
BIOSTORIES
Dynamic Multimedia Interfaces based on Automatic Real-time
User Emotion Assessment
Vasco Vinhas, Eugénio Oliveira and Luís Paulo Reis
FEUP - Faculdade de Engenharia da Universidade do Porto, Rua Dr. Roberto Frias s/n, Porto, Portugal
LIACC - Laboratório de Inteligência Artificial e Ciência de Computadores, Rua do Campo Alegre 823, Porto, Portugal
Keywords: Emotion Assessment, Biometric Channels, Dynamic Interfaces, Multimedia Content.
Abstract: BioStories is the outcome of a three and a half years research project focused in uniting affective and
ubiquitous computing with context aware multimedia content generation and distribution. Its initial premise
was based in the possibility of performing real-time automatic emotion assessment trough online biometric
channels monitoring and use this information to design on-the-fly dynamic multimedia storylines
emotionally adapted, so that end users would unconsciously be choosing the story flow. The emotion
assessment process was based on dynamic fusion of biometric channels such as EEG, GSR, respiration rate
and volume, skin temperature and heart rate on top of Russell’s circumplex model of affect. BioStories’
broad scope also allowed for some spin-off projects namely mouse control through EMG that resulted in a
patented technology for alternative/inclusive interfaces. Exhaustive experiments showed 87% of success
rate for emotion assessment in a dynamic tridimensional virtual environment with an immersiveness score
of 4.2 out of 5. The success of the proposed approach allows the vision of its appliance in several domains
such as virtual entertainment, videogames and cinema as well as direct marketing, digital TV and domotic
appliances.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, there have been numerous and
serious academic and industrial efforts and
investment in introducing innovation to traditional
user interfaces and more generally in the field of
human computer interaction. These approaches
resulted, ultimately, in cross-generation consumer
products like the Nintendo WiiMote and Apple iPod
and iPhone or exclusive luxury goods such as
Microsoft Milan Table or the Diamond Touch from
the Mitsubishi Electric Research Laboratories.
Despite the distinct commercial success, the fact is
that new interaction paradigms are arising and
imposing themselves in everyday life.
Simultaneously, there is also a growing
investment and attention being paid to both affective
and ubiquitous computing. The continuous hardware
miniaturization linked with more disseminated,
powerful and cheaper wireless communication
facilities constituted the cornerstone for context-
aware computing possibilities. As traditional
multimedia distribution, such as television, has been
suffering from extreme content standardization and
low levels of significant user interaction, it is
believed to exist an important breakthrough
opportunity in uniting real-time emotion assessment
based on biometric information and dynamic
multimedia storylines so that interaction and
decisions can be performed at a subconscious level,
thus providing greater immersiveness through
combining affective and ubiquitous computing
towards new interaction paradigms.
It has been in this context that BioStories have
arisen as a prototype proposition for generating and
distributing highly dynamic multimedia content not
confined but with special focus in immersive
tridimensional environments in which storylines are
based and determined on user’s online emotional
states that are assessed in real-time by means of
minimal invasive biometric channel monitoring and
fusion.
As the set of biometric sources is also intended
to be as flexible as possible, so that the system can
be used in diverse contexts, it encloses the resource
of distinct sources namely: electroencephalography,
galvanic skin response, respiration rate and volume,
skin temperature and heart rate. In order to cope
21
Vinhas V., Oliveira E. and Reis L. (2010).
BIOSTORIES - Dynamic Multimedia Interfaces based on Automatic Real-time User Emotion Assessment.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Human-Computer Interaction, pages 21-29
DOI: 10.5220/0002866700210029
Copyright
c
SciTePress

with the need to perform continuous and smooth
emotional assessment, the representation underneath
the classification is a variation of the bidimensional
Russell’s circumplex model of affect.
Due to the broad spectrum of the global project,
there were several spin-off opportunities from which
the mouse control through electromyography is
elected for further depiction as an alternative,
inclusive and complementary user interface
proposition. Considering the BioStories main track,
its latest version achieved a success rate of eighty-
seven percent regarding emotion assessment with
elevated content immersive levels, allowing the
forecast of the technology appliance to several
domains such as traditional interfaces extension,
domotic environments, virtual entertainment and
cinema industry as well as digital television, direct
marketing and psychiatric procedures
This document is structured as follows: in the
next section a global state of the art study is depicted
considering emotion assessment, dynamic
multimedia contents, hardware solutions and global
integrating projects; in section three the broad
BioStories work is described in detail by depicting
its global architecture, referring spin-off projects and
defining the emotion assessment process as well as
the multimedia content generation in a
tridimensional highly immersive environment. In the
following section, the experimental results are
presented both for the mouse control through EMG
and the main BioStories project; finally the last
section is devoted to critical analysis, conclusion
extraction and future work areas identification by
means of application domains recognition.
