
ITERATIVE IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION METHODS IN CONE
BEAM CT APPLIED TO PHANTOM AND CLINICAL DATA
W. Qiu, M. Soleimani, C. N. Mitchell
Dept. of Electronic and Electrical Engineering, University of Bath, Bath, BA2 7AY, U.K.
T. Marchant, C. J. Moore
The Christie NHS Foundation Trust, Wilmslow Road, Manchester, M20 4BX, U.K.
Keywords:
Iterative reconstruction algorithms, Cone beam CT.
Abstract:
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) enables a volumetric image reconstruction from 2D projection
data. In CBCT reconstruction, iterative methods of image reconstruction offer the potential to generate high
quality images and would be an advantage especially for sparse data sets. CBCT image reconstruction software
has been developed based on Multi-Instrument Data Analysis System (MIDAS) tomography toolbox. In this
paper, we present a comparative study of SIRT and ART algorithms, developed in MIDAS platform. The
results will be shown using phantom and clinical patient data.
1 INTRODUCTION
Cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) provides
a volumetric image reconstruction from tomographic
projection data, while in commercial CT system,
though many algorithms exist, filtered back projec-
tion (FBP) like reconstruction algorithm based on
FDK (Feldkamp et al., 1984) is still being used.
Recently, iterative reconstruction algorithms are be-
ing investigated for clinical application (Wang et al.,
2009), as challenges still exist for image reconstruc-
tion due to computational time, parameters selec-
tion and down sampled data in some practical ap-
plications. Iterative algorithms provides an alterna-
tive for commercial tomographic image reconstruc-
tion methods. In this paper the iterative methods have
been studied and results show that they have potential
to performed better in various situations, especially
when projection data are not fully available (Ander-
sen, 1989). In addition, most of the papers describe
the behaviour of iterative algorithms by using phan-
tom data only (Mueller et al., 1999) without applying
to clinical patient measurement. In our work, compar-
ison of the CBCT iterative algorithms (ART (Gordon
et al., 1970) and SIRT (Gilbert, 1972)) implemented
in the Multi-Instrument Data Analysis System (MI-
DAS) (Mitchell and Spencer, 2003) tomography soft-
ware are presented by applying to phantom and clin-
ical data. Convergence rate, edge recovery, compu-
tational time and quality of the image are the main
criteria for considerations. Results are presented with
the image reconstructed from full data sets of CBCT
projection data using iterative algorithms (ART and
SIRT). They are compared in terms of the criteria
mentioned while a FDK image from the same system
is used as a reference.
2 THE CBCT SYSTEM AND DATA
In this study, the measured projection data were
provided by North Western Medical Physics at The
Christie hospital in Manchester. A ’RANDO’ anthro-
pomorphic head phantom
1
was scanned to produce
360 X-ray projection images, approximately evenly
spaced over an angular range of -100 to +100 de-
grees. Images were acquired at 100kV, 10mA and
10ms per projection, with total imaging dose of ap-
proximately 1.5mGy. Each projection image contains
512x512 pixels of dimension 0.8x0.8mm. Figure 1
shows the imaging system used in this study.
Using the full 360 projection data set a 3D re-
construction of 256x256x256 voxels with resolution
1mm in each direction was produced using iterative
1
The Phantom Laboratory, Salem, NY, USA.
550
Qiu W., Soleimani M., N. Mitchell C., Marchant T. and Moore C. (2010).
ITERATIVE IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION METHODS IN CONE BEAM CT APPLIED TO PHANTOM AND CLINICAL DATA.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 550-553
DOI: 10.5220/0002892005500553
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Figure 1: Medical linear accelerator with integrated X-ray
cone-beam CT system.
techniques. A ’reference image’ was reconstructed
using the COBRA cone beam software developers
package from EXXIM
2
. This contains an implemen-
tation of FDK FBP, which is a useful benchmark for
the iterative techniques described in this paper.
3 METHODS
The classic ART algorithm is
f
(i+1)
j
= f
(i)
j
+ λ
p
k
−
∑
N
n=1
f
(i)
n
w
nk
∑
N
n=1
w
2
nk
w
jk
(1)
where λ is the relaxation parameter, which controls
the convergence rate. f (x,y, z) are the image values;
j is the index for the voxel of f ; i is the number of it-
eration; p is the projection data; k is the total number
of rays. N is the number of cells; w is the weight-
ing factor and k is the kth image cell intercepted by
the nth ray. Including a relaxation parameter can im-
prove the quality of ART reconstructions, but usually
at the expense of the speed of convergence. Depend-
ing on the application, different strategies are applied
for choosing the most appropriate relaxation parame-
ter and other settings. Besides ART, there is another
approach of implementation, which is SIRT and de-
fined as
f
(i+1)
j
= f
(i)
j
+ λ
∑
N
n=1
[w
jn
(p
k
−
∑
N
n=1
f
i
n
w
nk
)/
∑
N
n=1
w
nk
]
∑
N
n=1
w
nk
(2)
The convergence of the algorithms are used by
comparing the mearused and calculated projection
data, we define residual norm as
||x|| =
q
x
2
1
+ x
2
2
+ ... + x
2
k
, {1 ≤ k ≤ N },
where x is a vector of the difference between the
calculated and measured data. The differences be-
tween the iteratively calculated and measured projec-
tion data are then used for comparison as defined in
Equation 3.
