
IDENTIFICATION OF AREAS WITH SIMILAR WIND
PATTERNS USING SOFM
J. C. Palomares Salas, A. Agüera Pérez, J. J. G. de la Rosa and J. G. Ramiro
Research Unit PAIDI-TIC-168, University of Cadiz, Electronic Area, Escuela Politécnica Superior
Avda. Ramón Pujol, S/N. E-11202-Algeciras-Cádiz, Spain
Keywords: Cluster Analysis, Clustering Applications, Data Mining, Self-Organizing Feature Map.
Abstract: In this paper it is shown a process to demarcate areas with analogous wind conditions. For this purpose a
dispersion graph between wind directions will be traced for all stations placed in the studied zone. These
distributions will be compared among themselves using the centroids extracted with SOFM algorithm. This
information will be used to build a matrix, letting us work with all relations simultaneously. By permutation
of elements in this matrix it is possible to group relationed stations.
0B1 INTRODUCTION
Clustering is a method of unsupervised learning, and
a common technique for statistical data analysis
used, the majority of times, in data mining, machine
learning, pattern recognition, image analysis,
bioinformatics or dimension reduction. However, in
many such problems, there is a little prior
information (e.g., statistical models) available about
the data, and the decision-maker must make as few
assumptions about the data as possible. It is under
restrictions that clustering method is particularly
appropriate for the exploration of interrelationships
among the data points to make an assessment
(perhaps preliminary) of their structure.
This method is used when to compile and
classify by hand is expensive, and the
characterization of the patterns change with time. On
the other hand, lets to find useful characterization to
build classifiers, and the discovery of class and
subclass that to reveal the nature of the problem
structure.
There are many clustering techniques; the most
widely used are hierarchical clustering and dynamic
clustering (Xiaozhe, 2006). The first are the called
clustering tree and is one of the most widely used
clustering approaches due to the great visualization
power it offers. Hierarchical clustering produces a
nested hierarchy of similar groups of objects,
according to a pairwise distance matrix of the
objects. One of the advantages of this method is its
generality, since the user does not need to provide
any parameters such as the number of cluster.
However, its application is limited to only small
datasets, due to its quadratic computational
complexity. The second is the well knows k-means.
While the algorithm is perhaps the most commonly
used clustering algorithm in the literature, it does
have several shortcomings, including the fact that
the number of clusters must be specified in advance.
Both of these clustering approaches, however,
require that the length of each time series is identical
due to the Euclidean distance calculation
requirement, and are unable to deal effectively with
long time series due to poor scalability. As in
supervised classification methods, there is not
clustering technique that is universally applicable.
The demarcation of different zones with
connected wind patterns could have an important
contribution to prediction models based on data
acquired in meteorological stations placed in the
studied area. When these models are based on the
statistical learning of data (Neural Networks,
ARMAX, Genetic Fuzzy Learning…), the inclusion
of not correlated or erroneous stations can
destabilize the process of obtaining the desired
knowledge.
In this article, we will use the self-organizing
feature map (SOFM) clustering analysis technique to
classify zones with similar wind patterns. The main
reason of to apply this algorithm is the capability of
the learning by example held in SOFM model (Kun-
Lin, 2007). One time that this first clustering has
been realized, we propose a new method based on
Genetic Algorithms for to optimize the final
classification of the study zone.
40
Palomares Salas J., Agüera Pérez A., J. G. de la Rosa J. and G. Ramiro J. (2010).
IDENTIFICATION OF AREAS WITH SIMILAR WIND PATTERNS USING SOFM.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Artificial Intelligence and Decision Support Systems, pages
40-45
DOI: 10.5220/0002896300400045
Copyright
c
SciTePress

1B2 AREA AND WIND DATA
In this work the daily mean wind speed and direction
of 88 met stations, from 2005 to 2008 have been
used. The map of the region and the location of these
stations are depicted in Fig. 1. These stations are
distributed over 87000 Km
2
and they are orientated
to measure agriculture variables (Red de
Información Agroclimática). In this way, wind
records have not enough reliability because, despite
of the most of them are located in open zones, the
anemometer height is 1,5 m and is highly affected
by obstacles and ground effects. (This fact add value
to this study because this kind of meteorological
records are more frequent than the good ones, and is
interesting to build a structure that allows to use
them in order to the wind resource evaluation.)
