
NONLINEAR INTO STATE AND INPUT DEPENDENT FORM
MODEL DECOMPOSITION
Applications to Discrete-time Model Predictive Control with Succesive
Time-varying Linearization along Predicted Trajectories
Przemyslaw Orlowski
Institute of Control Engineering, West Pomeranian University of Technology, Szczecin, Poland
Keywords: Non-linear systems, Successive linearization, Predictive control, Optimal control, Discrete time systems.
Abstract: Linearization techniques are well known tools that can transform nonlinear models into linear models. In the
paper we employ a successive model linearization along predicted state and input trajectories resulting in
linear time-varying model. The nonlinear behaviour is represented in each time sample by recurrent set of
linear time-varying models. Solution of the optimal non-linear model predictive control problem is obtained
in an iterative way where the most important step is the linearization along predicted trajectory. The main
aim of this paper is to analyse how the nonlinear system should be transformed into linear one to ensure
possibly fast solution of the model predictive control problem based on the successive linearization method.
1 INTRODUCTION
Model predictive control (MPC) is attractive control
strategy, which have 3 common properties
(Camacho et. al. 2004): explicit use of a model to
predict the output at future time instants, calculation
of a control trajectory minimizing an objective
function and receding horizon (moving horizon)
strategy. MPC issues for linear systems including
stability are well known (Camacho et. al., 2004),
(Morari et. al. 1999), (Tatjewski, 2007), (Mayne et.
al., 2000) also (Qin et. al. 2003), (Magni et. al.
1999), including fast algorithms (Blachuta, 1999)
and discrete-time system with delays (Kowalczuk et.
al. 2005). Many real systems are inherently
nonlinear. Due to higher product quality
specifications, some important environmental and
economical reasons linear models are often
inadequate to describe the system properties.
Computing the optimal control trajectory directly for
nonlinear model is difficult, non-convex
optimization problem. Generally there is no
guarantee that the computed solution is global
optimal solution. Moreover it is difficult to prove
global stability of the system using directly the
nonlinear model for control synthesis. In practise
some transformations and simplifications are applied
to the nonlinear model in order to prove stability,
and also to take advantages of theory for linear
systems.
Among some existing approaches in nonlinear
model predictive control in the paper we consider
successive model linearization along predicted state
and input trajectories with recurrent linear time-
varying (LTV) model. A large class of these
methods uses a common algorithm, i.e.
(Kouvartiakis et. al., 1999) employ an optimal
control trajectory calculated at the previous time
instant of the control algorithm for NMPC. (Lee et.
al., 2002) use a similar methodology and employ a
linearization at points of the seed trajectory for the
discrete-time model of the system. Also the
technique presented in (Dutka et. al., 2004), (Ordys
et. al., 2001), (Mracek et. al., 1998), (Grimble et. al.,
2001), (Dutka et. al., 2003) uses similar idea to
(Kouvartiakis et. al., 1999), (Lee et. al., 2002) but
with a different model representation and an
optimisation technique. Similar approach for the
construction of an explicit nonlinear control law
approximating nonlinear constrained finite-time
optimal control using approximate mapping of a
general nonlinear system into a set of piecewise
affine systems is presented in (Ulbig et. al., 2007).
The main aim of this paper is to analyse how to
linearize (decompose) nonlinear system into linear
one for using with the successive model linearization
method along predicted state and input trajectories.
87
Orlowski P. (2010).
NONLINEAR INTO STATE AND INPUT DEPENDENT FORM MODEL DECOMPOSITION - Applications to Discrete-time Model Predictive Control with
Succesive Time-varying Linearization along Predicted Trajectories.
In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics, pages 87-92
DOI: 10.5220/0002928700870092
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The main difficulty is to find proper transformation
method, which ensure fast computation of stable and
optimal solution for nonlinear control problem.
2 SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
Let us assume general discrete-time, time-varying
nonlinear model in the following form:
()
(
)()
(
)
1,,kkkk+=xfxu
(1)
The nonlinear system can be transformed into
following discrete-time, time-varying state-
dependent form:
()
() ()
()
() () ()
()
()
1
,, ,,
k
kkkk kkkk
+=
+
x
Ax u x Bx u u
(2)
where
() ()
()
() ()
()
,,, ,,kkk kkkAx u Bx u
are
state and input dependent matrices calculated for
given initial condition x
0
and control trajectory
(
)
ku
at each time instant.
