
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING WITH 3D PGA CLM
Meng Yu and Bernard Tiddeman
School of Computer Science, University of St. Andrews
St. Andrews, U.K.
Keywords:
Active appearance models, Multi-view face models, Constrained local model, Face feature tracking, Face
feature detection.
Abstract:
In this paper we describe a system for facial feature detection and tracking using a 3D extension of the Con-
strained Local Model (CLM) (Cristinacce and Cootes, 2006) algorithm. The use of a 3D shape model allows
improved tracking through large head rotations. CLM uses a shape and texture appearance model to generate
a set of region template detectors. A search is then performed in the global pose / shape space using these
detectors. The proposed extension uses multiple appearance models from different viewpoints and a single 3D
shape model built using Principal Geodesic Analysis (PGA) (Fletcher et al., 2004) instead of direct Principal
Components Analysis (PCA). During fitting or tracking the current estimate of pose is used to select the ap-
propriate appearance model. We demonstrate our results by fitting the model to image sequences with large
head rotations. The results show that the proposed multi-view 3D CLM algorithm using PGA improves the
performance of the algorithm using PCA for tracking faces in videos with large out-of-plane head rotations.
1 INTRODUCTION
This paper describes a method for tracking human
face features using a 3D shape model and view-
dependent feature templates. We match the 3D face
model to previously unseen 2D video sequences of
human faces by applying a shape constrained search
method, using an extension of the constrained local
model algorithm.
The original CLM algorithm (Cristinacce and
Cootes, 2006) works with limited rotations from the
front face view. Yu et al. (Yu and Tiddeman, 2010)
extended the algorithm to a multi-view 3D CLM al-
gorithm works not only on the front face view but
also on the face with large head rotations in videos. It
consists of a 3D shape model and several 2D appear-
ance models from multiple views. Fifteen appearance
models at intervals of 30
◦
are used. The system covers
100
◦
in the vertical direction and 160
◦
in the horizon-
tal direction.
Fletcher et al. have shown that principal geodesic
analysis (PGA) (Fletcher et al., 2004) is more effec-
tive for presenting geometric objects. In this imple-
mentation, a PGA shape model is adapted instead of
the direct PCA shape model in the previous methods.
The shape templates are first projected to the local
area before the PCA applied to increase the fitting ac-
curacy. The searching process is similar to the pre-
vious methods. First, some suitable initialisation (ap-
proximate rigid body alignment, scaling) is given to
the shape model. In each subsequent iteration square
region are sampled around each feature point and pro-
jected into the allowed appearance model space. The
shape and pose parameters are then found that max-
imise the correlation between the synthesised appear-
ance template patches and patches extracted around
the current estimates of the feature point locations in
image space.
After a brief review of face and face feature detec-
tion, we will describe the model building and fitting
methods in more detail, followed by experimental re-
sults demonstrating the performance of the proposed
multi-view 3D CLM method using PGA.
2 RELATED WORK
The problems of facial feature detection and tracking
have received a great deal of attention in the litera-
ture, here we only cover the more immediately rel-
evant work. Active Shape Models (ASM) (Cootes
et al., 1995) use Principal Component Analysis (PCA)
to learn the main axes of variation from a training set
44
Yu M. and Tiddeman B. (2010).
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING WITH 3D PGA CLM.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 44-53
DOI: 10.5220/0002829800440053
Copyright
c
SciTePress

of labelled examples. Fitting the shape model to a
new image involves local searches for matching fea-
tures alternated with projection of the shape estimate
back into the allowed model space.
Active Appearance Models(AAMs) (Cootes et al.,
2001) use the same PCA based shape model as ASMs
together with a PCA based model of appearance
(i.e. shape normalised texture). It has been used
for face modelling and recognising objects (Lanitis
et al., 1997) (Jones and Poggio, 1998), fitting un-
seen images (Gross et al., 2005) (Peyras et al., 2007),
tracking objects(Ahlberg, 2001), (Stegmann, 2001)
and medical image processing (Cootes and Taylor,
2001), (Mitchell et al., 2001). The original imple-
mentation (Cootes et al., 2001) learnt a linear model
relating the error image (between the model and the
image) and the required parameter updated at each
time step. Following the forwards additive algorithm
(Lucas and Kanade, 1981), the inverse additive al-
gorithm (Hager and Belhumeur, 1998), and the for-
wards compositional algorithm (Shum and Szeliski,
2001), Mathews and Baker (Baker and Matthews,
2001), (Baker and Matthews, 2002), (Matthews and
Baker, 2004) derived more mathematically elegant
methods in which the updates are always calculated
in the average shape and then concatenated with the
current guess. This inverse compositional method al-
lows the pre-computation of the gradient images and
inverse Hessian matrix for greater efficiency. Later
work demonstrated that the inverse compositional al-
gorithm is only really suitable for person-specific fit-
ting and tracking, and that simultaneous estimation of
the shape and appearance parameters was required for
robust face fitting (Gross et al., 2005).
