
MODELLING COLLABORATIVE SERVICES
The COSEMO Model
Thanh Thoa Pham Thi
1
, Thang Le Dinh
2
1
School of Computing, Dublin City University, Glasnevin, Dublin 9, Ireland
2
Université du Québec à Trois-Rivières, Trois-Rivières, Quebec, Canada
Markus Helfert
3
, Michel Leonard
4
3
School of Computing, Dublin City University, Glasnevin, Dublin 9, Ireland
4
Department of Information Systems, University of Geneva, Switzerland
Keywords: Service Modelling, Collaboration, Sharing Data and Processes, Collaborative Services.
Abstract: Despite the dominance of the service sector in the last decades, there is still a need for a strong foundation
on service design and innovation. Little attention has been paid on service modelling, particularly in the
collaboration context. Collaboration is considered as one of the solutions for surviving or sustaining the
business in the high competitive atmosphere. Collaborative services require various service providers
working together according to agreements between them, along with service consumers, in order to co-
produce services. In this paper, we address crucial issues in collaborative services such as collaboration
levels, sharing data and processes due to business interdependencies between service stakeholders.
Subsequently, we propose a model for Collaborative Service Modelling – the COSEMO model, which is
able to cover identified issues. We also apply our proposed model to modelling an example of Travelling
services in order to illustrate the relevance of our modelling approach to the matter in hand.
1 INTRODUCTION
Service science has emerged in the last few years as
an interdisciplinary research domain that addresses
challenges in service innovation in the service
sector. The service sector includes all economic
activities whose output is not a tangible product and
is generally consumed at the same time it is
produced and provides added value in intangible
forms (Quinn et al., 1987). Today, more and more
business organizations have been seeking
collaborations as one amongst solutions to sustain
their business in high competitive environments. For
instance, they use the supply chain model or alliance
model. In such context, collaborative service is a
kind of business collaboration in the service sector
in which several business organizations work
together to co-produce services.
Although the dominance of the service sector in
recent years, a strong foundation on service design
and innovation is still needed (Bitner et al, 2008).
Service
modelling is undertaken in the service
design and innovation. Service modelling amounts
to the representation of relations between what is
provided to customers, how it is provided, the
technical definition of the service, and resources
needed for operating the service (Vilho Raisanen,
2006). Therefore at the informational level, service
modelling should describe the creation and
transformation of information between service
stakeholders.
Due to data and process sharing in the
collaboration context, some critical issues have
emerged, such as various data sharing levels –
collaboration levels, and the consistency of data and
process sharing across organizations to ensure
correct performing of business activities.
Current approaches for service modelling often
focus on single services. There are few approaches
working on inter-organizational business process
collaboration. However, they do not cover issues
mentioned. In this paper, we propose our approach
for collaborative service modeling as a solution to
the matter in hand.
79
Thoa Pham Thi T., Le Dinh T., Helfert M. and Leonard M. (2010).
MODELLING COLLABORATIVE SERVICES - The COSEMO Model.
In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 79-82
DOI: 10.5220/0002929800790082
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The rest of the paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 dues with related work in service and
collaborative service modelling. Section 3 brings out
crucial challenges in collaborative services and
presents our modelling concepts that address these
challenges. Finally, we conclude our work and give
some research directions in Section 4
.
2 RELATED WORK
Services are defined as “the application of
competences for the benefit of another, meaning that
service is a kind of action, performance or promise
that is exchanged for value between provider and
client” (Spohrer, 2007).
In our viewpoint, collaborative services are
services created based on collaborations of service
co-providers. For instance, we take an example of
Travelling service for the illustration. A hotel
collaborates with a travel agency who provides
booking services to customers. Customers can
contact the travel agency for their booking or
cancellation, or they can also book or cancel their
reservation directly with the hotel. The hotel also
collaborates with a cleaning agency for the cleaning
service.
In literature, there are some approaches to
modelling single services which deals with only one
service provider and service consumer(s) such as
Molecular model, and Blueprinting approach.
