
COMPUTATIONALLY EFFICIENT SERIAL COMBINATION OF
ROTATION-INVARIANT AND ROTATION COMPENSATING IRIS
RECOGNITION ALGORITHMS
Mario Konrad, Herbert St
¨
ogner
School of Communication Engineering for IT, Carinthia Tech Institute, Austria
Andreas Uhl, Peter Wild
Department of Computer Sciences, University of Salzburg, Austria
Keywords:
Iris recognition, Multibiometrics, Serial classifier combination, Rotation compensation.
Abstract:
Rotation compensation is one of the computational bottlenecks in large scale iris-based identification schemes,
since a significant amount of Hamming distance computations is required in a single match due to the neces-
sary shifting of the iris codes to compensate for eye tilt. To cope with this problem, a serial classifier com-
bination approach is proposed for iris-based identification, combining rotation-invariant pre-selection with a
traditional rotation compensating iris code-based scheme. The primary aim, a reduction of computational com-
plexity, can easily be met - at comparable recognition accuracy, the computational effort required is reduced
to 20% or even less of the fully fledged iris code based scheme. As a by-product, the recognition accuracy is
shown to be additionally improved in open-set scenarios.
1 INTRODUCTION
Iris recognition technology has been dominated over
years by the commercially successful algorithm of
J. Daugman (Daugman, 2004). This algorithm ba-
sically extracts local iris features from polar iris im-
ages by convolution with 2-dimensional complex Ga-
bor atoms, quantizing the resulting phase information
into 2 bits per coefficient. The basic idea of extract-
ing local intensity variations from iris texture has been
followed employing other types of transforms and
methods as well, e.g. in the spatial domain or in the
wavelet domain. All these approaches share the prop-
erty of being sensitive against eye tilt, i.e. they are
intrinsically not rotation invariant due to the usage of
local spatial information. Therefore, in order to com-
pensate potential rotation, in all these algorithms the
templates in the matching process are shifted against
each other for a certain amount, and taking the mini-
mal template distance among all shifted versions as
the actual distance. Obviously, depending on the
amount of shift that is required for a certain applica-
tion (i.e. the amount of rotation that is to be expected),
these operations may amount to a significant number
of matching operations performed, which can become
prohibitive in an identification scenario.
Rotation-invariant iris features therefore represent
an attractive alternative. Due to the significant com-
putational demand associated with transform domain
processing, spatial domain techniques working di-
rectly on the iris texture are of specific interest in our
context. Du et al. (Du et al., 2006) employ first order
moments of the iris texture line-histograms. While
this technique is successful in providing rotation in-
variance and consequently fast matching procedures
independent of the eye’s position, it fails in terms of
recognition accuracy.
This is where our approach comes in. In this work
we combine a spatially-based rotation invariant iris
recognition approach with a traditional local-feature
based scheme into a serial classifier combination.
The aim is to result in reduced overall computa-
tional demand as compared to classical rotation com-
pensating schemes while at least maintaining their
recognition accuracy. This is achieved by using the
first scheme to determine a certain amount of the
highest matching ranks of the entire database (this can
be done quickly due to the high speed of the first
85
Konrad M., Stögner H., Uhl A. and Wild P. (2010).
COMPUTATIONALLY EFFICIENT SERIAL COMBINATION OF ROTATION-INVARIANT AND ROTATION COMPENSATING IRIS RECOGNITION
ALGORITHMS.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 85-90
DOI: 10.5220/0002821100850090
Copyright
c
SciTePress

scheme), while the second (and more accurate)
scheme is then only applied to this predetermined
subset to determine the final matching result. Serial
classifier combination aiming at a reduction of iden-
tification time is a relatively new research topic in
biometrics, see (Uhl and Wild, 2009; Gentile et al.,
2009) for applications in hand biometrics and iris
biometrics. This work is the first multi-algorithm
multibiometric (Ross et al., 2006) approach combin-
ing rotation-invariant with rotation compensating iris
recognition algorithms serially to reduce computa-
tional demands. Besides the aimed reduction in com-
putational effort it is of particular interest, if the com-
bination of two very different feature types can also
lead to improved recognition results. Since features
used in classifier combinations need to be as uncor-
related as possible to result in better results as com-
pared to their single classifier counterparts, a recog-
nition improvement might be expected as well in our
case, since the features of the two classifiers used are
of significantly different nature.
