
VALIDATION OF A MEASUREMENT FRAMEWORK OF
BUSINESS PROCESS AND SOFTWARE SYSTEM ALIGNMENT
Lerina Aversano, Carmine Grasso and Maria Tortorella
Institute of Department of Engineering University of Sannio, Via Traiano 1, 82100 Benevento Italy
Keywords: Software evolution, Business process evolution, Software measure, Process measure.
Abstract: The alignment degree existing between a business process and the supporting software systems expresses
how the software systems support the business process. This measure can be used for indicating business
requirements that the software systems do not implement. Methods are needed for detecting the alignment
level existing between software systems and business processes and identifying the software changes to be
performed for increasing and keeping an adequate alignment level. This paper proposes a framework
including a set of metrics codifying the alignment concept with the aim of measuring it, detecting
misalignment, identifying and performing software evolution changes. The framework is, then, validated
through a case study.
1 INTRODUCTION
The alignment of a business process and supporting
software system is a critical concern for the
organizations, as it directly affects their
performance. It indicates at which extent the
software system and all its components were
designed and implemented for adequately
supporting a business process when it is executed
(Henderson, 1993) (Papp, 2001).
Software engineers can deal with cases in which
some misalignment occurs, and, as a consequence
the business process is not effectively supported by a
software system. A misalignment can be the cause
of a decreasing of the performance of the business
process.
Unfortunately, even if business processes and
supporting software systems are aligned in a certain
operative context, modifications of this context can
cause a misalignment between them. It can be due to
either technological and/or management
innovations, or unchecked change in the way the
activities are executed or the supporting software
systems are exploited. Furthermore, a modification
may usually not only regard the objects directly
changed, but it can also impact other objects having
a dependence relation with the modified ones.
Software changes need to be planned to improve the
alignment level between business processes and
supporting software systems. In the best of the
authors’ knowledge, research and industry have only
marginally addressed these aspects (Pereira, 2003).
The alignment concept should be continuously
monitored for detecting misalignment, if it occurs,
and identifying and executing alignment actions.
With this in mind, approaches are required for
characterizing the alignment level existing between
business process and software systems, so that it can
be quantitatively evaluated and possible
misalignment can be detected. The quantitative
evaluation of the alignment degree has to facilitate
the identification of the evolution actions that need
to be executed for improving the alignment
measures. The evolution actions can involve one or
more objects of the analyzed business activities and
components of the supporting software systems and
they have to be performed, so that the impacted
business and software components are also
considered (Aversano, 2009). This paper proposes a
measurement framework aiming at characterizing
the alignment level existing between business
process and software system and quantitatively
measuring it. The framework allows the
measurement of the alignment at activity, artefact
and resource level.
The measurement should be iteratively executed
for continuously monitoring the existing alignment
degree between business process and software
system with the aim of identifying additional
470
Aversano L., Grasso C. and Tortorella M. (2010).
VALIDATION OF A MEASUREMENT FRAMEWORK OF BUSINESS PROCESS AND SOFTWARE SYSTEM ALIGNMENT.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Information Systems Analysis and Specification, pages
470-474
DOI: 10.5220/0002903704700474
Copyright
c
SciTePress

software changes to be performed as the operative
business context evolves.
The measurement framework considers the
assessment of two main attributes expressing the
Technological Coverage of a business process and
Technological Adequacy with which the business
activities are technologically supported. In
(Aversano, 2005), a coarse grained strategy was
suggested for measuring these attributes. The
measurement framework used in this paper enhances
the previous work and proposes a set of metrics that
can be directly evaluated by analysing business and
software models (Aversano, 2010).
The paper validates the adopted measurement
framework by considering a business process
supported by a software system. The alignment level
existing between them was first evaluated and the
measurement results helped identifying a set of
software changes, whose execution brought to an
evolved software system better aligned to the
considered business process.
The improved alignment results highlight the
usefulness of the approach and effectiveness of the
measurement framework for evaluating the
alignment level existing between business process
and software system.
