, Children’s Media 99084 Erfurt, Germany
Keywords: Serious games, Intellectual disabilities, Observatory research, Requirement specification, Game design.
Abstract: People with intellectual disabilities are a part of our society, but unfortunately, they are often excluded.
Their assistance includes everything they need in their lives. The work in the various workshops for people
with disabilities often gives them the feeling that they are needed, but few can find access to an independent
life by further developing and training of themselves. The pleasure of (digital) game playing and learning
with a game is not yet considered a standard constituent of leisure time activities in sheltered workshops for
people with an intellectual disability. Qualitative studies with off-the-shelf digital games have demonstrated
enormous potentials of game playing for the assistance of people with an intellectual disability. However,
conventional off-the-shelf digital games have severe limitations. The authors’ qualitative studies lead (i) to a
requirement specification and (ii) to the design and implementation of a completely new digital game
meeting essential needs of people with an intellectual disability. The present publication surveys the results
of the qualitative observations and leads to the recently completed game design.
1 INTRODUCTION
The authors’ main motivation is to contribute to the
quality of the life of people with intellectual
disabilities, who work regularly in sheltered
workshops.
An intellectual disability is impaired if cognitive
and partially physical abilities are permanently
limited and when help is needed to participate in
everyday life and work. The intellectual disability
and the intended help by others should not lead into
negative consequences concerning the personality,
family and the attendance in public life (World
Health Organization, 2001), (Bundesregierung,
2004), (Cloerkes, 1988).
Contributions to the peoples’ life quality may
become part of a systematic assistance. The present
work focuses on the usage of digital games.
Which role do digital games play in the current
assistance of people with an intellectual disability, in
general, and in their supervised leisure time, in
particular? In case game playing is not just fun,
which other effects (maybe educational, e.g.) may be
observed? What about the potentials of off-the-shelf
commercial games? Do we need ad hoc game
designs and implementations?
Beyond the contribution to those peoples’
quality of life, the authors are focussing training and
learning. It is the authors’ strong belief that people
with an intellectual disability do need more support
in daily life, in particularly in playful learning and
training.
The authors want to clarify that the issue of
accessibility is certainly one of the main require-
ments of the special education. In the case of games,
the following study indicated that there are some
special needs which can be supported individually
and personalized by ‘special games’. Technology-
enhanced approaches are probably quite promising,
but seem to be much underrepresented in the
scientific discourse, in general, and on leading
conferences such as CSEDU, in particular, at least
for adults with intellectual disabilities.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
An enormous number of authors have investigated
the challenge of getting computer systems engaged
for educational purposes including the special needs
of persons with an intellectual disability. An
overwhelming majority of publications ranging from
(Gresham and Elliott, 1987) to (McCray, Vaughn
220
Hofmann A., Hoppe I. and Jantke K. (2010).
THE NEED FOR SPECIAL GAMES FOR GAMERS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 220-225
DOI: 10.5220/0002781102200225
Copyright
c
SciTePress

and Neal, 2001), (Sullivan, Lautz and Zirkel, 2000),
(Deeney, Wolf and O’Rourke, 2001), (Weiss and
Lloyd, 2003), (Frederickson and Turner, 2003),
(Fuchs and Fuchs, 2005), and (Graham and Harris,
2005), are focusing children and school problems. In
contrast, the present approach is addressing the
needs of adults.
Furthermore it is stated as an important target of
special education to support the computer literacy,
because the use of computers became central in
everyday life and the employment market
(Sonderschul-net.de, 1997). Usability and regular
feedbacks were stated as main requirements of
software programs for people with special needs. In
a majority of publications such as (Cosden et al.,
1987), (MacArthur et al., 1986), (Rieth et al., 1988),
authors have complemented the potentials by
varying hints to the limitations of information and
communication technologies.
It is only natural that a larger number of authors’
response is the dedicated ad hoc development of
special purpose approaches as surveyed in (Riva,
1997). There is the particularly important aspect that
“any educational innovation is filtered through
teachers as they modify instructional activities to fit
their beliefs and the instructional and management
routines in their classrooms” (MacArthur and
Malouf, 1991).