In iris recognition, several single-sensor multibio-
metric approaches have been suggested yet, however,
mostly focussing on an improvement of recognition
accuracy. Sun et al. (Sun et al., 2005) “cascade” two
feature types employing global features only in ad-
dition to a Daugman-like approach if the matching
value of the latter is in a questionable range. Also
Zhang et al. (Zhang et al., 2004) use a similar strat-
egy while interchanging the role of the global and the
local features. Vatsa et al. (Vatsa et al., 2005) com-
pute the Euler number of connected components as
global feature, while again using an iris code as local
texture feature. Park and Lee (Park and Lee, 2006)
decompose the iris data with a directional filterbank
and extract two different feature types from this do-
main. Combining the results leads to an improvement
of the single techniques applied.
Approaches closer related to our work are quick
screening or pre-classification techniques. Several au-
thors have developed techniques to divide iris data
into a certain number of categories in order to achieve
a rough pre-classification before applying a more ac-
curate matching technique. Qui et al. (Qui et al.,
2007) use iris textons to generate five classes, and
Yu et al. (Yu et al., 2006) use fractal dimension to
generate four classes. The approach as described in
this work is different from the techniques proposed so
far in several ways. First, it is different compared to
the single-sensor multibiometric approaches combin-
ing global and local features suggested since we
• mainly focus on a reduction of computational ef-
fort by limiting the required rotation compensa-
tion in matching instead of aiming at better recog-
nition accuracy and
• we apply a specific type of serial classifier combi-
nation to accomplish this (i.e. contrasting to many
other approaches not both classifiers are applied to
the entire dataset).
Second, it is different to the developed screening
approaches since we
• do not partition the templates into a certain num-
ber of classes and do therefore not limit the actual
matching to the common class of database tem-
plate and sample template and
• we actually combine our “screening approach”
with a classical technique in serial manner and
provide actual computational performance and
classification accuracy results.
In contrast to recently introduced serial iris fea-
ture combinations (Gentile et al., 2009), we employ a
rotational-invariant pre-selecting feature making bit-
shifts in the first classifier unnecessary.
Section 2 describes the iris recognition tech-
niques, which are part of our serial matching approach
and explains the applied serial classifier combination
technique. In Section 3, the experimental setup is dis-
cussed and experimental results are provided. First,
we illustrate the results of the classical approach us-
ing local features and rotation compensation. Sub-
sequently, we discuss and present the experimental
results for the serial classifier combination for the
open-set scenario with respect to time consumption
as well as recognition performance of the different ap-
proaches. Section 4 concludes the paper.
2 SERIAL CLASSIFIER
COMBINATION IN IRIS
RECOGNITION
The applied serial classifier combination mainly aims
at reducing computation demand in identification sce-
narios. The basic idea is to employ a faster recog-
nition scheme with rotation invariant (more global)
features for a first screening sweep across the entire
database. The screening procedure does not result in
a certain number of classes, which can then be used to
restrict the subsequent search to a single class, but re-
sults in a ranking of the enrolled database templates.
This ranking is subsequently used to determine actu-
ally two classes, where the subsequent search is lim-
ited to one of these classes then – obviously this is
the class with the highest ranks. An important pa-
rameter of this approach is the amount of top ranked
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
86

templates that is contained in the class subject to fur-
ther search. We denote this parameter p and it is ex-
pressed in percent of the database, e.g. if p = 25, the
25% top ranked templates are subject to further pro-
cessing by the second, computationally more expen-
sive approach (which relies on local texture features
and requires rotation compensation). Obviously, for
increasing p the computational demand is increased.
The main question addressed in the experimental sec-
tion is whether the recognition accuracy can be main-
tained for decreasing p, or otherwise, in how far the
decrease of p is coupled to a decrease of recognition
accuracy.