Constrained Local Model (CLM) algorithm
(Cristinacce and Cootes, 2006) is a patch based
method with the similar appearance model to that
used in the AAMs (Cootes et al., 2001). It learns
the variation in appearance of a set of template re-
gions surrounding individual features instead of tri-
angulated patches. The fitting algorithm first finds the
best match of the combined shape-appearance model
to the current guess, then searches locally using a non-
linear optimiser to find the best match to the model.
Further study on patch based appearance models have
been carried out – exhaustive local search (ELS) algo-
rithm (Wang et al., 2007), generic convex quadratic
fitting (CQF) approach (Wang et al., 2008) and
Bayesian constrained local models (BCLM) (Paquet,
2009). The approach has been proven to outperform
the active appearance models (AAMs) (Cootes et al.,
2001) as it is more robust to occlusion and changes in
appearance and no texture warps are required. ELS,
CQF and BCLM all showed some improvements over
CLM fitting to certain databases.
Active appearance models (AAMs) (Cootes et al.,
2001) were originally formulated as 2D and most
of the algorithms for AAM fitting have been single-
view (Cootes and Kittipanyangam, 2002). Automati-
cally locating detailed facial landmarks across differ-
ent subjects and viewpoints, i.e. 3D alignment of a
face, is a challenging problem. Previous approaches
can be divided into three categories: view (2D) based,
3D based and combined 2D+3D based. View based
methods (Cootes et al., 2000), (Zhou et al., 2005),
(Faggian et al., 2005), (Peyras et al., 2008), train a
set of 2D models, each of which is designed to cope
with shape or texture variation within a small range
of viewpoints. We have found for some applications
that switching between 2D views can cause notable
artifacts (e.g. in face reanimation). 3D based meth-
ods (Blanz and Vetter, 1999), (Romdhani et al., 2002),
(Brand, 2001), (Jones and Poggio, 1998), (Vetter and
Poggio, 1997), (Zhang et al., 2004), in contrast, deal
with all views by a single 3D model. 3D Morphable
model fitting is an expensive search problem in a high
dimensional space with many local minima, which of-
ten fails to converge on real data. 2D+3D based meth-
ods (Xiao et al., 2004), (Hu et al., 2004), (Koterba
et al., 2005), (Ramnath et al., 2008) used AAMs and
estimated 3D shape models to track faces in videos,
but these algorithms are generally most suitable in
the person specific context. A view-based multi-view
3D CLM algorithm (Yu and Tiddeman, 2010) derived
from the original CLM algorithm (Cristinacce and
Cootes, 2006) have gained some improvements track-
ing unseen faces with large head rotations.
A standard linear technique of shape analysis is
principal component analysis (PCA) which can effi-
ciently represent a complex data set with the reduced
dimension. However, PCA is limited if the data is ly-
ing in a geodesic space instead of an Euclidean vector
space such as the template of the human face features.
Fletcher et al. proposed a principal component analy-
sis (PGA) method (Fletcher et al., 2004), a generalisa-
tion of principal component analysis to the manifold
setting to deal with the problem. Results show that
it can efficiently describe the variability of data on a
manifold.
3 ALGORITHM
3.1 An Overview
The model (Figure 1) consists of a model of 3D shape
variation and 15 models of the appearance variations
in a shape-normalised frame. A training set of la-
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING WITH 3D PGA CLM
45

Figure 1: The Multi-view CLM consists of a shape model
and several appearance models from different views. There
are 15 rotations and 3 scales used to cover all the likely cir-
cumstances in the application. (There are only 9 rotations in
the figure because the views from the right side are approx-
imately mirroring copies of the ones from the left side.)
belled images, where key landmark points are marked
on each example object, is required. We use landmark
points placed on a set of 3D face models to generate
the 3D shape model. The appearance model for each
view is found by rendering the face model from the
appropriate viewpoint and sampling square patches
from the rendered image about the projected location
of the feature point.
