
SUPPORTING INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN RSS FEEDS
Georges Dubus, Mathieu Bruyen and Nac
´
era Bennacer
E3S - SUPELEC, 3 rue Joliot-Curie, F-91192, Gif-sur-Yvette, France
Keywords:
Information retrieval, Text mining, Partitioning clustering, k-means, RSS feeds, XML, TFIDF.
Abstract:
Really Simple Syndication (RSS) information feeds present new challenges to information retrieval technolo-
gies. In this paper we propose a RSS feeds retrieval approach which aims to give for an user a personalized
view of items and making easier the access to their content. In our proposal, we define different filters in
order to construct the vocabulary used in text describing items feeds. This filtering takes into account both
the lexical category and the frequency of terms. The set of items feeds is then represented in a m-dimensional
vector space. The k-means clustering algorithm with an adapted centroid computation and a distance measure
is applied to find automatically clusters. The clusters indexed by relevant terms can so be refined, labeled and
browsed by the user. We experiment the approach on a collection of items feeds collected from news sites.
The resulting clusters show a good quality of their cohesion and their separation. This provides meaningful
classes to organize the information and to classify new items feeds.
1 INTRODUCTION
Really Simple Syndication (RSS) information feeds
present new challenges to information retrieval tech-
nologies. These feeds allow people who regularly use
the web to be informed by the latest update from the
sites they are interested in. The number of sites that
syndicate their content as RSS feeds increases contin-
uously. Aggregator tools allow users to grab the feeds
from various sites and to display them. However, the
subscriber could be submerged by the number of pro-
vided news. Besides, different feeds items may speak
about the same information so it is interesting to make
an information more complete and less sparse for the
user. For example, the set of items speaking about Ira-
nian war should be grouped in the same cluster and
those about the ecology and the environment in Eu-
rope should be found in another cluster.
In this paper we propose a RSS Organizing and
Classification System (ROCS) approach which aims
to give for the user a personalized view of items and
making easier the access to their contents.
Many works investigate different aspects of text
information retrieval such mining knowledge, infor-
mation organization and search. In the vector space
model proposed in (Salton et al., 1975) the text is rep-
resented by a bag of terms (words or phrases). Then,
each term becomes an independent dimension in a
very high dimensional vector space. The vocabulary
selection depends strongly on the processed collec-
tion and may be based on statistical techniques, nat-
ural language processing, documents structures and
ontologies ((Cimiano et al., 2005), (Etzioni et al.,
2005) and (Thiam et al., 2009)). Unsupervised clus-
tering methods based on such a representation have
been used for automatic information extraction (Jain
et al., 1999).
In our proposal, we define different filters to se-
lect the vocabulary that will be used in the cluster-
ing model construction. The lexico-syntactic filter se-
lects words according to their lexical category. The
stop-words filter discards the words that are consid-
ered as non-informative. The statistical-based filter
selects the words according to their frequency on all
the items. Weighting terms represents the discrimina-
tory degree of terms using tfidf measure. The unsu-
pervised clustering algorithm k-means is applied with
k-means
++
centroid computation (Arthur and Vas-
silvitskii, 2007) which is a way of avoiding poor or
big clusters. The metric distance used on the vectors
space allows evaluating the similarity/dissimilarity
between items by taking into account the terms that
these items share. So, once the clusters are automat-
ically generated they can be validated, refined and
307
Dubus G., Bruyen M. and Bennacer N.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN RSS FEEDS.
DOI: 10.5220/0002809103070312
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technology (WEBIST 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-674-025-2
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

browsed by the user and new items can be classi-
fied. We experiment the approach on a set of items
feeds collected from news sites such as CNN, Reuters
and Euronews. The analysis of the resulting clusters
shows that the quality of their cohesion and their sep-
aration provides meaningful support to organize the
information and to classify new items feeds.
The remainder of the paper is organized as fol-
lows. The section 2 presents briefly the architecture of
ROCS approach. The section 3 presents the clustering
model construction. The section 4 presents the results
of first experiments and their evaluation. In section 5,
we conclude and present some perspectives.
2 ROCS ARCHITECTURE
2.1 Brief Description
The figure 1 depicts the components of the architec-
ture of ROCS. The items feeds are collected from
the feeds by the aggregator component. This col-
lection is then successively processed by the filtering,
the weighting and the clustering components.The user
can refine the clusters and modify them by moving
some items from a cluster to another. When new items
are extracted, the supervised classifier component as-
signs them according to the existing model (clusters).