2
Exxim Computing Corporation, Pleasanton, CA, USA.
E = ||p
(i)
− p|| (3)
In the mean while, a good residual norm result
may not always indicate a good reconstructed image,
as it considers the reconstruction from the projection
data side and one may not expect the projection data
differences to be minimised for the best image, since
the forward projection does not take into account all
physical processes affecting formation of the projec-
tion data. Therefore, comparison is made between
images. Besides norm differences comparison, im-
age row profiles are used, concentrating the edge area
in Equation 4.
P =
N
∑
a=1
f (a, b,c), {b ∈ Z,c ∈ Z | 1 ≤ b ≤ N,1 ≤ c ≤ N }
(4)
To compare with the reference image, a scaling
parameter σ have been used
∆P = σP
i
/P
re f
(5)
4 RESULTS
The new iterative software has been tested using sim-
ulated data as well as phantom data. This has also
been use for clinical data. Some results are presented
here. Figure 2 shows reconstruction of phantom data
using ART, SIRT and FDK.
Due to the different behaviour of ART and SIRT,
different range of λ are applied. Figure 3 presents the
convergence of ART and SIRT, where ART is with
λ of 0.0146 while SIRT with λ of 0.45 respectively.
It is clearly shown that ART owns a much quicker
convergence than SIRT and according to our imple-
mentation, it takes about three times more for SIRT to
converge the same level of mismatch projection errors
as ART.
The computational time for each ART and SIRT
iteration is shown in Table 1. It contains not only
for full data set, but also down sampled data. The
computer used is 64 bit 3.33GHz Linux with ram of
32GB.
Table 1: Time cost for one ART and SIRT iteration with
available data.
Full data 1/2 data 1/3 data 1/5 data
ART 1600s 800s 540s 320s
SIRT 2200s 1100s 740s 440s
Image row profiles of different iterative algo-
rithms comparing to FDK are then implemented as
ITERATIVE IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION METHODS IN CONE BEAM CT APPLIED TO PHANTOM AND
CLINICAL DATA
551
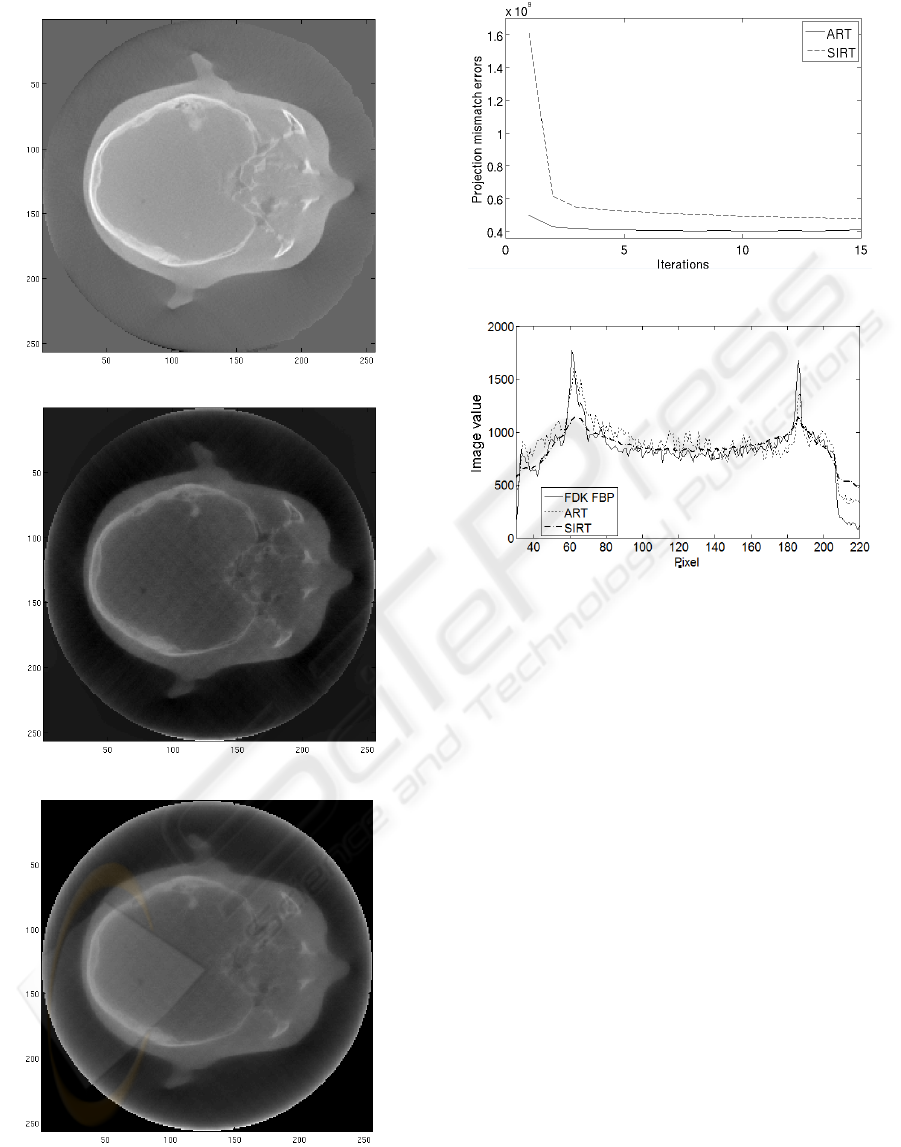
(a) FDK reconstruction
(b) ART reconstruction
(c) SIRT reconstruction
Figure 2: Reconstruction with different algorithms using
phantom data.
