
A GENERIC METHOD FOR BEST PRACTICE REFERENCE
MODEL APPLICATION
Stefanie Looso
Frankfurt School of Finance and Management, Frankfurt, Germany
Keywords: Method Engineering, Design Science Research, Best Practice, Reference Models, IT Governance.
Abstract: The perceived importance of the topic IT governance increased in the last decade. Best practice reference
models (like ITIL, COBIT, or CMMI) promise support for diverse challenges IT departments are confronted
with. Therefore, the interest in best practice reference models grows and more and more companies apply
BPRM to support their IT governance. But there is limited knowledge about how BPRM are applied and
there is no structured method to support the application and lift the full potential of BPRM. Therefore, this
paper presents the construction and evaluation of a generic method for the application of BPRM. Following
the language-based approach of method engineering, elements of methods will be derived and formally
described. The criteria of design science research presented by Hevner et al., 2004 will be applied to the
evaluation of the constructed method. Intention of this research is to reduce the inefficiencies caused by the
inconsistent use of best practice reference models.
1 INTRODUCTION
As a central instrument for the design of corporate
information systems within the field of information
systems research, information models have
traditionally been used for decades. Literature on
this subject suggests the concept of reference
modeling for an improvement in the development of
enterprise-specific models (see Hars, 1994; Becker,
1995; Frank; Scheer, Seel, & Georg, 2002; Goeken,
2002; Becker & Knackstedt, 2002; Loos & Fettke,
2005 among others).
A reference model is defined as a generic
conceptual model which is useful when developing
an individual model of a specific class. It formally
presents state-of-the-art knowledge and best practice
knowledge and is considered as an example for a
corporate model (Fettke & Loos, 2003, Rosemann &
van der Aalst, 2007) . Precisely the mentioned best
practice knowledge is contained in the models of IT
governance focused on herein. (Co-) produced by
practitioners these models contain profound and
consolidated knowledge based on experience in the
field of IT governance and tend to become quasi-
standards (PWC, 2006).
Thus, the part of the definition concerning best
practice knowledge is fulfilled by the models of IT
governance. However these models are conceived as
structured compilations of best practices rather than
semiformal conceptual models. Therefore, the part
of the definition which states reference models are
conceptual models is not fulfilled by all models of
IT governance.
By metamodeling these models they could be
described more formally (Goeken & Alter, 2009). A
meta model includes the inner structure of the best
practice knowledge and it is a first step to model
best practices as conceptual models. This
conceptualization makes some research findings of
reference model application utilizable. However, in
order to avoid misleading terms and misconceptions,
reference models of IT governance will be referred
to as best practice reference model (BPRM) in this
paper.
Those BPRM have reached a certain degree of
commonness in practice. Their application is still
growing, but seems to be inconsistent. The study "IT
Governance in Practice - Insight from leading
CIO’s" quotes one participant on the application: „I
use frameworks and standards for inspiration, and
we use what we think is useful and relevant for our
organization“(PWC, 2006, p.18). Other companies
use BPRM even more holistic and with a higher
degree of obligation. The missing methodical
support for their application results in several forms
of inconsistent application of one BPRM.
149
Looso S. (2010).
A GENERIC METHOD FOR BEST PRACTICE REFERENCE MODEL APPLICATION.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Information Systems Analysis and Specification, pages
149-158
DOI: 10.5220/0002870701490158
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Additionally to that one-model case the
simultaneous use of several BPRM increases in
enterprises (PWC, 2006). Simultaneous means that
an IT department for instance uses CMMI for the
development of new systems and COBIT to provide
IT governance. In this multi-model case the
inconsistent and simultaneous application can lead
to problems (Alter & Goeken, 2009, Siviy, Kirwan,
Marino, & Morley, 2008a and b). For example,
various different, sometimes contradicting,
languages are encountered which complicate
cooperative work spanning several divisions.
Furthermore, multiple BPRM produce overlaps and
contradictions among each other. This leads to
redundancies and further inefficiencies. Those
inefficiencies are clearly opposed to the nature of
reference models since the construction of
corporation-specific models based on customized
models or model components promises positive
effects on effectiveness and efficiency see Fettke &
Loos, 2002 (p.9), Goeken, 2002 (p.1) or Becker,
Delfmann, & Knackstedt, 2004 (p.1). Therefore this
paper presents a method for the methodical and
structured application of IT governance BPRM.
2 RESEARCH DESIGN
This paper presents a part of broader a research
project. This research project is designed as follows.
To broaden the understanding of BPRM application
the research design includes explorative expert
interviews in addition to an extend literature review
as a first step. Based on that knowledge, a method
has been constructed for the one-model case. The
generic method has been evaluated and its usability
has been tested by applying it to a specific BPRM
(COBIT). After that the methods is extend to the
multi-model case. Goal of the research project is to
support effective and efficient use of several BPRM.
This paper presents the generic method for the one-
model case. The illustrated method is a result of a
research process using the knowledge base of IS
research and the business needs concerning the topic
IT governance and BPRM application. Figure 1
shows the position of the research project in the well
known conceptual framework of Hevner, March,
Park, & Sudha, 2004.
According their framework the knowledge base
“provides the raw materials from and through which
IS research is accomplished. The knowledge base is
composed of foundations and methodologies. Prior
IS research and results from reference disciplines
provide foundational theories, frameworks,
instruments, constructs, models, methods, and
instantiations used in the develop/build phase of a
research study“ (p.80). Following this definition the
knowledge base for this research includes research
on reference models and modeling, method
engineering and on IT governance but also on
research methods like interview techniques.
The environment defines the problem space
which includes the phenomena of interest. „In it are
the goals, tasks, problems, and opportunities that
define business needs as they are perceived by
people within the organization“(p. 79).
Figure 1: Research project (according to Hevner et al.,
2004).
For research on the BPRM of IT governance this
environment is composed of IT employees, IT
organization, IT goals and processes and the existing
best practices.