2.2 RSS Structure Representation
A feed contains items with a title and an abstract for
each one. An item represent an article of the web site,
and the feed is modified each time an article is pub-
lished. The root markup of the XML is called rss, it
contains a node called channel.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<rss version="2.0" xmlns:atom=
"http://www.w3.org/2005/Atom">
<channel> ... </channel>
</rss>
The feed may contain other optional markups such as
the language markup which specifies the language
used in the feed. In additional to this information, the
feed contains several item markups which are located
under the channel one.
<item>
<title> the title of the item</title>
<category> the category of the content
according to the author,
its domain attribute,
categories </category>
<link> the url of the website
the feed is related to </link>
<description> the abstract of
the item </description>
<pubDate> the publication
date of the article </pubDate>
<guid></guid>
</item>
In the following, we construct the vocabulary from
title and description markups contents.
3 CLUSTERING MODEL
CONSTRUCTION
3.1 Definitions and Notations
Let I be a collection of n feed items: I = {I
1
···I
n
}
where I
i
is an item. Our aim is to split the collection
I into mutually disjointed subsets C
1
,···C
k
, where k
is the fixed number of clusters. So that each I
i
is in
exactly one cluster C
j
and each C
j
should have at least
one item assigned and it must not contain all items:
C =
S
k
i=1
C
j
, ∀ j C
j
6=
/
0, and C
i
∩C
j
=
/
0 ∀i 6= j
Let T = {t
1
···t
m
} the set of terms of the vocabu-
lary used in the items contents. We apply the vector
space model where each I
i
is represented by a point in
a m-dimensional vector space :
−→
I
i
(w
i1
···w
im
) where
w
ik
is the weight of term t
k
in the item I
i
. This weight
measures the contribution of a term in the specifica-
tion of the semantics of an item. The first step of our
approach is to select terms that can both characterize
and discriminate all the items by applying filters f
1
, f
2
and f
3
. Each item I
i
is then converted into vectors
−→
I
i
in | f
3
( f
2
( f
1
(T )))|-dimensional space. We denote
−→
I
the set of vectors
−→
I = {
−→
I
1
···
−→
I
n
}.
As a result, considering a distance measure, the
problem is reduced to a vector clustering problem
in an euclidean space. The second step consists in
grouping
−→
I
i
into k vectors clusters
−→
C
j
which is equiv-
alent to grouping I
i
into k clusters C
j
:
−→
I
i
∈
−→
C
j
⇔ I
i
∈ C
j
We denote
−→
C the set of vectors clusters
−→
C =
{
−→
C
1
···
−→
C
k
}.
3.2 Filtering Approach
In order to represent the items in the most precise
way, we need to select only the most relevant terms
that capture the meaning of an item. The core idea
is that the items which share the same terms are re-
lated. The granularity of term we consider is the
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
308
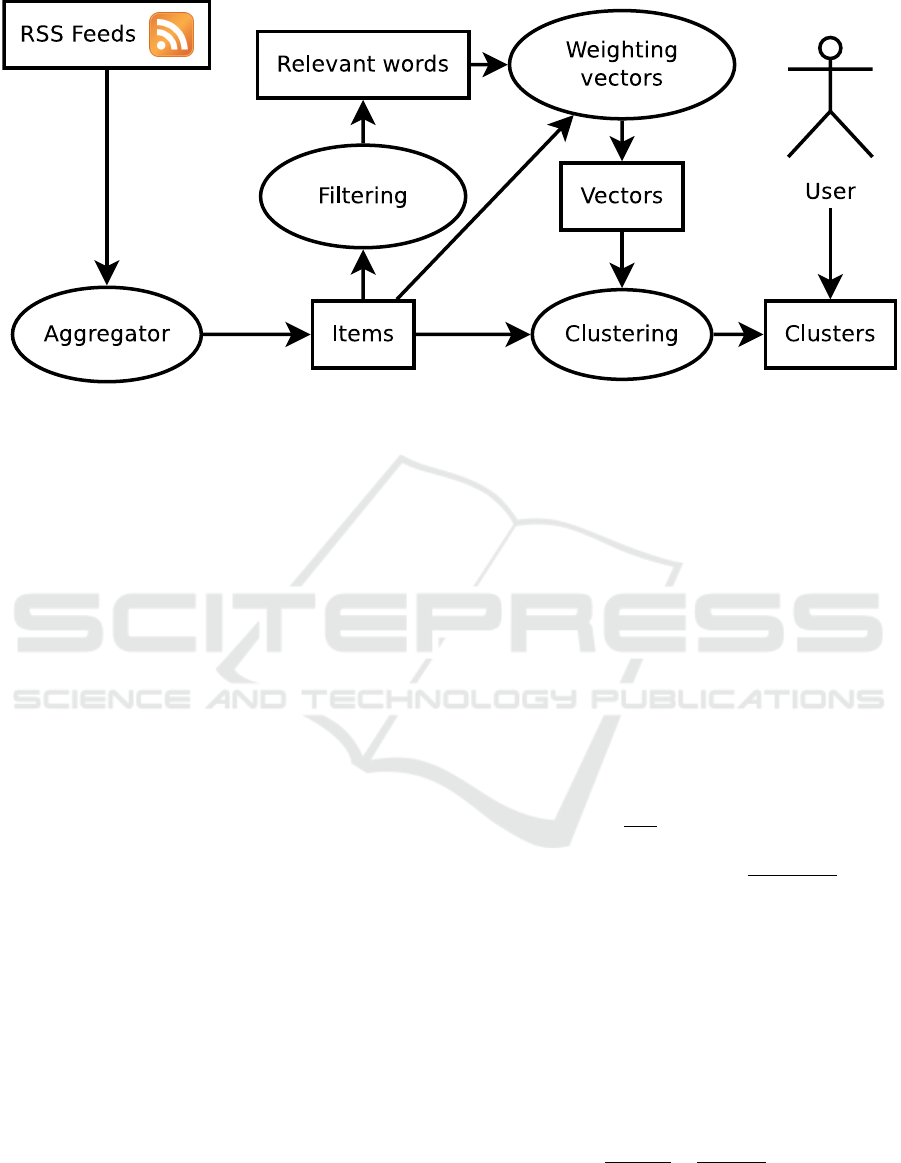
Figure 1: ROCS Architecture.
word. To choose relevant words, we combine suc-
cessively lexico-syntactic filter f
1
, stop-words filter f
2
and frequency-based filter f
3
.
3.2.1 Lexico-syntactic Filter
We can estimate the amount of information contained
