
HUMAN COMPUTER COLLABORATION TO IMPROVE
ANNOTATIONS IN SEMANTIC WIKIS
Anne Boyer, Armelle Brun and Hala Skaf-Molli
LORIA-Nancy Universit
´
e, 615, avenue du jardin botanique, 54506 Vandœuvre les Nancy, France
Keywords:
Recommender systems, Semantic wikis, Automatic annotation.
Abstract:
Semantic wikis are promising tools for producing structured and unstructured data. However, they suffer from
a lack of user provided semantic annotations, resulting in a loss of efficiency, despite of their high potential.
We propose a system that suggests automatically computed annotations to users in peer to peer semantic wikis.
Users only have to validate, complete, modify, refuse or ignore these suggested annotations. Therefore, the
annotation task becomes easier, more users will provide annotations. The system is based on collaborative
filtering recommender systems, it does not exploit the content of the pages but the usage made on these pages
by the users. The resulting semantic wikis contain several kinds of annotations with different status: human,
computer or human-computed provided annotations.
1 INTRODUCTION
Web 2.0 provides an easy way to produce new content
and to make it broadly available on Internet. Users
collaborate all together to increase quantity and qual-
ity of available contents by using for instance, wikis
and blogs. This large production increases the diffi-
culty to access the right information at the right mo-
ment. The question is no more to determine if a spe-
cific content exists but to find where it is available
and how to access it. Therefore, it is mandatory to
develop tools to help users finding the pertinent in-
formation on the web. Semantic wikis are one of the
most promising approach to overcome this problem.
Compared to classical wikis, they allow users to add
semantic annotations in the wiki pages. These seman-
tic annotations are not necessarily mapped to an ex-
isting ontology compared to the approaches detailed
in (Reeve and Han, 2005). In semantic wikis, seman-
tic annotations allow the emergence of ”lightweight”
ontologies in a cooperative way. Users do not only
collaborate for writing the content of the wiki pages
but also for writing the semantic annotations that will
allow a better and easier usage of wiki pages. It will
be possible to answer queries by exploiting informa-
tion from different wiki pages, based on the semantic
annotations. However, adding semantic annotations
is not an easy task and is time consuming. The conse-
quence is that only few users annotate pages semanti-
cally. As it is not easy to motivate users to provide an-
notations, many existing semantic wikis contain only
few annotations, that decreases their potential added
value. Having only manual semantic annotations is a
bottleneck for semantic wikis. One possible solution
is to propose a system that suggests pertinent annota-
tions to users.
This paper proposes a new kind of collaboration
between users and machine to produce pertinent, use-
ful and reliable annotations in semantic wikis based
on a recommender system. Many works about recom-
mender systems (Goldberg et al., 1992; Adomavicius
and Tuzhilin, 2005; Pazzani and Billsus, 2007) and
semantic wikis (Kr
¨
otzsch et al., 2007; Buffa et al.,
2008) can be found in the literature. However, few
existing works (Durao and Dolog, 2009) propose to
use recommender systems for navigation personaliza-
tion in semantic wikis. This paper proposes to suggest
new annotations to users by mining the automatically
collected observations about the real usages of wiki
pages. These ”computer recommended” annotations
are suggested to users that can either validate (and/or
complete), modify, refuse or ignore them. Based on
these suggested annotations, the task of the users is
made easier as the users do not have to create the an-
notation from the scratches.
Section 2 gives a brief overview of the proposed
system. Section 3 summarizes the required back-
ground in term of semantic wikis and recommender
systems. Section 4 describes how we use recom-
mender systems to automatically determine possible
89
Boyer A., Brun A. and Skaf-Molli H.
HUMAN COMPUTER COLLABORATION TO IMPROVE ANNOTATIONS IN SEMANTIC WIKIS.
DOI: 10.5220/0002797900890094
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technology (WEBIST 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-674-025-2
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

additional semantic annotations. It presents also how
the users and machines collaborate to provide reliable
semantic annotations. The last section concludes and
points out the perspectives of this work.