We use 14 subjects (8 males, 6 females) perform-
ing 7 posed expressions (neutral, happy, sad, disgust,
surprise, fear, anger) and 7 posed vise mes (/ah/, /ch/,
/ee/, /k/, /oo/, /p/, /th/) captured using a stereopho-
togrametric system (www.3dMD.com). From the set
of the landmark points a statistical model of shape
variation can be generated using Principal Geodesic
Analysis (PGA). We extract a 20x20 block of pix-
els around each feature point at each of 3 spatial
scales. (Figure 2) These patches are vectorised and
used to build the appearance model. All the features
are formed into a 500x20 block of the pixel strip be-
fore the PCA analysis is applied.
In the original CLM work (Cristinacce and
Cootes, 2006) a combined shape and appearance
Figure 2: Example of training images
models was created by performing PCA on the com-
bined shape and appearance parameter vectors, and
the search was carried out in this space. The use
of multiple appearance models in multi-view 3D al-
gorithm would require the use of multiple combined
models. In order to simplify the switching of the ap-
pearance model with a single shape model, separate
models of shape and appearance are used instead of
using a combined model in this paper.
3.2 Shape Model
To build a Principal Geodesic Analysis (PGA) shape
model, the global shape co-ordinates s(x, y, z) are con-
catenated into a vector X = (x
1
, y
1
, z
1
, ··· , x
n
, y
n
, z
n
).
The templates are then normalised into the local shape
vector v by the following equation.
v
i
=
x
i
− ¯x
p
∑
(x
i
− ¯x)(x
i
− ¯x)
(1)
Then we can use equation 2 and 3 to fold and un-
fold the vectors from and to the tangent space (Fig-
ure 3).
u(x) = v(x) ·
θ
sinθ
−
θ ·cos(θ)
sinθ
· ¯v (2)
where θ = arccos(
∑
¯v ·v
i
) is the spherical distance
from the base point p to the point v.
f (x) = u(x) ·
sinθ
θ
+ cos(θ) · ¯u (3)
where θ =
√
∑
v
i
·v
i
.
The intrinsic mean of the manifold is then estimate
with the following steps.
1. calculate the algorithm mean of the shape vectors
¯v.
2. repeat
(a) unfold the shape vectors into tangent plane iter-
atively and calculate the intrinsic mean s
i
.
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
46

Figure 3: A pictorial representation of the tangent space.
(b) fold the intrinsic mean back into sphere plane.
3. until
¯
v
0
< ε
The PGA shape model is built from the vectors
u(x) unfolded to the tangent space. To calculate the
principal components, the covariance matrix of the
vectorised points (u(x)) is created using the formula
and Jacobi’s method is then applied to find the eigen-
vectors and eigenvalues, which represent the principal
components and their distributions.
u(x) = ¯u + P
s
b
s
(4)
where ¯u is the mean shape, P
s
is a set of orthogo-
nal modes of variation and b
s
is a set of shape param-
eters. The equation can then be used to reconstruct
new shapes by varying the given shape parameters.
The two-dimensional coordinates of the shape
model can be calculated with the following equation:
s
2d
= M ·V · f ( ¯u + P
s
·b
s
)
(5)
where V is a vector of the pose (transla-
tion, rotation, scaling) transforming parameters
T
x
, T
y
, T
z
, S, θ, φ, γ and M is the opengl frustum projec-
tion matrix.
3.3 Appearance Models
To build a model of the appearance, we render each
3D face model in our training set from a particular
viewpoint and sample a square patch around each fea-
ture point. By transforming the face with different
scale, rotation, shift and lighting parameters, we build
a set of texture patches. After all the patches vec-
torised, PCA analysis is applied to the textures from a
particular viewpoint and scale to build an appearance
model:
g = ¯g + P
g
b
g
(6)
where ¯g is the mean normalized gray-level vector,
P
g
is a set of orthogonal modes of variation and b
g
is
a set of gray-level parameters. We build 45 appear-
ance models, one for each of 15 viewpoints across 3
Figure 4: The opengl alpha channel for background self oc-
clusion. The upper pair is the average texture patches image
and the alpha channel patches image from the frontal view.
The bottom pair is from a side view.
different scale to cover all the likely circumstances in
the application.
3.4 Other Features
To increase the stability with varied backgrounds, we
use visibility information from the rendered patches
to estimate occluded pixels. We grab the alpha chan-
nel (Figure 4) from the rendering canvas when we
extract the texture patches to mark out the edges be-
tween the face and the background.
A simple way is chosen to build the alpha chan-
nel information into the model. Before computing the
errors between the synthetic I
syn
and extracted image
patches I
ext
, the average image patches of alpha chan-
nel I
al pha
are applied as a mask to both images patches
by using pixel-wise multiplication.
During head rotation, facial features can be
blocked by other parts of the face. On the facial
boundary, the appearance of background pixels can
vary significantly. These effects could result in fail-
ure of the matching between the extracted image, g(x)
and the synthetic image, f (x). In order to exclude the
effects of these points, the appearance models for dif-
ferent views are built with different sets of features.