The rest of the paper is organized as follow:
Section 2 describes the proposed measurement
framework; Section 3 presents a case study, and
final remarks are given in the last section.
2 MEASUREMENT
FRAMEWORK
Measuring the alignment requires the quantitative
codification of the alignment existing between a
business process and the supporting software
systems. This involves the identification of suitable
metrics for codifying the alignment level. A set of
metrics is defined for achieving an objective
measure of the existing alignment level between
Business Process and Software System through the
assessment of the technological coverage and
adequacy. At this stage, if the business process and
supporting software system are not aligned, it is
necessary to proceed with the identification of
evolution actions to be performed to increase the
alignment level. The actions planned need to be
executed. This could require the implementation of
new classes and / or methods. The measure of the
alignment need to be iterated to allow a continuous
monitoring and management of the alignment level.
The alignment is quantified in term of (Aversano,
2005): T
ECHNOLOGICAL COVERAGE (TC), indicating
the percentage of process activities adequately
supported by a software system; and
T
ECHNOLOGICAL ADEQUACY (TA), derived from the
technological adequacy evaluated with respect to
each activity. In particular, the Technological
Adequacy of activity i (TA
i) indicated how adequate
was the used software system for supporting activity
i.
The evaluation of TA and TC require a fine-
grained analysis for obtaining more objective and
precise measures. With this in mind, a measurement
framework, based on the Goal Question Metrics
(GQM) paradigm is proposed.
In the analyzed context, the formulated goal is:
Analyse a business process and supporting
software systems with the aim of evaluating the
misalignment degree existing between them from
the point of view of the software engineer.
The questions to be answered for achieving this
goal are formulated in terms of Technological
Coverage (TC) and Technological Adequacy (TA)
of the business process.
The metrics considered in the method for
answering the questions are referred to the essential
aspects involved in a process model. In particular,
the evaluation of the metrics involves: Activity,
referring the lowest level of details of the performed
human tasks; Resource, regarding the inputs and
outputs data required to perform the activities; and
Control Flow, defining the flow among the process
activities.
All these aspects are considered in the analyzed
context together with their relation with the
attributes introduced in the questions. A detailed
description of the metrics is proposed in (Aversano,
2010).
In the proposed framework, the metrics
considered at the activity level are two, Activity
Coverage (AC) and Activity Accuracy (AA). They
are evaluated from the technological support point
of view, in terms of numbers of supported activities
and quality of the offered support. The metrics are
evaluated as follows:
ActivitiesocessOfNumber
SupportedActivitiesocessOfNumber
AC
_Pr__
__Pr__
=
SupportedActivitiesocessOfNumber
ExecutionforDegreeSupportActivity
AA
ytedActivitEachSuppor
__Pr__
____
∑
=
The metrics considered at the resource level are
evaluated through a careful analysis of the way the
activity resources (i.e., actors, input and output) are
VALIDATION OF A MEASUREMENT FRAMEWORK OF BUSINESS PROCESS AND SOFTWARE SYSTEM
ALIGNMENT
471
supported by the software system. The metrics
defined, are: Actor Coverage (AcC), Actor Adequacy
(AcA), Artefacts Coverage (AtC), Artefacts Accuracy
(AtA). They are calculated as follows:
ActorsessBuOfNumber
SupportedActorsessBuOfNumber
AcC
_sin__
__sin__
=
SupportedActorsocessOfNumber
AdequacySupportActor
AcA
tedActorEachSuppor
__Pr__
__
∑
=
ArtefactsocessOfNumber
SupportedArtefactsocessOfNumber
AtC
_Pr__
__Pr__
=
SupportedArtefactsocessOfNumber
AdequacySupportArtefact
AtA
ttedArtefacEachSuppor
__Pr__
__
∑
=
The last considered aspect is the control flow
that deals with the transitions of the business process
respect those automatically managed by the software
system. The consideration of this aspect is relevant
for determining how the software system effectively
support the execution of the business process. The
metric used in this case is just one, the Transition
Coverage (TtC), to be calculated as it follows:
TransitionocessOfNumber
SupportedTransitionocessOfNumber
TtC
_Pr__
__Pr__
=
The final value of the Technological Coverage
(TC) and the Technological Adequacy (TA) are
achieved by aggregating the presented metrics. In
particular, the Technological Coverage is computed
as average of AC, AcC , AtC and TtC and the
Technological Adequacy is computed as average of
AA, AcA and AtA.