2 RELATED PROJECTS
Ekman’s emotion model (Wang, 2004)
contemplated six main universal classes of affect but
in a discrete fashion: anger, joy, fear, surprise,
disgust and sadness. However Russell’s proposal of
a circumplex model based on a bidimensional
arousal/valence plane allows for a continuous,
analog emotional state mapping (Russell, 1980). The
introduction of a third dimension – dominance – also
proposed by Russell, is still discussed, although
generally accepted it lacks of biometric evidence for
automatic emotion assessment ends (Russell, 1977).
The resource to biosignals to perform automatic
emotional assessment has been conducted with
success using different channels, induction and
classification approaches. These emotion induction
proposals range from image presentation, stage actor
representation, personal stories recall or film and
multimedia projection (Kim, 2008), (Picard, 2001),
(Vinhas, 2009).
Concerning the set of biometric channels elected,
there is also a wide variety of incented research
work lines, but although some studies focus their
attention in multichannel EEG and fMRI with
promising results, these approaches are still believed
to be either extremely intrusive and/or not
convenient in real situations (Fairclough, 2009).
Most recent approaches are based in distinct
conjunctions of simple hardware solutions for
monitoring several biometric channels, namely GSR,
skin temperature, respiration parameters, heart rate
and blood pressure (van der Broek, 2009), (Kim,
2008), (Vinhas, 2008), each one with distinct
emotion classification methodologies but there is a
great acceptance and unanimity around the
continuous model of affect as well as the resource to
biosignals.
Although the common denominator of almost all
research project in this field consists in automatic
emotional assessment, for the main principle of the
proposed work, a special attention must be paid both
to online real-time classification and its integration
with external systems, particularly regarding human-
computer interfaces. There have been conducted
several efforts towards human emotion disclosure
exploring social networks and chat systems. Despite
the theoretical success of these proposals they have
faced some usability resistance when used in direct
human-human communication (Wang, 2004).
However, this limitation is suppressed when emotion
assessment integration is performed in pure human-
machine interfaces such as the efforts in order to
generate audio (Chung, 2006) and images (Benovoy,
2008) emotionally contextualized exemplify.
This integration research track has continuously
been pushed further in order to mix affective with
ubiquitous computing towards new interaction
paradigms that are emotionally context-aware, thus
enabling extreme interface dynamism to cope with
distinct user moods and emotional responses. These
proposals have envisioned and developed systems to
integrate real-time emotion assessment based on
biosignals processing into diverse domains such as
everyday computer interfaces (van der Broek, 2009),
or professional car driver environment optimization
(Katsis, 2008). This broad scope allows for a
plausible perspective of the appliance of such
systems in several and distinct human computer
interaction domains.
It is in this vibrant and alive research context
(Vinhas, 2009) that the current proposition stands,
intending to be a valid contribution towards
increasingly dynamic and emotionally aware human-
computer interaction but not limited to traditional
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
22
interfaces as the main goal is to, in real-time, mold
and provide dynamic multimedia content that fits the
audience emotional needs. In order to pursue this
aspiration, and based on the described state of the art
summary, the Russell’s bidimensional model of
affect is reused and adapted; GSR, skin temperature
and respiration volume and rate sensors are used as
biosignals to perform real-time emotion assessment
through fuzzy sensorial fusion and the outcome is
integrated into a flexible multimedia content
generation and distribution modular framework.
3 BIOSTORIES DESCRIPTION
The key design principles and requirements are
identified and listed below: Complete architecture
component modularity to ensure full freedom to
parallel development and path reversal possibility,
always critical in exploratory courses of action;
Biometric channels composition flexibility degree
maximization so that diverse conjugations could be
experimented to guarantee several emotional
assessment scenarios and promote third-party
suppliers independence; Stakeholders’ geographic
and logical distribution possibility as the project
contemplates a strong experimental component it
has been found imperative that the subjects,
coordinators and researchers would have the chance
of being apart for allowing controlled environments;
Real-time signal acquisition and processing
complemented with data storage for posterior
analysis to allow online emotion assessment and
multimedia distribution but also granting offline
critical processing; Third-party software
independence maximization to assure that although
some hardware solutions have to be adopted the
whole architecture shall not be limited or
constrained by external entities. The conducted state
of the art revision, specially the one dated from the
beginning of the research, showed the absence of
such framework ready for adoption (Vinhas, 2008).
