
EVALUATION OF DENOISING METHODS WITH RAW IMAGES
AND PERCEPTUAL MEASURES
Matteo Pedone, Janne Heikkil
¨
a
Department of Electrical and Information Engineering, University of Oulu, Finland
Jarno Nikkanen, Leena Lepist
¨
o, Timo Kaikumaa
Nokia Research Center, Tampere, Finland
Keywords:
Denoise, Demosaic, Evaluation, State-of-the-art, Perceptual quality assessment, Artifacts, Degradation, RAW
images, Real data.
Abstract:
In this paper we present a performance evaluation of different state-of-the-art denoising method, applied to
RAW images in Bayer pattern format. Several measures for assessing objective quality are considered. We
also propose, a novel and straightforward extension to the SSIM-Index that handles color information. The
evaluation is divided in two stages: first an entire set of images is artificially degraded and then restored
with the considered denoising/demosaicking methods. The second stage involved a subjective evaluation
with real noisy RAW images. We observed that the resulting qualities of the considered denoising methods
are in agreement between the two different evaluation stages, and the best performing algorithms are easily
identified. Moreover, the proposed extension of the SSIM-Index proved to behave more consistently in respect
to the artifacts introduced by the denoising algorithms, and its outcome was always in fair accordance with the
subjective perceived quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
It is a well-known fact that in any digital camera cir-
cuitry, the image which is acquired by the sensor array
is often degraded by different kinds of noise (Kurimo
et al., 2009). The process of estimation of the original
unknown signal, is called denoising, and it constitutes
one of the major research topics in signal and image
processing.
The nature and the intrinsic properties of noise
may vary according to the type of sensor array and
camera model, and they are usually known. This fact
is one of the key advantages of performing denoising
with RAW data; in fact, the final image which is com-
monly output to the user, is the result of a pipeline of
operations which would unavoidably alter the proper-
ties of noise.
The literature in denoising of color or grayscale
images is very extensive. A good overview on the
most recent trends in denoising can be found at (ISIT,
2007). In typical real scenarios, one has to face the
necessity of estimating a complete RGB image from
data which are scattered in regular patterns (demo-
saicking), and this led to the development of new
and promising joint-approaches, in which denoising
and demosaicking are treated as a unique problem
(Hirakawa and Parks, 2006). Such methods are cur-
rently in their infancy, and although they are theoret-
ically more appealing and produce perceptually good
results, they still lack an extensive evaluation pro-
cess. The work described in this paper is stimulated
by the fact that it is not a trivial issue to figure out
which are the most convenient ways to produce a fi-
nal image from noisy sensor data; we therefore at-
tempt to provide reasonable answers to this question
by considering an evaluation framework with several
state-of-the-art denoising algorithms, joint denoising-
demosaicking approaches, different quality measures,
and finally both real and artificially generated noise.
This paper is organized as follows: in Section 2
the main goals of this work are accurately stated. Sec-
tions 3-4 justify our choice of algorithms, and set
of images. In sections 5 we discuss the behavior of
the quality measures and propose an extension of the
SSIM-Index for color images. In the remaining part
of the paper we discuss the results obtained.
168
Pedone M., Heikkilä J., Nikkanen J., Lepistö L. and Kaikumaa T. (2010).
EVALUATION OF DENOISING METHODS WITH RAW IMAGES AND PERCEPTUAL MEASURES.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 168-173
DOI: 10.5220/0002831201680173
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 SCOPE OF THE EVALUATION
We express now the main goals of our work in the fol-
lowing list. In the following sections we will describe
how each of the considered aspects has been treated.
Our goals are:
• Select some among the most promising state-of-
the-art denoising methods, according their per-
formance measured both in PSNR and subjective
quality.
• Choose two suitable image databases for experi-
ments: one consisting of high-quality and virtu-
ally noise-free images; another one consisting of
real RAW data.
• Choose at least two suitable measures for quality
assessment, and justify their use.
• Evaluate the performance of RAW denoising
methods for both artificially degraded data and
real data.
3 SELECTING THE METHODS
In image denoising, quality is commonly measured
by the Peak-Signal-to-Noise-Ratio (PSNR). However
it has been frequently argued that the PSNR in many
cases may not reflect the perceived quality of the fi-
nal image (Wang et al., 2004). The importance of
perceptual quality has been seriously considered by
Vansteenkiste et al. in (Vansteenkiste et al., 2006).
