
TOWARDS THE FORMALISATION OF THE TOGAF CONTENT
METAMODEL USING ONTOLOGIES
Aurona Gerber, Paula Kotz´e and Alta van der Merwe
Meraka Institute of the CSIR, Pretoria, School of Information Technology, North-West University, Pretoria, South Africa
Keywords:
Formal ontologies, TOGAF content metamodel, Enterprise architecture, Conceptual model, Metamodel.
Abstract:
Metamodels are abstractions that are used to specify characteristics of models. Such metamodels are gen-
erally included in specifications or framework descriptions. A metamodel is for instance used to inform the
generation of enterprise architecture content in the Open Group’s TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel description.
However. the description of metamodels is usually done in an ad-hoc manner with customised languages and
this often results in ambiguities and inconsistencies. We are concerned with the question of how the quality
of metamodel descriptions, specifically within the enterprise architecture domain, could be enhanced. There-
fore we investigated whether formal ontology technologies could be used to enhance metamodel construction,
specification and design. For this research, we constructed a formal ontology for the TOGAF 9 Content Meta-
model, and in the process, gained valuable insight into metamodel quality. In particular, the current TOGAF
9 Content Metamodel contains ambiguities and inconsistencies, which could be eliminated using ontology
technologies.
In this paper we argue for the integration of formal ontologies and ontology technologies as tools into meta-
model construction and specification. Ontologies allow for the construction of complex conceptual models, but
more significant, ontologies can assist an architect by depicting all the consequences of a model, allowing for
more precise and complete artifacts within enterprise architectures, and because these models use standardized
languages, they should promote integration and interoperability.
1 INTRODUCTION
Dijkstra (2001) introduced the concept of a model into
computer science in the early ’70s. Models were rec-
ommended to simplify unmastered complexity. He
argued that the programmer and his mind are an im-
portant part of the computing process and that modu-
larised, goto-less programs lead to more efficiency in
the use of the computer. In order to create these mod-
ularised, goto-less programs, it was necessary to con-
struct models (Weiner, 1978). Avison and Fitzgerald
(2003) define a model as an abstraction and represen-
tation of part of the real world. Within this context,
abstraction means the process of stripping an idea or
a system of some concrete or physical features in or-
der to create a simplified representation of a complex
application. The true value of any model thus lies in
the fact that it is an abstraction or representation of re-
ality, which is useful for analytical purposes (Lippitt,
1973).
When using models, it is possible to represent va-
rious levels of system abstraction within different con-
texts. A model thus provides a way of viewing the
important aspects of a system at a specific level of
abstraction and within a specific context in such a
way that higher levels depict the essence of the sys-
tem and the lower levels show detail that does not
compromise the essence. An example of the this is
the popular Zachman Framework for enterprise archi-
tecture (Zachman, 2003). Zachman defined a frame-
work that defines the logical structure of models and
other descriptive representations necessary to clas-
sify and organise an enterprise. The Zachman frame-
work defines six different contexts or dimensions, and
within each dimension, different levels of abstraction
are specified.
In addition to models, metamodels is yet another
abstraction that is used to specify characteristics of
models. A model generated from a metamodel would
conform to the metamodel in the way that a com-
puter program conforms to the grammar of its pro-
gramming language (Pidcock, 2002). Common uses
54
Gerber A., Kotzé P. and van der Merwe A. (2010).
TOWARDS THE FORMALISATION OF THE TOGAF CONTENT METAMODEL USING ONTOLOGIES.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Artificial Intelligence and Decision Support Systems, pages
54-64
DOI: 10.5220/0002903200540064
Copyright
c
SciTePress

for metamodels are 1) a schema for semantic data
that needs to be exchanged or stored; 2) a language
that supports a particular method or process, and 3)
a language to express additional semantics of exist-
ing information (B´ezivin, 2003; Pidcock, 2002; Ernst,
2002). Metamodels are generally used in specifica-
tions or frameworks to describe models. For exam-
ple, TOGAF 9 uses a metamodel in its Content Meta-
model description to inform the generation of enter-
prise architecture content (The Open Group, 2009b),
the OMG (Object Management Group) uses meta-
models in specifications such as SPEM (Software
Process Engineering Metamodel) (OMG, 2008), and
HL7 (Health Level Seven, Inc. - the global authority
on standards for interoperability of health information
technology) specified the HL7 RIM (Reference Infor-
mation Model) as part of HL7 Version 3 (HL7, 2009;
Yang et al., 2009). HL7 RIM specifies the grammar of
HL7 V3 messages and specifically, the basic building
blocks of the language (nouns, verbs etc.), their per-
mitted relationships and data types (Benson, 2009).
The use of metamodels gained importance due to
the prolific growth of web-based and distributed ap-
plications. Metamodels are used to define the stan-
dards necessary for interoperability between applica-
tions and integration of systems. However, often these
metamodels are unclear and ambiguous and this de-
feats the purpose of using a metamodel at all. For ex-
ample, after the release of TOGAF 9, Walker (2009)
comments that the Content Metamodel is too high
level:
’TOGAF 9 does a great job at exploring the
architecture metamodel at a high level. There
needs to be a level or two deeper of consider-
ation here. I was looking for more detail...’
In another example, Adrian Campbell (2009)
comments:
’It’s great to finally see a metamodel pub-
lished with TOGAF 9. However for me the
centrality of Business Service concept seems
a bit wrong somehow. In some TOGAF 9 di-
agrams there is a confusion between Business
Service and Application Service...’
’There is also a confusion in TOGAF 9 with
the concept Function...’
’In TOGAF 9 there is much discussion of Ca-
pability, but in the metamodel this concept
seems to hang on it’s own somewhat...’
This paper is concerned with the question of how
metamodels, specifically within the enterprise archi-
tecture domain, could be enhanced with regards to
ambiguity and clarity. Specifically we investigate
whether ontology technologies could be used to en-
hance metamodel construction, specification and de-
sign.
Ontologies made an appearance within Computer
Science during the past ten to fifteen years. This
is mainly due to advances in reasoning and model-
ing technologies. Roughly speaking, an ontology for-
mally describes a domain model in a way that attaches
meaning to the terms and relations used for describ-
ing the domain. A more formal and widely used defi-
nition is that of Gr¨uber (1993)) who defines an ontol-
ogy as a formal specification of a conceptualisation.
The importance of this technology is evidenced by the
growing use of ontologies in a variety of application
areas, and is in line with the view of ontologies as the
emerging technology driving the Semantic Web ini-
tiative (Berners-Lee et al., 2001).