As a natural consequence, the decision was to
develop the envisioned platform following the
enunciated principles that resulted in the design
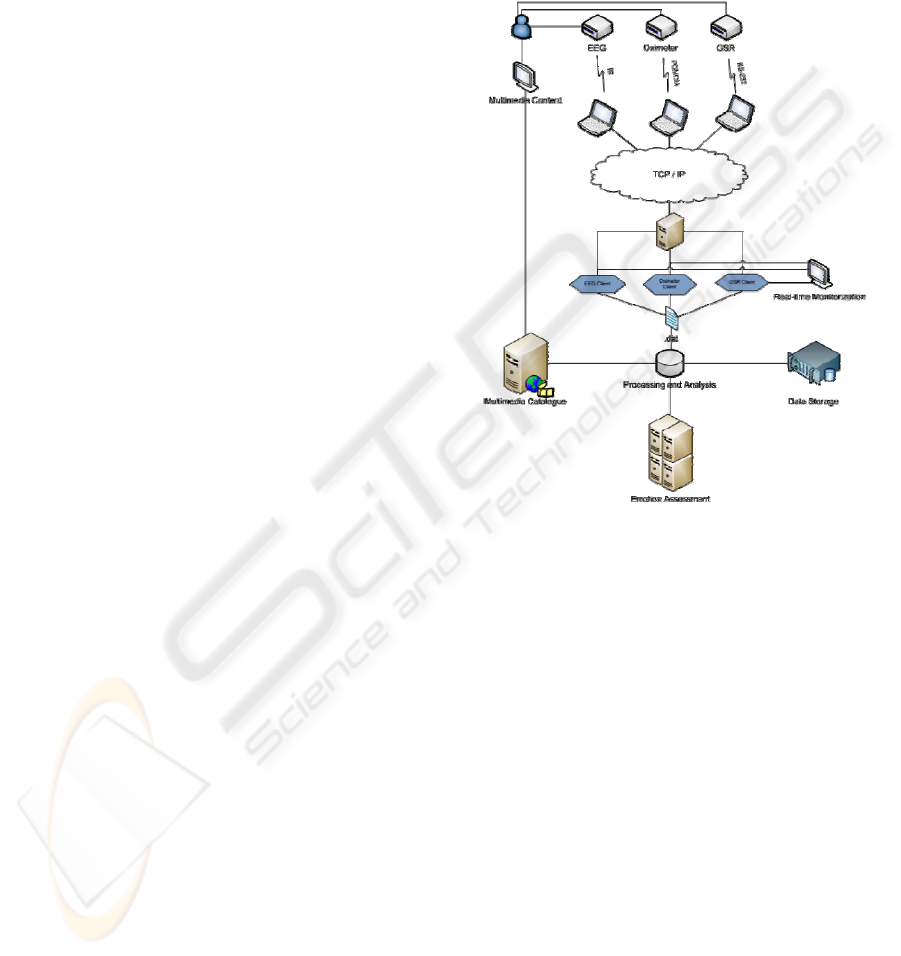
presented through Figure 1 (Vinhas, 2009).
The framework description might be done by
following the information flow in a cycle. So, first to
the end user a given multimedia content is presented
and several biometric signals are collected from one
or various equipments. In Figure 1, as example,
there have been referred three distinct channels each
one with a different data communication interface
for illustrating the framework versatility. For every
channel a software driver has been developed to
ensure independency and the collected data is further
made available through a TCP/IP network from
where different client applications can connect and
online access and process information. This
approach copes with the physical and logical
stakeholder’s independence and distribution.
Figure 1: BioStories Global Framework Architecture
Diagram.
At this end of the architecture, there is a client
for each biometric channel responsible both for pre-
processing activities and enabling real-time
monitoring. Their outputs are the input for the
processing and analysis backbone responsible for
data storage, emotion assessment and combined with
the emotional policy, choose from the multimedia
catalogue or generate the next multimedia content to
be provided to the end user.
The process of performing online emotion
assessment and its conjugation with the emotional
policy in order to influence the storyline is object of
depiction in the subsection devoted to BioStories,
where it is also visible the maintenance of the
architectural structure across all developed
prototypes, including the spin-off projects.
The initial stage of the research was
unsurprisingly characterized by the definition of the
already detailed framework and early biometric
equipment acquisition. Within this scope EEG and
heart rate acquisition hardware solutions were
BIOSTORIES - Dynamic Multimedia Interfaces based on Automatic Real-time User Emotion Assessment
23

purchased, namely Neurobit Lite™ and Oxicard®.
While the first ensured high portability levels
alongside with high usability levels, infrared data
transmission and API disclosure for driver
development; the second was caracterized by
reduced dimensions, high perfusion degree and also
API disclosure, thus enabling independent software
design.
During the preliminary experiments conducted
with the EEG equipment, due to an unforeseen
active electrode positioning protocol error, EMG
signals started to be registered due to its location in
the user’s temporal zone, between the eye and the
ear. As the signal pattern was so distinct and clear, it
was taken the decision of spinning off this
opportunity as an alternative interaction research
track based on intentional eye closure detection
(Gomes, 2008).
The basilar project principle was to provide a
simple yet effective method for wink detection and
map this into external actions in a way that it could
be faced either as in inclusive human machine
interface for disabled people or an alternative
interaction mechanism as an extension for traditional
interfaces. Another important premise was the need
to keep the assessment algorithm straightforward
enough to be computed in embedded systems
without serious processing effort.
This design resulted in the definition of an
algorithm based on the establishment of two
threshold parameters: peak and duration. The first
parameter represents the minimum signal amplitude
value so that intentional eye closure action might be
present. Only values above such limit are considered
to be potential winks. The duration parameter refers
to the minimum time span that the signal must
persist above the peak limit to complete the action
detection process and, therefore, assign wink
recognition. Once the signal processing assessment
procedure is conducted and wink recognition is
online performed, there is the need to trigger the
corresponding external action, result of the interface
purpose. This is been achieved by click operations
and drag mode activation emulation. These actions
were tested using the computer card game Microsoft
Hearts which experimental results are reserved to the
appropriated point in the following section.