They describe an important experiment carried out
with human subjects, and in summary, the main re-
sults were that the PSNR might sometimes not be in
accordance with the perceived quality, and also that
humans tend to prefer “denoised” images which (in
order of importance), are less blurry, have the least
amount of visual artifacts introduced by the denois-
ing algorithm, have the least amount of noise.
On the other hand this experiment also ended up
in confirming that among the perceptually best de-
noising method, one finds three methods which are
also state-of-the-art in terms of PSNR; these methods
are known as “Block Matching 3D” (Dabov et al.,
2006), “Shape Adaptive DCT” (Foi et al., 2006), and
“Bayesian Least Square Gaussian Mixtures” (Portilla
et al., 2003); all these have been considered in our
evaluation, as they were proven to yield highest qual-
ity results, both subjectively and objectively.
The aforementioned algorithms were proposed as
denoising methods for ordinary grayscale images
1
1
For some of them also a version for color images is
proposed.
and it is not trivial to predict if such methods are
still suitable when applied to a Bayer-pattern image,
followed by demosaicking. In (Hirakawa and Parks,
2006) the authors addressed this issue by showing that
demosaicking and denoising are essentially two prob-
lems of the same nature, and they proposed a joint
approach for denoising-demosaicking; more recent
work following the same lines has been done by Paliy
et al. (Paliy et al., 2007), who introduced a state-of-
the-art demosaicking algorithm, and proposed a vari-
ant that is able to deal with noisy Bayer data. Sum-
marizing the methods we considered are:
• Block Matching 3D (BM3D)
• Shape Adaptive DCT (SA-DCT)
• Bayesian Least Square Gaussian Mixtures in
Wavelet Domain (BLS-GSM)
• Hirakawa’s Joint demosaicking and denoising
• LPA-ICI Color Filter Array Interpolation for
noisy Bayer data (Oracle-Γ).
In order to provide a reasonably fair comparison be-
tween separate and joint approaches, a state-of-the-art
demosaicking method is also needed. Based on the
survey of (Li et al., 2008) we chose the standard ver-
sion of LPA-ICI CFAI Oracle-Γ.
4 CHOOSING DATA-SETS
The database of real noisy images consists of a set
of ten 1152x864 images taken with a consumer-
level mobile phone camera. These images are
used for a subjective evaluation only. Further-
more another database of high quality and vir-
tually noise-free images has been chosen, and
this is the popular Kodak database available
at www.cipr.rpi.edu/resource/stills/kodak.html which
includes 23 still color images (768x512). The im-
ages from the latter database are commonly used as
ground-truth in demosaicking literature (and often in
denoising literature too) for objective comparisons of
methods.
5 QUALITY MEASURES
Whenever the noisy images are obtained by artifi-
cially degrading the original ones, it is possible to use
the ground-truths for objective quality assessment.
The measures that have been considered are: the
Peak Signal-to-Noise Ratio (PSNR), and the Mean-
Structural-SIMilarity (MSSIM), which was recently
EVALUATION OF DENOISING METHODS WITH RAW IMAGES AND PERCEPTUAL MEASURES
169
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
20
22
24
26
28
30
32
34
36
Noise Level σ
Average PSNR
BM3D
SA−DCT
BLS−GSM
LPA-ICI
HIRAK.
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
Noise Level σ
Average MSSIM
BM3D
SA−DCT
BLS−GSM
LPA-ICI
HIRAK.
5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
0
0.1
0.2
0.3
0.4
0.5
0.6
0.7
0.8
Noise Level σ
Average Color−MSSIM
BM3D
SA−DCT
BLS−GSM
LPA-ICI
HIRAK.