The research findings could be distinguished in a
generic method and several specific methods,
derived from the generic method. The constructions
process of the generic method follows a rigor
research design by using the existing and proofed
knowledge of IS research. The various specific
methods represent relevant IS artifacts which
provide support for practical problems. Following
Hevner et al., 2004 these practical applications of
the presented generic method follow the design
science paradigm. The latter is “fundamentally a
problem solving paradigm. It seeks to create
innovations that define the ideas, practices, technical
capabilities, and products through which the
analysis, design, implementation, management, and
use of information systems can be effectively and
efficiently accomplished“(p.78). That means the
practical application of the specific method is an
application for the IT governance environment
whereas the generic method is a contribution to the
knowledge base. The generic method for the one-
model case is presented in this paper. Following the
argumentation of Hevner et al., 2004 using the
knowledge base to support the IT governance
environment leads to a rigor research design.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
150
3 METHOD CONSTRUCTION
3.1 Preliminaries: Method Engineering
Methods describe a systematic approach to the
solving of problems. A problem is defined as a
discrepancy between actual and desired state
(Becker, Knackstedt, Pfeiffer, & Janiesch, 2007).
Focused on the creation of methods, the research
area of method engineering is a commonly accepted
and frequently debated concept in construction-
oriented IS research. Brinkkemper, 1996 defines:
“method engineering is the engineering discipline to
design, construct and adapt methods, techniques and
tools for the development of information
systems“(p.276).
Since it is commonly accepted that no universal
method exists (see Brooks, 1987, Fitzgerald, Russo,
& O'Kane, 2003 among others), tendencies such as
"domain-specific method engineering“ (Kelly,
Rossi, & Tolvanen, 2005) and "situational method
engineering” (Brinkkemper, 1996, Brinkkemper,
Saeki, & Harmsen, 1999); (Harmsen, 1997) have
developed. Basically, there are two tendencies
within this area. Some approaches of method
construction emphasize aspects of the construction
process and project management (Kaschek, 1999).
In contrast, the approach of a language-based
construction of method elements focuses on the
artifacts created. In recent years the latter approach
has been focused on in the field of methods
engineering (Brinkkemper, 1996, Ralyté & Rolland,
2001, Karlsson & Wistrand, 2006).
A method is primarily taken as a tupel of a type
of exercise and a number of rules (Becker,
Knackstedt, Holten, Hansmann, & Neumann, 2001),
p.5. According to Zelewski, 1999 however, not all
potential tupels are a method per se. In order to
qualify as a method, an observation of certain
qualitative requirements has to be assured. For
instance, all elements and their relations to one
another need to have an unambiguous interpretation
for the support of which a fairly unified
documentation of methods should be used. A
language-based reconstruction of method elements
and formalized documentation thereof is thus
required (Becker et al., 2001, p.6).
The St. Gallen description model of method
engineering includes a schematic composition of the
elements: meta model, result, activity, technique,
tool, and role. According to its language-based
interpretation, the description of these elements
offers a systematic development of a method (Heym,
1993, Gutzwiller, 1994, Becker, 1998).
Unlike the St. Gallen model, the method
presented herein presumes a relation between
activity and technique for the application of BPRM.
Two of the required method elements, namely role
and tool, will not be addressed in this paper. The
paper does not primarily deal with personnel related
and psychological aspects of the element role. It
neither deals with the specific technical aspects of
tools. Thus, the generic elements result, activity, and
technique will be included in the construction of the
method in accordance to the language-based
approach. Following the description of the generic
method element types, the relations between these
elements will be exemplified on a detailed level by
presenting instantiations of the generic types.
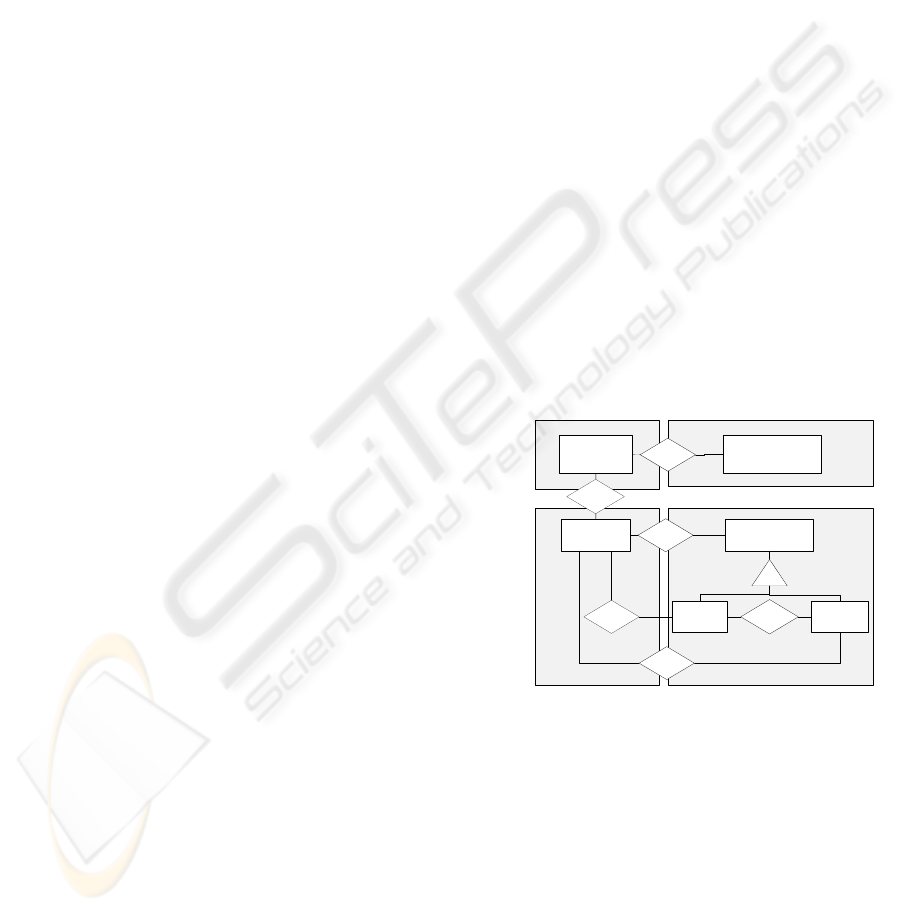
3.2 Method Element: Result Type
Results of the suggested method are several different
models. These belong to certain result types which
can be divided by two dimensions. The first division
is between two abstract levels, the meta level and the
model level. The second dimension distinguishes
between reference level and corporate level. Figure
2 depicts a metamodel of the method element result
type. The relationships shown in Figure 2 represent
possible transformations between several result
types. Their dynamic aspect will be described in
detail in section 3.4.