Following the successful approach, the detection
methodology has been extended to contemplate both
differential and conjunction eye analysis, thus
enabling left from right wink detection as well as
single from both eye intentional closure. This has
been performed by setting two extra pairs of
peak/duration parameters, necessarily lower for the
non-dominant eye and higher for both eyes.
Although standard parameter values are suitable for
most users, there is the possibility to tweak and fine
tune these in order to maximize classification
success rates.
Further considerations referring to this research
line are due to the results and critical analysis
sections, as the main BioStories track, namely the
emotion assessment and online multimedia
generation are depicted in the following subsection.
The main track research project designated as
BioStories has known several prototype versions.
The results achieved in one approach were analyzed
and the extracted conclusions were incorporated in
the next version until the final approach, now subject
of detail.
Figure 2: Framework Architecture Instantiated to
BioStories 3D Immersive Environment Prototype.
Having this in mind, and undertaking just a swift
contextualization, the initial approach was based on
EEG signal analysis complemented with GSR data.
It was found that subject gender alongside with
high-frequency EEG constituted key factors for
emotion assessment (Teixeira, 2008). These findings
were further explored in the first automatic emotion
assessment attempt based on data pre-processing
techniques together with offline cluster analysis
(Teixeira, 2008). As for enhancing the EEG data
collected multichannel equipment needed to be
acquired with both invasive and financial impact, it
was chosen to use GSR, respiration and skin
temperature sensors to perform real-time emotion
assessment. In order to close the information loop,
IAPS Library was used for multimedia content
supply (Vinhas, 2009). This prototype version was
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
24

further improved by replacing the still images for
dynamic multimedia content and refining the
emotion assessment methodology (Vinhas, 2009).
The described evolution has now taken the final step
with the latest BioStories prototype that enhances
both emotion assessment and multimedia
immersiveness levels.
Starting the project description by the framework
architecture instantiation, it is completed based and
adapted from the original one, as illustrated through
Figure 2. The main differences reside in the
biometric channels and equipments used. In this
version, Nexus-10 hardware solution was elected as
it congregates the simultaneous collection of ten
distinct channels in a compact portable unit with
data communication based on wireless Bluetooth
protocol thus granting complete software
independence. For this version, there have been used
as biometric channels: GSR; respiration sensors for
acquiring volume and rate; and skin temperature.
The remaining system components are very
similar to the previously described architecture with
the multimedia catalogue being replaced by an
aeronautical simulator responsible for tridimensional
environment generation and control – in this case
Microsoft Flight Simulator X. In order to promote
greater immersiveness levels, although not depicted
in Figure 2, there have been used tridimensional
goggles with three degrees of freedom – roll, pitch
and yaw – from Vuzix iWear.
It was found useful to employ Figure 3 as a
reference for module interaction description, as it
represents a running screenshot of the main
BioStories application: the Emotion Classifier. First
it is necessary to establish the connection to the
Collector for accessing online biometric data feed;
setting the link to the aeronautical simulator for real-
time environment parameterization; and finally and
optionally connect to a local or remote database for
processing data storage.
On the bottom of the screen there are two
separate areas for signal monitoring: the one on the
left provides the latest data collected and the one on
the right allows for baseline and interval definition
for each channel. In the middle of the screen, there is
the emotional policy control panel where session
managers are able to determine which emotional
strategy shall be activated from contradicting or
reinforce current emotional state, force a particular
one or tour around the four quadrants. Specifically
related to the emotion assessment methodology, the
dynamic chart on the right allows for real-time user
emotion monitoring as the big red dot stands for the
initially self-assessed emotional state and the smaller
blue dot for the current one. The classification
process is based on sensorial fusion on top of the
bidimensional Russell’s circumplex model of affect,
depicted in the state of the art section. The whole
process resides in the calculus of valence and
arousal values, being the first responsible for the
horizontal emotional movement across the x-axis
from displeasure to pleasure states; and the second
accountable for vertical emotional displacement
across y-axis from low to high excitement levels.
With the purpose of pre-processing data towards
real-time emotional assessment, a normalization
process is conducted so that both valence and
arousal values are mapped into the [-1,1] spectrum.
With this approach, emotional states are faced as
Cartesian points in a bidimensional environment.
Considering the mentioned normalization
process, it is important to detail the already
superficially mentioned calibration process. In spite
of any given Cartesian point represents a normalized
defined univocal continuous emotional state, it can
be the result of an infinite number of biosignals
conjugation.
Figure 3: BioStories Running Application Screenshot.
Equation 1: Dynamic Biometric Data Scaling Model.
,
1 .
.
⁄
.