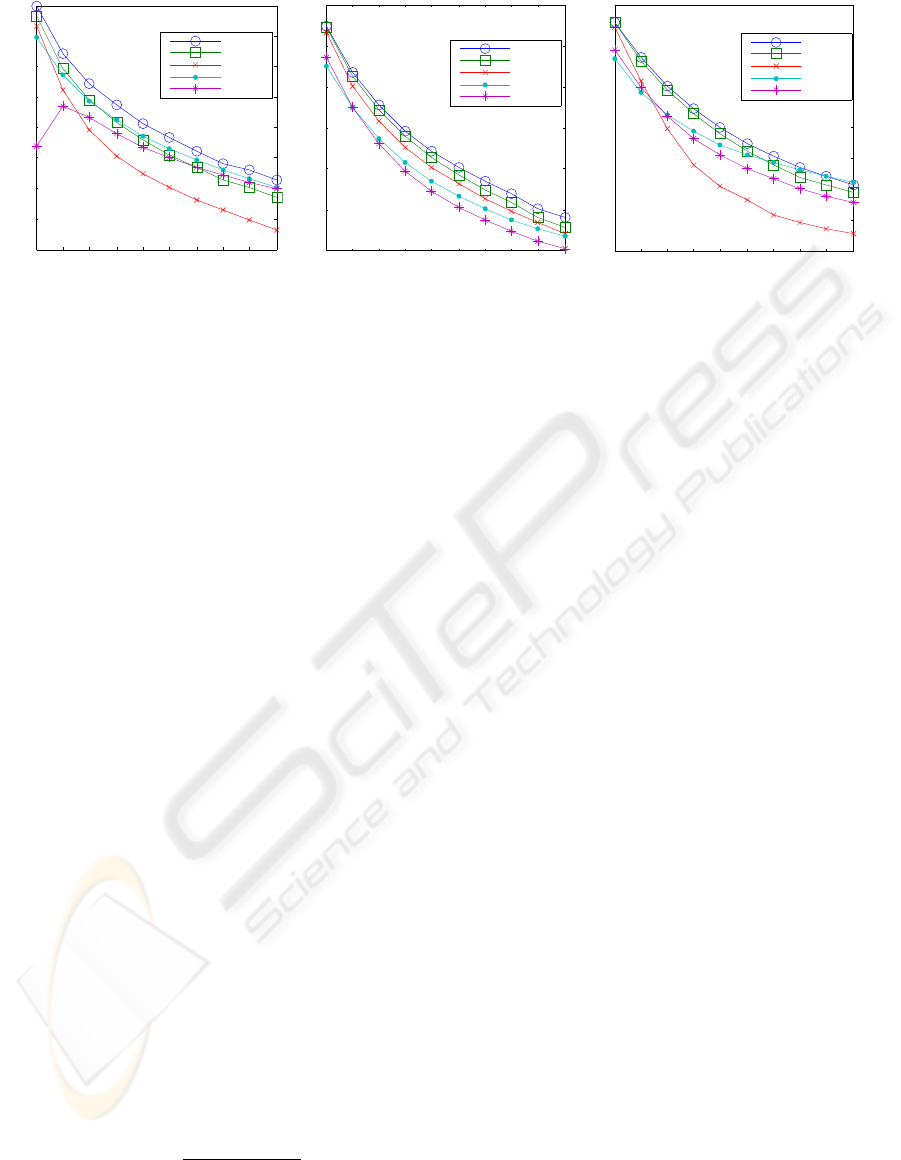
Figure 1: Mean performance of the denoising methods according to: (Left) PSNR; (Middle) Mean SSIM-Index; (Right)
proposed Mean CSSIM-Index.
proposed as a reliable solution for assessing percep-
tual image quality (Wang et al., 2004). The SSIM
is originally designed to work with grayscale images
only. As our application involves color images, we
now propose a straightforward workaround to this
problem. The SSIM-Index for two images x and y
is defined as follows:
SSIM(x, y) = [l(x, y)]
α
[c(x, y)]
β
[s(x, y)]
γ
(1)
where l,c,s are functions to measure respectively the
difference in luminance, contrast and structure be-
tween the two images; α, β, γ are parameters used
to adjust the relative importance between l, c and
s. Given two images x and y, all these three mea-
sures satisfy three axioms: symmetry: f (x, y) =
f (y, x), boundedness: f (x, y) ≤ 1 and unique maxi-
mum: f (x, y) = 1 iff x = y (Wang et al., 2004). A
possible extension can be obtained in the following
manner: we apply a color-space transformation from
RGB to CIE-Lab; let’s now denote by x
L
, y
L
and by
X
C
, Y
C
respectively the luminance components of the
images (in vector form), and the chrominance com-
ponents of the images treated as matrices with com-
plex elements of the form (a
j
+ ib
j
), for a pixel at lo-
cation j. The complex representation is perceptually
justified by the fact that, given a fixed white-point,
the absolute value encodes the saturation of a pixel,
while the phase angle encodes its hue. We choose to
represent the chrominances of the images by two real
vectors of singular-values σ
X
C
, σ
Y
C
respectively for X
C
and Y
C
. At this point, an obvious candidate measure
which satisfies the three aforementioned axioms, for
two complex matrices X, Y is:
k(X, Y) =
h
σ
X
, σ
Y
i
+ ε
k
σ
X
kk
σ
Y
k
+ ε
(2)
where ε is a small number to prevent numerical in-
stability due to low values. This strategy is essen-
tially analogous to the one described in (Wang et al.,
2008), in which the authors associate images to vec-
tor of singular values of matrices with quaternionic
quantities of the form Var
p
+iR
p
+ jG
p
+kB
p
, whose
components are respectively the local variance, and
the RGB values at the location p. Their measure can
be regarded as an alternative for SSIM and works with
color images too; nonetheless it is computationally
less efficient and it does not offer the flexibility to di-
rectly assign different importances to each single type
of degradation. This has been shown to be critical
in (Vansteenkiste et al., 2006) for modeling correctly
the perceived image quality, and it has been proba-
bly one of the causes for giving inconsistent quality-
scores in our experiments. However a deep investi-
gation regarding the actual performance of our mea-
sure against the others found in literature, remains
out of the scope of this paper. Our proposed mea-
sure k(X, Y) can be multiplied by the right term in (1)
yielding:
CSSIM(X, Y) = SSIM(x
L
, y
L
)[k(X
C
, Y
C
)]
δ
(3)
The parameter δ is a real exponent needed to adjust
the importance of color consistency in relation to the
other factors in (1). In our experiments we set ε =
0.001, and δ = 12, and use (3) to assess perceptual
quality of denoised/demosaicked color images.