Meta Level
Model Level
Reference Layer
Specific Company
Layer
Best Practice
Reference Model
Best Practice
RM Subset
Explicit
Model
Best Practice
Reference Meta
Model
Company Specific Best
Practice Reference Meta
Model
Company Model
is applied to
has Subset is adjusted to
is adjusted to
has high level
abstraction
is adjusted to
Figure 2: Meta classification of result types of the generic
method.
Hence, result type best practice reference model is
defined as a model on model and reference level. A
possible instantiation of this type would be the
BPRM COBIT 4.1. Result type best practice
reference model subset has partly been adjusted to
corporate-specific conditions, and is thus a result
type of the company layer. An exemplifying
instantiation is a COBIT 4.1 subset which contains
PO processes exclusively. The explicit model shows
the externalized consensus of individual subjects in
A GENERIC METHOD FOR BEST PRACTICE REFERENCE MODEL APPLICATION
151

relation to corporate reality (Becker, Niehaves, &
Knackstedt, 2004). The explicit model is more
closely adjusted to corporate conditions than is the
BPRM subset. Both are instantiations of the (meta)
type company model. Additionally, the method is
familiar with various forms of company models
apart from the aforementioned result types. All of
them are associated with the lower right section of
the matrix. Building a company model it could be
necessary to change the meta model the model is
based on. These changes of the best practice
reference meta model result in a company-specific
best practice reference meta model. These two
abstract result types complete the result types used
for the presented method.
3.3 Method Element: Technique Type
Technique is defined as “a procedure, possibly with
a prescribed notation, to perform a development
activity” (Brinkkemper, 1996), p.276. Structured
interviews or questionnaires are common examples
for techniques used in methods. Techniques used for
the application of best practice reference models
support activities transforming models to other
models. Therefore, techniques used in this method
are defined as adaptation mechanisms transforming
a reference model step by step to a company’s
model. These techniques could be derived from
available research on reference model application.
Conclusions from research on reference models can
be included especially if the methods themselves are
formally represented by models. The method
presented herein contains several models as result
types (shown in section 2.2). Thus, the concepts of
reference model application provide important
information about the design of techniques within
the presented method.
Becker et al., 2004 provide two types of
adaptation mechanisms: The mechanisms of
generative adaptation describe all modes of a
reference model’s configuration, given the existence
of rules which determine how to adjust the reference
model depending on mechanisms of configuration.
These rules should be included in the reference
model. As mentioned, best practice reference models
of IT governance are conceived as structured
compilations of best practice rather than conceptual
models. Therefore, BPRM do not usually contain
explicit rules for model configuration.
Apart from configuration, Becker et al., 2004
describe four mechanisms of non-generative
adaptation: what generally characterizes
mechanisms of non-generative adaptation is “that
while they support the creation of specific model
variants, they leave room for variety to be filled by
the user of the reference model” (Becker et al., 2007
p.1). As this matches the situation in the area of
BPRM, the four non-generative adaptation
mechanisms will be concisely described and
integrated into the method as technique types.
Ad 1) Aggregation requires the reference model
to be divided into its components which are
recomposed by aggregation for new solutions.
Combinations can be limited by defined joints.
Ad 2) Instantiation ultimately describes the
existence of deliberately vague formulations or
blank spaces as placeholders to be specified by
users. In order to develop a BPRM into an explicit
model system, placeholders have to be filled in a
corporation-specific way. A BPRM is more freely
and individually adaptable trough instantiation than
trough aggregation.
Ad 3 and 4) analogy construction and
specialization are very free forms of adaptation in
which prescriptions for adjustment are mostly
absent. However, Becker et al., 2004 stress that even
these free adaptation mechanisms should give details
for the user about which model elements are suitable
for specialization and analogy (p.259).
The use of adaptation mechanisms of reference
models within the area of method construction has
been accomplished several times. For instance
Harmsen, 1997 or Brinkkemper, 1996 use the
mechanism aggregation, whereas Baskerville &
Stage or Patel, de Cesare, Iacovelli, & Merico, 2004
use specialization. A broad overview is given from
Becker et al., 2007, p. 5, table 1. The herein
presented method includes the following types of
technique: aggregation, instantiation, specialization,
and analogy construction (their degrees of
prescription about adjustment in descending order).
3.4 Method Element: Activity Type
The method for reference model application
described by Fettke & Loos, 2002 includes two
phases. The phase reuse follows after the phase
construction of the model. Reuse is divided into four
sub phases, which adapt the model to the corporate-
specific situation. These sub phases represent
activities according to the language-based approach
of method engineering. A possibility to distinguish
these activities is presented by Schütte, 1998.
Firstly, compositional activities means that
individual parts of a model are erased, altered, or
added in order to improve a reference model’s fit.
Secondly, generic adaptation activities means
explicitly described rules of adaptation. These rules
are defined explicit within the model to be observed
for adjustment of the reference model. Thus,
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
152

activities needed to be taken before applying a
reference model to a corporate-specific model.
Generic adaptation activities are not usually
employed since most BPRM do not contain rules for
adaptation. Furthermore compositional adaptation
activities need to be divided into more parts. For the
presented method, there is a difference between the
two compositional adaptation activities “choice of
model components”, i.e. alteration of the model (e.g.
by erasing certain parts Gammelgard, Lindstrom, &
Simonsson, 2006) and “adaptation to corporate
conditions” (e.g. corporation-specific indices).
