
MINIMUM SPANNING TREE FUSING MULTI-SALIENT POINTS
HIERARCHICALLY FOR MULTI-MODALITY IMAGE
REGISTRATION
Shaomin Zhang, Lijia Zhi, Dazhe Zhao and Hong Zhao
College of Information Science and Engineering, Northeastern University, Shenyang, Liaoning, China
Key Laboratory of Medical Image Computing (Northeastern University) Ministry of Education, China
Keywords: Medical Image Registration, Entropic Spanning Graph Estimator, Minimum Spanning Tree (Mst), Rényi
Entropy, Salient Point.
Abstract: In this paper, we propose a novel registration algorithm based on minimal spanning tree. There are two
novel aspects of the new method. First, instead of a single feature points, we extracted corner-like as well as
edge-like points from image, and also added a few random points to cover the low contrast regions; Second,
the hierarchical mechanism which fusing multi-salient points is used to drive the registration during the
registration procedure. The new algorithm has solved the low robustness brought by the instability of
extraction of feature points and the speed bottleneck problem when using MST to estimate the Rényi
entropy. Experiment results show that on the simulated and real brain datasets, the algorithm achieves better
robustness while maintaining good registration accuracy.
1 INTRODUCTION
Medical image registration is the basis of medical
image fusion, and has been used in medical
diagnosis, treatment, research, etc. Information-
theoretic metrics, such as Shannon entropy, Rényi
entropy, Tsallis entropy, etc, have been widely used
in medical image registration. Information-theoretic
metric are needed to estimate the entropy from the
image data. Currently, there are three types of
nonparametric entropy estimation methods: plug-in,
sample-spacings and entropic spanning graphs
estimator (Beirlant et al., 1997; Hero et al., 2002).
Plug-in estimator is simple, and suitable for low
dimensional space. But in high dimensional space, it
will encounter “dimension disaster” problem.
Sample-Spacings estimator was originally developed
for one- dimensional samples. Miller (Miller, 2003)
extended this technique to higher dimensions using
Voronoi regions and Delaunay triangulations.
Graph-based entropy estimators have faster
asymptotic convergence rates, especially for non-
smooth densities and for low dimensional feature
spaces; they completely bypass the complication of
choosing and fine tuning parameters; they can be
easily extended to higher dimensional space (Hero et
al., 2002). Redmond and Yukich (Redmond and
Yukich, 1996) proved that when a graph is “quasi-
additive” in d-dimensional feature space, d>=2, the
graph can be used to estimate the entropy directly.
Hero (Hero et al., 2002) pointed that among the
currently known quasi-additive algorithms, the MST
is the fastest (with polynomial run time) and applied
it to image registration.
On this basis, scholars have done relevant
research in the field of medical image registration
(Sabuncu and Ramadge, 2004, 2008) and found that
it will encounter speed bottleneck when using MST
to estimate the entropy. In order to make
constructing MST feasible for image registration
problem, appropriate features must be extracted to
compress the original great amount of data. Ma (Ma
et al., 2000) registered two images using uniform
sub-sampling. Sabuncu (Sabuncu and Ramadge,
2004) proposed two (deterministic and stochastic)
non-uniform sub-sampling methods for improving
the efficiency. But, uniform sub-sampling method
treats each pixel equally during the registration
procedure, regardless of whether some voxels are
more important than others in registration. Gradient
based sub-sampling method is sensitive to noise, and
feature points are of poor stability.
33
Zhang S., zhi L., Zhao D. and Zhao H. (2010).
MINIMUM SPANNING TREE FUSING MULTI-SALIENT POINTS HIERARCHICALLY FOR MULTI-MODALITY IMAGE REGISTRATION.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 33-36
DOI: 10.5220/0002820700330036
Copyright
c
SciTePress

In this paper, we propose a novel hierarchical
multi-modality registration algorithm which fusing
multi-salient points based on minimal spanning tree.
This new method not only considers multi- salient
points, but also considers hierarchical mechanism
during the registration procedure to improve the
robustness of the registration. Experimental results
showed that the new method has higher success rate
than single feature and uniformly sub-sample
methods based on minimum spanning tree on the
images from BrainWeb (Collins et al., 1998) and
Vanderbilt Retrospective Registration Project(RREP)
(West et al., 1997).
