
LEARNING METHODOLOGIES AND THEIR SOFTWARE
TOOLS
An Approach to Definition of Possible Use Scenarios
Mario Massimo Petrone, Eugenio Pasquariello
University of Molise, Via De Sanctis, Campobasso, Italy
Roberto Valente, Massimo Brunale
University of Molise, Via De Sanctis, Campobasso, Italy
Keywords: e-Learning, Learning methodologies, Software tools.
Abstract: e-Learning represents the opportunity to design and facilitate learning process, redefining the standard
learning methods by using information technologies. The aim of this paper is to give a picture of the
different use scenarios of the tools used to reach our purposes in respect of the methodologies intended to
adopt. In particular, we analyze : specific relationships between e-learning tools, different usage methods,
interaction types and educational aims. Using the proposed model, the teachers can create teaching solutions
that exploit opportunities offered by the technology and aid students to learn in more effective way.
1 INTRODUCTION
Typically, e-learning is used to reduce unitary costs
for production/distribution of learning resources and
to increase the number of users. Direct interpersonal
relationships results more effective then
relationships mediated by ITC, but they are not
replicable and more expensive both for the teaching
assets (every new edition of a lesson has duplicated
costs) and for the learning assets (caused by the need
of teacher’s presence). Consequently, the strategies
offered by ICT learning solution reduce
organizational costs for training and result more
diffused.
In order to reach proposed learning aims adopting
intended methodologies, we propose, as explained in
this paper, a detailed picture about usage scenarios
of analysed teaching tools.
In particular, we analyze some specific relationships
between e-learning tools, different usage methods,
type of interaction and educational aims.
2 THE CONTEXT
The planning and the articulating phases of learning
processes are characterized by high chances to freely
choose typologies and characteristics of different
components used. For example, we refer to roles and
relationships between students and teachers, to time
dedicated to head-on lessons, to individual work, to
deductive and inductive approaches, to interactivity
level and to time dedicated to exercises.
Regarding on e-learning, these stages get more
complexes because of the use of technology. All this
gives an important role to actor’s competences: if we
suppose that a teacher is able to design and articulate
a traditional lesson, the lack of consolidated learning
models, the limited experience in technological tools
use and more the lack of knowledge of their
existence, can cause a possible inefficiency in the
learning process.
So, the use of e-learning solutions has a double
consequence : the opportunity of many potentialities
but a bigger complexity due to the absence of
experience. Then it is interesting to focus attention
on a model able to present scenarios for e-learning
process design.
277
Massimo Petrone M., Pasquariello E., Valente R. and Brunale M. (2010).
LEARNING METHODOLOGIES AND THEIR SOFTWARE TOOLS - An Approach to Definition of Possible Use Scenarios.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 277-283
DOI: 10.5220/0002798602770283
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The model we presented is addressed to that actors
that intend to use learning methodologies; it would
be useful to helps teachers in designing learning
solutions by using different opportunities offered by
ICT.
3 LEARNING MODELS AND
TECHNOLOGICAL TOOLS
During the development phase of our research, we
proposed some innovative learning experiences
regarding methodology and technological tools
adopted.
Due to the lacking of a theoretical framework based
on e-learning pedagogy, we don’t impose particular
constraints to teachers either regarding aims,
teaching methodologies and technological choices to
adopt, because we aim to obtain an experimental
dataset.
To enhance the aspects related to the learner, we
propose methods that are not substitutive but
additional to existing learning offer; so, the activities
to realize are intended not “instead of” but “together
with” the existing.
To give a set of possible usage scenarios of used
tools, we analyzed different forms. In particular, the
one regarding teaching models and the one regarding
technological tools.
3.1 Teaching Models
To focus on basic teaching models, we refer to three
main paradigms of learning and in particular :
Rational – informational;
Systemic – interactional;
Constructive – social.
Rational-informational paradigm refers to a teaching
model based on contents transmission which use a
learning process that consist in an actor who
transmits contents to another who receive these
contents. Thus the students read and use contents in
passive way; in this model is not foreseen much
interaction between students and teacher or between
students and students and the student’s evaluation
usually consists in some tests.