Corresponding to the results of the literature
review on the game market we mainly found games
for children with intellectual and physical dis-
abilities. Most recent games offer a training of single
cognitive skills and tasks, like counting. Some
representatives for the development of specific
hardware and software for children with disabilities
are “World of Genesis” (Genesis, 2008), “LifeTool”
(Clevy, 2008), “Läramera” (LäraMera Program AB,
2009) and “Inclusive Technology” (Inclusive
Technology, 2008). The dedicated hardware can be
used by adults, while the software has been
developed almost exclusively for children with
disabilities.
The conducted study deals with the question
which learning effect can be achieved by people
with intellectual disabilities while playing
educational games. In addition to this question it
should be clarified to what extent playing and
learning can be useful to this target group.
3 METHOD
As empirical method we choose a case study,
because we wanted to analyse how digital games
could be integrated into the daily life of the sheltered
workshops and how they affect the people working
there.
So the study was conducted in a sheltered
workshop (Germany/Thuringia) for adults with
intellectual disabilities who have completed their
compulsory education. The workshop is divided into
different areas, including the five workspaces wood,
metal, installation, kitchen and vocational training.
The study used a mixed-method-design and
integrates qualitative as well as quantitative
methods. The quantitative approach was needed to
answer certain predefined research questions and to
follow the duration of the analysed game, which
consists of 28 game units. The qualitative approach
was used to clarify the key dimensions of how
learning was enhanced by digital games and to reach
an in-depth understanding of these processes.
Therefore a longitudinal participant observation
(10/2008-01/2009) was chosen as main research
instrument. Within the observation a protocol was
used which integrated open plus well-structured
criteria to realise the qualitative and the quantitative
approaches. The structured, quantitative elements in
the protocol used scales ranging from 1 to 5 (Likert-
Scale).
Because in Germany there are no digital games
for adults with intellectual disabilities available, we
used the preschool games “Janosch – meine große
Vorschulbox”, “Lauras Vorschule” and “Die Mini-
Mäuse” as test objects. With these serious games the
main research questions could be analysed, because
they provide the requirements the supervisors of the
sheltered workshop defined and reach the target
group.
The sampling is characterised by the qualitative
approach taking very different people and their
varying computer literacy into account. The chosen
persons A (Age 40, female), B (Age 28, female) and
D (Age 25, female) have only a slight computer