Ontologies allow for the construction of complex
models, but more significant, ontologies can assist
a modeler by depicting all the consequences of her
model. Formal ontology technologies also allow a
modeler to view and understand the implicit conse-
quences of explicit statements and can help to en-
sure that a model is consistent. With regards to the
use of ontology technologies for metamodel construc-
tion, not a lot has been published. Pidcock (2002) de-
scribes the relationship between a metamodel and an
ontology as close, but not necessarily equivalent:
’IF: you create an ontology, which is a set
of terms naming concepts (classes) and rela-
tions, and you use that vocabulary to create a
set of data (instances of the classes, and as-
sertions that the instances are related to each
other according to the specific relations in the
vocabulary), and you think of the set of data
you create as the model of your domain
THEN: the ontology is the meta-model and the
set of data created is the model.’
The above statement enforced our notion that an
ontology could be used for a metamodel description,
and if successful, coherent and consistent models
could be constructed from the metamodel using on-
tology technologies. In this paper we want to argue
for the integration of formal ontologies and associated
technologies as mechanisms for metamodel develop-
ment and specification. In particular, we develop an
ontology for the TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel as ex-
ample to show that formal metamodel descriptions are
clear and less ambiguous.
The paper is structured as follows: Section 2 will
provide background information on ontologies in 2.1
and enterprise architectures and TOGAF in Section
2.2. Section 3 describes the case study where we con-
structed a formal ontology for the TOGAF 9 Content
Metamodel. Section 4 discusses our findings, as well
TOWARDS THE FORMALISATION OF THE TOGAF CONTENT METAMODEL USING ONTOLOGIES
55

as perceived advantages and disadvantages, and the
paper concludes in Section 5.
2 BACKGROUND
This section provides some background on ontologies
(Section 2.1), and then on enterprise architectures and
TOGAF (Section 2.2).
2.1 Ontologies
A formal ontology specifies a machine-readable vo-
cabulary in computer systems technology descrip-
tions. Generally such an ontology is defined as a
shared, formal, explicit specification of a conceptual
model of a particular domain (Broekstra et al., 2001;
Decker et al., 2000). A formal ontology typically
describes a hierarchy of resource concepts within a
domain and associates each concept’s crucial proper-
ties with it. Ontologies are used to define and man-
age concepts, attributes and relationships in a precise
manner (Bussler et al., 2002).
The concept of an ontology was inherited from
philosophy and only recently became commonplace
in computer systems technology descriptions where
an ontology specifies a machine readable vocabu-
lary (Palmer, 2001). The term ontology has become
widespread within ICT and is used at present to refer
to anything from a taxonomy, a domain vocabulary
and a conceptual model, to a formal ontology. Lassila
and McGuinness (2001) gave a spectrum of ontolo-
gies as depicted in Figure 1. Even Zachman refers
to his enterprise architecture framework as an ontol-
ogy, but this is in the sense that it depicts a conceptual
model of the architecture models necessary to depict
an enterprise (Zachman, 2003).
Figure 1: Ontologies may be viewed as a spectrum of detail
in their specification (Lassila and McGuinness, 2001).
The construction and maintenance of formal on-
tologies greatly depend on the availability of ontol-
ogy languages equipped with a well-defined seman-
tics and powerful reasoning tools. Fortunately there
already exists a class of logics, called description log-
ics or DLs, that provide for both, and is therefore the
ideal candidate for ontology languages (Baader et al.,
2003). That much was already clear fifteen years ago,
but at that time, there was a fundamental mismatch
between the expressive power and the efficiency of
reasoning that DL systems provided, and the expres-
sivity and the large knowledge bases that ontologists
needed. Through the basic research in DLs of the last
fifteen years, this gap between the needs of ontolo-
gists and the systems that DL researchers provide has
finally become narrow enough. Due to these advances
in DL research, there is growing interest in the use
of ontologies and related semantic technologies in a
wide variety of application domains. Arguably the
most successful application area in this regard is the
biomedical field (Wolstencroft et al., 2005; Hahn and
Schulz, 2007). Some of the biggest breakthroughs in
ontological reasoning can be traced back to the pi-
oneering work of Horrocks (2007), who developed
algorithms specifically tailored for medical applica-
tions. These advances have made it possible to per-
form standard reasoning tasks on large-scale medical
ontologies such as SNOMED CT—an ontology with
more than 300 000 concepts and more than a million
semantic relationships—in less than half an hour; a
feat that would have provoked disbelief ten years ago
(Suntisrivaraporn et al., 2007).
The Web Ontology Language OWL is based on a
family of expressiveDLs. OWL was accorded the sta-
tus of a World Wide Web Consortium (W3C) Recom-
mendation in 2004 and is the official Semantic Web
ontology language (W3C, 2006; McGuinness and van
Harmelen, 2004). One of the consequences of the
standardisation of OWL by die W3C is the develop-
ment of several tools and reasoners that support the
development of formal ontologies based on the OWL
standard. Notable ontology editors are Prot´eg´e 4 and
SWOOP (Prot´eg´e, 2009; SWOOP, 2009). Reason-
ers provide computable and complete reasoning for
OWL ontologies, and some are integrated into the
ontology editors. Notable reasoners are Fact++ and
Pellet (Fact++, 2009; Pellet, 2009). A summary of a
substantial number of Semantic Web tools, including
OWL ontology editors and reasoners, can be found at
http://esw.w3.org/topic/SemanticWebTools
.
From the above it is clear that, even though several
of these tools are still under development, the mo-
mentum generated will soon ensure that formal on-
tologies with their supporting technologies and tools
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
56

enter mainstream modeling applications and the use
of ontologies for metamodeling should result in valu-
able advantages.
When we use the term ontology in this paper, we
mean a formal ontology based on one of the OWL
standards which is DL-based.
2.2 Enterprise Architecture and
TOGAF
The term enterprise architecture (EA) originated from
the thinking around both the terms ’business’ and ’ar-
chitecture’. EA describes the business process of IT
by creating a relationship between the IT structure
that is used in the organization and in each specific
system, also ensuring that business and IT are aligned
with business strategy and policy (Kim et al., 2005;
Rood, 1994). Enterprise is thus an holistic term for
’business entity’ in all its facets.
Probably the most widely adopted definition for
enterprise architecture (EA) is the IEEE definition
where EA is described as a widely adopted means for
coping with organizations’ ever-increasing complex-
ity and for ensuring that organizations appropriately
use and optimize their technical resources. EA is an
integrated and holistic vision of a system’s fundamen-
tal organization, embodied in its elements (people,
processes, applications, and so on), their relationships
to each other and to the environment, and the princi-
ples guiding its design and evolution (IEEE, 2000).
