
FDI WITH NEURAL AND NEUROFUZZY APPROACHES
Application to Damadics
Y. Kourd, N. Guersi
Department of Control Engineering, Faculty of Science and Engineer, Mohamed Khider Biskra University, Algeria
Department d'Electronique, Université Badji Mokhtar Annaba, Algeria
D. Lefebvre
GREAH – Université Le Havre, 25 rue Philippe Lebon, 76058 Le Havre, France
Keywords: Fault Diagnosis, Modelling, Residual Generation, Residual Evaluation, Neural Classifier, Neurofuzzy
Classifiers.
Abstract: Fault diagnosis is a major challenge for complex systems as long as it increases the safety and
productivity. This work concerns faults diagnosis, based on artificial intelligence, neural networks, and
fuzzy logic. Thanks to an associative memory, neural networks have good capacities of organization,
approximation and classification. Combined with fuzzy logic, neural networks are an effective tool for
system modelling, fault detection and fault diagnosis. This paper illustrates the potential of these tools for
the modelling and the diagnosis of an industrial actuator (DAMADICS benchmark).
1 INTRODUCTION
Fault detection and isolation (FDI) is a major issue
for complex systems as long as it increases the
safety and productivity of these systems. Its first
vocation is the detection and the isolation of system
failures. The necessity to detect and isolate early the
failures calls upon techniques of the artificial
intelligence. These techniques have been recently
developed and improved by many researchers. The
point is that artificial intelligence makes easier the
task carried out by the operators as long as the
observation of symptoms and the data analysis or
information interpretation is carried out by the
diagnosis system.
Several methods exist for the diagnosis of
dynamical systems. Basically, model-based and
data-based methods can be distinguished (Chow,
1980; Patton et al. 1989; Gertler, 1991; Willsky,
1976). Model – based methods compare the
measured data with the knowledge provided by the
model of theconsidered system in order to detect and
isolate the faults that disturb the process. Such
techniques require a sufficiently accurate
mathematical model of the process.Data-based
methods require a lot of process measurements and
can be divided into signal processing methods and
artificial intelligence approaches. Model and data
based methods are used to design residual signals.
The fault detection results from the comparison of
the residuals with arbitrary thresholds: a fault is
detected each time one residual ccross over the
threshold. This comparison is calculated on line. To
isolate the faults, residuals are structured to be
robust and sensitive to some specific sets of faults.
In this context, our study concerns the
investigation of model-based FDI methods with
artificial intelligence, particularly neural networks
and fuzzy logic. Fuzzy logic can be used to describe
the system behaviours according to linguistic rules
and fuzzy sets. The advantage of fuzzy logic is that
it can be used in presence of uncertainties. The
drawback is that the number and expression of the
rules and also the parameters of the membership
functions that define the sets are not easy to be work
out. In that case, neural networks are helpful to
identify the unknown parameters according to
measured data and to learning algorithms.
This paper concerns the application of neural
networks, fuzzy logic and neurofuzzy systems
(ANFIS) for an industrial actuator from the sugar
factory in Lublin, Polen (Damadics, 2004).
368
Kourd Y., Guersi N. and Lefebvre D. (2010).
