
AUTOMATIC MINING OF HUMAN ACTIVITY
AND ITS RELATIONSHIPS FROM CGM
Nguyen Minh The, Takahiro Kawamura, Hiroyuki Nakagawa, Yasuyuki Tahara and Akihiko Ohsuga
Graduate School of Information Systems, The University of Electro-Communications
1-5-1, Chofugaoka, Chofu-shi, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords:
Human activity, Semantic network, Web mining, Self-supervised learning, Conditional random fields.
Abstract:
The goal of this paper is to describe a method to automatically extract all basic attributes namely actor,
action, object, time and location which belong to an activity, and the relationships (transition and cause)
between activities in each sentence retrieved from Japanese CGM (consumer generated media). Previous
work had some limitations, such as high setup cost, inability of extracting all attributes, limitation on the types
of sentences that can be handled, insufficient consideration of interdependency among attributes, and inability
of extracting causes between activities. To resolve these problems, this paper proposes a novel approach that
treats the activity extraction as a sequence labeling problem, and automatically makes its own training data.
This approach has advantages such as domain-independence, scalability, and unnecessary hand-tagged data.
Since it is unnecessary to fix the positions and the number of the attributes in activity sentences, this approach
can extract all attributes and relationships between activities by making only a single pass over its corpus.
Additionally, by converting to simpler sentences, removing stop words, utilizing html tags, google map api,
and wikipedia, the proposed approach can deal with complex sentences retrieved from Japanese CGM.
1 INTRODUCTION
The ability of computers to provide the most suit-
able information based on users’ behaviors is now an
important issue in context-aware computing (Matsuo
et al., 2007), ubiquitous computing (Poslad, 2009)
and social computing (Ozok and Zaphiris, 2009;
Phithakkitnukoon and Dantu, 2009). For example, a
service delivers shop information based on the users’
next destination (NTTDocomo, 2009), a service de-
livers advertisements based on the users’ context in-
formation (Jung et al., 2009). To identify the users’
behaviors, it is necessary to understand how to collect
activity data, how to express or define each activity
and its relationships. It is not practical to define each
activity and its relationships in advance, because it not
only takes enormous cost, but also cannot deal with
unpredictable behaviors.
Today, CGM is increasingly generated by users
posting their activities to Twitter, Facebook, their we-
blogs or other social media. Thus, it is not difficult
to collect activity sentences (that describe activities)
of different users from CGM. However, sentences re-
trieved from CGM often have various structures, are
complex, are syntactically incorrect. Thus, there are
lots of challenges to extract all activity attributes and
relationships between activities in these sentences.
Few previous works have tried to extract attributes in
each sentence retrieved from CGM. These works have
some limitations, such as high setup costs because of
requiring ontology for each domain (Kawamura et al.,
2009). Due to the difficulty of creating suitable pat-
terns, these works are unable to extract all attributes
(Perkowitz et al., 2004; Kawamura et al., 2009), lim-
ited on the types of sentences that can be handled
(Perkowitz et al., 2004; Kurashima et al., 2009; The
et al., 2010), insufficiently consider interdependency
among attributes (Perkowitz et al., 2004; Kurashima
et al., 2009), and are unable to extract causes between
activities (Perkowitz et al., 2004; Kurashima et al.,
2009; Kawamura et al., 2009).
Since each attribute has interdependent relation-
ships with the other attributes in every activity sen-
tence, we can treat attribute extraction as an open re-
lation extraction (Banko et al., 2007). In other words,
we extract an action and other word phrases that have
relationships with this action and describe their activ-
ity. In this paper, we propose a novel approach based
on the idea of O-CRF (Banko and Etzioni, 2008) that
applies self-supervised learning (Self-SL) and uses
285
Minh The N., Kawamura T., Nakagawa H., Tahara Y. and Ohsuga A. (2010).
AUTOMATIC MINING OF HUMAN ACTIVITY AND ITS RELATIONSHIPS FROM CGM.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 285-292
DOI: 10.5220/0002922802850292
Copyright
c
SciTePress

conditional random fields (CRFs) to the open relation
extraction. O-CRF is the state-of-the-art of the open
relation extraction from English web pages. Our ap-
proach focuses on Japanese CGM, and treats activ-
ity extraction as a sequence labeling problem. This
approach automatically makes its own training data,
and uses CRFs as a learning model. Our proposed ar-
chitecture consists of two modules: Self-Supervised
Learner and Activity Extractor. Given some activ-
ity sentences retrieved from the “people” category
of Wikipedia, the Learner extracts all attributes and
relationships between activities, by using deep lin-
guistic parser and some syntax patterns as a heuris-
tics. And then, it combines extracted results to auto-
matically makes training data. Finally, it uses CRFs
and template file to make the feature model of these
training data. Based on this feature model, the Ex-
tractor automatically extracts all attributes and rela-
tionships between activities in each sentence retrieved
from Japanese CGM.
