
FONTE
A Protégé Plugin for Engineering Complex Ontologies by Assembling Modular
Ontologies of Space, Time and Domain Concepts
Jorge Santos, Luís Braga
Departamento de Engenharia Informática, Instituto Superior de Engenharia, Porto, Portugal
Anthony Cohn
School of Computing, Leeds University, Leeds, U.K.
Keywords:
Ontologies, Knowledge engineering, Temporal/Spatial reasoning and representation.
Abstract:
Humans have a natural ability to reason about scenarios including spatial and temporal information but for
several reasons the process of developing complex ontologies including time and/or space is still not well
developed and it remains a one-off, labor intensive experience. In this paper we present FONTE (Factorising
ONTology Engineering complexity), an ontology engineering methodology that relies on a divide and conquer
strategy. The targeted complex ontology will be built by assembling modular ontologies that capture tempo-
ral, spatial and domain (atemporal and aspatial) aspects. In order to support the proposed methodology we
developed a plugin for Protégé, one of the most widely used open source ontology editor and knowledge-base
framework.
1 INTRODUCTION
Temporal and spatial concepts are ubiquitous in
human cognition hence representing and reasoning
about these knowledge categories is fundamental for
the developmentof intelligent applications (Harmelen
et al., 2008). Despite the extensive research regarding
the engineering of complex domain ontologies with
time and/or space (Staab and Maedche, 2001; Vale
et al., 2002; Milea et al., 2008) this process is still not
well developed and it remains a one-off, labour inten-
sive experience, mainly because: i) the engineering
process requires the consideration of several ontolog-
ical issues (e.g., primitives, density, granularity, di-
rection) often implying a complex trade-off between
expressiveness and decidability; ii) the domain ex-
perts often have an intuitive and informal perception
of time and space, whereas the existing models of
time and space are complex and formal; and iii) the
temporal componentintroduces an extra dimension of
complexity in the verification process, making it dif-
ficult to ensure system completeness and consistency.
These issues have been considered in the development
of FONTE (Factorising ONTology Engineering com-
plexity), an ontology engineering methodology that
relies on a divide and conquer strategy (Santos and
Staab, 2003a; Santos and Staab, 2003b). This type of
strategy has been successfully applied in the resolu-
tion of other complex problems (Cormen et al., 2000)
(e.g., mathematical induction or recursive algorithms
in computer sciences). The targeted complex ontol-
ogy will be built by factorising concepts into their
temporal, spatial and domain (atemporal and aspatial)
aspects, and then assembling the temporally/spatially
situated entity from these primitive concepts. This is
more similar to a Cartesian Product than a union of
ontologies. Each of these component ontologies will
be built/acquired independently, allowing a factorisa-
tion of complexity. The ontologies assembly will be
performed through an iterative and interactive process
that combines two types of inputs: i) human assem-
bly actions between the component ontologies; and
ii) automatic assembly proposals obtained from se-
mantic and structural analysis of the ontologies. This
process is propelled by a set of rules and a set of
constraints. The set of rules drives a semi-automatic
process proposing assembly actions; the set of con-
straints allows the assessment of which generated pro-
posals are valid.
A prototype tool implemented in Prolog was de-
93
Santos J., Braga L. and Cohn A. (2010).
FONTE - A Protégé Plugin for Engineering Complex Ontologies by Assembling Modular Ontologies of Space, Time and Domain Concepts.
In Proceedings of the 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Artificial Intelligence and Decision Support Systems, pages
93-102
DOI: 10.5220/0002908900930102
Copyright
c
SciTePress

signed to support the previous version of FONTE
method (just for time, not space), which provides
the essential functionalities for the assembly process
through a simple command line interface (Santos and
Staab, 2003b). This prototype was tested in the as-
sembly of ontologies specified in F-Logic. In this
paper, we present a plug-in for the Protége platform
that was designed to take benefit of the OWL format,
in particular of OWL-DL. Using OWL is an advan-
tage since it is currently the standard language for
the representation of ontologies; however, it does not
allow some operations of temporal assembling that
are based in the existence of generic axioms used by
F-Logic, which were very rich in expressivity. As
described further in this paper, the assembly method
uses a set of assembly rules that allow the tool be-
haviour to be defined. Additionally, a tool to facilitate
the specification of meta-modeling rules was devel-
oped.
The rest of the paper is organised as follows.
Firstly we provide a summary of related work in sec-
tion 2. Then we describe FONTE, the semi-automatic
process of assembling two ontologies (section 3),
with some detail for its main algorithm, data struc-
tures, assembling of classes and properties. Some ex-
amples of the engineering of temporal aspects in on-
tologies will be presented to illustrate the potential-
ities of the proposed methodology. To this end, the
temporal ontology Time-Entry and the domain ontol-
ogy SWRC about the Semantic Web Research Com-
munity will be used. We describe the support tool (a
Protégé plug-in) developed to drive the process, and
the tool developed for editing assembly rules (section
4). Finally in the section 5 we present the conclusions
and some possible directions for future work.
2 RELATED WORK
As mentioned above, temporal and spatial concepts
are ubiquitous in human cognition. Representing
and reasoning about these concepts is therefore fun-
damental in Artificial Intelligence, particularly when
approaching problems and/or applications like plan-
ning, scheduling, natural language understanding,
common-sense and qualitative reasoning and multi-
agent systems (Stock, 1997; Fisher et al., 2005).
