
3D PATH PLANNING FOR UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLES USING
VISIBILITY LINE BASED METHOD
Rosli Omar
1,2
and Dawei Gu
2
1
Faculty of Electrical and Electronic Engineering, Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia, Johor, Malaysia
2
Department of Engineering, University of Leicester, LE1 7RH, Leicester, U.K.
Keywords:
3D path planning, Visibility lines, Base line oriented visibility line, Optimization.
Abstract:
In path planning, visibility graph (or visibility line (VL)) method is capable of producing shortest path from
a starting point to a target point in an environment with polygonal obstacles. However, the run time increases
exponentially as the number of obstacles grows, causing this method ineffective for real-time path planning.
A 2D path planning framework based on VL has recently been introduced to find a 2D path in an obstacle-
rich environment with low run time. In this paper we propose 3D path planning algorithms based on the 2D
framework. Several steps are used in the algorithms to find a 3D path. First, a local plane is generated from a
local starting point to a target point. The plane is then rotated at several pre-defined angles. At each rotation,
a shortest path is calculated using 2D algorithms. After rotations at all angles have been done, the shortest
one is selected. Simulation results show that the proposed 3D algorithms are capable in finding paths in 3D
environments and computationally efficient, thus suitable for real time application.
1 INTRODUCTION
Uninhabited Aerial Vehicles (UAVs) are becoming
more popular in accomplishing tasks in adverse en-
vironments. For example UAVs have been used for
military purpose such as reconnaissance and combat
as well as to perform civil tasks such as weather fore-
casting, environmental research, search and rescue
missions and traffic control.
The advantage of UAVs in avoiding human loss
brings ”less” intelligence of the vehicle. In order
to make UAVs more practically useful, it is impor-
tant to raise the autonomy level of UAVs. Autonomy
means the capability of UAVs to make its own de-
cisions based on the available information captured
by sensors, and potentially covers the whole range
of the vehicle operations without human interven-
tion (Frampton, 2008). However, autonomy tech-
nology is still in its early stage and fairly under-
developed (http://www.theuav.com). It is the bottle-
neck for UAVs development in the future. Hence the
problem of autonomy has to be addressed before the
fully autonomous UAVs can be advanced. As path
planning is one of the crucial factors in enhancing the
autonomy level in UAVs, this paper focuses on this
topic.
Researches onpath planning amongpolygonalob-
stacles have been around probably since the beginning
of mobile robot. They have produced many meth-
ods and algorithms under several categories. Among
them are geometric-based (Omar and Gu, 2009; Cole-
man and Wunderlich, 2008; Tian et al., 2007; Bortoff,
2000; Nilsson, 1984), grid-based (Chen et al., 1995;
LingelBach, 2004) and potential field (Garibotto and
Masciangelo, 1991; Barraquand et al., 1992), to name
but three. One of the popular methods is geometric-
based category under which there is an approach
called visibility lines (VL).
VL was first proposed by Lozano-Perez and Wes-
ley (Lozano-Perez and Wesley, 1979) for path plan-
ning in the environments with polyhedral obstacles.
Since then several researchers (Nilsson, 1984; Huang
and Chung, 2004; Bygi and Ghodsi, 2006) used the
method with some variants. However one major dis-
advantage of VL is the computationaleffort grows ex-
ponentially as the number of obstacles increases. To
overcome such a problem, Huang and Chung (Huang
and Chung, 2004) introduced Dynamic VG (DVG)
which used local region to plan a path to speed up
the run time. The local region was determined by the
nodes that have maximum distance from a line drawn
from starting point to target point called S-G line. In
(Omar and Gu, 2009), we proposed 2D path plan-
ning algorithm which was based on VL called Base-
80
Omar R. and Gu D. (2010).
3D PATH PLANNING FOR UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLES USING VISIBILITY LINE BASED METHOD.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 80-85
DOI: 10.5220/0002881100800085
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Line Oriented Visibility Lines(BLOVL). Also there is
a sub-algorithm of BLOVL named Core. Core’s main
purpose is to find a path from a two-stage process.
First, a group of obstacles that lie on base line (BL)
and their extension are identified. BL is similar to S-
G line in (Huang and Chung, 2004). Second, a path
is calculated using Dijkstra’s algorithm. As the path
planned by Core might not collision-free, BLOVL is
used to further plan it. In addition BLOVL is designed
to be used for real-time path planning.