2 METHOD
2.1 Salient Point Extraction
Salient points contain structural and texture
information, which is important for image
registration. For example, the voxels that lie in the
region of interest or at the boundary of region are
more significant for image analysis. First, we
removed the background of the image by the
threshold of grey value. Second, similar to Harris
detector and Yang’s method (Harris and Stephens,
1988; Yang et al., 2007), we use auto-correlation
matrix as a single response measure to produce
potential corner like and edge like points. At each
pixel location x, the Auto-correlation matrix, μ is
computed,
2
11 12
2
21 22
() ()
() ()*
() ()
xxy
xy y
L
xLLx
xg
L
Lx Lx
mm
ms
mm
éù
éù
êú
êú
==
êú
êú
êú
êú
êú
ëû
ëû
(1)
Where g is a Gaussian function with standard
deviation σ. L
α
is the derivative computed in the α
direction. λ1 and λ2 are the eigenvalues of μ.
Potential corners are at pixels where λ1 /λ2>0.1.
Potential edge points are at pixels for which λ1 /
λ2<=0.1. Finally, we got the corner like points and
the edge like points. The result is illustrated in Fig.1.
(a) Potential corner-like points (b) Potential edge-like points
Figure 1: Salient point extraction.
2.2 Hierarchical Registration
Mechanism
In section 2.1, we have got potential corner and edge
points. However, there are two problems in
constructing MST. First, the sum of corner and edge
points is so many, resulting in the speed bottleneck.
Second, many low-contrast regions are not covered
by any of salient points, resulting in much
registration errors. So we use hierarchically
mechanism, which was first proposed by Shen and
Davatzikos (Shen and Davatzikos, 2002), to select
salient points as the active points to drive the
registration during the registration procedure. To
make these points local adaptive, we divided the
image into 10*10 sub-regions. In each sub-region,
we sort the voxels by corner measure and edge
measure respectively.
Corner measure: cornerness = det(μ(x)) – α
trace
2
(μ(x));
Edge measure: edgeness = trace(μ(x));
In order to make the distribution of the active
points more uniform and the method more
robustness, we add some random points to cover the
low contrast regions. The hierarchical selection of
active points in three registration phases is showed
as follows:
First phase: During the initial registration phase,
in each sub-region, the highest strength point of
the corner values is selected as active point. In
this way, we can also select edge point. If the
region doesn’t have any active points, we will
add two random points. If the region has only
one active point, we will add one random point
to the region.
Second phase: With progress of registration,
those second strength potential corner and edge
points will be selected as active points to drive
the image registration, leading to the refinement
of registration results. If the region doesn’t have
enough active points, we will add random points
as first phase.
Third phase: Finally, those third strength corner
and edge points will be considered as active
points for image registration. If the region
doesn’t have enough active points, we will add
random points as first phase.
In each registration phase, we will construct
MST on the active points.
2.3 Entropic Spanning Graph Estimator
Given V={P
i
|P
i
∈
R
2
, i=1,…,n} of n vertices, a
spanning tree is a connected acyclic graph which
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
34

passes through every vertex. All n vertices are
connected by edges E={e
ij
=( P
i
, P
j
)|i, j=1,…,n,
i≠j}. For a given edge weight exponent γ, the
minimum spanning tree is the spanning tree which
minimizes the total edge weight of the graph,
() | |
ij
r
ij
eMST
L
Ve
(2)
For a continuous pdf f, Rényi entropy H
α
(f) is
defined as,
1
() log ()
1
Hf fxdx
(3)
where α=(d-γ)/d.
Steele (Steele, 1998) has proved that the length
of the MST has the following asymptotic property,
()
lim ( )
n
LV
f
xdx
n
(4)
Where β is a constant independent of f.
Combining (3) and (4), we obtain an estimator of
Rényi entropy from the total edge weight of the
MST,
^
^
1()
() [log log ]
1
1()
() log
1
LV
Hf
n
LV
Hf
n
a
g
a
a
a
b
a
a
=-
-
µ
-
(5)
It follows directly from the results of Steele
(Steele, 1998) that the MST estimate
^
H
is a
strongly consistent estimator of H
α
.
3 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
(a) BrainWeb images
(b) RREP images
Figure 2: DataSets.
In this section, we present two sets of experiments.
The first set of experiments is used to test several
variations on the choice of salient points. The second
set is used to evaluate the performance of proposed
method, compared to traditional uniform sub-
sampling based multi-resolution image registration.
All experiments are tested on simulated and real 2D
MR brain images.
Figure 2(a) are the T1 and T2 MR brain images
with 5% noise and 20% intensity non- uniformity
obtained from the BrainWeb MR. Figure 2(b) are the
T1 and T2 MR brain images provided by RREP,
first of all, we register the two images by using their
fiducial markers, and then do the experiment.