A temporal representation requires the characterisa-
tion of time itself and temporal incidence (Vila and
Schwalb, 1996). Space must be characterised by ele-
ments representing basic spatial entities and primitive
spatial notions expressed over them (Stock, 1997).
Moreover, whereas the principal relations between
temporal entities are based on ordering, in the case
of space, many more different kinds of relations are
possible due to the higher dimensionality, includ-
ing richer mereotopological and directional relations
(Cohn and Renz, 2007).
An ontology is an explicit specification of a con-
ceptualisation about a specific portion of the world
(Gruber, 1993). The main purpose of ontologies is to
provide formal representations of models that can be
easily shareable and understandable both by humans
and machines. Ontologies have become an important
topic of research and are used in many areas, includ-
ing Knowledge Engineering (Staab and Studer, 2004).
The fast growth of the WWW has estab-
lished a knowledge sharing infrastructure, increas-
ing the importance of Knowledge Engineering
(Studer et al., 2004); consequently, ontologies
have gained renewed usage as artifacts within dis-
tributed and heterogeneous systems. The most re-
cent development in standard ontology languages is
OWL – Web Ontology Language (
www.w3.org/TR/
owl-features
). This has three sub-languages (Lite,
DL and Full) which present different grades of ex-
pressiveness/decidability; OWL-DL (based on De-
scription Logics) provides the most interesting and
widely accepted trade-offbetween expressivenessand
decidability.
In recent years, different ontologies about time
and space have been developed and are now
available in the public domain. There are two
types of such ontologies: specific ontologies about
time and/or space like OWL-Time (
www.w3.org/
TR/owl-time
), SWEET-Time and SWEET-Space
(
sweet.jpl.nasa.gov/ontology
) and upper on-
tologies (also called general) that include compo-
nents describing time and/or space like SUMO (
www.
ontologyportal.org
), OpenCYC (
www.opencyc.
org
) and GUM (
www.ontospace.uni-bremen.de/
ontology/gum.html
).
There is a growing interest in the topic of mod-
ularity in ontology engineering (Welty et al., 2006;
Lutz et al., 2007; Grau et al., 2007) mainly because
ontology engineering is a complex process that com-
prehends multiple tasks (e.g., design, maintenance,
reuse, and integration of multiple ontologies). Modu-
larity has been used to tackle complex processes such
as:
• engineering a rule-based system by task analysis
(Schreiber et al., 1999);
• engineering an ontology-based system by devel-
oping with patterns (Clark et al., 2000; Staab
et al., 2001) or developing sub-ontologies and
merging them (Noy and Musen, 2000).
All these methods promote the idea of sub-
dividing the task of building a large ontology by en-
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
94
gineering, re-using and then connecting smaller parts
of the overall ontology.
The MADS system (Parent et al., 2006) also
aims to support the engineering of temporal and spa-
tial aspects through a graphical system that supports
an Entity-Relationship analysis. MADS allows the
knowledge engineer to define temporal/spatial char-
acteristics for the model concepts. However, this
approach is very distinct from the one proposed by
FONTE, because the temporal/spatial modeling ac-
tions are not generated in a semi-automatic mode; and
the temporal and spatial theories are embedded in the
application interface so the ontology engineer is un-
able to select a specific theory of time and/or space.
3 FONTE METHOD
The assembly process comprises two main building
blocks. First, the specification of temporal and/or spa-
tial aspects for a domain ontology (atemporal and as-
patial) remains dependent on the conceptualisation of
the ontology engineer. Second, in order to facilitate
and accelerate the joint assembly of timeless domain
concepts with temporal and/or spatial notions, the in-
teractive process is supported by heuristics for asking