The main contributions of our approach are sum-
marized as follows:
• It has domain-independence, without requiring
any hand-tagged data.
• It can extract all attributes and relationships be-
tween activities by making only a single pass over
its corpus.
• It can handle all of the standard sentences in
Japanese, and achieves high precision on these
sentences.
The remainder of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. In section 2, we indicate challenges of extract-
ing attributes in more detail. Section 3 explains how
our approach makes its own training data, and extracts
activity in each sentence retrieved from Japanese
CGM. Section 4 reports our experimental results, and
discuss how our approach addresses each of the chal-
lenges to extract activity attributes. Section 5 consid-
ers related work. Section 6 consists of conclusions
and some discussions of future work.
2 CHALLENGES
2.1 Activity Attributes Definition
The key elements of an activity are actor, action, and
object. To provide suitable information to users, it
is important to know where and when activity hap-
pens. Therefore, we define an activity by five ba-
sic attributes: actor, action, object, time, and loca-
tion. We label these attributes as Who, Action, What,
When and Where respectively. In this paper, we focus
on the transitions and causes between activities, and
label these relationships as Next and BecauseOf re-
spectively. For example, Figure 1 shows the attributes
and the relationships between activities derived from
a Japanese sentence.
ha-ba-do daigaku (Harvard)
what BecauseOf what
kyugaku shita sougyou shita
who
(took a leave of absence)
(founded)
geitsu (Gates)
maikurosofuto (Microsoft)
Figure 1: The attributes and the relationship between the
activities derived from the activity sentence “maikurosofuto
wo sougyou suru tame ni, geitsu ha ha-ba-do daigaku wo
kyugaku shita” (To found Microsoft, Gates took a leave of
absence from Harvard.).
2.2 Challenges of Extracting Activity
Attributes
Extracting activity attributes in sentences retrieved
from CGM has many challenges, especially in
Japanese. Below, we explain some of them:
1. As shown in Figure 2, O-CRF extracts binary re-
lations in English, and these relations must occur
between entity’s names within the same sentence
(Banko and Etzioni, 2008). Additionally, O-CRF
determines entities before extracting, so it deal
with a single variable (relation). But Japanese
sentences do not follow the S-V-O rule, they have
many types of structures and flexible. Moreover
in this paper, we need deal with multi-variables
(five attributes, transition, and cause). Therefore,
we can not directly apply O-CRF for extracting
activities in Japanese.
object (O)
<p1>
Google
<p1> to
acquire
<p2>
YouTube
<p2>
entity1 relation entity2
subject (S) verb (V)
Figure 2: Limitation of O-CRF: relations must occur be-
tween entity names.
2. Since number and position of attributes are chang-
ing in different sentences, it is difficult to cre-
ate instances or patterns to extract all attributes
and relationships between activities. Addition-
ally, sentences retrieved from CGM are often di-
versified, complex, syntactically wrong, and have
emoticons.
ICSOFT 2010 - 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
286

3. It is not practical to deploy deep linguistic parsers,
because of the diversity and the size of the Web
corpus (Banko and Etzioni, 2008).
4. If extraction method is domain-dependent, then
when shifting to a new domain it will require a
new specified training examples. And, the extrac-
tion process has to be run, and re-run for each do-
main.
5. In Japanese, there are not word spaces, and
word boundaries are not clear . However, previ-
ous works in CRFs assume that observation se-
quence (word) boundaries were fixed. Therefore,
a straightforward application of CRFs is impossi-
ble.
3 HUMAN ACTIVITY MINING
USING CRFS AND
SELF-SUPERVISED LEARNING
3.1 Activity Extraction with CRFs
CRFs (Lafferty et al., 2001) are undirected graphi-
cal models for predicting a label sequence to an ob-
served sequence. The idea is to define a conditional
probability distribution over label sequences given an
observed sequence, rather than a joint distribution
over both label and observed sequences. CRFs offers
several advantages over hidden Markov models and
stochastic grammars, including the ability of relax-
ing strong independence assumptions made in those
models. Additionally, CRFs also avoids the label
bias problem, which is a weakness exhibited by max-
imum entropy Markov models (MEMMs) and other
conditional Markov models based on directed graph-
ical models. CRFs achieves high precision on many
tasks including text chunking (Sha and Pereira, 2003),
named entity recognition (McCallum and Li, 2003),
Japanese morphological analysis (Kudo et al., 2004).
By making a first-order Markov assumption that
has dependencies between output variables, and ar-
ranging variables sequentially in a linear-chain, activ-
ity extraction can be treated as a sequence labeling
problem. Figure 3 shows an example where activity
extraction is treated as a sequence labeling problem.
Tokens in the surrounding context are labeled using
the IOB2 format. B-X means “begin a phrase of type
X”, I-X means “inside a phrase of type X” and O
means “not in a phrase”. IOB2 format is widely-used
for natural language tasks (CoNLL, 2000). In this pa-
per, we use CRF++
1
to implement this linear-chain
1
Available at http://crfpp.sourceforge.net/
CRF.
