
USING FUZZY SET APPROACH IN MULTI-ATTRIBUTE
AUTOMATED AUCTIONS
Madhu Goyal
Faculty of Engineering and Information Technology, UTS, Broadway, Australia
Saroj Kaushik
Indian Institute of Technology, Delhi, India
Keywords: Automated Auctions, Bidding Strategy, Fuzzy Sets, Software Agents.
Abstract: This paper designs a novel fuzzy attributes and competition based bidding strategy (FAC-Bid), in which the
final best bid is calculated on the basis of the assessment of multiple attributes of the goods and the
competition for the goods in the market. The assessment of attributes adapts the fuzzy sets technique to
handle uncertainty of the bidding process. The bidding strategy also uses and determines competition in the
market (based on the two factors i.e. no. of the bidders participating and the total time elapsed for an
auction) using Mamdani’s Direct Method. Then the final price of the best bid will be determined based on
the assessed attributes and the competition in the market using fuzzy reasoning technique.
1 INTRODUCTION
Online auctions (e.g. eBay and Amazon) are popular
market institutions for conducting transactions
between the buyers and the sellers. The software
agent technology is well known paradigm in on-line
auctions for buying and selling the goods. Software
agents provide automated assistance for trading
through the knowledge of the market and the
requirements of the market (Rahman and Robert
2001).The agents can use different auction
mechanisms (e.g. English, Dutch, Vickery etc.) for
procurement of goods or reaching agreement
between agents.
The agent makes decisions on
behalf of consumer and endeavours to guarantee the
delivery of item according to the buyer’s
preferences. In these auctions buyers are faced with
difficult task of deciding amount to bid in order to
get the desired item matching their preferences. The
bidding strategies for the software agents can be
static or it may be dynamic. The static agents may
not be appropriate for the negotiating market
situations like extent of competition may vary as
traders leave or enter into the market, deadlines and
new opportunities may increase the pressure. The
dynamic or we can say flexible negotiation
capabilities for software agents in the online
auctions have become a central concern (Murugesan
2000). Agents need to be able to prepare bids and
evaluate offers on behalf of the users they represent
with the aim of obtaining the maximum benefit (Ma
and Leung 2007) for their users according to the
changing market situation.
Much research has
already been done by the researchers to formulate
different bidding strategies according to the
changing market situations.
Strategies based on flexible negotiation agents
perform better as compared to the strategies based
on fixed negotiation agents (Kwang and Wang
2004). Faratin et al (Faratin, Sierra and Jennings
1998) developed strategies based on time, attitude,
resources, but many more factors such as
competition, trading alternatives are not considered.
In this paper we focus on the design of a novel
bidding strategy based on the above mentioned
factors to be used by the software agent in a online
auction. A fuzzy attributes and competition based
bidding strategy(FAC-Bid) is designed, in which the
final best bid is calculated on the basis of the
assessment of the attributes of the goods as well as
the competition for these goods in the market.
81
Goyal M. and Kaushik S. (2010).
USING FUZZY SET APPROACH IN MULTI-ATTRIBUTE AUTOMATED AUCTIONS.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Software Agents and Internet Computing, pages 81-85
DOI: 10.5220/0002897900810085
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 A FUZZY ATTRIBUTE AND
COMPETITION BASED
BIDDING STRATEGY
(FAC-BID)
In fuzzy attribute and competition based bidding
strategy (FAC-Bid) (Fig. 1), the factors which are
focused are assessing attributes of the goods and
competition for the goods in the market. For
estimation of the price for a bid for winning an
auction, the agent must have a balanced behaviour
between these factors i.e. the assessment of the
good’s attributes and finding the competition for the
goods in the market. The bidding price of the quality
goods is more as compared to the less quality goods.
Also the increasing competition for the goods in the
market increases the bidding price for that good.
The competition in turn depends on the number
of bidders and the time elapsed for the auction.
As the number of bidders increases, the competition
among them also increases, resulting in a higher
price. In the beginning of the auction the
competition is less and it increases as time elapses
and it is at the peak when time approaches
approximately in the middle of the auction period.
At the end of the auction period the competition
among the bidders decreases.