This evidence alongside with the extreme
biosignals baseline definition discrepancy between
two people or even for the same individual across
time – either due to morphologic differences or
context variations such as sleep time and quality,
erratic food habits or external weather conditions –
leads to the absolute need for a standard calibration
and biometric channels fusion.
The calibration is performed through a self-
assessment process at the beginning of the session,
although it can be repeated without limitation also
during the experimental protocol, by directly
pinpointing the predominant current emotional state.
This action enables the definition of the normalized
BIOSTORIES - Dynamic Multimedia Interfaces based on Automatic Real-time User Emotion Assessment
25

baseline point according to the real-time assessed
biometric information and for each channel it is
considered an initially non binding twenty percent
signal variability allowance. Whenever overflow is
detected, the dynamic scaling process is activated as
illustrated through Equation 1 and might be
summarized as the stretching of the biometric signal
scale when normalized readings go beyond the
interval of [-1,1]. This process is conducted
independently for each of the channels and results in
a non-linear scale disruption, ensuing in a greater
density towards the limit breach. First, c1 – any
given biometric channel – maximum value is
determined by comparing current reading with the
stored value – Equation 1(a). If the limit is broken,
the system recalculates the linear scale factor for
values greater than the baseline neutral value, having
as a direct consequence the increasing of the
interval’s density – Equation 1(b). Based on the new
interval definition, subsequent values shall e
normalized accordingly – Equation 1(c)(d). With
this approach, and together with dynamic calibration
and data normalization, it becomes possible for the
system to perform real-time adaptations as a result
of user’s idiosyncrasies and signal deviations, thus
assuring continuous normalized values.
Considering the aeronautical simulator as a
tridimensional multimedia engine, the current
emotional state and the target one, determined by the
policy, influence the simulation parameters, namely
weather conditions, scenery and maneuvering. The
two quadrants associated with displeasure determine
worse climacteric conditions ranging from
thunderstorms to fog to cope with high or low levels
of arousal. Fair weather conditions are associated
with the two quadrants related to pleasure. The main
routes are configurable and there have been designed
two courses: one very simple that consists of an
oval-shaped route around an island, and the second
with many closed turns at low altitudes. Also
maneuvering is controllable varying speed, heading
and altitude swiftly and suddenly for the first route
and for the second one applying additional features
like maximum bank and yaw damper which limits
the maximum roll during turns, and reduces rolling
and yawing oscillations, making the flight smoother
and calmer.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
In order to assess the adequability of the proposed
approach for human computer interaction objectives,
the following experiment was designed relating to
the mouse control through EMG. Thirty volunteers
selected from fellow laboratory researchers and
college students were randomly divided into two
groups. Group A emulated trained and experienced
end users with basic technology knowledge and
Group B represented inexperienced users without
any previous knowledge or contact with the system.
To the first group elements there have been
given the opportunity to try the prototype for ten
minutes after a short theoretical formation while the
second group elements jumped straight to the
validation experiment. The session consisted in the
users performing ten intentional dominant eye
closures – or the system classified as winks ten
actions as result of false positives.
The thirty sessions result distribution, divided
into the two groups, showed the positive impact of
the initial contact with the technology and system as
well as performing parameter fine tuning.
Nevertheless it also shows that the learning curve is
easily beaten, stating high usability levels and user
adaptation. The trained users group reached a mean
success rate of ninety percent with the minimum
value of sixty five percent with some error free
records. The lack of training prevented such success
levels as the mean assessment success rate is less
than seventy percent with values varying between
twenty five and eighty percent.
These results corroborate the initial hypothesis
that stated that electromyography could be used
through a simple approach with low computer
resources consumption as a technique to perform
effective, inclusive and alternative user interfaces.
The conducted experiments also pointed to the
positive impact of user training and technology
familiarity without requiring overcoming a hard
learning curve slope. This spin-off effort also
resulted in filing a patent.