Figure 3: Convergence for ART and SIRT.
Figure 4: Image profiles for ART, SIRT and FDK FBP at
f (x = 128, y,z = 128).
shown in Figure 4, where ART is with λ of 0.0146 at
the 8th iteration using full data set while SIRT with λ
of 0.45 at the 40th iteration using full data set respec-
tively. Because ART is sequential method, in which
only a single projection is used in each step, whereas
SIRT uses all projections in each step simultaneously.
SIRT owns a better uniformity than ART and Figure
4 illustrates the expectation. Both the profiles of ART
and SIRT are closely fit with the plot of the profiles of
FDK. However, compared to SIRT, the plot of ART
is more fluctuated, especially from y = 60 : 180. The
visualised images of ART (with λ of 0.0146, 8th iter-
ation, full data) and SIRT (with λ of 0.45, 40th itera-
tion, full data) are presented in Figure 2(b) and 2(c).
The implementation and phantom results suggest
that the ART is more efficient provides suitable re-
sults, but by considering the quality of the recon-
structed image, SIRT performs better due to the fact
that ART is sequential method but SIRT updates the
image simultaneously. Figure 5 shows reconstruction
of ART and SIRT compared to commercial FDK in
clinical patient data.
VISAPP 2010 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
552

(a) FDK reconstruction
(b) ART applied to clinical data
(c) SIRT applied to clinical data
Figure 5: Reconstruction with different algorithms using
clinical patient data.
5 CONCLUSIONS
Iterative reconstructions using ART and SIRT are in-
vestigated and implemented in MIDAS. Convergence,
computational time, edge recovery and reconstructed
images are considered. The results indicate that ART
converge faster than the SIRT while SIRT has a better
uniformity. The reconstructed image of ART can be
improved by updating simultaneously which is con-
sidered as simultaneous algebraic reconstruction tech-
nique (SART) (Andersen and Kak, 1984) while in
terms of speed, various methods exist such as GPU
computing which can potential improve the speed by
a factor of 40-100 times.
In our continued effort we are working towards
further optimisation of iterative methods as well as
their clinical relevance, especially when down sam-
pled data are applied. The MIDAS platform will en-
able us to develop further innovative approaches. As
this work is rapidly progressing and we are hoping to
present more results during conference presentation.
REFERENCES
Andersen, A. H. (1989). Algebraic reconstruction in CT
from limited views. IEEE Transactions on Medical
Imaging, 8(1):50–55.
Andersen, A. H. and Kak, A. C. (1984). Simultaneous alge-
braic reconstruction technique (SART): a superior im-
plementation of the ART algorithm. Ultrasonic imag-
ing, 6(1):81–94.
Feldkamp, L. A., Davis, L. C., and Kress, J. W. (1984).
Practical cone-beam algorithm. Journal of the Optical
Society of America A, 1(6):612–619.
Gilbert, P. (1972). Iterative methods for the three-
dimensional reconstruction of an object from projec-
tions. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 36(1):105–117.
Gordon, R., Bender, R., and Herman, G. T. (1970). Al-
gebraic reconstruction techniques (ART) for three-
dimensional electron microscopy and X-ray photogra-
phy. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 29(3):471–481.
Mitchell, C. N. and Spencer, P. (2003). A three-dimensional
time-dependent algorithm for ionospheric imaging us-
ing GPS. Annals of Geophysics, 46(4):687–696.
Mueller, K., Yagel, R., and Wheller, J. J. (1999). Anti-
aliased three-dimensional cone-beam reconstruction
of low-contrast objects with algebraic methods. IEEE
Transactions on Medical Imaging, 18(6):519–537.
Wang, J., Li, T., and Xing, L. (2009). Iterative image re-
construction for CBCT using edge-preserving prior.
Medical Physics, 36(1):252–260.
ITERATIVE IMAGE RECONSTRUCTION METHODS IN CONE BEAM CT APPLIED TO PHANTOM AND
CLINICAL DATA
553