The definition that is preferred by the authors is
defined by the Enterprise Architecture Research Fo-
rum (EARF, 2009), which states that ’Enterprise ar-
chitecture is the continuous practice of describing the
essential elements of a sociotechnical organization,
their relationships to each other and to the environ-
ment, in order to understand complexity and manage
change’.
In 1997 John Zachman already coined enterprise
architecture as the issue of the century, mainly be-
cause it is primarily concerned with bridging the
gap between strategy and implementation, and mak-
ing sure business activities are aligned (Zachman,
1997). Recent activities and the adoption rate of en-
terprise architecture within industry. government and
academia indicate fast growing interest in enterprise
architecture as a practice, or even a discipline (Kaisler
et al., 2005; Ernst et al., 2006). Notable is the adop-
tion by various governments of enterprise architecture
frameworks as a mechanism for interoperability and
alignment between policy and practice (Janssen and
Hjort-Madsen, 2007; GITOC, 2009). Another recent
example of government enterprise architecture adop-
tion is the South African government that is now the
first public sector entity to formally adopt and adapt
TOGAF 9 for enterprise architecture (EA) delivery in
government. The framework that resulted is referred
to as the Government Wide Enterprise Architecture
(GWEA) Framework (GITOC, 2009).
TOGAF is an acronym for The Open Group
Architecture Framework. It is described by The Open
Group as ’a comprehensive architecture framework
and methodology which enables the design, evalua-
tion and implementation of the right architecture for
an enterprise’. The Open Group is a vendor- and
technology-neutral consortium focused on a diverse
range of open standards and affiliated certification
programmes, and also the advancement of the enter-
prise architecture profession. TOGAF was developed
through the collaborative efforts of 300 Architecture
Forum member companies from some of the world’s
leading IT customers and vendors, and it currently
maintained as a standard by The Open Group. TO-
GAF is seen as one of the four most popular meth-
ods used in enterprise architecture (The Open Group,
2009a; Session, 2007). The most recent version of
TOGAF, TOGAF 9, is at present regarded as an ac-
ceptable industry standard for enterprise architecture
development due to factors such as listed below (The
Open Group, 2009b; Walker, 2009):
• TOGAF has logged more than 90,000 downloads
proving at least significant interest. All documen-
tation for TOGAF is published online.
• In 2009 there were over 8,491 certified TOGAF
practitioners.
• There are more than 180 corporate members of
The Open Group Architecture Forum.
• In 2009 over 20,000 TOGAF series books were
shipped.
• The online forum Association of Open Group En-
terprise Architects has had a significant impact
and it membership is at more than 8,500.
The first version of TOGAF was released in 1995.
TOGAF 7 (’Technical Edition’) was published in De-
cember 2001, TOGAF 8 (’Enterprise Edition’) was
first published in December 2002 and updated and
republished TOGAF 8.1 in 2003 and TOGAF 8.1.1
2006. The latest version is TOGAF 9, launched on 2
February 2009 (The Open Group, 2009a).
One of the enhancements introduced by TOGAF
9 is the introduction of a Content Metamodel. The
TOGAF 9 manual states ’The core metamodel pro-
vides a minimum set of architectural content to sup-
port traceability across artifacts. Additional meta-
model concepts to support more specific or more in-
depth modeling are contained within a group of ex-
tensions that logically cluster extension catalogs, ma-
trices, and diagrams, allowing focus in areas of spe-
TOWARDS THE FORMALISATION OF THE TOGAF CONTENT METAMODEL USING ONTOLOGIES
57

cific interest and focus’. The core metamodel entities
are based on the terminology used to define the TO-
GAF architecture development method (ADM) as ba-
sis. All the extension entities added to the metamodel
are optional and should be selected during the prelim-
inary phase of the architecture development to meet
the needs of the organization. This core and exten-
sion concept is intended as a move towardssupporting
formal method extension approaches within TOGAF
(The Open Group, 2009b).
Given the importance and adoption of TOGAF 9
for enterprise architecture development, the TOGAF
Content Metamodel will be play a crucial role in the
future of enterprise architecture development. How-
ever, as indicated, metamodels are often ambiguous
and unclear even though they sometimes use a stan-
dard language such as UML for their description. The
TOGAF Content Metamodel is no exception. Even
though it seems to be using a variant of the UML class
diagram, this is not stated explicitly anywhere. We
will however use UML notation to interpret its mean-
ing.
3 USING A FORMAL ONTOLOGY
TO MODEL THE TOGAF 9
CONTENT METAMODEL
In this section we discuss the developmentof an OWL
2.0 ontology using the latest versions of Prot´eg´e 4 for
the TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel.
3.1 Approach
The steps followed were roughly based on the on-
tology engineering methodology defined by Horridge
(2009) and the steps followed include:
1. Identification of the concepts and concept hierar-
chy.
2. Identification of the disjoint concepts.
3. Modeling composition.
4. Addition of all the relationships between con-
cepts.
5. Identification of definitions.
6. Addition of annotations.
7. Refinement of the ontology through various itera-
tions of the above steps.
We used Prot´eg´e 4 to develop an OWL 2.0 on-
tology for this metamodel. We used Build 112
of Prot´eg´e 4 on a laptop with Ubuntu 9.10. The
level of the ontology engineer could be described as
intermediate-advanced if we define three levels: be-
ginner, intermediate and advanced. During the exe-
cution of the above mentioned steps, numerous am-
biguities and unclarities were encountered and cer-
tain modeling decisions were made in the ontology
in order to have an unambiguous, clear and consistent
model description. It is also noteworthy that we re-
fined the model by executing various iterations of the
abovesteps, and not necessarily in the same sequence.
During modeling both reasoners included in Prot´eg´e 4
(Fact++ and Pellet 1.5) were used constantly to de-
bug the ontology and ensure consistency. Problems
encountered, modeling decisions, as well as our solu-
tions are discussed according to the mentioned steps
in the next section.
The complete TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel with
entities and their relationships as specified in TOGAF
9 is depicted in Figure 2. We added some numbering
for reference purposes.
3.2 Experience
In this section our experience with the construction
of the TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel ontology is dis-
cussed with regards to the different steps in the ap-
proach.