Considering the BioStorie’s main track, both
Table 1 and Table 2 condense by means of
confusion matrixes the results of automatic emotion
induction and assessment, respectively. Both
perspectives are based in the discretization into the
four basic quadrants of the Russell’s circumplex
model and the user self-assessment is directly
compared to the described automatic process – in the
induction method emotional policy is used instead
and reports to IAPS Library based prototype
(Vinhas, 2009). The induction process overall results
Table 1: Automatic Emotion Induction Confusion Table.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
26
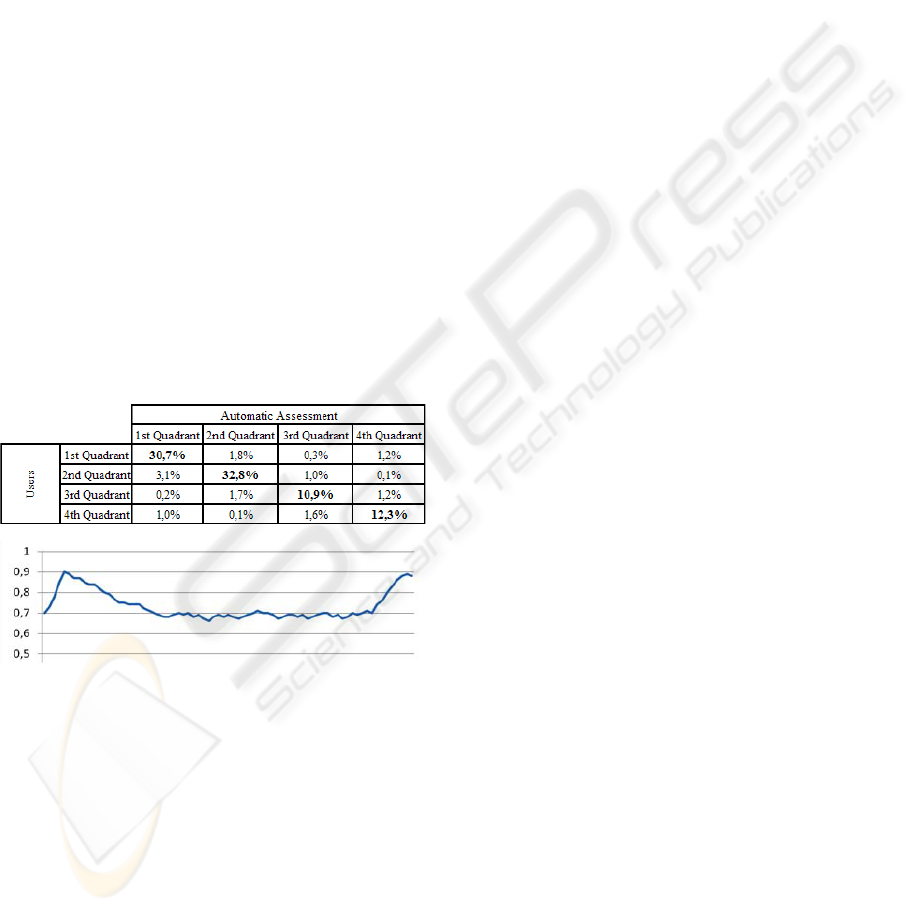
point to a success rate of sixty-five percent, greatly
due to the lack of second quadrant precision as some
pictures were considered context and cultural
dependent.
In what regards to the emotion assessment based
on the proposed fuzzy sensorial fusion, and taking
into account the tridimensional virtual aeronautical
environment, the global success rate achieves almost
eighty-seven percent with most users facing the
experience with high arousal levels as seventy-one
percent of the situations were self-assessed in first
and second quadrants. The emotion classification
error was distributed in a fairly linear fashion.
Taking into account the second subject, the
simulation engine acted as predicted allowing for
full context control and route definition. With direct
correspondence with the emotional response and
assessment all the accessed simulation parameters
initially enunciated such as weather conditions,
routes and general maneuvering controls were
successfully dynamically accessed and tweaked in
real-time as SimConnect API from Microsoft Flight
Simulator X acted as predicted while being
integrated into the projected base framework as an
additional module.
Table 2: Automatic Emotion Assessment Confusion
Table.
Figure 4: Average Arousal Levels During Simulation.
Between the simulation and the integration topic,
it has been conducted a survey amongst the twenty
one subjects – thirteen males and seven females,
aging between twenty one and fifty six – in order to
assess the immersiveness level of the whole
experiment – that consisted in three sequential stages
from take-off, fifteen minute cruising and the final
landing phase. The results showed an average
classification of four point two score out of five with
a minimal classification of three, thus demonstrating
a significant success in providing realistic immersive
environments greatly potentiated by the used
tridimensional tracking eye-wear.
As take-off and landing are traditionally
associated with higher apprehension and anxiety
levels amongst passengers, it has been conducted a
specific arousal monitoring across the simulation
sessions. The results are depicted through Figure 4
that exposes the predicted peak zones with high
normalization latency after take-off, therefore
strengthening the realism assessment conducted in
the course of the referenced survey.
Considering the last topic, dedicated to
integration and information loop completion, one
must refer to the absolute framework reliability and
flexibility across the latest prototype development
and test. It has accommodated the dynamic change
of biometric channels with distinct hardware
solutions and has coped efficiently with data
communication distribution and analysis in real-time
as well as enabled full third-party integration and
modular operability. Finally, it has been confirmed
the complete information loop closure, since initial
multimedia presentation, biosignals acquisition,
distribution and processing, real-time emotional
state assessment and online multimedia content
generation and further cycle iteration.
The latest prototype and approach took
advantage of multimedia presentation reformulation
as well as greatly enhanced both multimedia realism
and emotion assessment proposed methodology by
enabling continuous and discrete emotional state
definition and monitoring.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The single fact of the framework design being able
to cope with the distinct BioStories prototype
versions alongside with its usage to support spin-off
projects, proved that the initial option to develop
from scratch a common support framework was a
successful call. All of the initially proposed
functional and non-functional requirements were
totally met, thus accomplishing a stable yet flexible
and dynamic test bed and an innovative standalone
human computer interaction platform. These
achievements might be instantiated by means of the
complete architecture modularity as all its
components are strictly compartmented therefore
enabling extreme physical and logical stakeholders
distribution. On top of this, it has been attained an
extremely plastic biometric channel set and emotion
assessment method allows for diverse combinations
according to environment conditions while assuring
manufacturer and third-party independence. Finally
the possibility or performing real-time emotion
assessment while storing the raw collected data for
BIOSTORIES - Dynamic Multimedia Interfaces based on Automatic Real-time User Emotion Assessment
27

posterior analysis alongside with multimedia content
generation and distribution constitute a powerful
cornerstone of the whole research project.
