
A
HUB ARCHITECTURE FOR SERVICE ECOSYSTEMS
Towards Business-to-Business Automation with an Ontology-enabled Collaboration
Platform
Alex Norta
Department of Computer Science, University of Helsinki
P.O. Box 68 (Gustaf H
¨
allstr
¨
omin katu 2b), FI-00014 Helsinki, Finland
Keywords:
SOC, BPM, B2B, Broker, Hub, Collaboration, Trust, Reputation, Ontology.
Abstract:
The management and coordination of business process collaboration experiences changes because of glob-
alization, specialization, and innovation. Service-oriented computing (SOC) is a means towards business-
process automation and recently, many industry standards emerged to become part of the service-oriented
architecture (SOA) stack. In a globalized world, organizations face new challenges for setting up and carrying
out collaborations in semi-automating ecosystems for business services. A need emerges for service Hubs that
not only store service offers and requests together with their issuing organizations and assigned owners, but
that also allow an evaluation of trust and reputation in an anonymized electronic service marketplace. In this
paper, we explore the features of a semi-automating ecosystem in which business processes are expressed as
services and where Hubs are essential for bringing together service offers and requests. The presented Hub
architecture is designed so that business managers benefit from an interface that borrows concepts of social-
networking sites while the complex computing machinery for matching service offers and requests remains
hidden from the user. The partial implementation of service-Hub components demonstrate the feasibility of
our approach.
1 INTRODUCTION
In a globalized business setting, enterprizes may run
complex supply chains across several tiers that com-
prise many geographical regions. Original equip-
ment manufacturers (OEM) maintain intricate in-
house processes of which parts are outsourced to sup-
pliers. With the emergence of SOC (Allen et al.,
2006; E.A.Marks and Bell, 2006), such business-to-
business (B2B) collaboration with business processes
as a service (BPaaS), may be semi-, or fully auto-
mated.
The predicted increase in BPaaS leads to a con-
siderable communication overhead for enterprises. A
system model is missing for a BPaaS-Hub so that
business- and logistics managers, industrial marketers
and so on, engage in setting up cross-organizational
B2B collaboration in a semi-automated way. Such a
BPaaS-Hub should permit laymen to engage in ser-
vice matching while the required computing com-
plexity remains hidden. This paper fills the gap and
presents a BPaaS-Hub architecture.
The structure of the paper is as follows. Sec-
tion 2 presents high-level characteristics of B2B col-
laboration from which we deduct requirements for
the BPaaS-Hub architecture that Section 3 comprises.
Section 4 discusses preliminary implementations and
what existing systems realize the BPaaS-Hub archi-
tecture. Section 5 concludes the paper and presents
future work.
2 B2B CHARACTERISTICS
Observing B2B collaborations in the EU research
project CrossWork (Mehandjiev and Grefen, 2010),
particular features are characteristic. An OEM orga-
nizes an in-house business process that is decompos-
able into different perspectives, e.g., control flow of
tasks, information flow, personnel management, allo-
cation of production resources, and so on. A complex
product of an OEM comprises many components of
which several need to be acquired from suppliers. The
reasons for acquiring parts externally are manifold,
e.g., the OEM cannot produce with the same quality,
or an equally low price per piece, the production ca-
pacity is not available, required special know-how is
lacking, and so on.
240
Norta A.
A HUB ARCHITECTURE FOR SERVICE ECOSYSTEMS - Towards Business-to-Business Automation with an Ontology-enabled Collaboration Platform.
DOI: 10.5220/0002857302400243
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technology (WEBIST 2010), page
ISBN: 978-989-674-025-2
Copyright
c
2010 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Figure 1: A collaboration pyramid in B2B.
In the scenario of Figure 1, the horizontal ellipses
denote the client/server integration of ourtsourced
parts of the in-house process to lower-level clients of
the tier (Norta and Eshuis, 2009). The outsourced
business process is refined by the supplier without the
OEM’s awareness while the supplier only has aware-
ness of the OEM’s outsourced process.
Vertical ellipses in Figure 1, depict a peer-to-
peer (P2P) collaboration within a cluster of small and
medium sized enterprises (SME). If several SMEs
form a composed service in a P2P way, they become
a supplier for a higher-level service consumer. For
managing such P2P service collaboration (Kutvonen
et al., 2007), their lifecycle needs to be managed (a)
for business-community formation to compose ser-
vices, (b) for the evolution of such business communi-
ties through epochs with changing members and mod-
ified services, and eventually (c) for the dissolution of
P2P business communities.
For the BPaaS-Hub, we consider a stepwise
”fuzzy matching” approach. The first step is a
matching of service offers and requests based on
extracted and ontologically clarified keywords con-
tained in service descriptions. A matching of left over
services subset requires on the next level machine-
readable service-level agreements (SLA) with, e.g.,
WS-Agreement (Andrieux et al., 2007) or WSLA
1
.