in a word knowing its lexical category. For exam-
ple, nouns and verbs contains more information than
pronouns and prepositions. In order to determine the
lexical category, we use part-of-speech tagging tools.
The vocabulary T is represented by the set of words,
each one is represented by its stem. The filter f
1
se-
lects common and proper nouns and verbs.
3.2.2 Stop-words Filter
Some words such as auxiliaries, while they may be
tagged as verbs, appear frequently in the vocabulary
and don’t discriminate the items. The filter f
2
discards
such words from f
1
(T ) by using a list of stop-words.
This list contains words like “do”, “have” and “make”
and may be enriched or modified by the user.
3.2.3 Frequency-based Filter
Some words carrying some meaning may not discrim-
inate the items, because they only appear once, or too
often in the entire collection. In order to prevent these
words from being selected, we analyze the frequency
of the word in the collection. A word appearing in
only one item won’t be selected, neither a word ap-
pearing in almost all the items. For example, in a set
f
2
( f
1
(T )) that contains 375 words 299 of them were
present in only one item, and thus had been discarded
by the filter f
3
. This enables us to reduce the vectors
dimension without losing relevant words. On the op-
posite, removing the word present in too much items
is nearly useless, as most of that words are removed
as stop-words.
3.3 Weighting Vectors
Term weighting is an important aspect of text re-
trieval. The “Text Frequency Inverse Document Fre-
quency” measure (tfidf) aims at balancing the local
and the global word occurrences. Each item vec-
tor
−→
I
i
is linked to a word w
k
by a weight w
ik
de-
pending on the frequency of the word in the item
I
i
and in the all set I. It will more weight words
that appear in fewer items. Let n
ik
be the number
of occurrences of the word w
k
in the item I
i
. The tf
measure is t f
ik
=
n
ik
∑
l
n
il
. The idf measure calculates
the normalized inverse of the number of items that
contain the word w
k
: id f
k
= log
|I|
|{I
i
∈I/w
k
∈I
i
}|
. Thus
w
ik
= t f id f
ik
= t f
ik
id f
k
.
3.4 Similarity Measure
The quality of the clusters is largely dependent on the
similarity or dissimilarity measure that determines if
two items are close or not. In ROCS, well-known
metric distances as Euclidian, Manhattan and Muller
distances are implemented. In our experiments, the
Muller distance has better results than the others. It is
defined as follows:
m
i
− m
i j
m
i
+
m
j
− m
i j
m
j
where m
i
is the number of words in the item I
i
, m
j
the
number of words in the item I
j
and m
i j
the number of
words that are in both items.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN RSS FEEDS
309

3.5 Clustering Algorithm
Clustering algorithms are unsupervised and automatic
methods that aim at grouping items into clusters with-
out a priori knowledge about clusters. The collection
of items falling into the same cluster are more simi-
lar to each other than those found in different clusters.
k-means algorithm is a partitioning clustering method
which splits iteratively
−→
I points (vectors) into k clus-
ters as follows:
1. Arbitrarily choose k initial centers
−→
c
1
,··· ,
−→
c
k
.