On the other hand, Systemic-interactional paradigm
refers to a cooperative teaching model. The lessons
consists not only in supplying and using contents
but, especially, in exchanging and comparing
experiences and competences. Learning is done by
teams and every member of a team give an
important contribution to the learning process. It is
the most diffused and effective model.
Constructive-Social paradigm consists to a teaching
model based on laboratory approach. Work by team
becomes very important. It aims to interaction
willing to realize a product creating a learning
community able to operate beyond time and space
bounds of the physical class.
Starting from this paradigms we found that the
different types of interaction, in presence or at
distance, between actors involved in learning
solution are:
Teacher – student/s;
Student/s- Student/s;
Student-Computer.
Educational aims to reach the object to help students
to learn are:
learn to retrieve, organize and analyze
information;
activate critical thinking;
stimulate students to be involved to
cooperation;
help to realize what learned in theory
(deductive approach);
promote learning-by-doing (inductive
approach).
In table 1 [S. Genone, C.Matri, L.Mari, 2002] are
presented all the entities mentioned before and their
relationships. In particular :
in columns EDUCATIONAL AIMS and
INTERACTION TYPE are reported entries
mentioned before;
in column TYPE OF TOOL are reported
type of tools that can be used;
in column USAGE METHODS is
described how instruments can be used,
explaining time/space dimension (in
presence/ at distance, in
synchronous/asynchronous way).
3.2 Technological Tools
Employment of technological tools in e-learning
determine often a digital divide between users
regarding the available band, the higher familiarity
in the use and the “integration” of these tools in
daily life.
To limit mentioned digital divide is necessary to
design every decision:
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
278
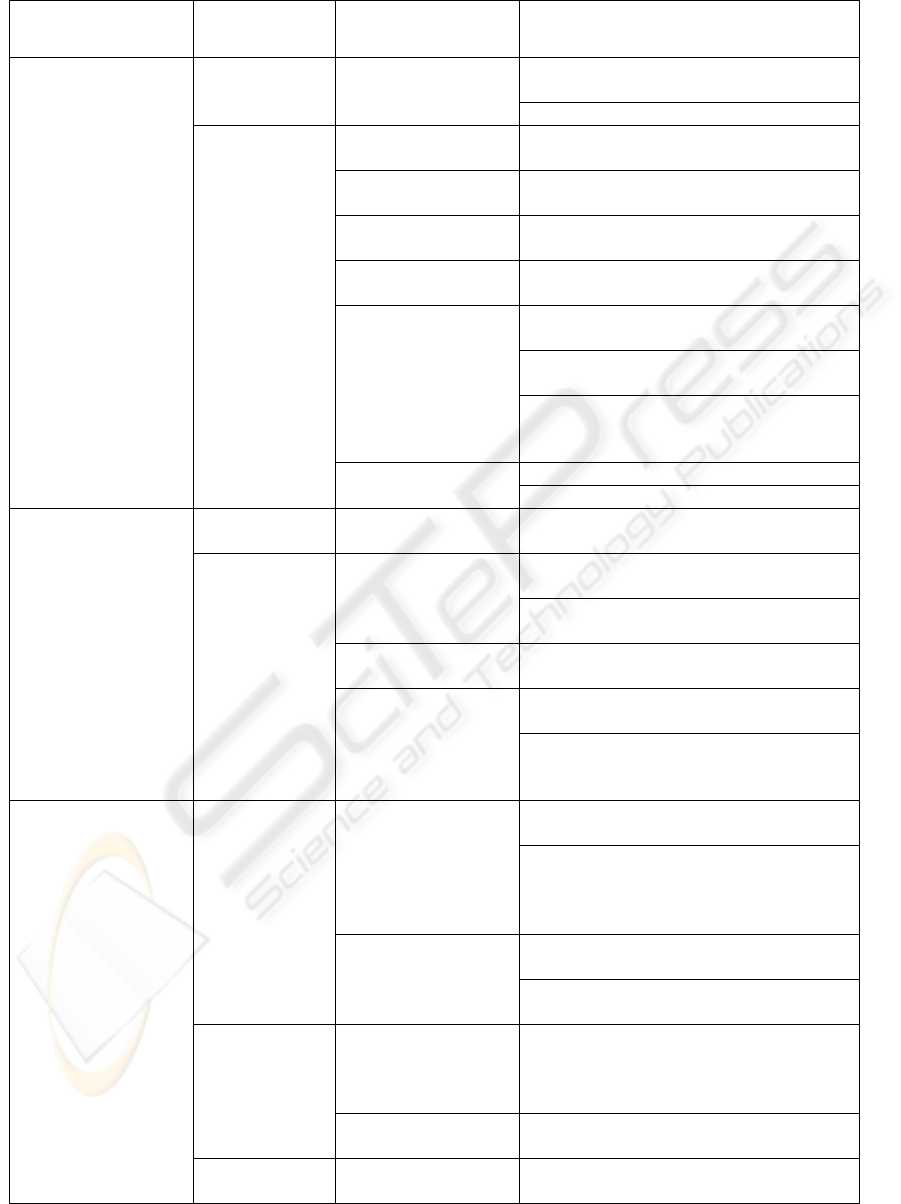
Table 1: Relationship between aims, interactions, tools and usage methods.
Educational Aims
Interaction
Type
Type of tool Usage methods
Learn to retrieve,
organize and analyze
information.
Teacher –
Student/s
Forum
At distance – to communicate and exchange
materials during meetings.
At distance – to manage FAQs.
Student/s –
Computer
Animation
In presence or at distance - to support
students in employment procedures.
Movie
In presence – to support theory through
presentation of a token.
Glossary
In presence or at distance – used by students
to make key concepts more clear.
Multimedia
presentation