Current Bid New Bid
Figure1: A Fuzzy Bidding Strategy (FAC-Bid) Mode.
The steps of the design of fuzzy attribute and
competition based bidding strategy (FAC-Bid) are as
follows:
• First, each attribute is evaluated
• Then the assessment of all these attributes will
be aggregated to form an overall assessment of
the goods.
• next the level of competition as the function of
no. of bidders and time elapsed for the auction
will be found
• Finally the best bid is calculated on the basis of
the overall assessment of the good’s attributes
and the competition for the goods in the market.
In this paper we have used fuzzy set methods to deal
with the uncertainty, which exists during the
determination of overall assessment of the goods for
their attributes, the level of competition in the
market and to find the final bid price. First of all,
this paper uses a satisfactory degree measure as the
common universe of assessment, i.e., an assessment
is treated as a fuzzy set on the satisfactory degree.
Secondly, competition is expressed as a fuzzy set on
the fuzzy sets of the no. of bidders and the time
elapsed of the auction. Thirdly, bid displacement
factor for finding the final bid is expressed as a
fuzzy set on the fuzzy set of assessment of the
attributes and the competition for the goods in the
market.
2.1 Attribute Evaluation
The attribute evaluation is done in two parts (Goyal
and Ma 2009). The first one is individual attribute
assessment and the second one is assessment
aggregation. To implement attribute evaluation,
three issues are concerned i.e. attribute weights
(relative importance) adjustment, assessment
expression and assessment aggregation.
Weight Adjustment. Weight adjustment
implements dynamically change relative importance
of multiple criteria. In a real situation an agent’s
personal preference on the attributes seldom has
quickly fluctuation, i.e., the weights for criteria is
relatively stable in a long run. The adjustment of
weights resulted from the price should be limited to
a rational range. Moreover, the adjustment shouldn’t
change the relative significance among criteria other
than the price because raising price alters the relative
significance of it to other criteria. In the following,
the agent’s preference is treated as an initial weight
vector which is the basis of the adjustment. To
construe an initial weight vector, the Analytic
Hierarchy Process (AHP) method is applied because
it is proved validate in practice although it may
induce inner inconsistency. Suppose obtained initial
weight vector is W
(0)
.
Suppose the current bid p
c
belongs to [p
l
, p
u
]
where p
l
and p
u
are the lower and upper boundaries
Multi-attribute
Assessment
Competition
Assessment
Price Determination
Bid Server
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
82
of possible bids respectively which are determined
by the auction. Let C = {c
0
,c
1
, . . . , c
K
} be the set of
K +1 attributes and W = {w
0
,w
1
, . . . , w
K
} is the set
of weights for attributes in C. Because except the
price agent’s assessments on other criteria do not
change, the adjustment of weight for price should be
determined first. Suppose [−δ, δ] is the adjustable
range of the weight for price and the current net
increasing of weight for price is Δw
0
, then the
current weight vector is determined by
w’
0
=w
0
+Δw
0
(1)
1-w’
0
w’
k =
w
k
_________
1-w
0
(2)
where w
k
(k = 0,1, . . . ,K) is the component of W
(0)
..
Obviously,
∑ w
k
= 1 for k=0 to 1
(3)
and the relative significance of the criteria except for
the price will not change after this adjustment.
Assessment Expression. Since uncertain
expressions are often used in a real situation, this
paper uses linguistic terms to express assessments.
These linguistic terms are illustrated by fuzzy set.
Moreover, the universe of these fuzzy set are unified
to real interval [0,1] which means the satisfactory
degree of the agent to a particular attribute.