In the next two subsections we will briefly review
the two iris recognition schemes, which we use to
combine into a serial classifier combination.
2.1 Rotation-invariant Screening
Du et al. (Du et al., 2006) have proposed a rotation
invariant 1D signature approach, which we employ
as the first screening stage. As preprocessing, lo-
cal texture patterns (LTPs) are generated, which sub-
stract a localized mean value from the data. By av-
eraging LTP values of an entire row of the LTP polar
iris image (which is generated in a first preprocessing
stage after iris detection), one value of the 1D sig-
nature is generated. While the upper and lower three
rows of the polar iris data are discarded, the remaining
rows are used to create the final 1D signature. In re-
cent work (Matschitsch et al., 2008) this approach has
been extended by using entire row histograms instead
of first order moments only, which results in 2D sig-
natures in some sense. Clearly, both the original 1D
and the extended 2D signatures are rotation invariant.
Two 1D signatures are compared by using the Du
measure (Du et al., 2006). For the extension to 2D
signatures, we apply the “accumulated errors” ap-
proach (Matschitsch et al., 2008), where the Du mea-
sure is computed for each row between the single his-
tograms and the resulting distances are accumulated
afterwards for all rows. We apply the accumulated er-
rors strategy using 256 histogram bins. Moreover, a
weighting factor > 1 is used for the distance of polar
image rows, which are close to the pupil and a fac-
tor = 1 is proposed for rows, which are close to the
sclera of the eye. The weighting factors for the rows
in between are obtained by linear interpolation.
2.2 Local Texture Features – Iris Code
For the original iris code (Daugman, 2004), the po-
lar images are subject to a 2D complex Gabor filter-
ing process, subsequently the available phase infor-
mation is quantized into four different levels, one for
each of the four possible quadrants in the complex
plane. Hence, for each pixel of the polar image, two
bits are obtained, which are combined and form the
iris template (i.e. iris code), which can be compared
to other iris codes by computing the Hamming dis-
tance. This measure is highly localized and needs
to compensate for possible rotation between irises –
this is done by applying the Hamming distance cal-
culation several times while shifting the polar images
against each other. The lowest matching value then
determines the final distance.
In this work, we use an open-source MatLAB im-
plementation, which applies a 1D Gabor-filter version
of the iris code strategy for iris recognition. Due to its
free availability
1
and the lack of other publicly avail-
able iris recognition software, it has gained significant
popularity in the community.
3 EXPERIMENTS
3.1 Experimental Setup
We use the CASIA V1.0 and the CASIA V3.0 Inter-
val
2
as well as the MMU V1.0
3
datasets where for
each database two different subsets are selected. For
the CASIA V1.0, which consists of 756 images ac-
quired from 108 eyes (7 images per eye), the first
subset contains 630 iris images and the second subset
comprises 126 images. For the CASIA V3.0, the first
subset consists of 1705 iris images acquired from 341
different eyes (5 images for each eye). The second
subset includes 117 images from 53 eyes with vari-
ous numbers of images per eye. For MMU, the first
dataset is composed of 400 iris images from 80 eyes,
while the second set contains 50 images (again 5 im-
ages per eye). For all three databases, the first dataset
is used to serve as database of enrolled persons and
the second dataset contains images that are unknown
to the recognition system (which are needed in the
open-set scenario). Out of all datasets, we extract po-
lar iris images with 360 × 65 pixels, which results in
1D/2D signatures with length 59 since only 59 out of
65 LTP rows are used.
We consider the open-set scenario (or watchlist
scenario). Here it is not guaranteed that the per-
son that should be identified is truly member of the
database. Hence, an identification attempt results in
1
http://www.csse.uwa.edu.au/˜pk/
studentprojects/libor/sourcecode.html
2
http://www.sinobiometrics.com
3
http://pesona.mmu.edu.my/ccteo/
COMPUTATIONALLY EFFICIENT SERIAL COMBINATION OF ROTATION-INVARIANT AND ROTATION
COMPENSATING IRIS RECOGNITION ALGORITHMS
87

a correct identification whenever an enrolled person
is correctly recognized. If a not enrolled person is
falsely labelled as database member, the attempt will
result in a false accept. The rank-1 recognition rate as
well as the false accept rate is used in order to assess
this type of system.