Then, using the past input and state trajectories,
matrices
() () ()
()
() ()
(
)
()
,,, ,,k k kk k k kk==A Axu B Bxu
may be calculated for the subsequent points of the
trajectories and the nonlinear system (1) is
approximated by the LTV model with matrices
(
)
(
)
, kkAB
. Discrete-time LTV system is given in
the state space form:
()()
(
)()()
1kkkkk+= +xAxBu
(3)
where
() ()
,
nn nm
kk
××
∈∈ABRR
,
00
,..., 1kk k N=+−
and
N is the prediction horizon.
Linear time-varying discrete-time system can be
equivalently defined using evolution operators or in
the finite horizon case, also by following block
matrix operators
ˆˆˆ
,,LNB
:
0
0
00
00
1
1
11
11
ˆ
k
k
kN kN
kkN
φ
φφ
+
+
++
++
−−
−
⎡⎤
⎢⎥
⎢⎥
=
⎢⎥
⎢⎥
⎢⎥
⎣⎦
I0 0
I0
L
I0
I
,
0
0
0
0
1
ˆ
k
k
kN
k
φ
φ
+ −
⎡⎤
⎢⎥
=
⎢⎥
⎢⎥
⎢⎥
⎣⎦
N
(4)
()
()
0
0
ˆ
1
k
kN
⎡⎤
⎢⎥
=
⎢⎥
⎢⎥
+−
⎣⎦
B0 0
B0 0
00B
(5)
where
(
)
(
)
(
)
1
k
i
kk i
φ
=−AA A…
. For state and
input trajectories
ˆˆ
, xu
we use the following block
column vector notation, i.e.
()( )
00
ˆ
1
T
TT
kkN
⎡
⎤
=+ +
⎣
⎦
xx x
(6)
() ( )
00
ˆ
1
T
TT
kkN
⎡
⎤
=+−
⎣
⎦
uu u
(7)
It follows that the mathematical model can be
rewritten in the final form as
0
ˆˆ ˆ
ˆˆ
=+xLBuNx
(8)
We assume that at each time instant the system can
be analyzed as starting from time sample equal to
zero with a current initial condition
(
)
00
k=xx
up
to N steps into the future (prediction horizon).
The operator
ˆˆ
LB
is a compact and Hilbert-Schmidt
one from l
2
into l
2
and boundedly maps signals
[
]
200
() , 1klkkN
∈
=+−u L
into signals
x ∈ X
.
For simulation purposes we employ cost function in
the following form:
(
)
(
)
ˆ
ˆ
ˆˆ ˆˆ ˆ ˆ
T
T
ref ref
J =− − +xx Pxx uQu
(9)
where
(
)
(
)()()
ˆ
ˆ
,
nN nN mN mN××
∈∈PQRR
are weighting
operators, constructed with weighting matrices
(
)
(
)
, 1... , , 0... 1
nn mm
kkNk kN
××
∈
=∈=−PQRR
,
respectively usually given in following block matrix
form:
(
)
()
(
)
()
10
ˆ
ˆ
,
1NN
⎡
⎤⎡ ⎤
⎢
⎥⎢ ⎥
==
⎢
⎥⎢ ⎥
⎢
⎥⎢ ⎥
−
⎣
⎦⎣ ⎦
P00 Q 0 0
P0 0Q 0 0
00P 0 0Q
Usually weighting matrices are time-invariant with
the exception of
(
)
NP
which represents the
terminal cost. Equivalently the cost function can be
rewritten in the following form:
()
()
()
()
()
()()()
00
1
00
1
00
0
T
N
k
ref ref
N
T
k
kk kk
Jk
kk kk
kk k kk
=
−
=
⎛+ ⎞ ⎛+ ⎞
=
⎜⎟⎜⎟
⎜⎟⎜⎟
−+ −+
⎝⎠⎝⎠
++ +
∑
∑
xx
P
xx
uQu
(10)
where the term
()
()
()
()
()
00
00
T
ref ref
Nk Nk
N
Nk Nk
⎛+ ⎞ ⎛+ ⎞
⎜⎟⎜⎟
⎜⎟⎜⎟
−+ −+
⎝⎠⎝⎠
xx
P
xx
for k=N in the first sum of (10) is the terminal cost.