Still in the initial subject, it is worth to examine
the results attained by the most significant spin-off
project, namely the mouse control through
electromyography. This prototype as a proof-of-
concept demonstrated that a simple minimal
invasive approach using EMG to perform intentional
eye close action detection was able to achieve high
hit ratios while having a negligible impact in user’s
environment. Its practical appliance to emulate
discrete mouse movements and clicks verified the
possibility of constituting a stable interaction
paradigm both for inclusive proposes for disabled
people but also as an extension for traditional user
interfaces whenever manual usage is not advisable
or already overloaded.
The results presented concerning BioStories
confirmed the initially enunciated hypothesis that
multimedia content could be generated and/or the
base storyline could be dynamically changed
directly according to the audience emotional state
assessed in real-time by means of biometric channel
monitoring. Equally, the emotional model, adapted
from Russell’s circumplex model of affect,
confirmed its ability to realistically represent
emotional states in a continuous form while enabling
their discretization. Specifically in what concerns the
emotional assessment methodology, the proposed
approach based on sensorial fusion with high levels
of personalization enhanced individual and temporal
biosignals independence and adaptability. Still in
this particular domain, this dynamic method allowed
for high levels of flexibility in what concerns
biometric channel set definition, thus permitting
further developments and system employments.
Taking into account the multimedia content
division of the project, earlier BioStories prototypes
illustrated that the usage of still images did not
provide the needed immersiveness for strong and
evident emotions, thus the latest option being
concentrated continuous environments distributed
through immersive goggles. The achieved results
showed that this proposal was effective and the
method for scene generation alongside with the
content visualization method provided the levels of
immersion and realism required for triggering and
sustain real emotional responses.
Probably the most immediate application of the
proposed technology is the videogame and virtual
entertainment industry. The possibility of real-time
rich immersive virtual dynamic environments – as
this domain is defined – in conjunction with online
user emotional state retrieval constitute a perfect fit
for this approach. On top of these factors, traditional
end users offer little resistance in adopting new
enhancing interaction solutions. Another positive
factor resides in that the system could be designed
for single user and single distribution as multiplayer
platforms are greatly online based. The greatest
challenge in this application is believed to be the
biometric hardware miniaturization without signal
quality loss in a way that they could be integrated
into a single electronic consumer good.
The second line of prospect resides on the
cinematographic industry. In this case the challenges
are much different as the multimedia contents are
not continuous but discrete and thus generating tree
storylines has an economic impact as further scenes
need to be shot but as the film depth and amplitude
would be enhanced it is believed that these hurdles
could be suppressed as the content would not expire
in a single view. From a technical stand, it is also
needed to define if the content distribution is to be
individualized or centralized in a common screen
just like nowadays. The first option enables full
individual content adaptation but prevents the
traditional cinema experience, while the second does
not allow for fully individualized emotional control.
Regarding the emotion assessment process, as
attaching physical equipment to all the audience is
not feasible, it is envisioned the usage of intelligent
seats equipped with position sensors as well as
infrared cameras for skin temperature and body
position evaluation.
As a natural extension of the previous point,
digital television arises. The advent of bidirectional
communication opportunity in digital television has
been, until the present day, modestly explored and
confined to basic interaction mechanism such as
televote or programming guide description. It is
believed that the appliance of the proposed approach
would enable the exponentiation of these levels
allowing greater dynamism in recorded contents and,
above all, promote real-time programmatic changes
to live content according to the online audience
response. One can image its massive impact when
addressing advertising, editorial line options or
political impact of declarations and news. The
promoted changes with this technology would
instigate the creation of a TV2.0 replicating the huge
leap forward taken by the designated Web2.0. The
technologically challenges are in the middle of the
first and the second domains, as they can be tackled
from a controlled personalized environment but the
hardware solutions must be as minimal invasive as
possible.
Direct marketing applications might start
precisely with its appliance to digital television. As
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
28

soon as marketers have access to costumers
emotional states, specific designed advertisements
can be developed and distributed exactly to match a
particular emotion profile in order to potentiate
campaign returns. In these alternative scenarios it
would be needed the development of non invasive
solutions based on video monitoring and real-time
location systems in a complementary way of that
exposed in the cinematographic domain.
In order to bring to a close the identification of
future work areas and application opportunities, one
shall point the chance to apply this approach to
medical procedures in general, and in psychiatric
procedures, in particular. The patient’s emotional
state knowledge by the physician is a valuable key
both for diagnostic and treatment proposes. This
statement is even accentuated when referring to
psychiatric domains such as phobias and depression.