On the other hand, 3D path planning problems
have been studied extensively for many years. There
were several different approaches available includ-
ing Evolutionary Algorithms (EA) (Hasircioglu et al.,
2008; Mittal and Deb, 2007), VL (Jiang et al., 1993)
and Dubin circles (Ambrosino et al., 2006), to name
but three. In (Hasircioglu et al., 2008) EA and B-
spline curves for off-line 3D path planning were used.
To increase the performance of the path, the number
of generations had to be increased hence increased
the run-time. Like (Hasircioglu et al., 2008), Mittal
and Deb (Mittal and Deb, 2007) presented an off-line
path planner with multi-objective EA and B-spline.
The results of their work were several optimal 3D
paths. (Ambrosino et al., 2006) used Dubin circles to
first obtain estimate of a 3D path. Then the path was
divided into three sub-paths. However, (Ambrosino
et al., 2006) assumed that no obstacle to be avoided
during the path generation.
In this paper, we propose a 3D path planning al-
gorithm, BLOVL
3D
which consists of several sub-
algorithms namely BasePlane, Rotate
3D
as well as
BLOVL. Basically BLOVL
3D
find the 3D path from a
series of rotations of local planes. This algorithm and
its sub-algorithms have been realized into a Matlab’s
graphical user interface (GUI) environment for simu-
lation purpose to evaluate its effectiveness. The rest of
this paper is organized as follows. Section 2 reviews
the 2D path planning using Core and BLOVL algo-
rithms. Section 3 explains our proposed 3D path plan-
ning algorithm in details. Section 4 shows an example
of results from the proposed algorithms. In Section 5
we demonstrate the simulation results in term of run
time. Section 6 concludes the paper.
2 2D PATH PLANNING
In order to make path calculation faster by visibility
lines (VL) means, the number of obstacles used in the
calculation has to be minimized. Thus Core has been
designed to perform this task. Figure 1 illustrates the
process of Core while Algorithm 1 shows the steps
of it.
Figure 1: Core algorithm.
Algorithm 1: Core.
1: Create a base line (BL) from starting point, u
start
to target point, u
target
2: Construct a set of nodes, N
S
, from the four cor-
ners of each obstacle that lies on the base line and
their extensions, including u
start
and u
target
3: Create a cost matrix, C
M
from N
S
4: Find local path, U(u
0
, . .. , u
m
) from C
M
using Di-
jkstra’s algorithm where u
0
= u
start
and u
m
=
u
target
Core begins with creating a base line (BL) from a
local starting point, u
start
to a target point, u
target
. The
obstacles that lie on BL and their extension, O
BL
will
be used for path calculation. The idea on how O
BL
is
identified is illustrated in Figure 2. In the figure, the
obstacles that intersect with BL arenumberedas 1 and
2 while the extended obstacles are 3 and 4. Obstacle 5
is ignored as it is neither on BL nor an extension of the
obstacles on BL. As a result O
BL
contains obstacles
with the number of 1, 2, 3 and 4.
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
−10
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
1
2
3
4
5
X
Y
Starting point
Target point
Base line
Included obstacles
Ignored obstacle
Figure 2: Obstacles identification using Core.
In Step 2 of Core, O
BL
is used to build up a set
of nodes stored in N
S
. Then each pair of mutually
visible nodes in N
S
is connected by a line segment
and given a cost based on its Euclidean distance. On
the contrary, two mutually-invisible nodes are given
infinity costs and are thus ignored. Based on N
S
, in
the next step of Core, a cost matrix, C
M
is created.
C
M
stores the indexes of paired nodes and the lines
segment Euclidean distances (costs). If all pairs of
mutually-visible nodes are connected together by line
segments, they will form a plane with zero altitude as
shown in Figure 3.