The generic method considers this by the activity
types subset selection and adjustment. If a BPRM is
not entirely used, it is limited by selecting a BPRM
subset to the part relevant for a corporation. The
reason for this decision does not necessarily based
within the model itself but can be entirely strategic
(Bowen, Cheung, & Rohde, 2007). Hence activity
type subset selection is take place before activity
type adjustment. During the subsequent adaptation,
the chosen subset is continuously adjusted to the
corporation. The activity type application completes
the generic activity types. In the following, all three
types of activity will be described in detail jointly
with their proposed techniques. The order of the
activity types in the method is depicted in Figure 3.
Figure 3: Event-driven-chain the proposed method.
Activity 1. Subset Selection
By selecting a model subset the BPRM is
transformed resulting in a BPRM subset. The
process of selection itself with its internal
organizational and communicative aspects is not
addressed in this paper. However, possible kinds of
this subset are interesting for this research. The
criterion to classify subsets is completeness. Two
cases occur in the first place, complete and partial
use. The former makes the result type subset
obsolete as the BPRM and the subset are identical.
But if some parts are selected while others are not,
the following applies to the contents described
within the model: BPRM Subset <= BPRM.
For detailed specification, further classification
criteria are required. These criteria can be derived by
abstraction of BPRM into a best practice reference
meta model. A meta model created by semantic
abstraction can show possible sub divisions of the
case “partial application” by means of content and
structure (Alter & Goeken, 2009). A model’s
structure is defined by its meta model components.
A Limitation of the applied meta model components
typical for a reduction of a model’s range, for
instance a subset which only contains the meta
model component COBIT control objectives
(Simonsson & Johnson, 2008, De Haes & van
Grembergen, 2008). It turns out that the structure of
a model is changed. Still, chosen model components
need to be aggregated into BPRM subset
,
the form of
aggregation being defined by internal relations
within the meta model. A coherent subset does not,
for instance, allow the use of metrics of the COBIT
processes unless the goals of the process are used as
well. This is because the component goal links
process with metrics. Thus, the meta model shows
options of aggregation.
The second case to be regarded is defined by
reduction of the model’s profundity. Accordingly,
all meta model components are employed in respect
to the COBIT model but not all model components.
Thus the content is reduced. These subsets leave the
model’s structure unchanged (Gammelgard et al.,
2006). The reduction of model components results in
different problems than the reduction of meta model
components does. This is due to interconnections of
content, such as predecessor-successor-relations,
which can cause successors to be left without any
input or the output of a process to remain unused
even though links within the meta model are intact.
Hence, model components have to be aggregated on
a model level as well. This aggregation of model
components (e.g., several COBIT processes) can be
supported by the connection among meta model
A GENERIC METHOD FOR BEST PRACTICE REFERENCE MODEL APPLICATION
153
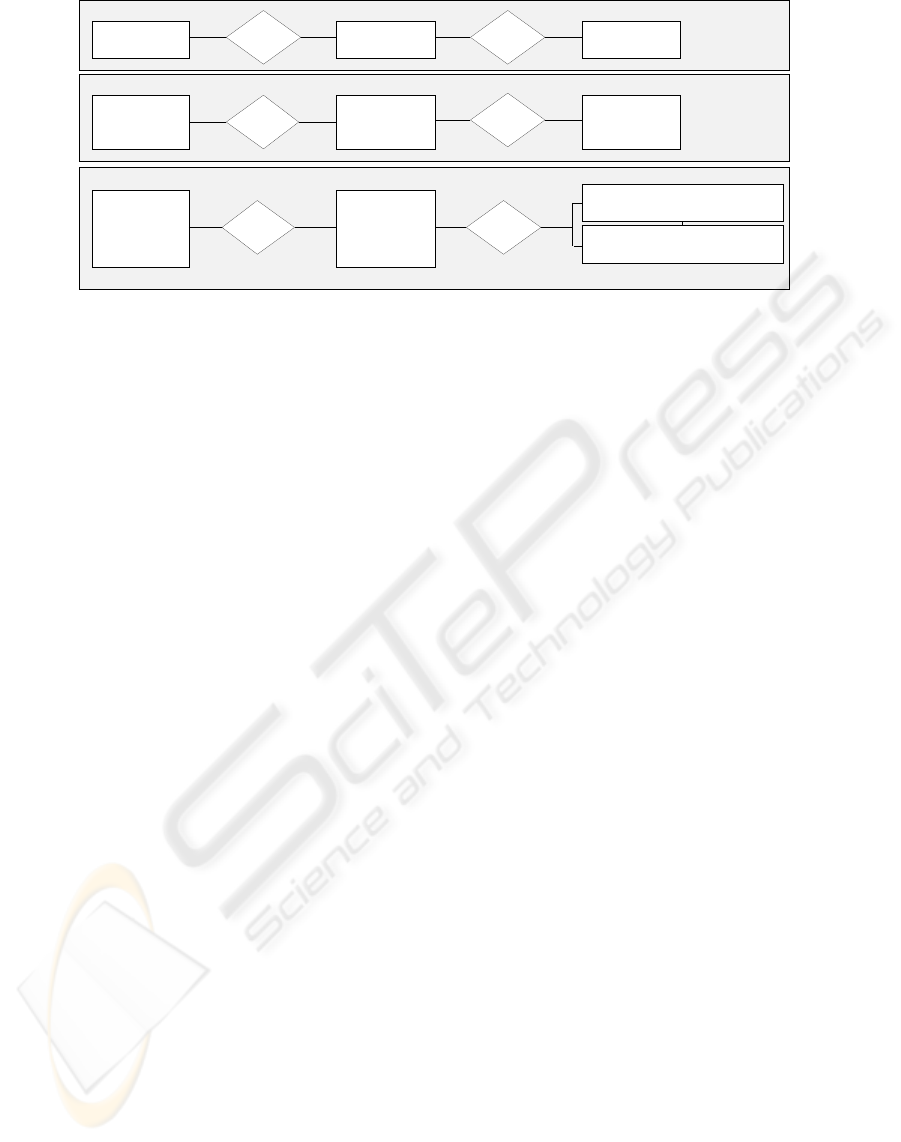
Instantiations
Model Level
Meta Level
Goal
is
me asured
by
Met ri csupportsProcess
Deliver Projects on
Ti m e an d on Bu dg et
M eet in g Q u ali ty
Standards
is
me asured
by
Percent of Projects
M eet in g Sta keh ol de r
E x pe c ta tio ns
supports
Re fe ren ce Pr o cess
PO 10
Deliver Projects on
Ti m e an d on Bu dg et
M eet in g Q u ali ty
Standards
is
measured
by
Pe rc ent of P roj ects Mee tin g 90 % o f IS O 90 00
R equ ir em en ts
supports
Co mpan y’ s P roce ss
PO 10 Manage
Projects
Perc ent of Pr oj ect s on Ti me ( 1,2 5-fold of
Ta rg et Du ra tio n)
Figure 4: Instantiation of a COBIT metric.
components. These convenient options of
aggregation can be derived from the meta model.