3 VALIDATION
To validate the effectiveness of the framework
proposed for measuring the alignment degree, a
business process managing the object donations to
needy children has been considered. The process is
supported by a software system, named
S
ANTACLAUS (http://santaclaus.beneslan.it/santaclaus/).
In particular, the steps of the validation are:
- evaluation of the initial alignment value of the
software system and supported business process;
- identification of the evolution actions to be
performed and their implementation;
- evaluation of the final alignment value is measured
to validate if improvements have been achieved.
S
ANTACLAUS is a web application written in PHP
and Java. It has been developed for supporting the
business process used by a voluntary association,
named B
ENESLAN, to manage object donations for
needy children (
http://santaclaus.beneslan.it/santaclaus/).
The analytical data measured for each activity,
artefact and actor are provided in the second column
of Table 1. The second column of Table 2 includes
just the summary of the evaluation of the metrics.
The aggregation of all the measures leads to a value
of 0.465 calculated for the Technological Coverage,
TC, and a value of 0.395 computed for the
Technological Adequacy, TA. These data indicate
that the support offered by the S
ANTACLAUS
software system does not reach a good level of
coverage and adequacy. In particular, considering
the values of the metrics, it is possible to notice that
the main lack of support is related to the way the
activities are supported. Actually, the supported
activities are just 6 on 14, as many of them are
manually executed. Moreover, some of the 6
automated activities are only partially supported. 4
of them are adequately supported and their adequacy
level reaches the value 1. On the contrary, the
identification of goods to donate and receipt of a
request activities are just partially supported. This
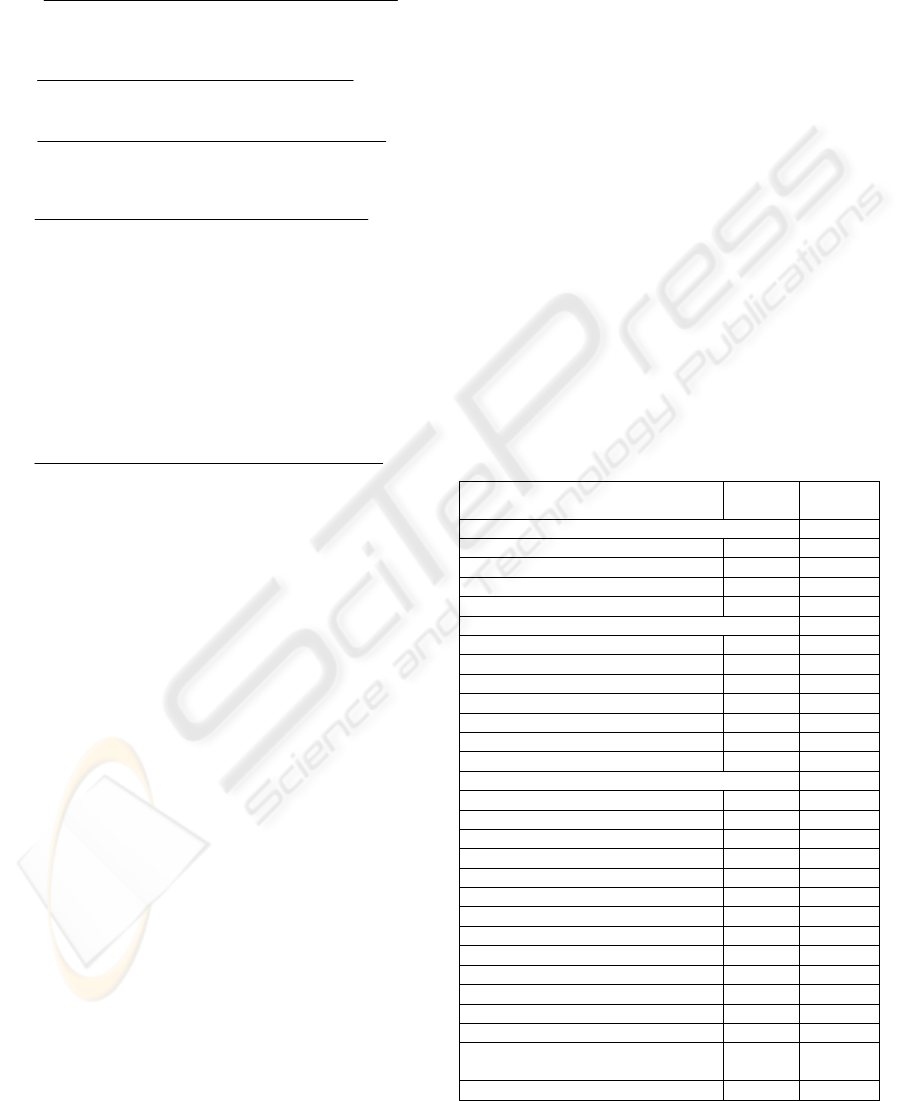
Table 1: Detailed values obtained for Santaclaus.