With respect to serial classifier combination,
we investigate set reductions to top-ranked p =
1, 5, 10, 15 candidates subjected to further processing.
Rotation compensation for the “pure” iris code tech-
nique is conducted with 2, 4, and 8 shifts of the iris
code in each direction (which sums up to 17 Ham-
ming distance calculations in the case of 8 shifts), in
the context of the serial combination rotation compen-
sation is conducted using 8 shifts in the second stage
of the identification.
3.2 Results
First, we create reference results by analyzing the per-
formance of the “pure” iris code approach. Table 1
illustrates the time consumption to search the entire
database, which obviously strongly depends on the
amount of shifts (AMD Athlon 2200+ processor, 512
MB RAM, Windows XP and MatLAB R2007b). For
comparison, the required amount of time to search
the database with the Du approach is also displayed.
When conducting only a single Hamming distance
computation (instead of already 5 in the case of two
shifts), the iris code algorithm would be only slightly
slower compared to the Du approach. Only rotation
compensation degrades its performance significantly.
Note, that the image segmentation and generation of
the polar iris image was performed prior to the analy-
sis and is excluded from the timing results. The time
effort for these computations is 52 seconds for the
CASIA V1.0 dataset and 59 seconds for the CASIA
V3.0 dataset, for example.
In Figure 1, we show the effect of applying a vari-
able amount of shifts on recognition accuracy in the
iris code approach for CASIA V3.0 as an example.
In accordance to literature, 8 shifts yield only slightly
better results than 4 shifts overall, but this effect is
more pronounced for the important case of lower false
accept rates, which makes the application of 8 shifts
sensible in this case as well. Therefore, further results
refer to 8 shifts in the “pure” iris code approach as
Table 1: Time consumption of iris code-based identification
with a various number of shifts and Du’s approach.
Du Iris code 2s Iris code 4s Iris code 8s
Cv1 12.5 s 77.2 s 105.8 s 176.3 s
Cv3 32.1 s 215.7 s 322.7 s 507.1 s
MMU 8.1s 48.3 s 69.3 s 111.5 s
Figure 1: Performance in terms of recognition accuracy of
the iris code approach for CASIA V3.0 with varying amount
of shifts.
Figure 2: Time consumption (in seconds) of the iris code
approach and the serial combination approach with p =
1, 5, 10,15 for 1D signatures.
well as in the second stage of the serial combination.
Figure 2 displays the time needed to perform iden-
tification over the entire datasets and compares the
iris code approach using 8 shifts (denoted Masek’s-
daugman in this plot) with the serial approach using
1D signatures with p = 1, 5, 10, 15. The time reduc-
tion achieved even for p = 15 is impressive.
Table 2 summarizes the time consumption of the
different serial combination variants for 1D (S1DpX)
and 2D signatures (S2DpX). As expected, it is con-
firmed that the serial approach is much faster than the
classical iris code method (IC8s). Although the ap-
plication of 2D signatures raises the computational
effort, the results are also clearly superior. Apply-
ing a weighting factor (w=4) to the signatures does
only slightly increase the computational demand in
a negligible manner (not shown). For example, for
1D signatures with p = 10 (which is better in term of
recognition accuracy in many cases compared to the
iris code case as we shall see), the serial approach is
faster more than a factor of 6, and still for 2D signa-
tures the serial approach is faster by a factor of 5.