Molecular model is one of the earliest models for
service and product modelling developed by
Shostack (Shostack, 1982). The centre of molecular
model describes core benefit provided to customers
which includes service elements, product elements,
relationships between elements, and service
evidences. These elements can be visualised with
graphical notations. Other elements such as price
strategy, distribution strategy, and advertisement
strategy, etc. are layers outside the core of molecular
describing the total market entity.
The blueprinting is also developed by Shostack
(Shostack, 1984) and then evolved by (Kingman-
Brundage, 1995), (Vilho Räisänen, 2006),
(Zeithaml, 2008) which has focused on processes
that constitute the service. A service blueprint is a
two-dimensional diagram. The horizontal axis
represents the chronology of processes or functions
in the service. The vertical axis represents different
processes areas.
Recently, the Business Process Modelling
Notation (BPMI, 2004) has been adapted for
collaborative business process modelling for the
Service Oriented Architecture design (Touzi et al,
2009).
Similar, (Grossman, 2008) has proposed some
extensions to business process modelling languages
which enable them to describe various types of inter-
process dependencies across organizations. They are
for example, Triggering dependencies, Enabling
dependencies, Cancelling dependencies, Disabling
dependencies.
In the Service Oriented Computing paradigm,
service composite and orchestration describe
aggregating multiple services into a single
composite service (Papazoglou et al. 2007). The
composite service is often modelled with Petri Nets
(Gehlot, Edupuganti 2009; Yoo et al. 2010).
These approaches have some limitations on
describing various collaboration degrees, monitoring
data consistency and monitoring shared processes
performed across organizations.
3 ISSUES IN MODELLING
COLLABORATIVE SERVICES
In this section firstly we present our meta modelling
concepts, then we address crucial issues in
collaborative services modelling and illustrate how
to overcome it with our concepts.
3.1 Modelling Concepts -
The COSEMO Model
We focus on data and process sharing between
organizations during the production of services. The
relevant concepts are as follows:
- Role describes organizational units inside/outside
an organization or participants in the collaboration
context
- Process is a business activity, a task or function
-Class represents information/data created/
transferred/transformed by process.
- Privileges on data: a role can have privileges of
creation on data (i.e. class), and privilege of
suppression, modification, reference on their own
data (data created by this role). Moreover, a role can
have privileges of creation, suppression, and
reference on data created by other roles. In this case,
they are denoted by suppression+, modification+,
and reference+
- Responsibility on process: a role has responsibility
on the performing of a process
- Available/Unavailable data: data in a class can be
ICSOFT 2010 - 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
80
available or unavailable to certain processes in
certain times (i.e. is able to participate in the process
or is not). This often concerns data status changes.
For example a booking is available to the Cancel
and Confirm processes. If the booking becomes
cancelled (after performing cancel process), then it
is becomes unavailable to Cancel and Confirm
process. But a confirmed booking is available to
Cancel process.
In the following sections we will describe
challenges in collaborative service modelling and
illustrate with our concepts.