2 OVERVIEW OF THE SYSTEM
Semantic wikis allow users to add semantic annota-
tions in the wiki pages. These semantic annotations
are used for reasoning and finding pertinent answers
to complex queries. The efficiency of semantic wikis
relies among others on the quantity and the quality of
the available semantic annotations. An essential prob-
lem still remains: how can we encourage and support
users to provide semantic annotations? This paper ad-
dresses this question by introducing the machine as a
partner of the collaborative process of annotation in
peer to peer semantic wikis. The community of users
becomes a community gathering humans and com-
puters working together to produce semantic annota-
tions. Humans and computers do not have equivalent
roles within the community: computers can only sug-
gest new semantic annotations but they do not have
any influence on the final decision to keep, modify
or discard them. In contrast, humans can add new
semantic annotations and participate to the final deci-
sion of integrating or not a given annotation provided
by computers. We propose a semi-automatic annota-
tion tool for semantic wikis. A specific recommender
suggests possible annotations to humans. Every hu-
man can decide to ignore, accept (and/or complete)
or refuse them. If agreed, the status of the annotation
will change to become a Human Computer Annota-
tion. If refused, the annotation will be discarded but
memorized by the system as Refused Annotation to
avoid to suggest it again. The validated annotations
will be added to the usual annotations resulting from
human collaboration. An annotation can thus have
four different status :
• Human Annotation (HA) : this annotation results
from human collaboration;
• Computer Annotation (CA) : this annotation is
suggested by the recommender but not reviewed
by humans;
• Human Computer Annotation (HCA) : this is
a computer annotation that has been validated
(and/or completed) by the users;
• Refused Annotation (RA) : this is a computer an-
notation that has been discarded by humans.
Both HA and HCA annotations are used to support
navigation and answer semantic queries, the CA an-
notations can only be used to support navigation when
no other annotation is available.
This work uses collaborative recommendation
based on usage mining to compute annotations. The
recommender exploits the usages of the wiki pages by
the humans to determine pertinent suggestions of an-
notations. It exploits implicit collaboration between
users: we consider that users who share usages col-
laborate implicitly. This approach does not take into
account the content of pages to perform recommenda-
tions, only the usage is considered. The system inte-
grates three levels of collaborations. Level 1: Explicit
human collaboration when users write annotations,
HA. Level 2: Implicit human collaboration when the
system suggests CA. Level 3: Human-computer col-
laboration when users validate and complete CA that
become HCA. Suppose we apply Human-computer
collaboration to a semantic wiki about ”France”, let
two semantic wiki pages ”Eiffel Tower” and ”Mont-
martre”, these two pages are not directly linked by
semantic annotations. The ”Eiffel Tower” page has
the semantic annotation : ”Gustave Eiffel” as a ”De-
signer”. However, ”Eiffel Tower” and ”Montmartre”
are two well known touristic buildings in ”Paris”,
therefore, the semantic wiki pages of these two build-
ings should be semantically linked. And usually
users interested in ”France” often consult both pages.
Our HCA system will automatically discover this link
based on the users usage and it will be recommended
to users as a CA annotation. The semantic annotations
will be enriched and the usability of the semantic wiki
will be improved.
3 BACKGROUND
This section presents backgrounds on semantic wikis
and recommender systems.
Semantic Wikis are an extension of wiki systems,
they embed semantic annotations in the wiki content.
These annotations allow to better organise and struc-
ture the wiki contents. Semantic wikis allow mass
collaboration for creating and emerging ontologies.
They guide the users from informal knowledge con-
tained in texts to more formal structures. Many se-
mantic wikis are being developed such as Semantic
MediaWiki (SMW) (Kr
¨
otzsch et al., 2007), Sweet-
Wiki (Buffa et al., 2008) and Swooki (Skaf-Molli
et al., 2009). In SMW, links between wiki pages are
typed. For instance, a link between the wiki pages
”France” and ”Paris” may be annotated by a user as
”has Capital”. The following example shows of a wiki
page and its corresponding semantic wiki page.