Currently, a fixed visibility model is built for each
viewpoint based on the feature points that are typi-
cally visible in that view. Self occlusion can be de-
tected in the training set by identifying model points
that are further from the virtual camera than the ren-
dered point, as given by the depth-buffer value. If the
point is occluded in more than 50% of the training
examples it is excluded from the model for that view.
An example of an appearance model from a side view
can be seen in Figure 5.
Multi-scale techniques are standard in computer
vision and image processing. They allow short range
models to extend over longer ranges and optimisa-
tion to be achieved in fewer steps. In our model, a
Gaussian function is used to build a multi-scale tex-
ture pyramid. The processing time is much shorter
with lower resolution images. So we fit the unseen
image with the lowest resolution image first to im-
prove the performance. When fitting we also use a
Gaussian pyramid built for each frame and then the
CLM search is applied at each layer from the coars-
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING WITH 3D PGA CLM
47

Figure 5: The appearance model with hidden features from
a side view. The hidden features are not extracted for the
model.
Figure 6: A skeleton of the three scales image searching
technique.
est to the finest. The process can be illustrated in the
Figure 6.
3.5 Search Algorithm
With the texture model selection algorithm, we can
extend the searching method (Cristinacce and Cootes,
2006) for use with a three-dimensional model.
For a given set of initial points, X =
(x
0
, y
0
, z
0
, x
1
, y
1
, z
1
··· , x
n−1
, y
n−1
, z
n−1
), the ini-
tial pose parameters V are estimated for the shape
model built previously. Then the multi-view ap-
pearance CLM algorithm shown in Figure 7 is
applied.
1. Initialise with the global face detector.
2. Estimate the initial pose parameters V .
3. From low to high resolutions
(a) Repeat
Figure 8: Multiple appearance models.
i. Compute the feature coordinates, s, and ex-
tract the feature patches, g.
ii. Estimate the texture model from the pose pa-
rameters V .
iii. Synthesise the feature patches from the up-
dated coordinates and the selected texture
model.
iv. Apply the alpha channel feature, the hidden
points feature to the extracted and synthetic
feature patches.
v. Optimise the error metrics with the shape tem-
plate update methods to get a new set of pose
and shape parameters, V , b
s
.
(b) Until converged.
4. Until converged for all selected scales.
3.6 Texture Model Selection
In the proposed algorithm, there is a global three-
dimensional shape model and fifteen texture models.
One additional step to the original algorithm is the se-
lection of the texture model while searching with the
multi-view CLM algorithm. For tracking face move-
ments, the algorithm needs to select the correct tex-
ture model for the current pose automatically. As each
texture model is built from a certain view, we can use
the rotation parameters θ, φ to estimate the view by
testing the criteria shown in Figure 8. θ and φ can
be obtained from the current estimate of head rotation
using one of the shape template update methods.
The texture model selection process is given by
the following steps repeatedly until the end of the
tracking.
1. The multi-view CLM algorithm is applied to the
given frame accompanied with the initial parame-
ters.
2. A set of new parameters are obtained including θ
and φ which is the estimated rotation angles for
the current face pose.