Having shown that the aim of significant reduction
of the computational effort has been met, we investi-
gate the impact of the serial classifier combination on
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
88
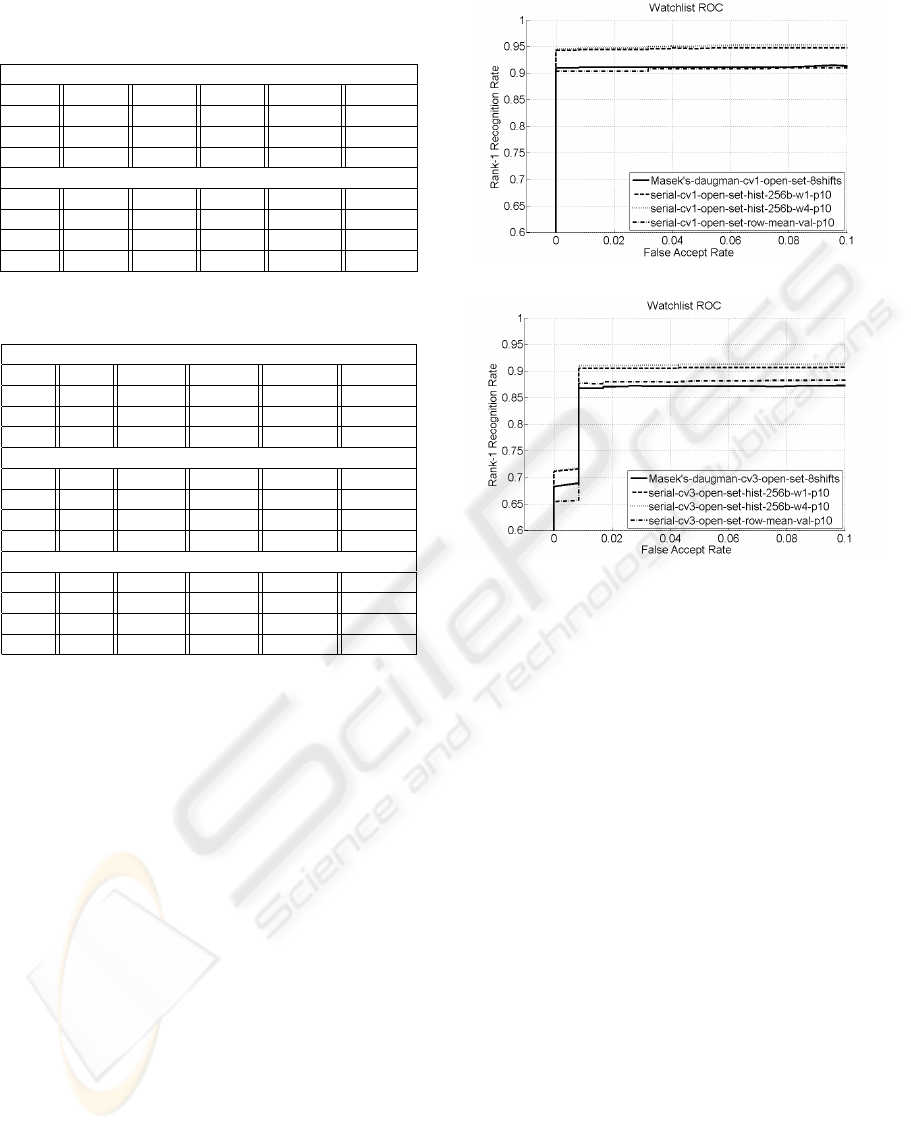
Table 2: Time consumption (in seconds) of the iris code
approach and the serial combination approach with p =
1, 5, 10, 15 for 1D (above) and 2D signatures (below).
1-D signatures
IC8s S1Dp1 S1Dp5 S1Dp10 S1Dp15
Cv1 181.5 s 14.1 s 21.3 s 30.3 s 39.3 s
Cv3 507.1 s 36.9 s 56.6 s 79.7 s 104.7 s
MMU 111.5 s 9.5 s 14.1 s 19.8 s 25.5 s
2-D signatures
IC8s S2Dp1 S2Dp5 S2Dp10 S2Dp15
Cv1 181.5 s 19.7 s 27.0 s 35.0 s 45.0 s
Cv3 507.1 s 52.5 s 71.7 s 95.7 s 120.0 s
MMU 111.5 s 13.4 s 18.1 s 23.9 s 29.8 s
Table 3: Rank-1 Recognition Rate (RR-1) at certain False
Accept Rate (FAR) values.