and directing the ontology engineer.
3.1 Assembling Algorithm
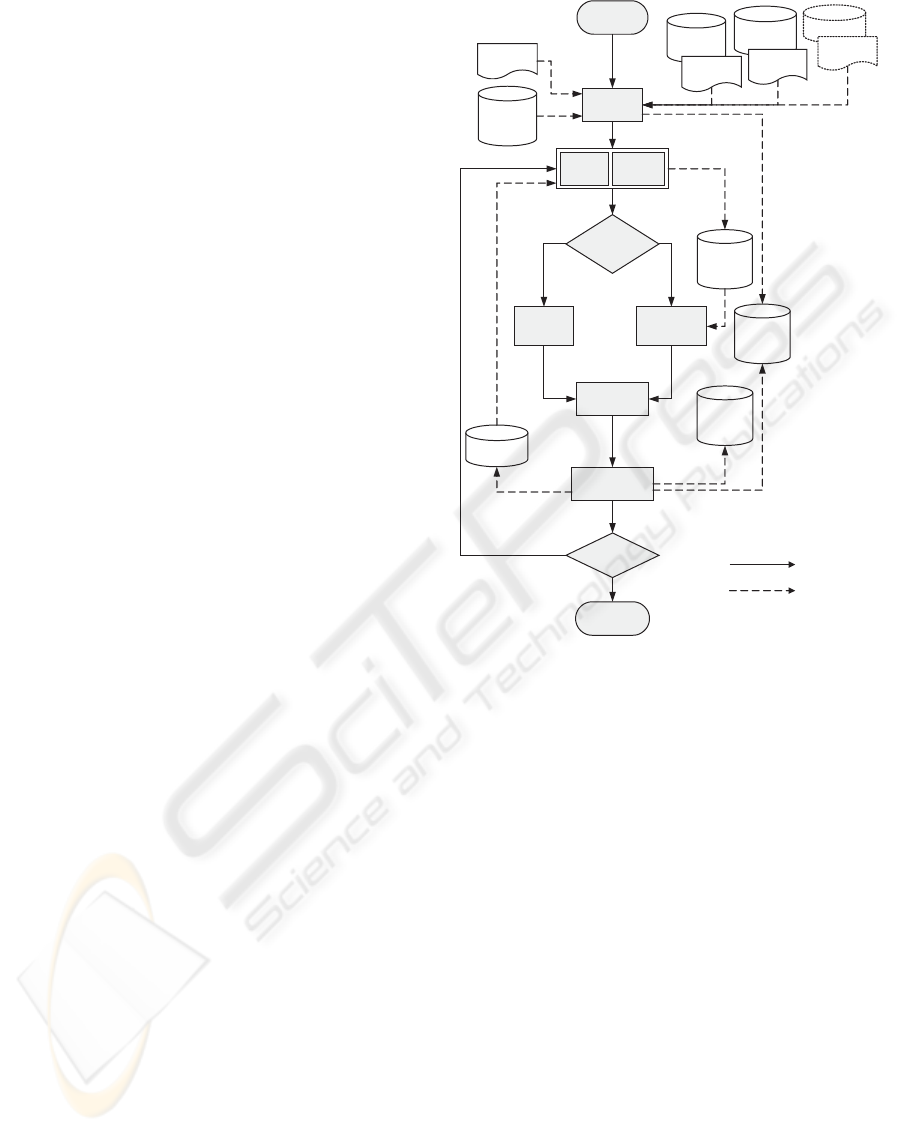
The assembly process runs as depicted in figure 1.
The process starts by an
Initial Setup
. Some basic
operations are performed, namely loading the ontolo-
gies to be assembled, loading a set of rules (one set
for each ontology) to drive the process and initialis-
ing some process parameters. The rules and param-
eters are defined separately from the tool in order to
allow for adaptations to the particular needs of differ-
ent time ontologies. However the rules and parame-
ters do not change when a new domain ontology is to
be assembled. The
Target Ontology
initially corre-
sponds to the union of the timeless domain ontology
and the time theory.
The user may commence by restructuring some
part of the domain ontology to include temporal
and/or spatial aspects through defining and perform-
ing (what we call) task instances. Each task in-
stance (either user initiated or automatically pro-
posed) aims to create a new temporal/spatial concept
by assembling an atemporal/aspatial domain concept
or role with a temporal/spatial one. When perform-
ing such restructuring task instances, a
Structural
Analysis
aims to find related classes (e.g., sub or
super classes in the domain ontology) and puts the
Historic
of Task
Instances
USER:
Iterate
Conclude
Process
Execute Task
Instance
Proposed
Task
Instances
Constraints
USER:
Create or
accept
Process Flow
Data Flow
Create new
Task
Instance
Accept
proposed
Task Instance
Verify
Consistency
Domain
Concepts
Ontology
Structural
Analysis
Semantic
Analysis
Begin
Process
Initial
Setup
Target
Ontology
Ontology 1
(e.g. Time)
Assembling
Rules 1
Ontology 2
(e.g. Space)
Assembling
Rules 2
Ontology N
Assembling
Rules N
Parameters
Figure 1: Assembly process.
appropriate task instances into the
Proposed Task
Instances
.
In the
Structural Analysis
step, a set of tests
is performed that restrict the set of possible task in-
stances to plausible ones, which are then proposed by
insertion into the
Proposed Task Instances
. As
more information becomes available in subsequent
iterations, the usefulness of results provided by the
structure analysis improves.
In subsequent iterations, the engineer decides
whether to accept an automatically proposed task in-
stance from the
Proposed Task Instances
. Alter-
natively, the user may take new initiatives and define
and execute a new task instance from scratch.
For manually defined task instances, a set of log-
ical tests (
Verify Consistency
) is performed to
detect the existence of any knowledge anomalies
(e.g., circularity or redundancy). In contrast, the ac-
ceptance of a proposed task instance does not require
further checks since no invalid task instance can be
proposed.
In the
Execute Task Instance
step, the corre-
sponding changes are made to the target ontology.
The user may subsequently decide either to perform
FONTE - A Protégé Plugin for Engineering Complex Ontologies by Assembling Modular Ontologies of Space, Time and
Domain Concepts
95

another iteration or to go to
Conclude Process
and
accept the current
Target Ontology
as the final ver-
sion.
3.2 Data Structures
We have already informally used the notion of
task
in order to describe to an action template (i.e., a
generic task) that may be instantiated and executed
in order to modify a current target ontology. A task
is defined by the
Task Code
and the
Task Question
.
Task Code. A procedure that uses: a set of keywords
with the commonly expected semantics of structured
programming (e.g.,
if
,
then
,
else
); some special
keywords (
do
,
propose
and
check
, whose semantics
we provide later in this section); and the evocation of
other tasks.
Task Question. Before the execution of a task, the
system prompts a task question in natural language
to the engineer in order to determine if the proposal
should really be accepted or not and in order to ask
for additional constraints that the user might want to
add. The task question is defined by a List of words
and parameters used to compose a sentence in natural
language.