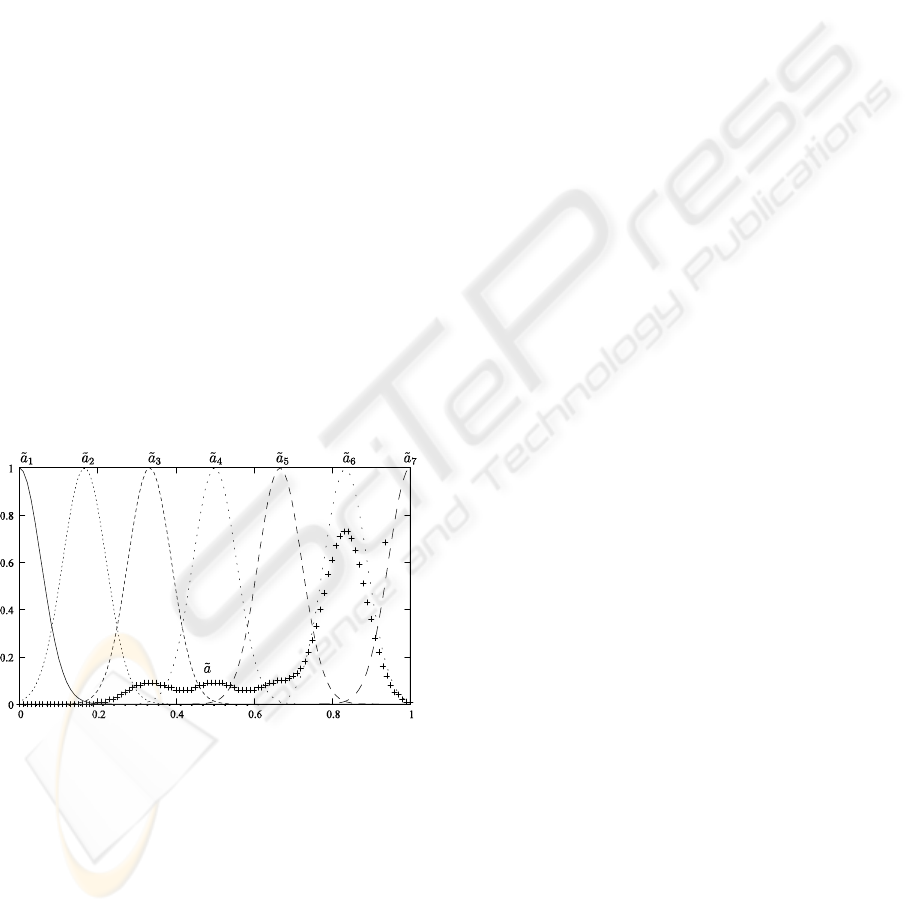
Figure 2: Obtain overall assessment.
Therefore, all fuzzy sets have same universe which
is convenient for aggregating assessments. Let g
k
(k
= 0,1, . . . ,K) is the satisfactory degree measure for
attribute c
k
. Then an agent’s opinion on the goods in
terms of attribute ck is denoted by g
k
(u) where u(א
U
k
) is the real attribute value of attribute c
k
and U
k
is
the real universe for attribute ck. For instance,
departing time is an attribute for a flight ticket. The
possible departing time in a day is from 0:00 to
23:59. For any time slot u, a client may present a
satisfactory degree such as departing at 7:30 is with
satisfactory degree 0.9 and departing at 3 : 00 is with
0.3. In the following, A = {a
1
, . . . ,a
n
} be the set of
used assessment terms which are fuzzy sets on
satisfactory degree [0,1]. Then a numeric
satisfactory degree is transformed to a linguistic
term. In the above example, suppose the assessment
set is as shown in figure 2. Notice that a7 is with the
biggest membership degree for 0.9, the assessment
for departing at 7:30 is a
6
by the maximum
membership degree principle. Similarly, the
assessment for 0.3 is a
2
.
Assessments Aggregation. An aggregated
assessment is the agent’s overall opinion/preference
on the goods in terms of multiple attributes. Take
booking a flight ticket for example, an assessment is
made on a ticket usually based on the airlines, flight
departure and arrival time, flight type, aircraft types,
seat positions, as well as price. The change of an
attribute’s value may leads to the alternation of an
assessment. Instinct natures of different attributes
increase the difficulty and uncertainty for obtaining
an overall assessment. Notice that an agent’s
preference on an individual attribute can be
expressed through the agent’s satisfactory degree on
that attribute. This paper uses an satisfactory degree
measure as the common universe of assessment.
Based on assessment on each individual attribute, an
overall assessment can be obtained as follows.