literacy. Person C (Age 21, male) has basic
knowledge about using the computer.
These games were played over a period of 14
weeks with 2 game units per week, each lasting 45
Minutes. The structure of the participant observation
was to set up a scenario in which the participants
were asked to play the game while the observer sits
aside.
The results of the empirical study will be
outlined as requirements in chapter 4 and should
serve as guidelines for designing and programming a
digital learning game (see chapter 5).
THE NEED FOR SPECIAL GAMES FOR GAMERS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS
221
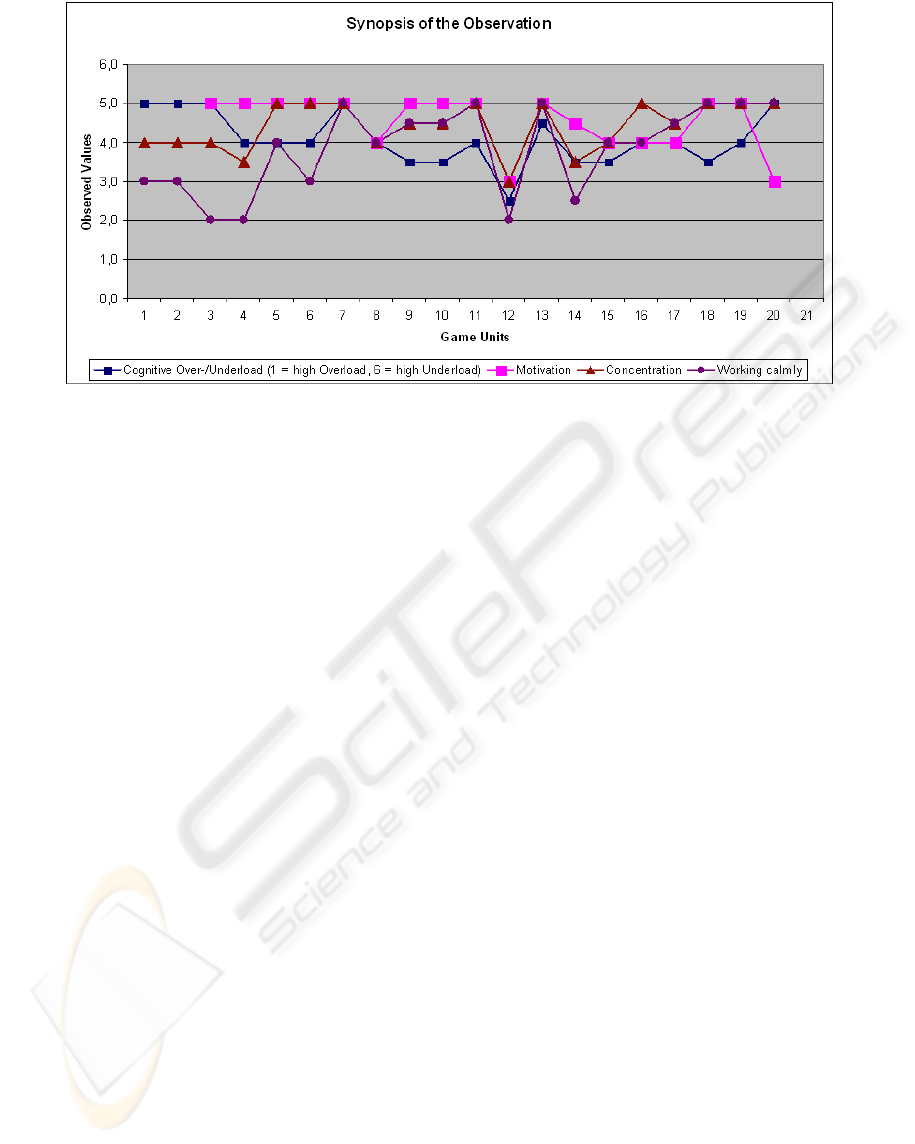
Figure 1: Selected results of participant C concerning the quantitative part of the observation.
4 RESULTS
The results showed both positive effects on learning
and negative aspects of game usage.
The main positive effects on the learning
process are characterised by improvements
concerning the computer literacy, for example
handling the input devices. The observation
protocols indicated increasing concentration,
perseverance and patience as well as an
improvement in working very calmly and precisely
concerning playing the game and solving the tasks.
Figure 1 shows a clear correlation between an
adequate difficulty and a high motivation (game
units 9-10).
An increase of competences and knowledge
regarding the daily-life topics was ascertained, e.g.
nutrition, traffic rules, and dealing with money.
Regarding the motor skills while handling the
computer we found an improvement in the ability to
react, the eye-hand-coordination and the orientation
in virtual rooms.
Also some negative aspects of game usage were
analysed. The learning topics within the chosen
games do not concern aspects of the reality of the
participants. All tested games communicate the
instructions and explanations either through an
acoustic or a written mode, which was problematic
for those, who are not able to read.
As mentioned earlier the concentration decreases
if the game levels are either too easy or too
complicated (see figure 1, e.g. game units 11-13). In
the tested games there were only a few possibilities
to modify the navigation tools. Only one game
offered the option of printing out a certificate about
the achieved score, a detail which was very much
appreciated by all participants of the study.
Because of the fixed order of the given answers,
the participants recognised response patterns, which
were often experienced as negative.
Summarising, the results of the study show a
strong interest and motivation in playing digital
games across all participants, e.g. participant B said:
“That’s why I’m here: to learn something, finally!”
(“Dafür bin ich ja da, um was zu lernen, endlich!”);
participant D claimed: „Please, remember me that
we train calculation next week!” (“Erinner’ mich
nächste Woche daran, dass wir Rechnen üben!“).