3.1 Choice of Salient Points
T1 and T2 MR Brain images of the two datasets
were used to evaluate variations on the choice of the
salient points. T1 image is transformed by a angle
randomly generated from the different range of
degree, and two translations (T
x
, T
y
) from the
different range of pixels. For simulated BrainWeb
dataset, the range is [-15, 15] and [-20, 20], while for
the real RREP dataset, the range is [-10, 10] and [-15,
15]. Each dataset generates 50 randomly
transformed T1. Then the T2 image is registered to
the transformed T1. The registration is regarded as
success if the translation errors on both axes are
below 2 pixel and rotation error below 2 degree. The
success rates of all salient point- based registration
methods were listed in table 1.
Table 1: Comparison of the choice of the salient points.
DataSet Range
Success Rate (%)
Our
Corner-
only
Edge-
only
BrainWeb
[-15, 15] 98 88 82
[-20, 20] 84 84 70
RREP
[-10, 10] 100 92 98
[-15, 15] 72 68 68
From Table 1, we can conclude that this
combination of multi-salient points performed better
than both methods alone for two test datasets.
Particular for BrainWeb image with 5% noise and
20% intensity non- uniformity dataset, the
performance of the edge-based method is lower than
our method due to the edge-base method is more
sensitive to noise.
3.2 Comparison of Registration
Methods
Similar to section 3.1, the success rates of our
propose method and uniform sub-sampling based
method was calculated and listed in Table 2. It is
MINIMUM SPANNING TREE FUSING MULTI-SALIENT POINTS HIERARCHICALLY FOR MULTI-MODALITY
IMAGE REGISTRATION
35
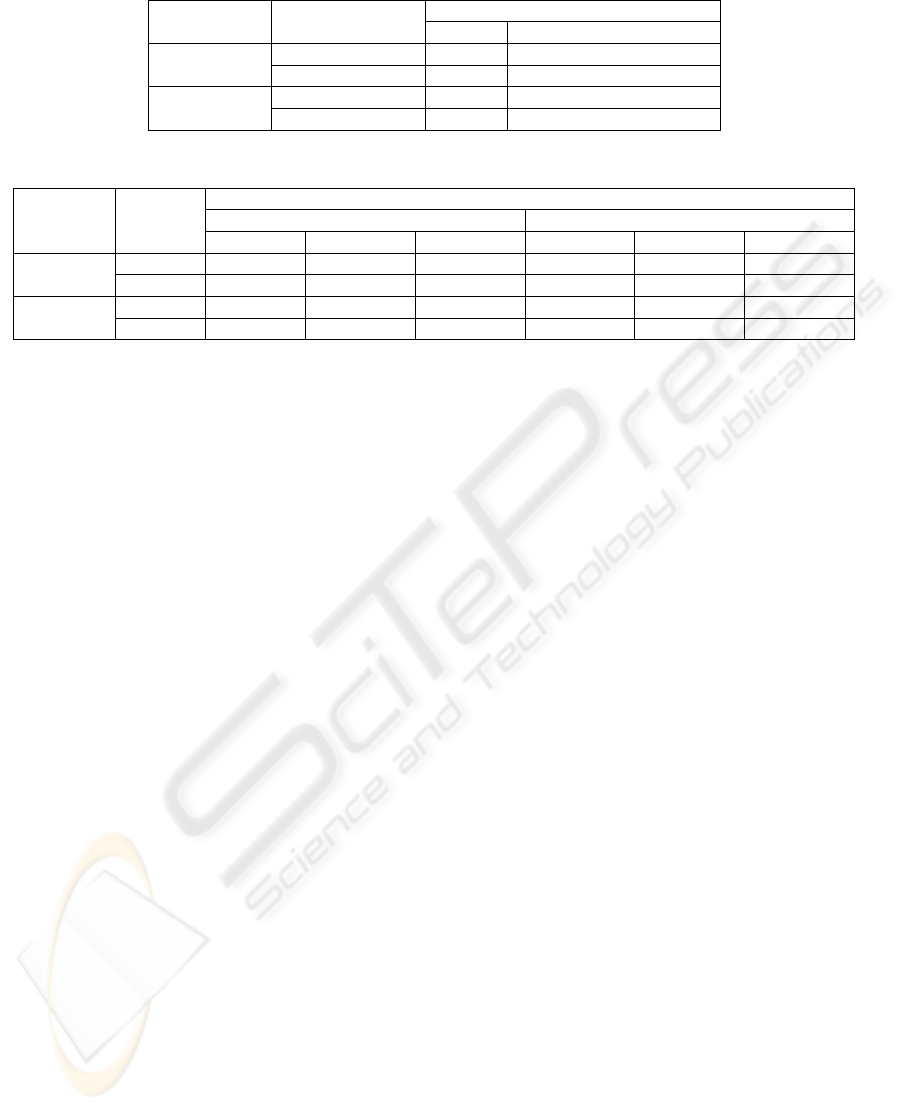
Table 2: Comparison of registration methods.