On the other hand, there is a need for stricter and
more reliable emotion assessment even if real-time
can be sacrificed, thus classification methods are on
the line for improvement as future work research
lines in this scope.
As a final remark, it is important to distinguish
the quantity and diversity of potential practical
application of the proposed approach and technology
thus enabling several research lines opportunities
with a potential colossal impact not only, but with a
special focus, in the field of human computer
interaction.
REFERENCES
António Gomes, Vasco Vinhas, Mouse Control Through
Electromyography, in BIOSIGNALS 2008 –
International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and
Signal Processing, pp. 371-376, 2008.
Benovoy, M., Cooperstock, J., Deitcher, J., Biosignals
Analysis and its Application in a Performance Setting
- Towards the Development of an Emotional-Imaging
Generator, in Proceedings of the First Inte Conference
on Biomedical Electronics and Devices, pp. 253-258,
2008.
Egon L. van den Broek et al, Biosignals as an Advanced
Man-Machine Interface, in BIOSTEC International
Joint Conference on Biomedical Engineering Systems
and Technologies, pp.15-24, 2009.
Ekman P., Emotion in the Human Face, Cambridge
University Press, pp. 39-55, 2005.
Hua Wang, H. Prendinger, T. Igarashi, Communicating
emotions in online chat using physiological sensors
and animated text, in Conference on Human Factors
in Computing System, pp 1171-1174, 2004.
Jae-woo Chung, G. Scott Vercoe, The affective remixer:
personalized music arranging, in Conference on
Human Factors in Computing Systems, pp 393-398,
2006
Jorge Teixeira, Vasco Vinhas, Eugénio Oliveira, Luís
Paulo Reis, General-Purpose Emotion Assessment
Testbed Based on Biometric Information, KES IIMSS -
Intelligent Interactive Multimedia Systems and
Services, pp.533-543, University of Piraeus, Greece,
2008.
Jorge Teixeira, Vasco Vinhas, Eugénio Oliveira, Luís
Paulo Reis, MultiChannel Emotion Assessment
Framework - Gender and High-Frequency
Electroencephalography as Key-Factors, in
Proceedings of ICEIS 2008 - 10th International
Conference on Enterprise Information Systems, pp.
331-334,, 2008.
Jorge Teixeira, Vasco Vinhas, Eugénio Oliveira, Luís
Paulo Reis, A New Approach to Emotion Assessment
Based on Biometric Data, WI-IAT '08 -
IEEE/WIC/ACM International Conference on Web
Intelligence and Intelligent Agent Technology, 9-12
Dec, Sydney, Australia, pp. 505-511, 2008.
Katsis, C., Katertsidis N., Ganiatsas G. and Fotiadis D.,
Towards Emotion Recognition in Car-Racing Drivers:
A Biosignal Processing Approach, in IEEE Tran. on
Systems, Man, and Cybernetics – Part A: Systems and
Humans, Vol. 38, No 3, pp. 502-512, 2008.
Kim, J., André, E., Multi-Channel BioSignal Analysis for
Automatic Emotion Recognition, in Proceedings of the
First International Conference on Biomedical
Electronics and Devices, 2008.
Picard, R. W., Vyzas, E., Healey, J., Toward Machine
Emotional Intelligence: Analysis of Affective
physiological state. IEEE Transactions on Pattern
Analysis and Machine Intelligence, Vol 23, Issue 10,
pp.1175-1191, 2001.
Russell, J. A., A Circumplex Model of Affect, in Journal
of Personality and Social Psychology, No 39, pp
1161-1178, 1980.
Russell, J. A., Evidence for a Three-Factor Theory of
Emotions, in Journal of Research in Personality, Vol
11, pp 273-294, 1977.
Stephen H. Fairclough, Fundamentals of Physiological
Computing, in Interaction with Computers, Vol 21,
Issue 1-2, pp. 133-145, 2009.
Vasco Vinhas, Eugénio Oliveira, Luís Paulo Reis,
Realtime Dynamic Multimedia Storyline Based on
Online Audience Biometric Information, KES IIMSS -
Intelligent Interactive Multimedia Systems and
Services, pp.545-554, University of Piraeus, Greece,
2008.
Vasco Vinhas, Eugénio Oliveira, Luís Paulo Reis,
Dynamic Multimedia Content Delivery Based on
Real-Time User Emotions – Multichannel Online
Biosignals Towards Adaptative GUI and Content
Delivery, in International Conference on Bio-inspired
Systems and Signal Processing, pp.299-304, , 2009.
Vasco Vinhas, Daniel Castro Silva, Eugénio Oliveira, Luís
Paulo Reis, Dynamic Multimedia Environment Based
On Real-Time User Emotion Assessment – Biometric
User Data Towards Affective Immersive
Environments, ICEIS 2009 – International Conference
on Enterprise Information Systems, 2009.
BIOSTORIES - Dynamic Multimedia Interfaces based on Automatic Real-time User Emotion Assessment
29