B-Who O B-What O B-Action I-Action
geitsu ha maikurosofuto wo sougyou shita
Gates Microsoft founded
(Gates founded Microsoft)
Figure 3: Activity extraction as sequence labeling.
3.2 Proposed Architecture
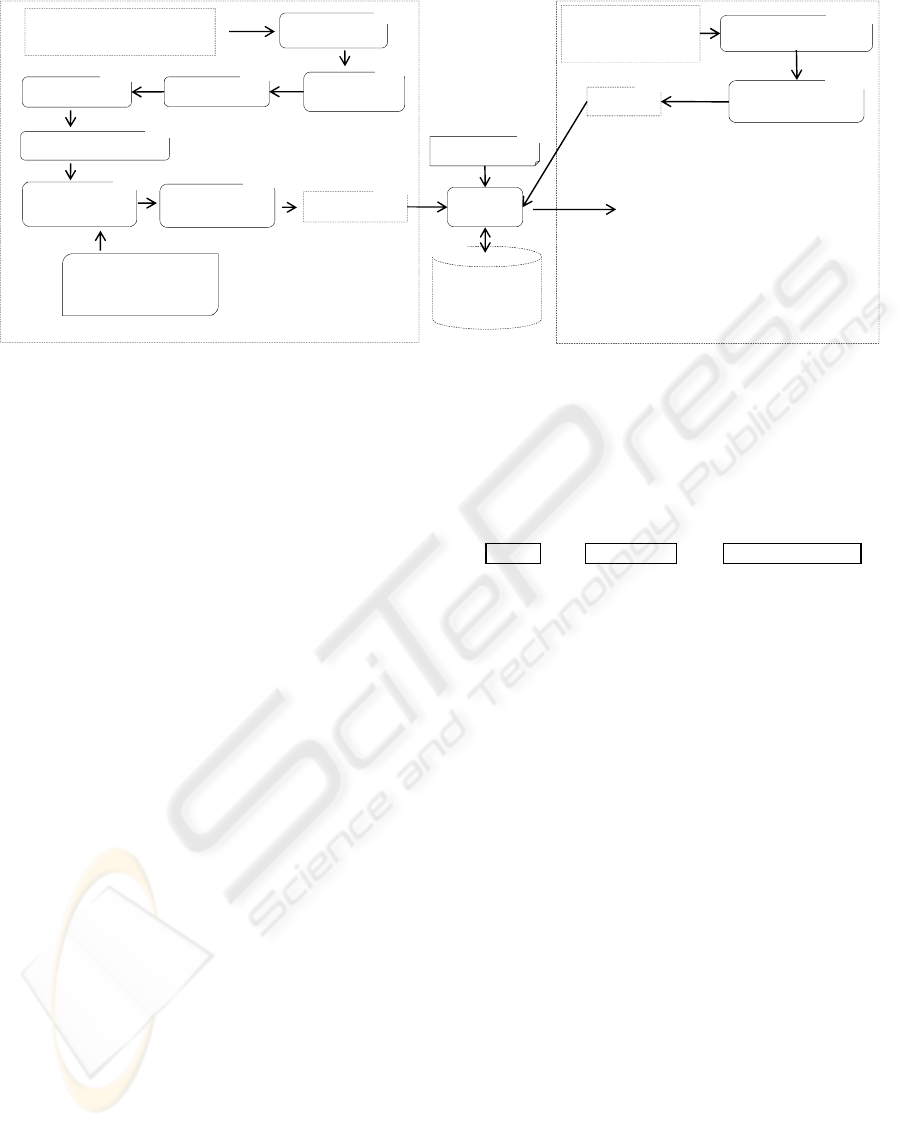
As shown in Figure 4, the architecture consists of two
modules: Self-Supervised Learner (I in Figure 4) and
Activity Extractor (II in Figure 4). Sentences retrieved
from the “people” category of Wikipedia (Wikipedia,
2009b) are often syntax correct, activity describable,
and easy to parse. Therefore, we parse these sen-
tences to get activity sentences, and then send these
activity sentences as sample data to the Learner. The
Learner deploys deep linguistic parser to analyze the
dependencies between word phrases. Based on the
prepared list of Japanese syntax, it selects trustwor-
thy attributes to make training data, and the feature
model of these data. The Extractor does not deploy
deep parser, it bases on this feature model to automat-
ically extract all attributes, and relationships between
activities in sentences retrieved from Japanese CGM.
Below, we describe each module in more detail.
3.2.1 Self-supervised Learner Module
We will use the example sentence “geitsu ha
maikurosofuto wo sougyou shita” (Gates foundedMi-
crosoft) to explain how the Learner works and makes
its own training data. As shown in Figure 4, the
Learner consists of nine key tasks:
1. By using Mecab
2
, it parses the sample data to get
words and their POS tags in each sentence (I.1 in
Figure 4).