3 PROBLEM DESCRIPTION
The nonlinear system described by the discrete-time
nonlinear state space model can be rearranged into
the so-called state and control dependent linear form
(Mracek et. al., 1998), (Huang et. al., 1996). The
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
88

non-linear behaviour of the system is included in the
state and control dependent matrices. If the
trajectory prediction for the system may be obtained
within the algorithm then one can pretend that the
future behaviour is known during the prediction
horizon (Dutka et. al., 2004). Such a system can be
treated as a linear time-varying (LTV) one. Most
often the algorithm, shown on fig. 1 has common
steps (Kouvartiakis et. al., 1999), (Orlowski, 2005).
Figure1: Algorithm of the time-varying linearization along
predicted trajectory.
In general there no restrictions to the cost function.
For simulation purposes we employ cost function
given by eq. (9). However in practise the method can
be also used with different frequently used in MPC
cost functions and stabilizing conditions, e.g.:
terminal cost function, terminal equality constraint,
terminal constraint set. It is only required to define
an MPC problem for the LTV system.
The second important problem is choosing initial
control trajectory. The simplest choice could be step
control signal with amplitude from normal operating
range for the control. Another possibility is to use at
the beginning a few initial control trajectories and
choose the one which results in the smallest cost
function. The trajectory is required only for
linearization purposes and only in the first iteration
of the algorithm for the first time step. For the
consecutive time steps on receding horizon it may be
assumed from previous control predictions.
Definition 1. The algorithm from fig. 1 is
convergent if there exists a limiting control sequence
ˆ
opt
u
such that for any arbitrarily small positive
number ε>0, there is a large integer I such that for
all i≥I,
()
ˆˆ
opt
i
ε
−
≤uu
. The algorithm that is not
convergent is said to be divergent.
The algorithm converges both for local or global
optimal solutions. Divergent algorithm cannot
satisfy a stopping condition usually given by
following absolute tolerance condition:
() ( )
1
ˆˆ
ii
ε
−
−
≤uu
(11)
for arbitrarily small
ε
.
The control can be computed using arbitrary method
for LTV systems, including algorithms with signal
constraints. The algorithm from fig. 1 refer only to
one time step computation. Usually it is employed
with receding horizon. The algorithm must be
repeated for successive time steps
00
1kk=+
.
4 NONLINEAR SYSTEM
DECOMPOSITION
To transform of the non-linear model (1) into the
time-varying state dependent form given by eq. (2)
one needs to decompose nonlinear function
(
)
(
)
(
)
,,kkkfx u
into 2 factors corresponding to
state and input matrices such that:
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)()()
(
)
,,kk kk k kk+=Ax Bu fx u
.
For example, let us assume nonlinear function:
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
, sin arctan
f
xk uk xk xk uk uk=+
Transformation into state and input dependent form
can be easily done by simple expansion terms
dependent on state and input only, i.e.:
(
)
(
)
(
)
() ()
()
sin , arctankxkk uk==AB
More difficult problem is decomposition of a system
consisting coupled input-state terms. Assume for
example function
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
,
f
xk uk xkuk=
. One
Choose the cost function, signal constraints, the reference
trajectory and the initial control trajectory
()
0
ˆ
u
.
Transform the non-linear model given in general form
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
1,,kkkk+=xfxu
into the time-varying state dependent form
()
1k +=x
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
(
)
,, ,,kkkk kkkk+Ax u x Bx u u
Increase iteration number j=j+1
Calculate new control
()
ˆ
i
u
Check stopping condition
() ( )
1
ˆˆ
ii
ε
−
−≤uu
Satisfied ?