Step 1: Identification of the Concepts and Con-
cept Hierarchy. Initially the execution of this step
seems straightforward as each object in the Meta-
model would translate into a concept. However, fur-
ther investigation shows that the model is not triv-
ial. The Metamodel consists of a multi-layer diagram
not adhering to any specific notation (UML class di-
agrams does not support multi-layer diagrams other
than packages). In a multi-layer diagram, classes such
as Organization and Driver (indicated by (1) in Figure
2) are on top of the block indicating the Business Ar-
chitecture (indicated by (2) in Figure 2). In addition,
colours of classes are used to indicate specific features
such as the content extensions (see (3) in Figure 2).
When constructing an ontology, we are concerned
with concept hierarchies, so we will be identifying
more general concepts from the information avail-
able. We therefore defined a concept Architecture-
Component as a superconcept of all the architecture
classes depicted in the metamodel. In addition, the
concept Architecture was defined as a superconcept
and the four types of architectures depicted, namely
BusinessArchitecture, DataArchitecture, Application-
Architecture and TechnologyArchitecture, were added
as subconcepts. Subconcepts for ArchitectureCom-
ponent concept were defined to represent the compo-
nents of the different architectures.
The meaning of top block in the metamodel is un-
clear. It is labeled ARCHITECTURE PRINCIPLES, VI-
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
58
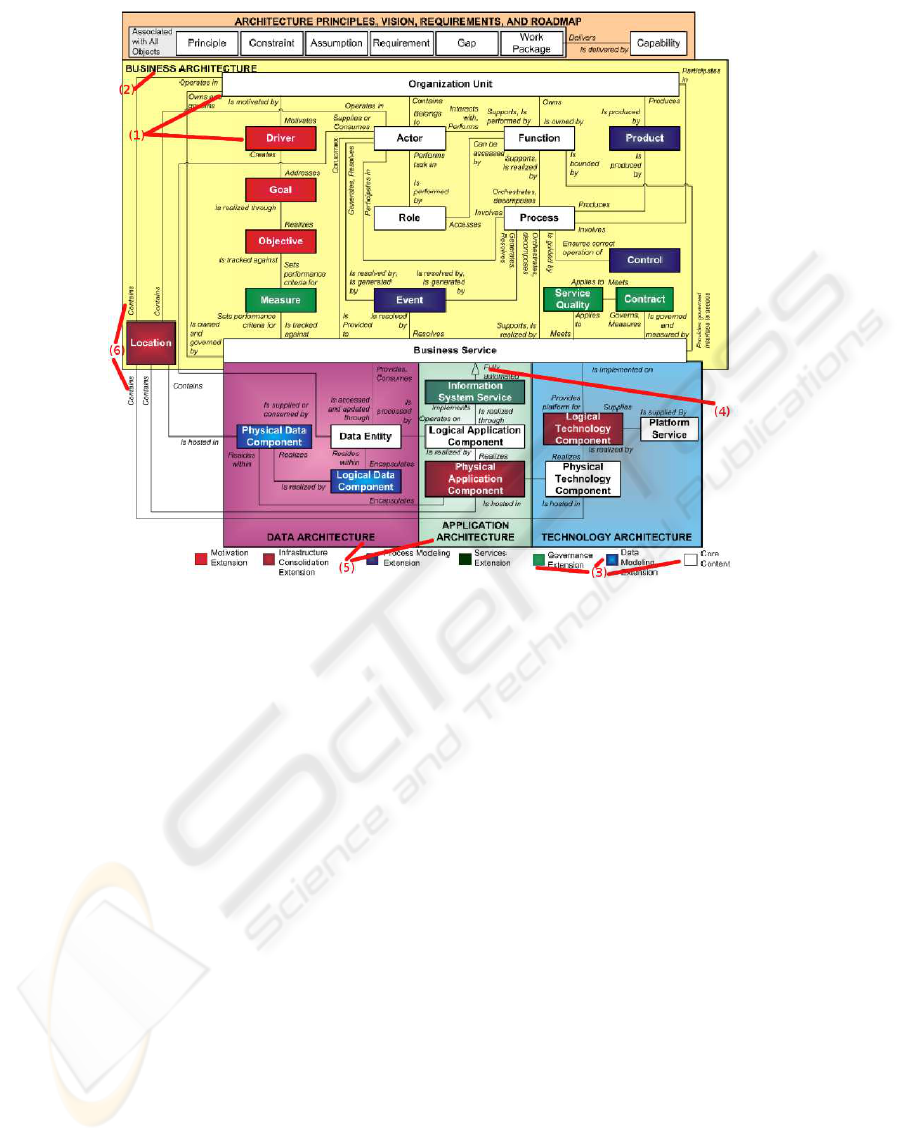
Figure 2: The TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel (The Open Group, 2009b). The numbering is our own.
SION, REQUIREMENTS, AND ROADMAP. It is there-
fore clearly not an architecture even though it, to-
gether with its components, are depicted in a similar
manner as the other architectures in the model. The
components are also not named according to the list
in the label: refer to, for example, VISION in the la-
bel and Gap or Constraint components. In addition,
the first six components are blocked together with a
label Associated with all objects, but Capability is not
included. It is not clear whether all architecture com-
ponents must have these objects associated with them
or whether they may have associations with these ob-
jects. We made a modeling decision to model these
objects as AssociationObjects, and the superconcept
AssociationObject have subconcepts Principle, Con-
straint, etc.
Another interesting characteristic of the meta-
model is Information System Service which is indi-
cated as being a subclass of Business Service. This
is identified by number (4) in Figure 2. In our ontol-
ogy we made the concept InformationSystemService
a subconcept of the concept BusinessService.
Lastly, we addressed the colour coded content ex-
tensions ((3) in Figure 2). We defined a concept Con-
tentClassification and modeled the Core Content and
all the extensions as subconcepts. Subsequently, we
used multiple inheritance to state that all architecture
components and association objects are also subcon-
cepts of the ContentClassification concepts. This cap-
tures the meaning of the colour coded concepts that
are architecture components but also adhere to some
content classification criteria. In Figure 4, the arrows
depict concepts that have both CoreContent and Busi-
nessArchitectureComponent as superclasses.
We used both reasoners included in Protg´eg´e 4
(Fact++ and Pellet 1.5) to ensure that the concept hier-
archy is consistent. The concept hierarchy is partially
depicted in Figure 3.
Step 2: Identification of Disjoint Concepts. Dur-
ing this step we specifically stated disjointness in the
ontology. This is a specific feature of DL based on-
tologies that disjointness of concepts should be ex-
plicitly stated, otherwise concepts may be the same
or partially the same as other concepts. Generally, in
UML diagrams, classes are assumed to be disjoint.