In order to manage various task instances, the
assembling algorithm uses the following data struc-
tures:
Proposed Task Instances. List of tuples
(TaskInstance, TriggersList, Weight)
storing proposed task instances together with the
triggers that raised their proposal and their weight
according to which they are ranked on the task list.
TriggersList. Denotes the list of items that
have triggered the proposal. A trigger is a pair
(TriggerType,TriggerId)
where
TriggerType
has one of the values
class
,
property
or
axiom
and
the
TriggerId
is the item identifier. For instance, the
pair
(concept,
Person
)
is a valid trigger. The list is
useful to query for proposals raised by a specific item
or
TriggerType
.
Weight. Since competing task instances may be pro-
posed,
Weight
is used to reflect the strength of the
proposal on the
TaskList
. Additionally, since a task
instance may be proposed as a consequence of the as-
sembly different classes and/or properties, the weight
is increased in order to reflect the probability of being
accepted.
History of Task Instances. List of all tasks that were
previously performed. This list is useful to allow the
undo operation and to provide statistics about the
assembly process.
Task Constraints List. List of tuples
(TaskInstance,Expression)
storing logical
constraints about previously performed task in-
stances.
do(TaskInstance). The function
do
performs
logical tests over existing task constraints about
TaskInstance
. If there is no impediment, it executes
the task instance and creates a corresponding entry
on the
Task History
.
propose(TaskInstance,Trigger,Weight). The
function
propose
creates a proposal by asserting the
corresponding tuple in the list of
Proposed Task
Instances
.
check(Condition). The function
check
performs a
logical test in order to check if the
Condition
is true
or false in the scope of the participant ontologies.
3.3 Input Modular Ontologies
In order to illustrate the assembly process two ontolo-
gies will be used as building blocks for the target on-
tology, the temporal ontology Time-Entry and the do-
main ontology SWRC about Semantic Web Research
Community.
The Time-Entry (
www.isi.edu/~hobbs/
owl-time.html
) is a sub-ontology of OWL-Time
(see figure 3 for the UML-like depiction of an ex-
cerpt) that embodies concepts like Instant or Interval
often found in ‘standard’ ontologies like SUMO and
assumes a standard interpretation by representing
time points and time intervals as real numbers and
intervals on the real line. As mentioned before, a
temporal representation requires the characterisation
of time itself and temporal incidence; these are rep-
resented in our temporal ontology by TemporalEntity
and Event, respectively.
Temporal Entities. In the temporal ontology we
used as a case study there are two subclasses of
TemporalEntity: Instant and Interval. The relations
before,after and equality can hold between Instants,
respectively represented by the symbols:≺, ≻, =,
allowing to define an algebra based on points (Vilain
et al., 1989). It is assumed that the relations before
and after are irreflexive, asymmetric, transitive
and strictly linear. The thirteen binary relations
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
96
Event
InstantEvent
TemporalEntity
IntervalInstant IntervalEvent
InstantThing
TemporalThing
before:TemporalThing
begins:InstantThing
ends:InstantThing
IntervalThing
inside: InstantThing
Figure 2: Excerpt of Time-entry ontology.
proposed in Allen’s interval algebra (Allen, 1983)
can be defined in a straightforward way based on the
previous three relations (Freksa, 1992).
Events. There are two subclasses of Event, Inter-
valEvent and InstantEvent, in order to be possible to
express continuous and instantaneous events. This
temporal ontology provides the properties begins and
ends which allow to capture the beginning and ending
instants of an event.
The assembly process can be used either for the
development of ontologies with time from scratch, or
for re-engineering existing ones in order to include
time. For our case study we have used the time-less
SWRC-Semantic Web Research Community (
www.
ontoware.org/swrc/
) ontology that served as a
seed ontology for the knowledge portal of OntoWeb.
SWRC comprises 54 classes, 68 restrictions and 44
properties. In figure 3 we present an excerpt of the
SWRC ontology that was used in order to elucidate
the assembly process.
Organization Topic
SWRC
EmployeeUniversity
Project
isAbout:Topic
Person
member:Project
Student
studiesAt:University
Figure 3: Excerpt of the SWRC ontology.
3.4 Assembly of Classes
As mentioned before, system proposals are generated
based on rules and constraints. In the initial phase, the
engineer takes the initiative. From the initial modifi-
cations, some proposals may then be generated auto-
matically, and from these, further new proposals are
spawned. Furthermore, the assembly of classes with
temporal attributes needs to fulfill fewer constraints
than the assembly of properties. Thus, proposals for
modifications with classes are typically made first —
and elaborated in this subsection.
Figure 4 shows an excerpt of the ontology SWRC
emphasising some of its classes and properties,
namely, the classes Project and Person, as well as
the sub-classes of the latter: Employee, Student, Aca-
demicStaff and PhDStudent. The property supervises,
and its inverse property supervisor, capture the re-
lationship between AcademicStaff and PhDStudent;
the property worksAtProject captures the notion that
both an AcademicStaff as a PhDStudent can work in a
given Project.
Employee Student
AcademicStaff PhDStudent
worksAtProject
Project
worksAtProject
isA isA
supervises
supervisor
Person
isA isA
Figure 4: Excerpt of the SWRC ontology.