2. By using Cabocha
3
, it analyzes the interdepen-
dency among word phrases in each sentence (I.2
in Figure 4). Up to this step, the Learner
can detect verb phrase (VP), noun phrase (NP),
POS tags, named entity, and the interdependency
among word phrases in each sentence.
3. In addition to the aboveanalytical result, based on
the Japanese regular time-expressions such as VP-
taato, VP-maeni, toki...etc, the Learner extracts
the time of activity and labels it as When (I.3 in
Figure 4).
2
Available at http://mecab.sourceforge.net/.
3
Available at http://chasen.org/ taku/software/cabocha/.
AUTOMATIC MINING OF HUMAN ACTIVITY AND ITS RELATIONSHIPS FROM CGM
287
Taro 44 B-Who
ha 16 O
eigo 38 B-What
wo w O
manan v B-Action
de 18 I-Action
iru 33 I-Action
Label of attributes & relationships (output)
Activity Extractor Module ( II )
(Taro is learning English)
Self-Supervised Learner Module ( I )
Dependency
analysis
CRF
Test data
Feature Model
of
Training Data
Template File
Get words & POS tags
Convert to
simpler sentences
Activity sentences
retrieved from CGM
(input)
Heuristics:
- S, {O,C} , V
...
Extract actor,
action, object
Morphological
analysis
Extract time
Extract
location
Detect person's name
Extract
relationships
Training Data
I.1
I.2
I.3
I.4
I.5
I.6
I.7
I.8
II.1
II.2
II.3
II.4
T
Activity sentences retrieved
from Wikipedia (sample data)
I.9
Figure 4: Proposed Architecture: by using deep linguistic parser and a heuristics, the Learner makes its own training data.
4. To improve precision of location extraction, in ad-
dition to the above analytical result, the Learner
uses the google map api (Google, 2009) to extract
the location of activity and labels it as Where (I.4
in Figure 4).
5. Japanese natural language processing (NLP) tools
often have errors when analyzing foreign person
name. In this case, the Learner utilizes the “hu-
man names” category of Wikipedia (Wikipedia,
2009a) to improve precision of person name de-
tection (I.5 in Figure 4).
6. To select trustworthy activity sentences, we pre-
pare the list of nine Japanese syntax patterns as,
• {O, C}, {wo, ni, he}, V
• S, {O, C}, {wo, ni, he}, V
• {O, C}, {wo, ni, he}, V, S
• S ga V ha {O, C}
• S ga V {C} ha {O}
• S ha N ga V
• wo N
• N ga (ha) V
• N wo N ni
where O means object, C means complement, V
means verb, N means noun, “ha/ga/wo/ni/he” are
postpositionalparticles in Japanese. Actor,action,
object correspond to S, V, O respectively. Based
on these syntax patterns, the Learner extracts ac-
tor, action, object, and then labels them as Who,
Action, What respectively (I.6 in Figure 4).
7. Based on Japanese syntax patterns such as V-
taato, V-mae, V-node...etc, the Learner extracts
the relationships between activities, and labels as
Next or BecauseOf (I.7 in Figure 4).
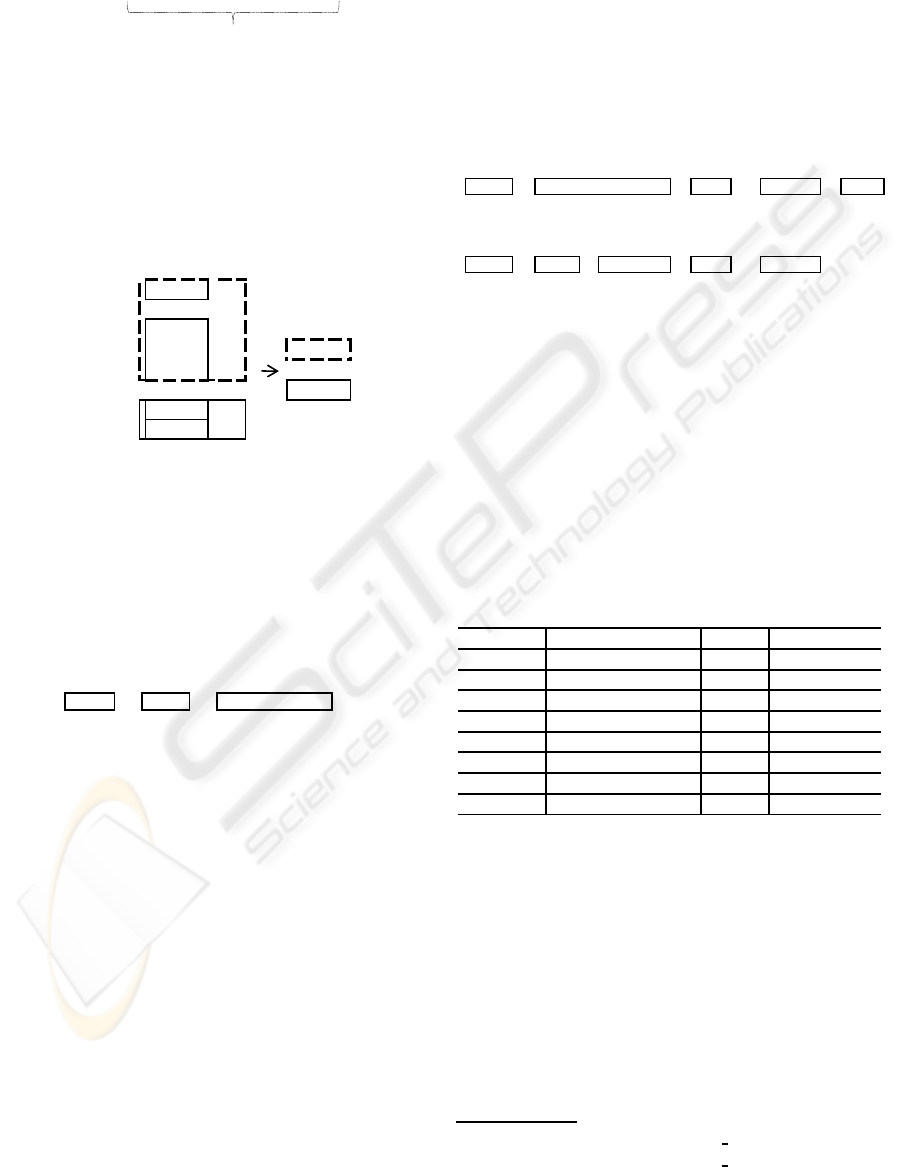
8. As shown in Figure 5, training data are automati-
cally created by combining the above results (I.8
in Figure 4).
B-Who O B-What O B-Action I-Action