FDI WITH NEURAL AND NEUROFUZZY APPROACHES - Application to Damadics.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 368-372
DOI: 10.5220/0002928103680372
Copyright
c
SciTePress
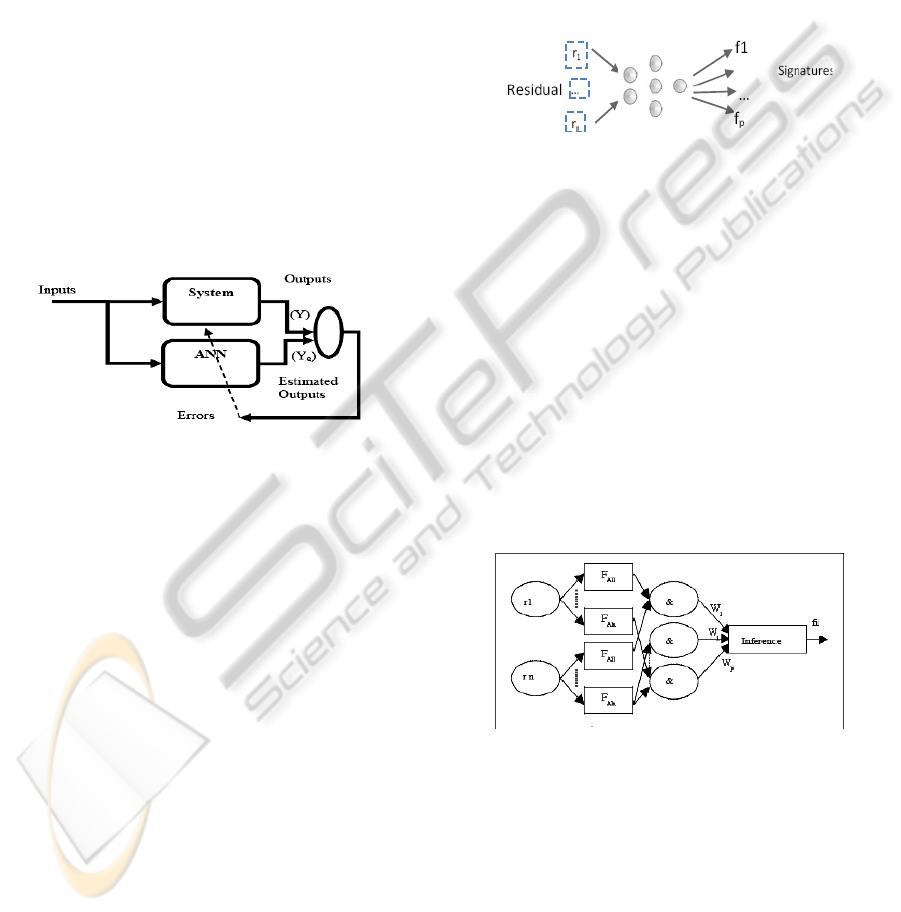
2 FDI METHODS
The proposed approach can be presented with 3
stages (1) the design of a data – based model; (2) the
fault detection according to a residual generator; (3)
the fault isolation thanks to neural or neurofuzzy
classifiers.
2.1 Reference Model Design
In the following we consider dynamic systems with
q inputs u
i
(t) and n outputs y
j
(t) and it is assumed
that the state variables are no measurable. Such
systems exhibit often complex dynamics, with
strong nonlinearities. As a consequence, knowledge
–based models are not easy to obtain. Another
approach lies in the data–based models. Artificial
neural networks (ANN) are often used for that
purpose (Juditsky et al. 1995). The goal is to design
a model that will be used for the generation of
residuals (figure 1).
Figure 1: Data-based model design.
In order to get the best ANN architecture, several
configurations are tested according to a trial – error
processing that uses pruning to eliminate the useless
nodes. The learning of the ANN is obtained
according to the Levenberg-Marquardt algorithm
with early stopping. This algorithm is known for its
rapid convergence. During learning stage, the ANN
is trained with data collected during the normal
functioning of the system. Then the ANN reference
model is validated with another set of data.
2.2 Fault Detection
The considered system may be affected by p faults
Fi with the assumption that simultaneous faults do
not occur. The vector r(t) of n residuals r
i
(t) is
calculated according to the difference between the
outputs vector of the system y(t) and the output
vector of the ANN model y
e
(t). As long as the
system has no fault, the estimated output y
e
(t)
remains in the neighbourhood of the actual output
y(t) and the residual r(t) is near zero. When a fault
occurs, at least one estimated output becomes
different from and the actual one and the
corresponding residual is no longer near zero.
2.3 Fault Isolation with ANN
A neural classifier has been developed to isolate the
faults after detection (Kourd et al., 2008). This
classifier is a multilayer Perceptron ANN (figure 2).
The inputs are the n residuals r
i
(t) and the outputs
are the p signatures f
i
of the faults F
i
that are under
consideration.
Figure 2: Neural classifier.
The neural classifier is trained and validated with
a learning algorithm similar to the one used for
reference model design.
2.4 Fault Isolation with ANFIS
In order to deal with improve the isolation, a
neurofuzzy classifier has also been developed
(figure 3). Such a classifier has an hybrid
architecture that takes advantages from fuzzy logic
and neural networks (Nauck et al. 1995). This
classifier is design as a double Takagi- Sugeno
ANFIS networks. The inputs are the n residuals r
i
(t)
and the outputs are the p signatures f
i
of the faults F
i
that are under consideration.
Figure 3: Double neurofuzzy ANFIS classifiers.
3 APPLICATION TO DAMADICS
3.1 System Description
The system under consideration is the DAMADICS
valve (figure 4). It is composed of a pneumatic
servomotor and a controller that drives the valve.
FDI WITH NEURAL AND NEUROFUZZY APPROACHES - Application to Damadics
369

Figure 4: Actuator shema.
This system has four input variables (CV, P1, P2,
T1) and 2 outputs variables (X, F) that are described
in table 1 (DAMADICS 2004). The other variables
are not considered in our application.
Table 1: Input and output variables.