6 EXPERIMENTS
We performed two experiment sessions in relation to
the type of noise considered. In the first one we ap-
plied artificially added noise, while for the second
one, real noisy RAW images were used.
The 23 images from the Kodak database were
down-sampled according to the structure of the Bayer
pattern. They were successively degraded with addi-
tive Gaussian noise, and finally denoised and demo-
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
170

Figure 2: Images corrupted with additive Gaussian noise (σ = 20: first two rows, σ = 50: last two rows) and denoised with
(from left to right) BM3D, SA-DCT, BLS-GSM, LPA-ICI (Oracle- Γ), Hirakawa’s method.
saicked. The availability of ground-truth images en-
ables us to compare objectively the performances in
terms of PSNR, Mean-SSIM, and Mean-CSSIM. The
noise levels considered correspond to σ = 5k, with
k = 1..10. When using the Mean-SSIM only the lu-
minance channel is taken into account.
The real noisy Bayer images were denoised with
all the methods previously listed. The noise parame-
ters related to the specific model of the camera sen-
sor used were not known; as a consequence, for most
denoising methods the noise parameters were manu-
ally calibrated in order to obtain the best visual result,
while the method-specific parameters were left to the
default values. The images did not have correspond-
ing ground truth, hence they were evaluated only sub-
jectively.
7 DISCUSSION
We report, for each value of σ, the corresponding
mean performance of the denoising methods, ob-
tained by averaging the resulting PSNR’s, SSIM’s and
CSSIM’s of the whole set of images (Figure 1). A
quick analysis of the plots, immediately reveals that
there are several inconsistencies between the three
measures. In fact, the Mean-SSIM suggests that for
all the noise levels, the three separate approaches are
always better than the joint-algorithms. However a
visual inspection revealed that when the amount of
noise increases, the BM3D, SA-DCT and BLS-GSM
fail in rendering correct color tones (see Figure 2).
In this sense, the worst performance is reached by
the BLS-GSM, which produces almost totally desatu-
rated images. We regard such results as unacceptable,
and this fact is indeed reflected by the plot related to
the CSSIM, in which the quality factor of the BLS-
GSM immediately drops to very low values, as ob-
served.