43 16 45 w v 25
geitsu ha maikurosofuto wo sougyou shita
Gates Microsoft founded
(Gates founded Microsoft)
Figure 5: Training data of the example sentence.
9. The Learner uses CRF and template file to auto-
matically generate a set of feature functions (f 1,
f 2, ..., f n) as illustrated in Figure 6. The feature
model of these training data is created from this
set of feature functions (I.9 in Figure 4).
3.2.2 Activity Extractor Module
We parse Japanese CGM pages to receiveactivity sen-
tences, and then remove emoticons, and stop words in
these sentences. In this case, stop words are the words
which do not contain important significance to be
used in activity extraction. After this pre-processing,
we send activity sentences to the Extractor. As shown
in Figure 4, the Extractor consists of four key tasks:
1. The Extractor uses Mecab to get words and their
POS tags (II.1 in Figure 4). As shown in Figure 7,
in addition to analytical result by Mecab, the Ex-
f 1 = if (label = "B-Who" and POS="43") return 1 else return 0
f 2 = if (label = "O" and POS="16") return 1 else return 0
….
f n = if (label = "B-Action" and POS="v") return 1 else return 0
Figure 6: Feature functions.
ICSOFT 2010 - 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
288
tractor utilizes html tags to detect a long or com-
plex noun phrases.
<a href="...">Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation</a>
detect as a noun phrase
Figure 7: Using html tags to detect a noun phrase.
2. To avoid error when testing, the Extractor con-
verts complex sentences to simpler sentences by
simplifying noun phrases and verb phrases (II.2
in Figure 4). When converting, we must keep the
POS tags of these word phrases. Figure 8 shows
the example of converting the complex sentence
to the simpler sentence.
location chiiki
38
, 9
study abroad ryugaku 36
no 24 NP
38
documents syurui
38
wo w
wo w VP v
choose erabi v
begin hajimaru v
Figure 8: Convert “chiiki, ryugaku no syurui wo erabi-
hajimaru” (Begin choosing region, documents for study
abroad) to the simpler sentence.
3. The Extractor makes test data by combining the
above results (II.3 in Figure 4). As shown in Fig-
ure 9, unlike training data, test data does not have
label row. This label row is predicted when test-
ing.
44 16 38 w v 18 33
taro ha eigo wo manan de iru
Taro
English
Learning
Figure 9: Test data for the example sentence “taro ha eigo
wo manan de iru” (Taro is learning English).
4. Based on the feature model, the Extractor auto-
matically extracts all attributes and relationships
between activities in each sentence of the test data
(II.4 in Figure 4).
3.2.3 Template File
We use the feature template file to describe features
that are used in training and testing (T in Figure
4). The set of features includes words, verbs, part-
of-speech (POS) tags and postpositional particles in
Japanese. To model long-distance relationships, this
paper uses a window of size 7.