Moreover, they affirmed that playing digital
games challenged them in a positive manner and
varied their daily life routines within the sheltered
workshop. During the study this interest decreased a
little, especially when the participants felt
unchallenged by the game. Participant C showed this
significantly: “Today, I have no passion to play this
game, it is always the same.” (“Darauf habe ich
heute keine Lust, das ist ja immer wieder das
Gleiche”). This perceived cognitive underload
differed from person to person, depending on their
knowledge, motivation and computer skills. As a
main intervening variable on learning processes the
ever-changing disposition and concentration were
analysed. One of the most striking results is the huge
interest in computer-related knowledge, e.g. to get to
know how a computer works. However, only a few
changes in the social behaviour of the participants
have been observed, e.g. one participant became
more outgoing, as the supervisors told us.
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
222

Even more, the supervisors reported that the
game showed the participant’s skills more detailed
than they expected.
5 REQUIREMENT ANALYSIS
Based on these empirical results a requirement
analysis was outlined. The requirement analysis
provides a first step to encourage the development of
„special games“ for adults. The main concept to
realise the requirements through a digital game is
adaptivity, which affects several requirements.
5.1 Basic Framework Requirements
One of the major requirements is drawn from the
literature (see chapter 2) and claims to stage the
game closely to the reality of the players, e.g.
using symbols (words, pictures) which are well
understandable and commonly known. The content
should display the every-day life of the participants
so that the lessons learned during the game can be
easily transferred and put into practice. Therefore
the game designers should clarify beforehand which
learning areas should be enhanced. We suggest
using mini-games with single delimitable steps to
avoid a cognitive overload and to allow individual
interruptions without loosing the game. Regarding
the instructions we argue for using all possible
perceptional modes (oral, written,...) at the same
time, so that the user (or their supervisors) can
choose how the instructions should be
communicated. Thereby a wide range of intellectual
disabilities are taken into account. The possibility of
an individual key assignment is considered as very
helpful. Furthermore the possibility of choosing and
combining different input devices, like the mouse
and keyboard, should be given. This demand is
caused in disabilities, which do not allow writing or
reading. Since some users are not able to insert a
CD-ROM into the drive due to their limited physical
abilities, the game should be playable without a
CD-ROM or other additional preparations. In
general it should be possible to play the game
autonomously so that the need of permanent
assistance can be avoided. Hence an excellent and
invisible help function is needed. It should be
prevented to give monotone answers and feedback
patterns, because this seems to be exhausting,
especially for people with intellectual disabilities. A
simple graphic design with high-contrast colours
will encourage the visual perception and support the
orientation within the game. The menu’s structure
should be as simple as possible, so that the main
functionalities like saving the game are easy to find.
The menu should also integrate a button to print
documents, like the certificate with the reached high
score. For supervisors as well as for parents it is
helpful to have a game protocol, which should be as
well available though the menu.
5.2 Didactical Requirements
One of the major didactical principles is to support
and to challenge the learner individually. So there
is a need for a well-adjusted balance (Mortimore,
1999). Thereby a cognitive overload as well as a
cognitive underload should be avoided. To impede
an overload of the participants, e.g. the possibility to
repeat tasks and levels is needed. To impede
underload new stimuli can be given through regular
updates of certain tasks, levels or mini-games.
Additionally a motivating, friendly and varying
feedback will create a supporting learning
environment. For the supervisors it would be a
benefit to be able to assess the skills and knowledge
of new participants by the digital game.
It would be an engaging tool to create a
competitive atmosphere for those players, who seek
for some challenges. This can be reached by offering
a game level with a high score.
5.3 Adaptivity as Main Requirement
Adaptivity is a key feature of modern information
and communication systems offering added value to
literally all users or customers through the system’s
ability to adapt to individual needs and desires.
A certain system’s adaptivity, naturally, requires
the system “to know” something about the user for
being able to offer varying services to different users
(Popescu et al., 2007). Therefore, adaptivity requires
user modelling, a key issue not to be discussed here
in more depth.
To many people, adaptivity is a nice feature that
makes products and services more attractive and,
perhaps, more useful. To producers and service
providers, adaptivity is a nice feature that helps to
gain advantage over competitors.
To people with intellectual disabilities, the
adaptivity of the given system is not only nice to
have, but a feature of decisive relevance. The
authors’ results (see section 4.2 above) exhibit that
people with intellectual disabilities are not very
much tolerant to deviations from their needs and
requirements. If a system such as a game does not
closely enough fit their individual needs, it is very
THE NEED FOR SPECIAL GAMES FOR GAMERS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS
223

likely to fail in general.