METRIC NAME BEFORE
CHANGES
AFTER
CHANGES
Actors Adequacy: ActorA
i
Actor
1
: operator 1.000 1.000
Actor
2
: beneficiary 0.000 0.667
Actor
3
: administrator 0.000 0.000
Sum: 1.000 1.667
Artefact Adequacy : AtfA
i
AtfA
1
: artiche 0.909 0.909
AtfA
2
: donation 0.000 1.000
AtfA
3
: user 0.667 0.667
AtfA
5
:category 0.800 0.889
AtfA
5
:assignation 0.000 0.000
AtfA
6
: BeneficiarySupports - 1.000
Sum: 2.376 4.465
Activity Adequacy: AA
i
AA
1
: make a demand 0.000 1.000
AA
2
: receipt of a request 0.500 1.000
AA
3
: identification of goods to donate 0.750 1.000
AA
4
: selection of the goods donated 1.000 1.000
AA
5
: recovery of the addressee card 1.000 1.000
AA
6
: creation of the addressee card 1.000 1.000
AA
7
: storing the donation data 1.000 1.000
AA
8
: evaluation the donation request 0.000 0.000
AA
9
: not admissible 0.000 0.000
AA
10
: admission of the request 0.000 0.000
AA
11
: acceptance of the donated goods 0.000 0.000
AA
12
: notification of the delivery data 0.000 0.000
AA
13
: acceptance of the signature 0.000 1.000
AA
14
: delivery of the goods to the
addressee
0.000 0.000
Sum: 5.250 8.000
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
472
can be evicted from Table 1 with reference to the
first cited activity.
The Artefact Adequacy, AtfA, is the metric that
reaches the highest adequacy value. This aspect also
emerges by looking at the coverage values.
Table 1 highlights that: the donation artefact is
taken in consideration by the business activities, but
the software system does not implement classes for
their automatic management. This is confirmed by
the fact that, some artefacts (category and article)
are considered by the business process, but not all
the operations needed for managing them are
implemented in the corresponding software classes.
In any case, Table 1 highlights that the business
artefact article is adequately supported, but the
positive values its adequacy reaches is negatively
affected by the assignation and donation
technological adequacy.