Using C
M
, Dijkstra’s algorithm will then be ap-
3D PATH PLANNING FOR UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLES USING VISIBILITY LINE BASED METHOD
81
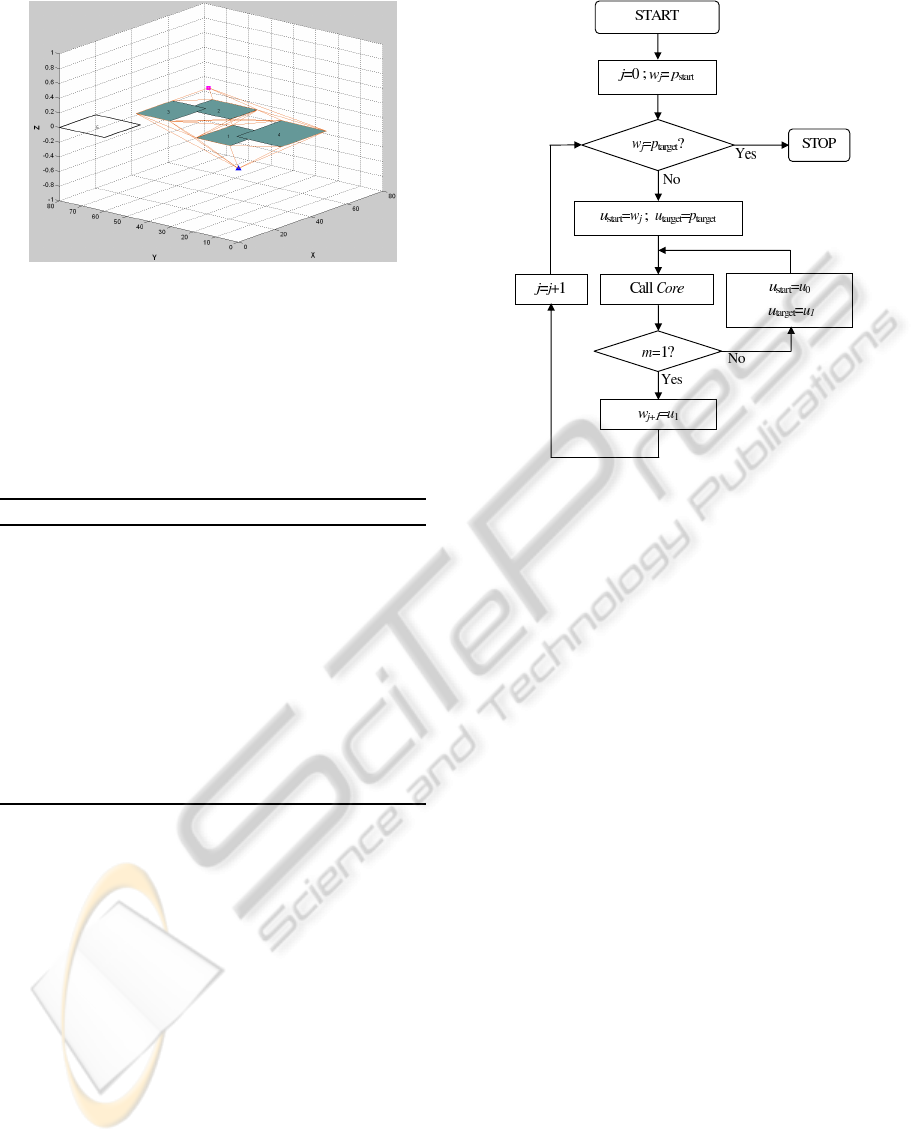
Figure 3: A plane formed by visibility lines with zero alti-
tude.
plied in Step 4 of Core to find a local optimal path,
U by minimizing the total path length from u
start
to
u
target
. To ensure that the path is collision-free and
capable to be used for real-time path planning, Core
has to be associated with BLOVL as shown in Algo-
rithm 2. Figure 4 shows the BLOVL process.
Algorithm 2: BLOVL.
1: Set j = 0 and w
j
= p
start
2: while w
j
6= p
target
do
3: set u
start
= w
j
and u
target
= p
target
4: call Core
5: if m = 1 then
6: set w
j+1
= u
1
7: else
8: set u
target
= u
1
9: goto line 4
10: end if
11: set j = j + 1
12: end while
The first step of BLOVL is setting the current
starting point/waypoint, w
j
to p
start
where j is ini-
tialized to 0. Then w
j
is compared with the p
target
.