Therefore we defined all association objects, archi-
tecture components and architectures to be disjoint
among themselves and at superconcept level. An ar-
chitecture component, for instance, is clearly not an
architecture, and a data architecture not a application
architecture.
Because of the multiple parent model we used for
TOWARDS THE FORMALISATION OF THE TOGAF CONTENT METAMODEL USING ONTOLOGIES
59
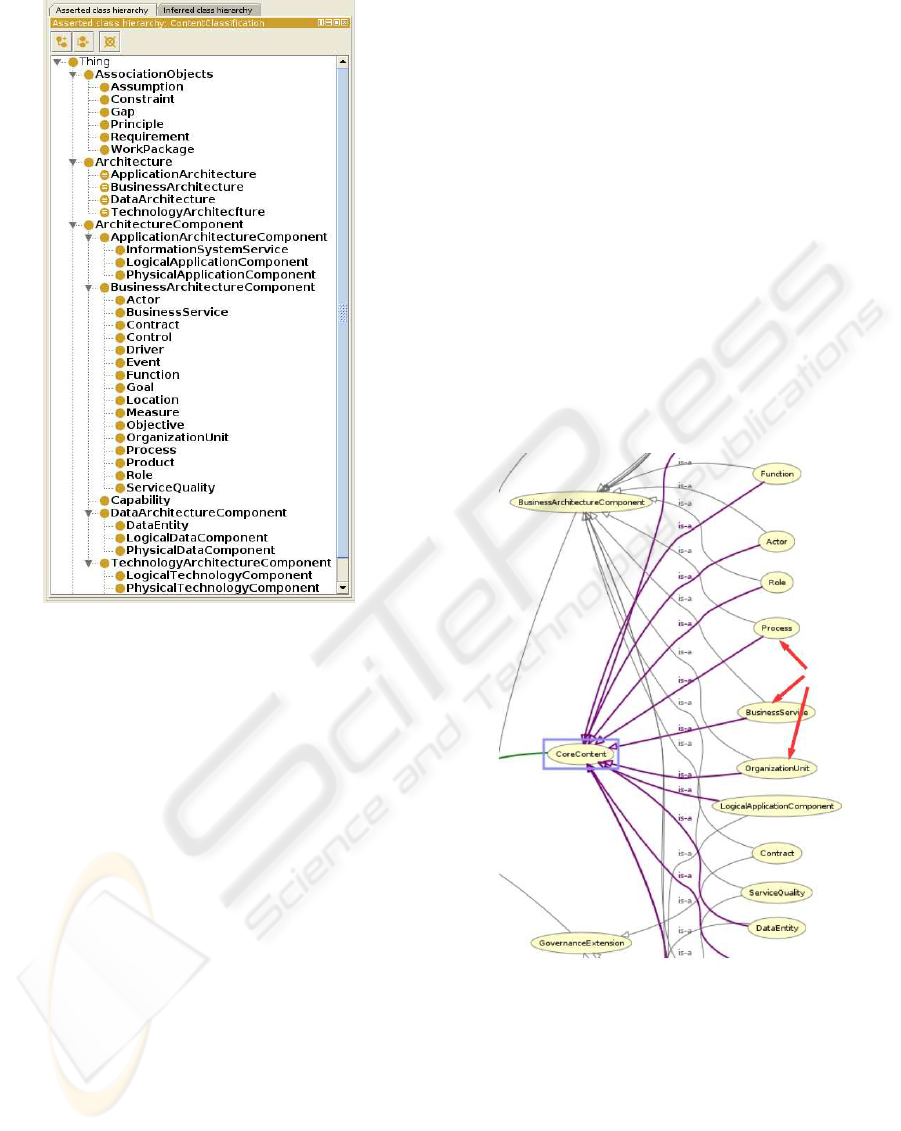
Figure 3: The Content Metamodel concept hierarchy.
the ContentClassification concept, we did not specify
disjointness of ContentClassification with other sib-
ling or subconcepts.
We used the reasoners to verify consistency, and
the result was that InformationSystemService was
an inconsistent concept (see Figure 5). This is ex-
plainable since BusinessArchitecture with all its ar-
chitecture components (BusinessArchitectureCompo-
nents), including BusinessService, is disjoint with Ap-
plicationArchitecture with all its architecture compo-
nents (ApplicationArchitectureComponents), includ-
ing InformationSystemService. This means that none
of the BusinessArchitectureComponentscould ever be
the same as any of the ApplicationArchitectureCom-
ponents. However, in our concept hierarchy, we spec-
ified InformationSystemService as a subconcept of
BusinessService which has the semantics that Infor-
mationSystemService is-a BusinessService. This ex-
plains that InformationSystemService is inconsistent.
The subclass relationship in the Content Meta-
model as indicated by number (4) in Figure 2 was in-
tentional and is described as follow in the TOGAF 9
manual (The Open Group, 2009b):
• IS Service is added as a new metamodel entity,
extending business service.
• IS Service inherits all the relationships of a busi-
ness service.
• A new relationship is created linking an IS service
to a business service.
The above indicate that the subclass relationship
in the Content Metamodel was considered to be cor-
rect. What the ontology technologies could do, is
point out the inconsistency in the meaning. If Archi-
tectures are disjoint as depicted in the model, their
components have to be disjoint and cannot inherit
from superconcepts across architecture boundaries.
In order to remove the inconsistency, we hence-
forth removed the subsumption or is-a relationship
between BusinessService and InformationSystemSer-
vice. Subsequent information obtained from the TO-
GAF 9 model indicates also a realizes relationship
between BusinessService and InformationSystemSer-
vice which we then used rather than the is-a relation-
ship.
Figure 4: ContentClassification hierarchy is also a super-
class of architecture components.