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
48
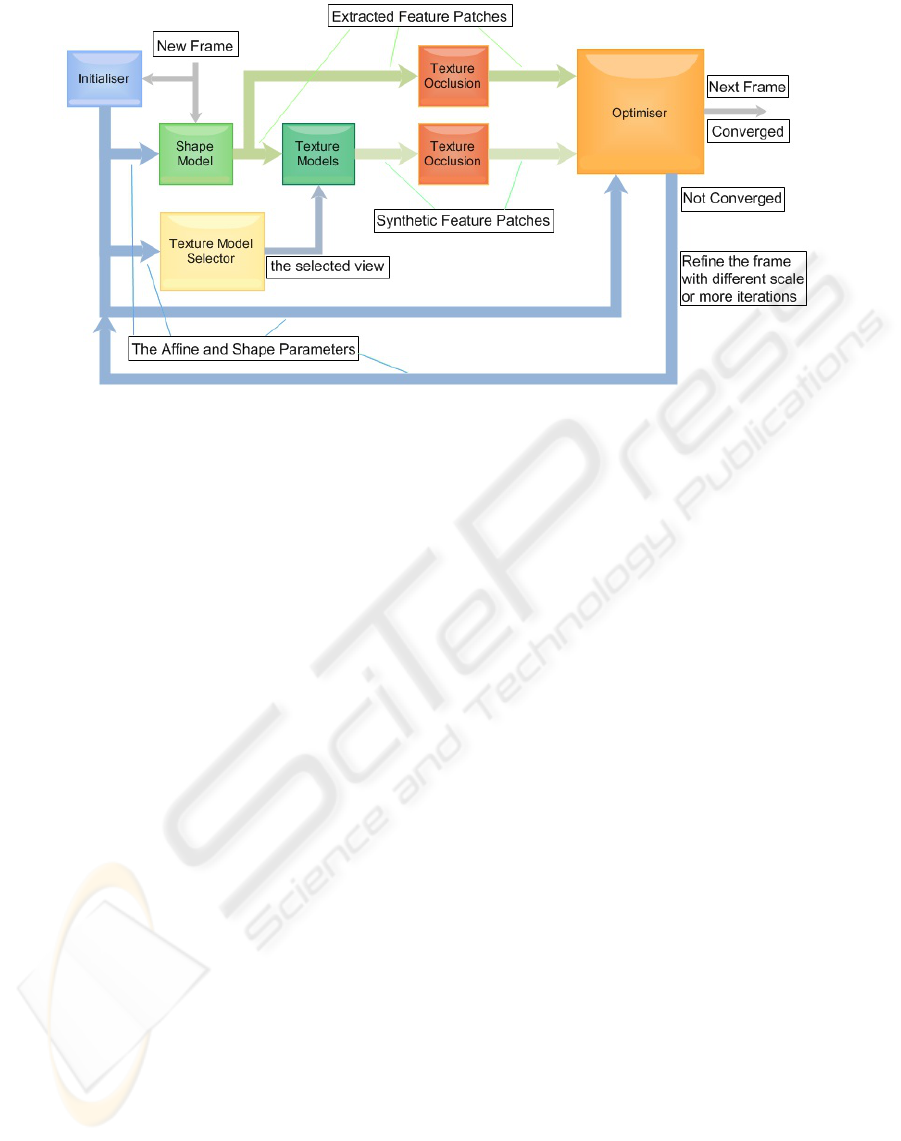
Figure 7: Multi-view CLM tracking process
3. To estimate the next frame, θ and φ is then passed
into the texture model selection module to choose
the proper appearance model.
3.7 Shape Update Methods
The original CLM algorithm (Cristinacce and Cootes,
2006) used the Nelder-Meade simplex algorithm
(Nelder and Mead, 1965) to optimize the Cross Cor-
relation. This algorithm works by using N+1 samples
in the N dimensional parameter space. Each itera-
tion the worst sample is discarded and a new sample
is added based on a set of simple heuristics. In this
work we use Powell’s method (Press. et al., 2007)
as this is supposed to typically require fewer function
evaluations than the Nelder-Meade algorithm.
Optimisation techniques based on off-the-shelf
non-linear optimisers like those described above are
typically slow to converge. We compare optimisation
using Powell’s method with a direct method for op-
timising the global NCC using an estimate of the Ja-
cobean and Hessian matrices and solving a linear sys-
tem and a quadratic equation (Tiddeman and Chen,
2007).
We also compare the techniques described above
with minimisation of the sum of squared errors (SSE)
as an error metric. This is similar to the above, requir-
ing the Jacobean and inverse Hessian matrices and so-
lution of a linear system. This method is essentially
equivalent to the additive inverse compositional AAM
alignment, (Hager and Belhumeur, 1998), (Matthews
and Baker, 2004) wrapped in a slightly different fit-
ting algorithm.
4 RESULTS
We have evaluated the proposed algorithms using a
mixture of synthetic and real data. Synthetic data is
generated by rendering multiple 3D face scans from
different viewpoints, and is useful because the 3D
models provide accurate ground-truth data. We also
test the algorithms on real video data with hand-
labelled feature points.
We have designed two experiments to evaluate
the proposed multi-view appearance 3D CLM using
shape PGA. The first is to compare the multi-view
CLM using PCA to the proposed multi-view 3D CLM
using shape PGA. The second set of experiments
compare the various optimisation algorithms within
the multi-view CLM using shape PGA framework.
The most four significant components of the shape
model and the apperance models are used in both ex-
periments.