At distance – by self learning, to revise and
examine contents dealt at lesson.
Hypertext structure
In presence – to organize arguments and
relative contents for navigation by students.
In presence – to show links and relationship
between didactical resources.
In presence – to give an unique view of
dealt theme, presenting didactical resources
through conceptual maps.
Test
At distance – for self evaluation.
In presence – to discuss results together.
Activate critical
thinking
Teacher –
Student/s
Forum
In presence – to open discussion regarding
specific theoretical thematics.
Student/s -
Computer
Movie
In presence – to support theory through
presentation of a token.
In presence – to discuss starting from a real
situation and gain the general conclusions.
Multimedia
presentation
At distance – by self learning, to revise and
examine contents dealt during the lesson.
Hypertext structure
In presence – to show links and relationship
between didactical resources.
In presence – to give an unique view of
dealt theme presenting didactical resources
through conceptual maps.
Stimulate
students to be
involved to
cooperation
Teacher –
student/s
Virtual community
In presence – to manage classroom in real
time during practice.
In presence – to allow the exchange of
contributions and files in real time between
teacher, students and student groups during
driven exercises.
Forum
In presence – to open discussions about
specific theoretical thematics.
In presence – to suggest exercises and get
results of assignments.
Student/s-
student/s
Virtual community
In presence – to allow the exchange of
contributions and files in real time between
teacher, students and student groups during
driven exercises.
Forum
At distance – to communicate and exchange
materials during meetings
Student/s-
computer
Movie
In presence – to discuss starting from a real
situation and gain the general conclusions.
LEARNING METHODOLOGIES AND THEIR SOFTWARE TOOLS - An Approach to Definition of Possible Use
Scenarios
279

Table 1: Relationship between aims, interactions, tools and usage methods.(cont.)
Educational Aims
Interaction
Type
Type of tool Usage methods
Business/game
simulator
In presence - to apply the concepts
presented in theory.
In presence – to start from a real issue and
reach the related theoretical concepts.
Test
At distance – for self evaluation.
In presence – to discuss results together.
Help to realize
what learned in theory
(deductive approach)
Student/s-
computer
Animation
In presence or at distance - to support
students in employment procedure.
Exercise
In presence or at distance – to apply the
concepts presented in theory.