3 METHOD FOR
EXPLORATORY DATA
ANALYSIS
There exist several methods for quickly producing
and visualizing simple summaries of data sets. A
main goal in the field of exploratory data analysis is
to extract useful information out of large and usually
high-dimensional data sets. In the past, clustering
large datasets has been a domain of classical
statistical methods. More recently a new approach,
Kohonen's Self Organizing Feature Map (SOFM)
has been proposed in order to classify high
dimensional datasets, while having no analogous
traditional method for unsupervised data analysis
(Varfis, 1992).
As new approaches from the field of
connectionism were presented, those were compared
to classical methods and similarities among them
were said to be found. In particular the Kohonen
algorithm was said to be similar to the k-means
method, as it is stated, that the SOFM method is
closely related or a partitioning method of the k-
means type (Murtagh, 1995). The SOFMs aren’t
identical to k-means type and in some cases
outperform a variety of classical statistical
approaches.
3.1 The Self-organizing Map
Algorithm
Kohonen‘s Self-Organizing Feature Maps represent
one very well known and widely used Neural
Network Model which employs unsupervised
learning. This means that the result is formed by the
properties inherent to the data itself; there is no
master who tells what is true or false. So no previous
knowledge about the structure of the data is needed
to be able to use the algorithm.
Self-organizing feature maps (SOFM) learn to
classify input vectors according to how they are
grouped in the input space. They differ from
competitive layers in that neighboring neurons in the
self-organizing map learn to recognize neighboring
sections of the input space. Thus, self-organizing
maps learn both the distribution (as do competitive
layers) and topology of the input vectors they are
trained on.
Figure 1: Map showing the location of meteorological
stations.
The basic SOM consists of M neurons located on
a regular low dimensional grid, usually 1 or 2
dimensional. The lattice of the grid is hexagonal,
rectangular or random, see Fig. 2.
The neurons represent the inputs with reference
vectors m
i
, the components of which correspond to
synaptic weights. One reference vector is associated
with each neuron called unit in a more abstract
setting. The unit, indexed with c, whose reference
vector is nearest to the input x is the winner of the
competition:
(
)
{
}
2
minarg
i
i
mxxcc −==
(1)
Usually Euclidean metric is used, although other
choices are possible as well.
The winning unit and its neighbours adapt to
represent the input even better by modifying their
reference vectors towards the current input. The
amount the units learn will be governed by a