Step 3: Modeling Composition. It is not unrea-
sonable to interpret the multi-layering in the Content
Metamodel diagram as composition. Classes such as
Organization and Driver (indicated by (1) in Figure
2) are on top of the block indicating the Business Ar-
chitecture (indicated by (2) in Figure 2) and we inter-
preted this as that they are part-of the Business Ar-
chitecture. We modeled this by asserting a hasCom-
ponent object property in Protg´eg´e and then using ex-
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
60
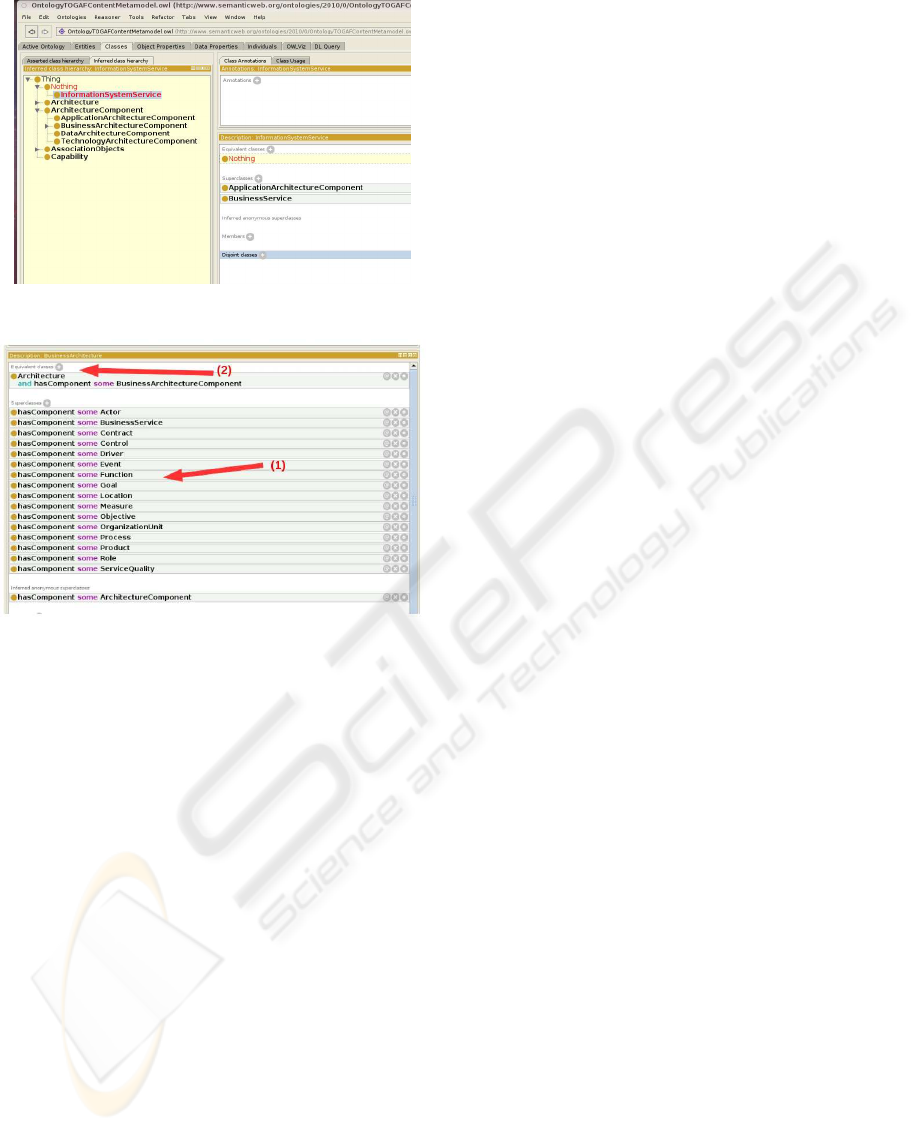
Figure 5: Inconsistency of InformationSystemService.
Figure 6: Architecture hasComponent Composition.
istential quantification to declare that an Architecture
concept has at least one ArchitectureComponent, We
then asserted that the BusinessArchitecture concept
has at least one of each of its architecture components.
As example, the BusinessArchitecture composition is
indicated by (1) in Figure 6.
Step 4: Addition of all the Relationships between
Concepts. For each relationship indicated in the
Content Metamodel, we asserted two object proper-
ties that are each others inverse in Prot´eg´e and then
used existential quantification to model the relation-
ships in both directions. This has the semantics that
there should exist at least one such link between the
concepts. A problem we experienced during this ac-
tivity is that several relationships have the same name
even though they are clearly not the same. As exam-
ple, see the Location object that has all relationships
labeled Contains (see (5) in Figure 2). In the ontology
construction we named each object property uniquely.
There is of course redundancy in the way we asserted
the relationships. It is only necessary to assert the in-
verse object property characteristic after defining the
two object properties and define a existential restric-
tion in one direction. The reasoner would infer the
inverse relation. Normally redundancy in ontologies
should be avoided due to possible maintenance issues
and performanceof the reasoners. The ontology could
therefore be refined in future.
It is also interesting to note that no cardinality was
indicated in the Content Metamodel. This seems to
be an omission as it is possible to define some cardi-
nality of relationships in the metamodel. A Physical
Data Component should, for instance, have only one
Location.
Step 5: Identification of Definitions. When build-
ing an OWL ontology, it is very useful to assert de-
fined concepts. This means that these concepts are ex-
actly defined and it is a powerful mechanism used by
reasoners for inferences. Given the ambiguity of the
Content Metamodel, it is not easy to define concepts
with such rigour. However, we decided that some de-
fined concepts could be added such Architecture. An
Architecture hasComponent ArchitcetureComponent,
and when anything has an ArchitectureComponent, it
is an Architecture. This was a modeling decision and
it is indicated by (2) in Figure 6.
Step 6: Addition of Annotations. We used the TO-
GAF 9 manual and added annotations of all the con-
cepts based on the provided descriptions of the ob-
jects. Annotations provide textual comments and de-
scriptions in an ontology.
Step 7: Refinement of the Ontology. We refined
the ontology by executing the steps in several itera-
tions and using the reasoners to check consistency and
syntax.
The next section summarises some findings of the
case study.
4 FINDINGS
The case study to construct a formal ontology
for the TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel resulted
in a first version ontology with expressivity 52
concepts and 89 object properties. The ontol-
ogy is available on the project page at
http:
//sites.google.com/site/ontologyprojects/
home/togaf-core-content-metamodel
. It is clear
that such an ontology could be constructed, but the
refinement and usefulness require further research.
Ontology engineering is also a collaborative exercise
because an ontology should reflect consensus about
a domain. Input from other stakeholders should also
TOWARDS THE FORMALISATION OF THE TOGAF CONTENT METAMODEL USING ONTOLOGIES
61

be obtained when refining the ontology in further
research.
The most significant finding is that our approach
allowed us to detect an inconsistency in the current
TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel, which is not evident
at first glance. Such an inconsistency in the model
have severe consequences for anybody trying to use
the model. It is not possible to construct a consistent
architecture from the current metamodel. An architect
will have to make a decision to ignore some of the
assertions of the model that leads to the inconsistency,
and different architects will ignore different assertions
resulting in interoperability issues.