2. For each i ∈ [1, k], set the vectors cluster
−→
C
i
to be
the set of points
−→
I
i
that are closer to
−→
c
i
than they
are to
−→
c
j
for all j 6= i.
3. For each i ∈ [1,k], recompute the new cluster cen-
ters
−→
c
i
to be the center of mass of all points in
−→
C
i
.
4. Repeat steps 2 and 3 until ∀i
−→
C
i
no longer changes.
The arbitrary choice of initial centers leads generally
to “empty” and too “big” clusters. The k-means
++
(Arthur and Vassilvitskii, 2007) provides an alterna-
tive way to select these points. It ensures that the
points are well-spread all over the space so that im-
proves the results.
1. Choose an initial center
−→
c
1
uniformly at random
from
−→
I .
2. Choose the next center
−→
c
i
, selecting
−→
c
i
=
−→
y ∈
−→
I with the probability
D(
−→
y )
2
∑
x∈χ
D(
−→
x )
2
, where D(
−→
x ) is
the distance to the closest center we have already
chosen.
3. Repeat Step 2 until we have chosen a total of k
centers.
3.6 Classification of New items
The clusters that we obtain from unsupervised and au-
tomatic clustering process are indexed by a list of the
most important words in the cluster (namely the most-
weighting coefficients of the centroid). These clusters
are refined and labeled by the user, then new items can
be classified in supervised manner. Each new item
I
c
is represented by the vector
−→
I
c
in the defined di-
mensional space where each element is weighted us-
ing tfidf measure, and assigned to the cluster whose
centroid is the closest. The number of new items in-
creases as RSS feeds updates. Thus the vocabulary
could change and could be enriched. In this case the
unsupervised and automatic clustering process could
be applied again in order to generate more adapted
clusters.
4 EXPERIMENT AND RESULTS
EVALUATION
4.1 Application Description
The different components of architecture de-
scribed in figure 1 are implemented in C++ using
the Qt toolkit (http://qt.nokia.org). The filtering
component exploits TreeTagger (http://www.ims.uni-
stuttgart.de/projekte/corplex/TreeTagger/) for the
part-of-speech analysis. The user interface enables
user the following functionalities: (1) download rss
feeds updates from Web sites to which the user is
subscribed, (2) update of the stop-words list, (3)
use of different similarity measures and setting the
number of clusters (4) visualization and validation of
the resulting clusters (5) classification of new items
using either unsupervised or supervised process.
The figure 2 is a screen copy of the ROCS inter-
face that visualizes the clustering results. The cluster
list is on the left column, where the feeds list stand
in traditional aggregators. The upper part of the main
section contains the list of the items in the selected
cluster, and the bottom part show a description of the
selected item along with the non null coefficients of
the vector that represents it. Each cluster is automati-
cally is indexed by the most important words appear-
ing in its items contents. The user can label a cluster
and move an item from a cluster to another. The mod-
ified clusters are then used to sort the new items.
4.2 Results Evaluation
Some measures are defined in the literature
(Aliguliyev, 2009) in order to make a quantita-
tive evaluation of clusters quality. The cohesion
and separation measure quantifies both the internal
cohesion of a cluster and its separation from the
other clusters. This measure is the ratio of the sum
of intra-cluster similarity deviation to inter-cluster
separation.
CS =
∑
k
p=1
n
1
|C
p
|
∑
I
i
∈C
p
max
I
j
∈C
p
{D(
−→
I
i
,
−→
I
j
)}
o
∑
k
p=1
min
q∈[1..k]
{D(
−→
c
p
,
−→
c
q
)}
Where D(
−→
x ,
−→
y ) is the distance between the points
of coordinates
−→
x and
−→
y . More the value of the
CS measure is lower than 1 more clusters are inter-
nally coherent and well separated. The first exper-
iments are made on 71 items and the vocabulary is
composed of 450 words stems before filtering. The
filtering reduces the vocabulary to 114 words. For
k = 15 clusters we obtain a CS value equal to 0.7. For
instance cluster 1 is indexed by ”fall, Wall, Berlin”
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
310

Figure 2: Results Visualization in ROCS.
contains 50% of items that speak specially about the
Berlin wall, the others concern news about Berlin.
The cluster 2 is indexed by ”people, scandal, US,
army, York” contains news about United-States, its
army or financial crisis. We underline that the word
”New” of ”New York” is not taken into account. The
cluster 3 is indexed by ”China, Visit, Friday, Bei-
jing” and speak about China and US relationships.