If w
j
is or at the vicinity of p
target
, then the process
is stopped. Otherwise w
j
and p
target
will be defined
as u
start
and u
target
respectively. With u
start
and u
target
being the input, Core is called to find a local shortest
path, U. Core will be called again if the number of el-
ements in U is greater than 2 as this shows that there
are obstacles between u
start
and u
target
. Note that the
element number in U is indicated by m. If m = 1,
it means that U has 2 elements and the resulted path
is unobstructed from u
start
and u
target
, and the next
waypoint w
j+1
will be set to u
1
. This process will be
repeated until w
j
is or near to p
target
. Notice that the
resulted path from BLOVL consists of a set of global
waypoints, W = w
0
, . . . , w
n−1
.
Figure 4: BLOVL process.
3 ALGORITHM FOR 3D PATH
PLANNING
In practice UAV flies in 3D environments. To en-
sure that the UAV’s paths are free from collision in
such environments, path in 3D has to be planned. For
such a purpose, we have developed 3D path planning
algorithm, BLOVL
3D
which consists of several sub-
algorithms i.e. BasePlane, Rotate
3D
and BLOVL.
BLOVL
3D
uses rotational planes to find 3D paths.
Figure 5 illustrates the process of BLOVL
3D
and Al-
gorithm 3 shows its steps.
BLOVL
3D
starts with initializing several neces-
sary parameters i.e. k = 0, Ps
k
= p
start
and i = 0. No-
tice that Ps is the global path with several waypoints
that will be built-up along the process. The final value
of k will determine the number of waypoints in Ps. i
represents the index of the rotational angles.
In the next step of BLOVL
3D
, the vector of rota-
tional angle, α is defined. It consists of b number of
angles. α will determine at which angle the plane will
be rotated. Next Ps
k
is compared with p
target
. If Ps
k
is p
target
or at the vicinity of p
target
the process will
be stopped. Otherwise u
start
will be set to Ps
k
while
u
target
is p
target
. Note that u
start
and u
target
are nec-
essary for Core of BLOVL in the later stage of the
algorithm.
In case of Ps
k
is not the p
target
or not at the
vicinity of it, BasePlane which is shown in Algo-
rithm 4 is then called. BasePlane generates a local
plane, Px
′
y
′
u
start
. As shown in Algorithm 4, the local
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
82

Figure 5: BLOVL
3D
process.
plane generated by BasePlane always change with the
change in u
start
hence it is named Px
′
y
′
u
start
.
To generate Px
′
y
′
u
start
using BasePlane, first a base
line, BL
3D
is drawn from u
start
to u
target
. As u
start
and u
target
have different altitude, the angle β between
BL
3D
and the horizontal global plane, Pxy
u
start
can be
calculated. BL
⊥
3D
that intersects u
start
and orthogonal
to BL
3D
is then defined. With BL
3D
and BL
⊥
3D
as the
x- and y-axis respectively, Px
′
y
′
u
start
that lies at β de-
gree from Pxy
u
start
is defined. Then the coordinate of
obstacles lying on Px
′
y
′
u
start
is projected accordingly.
As Px
′
y
′
u
start
has been defined, next is to rotate the
plane by α
i
degree to find a local optimal path, W
αi
from u
start
to u
target
. Rotating this plane is performed
by Rotate
3D
while finding W
αi
is accomplished by
BLOVL and Core. Algorithm 5 shows Rotate
3D
.
While i < b + 1, i is increased by 1 and α
i
is
updated accordingly and Rotate
3D
and BLOVL are
kept called to find W
αi
. When i = b + 1, all paths
(and their costs) that have been stored in W
α
are
compared with each other and path with the lowest
cost, Ws is then selected. Notice that Ws consists of
{Ws
0
, . . . ,Ws
n−1
} and the waypoints in Ws are ac-
cording to the global coordinate system.
In the next step, the index of global waypoints, k
is increased by 1 and the next global waypoint, Ps
k
is updated to be the second waypoint of the shortest
path i.e. Ws
1
. i then is initialized back to 0 and the
process as described above are repeated until Ps
k
is or
at the vicinity of p
target
.
Algorithm 3: BLOVL
3D
.
1: Set k = 0, Ps
k
= p
start
and i = 0.
2: Define the rotational angle vector, α.
3: while Ps
k
6= p
target
do
4: u
start
= Ps
k
; u
start
= p
target
.
5: call BasePlane to generate local plane,
Px
′
y
′
u
start
.
6: while i 6= b+ 1 do
7: call BLOVL.