Suppose the individual assessments of all attributes
are v
0
, v
1
, . . . , v
K
and the weights of them are w
0
,
w
1
,. . ., w
k
respectively. Then an overall assessment
is obtained by
a = Agg{(v
0
,w
0
), (v
1
,w
1
), . . . , (v
K
, w
K
)}
(4)
where Agg is a selected aggregation method, v
k
א
A
(k = 0,1, . . . ,K) is the linguistic assessment on
attribute c
k
. To get an overall assessment in terms of
a set of criteria, an aggregation method Agg is
applied. Here we use the weighted-sum-based
method to obtain an overall assessment as follows.
First, we construct a fuzzy set ã on [0,1] through
ã(u) =
∑
wk ·vk(u), u
א
[0,1] for k= 0 to 1
(5)
where v
k(u) is the membership degree of u in vk.
Next, we calculate the distance between ã and a
i
א
A, by
d(ã,a
i
) =∫ | ã−a
i
|dλ. (6)
Finally, we select the nearest term(s) a to ã as the
overall assessment. For example, A has seven terms,
namely , a
1
,a
2
,…..a
7
as shown in figure 2. Suppose ã
is the obtained fuzzy set. By comparing the distances
between ã and each element in A, we know a
6
is the
USING FUZZY SET APPROACH IN MULTI-ATTRIBUTE AUTOMATED AUCTIONS
83

nearest item to ã. Hence , a
6
will be taken as the
overall assessment.
2.2 Competition Assessment
The level of competition in an auction may be
captured by the number of bidders and the time
elapsed. Competition among bidders plays an
integral role in price formation (Reddy and Dass
2006). As the number of bidders increases, the
competition among them also increases, (Fig. 3)
resulting in a higher price. Bapna, Jank and Shmueli
found the number of bidders to be positively
associated with the current price of the item.
Furthermore, it is observed that, typically, the
middle of the auction experiences a smaller amount
of bidder participation as compared to the early and
later stages of the auction. Bidders generally utilize
this time to scrutinize the auctioned item or just
simply wait to see how other bidders behave.
Therefore, it would be interesting to see how this
competition characteristic affects the on-line
auction’s price formation. We anticipate that the
number of bidders has a significant positive
relationship with price levels. In the beginning of the
auction the competition is less and it increases as
time elapses and it is at the peak when time
approaches approximately in the middle of the
auction period. At the end of the auction period the
competition among the bidders decreases (Fig. 4).
Figure 3: Competition versus Number of Bidders.
Here we will describe the competition factor in
terms of no. of bidders (b) and the total time elapsed
(t) for the auction of items. We will consider the
competition as a set fuzzy set of values c
1
,c
2
,……c
n
,
no. of bidders B as a fuzzy set of values y
1
,y
2
……y
n
.
And the time elapsed as another fuzzy set T of
values x
1
,x
2
,…..x
n
. According to Mamdani’s Direct
Method (Tanaka 1991) we can find adaptability n
no. of rules w
1
, w
2
,…….w
n
as
w
i
=µx
i
(T) ٧ µy
i
(B) for i=1 to n
Then the conclusion of each rule can be found as
µc’
i
(C) =w
i
٧ µc
i
for i=1 to n
These conclusions can be aggregated to find the
final conclusion
µc (C) =µc’
1
(C) ^µc’
2
(C) ^…………^ µc’
n
(C)
To find the definite value for the conclusion, here
centre of gravity of the fuzzy set has been applied as
follows
∫µz (C) CdC
C= __________
∫µz (C) dC
(7)
Figure 4: Competition versus Time Elapsed.
2.3 Agent Price Determination
Price of the goods depends on the assessed attributes
of the goods and the competition in the market for
that good. If the assessment of the attributes of the
goods is good and also competition for that product
in the market is high then the price of the item is
high. If the assessment of the attributes of the goods
bad and competition is also low then the price for
that item is obviously be low. If the attribute’s
assessment is good and the competition is low then
the price is going to be medium and so on.