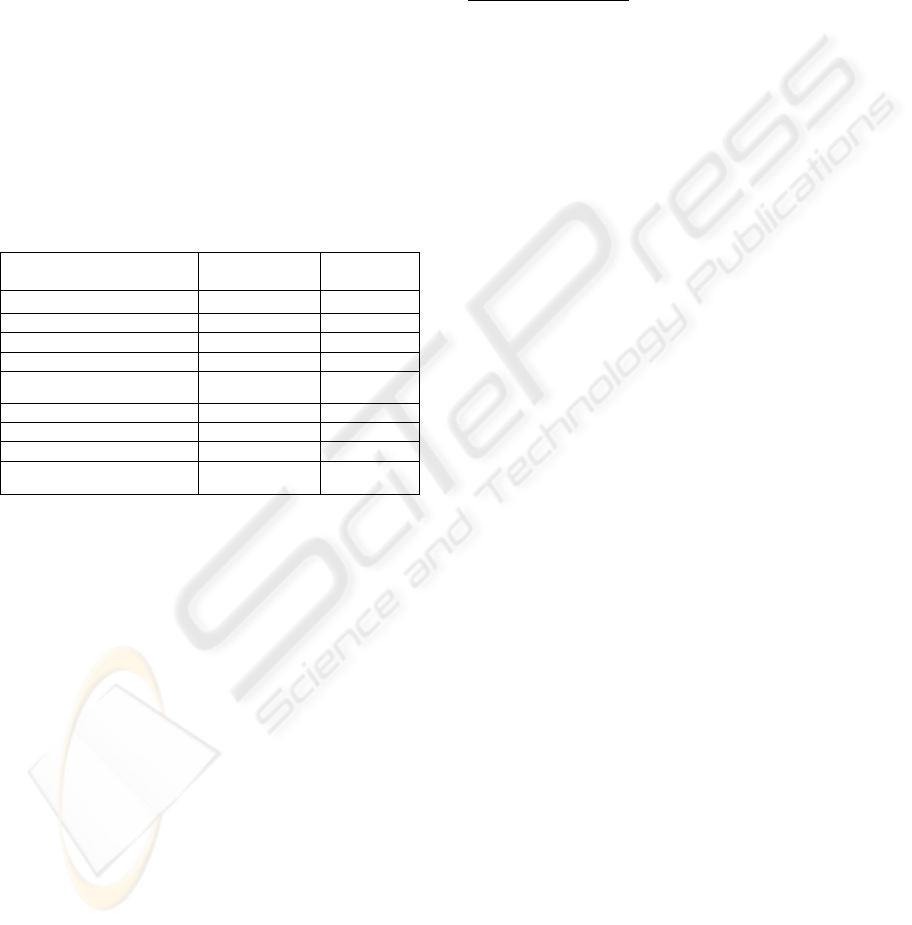
Table 2: TA and TC values obtained for Santaclaus.
METRIC NAME BEFORE
CHANGES
AFTER
CHANGES
Activity Coverage (AC) 0.428 0.500
Actor Coverage (ActorC) 0.334 0.667
Artefacts Coverage (AtfC) 0.600 0.833
Transition Coverage (TC) 0.500 0.571
Technological Coverage 0.465 0.643
Artefacts Adequacy (AtfA) 0.475 0.744
Activity Adequacy(AA) 0.375 0.571
Actor Adequacy (ActorA) 0.334 0.556
Technological Adequacy 0.395 0.623
Regarding the actor technological adequacy,
ActorA, it reaches the lowest value, highlighting a
bad support of the software system provided to the
actors involved in the activity execution. In addition,
the actor technological coverage, ActorC, confirms
this result, as just 1 of the 3 are automatically
supported.
From the assessment of the alignment level, it
emerges that the business process and supporting
software system were not aligned. Therefore, it was
necessary to identify evolution actions to be
performed for increasing the alignment. In
particular, focusing on the detailed values in the
second column of Table 1 the identified evolution
changes were the following:
- introduction of an automatic support to the
beneficiary’s activities. This need emerged from:
the low value of the Actor Adequacy, see Table 2;
the null value of ActorA
2
, concerning the
beneficiary actor; it was evident that the business
actor beneficiary was included in the business
process but not considered by the software system.