The following lists describes our findings with
regards to the approach and tools (notably Prot´eg´e,
FaCT++ and Pellet 1.5) used, as well as our findings
with regard to the use of ontology technologies for
metamodel construction.
Findings with regard to the Approach and Tools.
• An ontology could only be constructed by making
several modeling decisions about aspects of the
Content Metamodel that were unclear. The deci-
sions are often based on assumptions that may not
be correct. However, anybodyintending to use the
metamodel will be confronted with the same am-
biguities and lack of information and clarity. It is
therefore useful to construct a formal model with
explicit meaning that we could refine rather than
to have an unclear model.
• Familiarity with the DL modeling constructs re-
main a prerequisite for ontology construction, ir-
respective of the tools used.
• Prot´eg´e 4 was easy to use and enabled us to eas-
ily create the formal ontology. The only drawback
was the graphical rendering of the model similar
to the original diagram. Graphical displays will
always remain important for modeling and ontol-
ogy comprehension.
• The reasoners bundled with Prot´eg´e 4 (FaCT++
and Pellet 1.5) depict all consequences of our
model, not only the explicit statements we made,
but also implicit consequences. In our case study
these are relatively trivial, but it was evident that
implicit consequences will be very valuable once
the model is complex.
• Ontology editors such as Prot´eg´e 4 assists archi-
tects to specify models in a standardised formal
language (usually OWL) which promote interop-
erability for enterprise architectures derived from
the metamodel.
• Prot´eg´e 4 still lacks graphical rendering of differ-
ent aspects of the models often making it difficult
to understand or comprehend consequences. It is
not standard with tools such as Prot´eg´e 4 to graph-
ically display property characteristics, as well as
existential and universal restrictions.
• There are still at present no firmly established
methodologies for ontology engineering. It is
generally recognised that this is a research topic
that warrants urgent attention (G´omez-P´erez et al.,
2004). Within an enterprise architecture frame-
work, this is even more important and will proba-
bly have to be tailored towards the specific archi-
tecture model required within the framework.
• Available ontology tools still have limited func-
tionality. The most evident was mentioned al-
ready, namely the ability to generate advanced
graphical displays of an ontology that resembles
the original departure point. In addition, assis-
tance with debugging such as tools that explains
an inference, are only experimental. This remains
a drawback, especially when models are complex.
• It was also evident that, although a variety of tools
exist for ontology construction and maintenance
(Sirin et al., 2007; Kalyanpur et al., 2005; Prot´eg´e,
2009), these tools remain really accessible mainly
to those users that have specialised knowledge
about the theory of ontologies. A good example
of this are inconsistencies. The reasoner only de-
pict a concept as inconsistent and does not offer a
reason or explanation. A modeler has to resolve
errors using trial and error, and these errors were
often due to unexpected consequences of asser-
tions made earlier.
Findings with regard to the use of Ontology Tech-
nologies for Metamodel Construction.
• The most significant advantage is that the use
of formal ontology technologies allow for clear
and consistent metamodels because the ontology
is constructed with assertions that has specific
meaning. The assertions are unambiguous and
their meaning is clear. Even if domain experts do
not agree completely with an assertion, the mean-
ing thereof is clear and could be altered to reflect
consensus.
• The use of ontology technologies allowed us to
detect an inconsistency in the current TOGAF 9
Content Metamodel which could be eliminated.
• The use of this approach allows an architect to
specify concise definitions of concepts and rela-
tions for his metamodel descriptions that could be
used by architects to construct models that adhere
to the core specification. These models should en-
able interoperability and integration.
• The use of a precise and formal definition of con-
cepts assists with debugging of a metamodel such
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
62

as demonstrated by the elimination of the incon-
sistency we detected in the Content Metamodel
with Information System Service that is a subclass
of BusinessService.
5 CONCLUSIONS
From the case study it is clear that formal ontologies
and the associated technologies can play a substantial
role to enhance the quality of metamodels in enter-
prise architecture frameworks. Ontologies are more
explicit, precise and consequences can be exposed.
Ontologies can represent the required information of
metamodels but in a much more precise and unam-
biguous manner than that of metamodel notations cur-
rently being used. Ontologies are also based on stan-
dardised languages and this should promote interop-
erability of models within an enterprise architecture
framework and enterprise architecture implementa-
tions. The formalisation of metamodels, and specifi-
cally the TOGAF 9 Content Metamodel using ontol-
ogy technologies should assist in the generation of en-
terprise architectures that are clear and unambiguous.
REFERENCES
Avison, D. and Fitzgerald, G. (2003). Information Systems
Development: Methodologies, Techniques and Tools.
McGraw-Hill, UK, third edition.
Baader, F., Calvanese, D., McGuinness, D., Nardi, D., and
Patel-Schneider, P. (2003). The Description Logic
Handbook: Theory, Implementation, and Applica-
tions. Cambridge University Press.
Benson, T. (2009). Principles of Health Inter-
operability HL7 and SNOMED. Springer
(http://www.springer.com).
Berners-Lee, T., Hendler, J., and Lassila, O. (2001). The
semantic web. Scientific American, 284(5):34–43.
B´ezivin, J. (2003). On the unification power of models. In
UML’2003. http://atlanmod.emn.fr/www/papers/ On-
TheUnificationPowerOfModels.pdf.
Broekstra, J., Klein, M., Decker, S., Fensel, D., van Harme-
len, F., and Horrocks, I. (2001). Enabling knowl-
edge representation on the web by extending rdf
schema. In Proceedings of the 10th International
World Wide Web Conference (WWW10), Hong Kong,
volume ACM 1-58113-348-0/01/0005, page 467. last
accessed 18/3/2006.
Bussler, C., Fensel, D., and Maedche, A. (2002). A concep-
tual architecture for semantic web enabled web ser-
vices. ACM SIGMOD, SPECIAL ISSUE: Special sec-
tion on semantic web and data management, 31, issue
4:24 – 29.
Campbell, A. (2009). Enterprise architecture: From strat-
egy to execution. meta model post. Wiki. Accessed
January 2010 at http://iea.wikidot.com/.
Decker, S., Melnik, S., van Harmelen, F., Fensel, D., Klein,
M., Broekstra, J., Erdmann, M., and Horrocks, I.
(2000). The semantic web: The roles of xml and rdf.
IEEE Internet Computing, 4:63–74.
Dijkstra, E. W. (2001). The end of computing science?
Communications of the ACM, 44(3):92.
EARF (2009). Definition of enterprise archi-
tecture. Retrieved January, 2010, from
http://earf.meraka.org.za/earfhome/defining-ea/.