For the COBIT meta model, the meta model
component result proves to be an initial point for
interconnection of model component process.
It turns out that connections occur on a meta
model level when transforming generic BPRM into
specific BPRM sections that can be used for
aggregation. With its components, the meta model of
a BPRM offers possibilities for aggregation of both
meta model components and model components.
Hence, the quality of meta models in best practice
reference models is crucial for this research project
(Alter & Goeken, 2009, Goeken & Alter, 2009).
Activity 2. Adjustment to Corporate Conditions
Once the relevant BPRM subset has been selected,
the next step is the transformation into the explicit
model particular to one specific BPRM and one
specific corporation. During instantiation the user
specifies those model sections which formerly
remained deliberately vague. However, it usually
remains unclear for BPRM which model sections
have remained vague on purpose and require
instantiation.
Order and design of the model component
“metric of process x” in the COBIT model allow the
assumption that metric is a components which
requires instantiation. Exemplary in character, the
metrics of a COBIT process should be completed
with individual metrics. Along with the mechanism
of adaptation in the present example, Figure 4
depicts the instantiation of the metric placeholder for
a number of corporate-specific metrics.
Other mechanisms are applied during the
development of the explicit model as well.
Supporting the instantiation both specialization and
analogy construction should be primarily used in the
following third step. This is due to the relation
between the BPRM and the explicit model. Here, the
explicit model is taken as an altered part of the
BPRM, which should basically remain recognizable
in this intermediate result. Control by IT auditors is
thus facilitated in case of COBIT. This can change
due to the more variable mechanisms of model
adaptation, which is why too much room for
variation in adaptation mechanisms should be
avoided in this activity.
Activity 3. Application to the Corporate Model
Depending on the BPRM the corporate model can
consist of either the process model of IT processes
or a smaller part such as a model of IT project
management. Specialization and analogy
construction are important mechanisms during this
phase since BPRM of IT governance usually specify
what to do rather than how to do it. Those challenges
of establishing have to be fulfilled by means of
analogy construction in which the explicit model
serves as a state-to-be and to inspire ideas.
„Analogies can be drawn from any aspect of the
reference model which can be indicated by the
annotation of analogy construction advices“(Becker
et al., 2007, p.3).
4 METHOD EVALUATION
In a second step the method obtained in a design-
oriented research process for the application of
BPRM is to be evaluated. The evaluation can be
carried out in two ways (Hevner et al., 2004).
Firstly, the method itself can be focused on;
secondly, the process of constructing the method
plays a role as well. Although Hevner's guidelines
were meant to enhance the probability for a
publication of design science research, they are also
used for support of a systematic evaluation of
research (Arnott & Pervan, 2008, Zelewski, 2007).
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
154

According to these criteria both artifact and research
process will be examined in the following (Hevner
et al., 2004).
1. The first guideline states that construction-
oriented research is supposed to create an innovative
artifact for the accomplishment of one task and to
solve an existing problem. While the application of
best practice reference models has not been
supported by scientifically developed methods, the
systematic design of the application process is a
manifest problem in corporate practice, particularly
in a multi-model case (Cater-Steel, Tan, &
Toleman, 2006, Siviy et al., 2008a and b). Thus,
construction of a method applicable to several
BPRM solves an existing problem.
2. The relevance of the scientific problem
characterizes the importance of the problem for
scientific practice. This importance might result
from specific sentences of relevance or the obvious
notion of problems within the respective decisive
constituent community (Zelewski, 2007). IT
governance is the relevant field of research for this
artifact. Various results provide a certain evidence
for an effect of applying BPRM on the achievement
of a corporation's goals. Simonsson & Johnson,
2008 prove the effect of governance maturity on IT
within a corporation. Governance maturity itself is
raised by use of BPRM. Wagner, 2006 presents a
case study in which a specific BPRM (ITIL) has a
positive effect of IT on corporate success. Studies by
Tuttle & Vandervelde, 2007 are based on the
positive influence of the use of COBIT on risk
management performance. Heier, Borgman, &
Maistry, 2007 prove the positive association of
governance software, governance processes, and IT
value contribution by empirical research. In another
case study they conclude that the performance of
governance processes is a critical factor for the
success of corporate goals (Heier, Borgman, &
Hoffbauer, 2008). An empirical study proves a
measurable connection between IT governance
software and a corporation's IT value contribution
(Heier, Borgmann, & Mileos, 2009). Based on this
connection, the case study by Larsen, Pedersen, &
Anderson, 2006 analyses 17 tools of IT governance,
including the BPRM of IT governance dealt with
herein. A Delphi study by De Haes & van
Grembergen, 2008 presents the ten most important
COBIT processes for achievement of IT goals and,
indirectly, corporate goals. As the author of this
paper points out, this implies that certain goals are
probably achieved by the application of COBIT or
its individual processes. Lunardi, Becker, &
Macada, 2009 examine the financial influence of „IT
governance mechanisms’ adaptation“ within
Brazilian companies. They distinguish between two
cases, adaptation by means of BPRM (ITIL, COBIT)
or without BPRM. The procedure of this adaptation
is not described. Debreceny & Gray, 2009 present a
case study on the effect of the BPRM COBIT on
maturity of processes and on IT capability. A survey
by de Espindola, Rodrigo Santos, Luciano, & Audy,
2009 proves that successful adaptation of BPRM
affects various corporate goals.