8: Save waypoints, W
α
i
generated by BLOVL.
9: Increase i by 1.
10: Rotate Px
′
y
′
u
start
by α
i
degree.
11: end while
12: Compare all paths in W
α
and find the shortest,
Ws. Ws = {Ws
0
, . . . ,Ws
o
}.
13: Increase k by 1 and update Ps
k
= Ws
1
. Ini-
tialise i to .
14: end while
Algorithm 4: BasePlane.
1: Draw a base line, BL
3D
connecting u
start
and
u
target
. Find out the angle β between BL
3D
and the horizontal plane Pxy
u
start
, which contains
u
start
.
2: Define a local plane, Px
′
y
′
u
start
, formed by BL
3D
and the straight line, BL
⊥
3D
which passes u
start
,
lies on Pxy
u
start
and is orthogonal to BL
3D
.
3: Define a local coordinate system on Px
′
y
′
u
start
,
with u
start
as the origin, BL
⊥
3D
as x-axis and BL
3D
as y-axis. Establish the coordinate transforma-
tion between this local coordinate system and the
global one.
4: Project the obstacles on Px
′
y
′
u
start
.
Algorithm 5: Rotate
3D
.
1: Rotate the plane Px
′
y
′
u
start
by α
i
degree.
2: Find out the coordinate transformation between
the new local system and the global one.
3: Project the obstacles on the new Px
′
y
′
u
start
plane.
4 EXAMPLE
A random scenario with 150 obstacles was gener-
ated as shown in Figure 6. Each obstacle was
3D PATH PLANNING FOR UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLES USING VISIBILITY LINE BASED METHOD
83
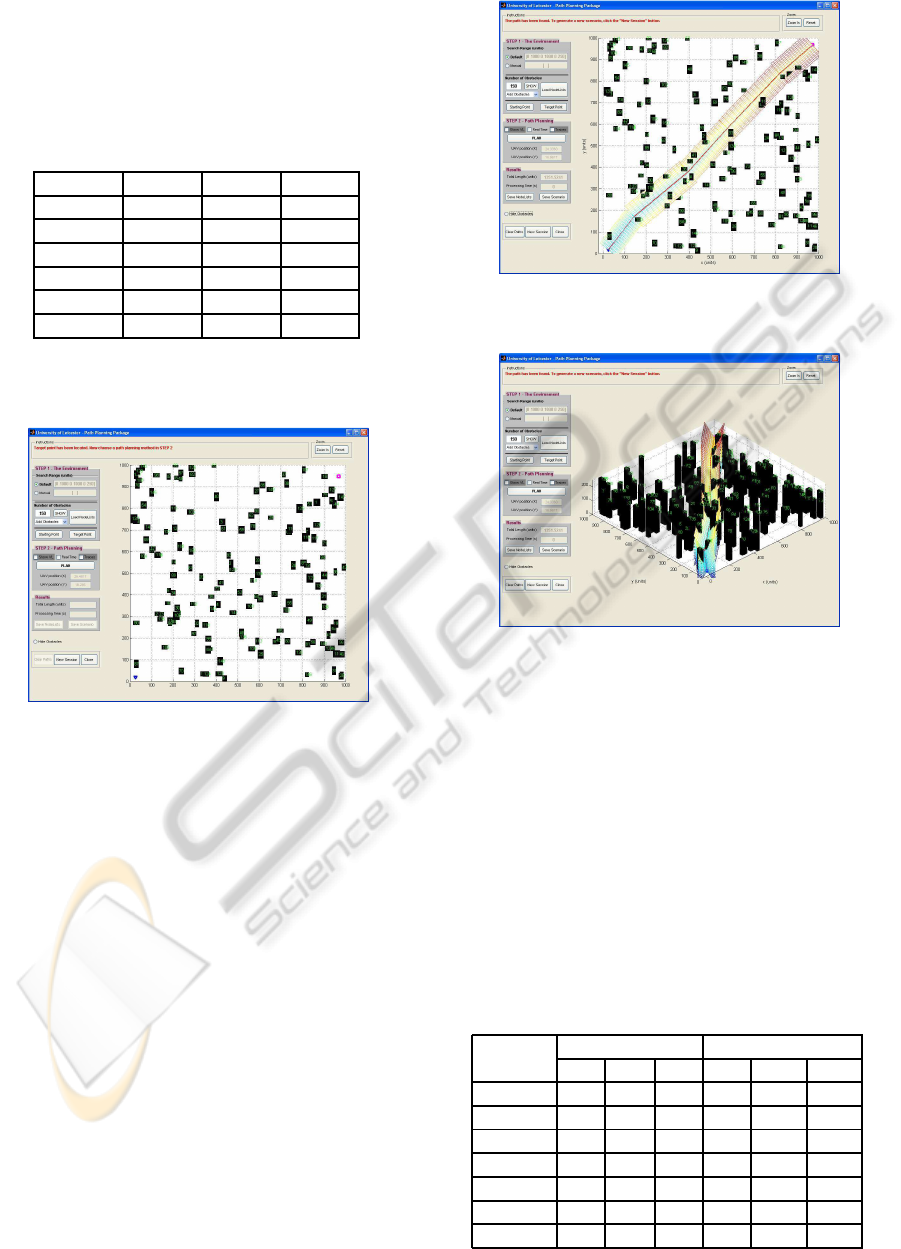
numbered and given a random height. Starting
point’s altitude was set to 20 while the target point’s
altitude was 150. The planes were rotated at
0, 10, 30, 45, 60, 120, 135, 150, 170. The resulted path
had the waypoints as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: The waypoints.
Number X Y Z
1 26.48 18.29 20.00
2 143.76 171.24 41.05
3 394.24 378.76 69.72
4 576.76 581.24 98.77
5 817.76 834.25 133.93
6 959.76 960.92 150.00
Figure 7 and Figure 8 show the top and 3D views
of the resulted path respectively.
Figure 6: A random scenario with obstacles shown in black.
The blue rectangle is the starting point and the square ma-
genta is the target point.
5 SIMULATION RESULTS
Scenarios with several numbers of obstacles were
simulated randomly to evaluate the performance of
the proposed 3D path planning algorithms. The num-
ber of obstacles used were 50, 75, 100, 125, 150, 175
and 200. To increase the reliability of the results,