Movie
In presence – to support theory through
presentation of a token.
Business/game
simulator
In presence – to apply the concepts
presented in theory.
Promote
learning-by-doing
(inductive approach)
Student/s-
computer
Exercise
In presence or at distance – to apply the
concepts presented in theory.
In presence – to start from a real issue and
reach the related theoretical concepts.
Movie
In presence – to discuss starting from a real
situation and gain the general conclusions.
Business/game
simulator
In presence – to start from a real issue and
reach the related theoretical concepts.
referring to technological mix and
integration between tools;
giving attention at daily used instruments
by users.
It’s necessary, in particular, to analyze different
possible uses of tools to:
collaborative building of contents;
materials sharing;
knowledge structuring.
So, for each available software tool it’s necessary to
get the following information:
aims;
main function;
(communications/collaboration/sharing/kno
wledge structuring)
minor function
(communications/collaboration/sharing/kno
wledge structuring);
type of tool;
type of interaction
(synchronous/asynchronous - one to one,
one to many , many to many);
predominant contents type (text, audio,
multimedia);
required knowledge (high/medium/low);
complex usage possibility
(high/medium/low);
Technological complexity
o Client side (high/medium/low)
o Server side (high/medium/low)
Management complexity
(high/medium/low)
Spread level (high/medium/low)
Costs (high/medium/low)
In table 2 is reported a form for evaluation of
software solution individuated based on information
mentioned before.
Table 2: Evaluation form for software tools.
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
280
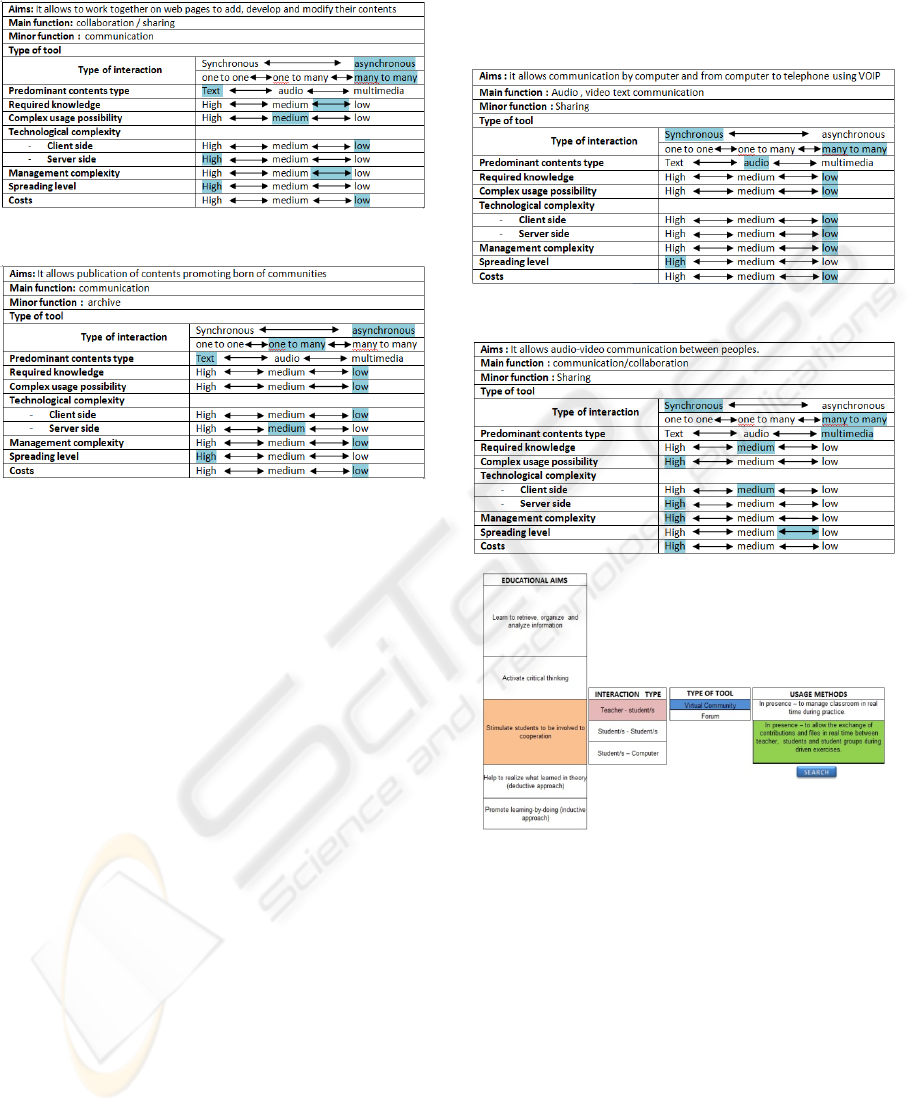
Table 3: Evaluation form for WIKI.