To sum up, literature frequently states that the
application of BPRM has, if only indirectly, positive
effects on the achievement of a company’s goals. It
has been shown that the “constituent community”
uses BPRM without dealing with their application in
great detail. The scientific and practical relevance is
proved but scientific work on the application is
almost entirely lacking. The method presented
herein fill parts of this gap by developing a method
for the application of BPRM.
3. The evaluation of research results includes
usefulness, quality, and effectiveness Results are to
be evaluated by strictly scientific evaluation
methods as Hevner et al. 2004 emphasize. They
suggest a number of methods for detection of
misbehavior of the artifact, prove of usefulness, etc.
The evaluation of the generic method includes two
steps due to the characteristics of the artifact. As the
method described has a generic character, it is partly
evaluated in a first step by application to a specific
case, in which its general usability is proven. The
specific methods then have to be evaluated
individually. The degrees of coverage and separation
of the elemental types in generic constructions have
been examined in a research project. It is
questionable whether all method elements required
in a specific method are available in the generic
model and whether they can unambiguously be
matched to model component types. If this is not the
case, the generic model needs to be adjusted.
4. Construction-oriented research, as any
research, has to contribute to the progress within a
field of research. Three characteristics are generally
employed for this: novelty, general validity, and
relevance. In addition, it is recommended for design-
oriented research to create an artifact providing
significance for an unsolved problem of scientific
community or a new application of existing
knowledge.
Novelty. Currently, there is no complete method for
the application of BPRM in IT governance. Existing
methods for application of reference models have
partly been included in the artifact. Apart from this,
experience from the area of BPRM and their
application in corporate practice have been
integrated and theoretically dealt with. Also, the
A GENERIC METHOD FOR BEST PRACTICE REFERENCE MODEL APPLICATION
155

artifact is a novelty as it recombines existing
knowledge from model theory and research on
method construction.
General Validity. The developed artifact is
generally valid. The method can be used to support
any BPRM. The degree of abstractness corresponds
with the differences between existing and future
BPRM of IT governance. If, for example, the
method is to be applied to a BPRM which does not
require subset selection this step can be omitted.
This is the case if a desired certificate is linked to a
complete use of a model.
Relevance. The relevance of the artifact for the field
of IT governance is demonstrated in the presented
research papers mentioned in guideline 2. The
described method allows a systematic application of
BPRM in scientific practice.
Significant Use for an Unsolved Problem. The
method presents a systematic procedure for the
application of BPRM for a corporation’s support.
The procedure is directly useful to solve company’s
problems. It also provides an indirect use as a basis
for the application of multiple BPRM for the multi-
model case.
5. This guideline prescribes a rigorous use of
scientific methods when constructing and evaluating
the artifact. According to Hevner et al., the scientist's
experience is required for „skilled selection of
appropriate techniques” (Hevner et al., 2004, p.80).
Also, they stress that scientific rigor is based on
consequent definitions, consistence within research,
and formal representation of the topic. Scientific
methods for evaluation have already been described.
The process of construction meets the criteria of
language-based method engineering. The artifact
components have been selected by means of the St.
Gallen approach of method engineering. Design and
composition of components have been obtained by
application and aggregation of available knowledge
taken from a broader literature review and structured
interviews with practitioners.
6. This guideline provides that “search for an
effective artifact requires utilizing available means
to reach desired ends while satisfying laws in the
problem environment“ (Hevner et al., 2004, p.81).
They describe means as a set of actions and
resources available to construct a solution. Thus, the
research process should follow a generate-test-cycle.
After creating a design alternative it has to be tested
against requirements and constraints. The
construction of the presented method follows this
cycle. The method is and will be tested and adjusted
several time during the research project.
7. This guideline deals with the communication
of research. It is crucial to present results adequate
to the appealed audience. It is also important that the
audience „understand [s] the processes by which the
artifact was constructed and evaluated“ (Hevner et
al., 2004, p.90). By publishing and presenting the
results in academia and practice results can broaden
the knowledge base for further research efforts and
construct solutions for practitioners.
5 CONCLUSIONS
By using the knowledge base of IS research and
business needs concerning BPRM application, we
have constructed and partly evaluated a generic
method for best BPRM application. This generic
method is on the one hand an addition to the
knowledge base of IS research and on the other hand
a possibility to support the application of BPRM in
practice. For this practical use the generic method
has to be instantiated to a specific method.
The paper follows the language-based method
engineering approach by presenting formally
described static method element types and their
instantiations. Furthermore the presentation includes
dynamic aspects by describing processes and
procedures concerning the transition between
various instantiations of the method element types.
This method aims to be an addition to the knowledge
base of IT governance research and a practical
solution for challenges IT departments are
confronted with.
In an ongoing research process a specific method
for the BPRM COBIT is derived from the presented
generic method. This specific method supports the
methodical application of the COBIT BPRM. These
research findings were also used to develop a
governance tool, based on semantic software which
supports the application of COBIT. Furthermore, the
method provides a sound basis for the construction
of methods for applying several BPRM, i.e. in the
multi-model case.
REFERENCES
Alter, S., & Goeken, M. (2009). Konzeptionelle
Metamodelle von IT-Governance-Referenzmodellen
als Basis der Kombination und Integration in einer
Multi-Model-Umgebung. In Hansen, H.R.,
Karagiannis, D., Fill, H.G. (Ed.), Business Services:
Konzepte, Technologien, Anwendungen.: 9.
Internationale Tagung Wirtschaftsinformatik, Band 1 .
Wien.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
156

Arnott, D., & Pervan, G. (2008). Eight key issues for the
decision support systems discipline. Decision support
systems, 44(3), 657–672.
Baskerville, R. L., & Stage, J. Accommodating Emergent
Work Practices: Ethnographic Choice of Method
Fragements: IFIP TC8/WG8.2 Working Conference
on Realigning Research and Practice in IS
Development: The Social and Organisational
Perspective, Boise, ID, 2001, pp. 12.28.