Casia V1.0
FAR IC8s S1Dp1% S1Dp5% S1Dp10% S1Dp15%
0% 90.9% 81.6% 88.1% 90.3% 91.9%
0.79% 91.1% 81.6% 88.6% 90.3% 91.9%
11.1% 91.1% 81.9% 89.2% 91.1% 92.5%
CASIA V3.0
FAR IC8s S1Dp1% S1Dp5% S1Dp10% S1Dp15%
0% 68.3% 69.2% 76.1% 65.5% 66.2%
0.85% 86.7% 77.9% 85.8% 87.7% 88.4%
11.1% 87.4% 78.4% 86.3% 88.3% 89.0%
MMU V1.0
FAR IC8s S1Dp1% S1Dp5% S1Dp10% S1Dp15%
0% 84.5% 49.8% 68.8% 73.8% 76.8%
0.85% 85.8% 52.5% 71.3% 75.8% 78.8%
11.1% 86.0% 53.3% 71.8% 76.3% 79.3%
the recognition results in the following. Table 3 shows
the results of the serial approach with 1D signatures
and using p = 1, 5, 10, 15 compared to the iris code
8-shifts variant for the three databases.
We notice, that the CASIA V1.0 dataset yields
overall better results than the CASIA V3.0 and MMU
V1.0 datasets. This fact may be due to the fact that
the pupil areas of the CASIA V1.0 dataset have been
post-processed and set to a uniformly dark gray value,
which eases the segmentation process and therefore
reduces errors coming from incorrect segmentation.
For the CASIA V1.0 dataset, only the p = 15 se-
rial variant (S1Dp15) yields better identification rates
than the iris code approach (IC8s). For higher false
accept rates (FAR=11%), the p = 10 variant leads to
similar results as compared to the iris code reference
case.
For the CASIA V3.0 dataset and zero false ac-
cepts, the p = 5 serial variant yields the best identi-
fication rate (76.1%) and also p = 1 is surprisingly
better than the iris code approach. The decreasing
identification accuracy for increasing values of p may
be surprising at first, however, these results are due
to the fact that a larger set of preselected templates
can increase the chance for false positives, which have
(a) CASIA V1.0
(b) CASIA V3.0
Figure 3: Performance of the 2D serial approach compared
to the iris code approach for the CASIA datasets.
been excluded for lower values of p. For higher false
accept rates (FAR), the p = 15 percent variant pro-
duces the best results (89% @ 0.85% FAR) while also
p = 10 performs better as compared to the iris code
reference and still p = 5 delivers comparable recog-
nition performance.
For both datasets these recognition results are not
obvious since a coarse pre-selection could be ex-
pected to exclude potential genuine templates too. In
contrary, the pre-selection helps to avoid false positive
matches. This may be explained by the fact that the
Du approach yields good results for partial iris recog-
nition (e.g., heavy eyelid occlusion or segmentation
errors) and noisy images (Du et al., 2006).
In contrast, the results for the MMU dataset are
worse for the serial combinations as compared to the
classical iris code approach for all values of p =
1, 5, 10, 15. We also notice that recognition accuracy
increases monotonically with increasing p so that we
can expect at least equal performance for larger values
of p.
In Figure 3 we further analyze the possible im-
provement of the serial approach for p = 10 by us-
ing 2D signatures and weighting of inner rows with
weight 4. For both datasets shown (CASIA V1.0 and
COMPUTATIONALLY EFFICIENT SERIAL COMBINATION OF ROTATION-INVARIANT AND ROTATION
COMPENSATING IRIS RECOGNITION ALGORITHMS
89

Figure 4: Performance of the 2D serial approach compared
to the iris code approach for the MMU dataset.
V3.0), the 2D variant (hist-256b-w1) improves per-
formance compared to 1D signatures considerably,
while weighting (hist-256b-w4) only results in minor
improvement. The performance of the serial approach
with 2D signatures is better as the iris code technique
for all cases for both CASIA datasets.