There exist 20 possible faults that may affect the
functioning of the actuator (DAMADICS 2004).
Some faults may be abrupt or incipient ones.
3.2 Model Design
The actuator is modeled with two multilayer
perceptrons ANN that represent the interaction
between the inputs and the outputs according to (1):
netX = netX (CV, P1, P2, T1)
(1)
netF = netF(X, P1, P2, T1)
To select the structure of the neural networks
netX and netF, numerous tests have been carried out
to obtain the best architectures (i.e. number of
hidden layers and number of neurons by layer) in
order to model the operation of the actuator. The
training and test data were generated by the
simulation of the Matlab-Simulink actuator model
(Kourd et al. 2008).
From table 2, we notice that netX(6,3,1) and
netF(6,3,1) give the best results. When the training is
over, the ANN netF provides estimated outputs that
are not far from the actual ones. Validation is done
with the measured data provided by the ‘Lublin
Sugar Factory in 2001 (DAMADICS, 2004).
Validation is illustrated on figure 5.
Table 2: netX and netF neural networks structure.
Figure 5: Actual output F and estimated output netF (up);
Instantaneous error (down).
The modelling error is acceptable. Similar
conclusions are obtained with ANN netX. Let notice
that the output of netX is an input for netF and the
sensitivity of the estimation depends strongly on the
error on netX. As a conclusion, both ANNs provide
a good approximation of the actuator dynamics.
3.3 Fault Detection
In the following four faults will be considered: F7
(medium cavity or critical flow) F10 (servo-motor's
diaphragm perforation) F15 (positioner spring fault)
and F17 (positioner supply pressure drop) in order to
illustrate the efficiency of the proposed approach.
Two residual are designed according to (2):
rF = F - netF
(2)
rX = X - netX
During normal functioning the residuals remain
near zero: their magnitude is in range [-0,2; 0,2].
The value 0.2 will be used as detection threshold
(Emami-Naeini, 1988; Ding and Frank, 1991). Let
us notice that a low pass filter is used to remove high
frequency noises. In figure 6, the residuals are
worked out when the fault F7 is simulated during
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
370
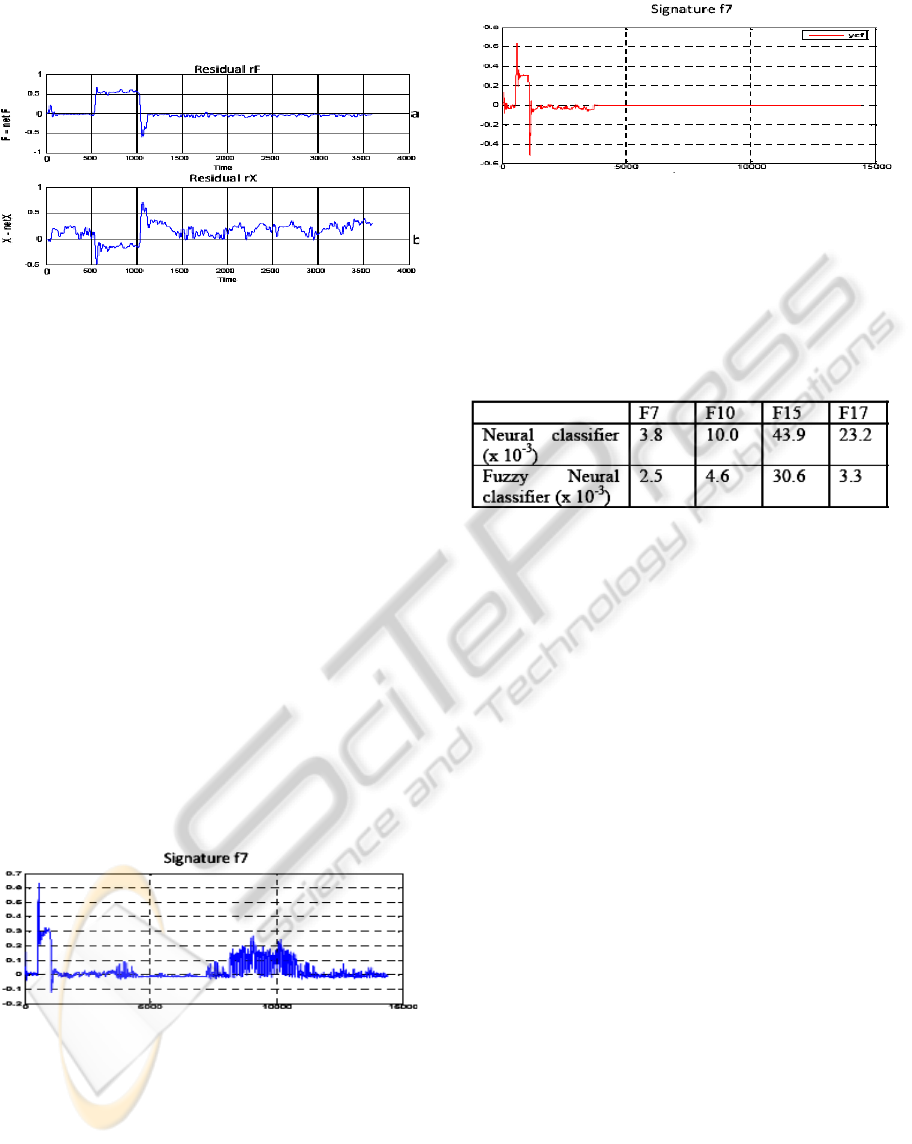
interval [500 1000] time units (times units are in
seconds).