Becker, J. (1995). Strukturanalogien in
Informationsmodellen – Ihre Definition, ihr Nutzen
und ihr Einfluß auf die Bildung der Grundsätze
ordnungsmäßiger Modellierung (GoM). In W. König
(Ed.), Wirtschaftsinformatik '95 –
Wettbewerbsfähigkeit, Innovation, Wirtschaftlichkeit
(pp. 133–150). Heidelberg.
Becker, J., Delfmann, P., & Knackstedt, R. (2004).
Konstruktion von Referenzmodellierungssprachen:
Ein Ordnungsrahmen zur Spezifikation von
Adaptionsmechanismen für Informationsmodelle.
Wirtschaftsinformatik, 46(4), 251–264.
Becker, J., & Knackstedt, R. (Eds.) (2002).
Referenzmodellierung 2002 Methoden – Modelle –
Erfahrungen (Vol. 90). Arbeitsberichte des Instituts
für Wirtschaftsinformatik WWU, 90. Münster.
Becker, J., Knackstedt, R., Holten, R., Hansmann, H., &
Neumann, S. (2001). Konstruktion von Methodiken:
Vorschläge für eine begriffliche Grundlegung und
domänenspezifische Anwendungsbeispiele
(Arbeitsberichte des Instituts für
Wirtschaftsinformatik No. 77). Münster: Westfälische
Wilhelms-Universität Münster, from
http://www.wi.uni-muenster.de/inst/arbber/ab77.pdf.
Becker, J., Knackstedt, R., Pfeiffer, D., & Janiesch, C.
(2007). Configurative Method Engineering: On the
Applicability of Reference Modeling Mechanisms in
Method Engineering. In Proceedings of the AMCIS
2007 .
Becker, J., Niehaves, B., & Knackstedt, R. (2004).
Bezugsrahmen zur epistemologischen Positionierung
der Referenzmodellierung. In J. Becker (Ed.),
Referenzmodellierung: Grundlagen, Techniken und
domänenbezogene Anwendung, mit 6 Tabellen (pp. 1–
17). Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag.
Becker, M. (1998). Umsetzung betrieblicher Prozesse:
Methode, Fallbeispiele, Workflow-Technologie.
Dissertation, Universität St.Gallen, St.Gallen, from
Universität St.Gallen: .
Bowen, P. L., Cheung, M.-Y. Decca, & Rohde, F. H.
(2007). Enhancing IT governance practices: A model
and case study of an organization’s effort.
International Journal of Accounting Information
Systems, 8, 191–221.
Brinkkemper, S. (1996). Method engineering: engineering
of information systems development methods and
tools. Information & Software Technology, 38(4),
275–280, from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/
article/B6V0B-3VTJK0G-
Y/2/4211ed8ea0fdafa25ee5b90754e89ea1.
Brinkkemper, S., Saeki, M., & Harmsen, F. (1999). Meta-
modelling based assembly techniques for situational
method engineering. Information Systems, 24(3), 209–
228, from http://www.sciencedirect.com/
science/article/B6V0G-3WXWT1F-
3/2/a253952d59a29fb748286910bcb97b8a.
Brooks, F. P. (1987). Essence and Accidents of Software
Engineering. IEEE Computer, 20(4), 10–19.
Cater-Steel, A., Tan, W. G., & Toleman, M. (2006).
Challenge of adopting multiple process improvement
frameworks. In Proceedings of the 14th European
Conference on Information Systems .
de Espindola, Rodrigo Santos, Luciano, E. Mezzomo, &
Audy, J. L. N. (2009). An Overview of the Adoption
of IT Governance Models and Software Process
Quality Instruments at Brazil - Preliminary Results of
a Survey. In HICSS 2009 - Proceedings of the 42th
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences .
Debreceny, R., & Gray, G. L. (2009). IT Governance and
Process Maturity: A Field Study. In HICSS 2009 -
Proceedings of the 42th Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences .
Fettke, P., & Loos, P. (2002). Methoden zur
Wiederverwendung von Referenzmodellen –
Übersicht und Taxonomie. In J. Becker & R.
Knackstedt (Eds.), Arbeitsberichte des Instituts für
Wirtschaftsinformatik WWU: Vol. 90.
Referenzmodellierung 2002 Methoden – Modelle –
Erfahrungen (pp. 9–30). Münster.
Fettke, P., & Loos, P. (2003). Classification of reference
models—a methodology and its application.
Information systems and ebusiness management, 1(1),
35–53.
Fitzgerald, B., Russo, N. L., & O'Kane, T. (2003).
Software Development: Method Tailoring at
Motorola, Communications of the ACM, 46(4), 65–70.
Frank, U. Conceptual Modelling as the Core of the
Information Systems Discipline – Perspectives and
Epistemological Challenges. In W. D. Haseman & D.
L. Nazareth (Eds.). Proceedings of the Fifth Americas
Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS 1999),
August 13-15, 1999. Milwaukee, Wisconsin
(pp. 695.697).
Gammelgard, M., Lindstrom, A., & Simonsson, M.
(2006). A reference model for IT management
responsibilities. In . EDOCW ’06: Proceedings of the
10th IEEE on International Enterprise Distributed
Object Computing Conference Workshops (pp. 26-26).
Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer Society.
Goeken, M. (2002). Grundlagen und Ansätze einer
Referenzmodellierung für Führungs informations
systeme: Fachbericht Nr.03.
Goeken, M., & Alter, S. (2009). Towards Conceptual
Metamodeling of IT Governance Frameworks: –
Approach – Use- Benefits. In . HICSS 2009 -
Proceedings of the 42th Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences .
Gutzwiller, T. (1994). Das CC RIM-Referenzmodell für
den Entwurf von betrieblichen,
transaktionsorientierten Informations systemen.
Heidelberg: Physica-Verlag.
Haes, S. de, & van Grembergen, W. (2008). An
exploratory Study into the design of an IT Governance
Minimum Baseline through Delphi Research.