N
Optimal control
()
ˆˆ
opt
i
=uu
found
Ye
NONLINEAR INTO STATE AND INPUT DEPENDENT FORM MODEL DECOMPOSITION - Applications to
Discrete-time Model Predictive Control with Succesive Time-varying Linearization along Predicted Trajectories
89

of possible decompositions is to divide the function
into following 2 additive terms:
() ()
()
()() ( )()
(
)
,1
f
xk uk xkuk xkuk
αα
=+−
where:
() ()
(
)( )()
, 1kuk k xk
αα
==−AB
In general we propose following method which
allow to decompose arbitrary nonlinear function
(
)
(
)
(
)
,,kkkfx u
into series of M additive
components. Using the simplified notation
(
)
(
)
(
)
,,
ii
kkk=ffx u
for a fixed input trajectory
and initial conditions we have
() ()
()
() ()
()
11
,, ,,
MM
ii
ii
kkk kkk
==
==
∑∑
fx u f x u f
(12)
Every system (1) can be decomposed into the state
dependent form (2). In general, this decomposition
takes the following form:
()
,,
111 11
1
MnM mM
iiji iji
iji ji
k
αβ
=== ==
⎛⎞⎛⎞
+= = +
⎜⎟⎜⎟
⎝⎠⎝⎠
∑∑∑ ∑∑
xf f f
(13)
()
,1 , ,1 ,
1111
1
MMMM
ii ini ii imi
iiii
k
ααββ
====
+=
++ + ++
∑∑∑∑
x
fff f……
(14)
What can be arranged into following vector-matrix
state and input dependent form:
()
[][][][]
11 11
11 11
1
nn mm
TT
nn mm
kx xu u
xx uu
+= ++ + ++
=+
=+
xaabb
aa bb
Ax Bu
……
(15)
where
,
1
,
M
jj iji
i
x
α
=
=
∑
af
(16)
,
1
,
M
jj iji
i
u
β
=
=
∑
bf
(17)
,,
11
1
nm
ij ij
i
jj
αβ
==
∀+=
∑∑
(18)
The component column vectors of matrices A(k) and
B(k) can be determined under assumption that the
following limits
00
lim , lim
jj
j
jjj
jx ju
j
j
x
u
x
u
→→
∀∀
ab
exist and
are finite. These vectors are given by expressions
0
0
lim 0
j
jj
j
j
j
jj
j
x
j
x
x
x
x
x
x
→
⎧
≠
⎪
⎪
=
⎨
⎪
=
⎪
⎩
a
a
a
(19)
0
u 0
lim u 0
j
jj
j
j
j
jj
j
u
j
u
u
u
u
→
⎧
≠
⎪
⎪
=
⎨
⎪
=
⎪
⎩
b
b
b
(20)
where
(
)
[
]
(
)
[
]
11
,
nm
kk==AaaBbb
, n – order, m –
number of inputs,
,
jj
ab
- column vectors with n
rows
Let us assume that function f(x,u,k) can be
decomposed into the following four additive terms:
(
)
() ( ) () ()
12 34
,,
,,,,
k
kkkk
=
+++
fxu
fxfxufuf
(21)
The vector functions f must be continuous and the
following limits calculated in respect to all
coordinates of f and x/u must be finite:
3
1
00
lim ,lim
→→xu
f
f
xu
(22)
and either
22
00
lim , or/and lim
→→xu
ff
xu
(23)
where
[]
[]
[] []
[] []
1
1
11 11
00
11
1
1
1
0
111
00
1
lim lim
, lim
lim lim
R
R
xx
R
RRR
xx
R
ff
f
x
x
fff
x
x
→→
→
→→
⎡
⎤
⎢
⎥
⎡⎤
⎢
⎥
⎢⎥
⎢
⎥
=
⎢⎥
⎢
⎥
⎢⎥
⎢
⎥
⎣⎦
⎢
⎥
⎣
⎦
x
f
f
x
∼
And the limit is finite if and only if all elements in
above matrix are finite.
Norms of matrices A, B should approach neither
zero nor infinity. The best performance is achieved
if the norms of matrices A, B have similar order of
magnitudes.
Although the convergence of the algorithm from fig.
1 for a given decomposition cannot be proved for
general nonlinear systems stability for linearized
ones follows directly from the applied computation
method for control. The conversion from a nonlinear
into LTV system can be successfully applied to all
systems for which the optimal nonlinear control lies
in the neighbourhood of the optimal control for the
linearized LTV system.