4 EVALUATION
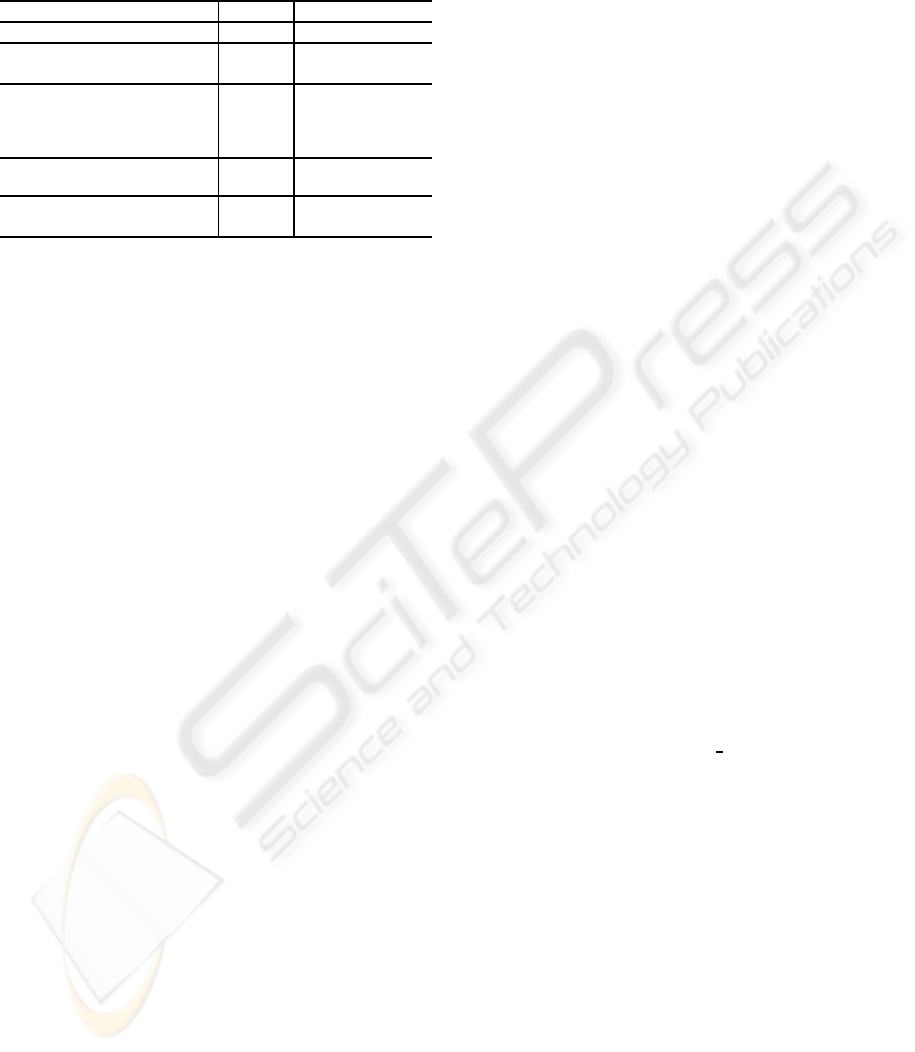
4.1 Experimental Results
To evaluate the benefits of our approach, we used the
set of 533 activity sentences
4
retrieved from Japanese
CGM. There are 356 sentences that describe one ac-
tivity, 177 sentences that describe two activities in this
experimental data. Figure 10 shows two sentences
which are used for this experiment.
kaunta- de, nihon no menkyosyou wo teiji shite
tetsudzuki
wo okonau
counter Japanese driver's license show then procedure do
(At the counter, shows the Japanese driver's license and then proceeds)
heya he modo te gaisyutsu no jyunbi wo shimashita
room come back going out preparation done
(Came back to the room, then prepared to go out)
Figure 10: Two activity sentences in our experimental data.
In this experiment, we say an activity extraction
is correct when all attributes of this activity are cor-
rectly extracted. The precision of each attribute is de-
fined as the number of correctly extracted attributes
divided by the total number. Using one PC (CPU:
3.2GHz, RAM: 3.5GB), the Extractor module makes
only a single pass over the entire experimental data
set, and gets the results
5
as shown in Table 1. This
process took only 0.27s.
Table 1: Experimental results.
@ Should be extracted Correct Precision (%)
Activity 710 631 88.87
Actor 196 182 92.86
Action 710 693 97.61
Object 509 479 94.11
Time 173 165 95.38
Location 130 120 92.31
Transition 26 22 84.62
Cause 42 36 85.71
4.2 Consideration
The experimental results have shown that our ap-
proach can automatically extract all attributes and re-
lationships between activities in each sentences by
making only a single pass with high precision. Addi-
tionally, our method took only 0.27s, while a widely
known deep parser such as Cabocha took over 46.45s
for parsing the experimental data (our approach out-
performs over 172 times). Below, we describe how
our approach resolves the limitations of the previous
4
http://docs.google.com/View?id=dftc9r33 1077g63vrjc5
5
http://docs.google.com/View?id=dftc9r33 1078cr9hd3mt
AUTOMATIC MINING OF HUMAN ACTIVITY AND ITS RELATIONSHIPS FROM CGM
289

works, and addresses the challenges indicated in sec-
tion 2.