The separation between clusters 2 and 3 is less good
because they share information about United-States.
The cluster 5 groups items that contain information
about Afghanistan. This clustering could be improved
if the stop-words is enriched by words such as ”fri-
day”, ”thursday” that appear in some indexes. More-
over, nominal groups are more relevant than individ-
ual words. The heterogeneity of RSS feeds could vi-
olate the principal hypothesis of clustering methods.
The quality of items may vary, some of them are too
long and others too short. Consequently the items are
not represented by the same number of words. An
analysis of items quality could be performed before
filtering in order to improve the clustering.
The purity of a cluster is an external measure that
compares a resulting partition with the true one. It
consists in counting the maximum number of items
common between the given cluster C
p
and the clusters
of user partition. Then the purity of the clusters is the
mean of each cluster purity weighted by the .
purity(C
p
) =
1
|C
p
|
max
q
u
∈[1..k
u
]
C
p
∩C
u
q
u
purity(C) =
k
∑
1
|C
p
|
|C|
purity(C
p
)
In our experiments, we consider the true partition the
one that the user validates. 80% of clusters have a pu-
rity value greater than 75%, the 20% are heterogenous
so it is difficult to compare them to the ”true” clusters.
The supervised classification 80% of new items
(15 items) are correctly classified, for instance
”Berlin Wall: Train of Freedom, leaving East Ger-
many ...” is classified in cluster 1. The ”Two U.S. sol-
diers missing, Afghan Taliban say have bodies ...” are
classified in the cluster 5. In fact, the most important
words of the considered item belong to the cluster in-
dex. This classification is done automatically without
user intervention. It could be improved if we consider
the clusters that are refined and validated by the user.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we propose an automatic, unsupervised
and clustering-based approach which aims to support
the information retrieval in RSS feeds. It relies on
lexico-syntactic and frequency terms filters that al-
lows reducing the vocabulary to relevant words. It
applies the vector space model widely used in text
mining where the term weighting corresponds to tfidf
which measures the discriminatory degree of a term
appearing in the text of the considered item. The re-
sulting clusters are indexed by relevant terms and can
so be refined, labeled and browsed by the user. They
provides meaningful classes to organize the informa-
tion and to classify new items feeds. This aspect deals
with both the evolution of information and the user
needs.
SUPPORTING INFORMATION RETRIEVAL IN RSS FEEDS
311

In order to enhance retrieval effectiveness we plan
to improve the lexico-syntactic filtering by consid-
ering terms such as nominal groups and named en-
tities like institutions, persons, cities and countries.
Indeed, such terms represent better items than indi-
vidual words. For instance if two items speaks about
“UN” or “Russian president” or “Iranian war”, they
are probably related to a common topic. The underly-
ing idea is to assign a higher weight to longer terms.
We also plan to apply other clustering methods in
particular clustering allowing the existence of an item
in different clusters.
Adding a search component which allows
keywords-based queries by exploiting clusters in-
dexes is an interesting perspective.
REFERENCES
Aliguliyev, R. M. (2009). Performance evaluation of
density-based clustering methods. In Information Sci-
ences, volume 179, pages 3583–3602.
Arthur, D. and Vassilvitskii, S. (2007). k-means++: the
advantages of careful seeding. In Proceedings of the
eighteenth annual ACM-SIAM symposium on Discrete
algorithms, pages 1027–1035. Society for Industrial
and Applied Mathematics.
Cimiano, P., Handschuh, S., and Staab, S. (2005).
Gimme’the context : Context driven automatic se-
mantic annotation with c-pankow. In Proceeddings
of Wide World Web Conference (WWW). ACM.
Etzioni, O., Cafarella, M., Downey, D., Kok, S., Popescu,
A., Shaked, T., Soderland, S., Weld, D., and Yates, A.
(2005). Unsupervised named-entity extraction from
the web: An experimental study. In Artificial Intelli-
gence Journal, volume 165(1), pages 91–134.
Jain, A. K., Murty, M. N., and Flynn, P. J. (1999). Data
clustering: a review. volume 31, pages 264–323.
Salton, G., Wong, A., and Yang, C. S. (1975). A vector
space model for information retrieval. In Communi-
cations of the ACM, volume 18(11), pages 613–620.
Thiam, M., Bennacer, N., Pernelle, N., and L
ˆ
o, M. (2009).
Incremental ontology-based extraction and alignment
in semi-structured documents. In Proceedings of Dexa
conference, LNCS 5690, pages 611–618. Springer.
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
312