- In particular, two changes were required:
• Automation of the activity for receiving the
donation requests, named make a demand;
• Automation of the activity for introducing the
digital signature for the beneficiary user,
indicated acceptance of the signature.
The automation of these two activities implied
the implementation of the new class
BeneficiarySupport.
The automation of the first
activity also implied the complete automation of
activity receipt of a request.
- introduction of an automatic support to the
donation artefact. In fact, Tables 1 and 2 indicates
the low value of Artefact Adequacy with particular
reference to AtfA
2
, regarding the donation artefact.
- finally, the completion of the automation of
activity identification of goods to donate could be
reached through the implementation of method
searchUserAbout of the category class.
The execution of the planned actions required the
implementation of new classes and methods. This
brought to an increasing of the alignment level.
The improvement of the alignment level is also
demonstrated by the new values reached by the
Technological Coverage and Technological
Adequacy, as the third column of Table 2 indicates.
In particular, a good improvement can be observed
not only in the two parameter values, 0.643 and
0.623, respectively, but also in each coverage and
adequacy value. The third column of Table 1 shows
the analytical evaluations obtained after the change
execution. It is possible to evict that two of the three
business actors are supported by the evolved
software system, implying the increasing of the
technological coverage and adequacy with reference
to the actors. The implementation of the activities
executed by the beneficiary, brought to the
increasing of the measured characteristics of its
activities. The evolved software system supports 8
of the 14 activities, against 6 of 14 activities
supported by the previous version. Finally, the
number of the artefacts is increased in the new
software system, but all of them, except the
assignation artefact, are supported, favouring the
increasing of the technological coverage and
adequacy with reference to the artefacts.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This work proposed a set of metrics codifying the
alignment concept with the aim of measuring it.
The results of the evaluation of these metrics allow
VALIDATION OF A MEASUREMENT FRAMEWORK OF BUSINESS PROCESS AND SOFTWARE SYSTEM
ALIGNMENT
473

for the identification of a possible misalignment. In
particular, they support the assessment of the
alignment level, giving a measure of the extent at
which the software systems used in a business
process provides a support to it.
The validation of the alignment measure was
described with a case study referring to a business
process and related software system.
The future work to be performed in the described
context will refer the completion of the experimental
activities aiming at understanding the formalism and
the framework applicability and refining the set of
chosen metrics and mechanisms for their
computation.
REFERENCES
Henderson, J.C., and Venkatraman, N., Strategic
Alignment: Leveraging Information Technology for
Transforming Organizations, IBM Systems Journal,
32, 1, 1993, pp. 4-16;
Papp, R. Introduction to Strategic Alignment, in R. Papp
(ed.), Strategic Information Technology: Opportunities
for Competitive Advantage, Idea Group, Hershey, PA,
2001, pp.1-24.
Aversano, L., Bodhuin, T., Tortorella, M.: Assessment and
Impact Analysis for Aligning Business Processes and
Software Systems, Proc. of the ACM Symposium on
Applied Computing, ACM press, 2005, pp. 1338 –
1343.
Pereira, C., Sousa, P.: Getting into the misalignment
between Business and Information Systems. In: 10th
European Conference On Information Technology
Evaluation. Madrid (2003)
Aversano, L., Grasso, C., Tortorella, M., Measuring the
Alignment between Business Processes and Software
Systems: a Case Study, Proc. of the 2010 ACM
Symposium on Applied Computing, ACM press,
2010.
Aversano, L., Tortorella, M.: Business Process-Aware
Maintenance Task: A Preliminary Empirical Study,
Proc. of Conference on Softawre Maintenance and
Reengineering, CSMR 2009, IEEE CS Press, pp. 233-
236.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
474