• It is domain-independent, and automatically cre-
ates training data. So that, our approach does not
take high setup costs.
• By treating activity extraction as a sequence la-
beling problem, our approach can express all at-
tributes of any activity. Additionally, by using the
heuristics (the list of Japanese syntax patterns),
our approach does not need to fix the position and
number of attributes. These are reasons for which
our approach is able to extract all attributes in any
activity sentence.
• Based on the list of the nine Japanese syntax pat-
terns, it makes training data for all typical sen-
tences. Additionally, it removes stop words, sim-
plifies complex sentences before testing, utilizes
html tags, google map api, and wikipedia. These
are reasons for which the Extractor could deal
with many type of sentences.
• The feature model contains features of interde-
pendencies among attributes in each sentence of
training data. Based on these features, the Ex-
tractor can consider interdependencies among at-
tributes in each sentence of testing data.
• It uses Mecab and html tags to get word phrases
in each sentence.
However, our approach also has some limitations.
Firstly, it only extracts activities that are explicitly de-
scribed in the sentences. Secondly, it has not yet ex-
tracted relationships between activities in document-
level. Finally, to handle more complex or incorrect
syntax sentences, we need improve our architecture.
4.3 Applying to other Languages
Our proposed architecture focus on Japanese, but it
could also be applied to other languages by changing
suitable syntax patterns for the Learner. We should
also re-design the template file to utilize special fea-
tures of the applied language.
5 RELATED WORK
There are two fields related to our research: human
activity extraction and relation extraction (RE) from
the Web corpus. Below, we discuss the previous re-
searches of each field.
5.1 Human Activity Extraction
Previous works on this field are Perkowitz (Perkowitz
et al., 2004), Kawamura (Kawamura et al., 2009),
Kurashima (Kurashima et al., 2009), and Minh (The
et al., 2010). Perkowitz’s approach is a simple key-
word matching, so it can only be applied for cases
of recipe web pages (such as making tea or coffee).
Kawamura’s approach requires a product ontology
and an action ontology for each domain. So, the pre-
cision of this approach depends on these ontologies.
Kurashima used JTAG (Fuchi and Takagi, 1998)
to deploy a deep linguistic parser to extract action and
object. It can only handle a few types of sentences,
and is not practical for the diversity and the size of
the Web corpus. Additionally, because this approach
gets date information from date of weblogs, so it is
highly possible that extracted time might be not what
activity sentences describe about.
In our previous paper (The et al., 2010), the
proposed approaches could not handle complex sen-
tences, and could not extract causes between activities
yet.
5.2 Relation Extraction
The main researches of RE are DIPRE (Brin, 1998),
SnowBall (Agichtein and Gravano, 2000), KnowItAll
(Etzioni et al., 2004), Pasca (Pasca et al., 2006), Tex-
tRunner (Banko et al., 2007), O-CRF (Banko and Et-
zioni, 2008).
DIPRE, SnowBall, KnowItAll, and Pasca use
bootstrapping techniques applied for unary or binary
RE. Bootstrapping techniques often require a small
set of hand-tagged seed instances or a few hand-
crafted extraction patterns for each domain. In ad-
dition, when creating a new instance or pattern, they
could possibly extract unwanted patterns around the
instance to be extracted, which would lead to ex-
tract unwanted instance from the unwanted patterns.
Moreover, it is difficult to create suitable instances
or patterns for extracting the attributes and relation-
ships between activities appeared in sentences re-
trieved from the Web.
TextRunner is the first Open RE system, it uses
self-supervised learning and a Naive Bayes classifier
to extract binary relation. Because this classifier pre-
dict the label of a single variable, it is difficultto apply
TextRunner to extract all of the basic attributes.
O-CRF is the upgraded version of TextRunner.
Because of the differences in tasks (activity, binary
relation) and languages (Japanese, English), it is dif-
ficult to compare our approach with O-CRF. We try to
compare them according to the some criteria as shown
ICSOFT 2010 - 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
290
in Table 2.
Table 2: Comparison with O-CRF.
O-CRF Our Approach
Language English Japanese
Target data
Binary
Relation
Human
Activity
Type of sentences
can be handled
S-V-O
{O, C}, V
S, {O, C}, V
...
all typical syntax
Relation must occur
between entities yes no
Requirement of determining
entities before extracting yes no
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper proposed a novel approach that uses CRFs
and Self-SL to automatically extract all attributes
and relationships between activities derived from sen-
tences in Japanese CGM. Without requiring any hand-
tagged data, it achieved high precision by making
only a single pass over its corpus. This paper also
explains how our approach resolves the limitations of
previous works, and addresses each of the challenges
to activity extraction.