EVALUATION OF DENOISING METHODS WITH RAW IMAGES AND PERCEPTUAL MEASURES
171
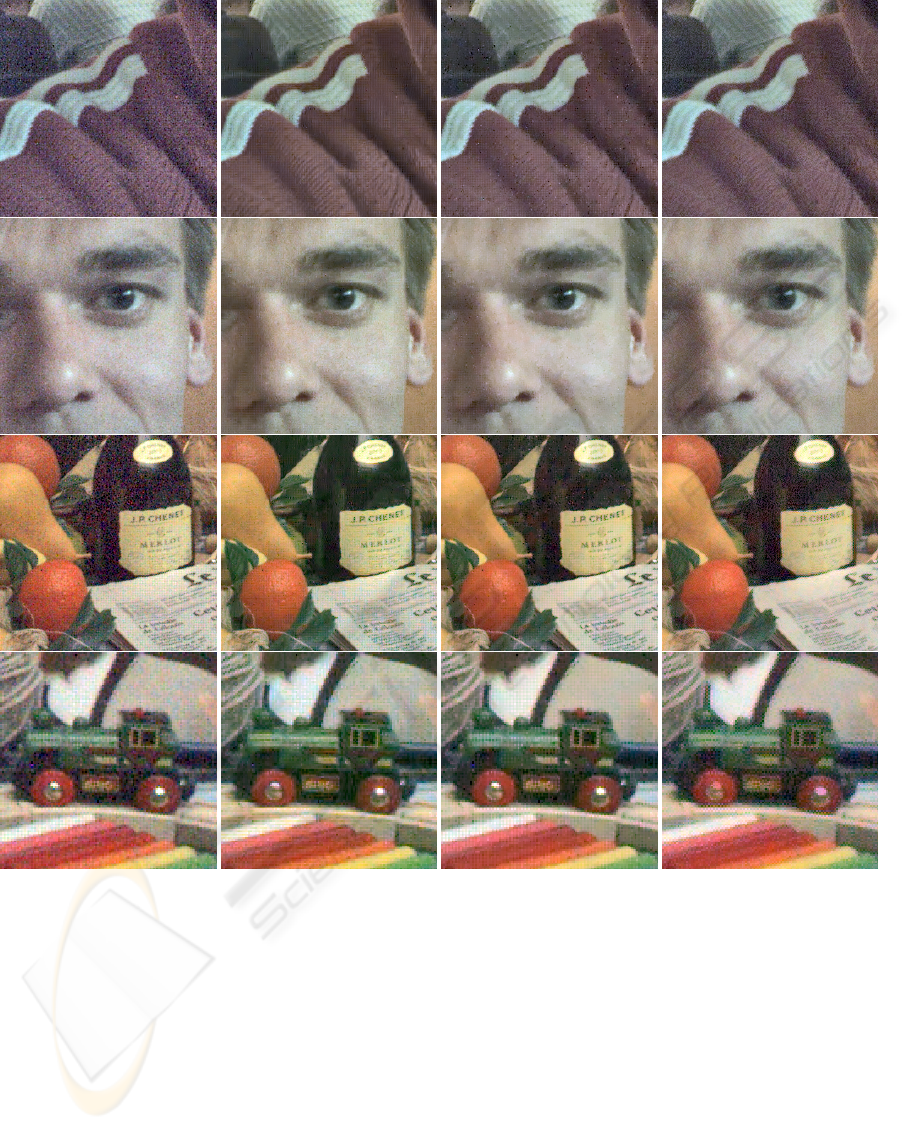

Figure 3: Details of real noisy RAW images and denoised counterparts. (From left to right) Noisy input; denoised with
BM3D; with LPA-ICI; with Hirakawa’s method.
Another interesting observation is that according
to the Mean-CSSIM, the joint approach proposed in
(Paliy et al., 2007), for amounts of noise larger than
σ ≈ 32 and σ ≈ 45, respectively performs better than
SA-DCT and BM3D, ranking as the best method for
critical degradations. In the same scenario the PSNR
classifies the BM3D always as the best method, al-
though it clearly yields images that are spoiled by
the introduction of vertical and horizontal structures
and suffer color desaturation. On the contrary the
CSSIM Index indicates the LPA-ICI be the most ef-
fective. The analysis for lower amount of noise is
more delicate. In fact, when the noise level approx-
imately reaches σ ≈ 20 there is an interesting dis-
agreement between the two measures. According to
the PSNR, the LPA-ICI starts to outperform the SA-
DCT, while the Mean-CSSIM Index still suggests that
the SA-DCT is yielding more perceptually accurate
results. As a matter of fact, the SA-DCT still suc-
ceeds in restoring high frequency details, which in-
stead are lost after applying the LPA-ICI. Nonetheless
when the image contains fairly large homogeneous
regions, the LPA-ICI works better, since the images
produced by the SA-DCT are impaired by visible ar-
tifacts, and look unacceptable (see Figure 2). Both
measures agree in classifying the BM3D as the best
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
172

method for lower noise conditions.