neighbourhood kernel h, which is decreasing
function of the distance of the units from the
winning unit on the map lattice. If the locations of
units I and j on the map grid are denoted by the
IDENTIFICATION OF AREAS WITH SIMILAR WIND PATTERNS USING SOFM
41
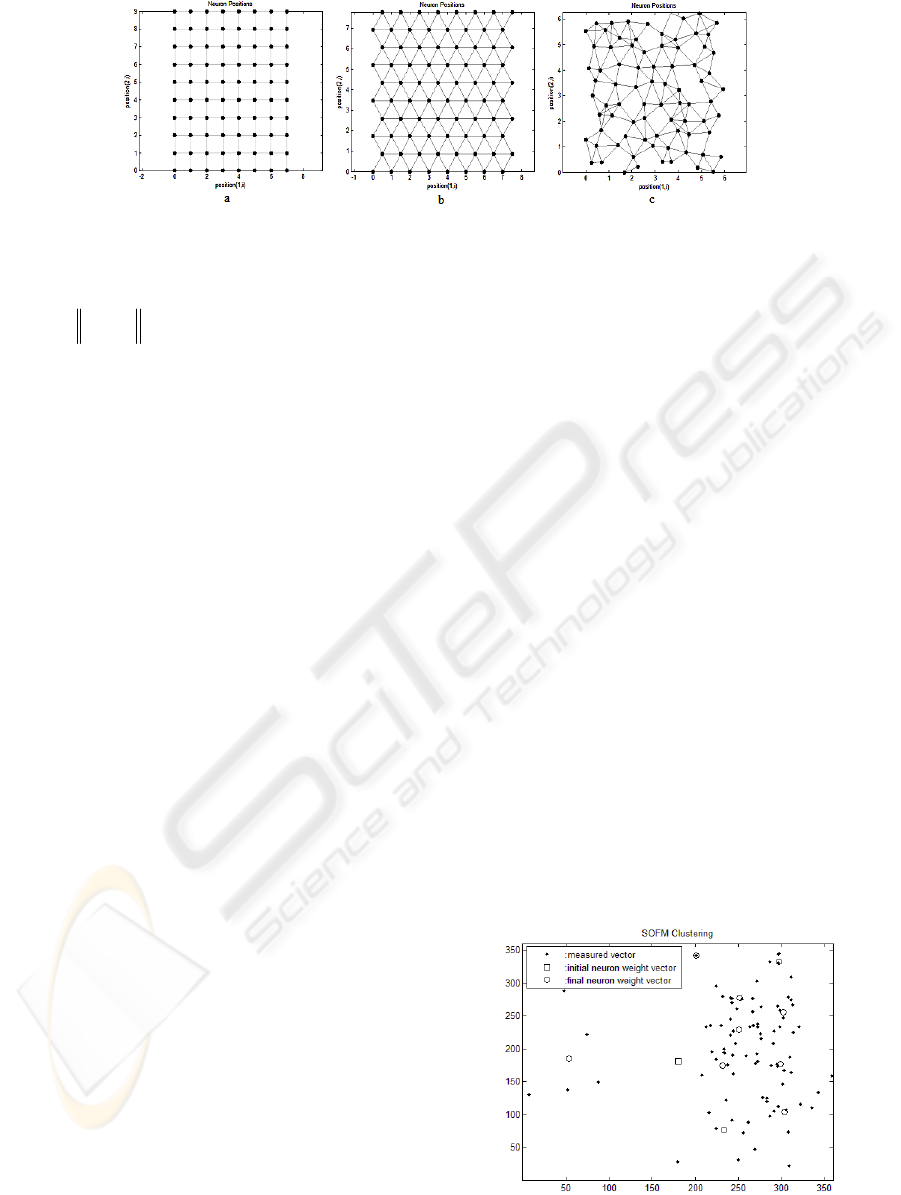
Figure 2: Topologies for the original neuron locations: (a) rectangular lattice, (b) hexagonal lattice, (c) random lattice.
two- dimensional vectors r
i
and r
j
, respectively, then
()
(
)
trrhth
jiij
;−= , where t denotes time.
During the learning process at time t the
reference vectors are changed iteratively according
to the following adaptation rule, where x(t) is the
input at time t and c = c(x(t)) is the index of the
winning unit:
( ) () () ()
(
)
[]
tmtxthtmtm
iciii
−+=+1 (2)
In practice the neighbourhood kernel is chosen to
be wide in the beginning of the learning process to
guarantee global ordering of the map, and both its
width and height decrease slowly during learning.
The learning process, consisting of winner
selection by equation 1 and adaptation of the
synaptic weights by equation 2, can be modelled
with a neural network structure in which the neurons
are coupled by inhibitory connections.
The main properties of such self-organizing
maps can be stated as (Ritter, 1989):
- The distance relationships between the input
data are preserves by their images in the map as
faithfully as possible. While some distortion is
unavoidable, the mapping preserves the most
important neighbourhood relationships between
the data items, i.e., the topology of their
distribution.
- The map allocates different numbers of nodes
to inputs based on their occurrence frequencies.
If different input vector appear with different
frequencies, the more frequent one will be
mapped to larger domains at the expense of the
less frequent ones.
4 PROPOSED PROCEDURE FOR
TO CLUSTER STATIONS
USING SELF-ORGANIZING
FEATURE MAPS (SOFM)
The following procedure has been executed to
demarcate areas with similar wind patterns:
4.1 Characterization of Stations
To characterize the measurement stations, wind
directions (WD) of all them have been chosen for
two random days to yield a vector of dimension
2x88. Once we have obtained this vector the SOFM
algorithm has been carried out. The SOFM module
in MATLAB 7.7.0 has been used to be our tool of
analysis. The configurations parameters related to
the implementation of SOFM by MATLAB 7.7.0
software were as follows: size of layer dimension, [2
5]; network topology, ‘hextop’; distance function,
‘linkdist’. With these parameters we perform the
training of the network to obtain the weights of the
network. Figure 3 shows the scatter plot of this
vector together with the initial weights of the
network and the finals weights of the network after
training.