As an example for this matching type, in (M
¨
uller
et al., 2009), matching templates and instantiations
involve computing the adherence of the latter to tem-
plates.
For the BPaaS-Hub architecture in the sequel, we
deduct requirements from the discussed B2B charac-
teristics.
1. A BPaaS-Hub must allow laymen who have no or
little SOC knowledge to engage in service discov-
ery and matching.
2. Since the Hub is part of an anonymized service
ecosystem, users must be able to check the trust-
1
http://www.research.ibm.com/wsla/
worthiness and reputation of service offers and re-
quests.
3. The Hub must support resolving ambiguities in
the human-and machine readable service repre-
sentations.
4. The Hub must support feasible service matching,
i.e., we assume pragmatic fuzzy matching as ex-
plained above.
5. The user interaction with the Hub must be logged
for extracting business intelligence.
3 A SERVICE-HUB SYSTEM
We specify a conceptual system architecture for the
BPaaS-Hub. For the BPaaS-Hub architecture, we fol-
low design principles, styles and patterns (Bengts-
son, 2002; Gamma et al., 1995). Architectural styles
comprise a description of component types and their
topology, a description of the pattern of data and con-
trol interaction among the components, and an infor-
mal description of the benefits and drawbacks of using
a particular style.
The conceptual architecture depicted in Figure 2
utilizes the principles of separation of concern, it fol-
lows a layer style, employs a pipes-and-filters pattern
and pattern-based components for abstracting data
repositories.
Separation of Concerns. In Figure 2, columns
show the separations. WHO: refers to the business
entities a user searches for, e.g., services in specific
domains, organizations, or persons. WITH: refers to
establishing on the fly the ontological infrastructure
needed to resolve ambiguity issues in service descrip-
tions. WHAT: refers to the need for pulling in addi-
tional service-related information from the Web cloud
for a trust-enhancing mashups. We define a mashup as
a Web page or application that combines data or func-
tionality from two or more external sources to create
a new service. HOW: refers to the application infras-
tructure necessary for the services to be matched and
enacted. Additionally, social mining techniques ana-
lyze the logged user interaction with the Hub for ex-
tracting business intelligence.
Layer Style. A layer style separates vertically the
BPaaS-Hub architecture with communication ex-
changes to the adjacent higher or lower layer to fa-
cilitate a decoupling and replacement with alternative
components. In Figure 2, the top layer called Views,
depicts all user-interface components. The middle
A HUB ARCHITECTURE FOR SERVICE ECOSYSTEMS - Towards Business-to-Business Automation with an
Ontology-enabled Collaboration Platform
241
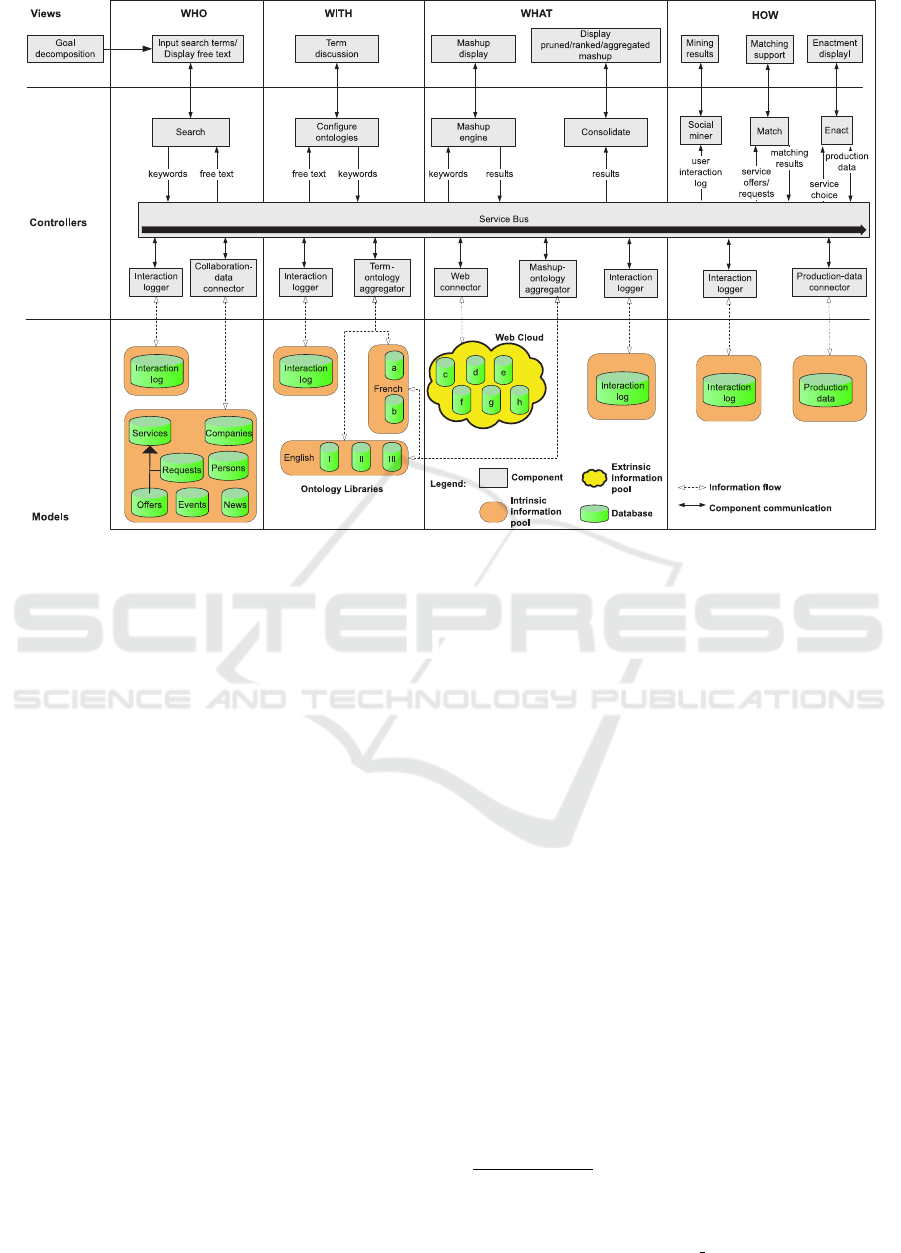
Figure 2: Architecture of a service Hub.
layer termed Controllers, shows components with ap-
plication logics while the lowest layer termed Mod-