Table 4: Evaluation form for “BLOG”.
4 PROPOSED PROTOTYPE TO
DEFINE SCENARIOS OF
TOOL’S UTILIZATION
(E-LEARNING TOOLS)
Basing on considerations done on teaching model
and technological tools, we explained a method that
starts from the educational aims and reaches the
different tools that can be used.
In particular, basing on information presented in
Table 1:
Educational aims;
Interaction type;
Instrumental type;
Usage modes;
it is possible to individuate available software
solutions that will be analyzed using aspects
contained in Table 2.
Regarding the technological tools we decided to not
define a list tools because:
it cannot be comprehensive;
it needs very frequent updates.
So we decided to create a collaborative web based
application that using users experiences, permits to
share knowledge. In our work the user can browse
the different tools evaluated previously by others,
and collaborate in evaluation of new tools. We
foresee the need of an committee to ensure fair
evaluations. Therefore we think to add a
functionality that permits user’s rating.
Table 5: Evaluation form for “SKYPE”.
Table 6: Evaluation form for “WEB CONFERENCE”.
Figure 1: The choosing of the different tools.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The use of the model presented in this paper has
revealed that different usage methods related to the
same tools can match different educational aims: to
properly design a didactical path is not enough
specify instrument, but it’s very important choose
specific methodologies whereby instrument is
intended to be used.
Therefore, thanks to the proposed prototype,
planning and articulating phases for learning
processes result in different learning context designs,
in terms of instruments, interactions and usage
methods.
LEARNING METHODOLOGIES AND THEIR SOFTWARE TOOLS - An Approach to Definition of Possible Use
Scenarios
281

Figure 2: Search results.
Figure 3: Description of choosed tools.
Figure 4: Evaluation parameters of choosed tools.
The teacher can individuate usage scenarios for
different technological tools by following reference
forms offered and, consequently, can realize
formative solutions that, using opportunities
provided by technologies, could help students to
make learning more effective.
Experience derived from our prototype utilization
could let, to increase awareness on teaching
opportunities offered by ITC utilization.
Furthermore we expertise that collaborative use of
our prototype, basing on users experiences, lead to a
correct multidimensional evaluation of learning tools
analyzed.
The goal we intend to reach is a correct and
opportune use of learning tools for didactical aims. It
becomes reachable trough the given possibility to
express assessments, to share experience and to
advise about correct use of interested tools.
In future, we intend to provide the opportunity to use
different methodologies, or make our starting model
better, acquiring user’s feedbacks.
In addition we intend to improve our prototype to
reach the goal of a close collaboration between
teaching theoreticians and tools developers. This can
be accomplished by introducing a set of
collaborative instruments that allow users to suggest,
ask and share information about tools,
methodologies and their practical use.
Finally we would make our web application
available through the Internet so it could be used by
e-learning communities.
REFERENCES
Ausubel D.P., Educazione e processi cognitivi, Angeli,
Milano, 1998, 101.
Badii A., Truman S. (2001), Cognitive Factors in Interface
Design: An E-Learning Environment for Memory
Performance and Retention Optimisation, in: Remenyi
D. e Brown A., (eds), Eighth European Conference on
Information Technology Evaluation, Oriel College,
United Kingdom, 479-490.