A GENERIC METHOD FOR BEST PRACTICE REFERENCE MODEL APPLICATION
157

Communications of the Association for Information
Systems, 22(Article 24), 443a.
Harmsen, A. F. (1997). "Situational Method Engineering.
Utrecht.
Hars, A. (1994). Referenzdatenmodelle – Grundlagen
effizienter Datenmodellierung. Wiesbaden:
Dissertation 1993 Saarbrücken.
Heier, H., Borgman, H., & Hoffbauer, T. (2008). Making
the most of IT governance software: understanding
implementation processes. In HICSS 2008 -
Proceedings of the 41st Annual Hawaii International
Conference on System Sciences, Washington, DC,
USA: IEEE Computer Society.
Heier, H., Borgman, H., & Maistry, M. (2007). Examining
the relationship between IT governance software and
business value of IT: evidzence from four case studies.
In, HICSS 2007: Proceedings of the 40th Annual
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences .
Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer Society.
Heier, H., Borgmann, H., & Mileos, C. (2009). Examining
the Relationship between IT Governance Software,
Processes, and Business Value: A Quantitative
Research Approach. In . HICSS 2009 - Proceedings of
the 42th Hawaii International Conference on System
Sciences .
Hevner, A. R., March, S. T., Park, J., & Sudha, R. (2004).
Design Science In Information Systems Research.
MIS Quarterly, 28(1), 75–106.
Heym, M. (1993). Methoden-Engineering - Spezifikation
und Integration von Entwicklungsmethoden für
Informationssysteme. Disseration, Universität
St.Gallen, Hallstadt, from Universität St.Gallen: .
Karlsson, F., & Wistrand, K. (2006). Combining method
engineering with activity theory: theoretical grounding
of the method component concept. European Journal
of Information Systems, 15(1), 82–90.
Kaschek, R. (Ed.). 1999. Entwicklungsmethoden für
Informationssysteme und deren Anwendung: EMISA
'99, Fachtagung der Gesellschaft für Informatik e. V.
(GI). Stuttgart, Leipzig.
Kelly, S., Rossi, M., & Tolvanen, J. P. (2005). What is
Needed in a MetaCASE Environment? Enterprise
Modelling and Information Systems Architectures,
1(1), 25–35.
Larsen, M. H., Pedersen, M. K., & Anderson, K. V.
(2006). IT Governance: Reviewing 17 IT Governance
Tools and Analysing the Case of Novozymes A/S. In
HICSS 2006: Proceedings of the 39th Annual Hawaii
International Conference on System Sciences,
Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer Society.
Loos, P., & Fettke, P. (2005). Referenzmodellierung:
Entwicklungsstand und Perspektiven, Information
Management & Consulting, 20(Sonderausgabe).
Lunardi, G. Lerch, Becker, J. Luiz, & Macada, A. C.G.
(2009). The Financial Impact of IT Governance
Mechanisms' Adoption: An Empirical Analysis with
Brazilian Firms. In HICSS 2009 - Proceedings of the
42th Hawaii International Conference on System
Sciences .
Patel, C., Cesare, S. de, Iacovelli, N., & Merico, A.
(2004). A Framework for Method Tailoring: A Case
Study. In . 2nd OOPSLA Workshop on Method
Engineering for Object-Oriented and Component-
Based Development . Vancouver.
PWC (2006). IT Governance in Practice - Insight from
leading CIOs. PricewaterhouseCoopers Johannesburg,
South Africa, IT Governance Institute Rolling
Meadows, USA.
Ralyté, J., & Rolland, C. (2001). An Assembly Process
Model for Method Engineering. In Lecture notes in
computer science: 13th International Conference on
Advanced Information Systems Engineering (CAiSE
2001) (pp. 267–283).
Rosemann, M., & van der Aalst, W. M. P. (2007). A
configurable reference modelling language.
Information Systems, 32(1), 1–23.
Scheer, A.-W., Seel, C., & Georg, W. (2002).
Entwicklungsstand in der Referenzmodellierung.
Industrie Management, 18(1), 9–12.
Schütte, R. (1998). Grundsätze ordnungsmäßiger
Referenzmodellierung: Konstruktion konfigurations-
und anpassungsorientierter Modelle (Vol. 233). Neue
betriebswirtschaftliche Forschung, 233. Wiesbaden:
Gabler.
Simonsson, M., & Johnson, P. (2008). The IT
Organization Modeling and Assessment Tool:
Correlating IT Governance Maturity with the Effect of
IT. In HICSS 2008 - Proceedings of the 41st Annual
Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences
(p. 431). Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer
Society.
Siviy, J., Kirwan, P., Marino, L., & Morley, J. (2008a).
Maximizing your Process Improvement ROI through
Harmonization (White Paper SEI). Software
Engineering Institute.
Siviy, J., Kirwan, P., Marino, L., & Morley, J. (2008b).
The Value of Harmonizing Multiple Improvement
Technologies: A Process Improvement Professional’s
View (White Paper SEI). Software Engineering
Institute.
Tuttle, B., & Vandervelde, S. D. (2007). An empirical
examination of COBIT as an internal control
framework for information technology. International
Journal of Accounting Information Systems, 8, 240–
263.
Wagner, H. Theo (2006). Managing the impact of IT on
Firm Success: The Link between the resources-based
view and the IT Infrastructure Library. In . HICSS
2006: Proceedings of the 39th Annual Hawaii
International Conference on System Sciences
Washington, DC, USA: IEEE Computer Society.
Zelewski, S. (1999). Grundlagen. In H. Corsten & M. Reiß
(Eds.), Betriebswirtschaftslehre (pp. 1–125). Wien.
Zelewski, S. (2007). Kann Wissenschaftstheorie behilflich
für die Publikationspraxis sein?: Eine kritische
Auseinandersetzung mit den Giudelines vn Hevner et
al. In F. Lehner & S. Zelewski (Eds.),
Wissenschaftstheoretische Fundierung und
wissenschaftliche Orientierung der
Wirtschaftsinformatik (pp. 71–120). Berlin: Gito.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
158