Figure 3: SOFM Training.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
42
Once the network has been trained we come back to
choose two random days and is simulated with
the obtained network configuration. The following
are make a note of what cluster each station belongs.
This process is repeated 373 times with what a
matrix of size (88x373) is obtained to end. After this
matrix is obtained, it is possible to determine how
many times two stations have been inserted en the
same cluster.
4.2 Matrix of Similarities
Once all stations are characterized by the position of
the weights of the network it is possible to establish
a parameter which indicates the degree of similarity
(DS) between two distributions. We propose (3) the
calculation of the mean distance between each
neuron, C, and the nearest one belonging to the
distribution of the other station, C’
i
. Thus, the lower
is the value of DS, the higher is the similarity of
both distributions.
n
CC
DS
n
j
n
i
n
ij
∑
−
=
(3)
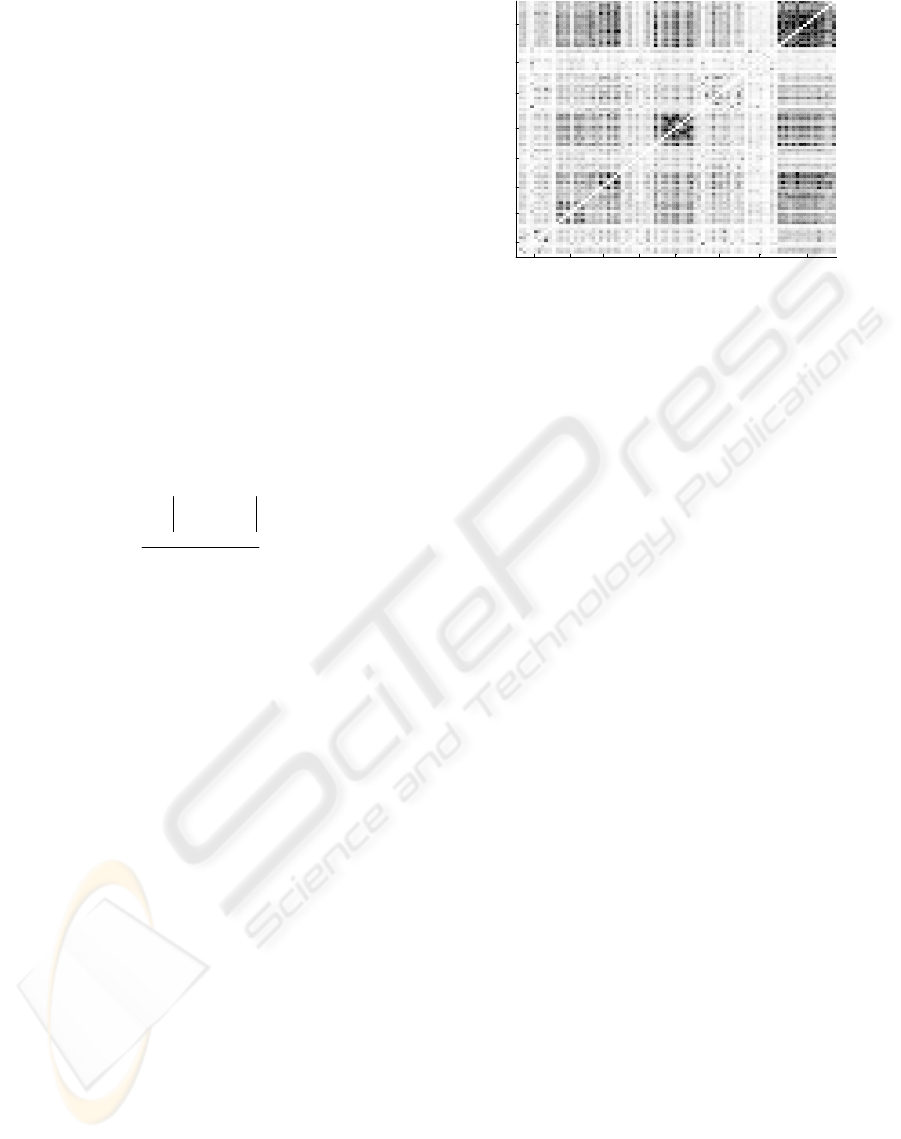
Calculating this parameter for all possible pairs
of stations, the matrix DS (composed of DS
ij
) can be
constructed. This matrix contains the relations
among all the wind patterns measured at the stations,
and it can be represented as figure 4 shows, grouped
by provinces. The order of grouping of the provinces
is Almería (Alm), Cádiz (Cad), Córdoba (Cor),
Granada (Gra), Huelva (Hue), Jaen (Jae), Málaga
(Mal), and Sevilla (Sev). The dark pixels are
associated to a low value of DS; therefore, they
connect stations with similar patterns. Thus, the
white cross observed over Málaga (Mal) stations
indicates that the most of them have not relations
with other stations, even if they are placed in the
same province. On the contrary, Huelva (Hue)
shows strong relations among the stations installed
in the area. Córdoba (Cor) presents the same pattern
in almost all the province, but this pattern is repeated
in Sevilla (Sev), as it is possible to infer from the
dark areas connecting these provinces. This fact
indicates that the classification of the stations
according to their provinces is not the best in order
to visualize the areas with a similar wind patterns.