ten different random scenarios were generated from
each number of obstacles. The simulations were per-
formed on Intel’s 2.4Ghz Core 2 Duo processor with
2GB DDR2 RAM. As no data for other 3D algorithms
available in the literature using the same scenarios as
we used here, no comparison was done. Thus we
compared the proposed 3D path planning algorithm
performance with that of 2D that was introduced by
(Omar and Gu, 2009) as both algorithms were de-
signed for such scenarios. The results of the simu-
lation were recorded in Table 2.
Figure 7: Top view of the resulted path (in red) with the
rotated planes.
Figure 8: 3D view of the resulted path with the rotated
planes.
From Table 2, using 2D algorithms no substantial
growth in run time as the number of obstacles were in-
creased while by 3D algorithms the calculation time
increased quite significantly. This is due to (i) in-
creased number of obstacles on the base line which
results in increased number of waypoints. (ii) number
of angles used to generate the rotational planes. If the
resulted path has k waypoints and the rotational angle
vector, α consists of b number of angles, the process-
ing time might be (b − 1) × k longer than that of 2D
path planning algorithms.
Table 2: Comparison of 2D and 3D path planning algo-
rithms performance (in sec).
Number of 2D Algorithms 3D Algorithms
obstacles Min Max Ave Min Max Ave
50 0.01 0.25 0.13 0.65 1.84 1.27
75 0.02 0.20 0.15 1.03 6.93 2.63
100 0.04 0.28 0.21 1.97 8.14 4.08
125 0.06 0.39 0.27 2.59 17.54 8.77
150 0.08 0.43 0.35 5.18 22.16 11.63
175 0.15 0.83 0.50 6.82 35.79 21.13
200 0.19 0.98 0.62 7.16 48.77 26.42
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
84

6 CONCLUSIONS
As visibility line (VL) method is effective in produc-
ing path with shortest length, it has been used to de-
velop a three-dimensional (3D) path planning algo-
rithm, BLOVL
3D
. BLOVL
3D
governsBasePlane, Ro-
tate
3D
as well as Base Line Oriented Visibility Line
(BLOVL) algorithms to find a 3D path. BasePlane
algorithm is used to establish a local plane. Next Ro-
tate
3D
algorithm rotates the plane. At each rotation
of the plane, a path with lowest cost is calculated by
BLOVL and recorded. After the local plane has been
rotated at all angles, the resulted paths are compared
to each other and the shortest one will be selected.