5 NUMERICAL EXAMPLE
In the example algorithm from fig. 1 is combined
with formula (24), where x
0
is current initial
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
90
condition
()
00
k=xx
and
ˆ
ˆ
, PQ
are weighting
matrices. Control is calculated iteratively using cost
function (9) with
ˆ
ref
=x0
, from following formula:
()
() ()
()
() () () ()
()
()()
1
1
0
ˆ
ˆ
ˆˆ ˆˆˆ ˆˆ ˆˆ
i
TT
ii ii ii ii
+
−
=
⎛⎞
−+
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
u
LB PLB Q LB PNx
(24)
We assume following model for the nonlinear
system:
223
1
0.5
kk kkk
x
xxuu
+
=+ +
(25)
The initial control trajectory is equal to
()
[
]
0
ˆ
0.5 1,1,1=−u
, the absolute tolerance, defined by
(11)
0.001
ε
=
and the weighting matrices are
unitary
ˆ
ˆˆ ˆ
, .
P
Q
==PI QI
The system (25) can be
decomposed into two following state and input
dependent parts:
()
(
)
()
22
1
(,)
(,)
0.5
kk
kk
kkkkk kkk
Ax u
Bx u
x
xxux xuu
αα
+
=+ ⋅+ − +⋅
(26)
The decomposition is dependent on parameter
α
.
Equation (26) is equivalent to (25) for arbitrary
values of α, although convergence of the algorithm
from fig. 1 is analysed for
[
]
5, 0.5
α
∈−
.
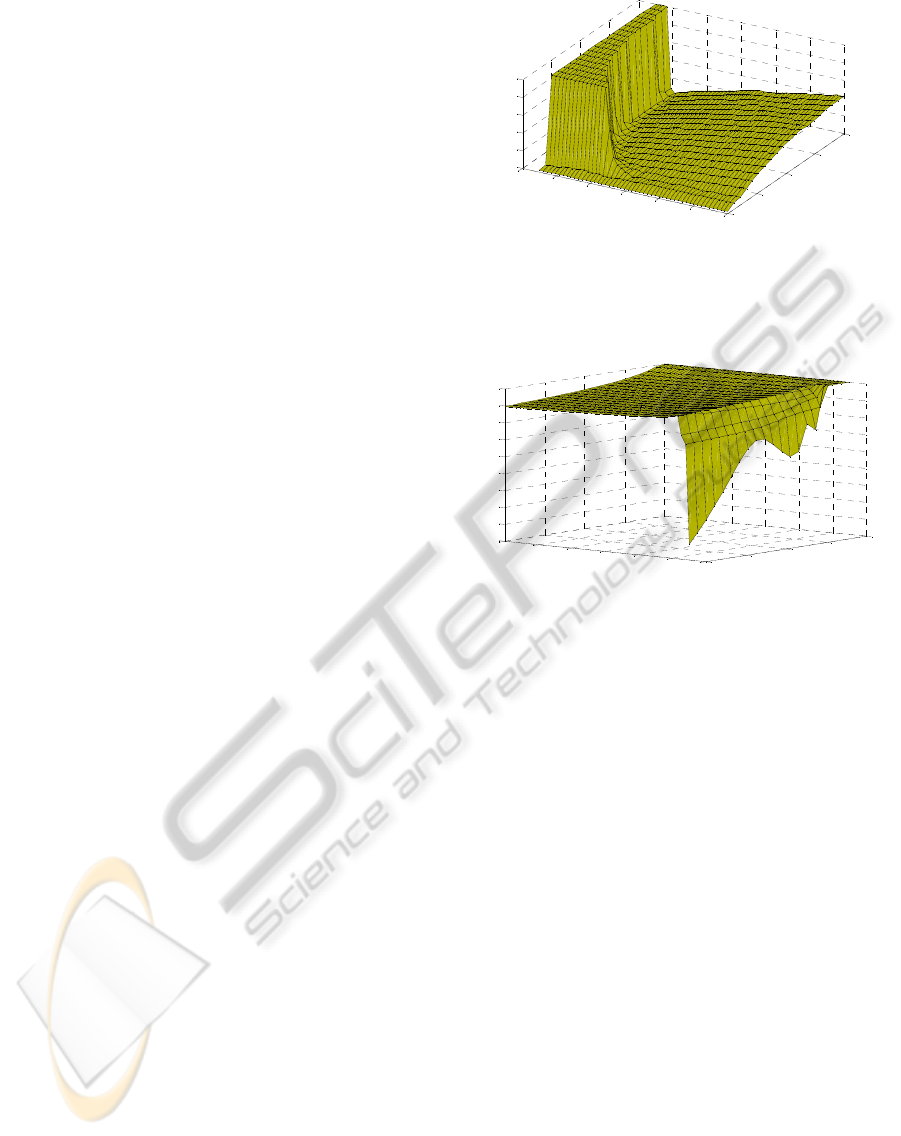
Figure 2 shows number if iterations η required to
converge to optimal control solution for given initial
state
(
]
0
0,8x ∈
and decomposition parameter
[
]
5, 0.5
α
∈−
. To improve readability of the figure 2
it is also assumed that η≤100. Value η=100
corresponds to a divergent solutions or solutions
with that require more than 100 iterations. It may be
concluded from fig. 2 that convergence of the
algorithm from fig. 1 is dependent both on the initial
state and the decomposition. Usually it is required
for the algorithm to be convergent and possibly fast
for all initial conditions from given range. To ensure
fast convergence (the minimal number if iterations)
for e.g.