3.2 Collaboration Level Modelling
The collaboration level between organizations/
service providers is described by the degree of
sharing data and process. There are four
collaboration levels:
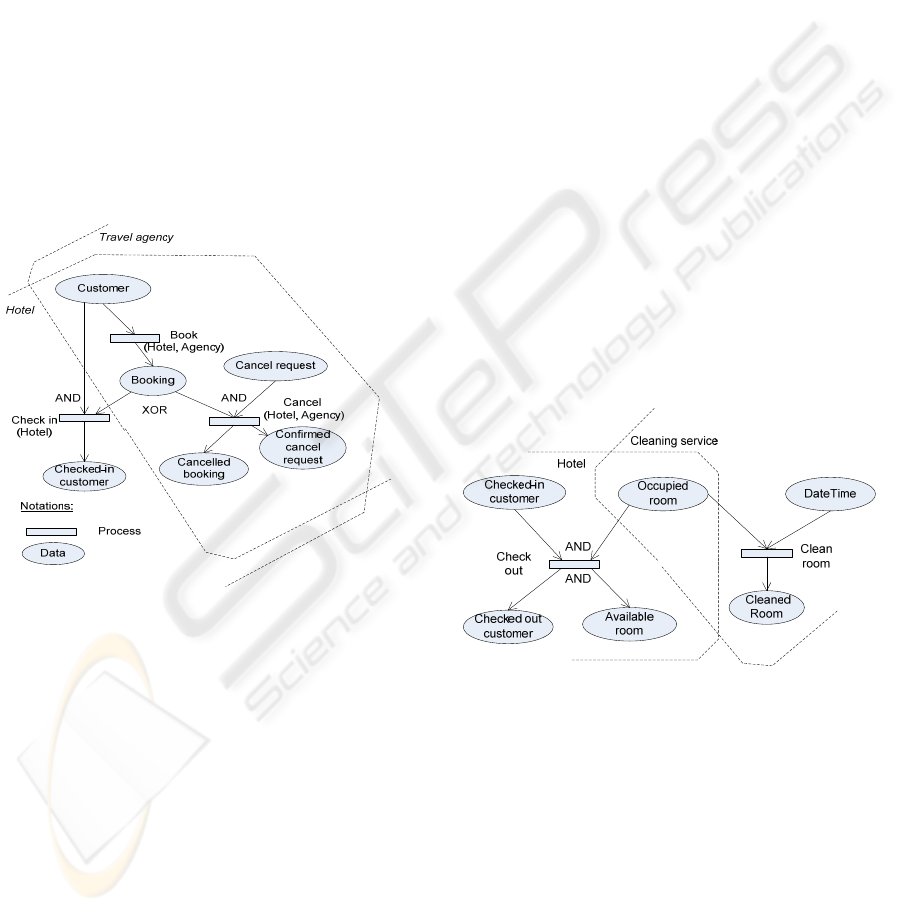
Figure 1: Very tight collaboration
Level 1 – very tight collaboration- data and process
sharing, it is allowed to modify the shared data.
Figure 1 illustrates this collaboration level with
the Travelling example. There are shared
information and common processes between the
hotel and the travel agency.
If a booking is made with the hotel then the
customer change booking information or cancel it
within the hotel. But if a booking is made with the
travel agency, then the customer can change booking
information or cancel it within the travel agency or
the hotel. Customer information created/owned by
the travel agency should be shared with the hotel,
but the hotel does not need to share information with
the Customer who directly booked with the hotel
(i.e. the hotel has the privilege reference+ on
Customer, but the travel agency just has the
privilege reference on Customer). The hotel can
modify Booking shared by the travel agency, but it
is not an inverse case (i.e. the hotel has privilege
modification+ on Booking, and the travel agency
just has privilege modification on Booking), and so
on.
Level 2 – tight collaboration- data and process
sharing, it is not allowed to modify the share data.
For instance, concerning travelling service, an
alliance of airlines shares the process of Bonus
Calculation for loyalty clients to each member. The
shared information between them for the performing
of this process is information on flights taken,
number of miles taken and concerning customer.
However, an airline can not modify this shared
information which is owned/created by other
airlines.
Level 3 – loose collaboration: actively data sharing,
it is not allowed to modify the shared data.
This case often concerns requesting other service
providers to carry out a business activity/process.
Figure 2 illustrates this level. For example, the hotel
shares occupied room data to the cleaning agency
for the cleaning service. Cleaning service just has
the only privilege of reference on occupied room.
Figure 2: Loose collaboration
Level 4 – very loose collaboration: passively data
sharing, it is not allowed to modify shared data.
A service provider passively shares some
information to other service provider for the
reference purpose, the shared information is not
allowed to modify. The receiver just has the
privilege of reference on shared data.
3.3 Data and Process Consistency
Control
Consistency issues emerged due to data and process
interdependencies among service providers.