For the running example here, we assume that
a user links the classes Person (from SWRC ontol-
ogy) with TemporalThing (from Time-Entry ontol-
ogy). This action triggers the execution of the rule
assembleClass
that subclasses a concept c1, viz.
Person, from a c2, viz. TemporalThing. The corre-
Algorithm 1: Assemble class task.
rule
assembleClass
(c1,c2)
if c2=TemporalThing then
do:
createRelation
(isA,c1,c2);
do:
assembleRelatedClasses
(c1,c2);
do:
assembleRelatedProperties
(c1,c2);
propose:
specializeClass
(c1,c2);
end
sponding task
assembleClass
(see algorithm 1) cre-
ates a new isA relation between the Person and Tem-
poralThing and then proposes further assembling tasks
FONTE - A Protégé Plugin for Engineering Complex Ontologies by Assembling Modular Ontologies of Space, Time and
Domain Concepts
97

for related classes and properties. Additionally, a pro-
posal will be created in order to allow further spe-
cialisation of Person; depending on the engineering
options Person could be later defined as IntervalTh-
ing, InstantThing, Event or TemporalEntity as detailed
in
specializeClass
task (see algorithm 2).
Algorithm 2: Specialize class task.
rule
specializeClass
(c1,c2)
if c2=TemporalThing then
answer ←
ask
(Select subclass of #c1);
if answer=IntervalThing then
do:
assembleClass
(c1,time:IntervalThing);
end
if answer=InstantThing then
do:
assembleClass
(c1,time:InstantThing);
end
if answer=Event then
do:
assembleClass
(c1,time:Event);
end
...;
end
The reader may note that this result crucially de-
pends on the temporal theory used, but that rules
could be easily modified to accommodate other the-
ories. Additionally, as mentioned before, the assem-
bly rules do not need to be modified when a new do-
main ontology (e.g., medicine, power systems) is to
be assembled since they are only dependent on the
time/space theory.
3.5 Assembly of Properties
From the assembly of classes there follow proposals
for the modification of properties (captured by OWL
restrictions). For instance, if Person has been mod-
ified to become a subclass of TemporalThing it be-
comes plausible that also the properties that are re-
lated to Person should also be temporalised. Also,
because the isA relation is transitive, is plausible to
say that some/all of its subclasses (direct or indirect)
are also temporal, so the properties that are related to
them should incur in changes too.
From the example, FONTE produces proposals for
temporal assembling the following restrictions:
• supervises(AcademicStaff, PhDStudent);
• supervisor(PhDStudent, AcademicStaff);
• worksAtProject(AcademicStaff, Project);
• worksAtProject(PhDStudent, Project).
The changes occur analogously to the tasks de-
fined for the assembly of classes. In addition however,
there arise further possibilities in order to constrain
the life-time of the actual relationship by the life-time
of the participating classes instances. Thus, super-
vises(AcademicStaff, PhDStudent) is replaced by su-
pervises(AcademicStaff, PhDStudent, Interval) and —
maybe — further constraints on the time instant as
added by the engineer. The most common approach to
dealing with predicates of higher arity than two in lan-
guages like OWL is to reify the relationships through
extension of each relation into an concept that itself
has binary relationships (Welty et al., 2006). One
of the approaches that isused to represent n-ary re-
lations is introducing a new class (token) for a rela-
tion. This pattern is well documented (
www.w3.org/
TR/swbp-n-aryRelations/
) and will be used in our
use case example. The methodology we propose is
independent from the approach used for processing
temporal/spatial reification.
Considering that one member of the academic
staff may work at a project during some time, the
restriction worksAtProject(AcademicStaff,Project)
should be temporalized. Through the use of the
chosen pattern, a new class is created/selected to play
the role of token class (WorksAtProjectRel). This
token captures the relation between AcademicStaff,
Project and Interval. So, it has two restrictions:
• has_value(WorksAtProjectRel, Project) (for
reasoning purposes its inverse property
is_value_for(Project, WorksAtProjectRel) is
also defined;
• intDuring(WorksAtProjectRel, Interval).
Since the restrictions worksAtPro-
ject(AcademicStaff, Project) and worksAtPro-
ject(PhDStudent, Project) proposed to be tempor-
alized are very similar (both use the same property
with the same range), the token class used to describe
the temporal relation would be the same, avoiding
the duplication of token classes. The final result of
temporal assembling is presented in figure 5.
Employee Student
AcademicStaff PhDStudent
isA isA
Person
isA isA
IntervalThing
isA
WorksAtProjectRel
Interval
worksAtProject
intDuring
worksAtProject
Project
has_value
is_value_for
Figure 5: Excerpt of the temporalised SWRC ontology -
property worksAtProject.
The restriction supervises(AcademicStaff, PhD-
Student) may also be temporal, since some mem-
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
98

ber of academic staff supervises PhD students dur-
ing a time-span. The process of temporal assem-
bling of this restriction is analogous to that previ-
ously described, with the assertion of an extra re-
striction supervisor(PhDStudent, AcademicStaff) that
may be specified to ensure the inverse reasoning
and keep the structural logic. The restriction super-
visor(PhDStudent, AcademicStaff) follows the same
procedure. Hence, the final result of the temporal as-
sembly with those two restrictions is presented in fig-
ure 6.
Employee Student
AcademicStaff PhDStudent
Person
isA
IntervalThing
isA
SupervisesRel
Interval
supervises
supervisor
startsOrDuring
has_value
is_value_for
isA
isAisA
Figure 6: Excerpt of the temporalized SWRC ontology -
property supervises.