x
0
=8 parameter α should be chosen in the
range
[
]
0.5,0
α
∈−
, whereas for x
0
=1.4 the smallest
number if iterations is for
[
]
3, 1.5
α
∈− −
. For x
0
<1
the algorithm is fast convergent for all α.
It should be underlined that the
convergence/divergence is a property of: the system,
the initial condition, the decomposition and the
initial control trajectory. First of all it is assumed
that the system is controllable and observable and
the state is reachable from arbitrary initial state x
0
.
Although changes in each of three above factors
may be effective to achieve convergence of the
algorithm, the easiest way to improve the method or
fasten the algorithm is to change the decomposition.
Convergence of the algorithm is strongly connected
with the conditional number
r
cond
of the inverse of
Figure 2: Number of iterations η required to converge
optimal control solution for given initial state x
0
and the
decomposition parameter α for unitary weighting
operators without terminal cost and time horizon N=3.
Figure 3: Logarithm base 10 of reciprocal condition
number estimate vs. initial state x
0
and the decomposition
parameter α for unitary weighting operators without
terminal cost and time horizon N=3.
matrix
() ()
(
)
() ()
ˆ
ˆˆ ˆˆˆ
T
ii ii
⎛⎞
+
⎜⎟
⎝⎠
LB PLB Q
. Logarithm base
10 of the conditional number is shown in figure 3.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The paper discuss selected problems concerned to
successive model linearization along predicted state
and input trajectories with linear time varying
model.
The paper mainly focus on the transformation
method from a general nonlinear form into the state
space dependent form. We formulate the problem
and introduce the generalised form of the algorithm.
Nonlinearities are decomposed into two additive
terms – state and input dependent matrices of the
state space dependent form and then model
predictive control can be calculated using methods
for linear systems.
An important consequence of the chosen
decomposition is reachability of the optimal solution
0
2
4
6
8
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
0
20
40
60
80
100
x
0
α
η
0
2
4
6
8
-5
-4
-3
-2
-1
0
1
-45
-40
-35
-30
-25
-20
-15
-10
-5
0
x
0
α
log
10
(rcond)
NONLINEAR INTO STATE AND INPUT DEPENDENT FORM MODEL DECOMPOSITION - Applications to
Discrete-time Model Predictive Control with Succesive Time-varying Linearization along Predicted Trajectories
91

and required computation time – number of
iterations. In many cases the number of iterations
can be cut down. The optimal decomposition, for
which the algorithm is convergent with minimal
number of iterations depends on the initial condition
– for receding horizon problems the initial condition
is the current state in each time sample. The
selection of the decomposition parameters
,
α
β
should be always connected with current value of
the state to ensure suitable value of conditional
number corresponding to the inverse of matrix in
formula (24).
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work was supported by the Ministry of Science
and Higher Education in Poland under the grant
N N514 298535.
REFERENCES
Błachuta, M. J. 1999. On Fast State-Space Algorithms for
Predictive Control. Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci.,
Vol. 9, No. 1, 149-160.
Camacho EF., Bordons C. 2004. Model Predictive
Control. Springer.
Chen H., Allgower F. 1998. A quasi-infinite horizon
nonlinear model predictive control scheme with
guaranteed stability. Automatica, 34(10):1205–1218.