4.1 Synthetic Data Experiments
This experiment aims to compare the performance
of the multi-view 3D CLM algorithm using shape
PGA to the algorithm using shape PCA. A set of
face sequences with fixed expression and head rota-
tion of over 40
◦
were synthesised using rendered im-
ages captured from the 3dMD system. We use 8 se-
quences comprising over 500 images in the experi-
ment. Both algorithms are applied to the same set
of face sequences using the FastNCC algorithm (Tid-
deman and Chen, 2007), Gauss-Newton algorithm
(Hager and Belhumeur, 1998), (Matthews and Baker,
2004), Powell’s method (Press. et al., 2007) as the
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING WITH 3D PGA CLM
49

Figure 9: Each row consists of a set of selected frames
from a tracking sequence with the synthetic texture patches
drawn on which indicates the location of the features. The
results at the top are from the single-view approach, at the
middle are from the multi-view CLM using shape PCA ap-
proach and at the bottom are from the multi-view CLM us-
ing shape PGA approach. When the rotating angle reaches
certain degrees(b,c), the algorithm continues tracking the
face well by auto-switching the appearance model to a side
view model while the patches start getting off the position
with single-view model.
Figure 10: The fitting results on synthetic images between
the multi-view CLM algorithm using shape PCA and shape
PGA. Powell’s method, FastNCC algorithm and Gauss-
Newton algorithm are applied as the optimisation methods.
optimisation methods. Four shape parameters An il-
lustration can be seen in Figure 9.
The statistical results of fitting in Figure 10 show
that the proposed multi-view 3D CLM algorithm us-
ing PGA gives better performance. However, the ex-
tra projecting step reduce the speed of fitting as we
Figure 11: The fitting speed on synthetic images.
Figure 12: Example images from the text video clips fitting
to.
can see in Figure 11.
The alignment accuracy is measured with the fol-
lowing equation:
d
e
=
∑
p
(x
std
−x
c
)
2
+ (y
std
−y
c
)
2
Nd
(7)
where x
std
, y
std
represent the manually placed
“ground truth” feature points locations, x
c
, y
c
repre-
sent the tracked feature points locations, d represents
the distance between the center of the eyes and N is
the number of features.
4.2 Real Data Experiment
We also apply the proposed algorithm on real video
data. The video data consists of four different subjects
showing expression, speech and some head rotation
(1280 frames in total) (Figure 12) These images and
subjects are independent of the training sets.
The image sequences are roughly initialised with
the face detector described in (Chen and Tiddeman,
2008) before a CLM search is applied to the frame and
the following frames while tracking. Three optimis-
ing methods are used for the experiments – Powell’s
method, FastNCC algorithm and the Gauss-Newton
method, a maximum of 4 iterations are used per frame
while tracking.
The fitting results are shown in Figure 13.
For Powell’s method and Gauss-Newton algorithm,
nearly 80 % of the points are within 0.15 d
e
. For Fast-
NCC algorithm, nearly 80 % of the points are within
0.17 d
e
. The proposed algorithm using PGA performs
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
50

Figure 13: The fitting results on real images between the
multi-view CLM algorithm using shape PCA and shape
PGA. Powell’s method, FastNCC algorithm and Gauss-
Newton algorithm are applied as the optimisation methods.
more robust using FastNCC and Gauss-Newton opti-
mising methods. PGA doesn’t show improvements
over PCA using Powell’s method.
Figure 14: Average fitting time estimated on the fitting us-
ing three optimising algorithms on the set of real images.
The fitting speed of fitting is shown in Figure 14.
Like the experiments on synthetic images, the algo-
rithm using PGA converges slower than the one us-
ing PCA. The Gauss-Newton algorithm is the fastest
method. The FastNCC algorithm performs at the
same level as those two methods. Powell’s method
takes much more time than the other two methods.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
The presented multi-view 3D CLM algorithm using
shape PGA is derived from the single-view 2D CLM
algorithm (Cristinacce and Cootes, 2006) and multi-
view 3D CLM algorithm (Yu and Tiddeman, 2010).
There are 15 texture models built from different views
of faces and a 3D shape model in the algorithm. For
each view, a constrained local search to match the
given image and the selected texture model and the
shape model. Instead of using the PCA shape model,
the proposed algorithm takes a PGA shape model to
represent the features.
This algorithm can be used to locate and track hu-
man facial feature in sequences with large head rota-
tions. We described two sets of experiments to eval-
uate the performance of fitting comparing to the pre-
vious algorithm using shape PCA. Based on the ex-
periments carried out, we have shown that the algo-
rithm using shape PGA gives better results when fit-
ting to unseen images with large head rotations (the
images are captured from 3dMD). The fitting is more
robust (Figure 10, 13) but slightly slower (Figure 11,
14) than the algorithm simply using shape PCA, es-
pecially at the face contour.