4 PROTÉGÉ PLUG-IN AND RULE
EDITOR
As described in section 3, a task consists of the defi-
nition of the actions to be performed in the target on-
tology after the performance of an assembly action
(e.g., creation of a relation isA between a domain and
a temporal concept).
Due to the characteristics of the platform (Pro-
tégé), two types of tasks were defined:
Internal Tasks. Allow basic operations to be per-
formed to manipulate the ontologies (e.g., create,
delete and modify classes or properties), and provide
access to the API functionalities of the Protégé
platform in a transparent mode;
External Tasks. Procedures (also called assembly
rules) written in a pseudo-code language that in-
cludes common programme language instructions
(e.g., if, then, else) and special keywords (e.g., do,
propose, check) which semantics has been previously
provided.
In order to facilitate editing/creation of tasks, a
specific tool supported with a graphical interface was
developed; details of this tool are presented in section
4.2.
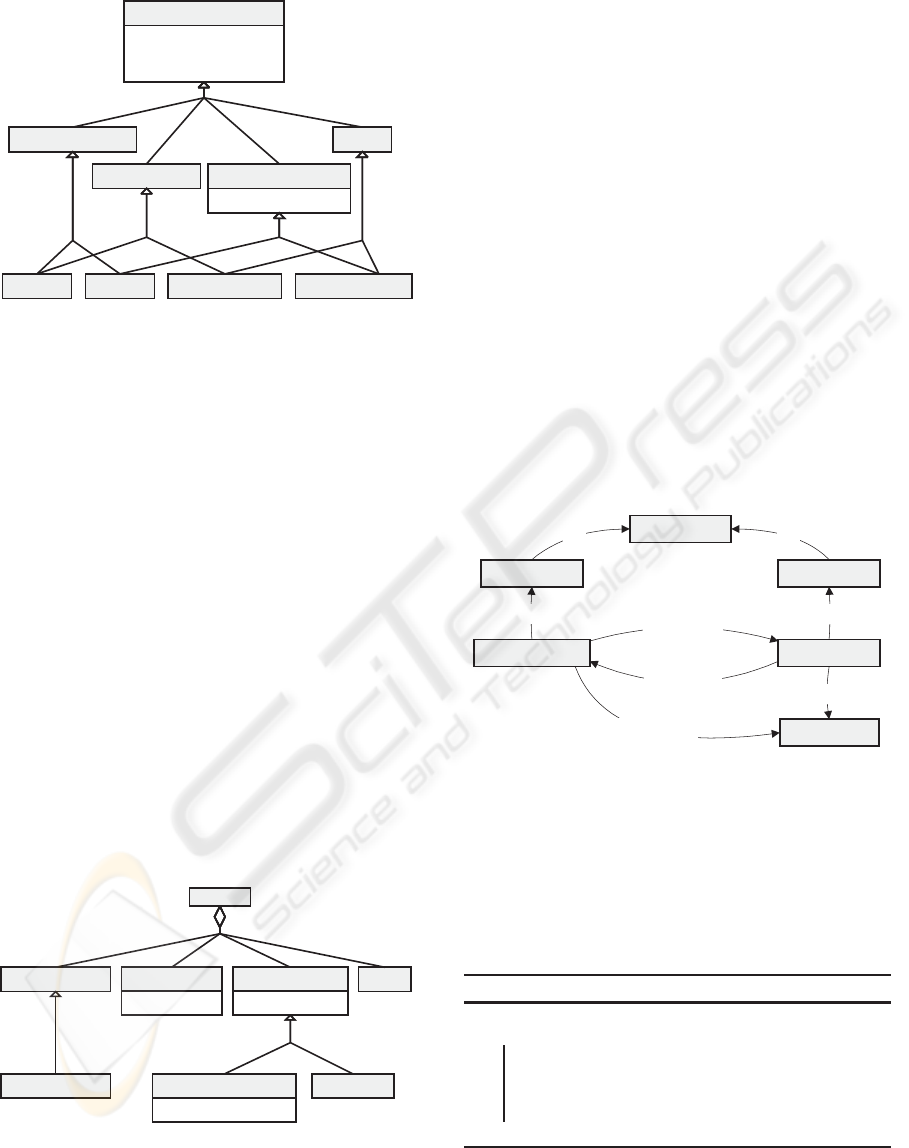
The FONTE plug-in architecture (see figure 7) re-
lies on different abstraction levels which present sev-
eral advantages for the knowledge engineer, such as:
• the knowledge engineer does not need to know the
specifics of the Protégé API to manipulate the on-
tologies. In addition, the Internal Tasks provide
an abstraction level between External Tasks and
Protégé API assuring independency between the
External Tasks and the Protégé API;
• the External Tasks may be created/edited during
execution time and do not require the alteration of
the application and consequent compilation;
• different rules set (which should be stored in
distinct files) allow the use of different tempo-
ral/spatial theories in the assembly process in a
flexible way.
Internal
Task
Task
isA
External
Task
uses
isA
Protégé
API
uses
FONTE
plugin
provides
Rule
Editor
create/edit
Figure 7: FONTE plug-in architecture.