De Nicolao G., Magni L., Scattolini R.. 2000. Stability and
robustness of nonlinear receding horizon control. In F.
Allgower and A. Zheng, editors, Nonlinear Predictive
Control, pp. 3–23. Birkhauser.
Dutka A. S., Ordys A. W., Grimble M. J. 2003. Nonlinear
Predictive Control of 2 dof helicopter model, IEEE
CDC proceedings.
Dutka, A., Ordys A. 2004. The Optimal Non-linear
Generalised Predictive Control by the Time-Varying
Approximation, Proc. of 10
th
IEEE Int. Conf. MMAR.
Miedzyzdroje. Poland. pp. 299-304.
Fontes F. A. 2000. A general framework to design
stabilizing nonlinear model predictive controllers.
Syst. Contr. Lett., 42(2):127–143.
Grimble M. J., Ordys A. W. 2001. Non-linear Predictive
Control for Manufacturing and Robotic Applications,
Proc. of 7
th
IEEE Int. Conf. MMAR. Miedzyzdroje.
Huang Y., Lu W.M. 1996. Nonlinear Optimal Control:
Alternatives to Hamilton-Jacobi Equation”, Proc. of
the 35th IEEE Conference on Decision and Control,
pp. 3942-3947.
Kouvaritakis B., Cannon M., Rossiter J. A. 1999. Non-
linear model based predictive control, Int. J. Control,
Vol. 72, No. 10, pp. 919-928.
Kowalczuk Z, Suchomski P. 2005. Discrete-Time
Predictive Control With Overparameterized Delay-
Plant Models And An Identified Cancellation Order.
Int. J. Appl. Math. Comput. Sci, Vol. 15, No. 1, 5–34.
Lee Y. I., Kouvaritakis B., Cannon M. 2002. Constrained
receding horizon predictive control for nonlinear
systems, Automatica, Vol. 38, No. 12, pp. 2093-2102.
Magni, L., De Nicolao, G., Scattolini, R. 1999. Some
Issues in the Design of Predictive Controllers. Int. J.
Appl. Math. Comput. Sci., Vol. 9, No. 1, 9-24.
Mayne D.Q., Rawlings J.B., Rao C.V., Scokaert P.O.M.
2000. Constrained model predictive control: stability
and optimality. Automatica, 26(6):789–814.
Morari M. and Lee J. 1999. Model predictive control:
Past, present and future. Comput. Chem. Engi., Vol.
23, No. 4/5, pp. 667–682.
Morari M., de Oliveira Kothare S. 2000. Contractive
model predictive control for constrained nonlinear
systems. IEEE Trans. Aut. Contr., 45(6):1053–1071.
Mracek C. P., Cloutier J. R. 1998. Control Designs for the
nonlinear benchmark problem via the State-Dependent
Riccati Equation method, International Journal of
Robust and Nonlinear Control, 8, pp. 401-433.
Ordys A. W., Grimble M. J. 2001. Predictive control
design for systems with the state dependent non-
linearities, SIAM Conference on Control and its
Applications, San Diego, California.
Orlowski, P. 2005. Convergence of the optimal non-linear
GPC method with iterative state-dependent, linear
time-varying approximation, Proc. of Int. Workshop
on Assessment and Future Directions of NMPC,
Freudenstadt-Lauterbad, Germany, pp. 491-497.
Primbs J., Nevistic V., Doyle J. 1999. Nonlinear optimal
control: A control Lyapunov function and receding
horizon perspective. Asian Journal of Control,
1(1):14–24.
Qin S. J. and Badgwell T. 2003. A survey of industrial
model predictive control technology. Contr. Eng.
Pract., Vol. 11, No. 7, pp. 733–764.
Scokaert P.O.M., Mayne D.Q., Rawlings J.B. 1999.
Suboptimal model predictive control (feasibility
implies stability). IEEE Trans. Automat. Contr.,
44(3):648–654.
Tatjewski P. 2007. Advanced Control of Industrial
Processes, Structures and Algorithms. London:
Springer.
Ulbig A., Olaru S., Dumur D., Boucher P. 2007. Explicit
solutions for nonlinear model predictive control : a
linear mapping approach, European Control
Conference ECC 2007, Kos, Grece.
ICINCO 2010 - 7th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
92