els, contains all system intrinsic or third-party extrin-
sic information sources from the Web cloud for trust-
building mashups.
Pipes and Filters Pattern. The components of the
controller layer instantiate a pipes-and-filters pattern
enforced by a service bus. The ontology-supported
Goal decomposition delivers input for what business
entities are sought after in a fully or semi-automated
way. A service search results both in human-readable
text and optional machine-readable WS-* specifica-
tions. An analysis of search results culminates in a dy-
namically linked library of ontology libraries for re-
solving ambiguities in the service representations. A
mashup engine performs automated searches in user-
selected information pools of the Web cloud. The re-
sults require consolidation, i.e., pruning, ranking and
aggregated. Mining the logged user interaction gen-
erates business intelligence. A matching of service
offers with service requests precedes the enactment
of machine-readable WS-* service representations.
Abstract Data Repository. On the controller layer
of Figure 2 are components of the architectural style
abstract data repository (Klein and Kazman, 1999).
This architectural style, on the one hand, keeps the
producers and consumers of shared ontologies from
having knowledge of each other’s existence. On the
other hand, abstract data repositories hide details of
shared data-repositories. The abstract interfaces to
the data repositories reduce the coupling between data
producers and consumers.
4 FEASIBILITY EVALUATION
In the framework of the ContentFactory
2
(CF) re-
search project, we implement the BPaaS-Hub archi-
tecture from Section 3 for conducting case studies
with industry. For satisfying Requirement 1, we im-
plement a business-service registry termed Collab
3
that links data of service offers and requests with
service-responsible persons and service-issuing orga-
nizations. For keyword extraction, Collab sends the
free-text description to the Likey (Paukkeri et al.,
2008) application.
For Requirement 2, a mashup component is part
of the BPaaS-Hub architecture. We consider the
PULS (Yangarber and Steinberger, 2009) applica-
tion for populating the mashup component. Ongoing
PULS extensions cater for an in-depth exploration of
2
ContentFactory, funded by Tekes (Finnish
Funding Agency for Technology and Innovation),
http://www.verkko-ope.net/cf/
3
http://db.cs.helsinki.fi/∼tkt coll/collab/
WEBIST 2010 - 6th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
242

business acquisition, investment, nomination, prod-
uct release, ownership/stake; divestment/reduction of
stake.
For Requirement 3, the BPaaS-Hub architecture
includes components for creating ontology libraries.
We use the TermFactory
4
application for allowing ter-
minologists to define extracted keywords that enter
ontology libraries for respective Hub-application con-
texts. The matching component in the Hub architec-
ture satisfies Requirement 4. Currently we implement
an application for realizing the matching heuristics
in (Eshuis and Norta, 2009).