France is l o c a t e d in [ Europe ]
The c a p i tal of France is [ P a r i s ]
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
90

France is l o c a t e d in [ locat e d In ::
Europe ] The capital of F r a n c e is
[ has C a p i tal :: P a r i s ]
Annotations express semantic relationships be-
tween wikis pages. They are usually written in a for-
mal syntax so they are processed automatically by
machines and are exploited by semantic queries. In
semantic wikis, semantic annotations are added by
users so they are Human Annotations they correspond
to the Level 1 of collaboration as presented in sec-
tion 2. Semantic wikis, as classical wikis, suffer
from scalability, availability and performance prob-
lems and they do not support offline works (Weiss
et al., 2007). To overcome these limitations, peer
to peer extensions for semantic wiki are proposed.
SWooki (Skaf-Molli et al., 2009) is a peer to peer
(P2P) semantic wiki that follows the same annota-
tion principles as SWM. It is a P2P network of au-
tonomous semantic wiki servers, every server hosts
a copy of all semantic wiki pages and the semantic
data. Every peer can autonomously offer all the ser-
vices of a semantic wiki server. When a peer updates
its local copy of data, it generates the corresponding
operation. This operation 1) is executed immediately
against the local replica of the peer, 2) it is broad-
casted to all other peers, 3) it is received by the other
peers, 4) and it is integrated to their local replica. If
needed, the integration process merges this modifica-
tion with concurrent ones, generated either locally or
received from a remote server.
Recommender Systems provide personalization
to users to cope with the well-known problem of
overload of information (Adomavicius and Tuzhilin,
2005). Among the possible approaches in rec-
ommender systems are content-based (Pazzani and
Billsus, 2007) and collaborative filtering approaches
(Goldberg et al., 1992). The first approache uses the
content of the resources to compute recommendations
for users, these approaches are accurate. However,
the content of all types of resources cannot be au-
tomatically analyzed (videos, audio, etc.), thus this
analysis often requires human interventions. More-
over, only resources directly linked to the resources
the user has consulted can be suggested: no ”novelty”
can be recommended to users, users may thus be frus-
trated. Collaborative filtering (CF) approaches do not
take into account the content of the resources. They
consider only the usage of these resources to com-
pute recommendations. The usage can be the consul-
tation made by users, the votes given by users, etc.
A CF-based recommender exploits the traces of us-
age to deduce information about the resources. CF-
based recommenders can either compute similarities
between resources (Sarwar et al., 2001) or exploit
data mining techniques to learn relationships between
the resources (Yong et al., 2005). As in content-
based recommender systems, given a user, his pre-
viously consulted resources are used and are linked/-
compared to all possible resources. The comparison
is no more made in terms of content but on the simi-
larities or relastionships computed between resources,
based on their usage. This approach allows to recom-
mend ”original” resources: resources that are not se-
mantically linked to the past resources consulted by
the user (but that are similar in terms of usage) can be
recommended.
4 RECOMMENDER SYSTEMS
FOR ANNOTATION
SUGGESTION
Existing recommender systems for Semantic Wikis
directly transpose recommenders to suggest wiki
pages to users as in (Durao and Dolog, 2009). In our
work, we go a step further by suggesting annotations
to wiki pages based on usage traces. We use CF-based
recommender systems to provide automatically pages
with additional annotations. We exploit the usage of
wiki pages: which users consulted which wiki pages
and which page(s) is(are) frequently consulted after
a given page? to deduce the links/relationships be-
tween pages, by using approaches similar to the ones
presented in (Sarwar et al., 2001; Yong et al., 2005).
Given the relationships between pages and the anno-
tations given by users (HA), the recommender sys-
tem will suggest additional annotations. These anno-
tations can be made on pages that either already have
HA or not. Suggested annotations correspond to the
implicit human collaboration level (level 2) .
4.1 Suggestion of Semantic Computer
Annotations
We propose two algorithms to compute annotations
to suggest to a given page P
j
. The first one is similar
to those used in item-based approaches and classifi-
cation of pages based approach (O’Connor and Her-
locker, 1999), the second one is based on data mining
techniques for recommendations (Mobasher, 2007).