The process continues with a newstarting point which
is the second waypoint of the previous shortest path.
The process is stopped if the target point has been
reached. Simulations results show that BLOVL
3D
and
its sub-algorithms are capable to effectively find sub-
optimal paths in term of path length in 3D environ-
ments and is very promising to be applied in real time
3D path planning.
REFERENCES
Ambrosino, G., Ariola, M., Ciniglio, U., Corraro, F.,
Pironti, A., and Virgilio, M. (2006). Algorithms for
3d uav path generation and tracking. In Proceedings
of the 45th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control,
pages 5275–5280. IEEE.
Barraquand, J., Langlois, B., and Latombe, J.-C. (1992).
Numerical potential field techniques for robot path
planning. In Proceedings of the IEEE Transactions on
Systems, Man and Cybernetics, pages 224–240. IEEE.
Bortoff, S. (2000). Path planning for uavs. In Proceedings
of the American Control Conference Chicago Illinois,
pages 364–368. ACC.
Bygi, M. and Ghodsi, M. (2006). 3d visibility graph. In 12th
CSI Computer Conference (CSICC 2006). Computer
Society of Iran.
Chen, D., Szczerba, R., and Uhran, J. (1995). Planning con-
ditional shortest paths through an unknown environ-
ment: A framed-quadtree approach. In Proceedings
of the International Conference on Intelligent Robots
and Systems, pages 33–38. IEEE.
Coleman, D. and Wunderlich, J. (2008). O3: An optimal
and opportunistic path planner (with obstacle avoid-
ance) using voronoi polygons. In International Work-
shop on Advanced Motion Control, pages 371–376.
IEEE.
Frampton, R. (2008). Uav autonomy. The Journal for De-
fence Engineering & Science, 1(Summer 2008):28–
31.
Garibotto, G. and Masciangelo, S. (1991). Path planning
using the potential field approach for navigation. In
Fifth International Conference on Advanced Robotics.
IEEE.
Hasircioglu, I., Topcuoglu, H., and Ermis, M. (2008). 3-d
path planning for the navigation of unmanned aerial
vehicles by using evolutionary algorithms. In Pro-
ceedings of the 10th Annual Conference on Genetic
and Evolutionary Computation, pages 1499–1506.
ACM.
Huang, H. and Chung, S. (2004). Dynamic visibility graph
for path planning. In Proceeding of International Con-
ference on Intelligent Robots and Systems. IEEE.
Jiang, K., Seneviratne, L., and Earles, S. (1993). Finding the
3d shortest path with visibility graph and minimum
potential energy. In Proceeding of the 1993 IEEE/RSJ
International Conference on Intelligent Robots and
Systems, pages 679–684. IEEE.
LingelBach, F. (2004). Path planning using probabilistic
cell decomposition. In Proceedings of the IEEE In-
ternational Conference on Robotics and Automation,
pages 467–472. IEEE.
Lozano-Perez, T. and Wesley, M. (1979). An algorithm for
planning collision-free paths among polyhedral obsta-
cles. In Contmum ACM, pages 560–570. ACM.
Mittal, S. and Deb, K. (2007). Three-dimensional of-
fline path planning for uavs using multiobjective evo-
lutionary algorithms. In Proceedings of the IEEE
Congress on Evolutionary Computation, pages 3195–
3202. IEEE.
Nilsson, N. (1984). Shakey the robot. Technical Report
JReport 323, 333 Ravenswood Avenue, Menlo Park,
CA 94025-3493.
Omar, R. and Gu, D.-W. (2009). Visibility line based meth-
ods for uav path planning. In ICROS-SICE Interna-
tional Joint Conference. ICROS-SICE.
Tian, Y., Yan, L., Park, G., S.Yang, Kim, Y., Lee, S.,
and Lee, C. (2007). Application of rrt-based local
path planning algorithm in unknown environment. In
Proceeding of the IEEE International Symposium on
Computational Intelligence in Robotics and Automa-
tion, pages 456–460. IEEE.
3D PATH PLANNING FOR UNMANNED AERIAL VEHICLES USING VISIBILITY LINE BASED METHOD
85