Bloom B., Taxonomy of Educational Objectives, Handbook
1: Cognitive Domain, Davis McKJay Lo Inc, New
York, 1956.
Calvani A., Varisco B.M., Costruire/decostruire significati.
Ipertesti, micromondi e orizzonti formativi, CLUEP,
Padova, 1995.
Calvani A., Rotta M., Comunicazione e apprendimento in
Internet. Didattica costruttivistica in rete, Centro Studi
Erickson, 1999.
Cenarle M., Biolghini D., Net learning - Imparare insieme
attraverso la rete, Etas, Milano, 2000.
Dede C. (1990), The Evolution of Distance Learning:
Technology - mediated Interactive Learning, Journal of
Research on Computing in Education, 22, 3.
Engines for Education, Learning by doing, available:
http://www.engines4ed.org/hyperbook/nodes/NODE-120-
pg.html
Gokhale A.A. (1995), Collaborative Learning Enhances
Critical Thinking in Digital Library and Archives,
Journal of Technology Education, 7, 1, Fall 1995,
available:
http://scholar.lib.vt.edu/ejournals/JTE/jte-v7n1/gokhale.jte-
v7n1.html
CSEDU 2010 - 2nd International Conference on Computer Supported Education
282

Gross Davis B., Tools for Teaching, Jossey-Bass
Publishers, San Francisco, 1993.
Keeton M., Sheckley B., Krejci-Griggs J., Effectiveness
and Efficiency in Higher Education for Adults, Council
on Adult and Experiential Learning, Kendall-Hunt,
Chicago, 2002.
Jacobson M.J. (1994), Issues in Hypertext and Hypermedia
Research: Toward a Framework for Linking Theory-to-
Design, in Journal of Educational Multimedia and
Hypermedia, 3, 2, 1994, 141-154.
Johnson D.W., Johnson R.T., Smith K.A., Active Learning:
Cooperation in the College Classroom, 2nd edn,
Interaction Book Company, Edina, MN, 1998.
Laeng M. (1996), La multimedialità da ieri a domani, in
Rivista dell’istruzione, 6, 1996, 905.
Maragliano R., Nuovo manuale di didattica multimediale,
Bari, Laterza,1998.
Piccoli G., Ahmad R., Ives B. (2001), Web-Based Virtual
Learning Environments: A Research Framework and a
Preliminary Assessment of Effectiveness in Basic IT
Skills Training, MIS Quarterly, 25, 4, December 2001,
401-426.
Saunders P., Werner K. (2000), Finding the right blend for
effective learning, Center for Teaching and Learning,
Western Michigan University, available:
http://www.wmich.edu/teachlearn/new/blended.htm
Tinzmann M.B., Jones B.F., Fennimore T.F., Bakker J.,
Fine C., Pierce J., What Is the Collaborative
Classroom?, NCREL, Oak Brook, 1990, available:
http://www.ncrel.org/sdrs/areas/rpl_esys/collab.htm
Trentin G., Insegnare e apprendere in rete, Zanichelli,
Bologna, 1998.
Trentin G. (2000), Lo Spettro dei Possibili Usi delle Reti
nella Formazione Continua e a Distanza, in: Lettera
Asfor, Offerta Formativa Technology Based: Linee di
Sviluppo e Criteri di Qualità, Milano, 1-6.
Tsichristzis D. (1999), Reengineering the University,
Communications of the ACM, 42:6, 93-100.
Weigel V. (2000), E-Learning and the Tradeoff Between
Richness and Reach in Higher Education, Change, The
Magazine of Higher Learning, available:
http://www.heldref.org/html/body_chg.html
Weimer M., Learner-Centered Teaching: Five Key
Changes to Practice, Jossey-Bass, 2002.
Wilson B.G., Constructivistic Learning Environments,
Educational Technology
Publications, Englewood Cliffs, N.J., 1996.
LEARNING METHODOLOGIES AND THEIR SOFTWARE TOOLS - An Approach to Definition of Possible Use
Scenarios
283