Figure 4 shows that also for the MMU dataset
improvements in terms of recognition performance
as compared to the iris-code approach are possible
if 2D signatures are used and p is set sufficiently
high. We observe that for p = 15 and 2D signa-
tures with weighting the iris code approach is outper-
formed across the entire range of considered false ac-
cept rates. Note that this improvement still is achieved
at a reduction of computational effort by a factor of
3.5 (compare Table 2).
4 CONCLUSIONS
As expected, we are able to reduce computational de-
mands with our proposed serial classifier combination
considerably. At a comparable recognition accuracy
we suffice with 20% - 30% or even less computa-
tion time for identification (the actual value depends
on the specific dataset considered). Interestingly, we
are even able to outperform the recognition accuracy
of iris code based recognition, since the serial clas-
sifier combination technique turns out to be more ro-
bust against false acceptances. This is especially in-
teresting, since we reveal that the rotation-invariant
first stage of the serial combination is able to exclude
candidates, which lead to false accepts in the entirely
rotation-compensating iris-code approach.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by the Aus-
trian Research Promotion Agency (FFG) FIT-IT Trust
in IT-Systems project 819382.
REFERENCES
Daugman, J. (2004). How iris recognition works. IEEE
Transactions on Circiuts and Systems for Video Tech-
nology, 14(1):21–30.
Du, Y., Ives, R., Etter, D., and Welch, T. (2006). Use
of one-dimensional iris signatures to rank iris pattern
similarities. Optical Engineering, 45(3):037201–1 –
037201–10.
Gentile, J. E., Ratha, N., and Connell, J. (2009). An effi-
cient, two-stage iris recognition system. In Biomet-
rics: Theory, Applications and Systems (BTAS’09),
pages 1–5.
Matschitsch, S., St
¨
ogner, H., Tschinder, M., and Uhl, A.
(2008). Rotation-invariant iris recognition: boosting
1D spatial-domain signatures to 2D. In Filipe, J.,
Cetto, J., and Ferrier, J.-L., editors, ICINCO 2008:
Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on
Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, vol-
ume SPSMC, pages 232–235. INSTICC Press.
Park, C.-H. and Lee, J.-J. (2006). Extracting and com-
bining multimodal iris features. In Proceedings of
the 1st IAPR International Conference on Biometrics
(ICB’06), number 3832 in Lecture Notes on Computer
Science, pages 389–396.
Qui, X., Sun, Z., and Tan, T. (2007). Coarse iris classifi-
cation by learned visual dictionary. In Proceedings of
the 2nd IAPR/IEEE International Conference on Bio-
metrics (ICB’07), number 4642 in Lecture Notes on
Computer Science, pages 770–779.
Ross, A., Nandakumar, K., and Jain, A. (2006). Handbook
of Multibiometrics. Springer.
Sun, Z., Wang, Y., Tan, T., and Cui, J. (2005). Improv-
ing iris recognition accuracy via cascaded classifiers.
IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man and Cybernetics,
35(3):435–441.
Uhl, A. and Wild, P. (2009). Parallel versus serial classifier
combination for multibiometric hand-based identifica-
tion. In Tistarelli, M. and Nixon, M., editors, Pro-
ceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Bio-
metrics 2009 (ICB’09), volume 5558 of LNCS, pages
950–959. Springer Verlag.
Vatsa, M., Singh, R., and Noore, A. (2005). Reducing the
false rejection rate of iris recognition using textural
and topological features. Int. Journal of Signal Pro-
cessing, 2(2):66–72.
Yu, L., Wang, K., and Zhang, D. (2006). A novel
method for coarse iris classification. In Proceedings of
the 1st IAPR International Conference on Biometrics
(ICB’06), number 3832 in Lecture Notes on Computer
Science, pages 404–410.
Zhang, P.-F., Li, D.-S., and Wang, Q. (2004). A novel iris
recognition method based on feature fusion. In Pro-
ceedings of the International Conference on Machine
Learning and Cybernetics, pages 3661–3665.
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
90