Item-based Approach. The algorithm first com-
putes a similarity matrix of wiki pages (Sarwar et al.,
2001). This matrix is computed based on the traces
of usage of the wiki pages. This approach is based
on the hypothesis that two similar pages may have
similar semantic annotations. Thus, given two similar
HUMAN COMPUTER COLLABORATION TO IMPROVE ANNOTATIONS IN SEMANTIC WIKIS
91

Figure 1: Automatic suggestion of HCA with the item-
based approach.
pages, the recommender suggests the semantic anno-
tations of the first one to the second one and suggests
the semantic annotations of the second one to the first
one. These suggested annotations are called CA. Fig-
ure 1 presents how the recommender computes candi-
date annotations. Given a page P
j
, the recommender
searches the pages that are similar to P
j
, those with
a high similarity value in the similarity matrix. The
recommender collects the HA from the pages simi-
lar to P
j
. The suggested CA to P
j
can be computed
by several policies: • The set of HA from the similar
pages are suggested. The recommender may propose
too many annotations, and some of them may be not
pertinent. • The set of HA present in at least n similar
pages are suggested. An appropriate value of n has
to be fixed. This policy proposes a lower number of
annotations and more “reliable” as they are present in
several pages. However, according to the value of n,
some pages may have no annotation. • Given a HA,
the similarity values of the pages containing that HA
are summed up. The HA with a sum of similarity val-
ues above a given threshold are suggested. This policy
is more accurate than the second one as the similarity
values are considered.
Classification-based Approach. In this ap-
proach, given a set of pages, the recommender first
computes a classification of these pages to create
classes of ”similar” pages (see Figure 2). As in the
item-based approach, the classification is based on the
usage of the pages by the users, not on the content of
the pages. Then, given a page P
j
, the recommender
searches its corresponding class, and exploits all the
pages in this class. All the policies presented in the
item-based approach can be used to compute annota-
tions.
The set of pages used to compute annotations is
predefined (the pages in the class) whereas it is dy-
namically computed in the item-based approach, that
can take time.
Data Mining based Approach. It exploits data
mining techniques to extract information about the
Figure 2: Automatic suggestion of HCA with the
classification-based approach.
usage of the resources. They study the sequences
of consultation of resources by using, for example,
association rules or Markov models to discover fre-
quent patterns (Bonnin et al., 2009). The algorithm
is based on the hypothesis: if two or more pages
are frequently consulted in sequence, then the links
used to traverse these pages are useful and it is impor-
tant to annotate semantically these links. The recom-
mender suggests CA to the users to annotate seman-
tically the frequently passed links. The provided an-
notations are not semantic annotations, they are just
annotations, as the type of the annotation cannot be
automatically discovered by the system. The recom-
mender suggests that an annotation at a given place
should be important. It can also specify the label of
the annotation. For instance, suppose in the example
given in the section 3, there is no semantic annotation
between the pages ”France” and” Paris”, the recom-
mender can learn that this link is highly passed, thus
annotating semantically this link may be useful. The
recommender suggests to the users the link ”Paris”.
The user can accept, modify, refuse or ignore this sug-
gested annotation and type it with [HasCapital], for
example. The annotation task is made easier as the
system suggests to the user where useful annotations
should be, the user is guided.