For Requirement 5, the Hub architecture includes
logging components for several stages of user interac-
tion and a social mining component for the extraction
of business intelligence, e.g., ProM
5
. Many options
exist for the Enact component, e.g., ActiveBPEL
6
.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we explore the characteristics of B2B
collaboration and present a framework for automating
the matching of service offers and service requests.
Based on extracted requirements for service match-
ing in the setting of business-to-business collabora-
tion, we present a Hub architecture for brokering busi-
ness processes as services. The Hub permits busi-
ness managers to explore with free text service offers
and requests, their issuing organizations and service-
managing persons. Ontology engines resolve ambi-
guity issues in the text and to establish trust and ex-
plore the reputation of services and their affiliated or-
ganizations and persons, Hub users employ mashups
comprising news feeds, blogs, wikis, and so on.
For future work, we pursue the integration of iden-
tified applications for implementing the Hub architec-
ture and plan to conduct case studies with industry
using the Hub for discovery and matching of service
offers and requests. Furthermore, we explore Hub ex-
tensions for integrating a service-tendering procedure
that allows users to place negotiable bids.
REFERENCES
Allen, P., Higgins, S., McRae, P., and Schlamann, H., edi-
tors (2006). Service Orientation: Winning Strategies
and Best Practices. CAMBRIDGE UNIVERSITY
PRESS.
4
http://www.helsinki.fi/∼lcarlson/CF/doc/TFManual.html
5
http://prom.win.tue.nl/tools/prom/
6
http://sourceforge.net/projects/activebpel/
Andrieux, A., Czajkowski, K., Dan, A., Keahey, K.,
Ludwig, H., Nakata, T., Pruyne, J., Rofrano,
J., Tuecke, S., and Xu, M. (2007). Web
Services Agreement Specification (WS-Agreement).
http://www.ogf.org/documents/GFD.107.pdf.
Bengtsson, P. (2002). Architecture-Level Modifiability
Analysis. PhD thesis, Department of Software Engi-
neering and Computer Science, Blekinge Institute of
Technology, Sweden.
E.A.Marks and Bell, M., editors (2006). Service-Oriented
Architecture (SOA): A Planning and Implementation
Guide for Business and Technology. John Wiley &
Sons, Inc., Hoboken, New Jersey.
Eshuis, R. and Norta, A. (2009). Constructing process
views for service outsourcing. In S.Y. Shin, S. O., edi-
tor, Symposium Proc. of the 2009 ACM Symposium on
Applied Computing (SAC), pages 1615–1616. ACM.
Gamma, E., Helm, R., Johnson, R., and Vlissides, J.
(1995). Design Patterns: Elements of Reusable
Object-Oriented Software. Professional Computing
Series. Addison Wesley, Reading, MA, USA.
Klein, M. and Kazman, R. (1999). Attribute-based archi-
tectural styles. TECHNICAL REPORT CMU/SEI-99-
TR-022 ESC-TR-99-022.
Kutvonen, L., Ruokolainen, T., and Metso, J. (2007). Inter-
operability middleware for federated business services
in web-Pilarcos. International Journal of Enterprise
Information Systems, Special issue on Interoperability
of Enterprise Systems and Applications, 3(1):1–21.
Mehandjiev, N. and Grefen, P. (2010). Crosswork: Internet-
based support for process-oriented instant virtual en-
terprises. IEEE Internet Computing. to appear.
M
¨
uller, C., Resinas, M., and Ruiz-Cort
´
es, A. (2009). Ex-
plaining the non-compliance between templates and
agreement offers in ws-agreement. In Baresi, L., Chi,
C., and Suzuki, J., editors, Service-Oriented Com-
puting - ICSOC 2009, 7th International Conference
,
volume 5900 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 237–252, Stockholm, Sweden. LNCS Springer.
Norta, A. and Eshuis, R. (2009). Specification and Verifica-
tion of Harmonized Business-Process Collaborations
- Preprint Version. Accepted for publication in the
journal of Information Systems Frontier, University of
Helsinki, Finland.
Paukkeri, M., Nieminen, I., P
¨
oll
¨
a, M., and Honkela, T.
(2008). Language-independent approach to keyphrase
extraction and evaluation. In Scott, D. and Uszko-
reit, H., editors, Proceedings of the 22nd Interna-
tional Conference on Computational Linguistics (Col-
ing 2008), pages 237–252, Manchester, UK.
Yangarber, R. and Steinberger, R. (2009). Automatic
epidemiological surveillance from on-line news in
medisys and puls. In Proceedings of IMED-2009:
International Meeting on Emerging Diseases and
Surveillance, Vienna, Austria.
A HUB ARCHITECTURE FOR SERVICE ECOSYSTEMS - Towards Business-to-Business Automation with an
Ontology-enabled Collaboration Platform
243