There are some recently proposed methods, which
outperform Cristinacce et al.’s original constrained lo-
cal model (CLM) algorithm (Cristinacce and Cootes,
2006) including Wang et al.’s exhaustive local search
(ELS) CLM algorithm (Wang et al., 2007), generic
convex quadratic fitting (CQF) CLM approach (Wang
et al., 2008) and Paquet et al.’s Bayesian constrained
local model (BCLM). These methods plus the inverse
compositional method and their extensions could be
extended to solve 3D problems and adapted to im-
prove the performance of the proposed multi-view 3D
CLM algorithm.
Pizarro et al. (Pizarro et al., 2008) pointed out
that combining the Light-Invariant theory with AAMs
can fit AAMs to face images efficiently for which
the lighting conditions are uncontrolled. Future re-
search could involve lighting and colour and more self
occlusion factors, which could improve the match-
ing rates under variant lighting, colour conditions and
even with unexpected occlusions.
REFERENCES
Ahlberg, J. (2001). Using the active appearance algorithm
for face and facial feature tracking. In International
Conference on Computer Vision Workshop on Recog-
nition, Analysis, and Tracking of Faces and Gestures
in Real-time Systems, pages 68–72.
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING WITH 3D PGA CLM
51

Baker, S. and Matthews, I. (2001). Equivalence and effi-
ciency of image alignment algorithms. In IEEE IEEE
Transactions on Computer Vision and Pattern Recog-
nition, pages 1090–1097.
Baker, S. and Matthews, I. (2002). Lucas-kanade 20 years
on: A unifying framework: Part 1. Technical Report
CMU-RI-TR-02-16, Robotics Institute, University of
Carnegie Mellon, Pittsburgh, PA.
Blanz, V. and Vetter, T. (1999). A morphable model for the
synthesis of 3d faces. In Computer graphics, annual
conference series (SIG-GRAPH), pages 187–194.
Brand, M. (2001). Morphable 3d models from video. In
IEEE computer society conference on computer vision
and pattern recognition, volume 2, pages 456–463.
Chen, J. and Tiddeman, B. P. (2008). Multi-cue facial fea-
ture detection and tracking. In International Confer-
ence on Image and Signal Processing, pages 356–367.
Cootes, T. F., Edwards, G. J., and Taylor, C. J. (2001). Ac-
tive appearance models. In IEEE Transactions on Pat-
tern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, pages 681–
685.
Cootes, T. F. and Kittipanyangam, P. (2002). Compar-
ing variations on the active appearance model algo-
rithm. In British Machine Vision Conference, vol-
ume 2, pages 837–846.
Cootes, T. F. and Taylor, C. J. (2001). Statistical models of
appearance for medical image analysis and computer
vision. In SPIE Medical Imaging, pages 236–248.
Cootes, T. F., Taylor, C. J., Cooper, D. H., and Graham, J.
(1995). Active shape models - their training and ap-
plication. Computer Vision and Image Understanding,
61:38–59.
Cootes, T. F., Walker, K., and Taylor, C. (2000). View-based
active appearance models. In IEEE International Con-
ference on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition,
pages 227–232, Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Com-
puter Society.
Cristinacce, D. and Cootes, T. (2006). Feature detection and
tracking with constrained local models. In British Ma-
chine Vision Conference, volume 3, pages 929–938.
Faggian, N., Romdhani, S., Sherrah, J., and Paplinski, A.
(2005). Color active appearance model analysis using
a 3d morphable model. In Digital Image Computing
on Techniques and Applications, page 59, Washing-
ton, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Fletcher, P. T., Lu, C., Pizer, S. M., and Joshi, S. (2004).
Principal geodesic analysis for the study of nonlin-
ear statistics of shape. IEEE transactions on medical
imaging, 23:995–1005.
Gross, R., Matthews, I., and Baker, S. (2005). Generic vs.
person specific active appearance models. Image and
Vision Computing, 23(11):1080–1093.
Hager, G. D. and Belhumeur, P. N. (1998). Efficient region
tracking with parametric models of geometry and illu-
mination. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 20:1025–1039.
Hu, C., Xiao, J., Matthews, I., Baker, S., Cohn, J., and
Kanade, T. (2004). Fitting a single active appearance
model simultaneously to multiple images. In British
Machine Vision Conference.
Jones, M. J. and Poggio, T. (1998). Multidimensional
morphable models: A framework for representing
and matching object classes. In International Jour-
nal of Computer Vision, volume 29, pages 107–131.
Springer Netherlands.
Koterba, S., Baker, S., Matthews, I., Hu, C., Xiao, J., Cohn,
J., and Kanade, T. (2005). Multi-view aam fitting
and camera calibration. In IEEE International Con-
ference on Computer Vision, pages 511–518, Wash-
ington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Lanitis, A., Taylor, C. J., and Cootes, T. F. (1997). Auto-
matic interpretation and codeing of face images using
flexible models. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Anal-
ysis and Machine Intelligence, 19(7):742–756.