4.2 HCA Approach
Every semantic wiki page has three sources of anno-
tations. Those added by humans (HA), they corre-
spond to the explicit human collaboration, those sug-
gested by the recommender system (CA), they come
from implicit human interaction. These annotations
are original annotations, they do not exist in classi-
cal semantic wikis, they will be used to encourage
the users to annotate semantically pages. Those re-
viewed by the user, Human computer collaboration
HCA. To integrate these annotations to a peer to peer
semantic wiki, we have to answer several questions :
how the recommender suggests annotations (CA) to
users? how to make the users validate (and/or com-
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
92
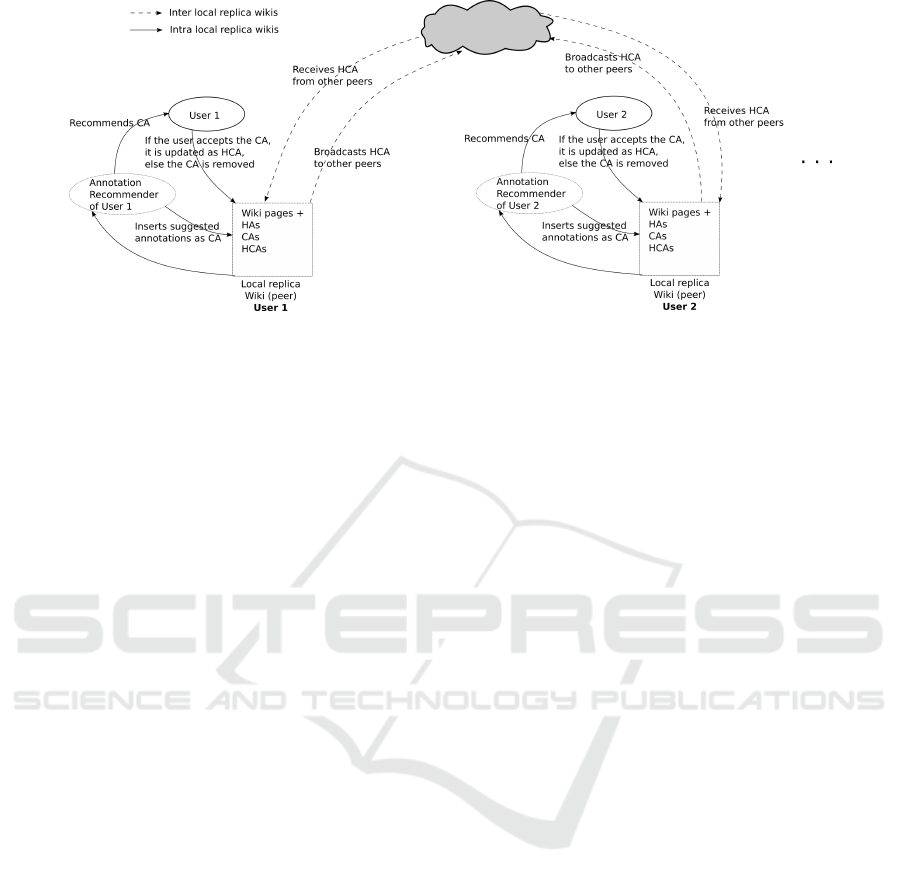
Figure 3: The way CA are proposed, validated (HCA) and propagated in a P2P semantic wiki.
plete), modify, refuse or ignore a CA? How to make
the other users know these annotations? The way we
propose to answer these questions is presented in Fig-
ure 3. When new annotations are suggested by the
recommender, they are broadcasted to all the local
replica with the status Computer Annotation (CA).
They are proposed to the users, in a pop-up box, for
example, to be differentiated from Human Annota-
tions HA. The user can choose among four possible
operations : 1) Ignore the CA annotation. 2) Accept
it, 3) modify (and) type it or 4) refuse it. If the user
does nothing, the annotations remain with a CA sta-
tus. If the annotations are typed (from item-based or
classification-based approaches), the user can either
validate, modify or refuse each of them. If the anno-
tations have no type (from data mining approach), the
user can complete (and thus validate), or modify each
of them. When a validation, completion or modifi-
cation action is made, the local replica of the user is
modified and the CA is updated to a HCA. The infor-
mation about this action is broadcasted to the other lo-
cal replica and the annotation is suggested to users as
a HCA. Let us notice that when a user does not agree
on a received HCA, he can modify it as in the case of
classical HA in semantic wikis. If the user refuses the
annotation, it is discarded from the set of CA and is
included in the set of RA and is also broadcasted to
other users. This set is used by the recommender to
avoid resuggesting annotations that have already been
refused by users. These RA can however be resug-
gested in the case the content of the wiki page has
been highly modified.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposes an original system to encourage
semantic annotations in semantic wikis. This ongo-
ing work is based on the observation that users do not
often semantically annotate pages in semantic wikis
as this task is not easy. This leads to semantic wikis
with few annotations, they are therefore less efficient
than they could be. The HCA system suggests an-
notations on the wiki pages to users. The users can
create semantic annotations as in a normal semantic
wiki and can also use the annotations suggested by the
system to annotate semantically pages. The HCA sys-
tem exploits the usage of the wiki pages by the users
and is based on classical collaborative filtering rec-
ommender systems, it uses item-based, classification-
based and data mining-based approaches. These ap-
proaches learn the similarities/links, in terms of us-
age, between the wiki pages. The HCA system ex-
ploits both these similarities/links and the semantic
annotations provided by humans that are present on
the pages, and suggests annotations to wiki pages.