The actual order of the matrix comes from
alphabetical and administrative criteria, but these
considerations have not relation with the concerned
problem, the wind classification. If the stations were
grouped according to the relations among them, by
Alm Cad Cor Gra Hue Jae Mal Sev
Alm
Cad
Cor
Gra
Hue
Jae
Mal
Sev
Figure 4: Representation, greyscale, of the matrix
composed of the values of DS for each pair of stations.
permutation of rows and columns of the matrix, the
relations and clusters could be clarified.
5 GENETIC ALGORITHMS
Genetic algorithms (GAs) have been recognized as
powerful approaches to solving optimization
problems. They are search algorithms based on
natural genetic and selection combining the concept
of survival of the fittest with a structured
interchanges, but aleatory of the information. These
concepts involve the preservation of the
characteristics of the best exponents of a generation
in the next generation; moreover introducing
aleatory changes in the new generation composition
by means of crossing over and mutation operations
(Lorena, 1997). One of the main advantages of GA
in opposite to the traditional search methods is that
this aleatory component prevents getting stuck into a
local maximum from which you can not escape to
reach a global maximum. Other advantage is its
utility of real time applications, in spite of not
providing the optimal solution to the problem it
provides almost the better solution in a shorter time,
including complex problems to solve by traditional
methods.
5.1 Ordering the Matrix DS with
Genetic Algorithms
Although the permutation of rows and columns to
put in order the DS matrix seems to be a simple
problem; the reality proves that this process could be
compared with a Rubik cube, since the order in a
part of the matrix could involve the disorder in other
one.
The result (or objective) of the recombination of
IDENTIFICATION OF AREAS WITH SIMILAR WIND PATTERNS USING SOFM
43

rows and columns must be a matrix in which the
stations with similar winds patterns and relations
will be neighbours, that is, the nearby elements of
the obtained matrix must be as similar as possible.
Figures 5a and 5b present two possible
recombination of the matrix represented in figure 4,
being the second one closer to the objective
explained before. To evaluate this idea of order, the
parameter p is proposed in equation 4, where p
0
, a
and b are constants related to the scale of the
problem. In this case p
0
= 25000, a = 100 and b =
415.
()
∑∑∑
=
=
−==
+⋅⋅=
88
1
3
3
88
1
0
1
j
k
ki
ijkijkij
BAF
p
p (4)
88
1
ji
F
ij
−
−=
)(
)( kjiij
ijk
DSDSa
a
A
+
++
=
b
DSDS
B
kjiij
ijk
)( +
−
=
Each column, j, which represents a station, is
compared with the six closer columns indexed by
j+k=j-3,...,j,...j+3, calculating two factors with their
i-th elements, A
ijk
and B
ijk
. The resulting value of A
ijk
+ B
ijk
is low when the sum of the elements is high
and the difference low. That is, nearby stations with
high similarities among them and with analogous
relations with the rest of the stations will contribute
with low values to the final result of p. The sum of
all these values, covering all the columns, gives an
objective measurement of the similarities among the
nearby columns and, therefore, an evaluation of the
global order of the matrix. For example the value of
p for the matrix shown in figure 4 is 0.902. As it was
expected, figures 5a and 5b obtain lower values
because they have been ordered in some sense.