Research into the adaptivity of digital games is a
current field of endeavours. Although there are
recent results of great interest (Charles et al., 2005),
(Torrente et al., 2008), these recent research
activities do not take into account the special needs
of people with intellectual disabilities.
Further work will have to weight the
requirements and to structure them regarding the
production process.
6 PROTOTYPING & OUTLOOK
Based on the requirements mentioned above the
authors are in the process of developing a game as
prototype for people with intellectual disabilities.
The prototype implements the most of the
requirements displayed in chapter 5.
To develop a realistic game environment, we
basically created a virtual copy of the sheltered
workshop, in which the study was conducted. The
images below show the main corridor of that
institution.
Figure 2: The virtual and the real sheltered workshop.
But because the game should not be exclusively
created for one single workshop, we decided to
design a holistic framework, in which different
ground plans of different sheltered workshops can be
depicted and staged as basic virtual game
environment (see figure 3).
As a side effect the content of the game as well
as the learning tasks are very comparable to the real-
life sheltered workshop so that possibilities of
knowledge transfer are given. It is even conceivable
that this has a positive impact on the individual
working performance.
Another learning objective is the expansion of
existing knowledge, as well as daily life oriented
skills, such as learning to read the clock and to use
money. Apart from this learning effect, people with
intellectual disabilities can hereby be encouraged
playfully to reach a more independent lifestyle.
The creation of a system that imparts learning
content playfully is one of the central objectives of
designing a computer game for people with
intellectual disabilities.
As an additional side effect, the target group is
engaged to use the computer as a learning medium
and instrument even for other contexts than games.
An anxiety-free use of new technologies on the one
hand and with the computer in particular is striven
here. Computer competences improve the chances to
be integrated into the employment market.
Figure 3: Ground plan of the virtual workshop.
The game will also provide the training of
various skills, such as the responsiveness,
concentration, endurance and patience. At least the
game should be funny and motivating.
For those reasons we chose mini-games,
especially to train certain skills selectively and for
doing this in an entertaining way. At the present
moment four mini-games are directly available
through the game environment and already
implemented. They train the visual perception,
orientation in rooms, handling of input devices,
counting, spelling and reading the time.
A main focus of the prototype is to implement
the adaptivity. This will be realised by an
incorporating user model. Within this user model all
relevant data about the individual users will be
stored. Because of this information the system
knows to what extent help and assistance are needed.
After finishing the prototype an evaluation will
be conducted. Using a similar research setting in the
same institution will make the results of the other
tested games comparable with the results of the
prototype. Moreover, we can analyse whether
positive learning effects and an entertaining
experience will occur and if these learning effects
are transferable to the daily-life reality of the
participants. The empirical research should as well
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
224

extend the evidence base concerning the usability in
general and especially in navigation. The results of
the empirical study will influence the redesign of the
prototype.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The present research and development has been
partially supported by the Thuringian Ministry for
Culture (TKM) within the project iCycle under
contract PE-004-2-1.
REFERENCES
Bundesregierung (2004). Sozialgesetzbuch. Rehabilitation
und Teilhabe behinderter Menschen.
Charles, D., Kerr, A., McAlister, M., McNeill, M.,
Kücklich, J., & Black, M. M., et al. (2005). Player-
Centred Games Design: Player Modelling and
Adaptive Digital Games. In Digital Games Research
Conference 2005, Changing Views: Worlds in Play,
June 16-20, 2005, Vancouver, British Columbia,
Canada .
Cosden, M. A., Gerber, M. M. and Semmel, D. S. (1987).
Microcomputer use within micro-educational
environments. Exceptional Children, 53:399–409.
Clevy (2008). Großtastatur. http://www.computer-fuer-
behinderte.de/produkte/2tast-grosstastatur.htm
Cloerkes, G. (1988). Behinderung in der Gesellschaft:
Ökologische Aspekte und Integration. In U. Koch
(Ed.), Handbuch der Rehabilitationspsychologie, 86–
100. Berlin: Springer.
Deeney, T.,Wolf, M., and O’Rourke, A. G. (2001). “I like
to take my own sweet time”: Case study of a child with
naming-speed deficits and reading disabilities. The
Journal of Special Education, 36(3):145–155.