DataSet Range
Success Rate (%)
Our Uniform sub-sampling
BrainWeb
[-15, 15] 98 96
[-20, 20] 84 86
RREP
[-10, 10] 100 70
[-15, 15] 72 58
Table 3: Comparison of means and standard deviations of registration errors.
DataSet Range
Mean and Standard deviation
Our Uniform sub-sampling based
Tx Ty Rz Tx Ty Rz
BrainWeb
[-15, 15] 0.27±0.17 0.21±0.16 0.20±0.17 0.25±0.17 0.16±0.11 0.21±0.14
[-20, 20] 0.21±0.14 0.19±0.15 0.20±0.14 0.27±0.17 0.16±0.14 0.23±0.17
RREP
[-10, 10] 0.66±0.43 0.58±0.43 0.66±0.32 1.03±0.56 0.59±0.43 0.51±0.45
[-15, 15] 0.93±0.57 0.79±0.58 0.69±0.34 0.93±0.54 0.58±0.49 0.47±0.36
clearly that the proposed method outperformed
traditional uniform sub-sampling based method.
For those successful cases of registration, mean
and standard deviations of rotation errors and
translation errors were calculated and summarized in
Table 3. We can observe that the accuracy of our
proposed method is comparable to that of uniform
sub-sampling based method.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we have presented a novel method of
constructing minimal spanning tree for multi-
modality image registration. The new method
hierarchically fuses multi-salient points to construct
MST. This new method integrates not only more
information obtained from multi-salient points to
improve robustness of image registration, but also
hierarchical mechanism to produce relatively
accurate registration results. Experiment results
show that on the simulated and real brain datasets,
the algorithm achieves better robustness while
maintaining good registration accuracy.
REFERENCES
Beirlant, J., Dudewicz, E. J., Gyorfi, L., and van der
Meulen, E.C. (1997). Nonparametric entropy
estimation: An overview. International Journal of
Mathematical and Statistical Sciences, 6(1):17–39.
Collins,D.L., Zijdenbos,A.P., Kollokian,V., Sled, J.G.,
Kabani, N.L., Holmes, C.J., and Evans, A.C. (1998).
Design and construction of a realistic digital brain
phantom. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag., 17:463-468.
Harris, C., Stephens, M. (1988). A Combined Corner and
Edge Detector. In Alvey Vision Conference, pages
147-151.
Hero, A., Ma, B., Michel, O., and Gorman, J. (2002).
Applications of entropic spanning graphs. IEEE Signal
Processing Magazine, 19(5):85–95.
Ma, B., Hero, A., Gorman, J., and Michel, O. (2000).
Image registration with minimal spanning tree
algorithm. In ICIP.
Miller, E. (2003). A new class of entropy estimators for
mult-dimensional densities. In Proc. ICASSP.
Redmond, C., Yukich, J. (1996). Asymptotics for
Euclidean functionals with power weighted edges.
Stochastic Processes and their Applications,
61(2):289-304.
Sabuncu, M. R., Ramadge, P.J. (2004). Gradient based
nonuniform subsampling for information-theoretic
alignment methods. In EMBC.
Sabuncu, M. R., Ramadge, P. J. (2008). Using Spanning
Graphs for Efficient Image Registration. IEEE
Transactions on Image Processing, 17(5):788-797.
Shen, D., Davatzikos, C. (2002). HAMMER: hierarchical
attribute matching mechanism for elastic registration.
IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging, 21(11): 1421–1439.
Steele, J. M. (1988). Growth rate of Euclidean minimal
spanning trees with power weighted edges. Ann.
Probab., pages 1767–1787.
West, J., Fitzpatrick, J.M., Wang, M.Y., Dawant, B.M.,
Maurer Jr., C.R., Kessler, R.M., Maciunas, R.J.,
Barillot, C., Lemoine, D., Collignon, A., Maes, F.,
Suetens, P., Vandermeulen, D., van den Elsen, P.A.,
Napel, S., Sumanaweera, T.S., Harkness, B., Hemler,
P.F., Hill, D.L.G., Hawkes, D.J., Studholme, C.,
Maintz, J.B., Viergever, M.A., Malandain, G., and
Woods, R.P. (1997). Comparison and evaluation of
retrospective intermodality brain image registration
techniques. J. Comput. Assist. Tomogr, (4):554–566.
Yang, G., Stewart, C., Sofka, M., Tsai C. (2007).
Registration of challenging image pairs: initialization,
estimation, and decision. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal.
Mach. Intell., 29(11):1973-1989.
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
36