We can calculate the price of the good based on
the assessed attributes and the competition
determined which is based on the no. of bidders and
time elapsed for the auction by applying Mamdani’s
Method for fuzzy relations and compositional rule of
inference (Tanaka 1991). Here we will describe the
price of goods in terms of assessment of the
attributes of the goods and competition in the market
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
84

for that good. We will consider bid displacement
factor ΔP as a fuzzy set of values p
1
,p
2
,……..p
n
,
assessment of the attributes A as a fuzzy set of
values a
1
,a
2
………a
n
and competition C as a fuzzy
set of values c
1
,c
2
,……..c
n
. According to Mamdani’s
Method for fuzzy relations and compositional rule of
inference the rule a
i
and cj→ pk can described by
µR(A,C,ΔP)= µa
i
(A)^ µc
j
(C )^ µp
k
(ΔP)
(8)
For n no. of rules, the compiled fuzzy relation R is
given as
R=R
1
UR
2
U……………..UR
n
For the input of fuzzy set A’ on A and fuzzy set C’
on C , the output fuzzy set ΔP’ on ΔP can be
obtained as follows
ΔP’=(A’andC’)o R=A’o (C’ oR)= C’o(A’oR)
(9)
And then the final price for the bid will be Final
bid= Current bid + ΔP’
3 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have designed a fuzzy attribute and
competition based bidding strategy (FAC-Bid),
which uses a soft computing method i.e. fuzzy logic
technique to compute the final bid price based on the
assessment of the attributes and the competition in
the market. Another unique idea presented in this
paper is that to deal quantitatively the imprecision or
uncertainty of multiple attributes of items to acquire
in auctions, fuzzy set technique is used. The bidding
strategy also allows for flexible heuristics both for
the overall gain and for individual attribute
evaluations. Specifically, the bidding strategy is
adaptive to the environment as the agent can change
the bid amount based its assessment of the various
attributes of item, and the competition in the auction
.The competition is calculated based on the number
of bidders and the time elapsed for the auction. It
was noticed that the strategies in which agent’s
behaviour depends on attributes and competition, are
easily adaptable to the dynamic situations of the
market. In future we will investigate about the
development of the bidding strategies for multiple
auctions. We will also compare our bidding
techniques with the other strategies to find out the
relative strengths and the weaknesses.
REFERENCES
Rahman, S. M, Robert J., 2001: Internet Commerce and
Software Agents: Cases, Technologies Opportunities,
Idea Group Publishing.
Murugesan, S., 2000.Negotiation by Software agents in
Electronic Marketplace, in:TENCON’00, Proceedings
of the 2000 IEEE Region 10 Conference on Intelligent
Systems and Technologies for the new Millennium,
Kuala Lumpur, Malaysia, pp.286--290.
Ma, H. Y., Leung, H. F., 2007: An Adaptive Attitude
Bidding Strategy for Agents in Continuous Double
Auctions. Electronic Commerce Research
Applications, 6 (4). Elsevier, 383—398.
Kwang, S. M., Wang, S. Y., 2004 In IEEE Transactions
on Systems, Man and Cybernetics- Part B:
Cybernetics. Vol.34, No.3.
Faratin, P., Sierra, C. and Jennings, N. R., 1998.
Negotiations decision functions for autonomous
agents, In International Journal of Robot Autonomous
System, Vol. 24, no.3, pp 159--182,.
Goyal, M. L., Jun, M., 2009. Using Agents’ Attitudes and
Assessments in Automated Fuzzy Bidding Strategy.
Proceeding of First International Conference on
Agents and Artificial Intelligence, Porto, Portugal.
Reddy, S. K., Dass, M., 2006.Modeling On-Line Art
Auction Dynamics Using Functional Data Analysis
Statistical Science Vol. 21, No. 2, 179--193 Institute
of Mathematical Statistics.
Bapna, R., Jank, W. and Shmueli, G., 2004. Price
formation and its dynamics in online auctions.
Working paper RHS-06-003, Smith School of
Business, Univ. Maryland (2004).
Tanaka, K., 1991. An Introduction to Fuzzy Logic for
Practical Applications, Axel Springer Verlag.
USING FUZZY SET APPROACH IN MULTI-ATTRIBUTE AUTOMATED AUCTIONS
85