Frederickson, N. and Turner, J. (2003). Utilizing the
classroom peer group to address children’s social
needs: An evaluation of the circle of friends
intervention approach. The Journal of Special
Education, 36(4):234– 245.
Fuchs, D. and Fuchs, L. S. (2005). Peer-assisted learning
strategies: Promoting word recognition, fluency, and
reading comprehension in young children. The Journal
of Special Education, 39(1):34–44.
Genesis (2008). Was steckt hinter Genesis? from
http://www.efi.fh-nuernberg.de/genesis/index.php?op
tion=com_content&view=article&id=45&Itemid=2.
Graham, S. and Harris, K. R. (2005). Improving the
writing performance of young struggling writers:
Theoretical and programmatic research from the
center on accelerating student learning. The Journal
of Special Education, 39(1):19–33.
Gresham, F. M. and Elliott, S. N. (1987). The Relationship
between Adaptive Behavior and Social Skills: Issues in
Definition and Assessment. The Journal of Special
Education, 21(1), 167-181.
Inclusive Technology (2008). Coping with Chaos, http://
www.inclusive.co.uk/catalogue/acatalog/coping_with_ch
aos.html
LäraMera Program AB (2009). Educational software for
children in pre-school age and up. http://
www.laramera.se/indexEng.htm
MacArthur, C. A. and Malouf David B. (1991). Teachers‘
Beliefs, Plans, and Decisions About Computer-based
Instruction. The Journal of Special Education, 25(5),
44-72.
MacArthur, C. A., Haynes, J. A., & Malouf, D. (1986).
Learning disabled students' engaged time and
classroom interaction: The impact of computer
assisted instruction. Journal of Educational
Computing Research, 2, 189-198.
McCray, A. D., Vaughn, S., and Neal, L. V. I. (2001). Not
all students learn to read by third grade: Middle
school students speak out about their reading
disabilities. The Journal of Special Education,
36(1):17–30.
Mortimore, P. (1999). Understanding pedagogy and its
impact on learning. London: Chapman.
Popescu, E., Trigano, P., and Badica, C. (2007). Adaptive
Educational Hypermedia Systems: A Focus on
Learning Styles. In EUROCON: The International
Conference on “Computer as a Tool"‘: Warsaw,
September 9-12, 2473–2478. Warsaw.
Rieth, H. J., Bahr, C. M., Okolo, C. M., Polsgrove, L., and
Eckert, R. (1988). An analysis of the impact of
microcomputers on the secondary special education
classroom ecology. Journal of Educational Computing
Research, 4:425–442.
Riva, G. and Melis, L. (1997). Virtual reality for the
treatment of body image disturbances. In Riva, G.,
editor, Virtual Reality in Neuro-Psycho-Physiology.
Amsterdam: ios Press.
Sonderschul-net.de (1997): Zum Einsatz des Computers in
der Schule für Geistigbehinderte (Sonderschule) mit
dem Schwerpunkt: Erstellung von
Übungsprogrammen mit Autorensystemen
einschließlich eines praktischen Beispiels, http://www.
foerderschwerpunkt.de/download/examen/ComputerSf
G.pdf.
Sullivan, K. A., Lantz, P. J., and Zirkel, P. A. (2000).
Leveling the playing field or leveling the players?:
Section 504, the americans with disabilities act, and
interscholastic sports. The Journal of Special
Education, 33(4):114–126.
Torrente, J., Moreno-Ger, P., and Fernandez-Manjon, B.
(2008). Learning Models for the Integration of
Adaptive Educational Games in Virtual Learning
Environments. In Edutainment, LNCS 5093, 463–474.
Berlin, Heidelberg: Springer-Verlag.
Weiss, M. P. and Lloyd, J. W. (2003). Congruence
between roles and actions of secondary special
educators in cotaught and special education settings.
The Journal of Special Education, 36(4):58–68.
World Health Organization (2001). International
Classification of Functioning, Disability and Health,
http://www.who.int/classifications/icf/en/.
THE NEED FOR SPECIAL GAMES FOR GAMERS WITH SPECIAL NEEDS
225