Especially the combination represented in 5b
presents a very low value of p (p=0.843) which
indicates a high degree of similarity (or order).
Now the problem of ordering the matrix of
similarities has been reduced to find a combination
of stations with a minimum value of p. We propose
to solve this minimization problem using Genetic
Algorithms (GA). Each matrix of similarities can be
characterized by a vector of 88 elements containing
the position of the stations. This vector could be
considered as a genome which defines univocally
the associated matrix. Furthermore, using the value
of p calculated with these matrixes, a population of
0 20 40 60 80
0
20
40
60
80
0 20 40 60 80
0
20
40
60
80
Figure 5: a) Ordination of stations from sparsely related to
highly related (p=0.854). 5b) Ordination according to
subjective criteria of permutation (p=0.843).
these vectors could be tested and ranked. In these
conditions, GA could improve this population using
evolutive operators as crossover, mutation,
migration, etc., in order to obtain the minimum value
of p (Goldberg, 1989).
As it has been introduced upper, the vectors used
as genome of the matrixes contain 88 elements.
These elements are non repeated integer numbers
between 1 and 88, and each of them is associated to
one of the used stations. The positions of this
numbers in the vector define the position of the
stations in the matrix and, thus, the value of p for
this combination can be calculated. Because of the
properties of the genome used in this work, the
evolutive operator selected to produce the new
generations is the Recombination. Recombination
permutes one or more elements of the genome, thus,
the resulting vector is composed of 88 non repeated
integers again; avoiding the repetitions, decimals
and values out of range given by other operators.
6 RESULTS
The matrix selected by the GA as best combination
of stations, after 1000 generations and a population
of 10
5
individuals is represented in figure 6. This
0 10 20 30 40 50 60 70 80
0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
6
3
1
7
2
4
5
Figure 6: Representation, greyscale, of the matrix obtained
after applying the Genetic Algorithm where the main
clusters have been selected with numbered squares.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
44
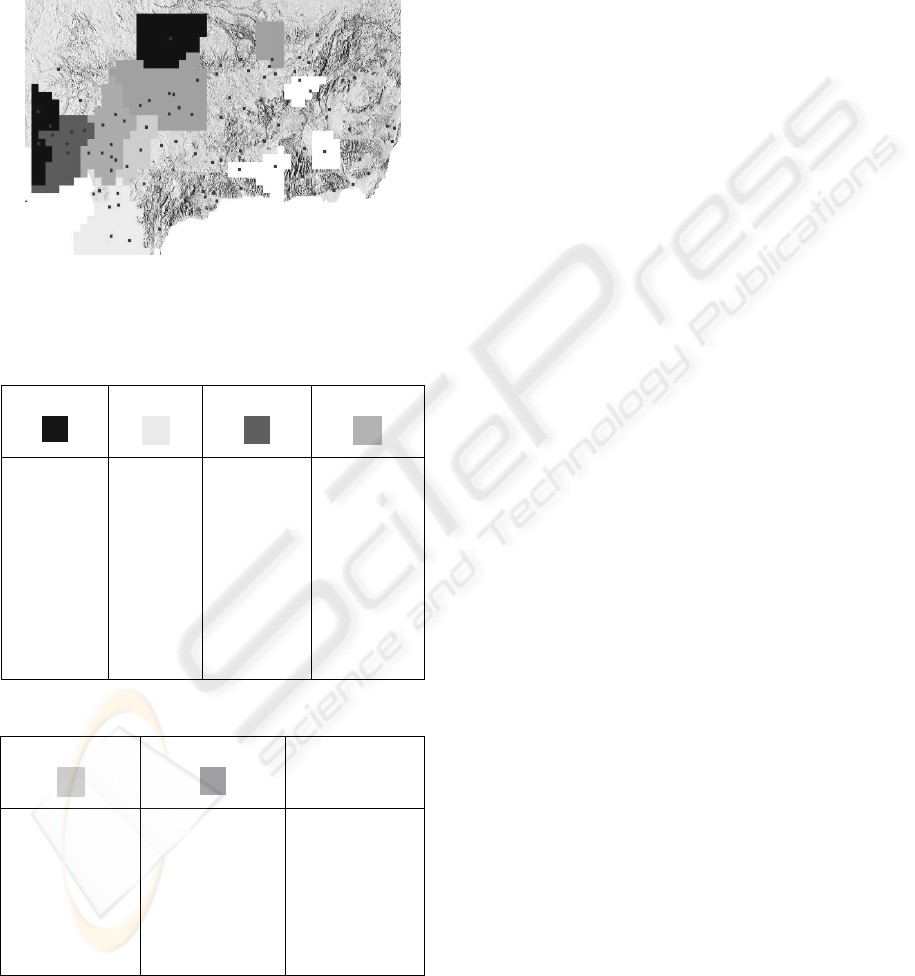
figure depicted the main clusters with squares and
the value of p associated to this matrix is 0.805.