4.1 FONTE Plug-in for Protégé
Protégé is one of the most widely used open source
ontology editor and knowledge-base frameworks,
which provides a powerful graphical interface. In
order to support the iterative and interactive process
used in FONTE, a plug-in for Protégé (version 3.4)
was developed. This plug-in provides a set of func-
tionalities, such as: i) linking concepts of the domain
and temporal/spatial ontology; ii) to accept, reject or
even delay the execution of a task; iii) and to visualise
statistics of the assembly process.
As presented in figure 8, the plug-in presents two
panels for the manipulation of ontologies (in the left-
hand side) and a list of proposals (in the right-hand
side). The panel further to the left contains the domain
ontology (SWRC, which is timeless and spaceless);
from this panel it is possible to access the classes and
properties hierarchies. The other panel contains the
temporal/spatial ontologies to be used as construction
blocks for the production of the target ontology. The
list of proposals contains the records of the task in-
stances generated by the system. Details of this list
are presented below.
To promote the assembly process, the knowl-
edge engineer needs to select the ontologies that will
participate in the assembly process as well as the
files containing the assembly rules for each ontology;
FONTE - A Protégé Plugin for Engineering Complex Ontologies by Assembling Modular Ontologies of Space, Time and
Domain Concepts
99

Figure 8: FONTE plug-in for Protégé.
these can be selected using the setup window (trig-
gered by the setup button showed in the figure).
All the tasks that are successfully performed (ei-
ther triggered manually by user-driven action or auto-
matically by the structural analysis module) are added
to a list containing the instance tasks history.
Associated to each task instance proposal there is
a question in natural language, a trigger list and the
task weight. The question in natural language is com-
posed of a phrase that summarises the proposal’s ob-
jective, instantiated with the elements contained in the
instance task. The trigger list is composed of the el-
ements that triggered the proposal. The weight pro-
vides an indication of the importance of each pro-
posal: the higher the weight, the higher the probabil-
ity of the proposal being accepted during the assem-
bly process.
As the assembly process progresses, more propos-
als are generated. If different concepts happen to pro-
pose the same task instance, all the elements that have
triggered that proposal are included in the trigger list
and the proposal weight is increased to reflect its rel-
evance.
All the proposed task instances are stored in the
list of proposals, which can be sorted by different cri-
teria (e.g., id, trigger or weight). The user can then
accept, reject, or even delay for later analysis, each of
the proposals.
In order to avoid overloading the knowledge engi-
neer with useless proposals, the system does not al-
low a reject proposal to be automatically re-proposed
However, the knowledge engineer has the ability to
manually recover a rejected proposal.
In addition to the functionalities previously de-
scribed, the plug-in also provides statistics about the
assembly process and allows to produce assembly
script files. The assembly process statistics sum-
marises the results of the tool performance, including
the initial and current status of the domain ontology,
the number of tasks that has been initiated by the user
and how many proposals have been accepted or re-
jected. A script file contains a sequence of performed
tasks; this is particularly useful when the knowledge
engineer needs to totally or partially repeat a certain
set of tasks.
4.2 External Rules Editor
An application was developed to facilitate the creation
of external files of rules. This supports the knowledge
engineer through a simple and interactive graphical
interface. The files management system (see figure
9) provides a graphical visualisation of the rules in-
cluded in each file and offers several functionalities,
such as: to sort the list through different criteria, to
modify the order in which the rules are interpreted
during the assembly process, to visualise the rules in
XML or pseudo-code, and also to remove, edit or cre-
ate new assembly rules.
The files of rules and the rules included in each
file can be enriched with a description.
In addition, the tool has a mechanism to support
the creation/edition of rules (see figure 10). This
mechanism alerts the knowledge engineer about po-
tential consistency errors (e.g., using a non declared
variable) or warnings (e.g., declaring a variable that is
not used).
The variables can also be enriched with a descrip-
tion. In addition, and as with most programming lan-
guages, comments can be added to the code, which
will be ignored by the plug-in parser/interpreter.
Several advantages acrue from the use of this tool,
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
100

Figure 9: Assembly rule file manager.
Figure 10: Editing an assembly rule.
namely:
• simple and intuitive manipulation of the files of
rules;
• the XML code is automatically generated, without
syntactic errors;
• easy management of the existing files of rules;
• automatic verification of consistency during the
creation/editing of rules.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this paper we described FONTE, a method that sup-
ports the engineering of complex ontologies including
temporal and/or spatial knowledge that allows factori-
sation of the process complexity by dividing the prob-
lem in parts: modelling the domain concepts ontology
(atemporal and aspatial), modelling or acquiring the
temporal and /or spatial ontology, and finally produc-
ing the target ontology by assembling these modular
ontologies.
A Protégé plug-in was developed in order to sup-
port the FONTE method , which allows FONTE to be
used in an integrated form in the development of on-
tologies. The FONTE methodology works indepen-
dently of the temporal/spatial theory since it allows
the definition/use of sets of assembly rules for each
specific theory. A tool to support the creation/editing
of these rule sets was also presented.