These annotations are not directly stored in the pages,
they are suggested to users that can validate, modify
or refuse these annotations. The resulting annotations
in the semantic wiki is based on several levels of col-
laboration: explicit human collaboration when writ-
ing HA, implicit human collaboration to suggest CA
and human-machine collaboration to produce HCA.
We are currently conducting experimentations and
user studies to validate our approach; the preliminary
results are very encouraging. As a future work, we in-
tend to refine the way the HCA are obtained; we aim
at not making a CA become directly a HCA when a
user validates or modifies it, or being a RA if a user
refuses it, but by waiting to have a consensus about
the actions of the users. This approach, that will be
based on a server of traces, will have the advantage
that annotations will not change constantly.
HUMAN COMPUTER COLLABORATION TO IMPROVE ANNOTATIONS IN SEMANTIC WIKIS
93

REFERENCES
Adomavicius, G. and Tuzhilin, A. (2005). Toward the next
generation of recommender systems: A survey of the
state-of-the-art. IEEE transactions on knowledge and
data engineering, 17(6):734–749.
Bonnin, G., Brun, A., and Boyer, A. (2009). A low-order
markov model integrating long-distance histories for
collaborative recommender systems. In Proceedings
of the ACM International Conference on Intelligent
User Interfaces (IUI’09), pages 57–66, Sanibel Is-
lands, USA.
Buffa, M., Gandon, F. L., Ereteo, G., Sander, P., and Faron,
C. (2008). Sweetwiki: A semantic wiki. Journal of
Web Semantics, 6(1):84–97.
Durao, F. and Dolog, P. (2009). Tag-based recommenda-
tion in kiwi. In Fourth Workshop on Semantic Wikis
(SemWiki2009) at the 5th European Semantic Web
Conference (ESWC 2009).
Goldberg, D., Nichols, D., Oki, B., and Terry, D. (1992).
Using collaborative filtering to weave an information
tapestry. Communications of the ACM, 35(12):61–70.
Kr
¨
otzsch, M., Vrandecic, D., V
¨
olkel, M., Haller, H., and
Studer, R. (2007). Semantic wikipedia. Journal of
Web Semantic, 5(4):251–261.
Mobasher, B. (2007). Data Mining for Web Personalization,
chapter 3, pages 90–135. LNCS 4321 - Brusilovsky,
P. and Kobsa, A. and Nejdl, W.
O’Connor, M. and Herlocker, J. (1999). Clustering items
for collaborative filtering. In Proceedings of the 22th
Annual International ACM SIGIR Conference.
Pazzani, M. and Billsus, D. (2007). The Adaptive Web,
chapter Content-Based Recommendation Systems,
pages 325–341. Springer Berlin / Heidelberg.
Reeve, L. and Han, H. (2005). Survey of semantic annota-
tion platforms. In Proceedings of the 2005 ACM Sym-
posium on Applied Computing.
Sarwar, B., Karypis, G., Konstan, J., and Reidl, J. (2001).
Item-based collaborative filtering recommendation al-
gorithms. In World Wide Web, pages 285–295.
Skaf-Molli, H., Rahhal, C., and Molli, P. (2009). Peer-
to-peer semantic wikis. In Bhowmick, S. S., K
¨
ung,
J., and Wagner, R., editors, DEXA, volume 5690 of
LNCS, pages 196–213. Springer.
Weiss, S., Urso, P., and Molli, P. (2007). Wooki: a p2p wiki-
based collaborative writing tool. In Web Information
Systems Engineering, Nancy, France. Springer.
Yong, W., Zhanhuai, L., and Yang, Z. (2005). Mining se-
quential association-rule for improving web document
prediction. In Proceedings of the Sixth International
Conference on Computational Intelligence and Multi-
media Applications (ICCIMA’05).
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
94