MODELLING COLLABORATIVE SERVICES - The COSEMO Model
81

Figure 1 describes an exclusive constraint
between Check-in process and Cancel process which
span across organizations. Figure 2 describes a more
complex situation which means “for every room, if
the check-out process is performed then the clean
room process is disabled, but it is not the case on the
contrary”.
We uses the concept of Available/Unavailable
data in our model to solve this issue. In the first case,
Booking becomes unavailable to the Cancel process
and Check-in process once it participated in one of
these processes. Therefore, if a booking is cancelled,
later it can be checked-in, or vice-versa. Meanwhile
in the second case, Occupied room is always
available to the Clean room process, therefore an
occupied room after cleaning is still occupied, until
the Check-out process is performed.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Researchers have contributed some work on
collaborative business process modelling, composite
service and orchestration modelling. However, in
this paper we showed that there are still some
limitations on describing critical issues in
collaborative service modelling which concerns the
description of collaboration levels, data and process
consistency across organizations due to data and
process sharing needs. By addressing these issues,
we proposed our meta-modelling concepts, the
COSEMO model. This modelling approach is
business oriented, not a formalism oriented approach
like Petri Nets, therefore our approach avoids
complex transformation of modelling due to
constraints on formalisms.
Our future research directions will address the
need of investigation of customer-centric
characteristics of services. This allows the service
customization and adaptation of customers
according to their needs. The the modelling should
be an adaptable approach which facilitates evolution.
REFERENCES
Bitner, M. J., Ostrom, A. L., Morgan F. N., 2008. Service
Blueprinting: A Practical Technique for Service
Innovation. In: California Management Review, Vol.
53, No. 3, pp.66--94.
Business Process Management Initiative (BPMI), 2004.
Business Process Modeling Notation, Version1.0.
Grossmann G., Schrefl M., Stumptner M., 2008.
Modelling Inter-Process Dependencies with High
Level Business Process Modelling Languages. In
Proc.5th Asia-Pacific Conference on Conceptual
Modelling, Wollongong, Australia.
Kingman-Brundage, J., George, W. R, 1995. Service
logic: achieving service system integration. In
International Journal of Service Industry
Management, 6 (4), 20-39.
Kosanke K., 2005. ISO standards for interoperability: a
comparison. In: Proceedings of the First International
Conference on Interoperability of Enterprise Software
and Applications INTEROP-ESA’05, Springer, Berlin,
pp.55–64, ISBN 1-84628-151-2.
Papazoglou M.P., Traverso P., Dustdar S., Leymann F.
2007. “Service-Oriented Computing: State of the Art
and Research Challenges”, IEEE Computer,
November, pp. 64-71.
Quinn, J. B., Baruch, J. J., and Paquette, P. C., 1987.
“Technology in Services”, Scientific American, Vol.
257, No. 6, pp.50-58.
Shostack, L. G., 1984. Design Services that Deliver. In
Harvard Business Review (84115), 133-139.
Shostack, L. G., 1982. How to Design a Service. In
European Journal of Marketing, 16(1), 49-63.
Shostack, L. G., 1987. Service Positioning Through
Structural Change, Journal of Marketing, pp.34-43.
Spohrer, J., Maglio, Paul P., Bailey, J., Gruhl, D., 2007.
Steps Towards a Science of Service Systems. In IEEE
Computer, No.1, pp.71-77.
Touzi J., Benaben F., Pingaud H., Lorre J. P., 2009. A
model-driven approach for collaborative service-
oriented architecture design. In International Journal
Production Economics, Elsevier Publisher, 121, pp.5-
20
Vilho Räisänen, 2006. Service Modelling: Principles and
Applications. Wiley.
Yoo T., Jeong B., Cho H. 2009. “A Petri Nets based
functional validation for services composition”, in
Journal of Expert Systems with Applications, Vol. 37,
pp. 3768-3776
Zeithaml, V., Bitner, M. J., Gremler, D., 2008. Services
Marketing, Irwin Mcgraw-Hill (2000) 22.
ICSOFT 2010 - 5th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
82