We are improving the architecture to handle more
complex or incorrect syntax sentences. Based on links
between web pages, we will try to extract relation-
ships between activities at the document-level. In the
next step, we will use a large data set to evaluate our
approach. We are also planning to build a large human
activity semantic network based on mining human ex-
periences from the entire CGM corpus.
REFERENCES
Agichtein, E. and Gravano, L. (2000). Snowball: Extracting
relations from large plain-text collections. In Proc.
ACM DL 2000.
Banko, M., Cafarella, M. J., Soderland, S., Broadhead, M.,
and Etzioni, O. (2007). Open information extraction
from the web. In Proc. IJCAI2007, pages 2670–2676.
Banko, M. and Etzioni, O. (2008). The tradeoffs between
traditional and open relation extraction. In Proc. ACL-
08.
Brin, S. (1998). Extracting patterns and relations from the
world wide web. In Proc. EDBT-98, Valencia, Spain,
pages 172–183.
CoNLL (2000). Conll 2000 shared task: Chunking.
http://www.cnts.ua.ac.be/conll2000/chunking/.
Etzioni, O., Cafarella, M., Downey, D., Popescu, A.-M.,
Shaked, T., Soderland, S., S.Weld, D., and Yates, A.
(2004). Methods for domain-independent information
extraction from the web: An experimental compari-
son. In Proc. AAAI-04.
Fuchi, T. and Takagi, S. (1998). Japanese morphological
analyzer using word co-occurence-jtag. In Proc. ACL-
98, pages 409–413.
Google (2009). Google maps api services.
http://code.google.com/intl/en/apis/maps/documentat
ion/geocoding/.
Jung, Y., Lim, S., Kim, J.-H., and Kim, S. (2009). Web min-
ing based oalf model for context-aware mobile adver-
tising system. The 4th IEEE/IFIP Int. Workshop on
Broadband Convergence Networks (BcN-09), pages
13–18.
Kawamura, T., The, N. M., and Ohsuga, A. (2009). Build-
ing of human activity correlation map from weblogs.
In Proc. ICSOFT.
Kudo, T., Yamamoto, K., and Matsumoto, Y. (2004). Ap-
plying conditional random fields to japanese mor-
phologiaical analysis. In Proc. EMNLP2004, pages
230–237.
Kurashima, T., Fujimura, K., and Okuda, H. (2009). Dis-
covering association rules on experiences from large-
scale weblogs entries. In Proc. ECIR 2009., LNCS vol
5478. Springer 2009.
Lafferty, J., McCallum, A., and Pereira, F. (2001). Con-
ditional random fields: Probabilistic models for seg-
menting and labeling sequence data. In Proc.
ICML2001.
Matsuo, Y., Okazaki, N., Izumi, K., Nakamura, Y.,
Nishimura, T., and Hasida, K. (2007). Inferring long-
term user properties based on users’ location history.
In Proc. IJCAI2007, pages 2159–2165.
McCallum, A. and Li, W. (2003). Early results for named
entity recognition with conditional random fields, fea-
ture induction and web-enhanced lexicons. In Proc.
CoNLL.
NTTDocomo, I. (2009). My life assist service.
http://www.igvpj.jp/contents en/activity09/ms09/list/
personal/ntt-docomo-inc-1.html.
Ozok, A. A. and Zaphiris, P. (2009). Online Communi-
ties and Social Computing. Third International Con-
ference, OCSC 2009, Held as Part of HCI Interna-
tional 2009, San Diego, CA, USA. Springer, ISBN-
10: 3642027733.
Pasca, M., Lin, D., Bigham, J., Lifchits, A., and Jain, A.
(2006). Organizing and searching the world wide web
of facts - step one: the one-million fact extraction
challenge. In Proc. AAAI-06, pages 1400–1405.
Perkowitz, M., Philipose, M., Fishkin, K., and J.Patterson,
D. (2004). Mining models of human activities from
the web. In Proc. WWW2004.
Phithakkitnukoon, S. and Dantu, R. (2009). A dimension-
reduction framework for human behavioral time se-
ries data. AAAIf09 Spring Symposium on Technosocial
Predictive Analytics, Stanford University, CA.
Poslad, S. (2009). Ubiquitous Computing Smart Devices,
Environments and Interactions. Wiley, ISBN: 978-0-
470-03560-3.
AUTOMATIC MINING OF HUMAN ACTIVITY AND ITS RELATIONSHIPS FROM CGM
291

Sha, F. and Pereira, F. (2003). Shallow parsing with con-
ditional random fields. In Proc. NAACL HLT, pages
213–220.
The, N. M., Kawamura, T., Nakagawa, H., Tahara, Y., and
Ohsuga, A. (2010). Self-supervised mining human ac-
tivity from the web. Technical report of IEICE (in
Japanese).
Wikipedia (2009a). Category:human names. http://en.wiki
pedia.org/wiki/Category:Human names.
Wikipedia (2009b). Category:people. http://en.wikipedia.
org/wiki/Category:People.
ICSOFT 2010 - 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
292