Figure 6: Residual in presence of fault F7; Residual rF
(up); Residual rX (down).
3.4 Fault Isolation
The classifiers presented in section 2 are trained
with a set of simulated faults. Then they are
validated according to the real data collected on the
Sugar factory:
During period [500, 1100], the fault F7 occurs.
During period [4100, 4600], the fault F10 occurs.
During period [7700, 9000], the fault F15 occurs.
At times 11300 and 11850 the fault F17 occurs.
The ANN classifier presented in section 2.3
receives two inputs: the residuals rX and rF and
delivers four outputs that are the signatures f7, f10,
f15, f17 of the faults F7, F10, F15, F17. The
signature f7 is given in figure 7. The neural classifier
gives acceptable results in the sense that the
signature of each fault is far from zero when the
considered faults occur. But misclassifications may
occur.
Figure 7: Magnitude of the fault signatures f7 in function
of time for ANN classifier.
The ANFIS classifier presented in section 2.4 has
also two inputs and four outputs. The resulting
signature f7 is given in figure 8.
Figure 8: Magnitude of the fault signature f7 in function of
time for ANFIS classifier.
The use of ANFIS classifier improves the
classification results. The number of
misclassifications decreases and the quadratic mean
square on error of the residuals decreases (table 3).
Table 3: Quadratic mean square error.
4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper uses neural networks and fuzzy logic for
the fault diagnosis. The neural networks are good
tools for the modelling and diagnosis of non linear
processes, but some problems remain in the
selection of the optimal architecture as well as the
number of layers, and the numbers of neurons in
each layer. The uses of neurofuzzy networks
improve the classification of faults.
In our further works we will consider numerical
criteria to compare both classifiers, we will also
compare our results with the existing results and we
will improve the neurofuzzy diagnosis system.
REFERENCES
Chow, E. Y., Failure detection system design
methodology, Thesis, Lab. Information and Decision
system, M.I.T, Cambridge, 1980.
Ding, X., Frank P. M., Frequency domain approach and
threshold selector for robust model-base fault
detection and isolation, Proc. SAFEPROCESS'91,
Baden-Baden, Germany, vol. 1, pp. 307-312, 1991.
Emami-Naeini, A. E. A., Effect of model uncertainty of
failure detection: the threshold selector, IEEE-TAC,
33, pp. 1106- 1115, 1988.
Gertler, J. J., Analytical redundancy methods in fault
detection and isolation – survey and synthesis, Proc.
FDI WITH NEURAL AND NEUROFUZZY APPROACHES - Application to Damadics
371

SAFEPROCESS’91, Baden-Baden, Germany, pp. 9-
21, 1991.
Juditsky, A., Hjalmärsson, H., Benveniste, A., Delyon, B.,
Ljung, L., Sjöberg, J., Zhang, Q., Nonlinear black-box
modelling in system identification: mathematical
foundations. Automatica, 31, pp. 1725-1750, 1995.
Nauck, D., Kruse, R., Nefclass – A neurofuzzy approach
for the classification of data, Proc. Symp. on Applied
Computing – ACM, Nashville, USA, 1995.
Patton, R. J., Frank, P. M., Clarck, R. N., Fault diagnosis
in dynamic systems, Prentice Hall, 1989.
Willsky, A. S., A survey of design methods for failure
detection in dynamic systems, Automatica 12, pp.
601-611, 1976.
Kourd, Y., Guersi, N., Lefebvre, D., A two stages
diagnosis method with neuronal networks, Proc.
ICEETD 2008, Hammamet, Tunisie.
DAMADICS (2004): Website of DAMADICS:
Development and Application of Methods for
Actuator Diagnosis in Industrial Control Systems.
http://diag.mchtr.pw.edu.pl/damadics/.
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
372