Figure 3 shows some details extracted from the
real-noisy images. Results obtained with BLS-GSM
and SA-DCT are omitted, as they introduced an unac-
ceptable amount of artifacts. The joint approach pro-
posed in (Hirakawa and Parks, 2006) performs rea-
sonably well, however it has the tendency to introduce
zipper artifacts, blurriness (especially in highlight re-
gions), and in some cases fails in preserving high fre-
quency details. More difficult is the comparison be-
tween the BM3D and the joint approach LPA-ICI: the
former is obviously the best in restoring the details
which were present in the original image; on the other
hand the results suffers from the presence of artifacts,
which are anyhow usually tolerable. The latter ap-
proach instead, produces almost artifacts-free images,
but images lack of details where instead the BM3D
performed well; also a considerable amount of noisy
grain is still present. We believe that, in this experi-
ment session, where the noise amount was not drastic,
the BM3D yielded the most satisfactory results. We
shall conclude that in general, for higher noise levels
the joint approach LPA-ICI performs best, while for
lower noise levels the Block-Matching 3D is prefer-
able.
8 CONCLUSIONS
We compared several solutions for noise removal with
RAW images, and evaluated their performances based
on the quality of the demosaicked output images.
Both joint denoise-demosaic, and separate (denoise,
then demosaic) approaches were considered. The
methods have been selected among the state-of-the-
art ones, both in terms of PSNR and perceived qual-
ity. Also, one state-of-the-art demosaicking method
was used whenever it was necessary to demosaic a
previously denoised image. Two different kinds of
comparisons were carried out: one with 23 high-
quality images (Kodak database), which were artifi-
cially degraded, and another one with 10 RAW im-
ages, corrupted by real noise. In the former case the
ground-truths were available. We adopted as quality
measures, the PSNR, the Mean-SSIM-Index, and our
extension to the SSIM-Index for color images (the
CSSIM-Index). We showed how the proposed mea-
sure behaves in satisfactory agreement with the per-
ceptual subjective quality. We also concluded that
among the method considered, the joint approach pro-
posed in (Paliy et al., 2007) is preferable when the
image is severely impaired by noise, while the Block-
Matching-3D is preferable when the amount of noise
is reasonably low. We finally confirmed this fact, by
visually inspecting the denoised RAW images which
were originally degraded by real noise. We believe
that our work can shed more light on which are the
most promising research directions for further im-
provements in RAW image denoising.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank Nokia Corporation
for providing the set of noisy RAW images.
REFERENCES
Dabov, K., Foi, A., Katkovnik, V., and K.Egiazarian (2006).
Image denoising with block-matching and 3d filtering.
In Proc. SPIE Electronic Imaging 2006.
Foi, A., Dabov, K., Katkovnik, V., and Egiazarian, K.
(2006). Shape-adaptive dct for denoising and im-
age reconstruction. In Proc. SPIE Electronic Imaging
2006.
Hirakawa, K. and Parks, T. W. (2006). Joint demosaicing
and denoising. In IEEE TIP August 2006.
ISIT (2007). Recent trends in denoising tutorial. htpp:
//www.stanford.edu/
˜
slansel/tutorial/.
Kurimo, E., Lepisto, L., Nikkanen, J., Gren, J., Kunttu, I.,
and Laaksonen, J. (2009). The effect of motion blur
and signal noise on image quality in low light imag-
ing. In Proceedings of SCIA2009.
Li, X., Gunturk, B., and Zhang, L. (2008). Image demosaic-
ing: a systematic survey. In Visual Communications
and Image Processing 2008.
Paliy, D., Katkovnik, V., Bilcu, R., Alenius, S., and Egiazar-
ian, K. (2007). Spatially adaptive color filter array
interpolation for noiseless and noisy data. In Int. J.
Imaging Sys. Tech., Sp. Iss. Appl. Color Image Pro-
cess., vol. 17, no. 3, pp. 105-122.
Portilla, J., Strela, V., Wainwright, M., and Simoncelli, E. P.
(2003). Image denoising using scale mixtures of gaus-
sians in the wavelet domain. In IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing. vol 12, no. 11, pp. 1338-1351.
Vansteenkiste, E., van der Weken, D., Philips, W., and
Kerre, E. (2006). Perceived image quality measure-
ment of state of the art noise reduction schemes. In
ACIVS06. Springer DOI Link 0609.
Wang, Y., Liu, W., and Wang, Y. (2008). Color image
quality assessment based on quaternion singular value
decomposition. In cisp, vol. 3, pp.433-439, 2008
Congress on Image and Signal Processing.
Wang, Z., Bovik, A. C., Sheikh, H. R., and Simoncelli, E. P.
(2004). Image quality assessment: From error visibil-
ity to structural similarity. In IEEE Transactions on
Image Processing, vol. 13, no. 4, Apr. 2004.
EVALUATION OF DENOISING METHODS WITH RAW IMAGES AND PERCEPTUAL MEASURES
173