Ernst, A. M., Lankes, J., Schweda, C. M., and Witten-
burg, A. (2006). Tool support for enterprise archi-
tecture management - strenghts and weaknesses. In
10th IEEE International Enterprise Distributed Ob-
ject Computing Conference, Hong Kong., pages 13 –
22.
Ernst, J. (2002). What is metamodeling, and what is it
good for? wIKI. http://infogrid.org/wiki/Reference/
WhatIsMetaModeling.
Fact++ (2009). Fact++ ontology reasoner. Web.
GITOC (2009). Government wide enterprise architecture
(gwea) framework. GITOC Website.
G´omez-P´erez, A., Fern´andez-L´opez, M., and Chorco, O.
(2004). Ontological Engineering. Springer.
Gr¨uber, T. (1993). A translation approach to portable on-
tology specifications. Knowledge Acquisition, 5:199–
220.
Hahn, U. and Schulz, S. (2007). Ontological founda-
tions for biomedical sciences. Artificial Intelligence
in Medicine, 39(3):179–182.
HL7 (2009). Health level seven. HL7 Website. Retrieved
on 5 January 2010 from http://www.hl7.org/.
Horridge, M. (2009). A practical guide to building owl on-
tologies using prot´eg´e 4 and co-ode tools: Edition 1.2.
WWW.
Horrocks, I. (2007). Semantic web: the story so far. In W4A
’07: Proceedings of the 2007 international cross-
disciplinary conference on Web accessibility (W4A),
pages 120–125, New York, NY, USA. ACM.
IEEE (2000). Recommended practie for architectural
description of software-intensive systems. IEEE Re-
port.
Janssen, M. and Hjort-Madsen, K. (2007). Analyzing enter-
prise architecture in national governments: The cases
of denmark and the netherlands. In Proceedings of
the 40th Hawaii International Conference on System
Sciences, pages 1530–1605.
Kaisler, S., Armour, F., and Valivullah, M. (2005). Enter-
prise architecting: Critical problems. In 38th Hawaii
International Conference on System Sciences, Hawaii,
USA.
Kalyanpur, A., Parsia, B., Sirin, E., Cuenca-Grau, B., and
Hendle, J. (2005). Swoop: A Web Ontology Editing
Browser.
TOWARDS THE FORMALISATION OF THE TOGAF CONTENT METAMODEL USING ONTOLOGIES
63

Kim, J.-W., Kim, Y.-G., Kwon, J.-H., Hong, S.-H., Song,
C.-Y., and Baik, D.-K. (2005). An enterprise archi-
tecture framework based on a - common informa-
tion technology domain (eafit) for improving interop-
erability among heterogeneous information systems.
In Third ACIS Int’l Conference on Software Engineer-
ing Research, Management and Applications, Cen-
tral Michigan University, Mount Pleasant, Michigan,
USA.
Lassila, O. and McGuinness, D. L. (2001). The role
of frame-based representation on the semantic web.
Technical report, Knowledge Systems Laboratory Re-
port KSL-01-02, Stanford University.
Lippitt, G. L. (1973). Visualizing Change: Model Building
and the Change Process. University Associates, Inc.
McGuinness, D. L. and van Harmelen, F. (2004). Owl web
ontology language overview. W3C Web site. Last
accessed 13/9/2006.
OMG (2008). Software process engineering meta-
model. OMG Website. Retrieved 4 January 2010
from http://www.omg.org/technology/documents/
formal/spem.htm.
Palmer, S. B. (2001). The semantic web: An introduction.
W3C Web site. Last accessed 16/9/2006.
Pellet (2009). Pellet: The open source owl dl reasoner. Web.
Pidcock, W. (2002). What are the differences be-
tween a vocabulary, a taxonomy, a thesaurus,
an ontology, and a meta-model? Wiki.
http://infogrid.org/wiki/Reference/PidcockArticle.
Prot´eg´e (2009). The prot´eg´e Ontology Editor.
http://protege.stanford.edu/.
Rood, M. (1994). Enterprise architecture: definition, con-
tent and utility. In Third Workshop on Enabling
Technologies: Infrastructure for Collaborative Enter-
prises, Morgantown, West Virginia.
Session, R. (2007). A comparison of the top four enterprise-
architecture methodologies, building distributed ap-
plication. Web.
Sirin, E., Parsia, B., Grau, B. C., Kalyanpur, A., and Katz,
Y. (2007). Pellet: A practical OWL-DL reasoner.
Journal of Web Semantics, 5(2).
Suntisrivaraporn, B., Baader, F., Schulz, S., and Spackman,
K. (2007). Replacing SEP-Triplets in SNOMED CT
using Tractable Description Logic Operators. In Pro-
ceedings of AIME 2007.
SWOOP (2009). Swoop - semantic web ontology editor.
Web.
The Open Group (2009a). The open group. The Open
Group Website. http://www.opengroup.org/.
The Open Group (2009b). TOGAF 9: The Open Group Ar-
chitecture Framework (TOGAF). Document Number:
G091. http://www.opengroup.org/architecture/togaf9-
doc/arch/.
W3C (2006). The world wide web consortium (w3c). W3C
Web site.
Walker, M. (2009). Togaf 9 release and impres-
sions. Blog. Accessed January 2010 from
http://blogs.msdn.com/mikewalker/archive/2009/02/
02/togaf-9-release-and-impressions.aspx.
Weiner, L. H. (1978). The roots of structured programming.
In Papers of the SIGCSE/CSA technical symposium
on Computer science education, pages 243–254, New
York, NY, USA. ACM Press.
Wolstencroft, K., Brass, A., Horrocks, I., Lord, P., Sattler,
U., Stevens, R., and Turi, D. (2005). A little semantic
web goes a long way in biology. In Proceedings of the
2005 International Semantic Web Conference (ISWC
2005), LNAI. Springer.
Yang, W.-Y., Lee, L.-H., Gien, H.-L., Chu, H.-Y., Chou, Y.-
T., and Liou, D.-M. (2009). The design of the hl7
rim-based sharing components for clinical informa-
tion systems. World Academy of Science, Engineering
and Technology, 53.
Zachman, J. (2003). The Zachman Framework for Enter-
prise Architecture. a primer for enterprise engineering
and manufacturing. Zachman International.
Zachman, J. A. (1997). Enterprise architec-
ture: The issue of the century. Database
Programming and Design Magazine.
http://www.cioindex.com/nm/articlefiles/63503-
EAIssueForTheCenturyZachman.pdf.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
64