Lucas, B. D. and Kanade, T. (1981). An iterative image
registration technique with an application to stereo vi-
sion. In International Joint Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, pages 674–679.
Matthews, I. and Baker, S. (2004). Active appearance mod-
els revisited. International Journal of Computer Vi-
sion, 60:135–164.
Mitchell, S. C., Lelieveldt, B. P. F., Geest, R. J., Bosch,
J. G., Reiber, J. H. C., and Sonka, M. (2001). Multi-
stage hybrid active appearance model matching: Seg-
mentation of left and right ventricles in cardiac mr im-
ages. In IEEE Transanctions on Medical Image, vol-
ume 20, pages 415–423.
Nelder, J. A. and Mead, R. (1965). A simplex method
for function minimization. Computer Journal, 7:308–
313.
Paquet, U. (2009). Convexity and bayesian constrained lo-
cal models. IEEE Transactions on Computer Vision
and Pattern Recognition, pages 1193–1199.
Peyras, J., Bartoli, A., Mercier, H., and Dalle, P. (2007).
Segmented aams improve person-independent face fit-
ting. In British Machine Vision Conference.
Peyras, J., Bartoli, A. J., and Khoualed, S. K. (2008). Pools
of aams: Towards automatically fitting any face im-
age. In British Machine Vision Conference.
Pizarro, D., Peyras, J., and Bartoli, A. (2008). Light-
invariant fitting of active appearance models. In IEEE
Conference on Computer Vision and Patter Recogni-
tion, pages 1–6.
Press., W. H., Teukolsky., S. A., Vetterling, W. T., and Flan-
nery, B. P. (2007). Numerical recipes - The art of sci-
entific computing. Cambridge University Press.
Ramnath, K., Koterba, S., Xiao, J., Hu, C. B., Matthews, I.,
Baker, S., Cohn, J. F., and Kanade, T. (2008). Multi-
view aam fitting and construction. In International
Journal of Computer Vision, volume 76, pages 183–
204.
Romdhani, S., Blanz, V., and Vetter, T. (2002). Face iden-
tification by fitting a 3d morphable model using linear
shape and texture error functions. In European Con-
ference on Computer Vision, pages 3–19.
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
52

Shum, H. Y. and Szeliski, R. (2001). Panoramic vision:
sensors, theory, and applications, chapter Construc-
tion of panoramic image mosaics with global and lo-
cal alignment, pages 227–268. Springer-Verlag New
York, Inc., Secaucus, NJ, USA.
Stegmann, M. B. (2001). Object tracking using active
appearance models. In Danish Conference Pattern
Recognition and Image Analysis, volume 1, pages 54–
60.
Tiddeman, B. P. and Chen, J. (2007). Correlated active ap-
pearance models. In IEEE Transactions on Signal-
Image Technology & Internet-Based Systems, pages
832–838.
Vetter, T. and Poggio, T. (1997). Linear object classes and
image synthesis from a single example image. In
Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, volume
19(7), pages 733–742.
Wang, Y., Lucey, S., Cohn, J., and Saragih, J. M. (2007).
Non-rigid face tracking with local appearance consis-
tency constraint. In IEEE International Conference on
Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition.
Wang, Y., Lucey, S., and Cohn, J. F. (2008). Enforcing con-
vexity for improved alignment with constrained local
models. In IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and
Pattern Recognition, volume Issue 23–28, pages 1–8.
Xiao, J., Baker, S., Matthews, I., and Kanade, T. (2004).
Real-time combined 2d+3d active appearance models.
In the IEEE computer society conference on computer
vision and pattern recognition, volume 2, pages 535–
542.
Yu, M. and Tiddeman, B. P. (2010). Facial feature detection
and tracking with a 3d constrained local model. Sub-
mited to International Conferences in Central Europe
on Computer Graphics, Visualization and Computer
Vision 2010.
Zhang, Z., Liu, Z., Adler, D., Cohen, M. F., Hanson, E., and
Shan, Y. (2004). Robust and rapid generation of ani-
mated faces from video images: A model-based mod-
eling approach. International Journal of Computer
Vision, 58(2):93–119.
Zhou, Y., Zhang, W., Tang, X., and Shum, H. (2005). A
bayesian mixture model for multi-view face align-
ment. In IEEE Computer Society Conference on Com-
puter Vision and Pattern Recognition, pages 741–746,
Washington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
FACE DETECTION AND TRACKING WITH 3D PGA CLM
53