Once we have selected the clusters are
represented in the study area. This is shown in figure
7 where it follows the same colour code. Tables 1
and 2 shows the information of the stations that have
been selected as cluster belongs.
Figure 7: Representation of study zone and the clusters
selected.
Table 1: Names selected stations in the clusters 1, 2, 3 and
4.
Cluster 1
Cluster 2
Cluster 3
Cluster 4
- Puebla
Guzmán
- Bélmez
- Gibraleón
- Lepe
- Conil
- Jerez
- Puerto
Santa Mª
- Vejer
- Basurta
- Moguer
- Cebollar
- Tojalillo
- Niebla
- Palma del
Condado
- Sanlúcar la
Mayor
- Guillena
- Almonte
- Rinconada
- Aznalcázar
- Puebla del
Río
- Lebrija
- Puebla del
Río II
- Isla Mayor
Table 2: Names selected stations in the clusters 5, 6 and 7.
Cluster 5
Cluster 6
Cluster 7
- Tomejil
- Los Molares
- Las Cabezas de
San Juan
- La Luisiana
- Palma del Río
- Écija
- Hornachuelos
- Lora del Río
- Santaella
- Córdoba
- Villanueva
- Linares
- Huesa
- Padul
- Zafarraya
- Fiñana
- San José de los
Propios
7 CONCLUSIONS
The results obtained demonstrate that the proposed
method is able to demarcate areas with analogous
wind patterns, even if the data acquired is affected
by low quality instruments or locations. In the same
way, erroneous stations, or stations not
representative of the wind climate in their zone, will
be identified since they will not be included in any
cluster. So, this tool could be useful in two aspects:
- In first steps of wind resource assessment,
when a preliminary description of the wind
climate in a zone is needed. Then, using the
information given by this matrix, it is possible
to associate the location of the target area with
an expected wind pattern.
- When a wind methodology, as Measure-
Correlate-Predict or the ones used in wind
temporal forecasting, needs support stations to
complete or extend the database used. In this
situation is very important to exclude stations
with errors or not representative of the studied
area because it could lead to important
differences between results and reality.
REFERENCES
Xiaozhe Wang, Kate Smith, Rob Hyndman, 2006.
Characteristic-Based Clustering for Time Series Data.
Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery. vol. 13,
number 3, pp. 335 – 364.
Kun-Lin, H., Cheng-Chang, J., I-Ching, Y., Yan-Kwang,
C., Chun-Nan, L., 2007. The study of applying a
systematic procedure based on SOFM clustering
technique into organism clustering. Expert Systems
with Applications: An International Journal. vol. 33,
pp. 330 – 336.
Varfis, A., Versino, C., 1992. Clustering of Socio-
Economic Data with Kohonen Maps. Neural Network
World. vol. 2(6), pp. 813 – 834.
Murtagh, F., Hernández-Pajares, M., 1995. The Kohonen
Self-Organizing Map Method: an Assessment. Journal
of Classification. vol. 12(2), pp. 165 – 190.
Ritter, H., Kohonen, T., 1989. Self-organizing semantic
maps. Biological Cybernetics. vol. 61, pp. 241 – 254.
Lorena, L.A.N., Lopes, L.S., 1997. Genetic algorithms
applied to computationally difficult set covering
problems. Journal of the Operational Research
Society. vol. 48, pp. 440 – 445.
Goldberg, D.E., 1989. Genetic Algorithms in Search,
Optimization and Machine Learning. Addison–Wesley.
Reading.
IDENTIFICATION OF AREAS WITH SIMILAR WIND PATTERNS USING SOFM
45