The tasks remain for future work:
• the generic characteristics of the proposed method
should be tested with different spatial/temporal
ontologies, including spatio-temporal ontologies
(also called 4D ontologies);
• it would also be interesting to develop a function-
ality to predict the impact of the acceptance of a
certain proposal;
• improving the generation of automatic propos-
als during the assembly process. This may be
achieved through the use of semantic analysis,
previously successfully used in diverse processes
of ontology engineering (e.g., merging, mapping
and alignment). This will allow the generation of
more and better assembly proposals at an earlier
stage of the process and consequently making it
progressively more automated, given that the cur-
rent FONTE version is limited to structural analy-
sis of the classes and properties hierarchy;
• application of the assembly process
in the automatic modification of rules
for ontology querying such SWRL
(www.w3.org/Submission/SWRL/) and RIF
(www.w3.org/2005/rules/wiki/RIF_Working_
Group).
REFERENCES
Allen, J. (1983). Maintaining knowledge about temporal
intervals. Communication ACM, 26(11):832–843.
Clark, P., Thompson, J., and Porter, B. (2000). Knowledge
patterns. In Proc. KR2000, pages 591–600.
FONTE - A Protégé Plugin for Engineering Complex Ontologies by Assembling Modular Ontologies of Space, Time and
Domain Concepts
101

Cohn, A. G. and Renz, J. (2007). Handbook of Knowledge
Representation, chapter Qualitative Spatial Represen-
tation and Reasoning, pages 551–596. Elsevier.
Cormen, T. H., Leiserson, C. E., and Rivest, R. L. (2000).
Introduction to Algorithms. MIT Press.
Fisher, M., Gabbay, D., and Vila, L., editors (2005). Hand-
book of Temporal Reasoning in Artificial Intelligence,
volume 1 of Foundations of Artificial Intelligence Se-
ries. Elsevier Science & Technology Books.
Freksa, C. (1992). Temporal reasoning based on semi-
intervals. Artificial Intelligence, 54(1):199–227.
Grau, B. C., Horrocks, I., Kazakov, Y., and Sattler, U.
(2007). A logical framework for modularity of ontolo-
gies. In In Proc. IJCAI-2007, pages 298–304. AAAI.
Gruber, T. (1993). Towards Principles for the Design of On-
tologies Used for Knowledge Sharing. In Formal On-
tology in Conceptual Analysis and Knowledge Repre-
sentation, pages 93–104. Kluwer.
Van Harmelen, F., Lifschitz, V., and Porter, B. (2008).
Handbook of Knowledge Representation. Elsevier.
Lutz, C., Walther, D., and Wolter, F. (2007). Conserva-
tive Extensions in Expressive Description Logics. In
Veloso, M., editor, In Proc. of Twentieth International
Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI’07),
pages 453–458. AAAI Press.
Milea, D., Frasincar, F., and Kaymak, U. (2008). An
OWL-Based Approach Towards Representing Time
in Web Information Systems. In In Proc. of 20th
Belgian-Dutch Conference on Artificial Intelligence,
pages 343–344.
Noy, N. and Musen, M. (2000). PROMPT: Algorithm and
Tool for Automated Ontology Merging and Align-
ment. M. P., editor, Proc. AAAI-2000, Austin, Texas.
Parent, C., Spaccapietra, S., and Zimányi, E. (2006).
Conceptual Modeling for Traditional and Spatio-
Temporal Applications: The MADS Approach.
Springer-Verlag New York, Inc., Secaucus, NJ, USA.
Santos, J. and Staab, S. (2003a). Engineering a complex
ontology with time. In 18th International Joint Con-
ference on Artificial Intelligence (IJCAI), pages 1406–
1407, Acapulco/Mexico.
Santos, J. and Staab, S. (2003b). FONTE - Factorizing
ONTology Engineering complexity. In The Second
International Conference on Knowledge Capture (K-
Cap’03), pages 146–153, Florida/USA.
Schreiber, G., Akkermans, H., Anjewierden, A., Hoog, R.,
Shadbolt, N., Van de Velde, W., and Wielinga, B.
(1999). Knowledge engineering and management,
The CommonKADS Methodology. MIT Press.
Staab, S., Erdmann, M., and Maedche, A. (2001). Engi-
neering ontologies using semantic patterns. In Proc.
IJCAI-01 Workshop on E-Business & the Intelligent
Web.
Staab, S. and Maedche, A. (2001). Knowledge portals: On-
tologies at work. AI Magazine, 22(2):63–75.
Staab, S. and Studer, R., editors (2004). Handbook on On-
tologies. Springer.
Stock, O. (1997). Spatial and Temporal Reasoning. Kluwer
Academic Publishers, Norwell, MA, USA.
Studer, R., Decker, S., Fensel, D., and Staab, S. (2004).
Knowledge Engineering and Agent Technology, vol-
ume 52, chapter Situation and Perspective of Knowl-
edge Engineering. IOS Press.
Vale, Z., Ramos, C., Faria, L., Malheiro, N., Marques,
A., and Rosado, C. (2002). Real-time inference for
knowledge-based applications in power system con-
trol centers. Journal on Systems Analysis Modelling
Simulation (SAMS), Taylor&Francis, 42:961–973.
Vila, L. and Schwalb, E. (1996). A theory of time and
temporal incidence based on instants and periods.
Proc.International Workshop on Temporal Represen-
tation and Reasoning, pages 21–28.
Vilain, M., Kautz, H., and Beek, P. (1989). Constraint
propagation algorithms: a revised report. Readings
in Qualitative Reasoning about Physical Systems.
Welty, C., Fikes, R., and Makarios, S. (2006). A reusable
ontology for fluents in OWL. In In Proceedings of
FOIS, pages 226–236.
ICEIS 2010 - 12th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
102
